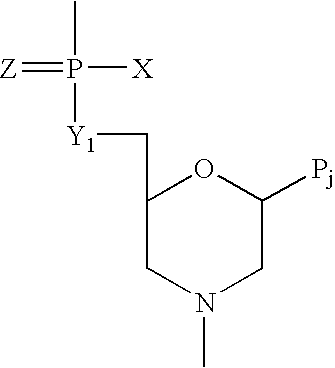
Patents
Literature
2296 results about "Influenzavirus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A non-taxonomic grouping of the viruses capable of causing the respiratory tract infection commonly called the flu.
Integrated health data capture and analysis system
ActiveUS20110093249A1Mitigate spreadReduce transmissionMedical simulationMedical data miningOutbreakChronic disease
The present invention provides an integrated health care surveillance and monitoring system that provides real-time sampling, modeling, analysis, and recommended interventions. The system can be used to monitor infectious and chronic diseases. When faced with outbreak of an infectious disease agent, e.g., influenza virus, the system can identify active cases through pro-active sampling in high risk locations, such as schools or crowded commercial areas. The system can notify appropriate entities, e.g., local, regional and national governments, when an event is detected, thereby allowing for proactive management of a possible outbreak. The system also predicts the best response for deployment of scarce resources.
Owner:LABRADOR DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Functional influenza virus-like particles (VLPs)
ActiveUS20050009008A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesMultiple copyVirus Structural Proteins
Recombinant influenza virus proteins, including influenza capsomers, subviral particles, virus-like particles (VLP), VLP complexes, and / or any portions of thereof, are provided as a vaccine for influenza viruses. The invention is based on the combination of two vaccine technologies: (1) intrinsically safe recombinant vaccine technology, and (2) highly immunogenic, self-assembled protein macromolecules embedded in plasma membranes and comprised of multiple copies of influenza virus structural proteins exhibiting neutralizing epitopes in native conformations. More specifically, this invention relates to the design and production of functional homotypic and heterotypic recombinant influenza virus-like particles (VLPs) comprised of recombinant structural proteins of human influenza virus type A / Sydney / 5 / 94 (H3N2) and / or avian influenza virus type A / Hong Kong / 1073 / 99 (H9N2) in baculovirus-infected insect cells and their application as a vaccine in the prevention of influenza infections and as a laboratory reagent for virus structural studies and clinical diagnostics.
Owner:NOVAVAX
Chimeric viruses presenting non-native surface proteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120122185A1Readily immunizeEffective immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-sensePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifEctodomainVirosome
The present invention provides chimeric negative-stand RNA viruses that allow a subject, e.g., an avian, to be immunized against two infectious agents by using a single chimeric virus of the invention. In particular, the present invention provides chimeric influenza viruses engineered to express and incorporate into their virions a fusion protein comprising an ectodomain of a protein of an infectious agent and the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain of an influenza virus protein. Such chimeric viruses induce an immune response against influenza virus and the infectious agent. The present invention also provides chimeric Newcastle Disease viruses (NDV) engineered to express and incorporate into their virions a fusion protein comprising the ectodomain of a protein of an infectious agent and the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain of an NDV protein. Such chimeric viruses induce an immune response against NDV and the infectious agent.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Multi plasmid system for the production of influenza virus
InactiveUS20050158342A1Easy to copyEnhanced ability to replicateSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsEmbryonated chicken eggEukaryotic plasmids
Vectors and methods for the production of influenza viruses suitable as recombinant influenza vaccines in cell culture are provided. Bi-directional expression vectors for use in a multi-plasmid influenza virus expression system are provided. Additionally, the invention provides methods of producing influenza viruses with enhanced ability to replicate in embryonated chicken eggs and / or cells (e.g., Vero and / or MDCK) and further provides influenza viruses with enhanced replication characteristics. In addition, the present invention includes an improved method of rescue, wherein animal cells (e.g., SF Vero cells) are electroporated with plasmids and vectors of the invention.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Compositions and methods for treating viral infections
InactiveUS20100081713A1Mortality rate is decreasedReduce rateBiocideAntiviralsViral infectionBiomedical engineering
The present invention provides compositions, methods, and kits for treating or preventing a viral infection (e.g., an infection caused by an influenza virus).
Owner:COMBINATORX SINGAPORE PTE +1
Non-tumorigenic MDCK cell line for propagating viruses
The present invention provides novel MDCK-derived adherent non-tumorigenic cell lines that can be grown in the presence or absence of serum. The cell lines of the present invention are useful for the production of vaccine material (e.g., viruses). More specifically, the cell lines of the present invention are useful for the production of influenza viruses in general and ca / ts influenza viruses in particular. The invention further provides methods and media formulations for the adaptation and cultivation of MDCK cells such that they remain non-tumorigenic. Additionally, the present invention provides methods for the production of vaccine material (e.g., influenza virus) in the novel cell lines of the invention.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Assembly of wild-type and chimeric influenza virus-like particles (VLPs)
InactiveUS20050186621A1Minimal numberSsRNA viruses negative-senseFungiHeterologousVirus-like particle
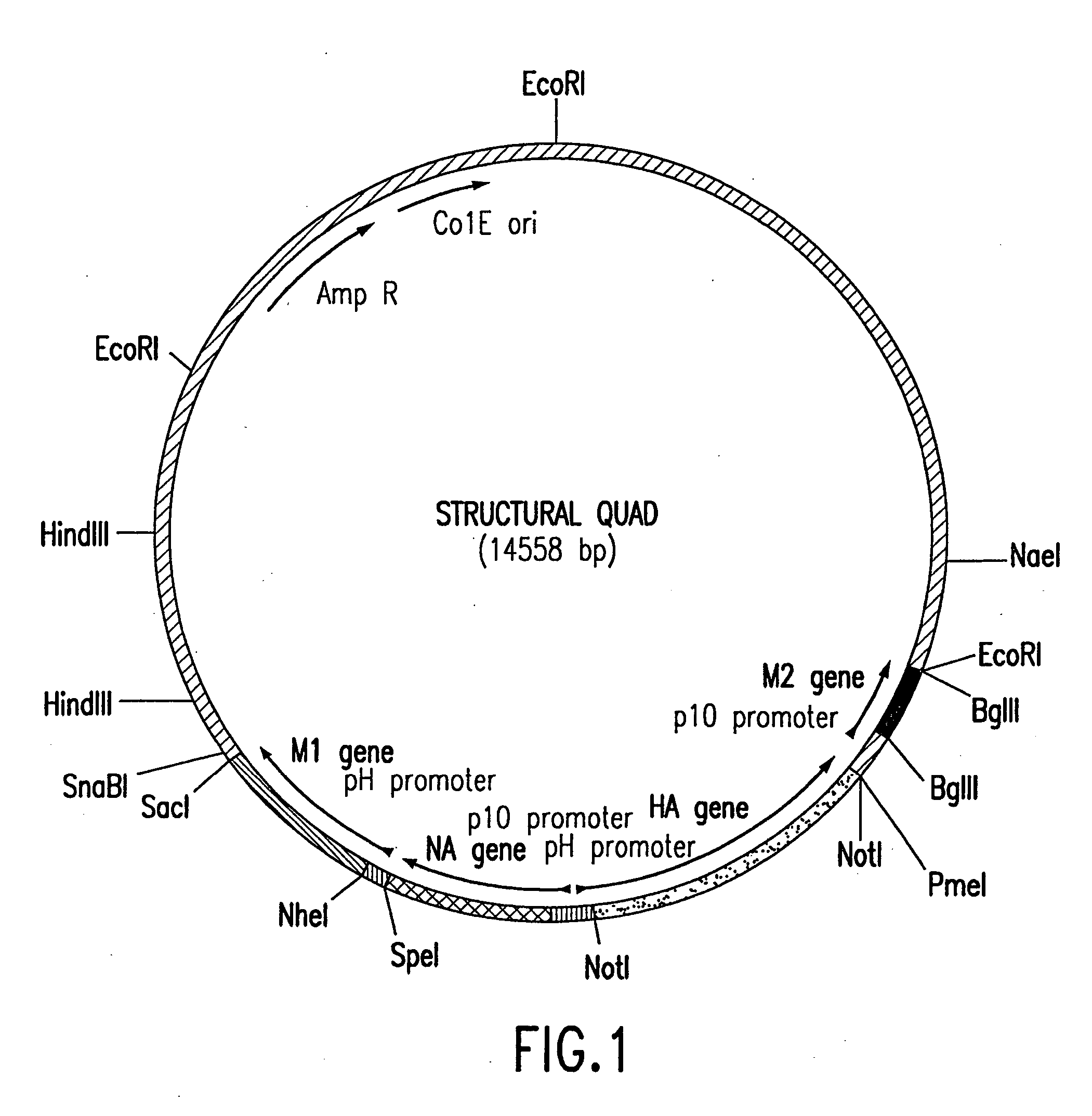
Influenza virus-like particles (VLPs) comprising the structural proteins HA, NA, M1 and M2 are described. VLPs are also generated containing M1 alone, as are VLPs with M1 and any one or two of HA, NA and M2. VLPs with HA from one influenza subtype and NA from a different influenza subtype are also described, as are VLPs in which a portion or all of HA or NA is replaced by a heterologous moiety not produced by influenza virus, so as to comprise chimeric VLPs.
Owner:WYETH HOLDINGS LLC
Adjuvanted influenza vaccines for pediatric use
ActiveUS8506966B2Enhance immune responseHigh seroprotection rateSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsAdjuvantSeroconversion
An influenza vaccine adjuvanted with a sub-micron oil-in-water emulsion elicits significantly higher immune responses in human pediatric populations. Compared to an existing unadjuvanted pediatric influenza vaccine, the adjuvanted vaccines provided herein can induce in children a longer persistence of high serum antibody titers and also longer seroconversion and seroprotection. The improvement in immune responses is seen for both influenza A virus and influenza B virus strains, but it is particularly marked for influenza B virus. Moreover, while the existing vaccine provides poor immunity in children after a single dose, the adjuvanted vaccine provides high seroprotection rates against the influenza A virus H3N2 subtype even after a single dose. Furthermore, the adjuvanted vaccine offers significantly better seroprotection against mismatched strains of influenza A virus.
Owner:SEQIRUS UK LTD
Attenuated negative strand viruses with altered interferon antagonist activity for use as vaccines and pharmaceuticals
InactiveUS6669943B1Impaired ability to antagonizeAvoiding and minimizing side effectSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesNegative strandPharmaceutical drug
Owner:AVIR GREEN HILLS BIOTECH RES DEVMENT TRADE +1
Influenza virus vaccines and uses thereof
ActiveUS20100297174A1Reduce severityImprove survivalSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsHemagglutininInfluenza virus vaccine
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
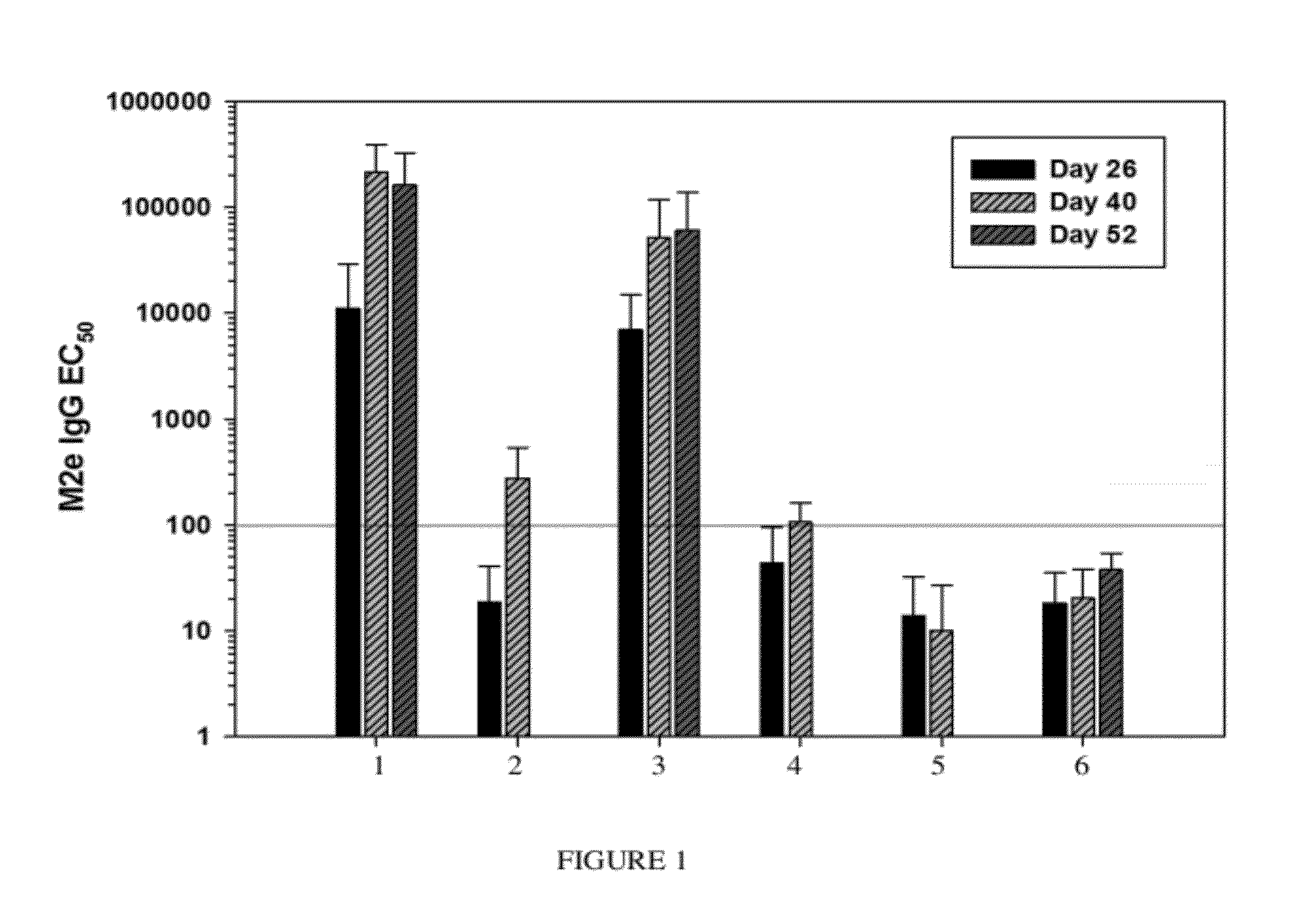
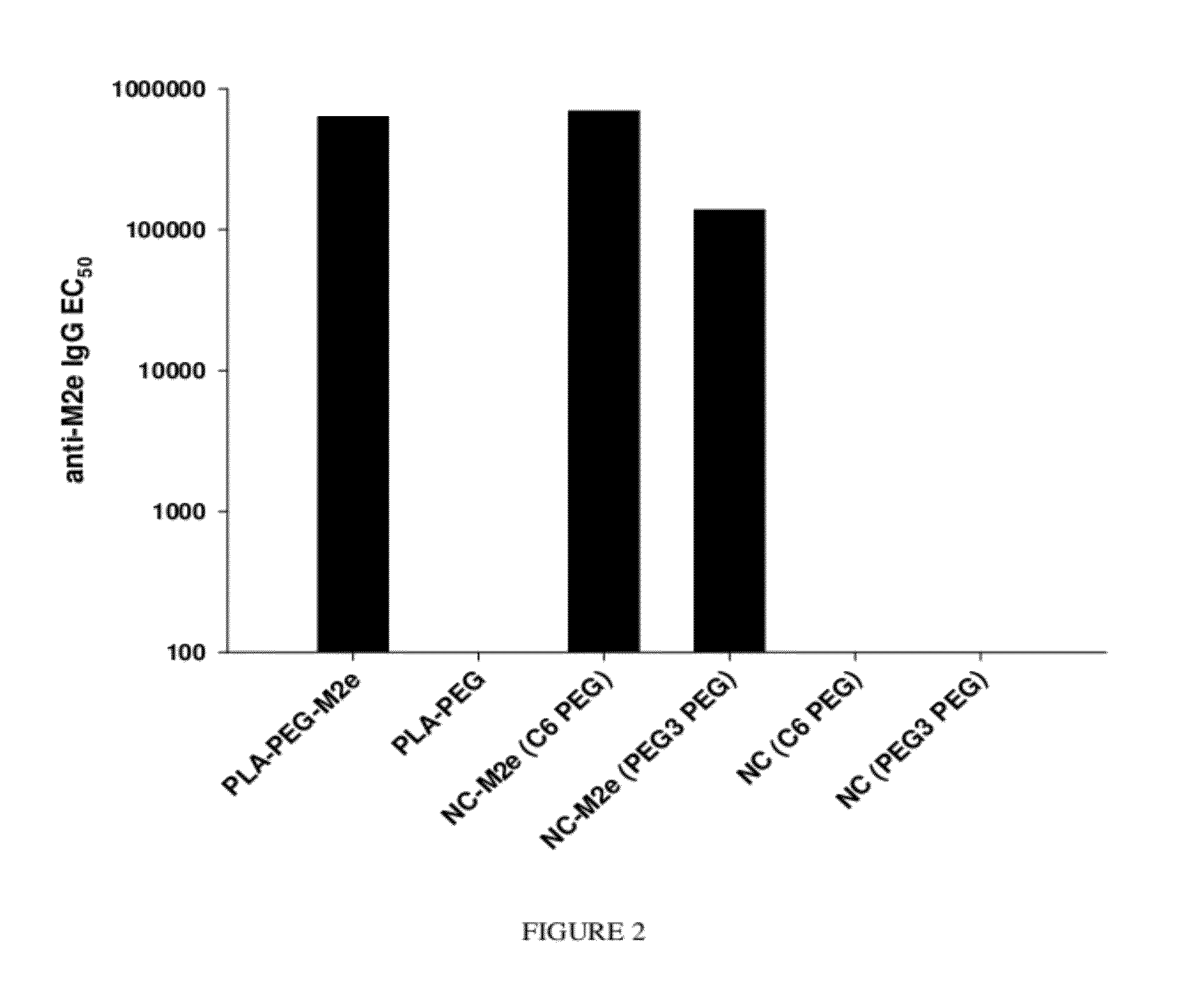
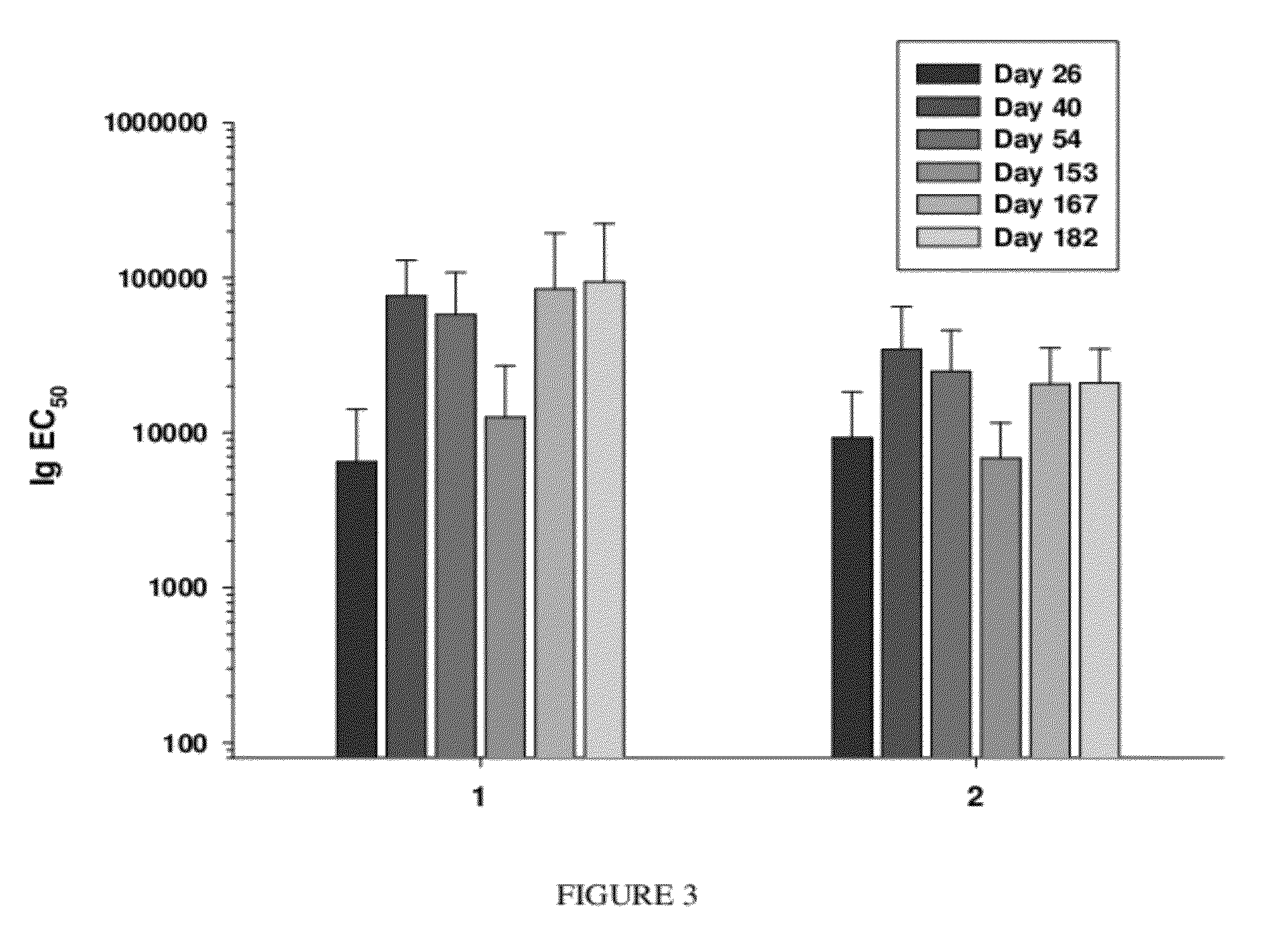
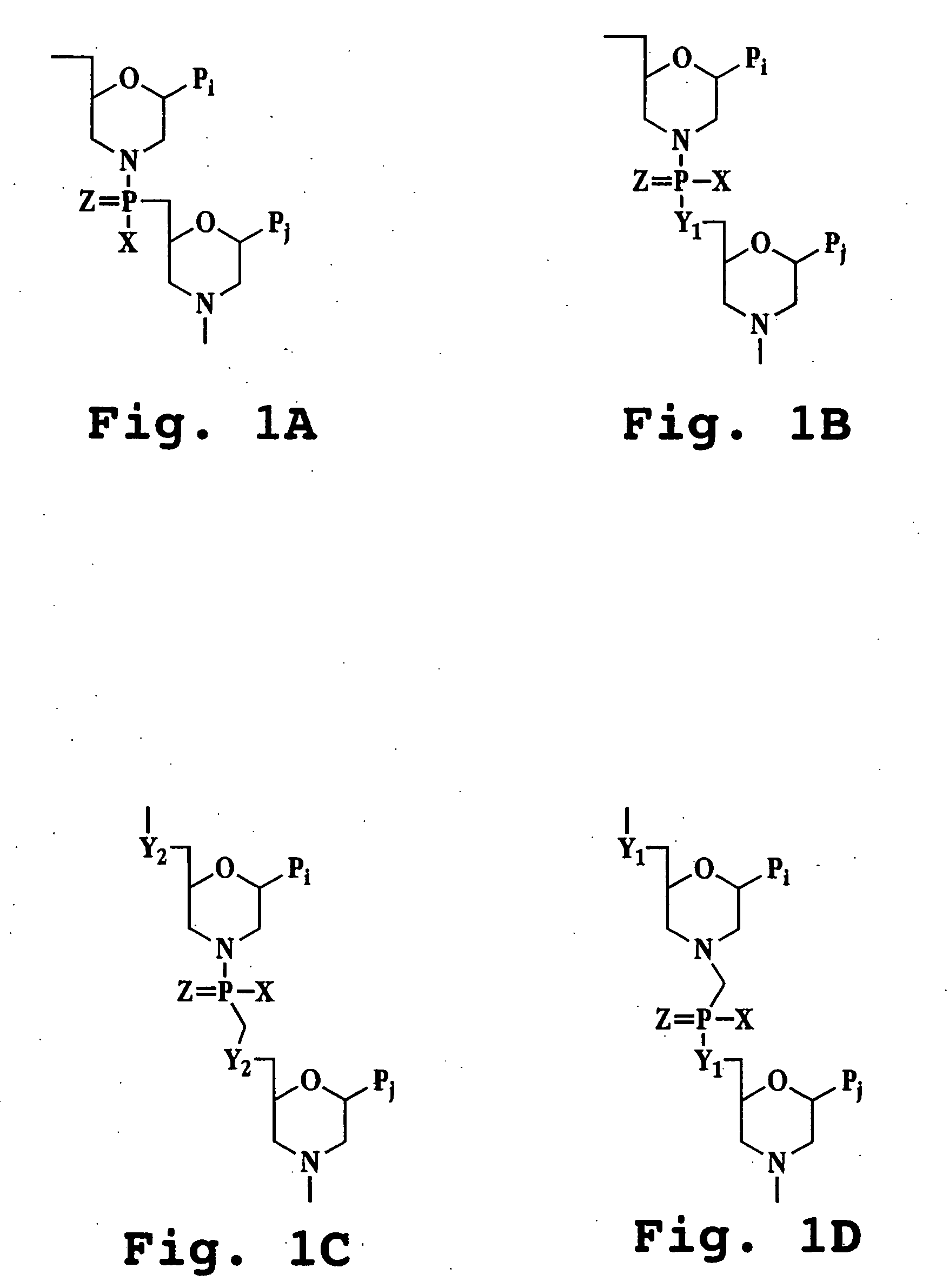
Synthetic nanocarrier vaccines comprising peptides obtained or derived from human influenza a virus m2e
InactiveUS20120058154A1Stimulate immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsHuman Influenza A VirusVector vaccine
This invention relates to compositions and methods that can be used immunize a subject against influenza. Generally, the compositions and methods include peptides obtained or derived from human influenza A virus M2 protein.
Owner:SELECTA BIOSCI
Antisense antiviral compound and method for treating influenza viral infection
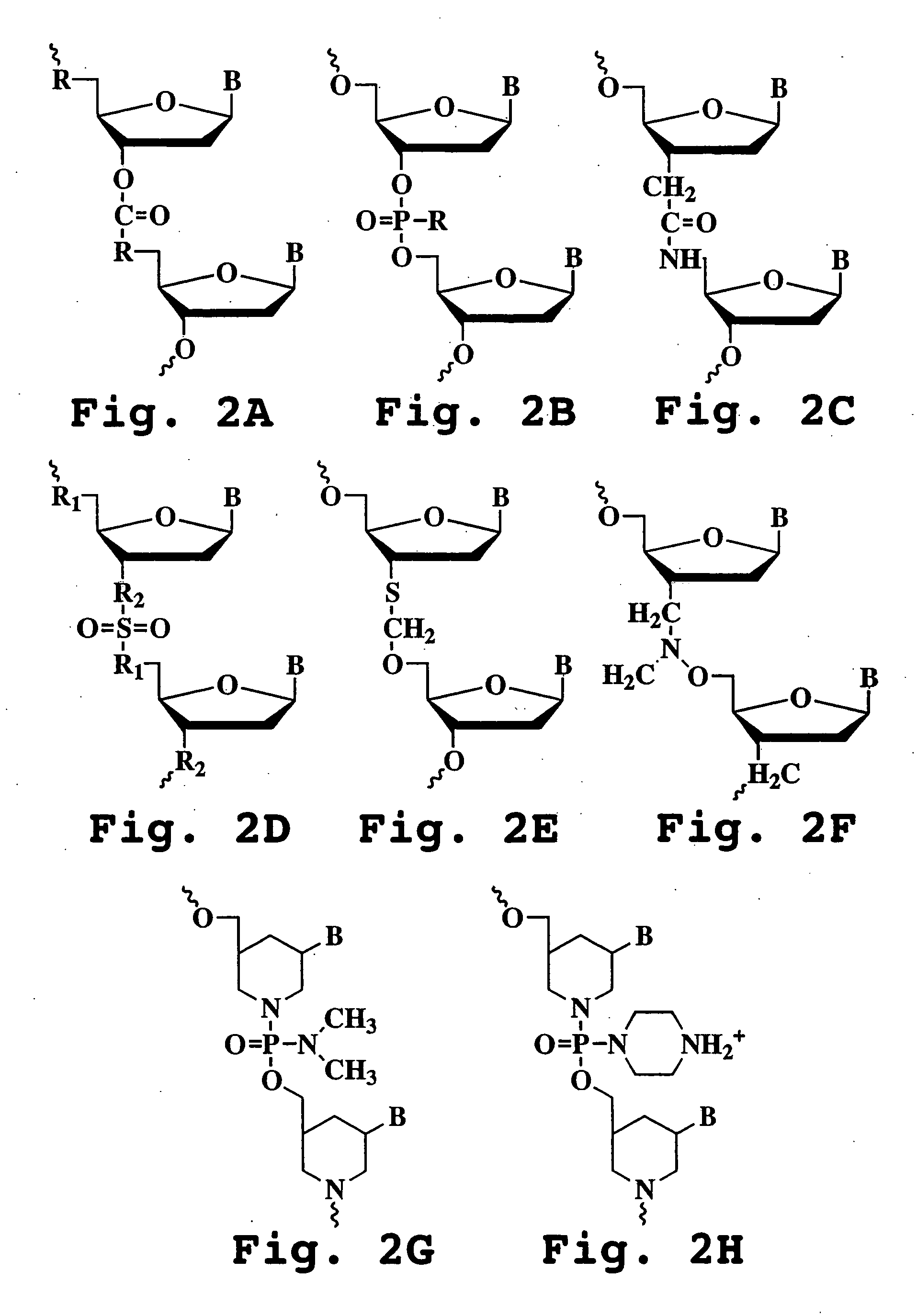
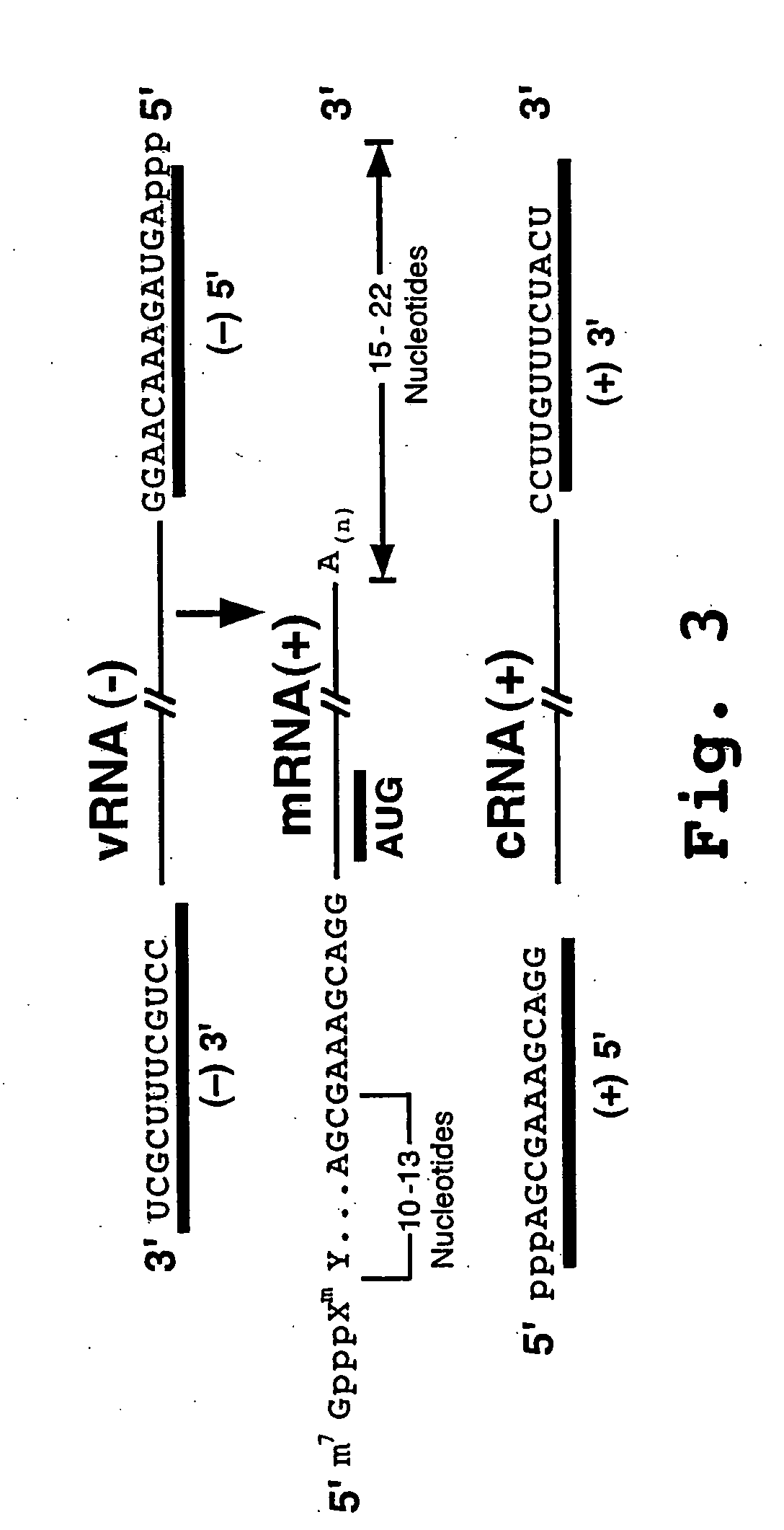
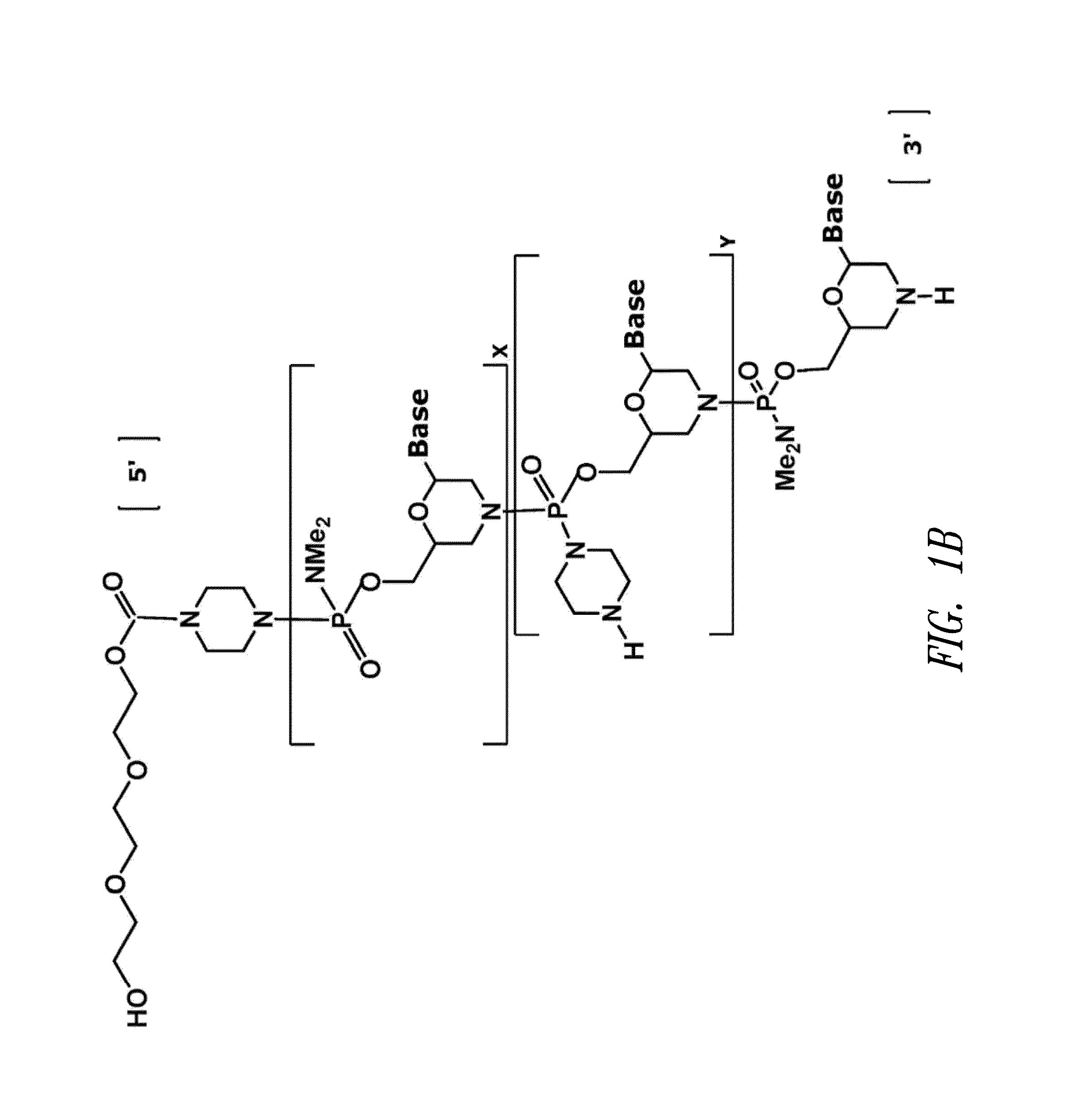
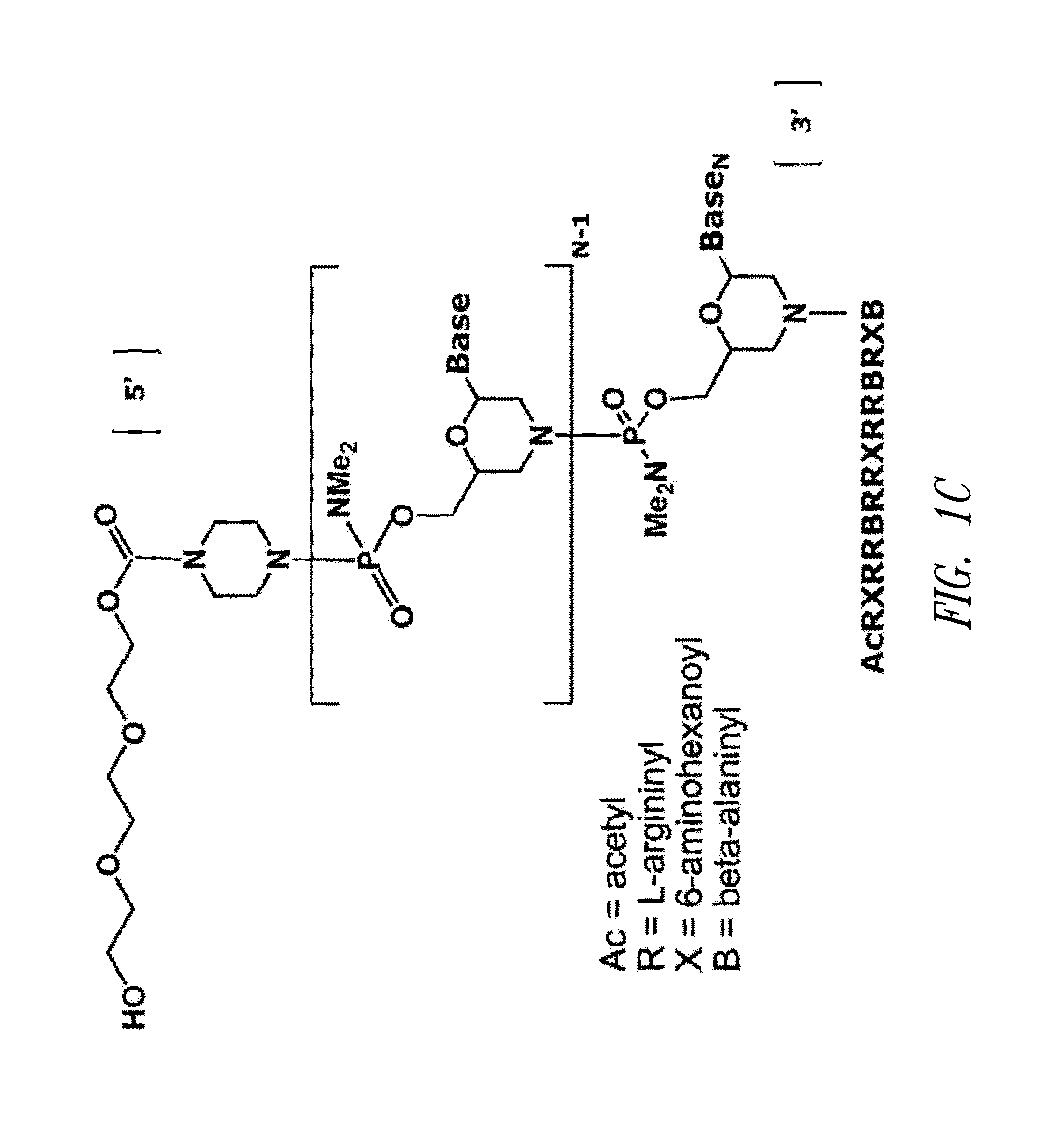
The invention provides antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Orthomyxoviridae family and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of influenza virus infection in a mammal. The antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged, including partially positively charged, morpholino oligonucleotides having 1) a nuclease resistant backbone, 2) 12-40 nucleotide bases, and 3) a targeting sequence of at least 12 bases in length that hybridizes to a target region selected from the following: a) the 5′ or 3′ terminal 25 bases of the negative sense viral RNA segment of Influenzavirus A, Influenzavirus B and Influenzavirus C; b) the terminal 25 bases of the 3′ terminus of the positive sense cRNA and; and c) the 50 bases surrounding the AUG start codon of an influenza viral mRNA.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Influenza virus vaccine composition and methods of use
InactiveUS20060024670A1Enhance transfectionHigh expressionSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesImmunogenicityImmunoreactive protein
The present invention is directed to enhancing the immune response of a human in need of protection against IV infection by administering in vivo, into a tissue of the human, at least one polynucleotide comprising one or more regions of nucleic acid encoding an IV protein or a fragment, a variant, or a derivative thereof. The present invention is further directed to enhancing the immune response of a human in need of protection against IV infection by administering, in vivo, into a tissue of the human, at least one IV protein or a fragment, a variant, or derivative thereof. The IV protein can be, for example, in purified form or can be an inactivated IV, such as those present in inactivated IV vaccines. The polynucleotide is incorporated into the cells of the human in vivo, and an immunologically effective amount of an immunogenic epitope of an IV, or a fragment, variant, or derivative thereof is produced in vivo. The IV protein (in purified form or in the form of an inactivated IV vaccine) is also administered in an immunologically effective amount.
Owner:VICAL INC
Functional influenza virus like particles (VLPs)
ActiveUS20070184526A1Protective responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsSeasonal influenzaAvian influenza virus
The present invention discloses and claims virus like particles (VLPs) that express and / or contains seasonal influenza virus proteins, avian influenza virus proteins and / or influenza virus proteins from viruses with pandemic potential. The invention includes vector constructs comprising said proteins, cells comprising said constructs, formulations and vaccines comprising VLPs of the inventions. The invention also includes methods of making and administrating VLPs to vertebrates, including methods of inducing substantial immunity to either seasonal and avian influenza, or at least one symptom thereof.
Owner:NOVAVAX
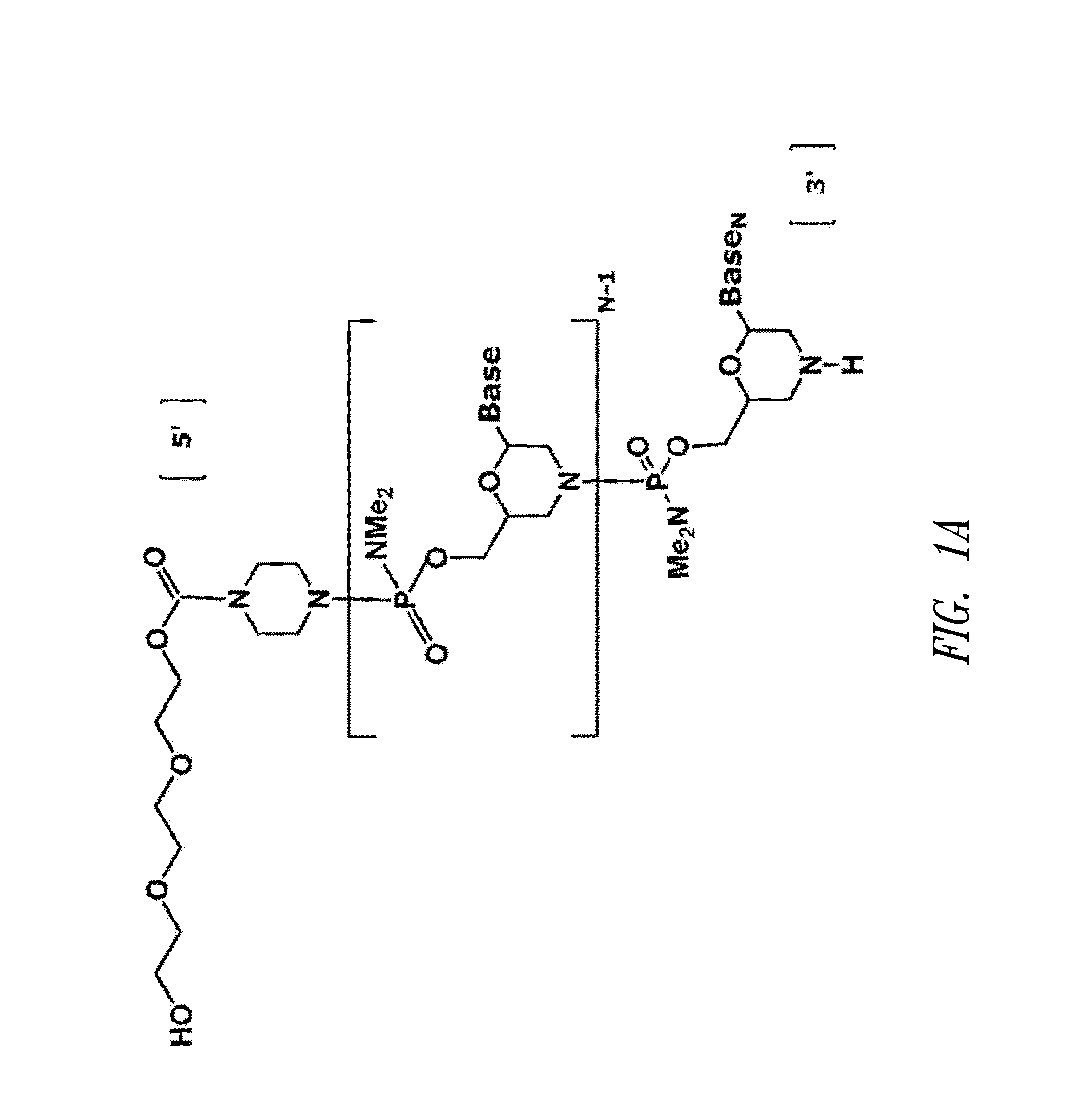
Antiviral compounds and methods of making and using thereof
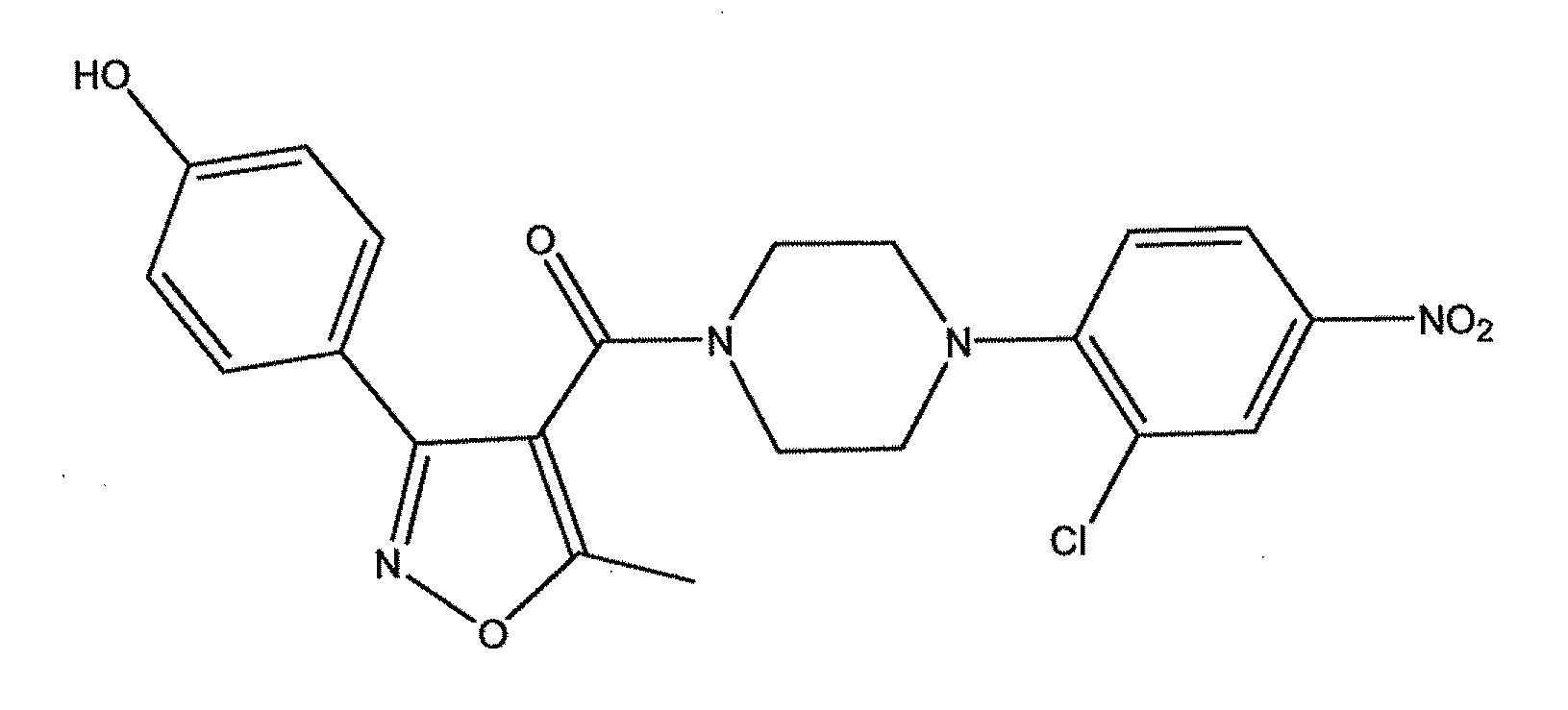
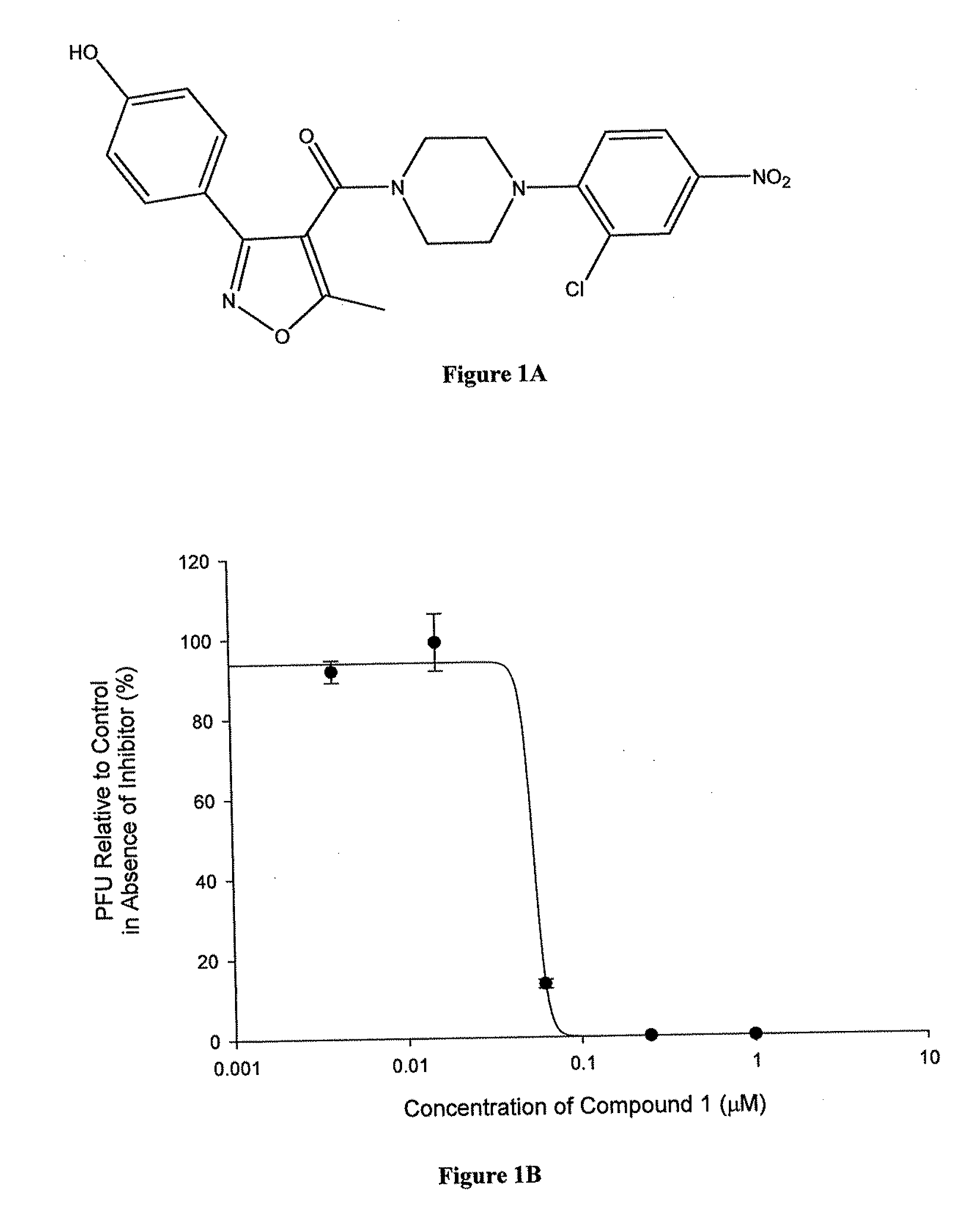
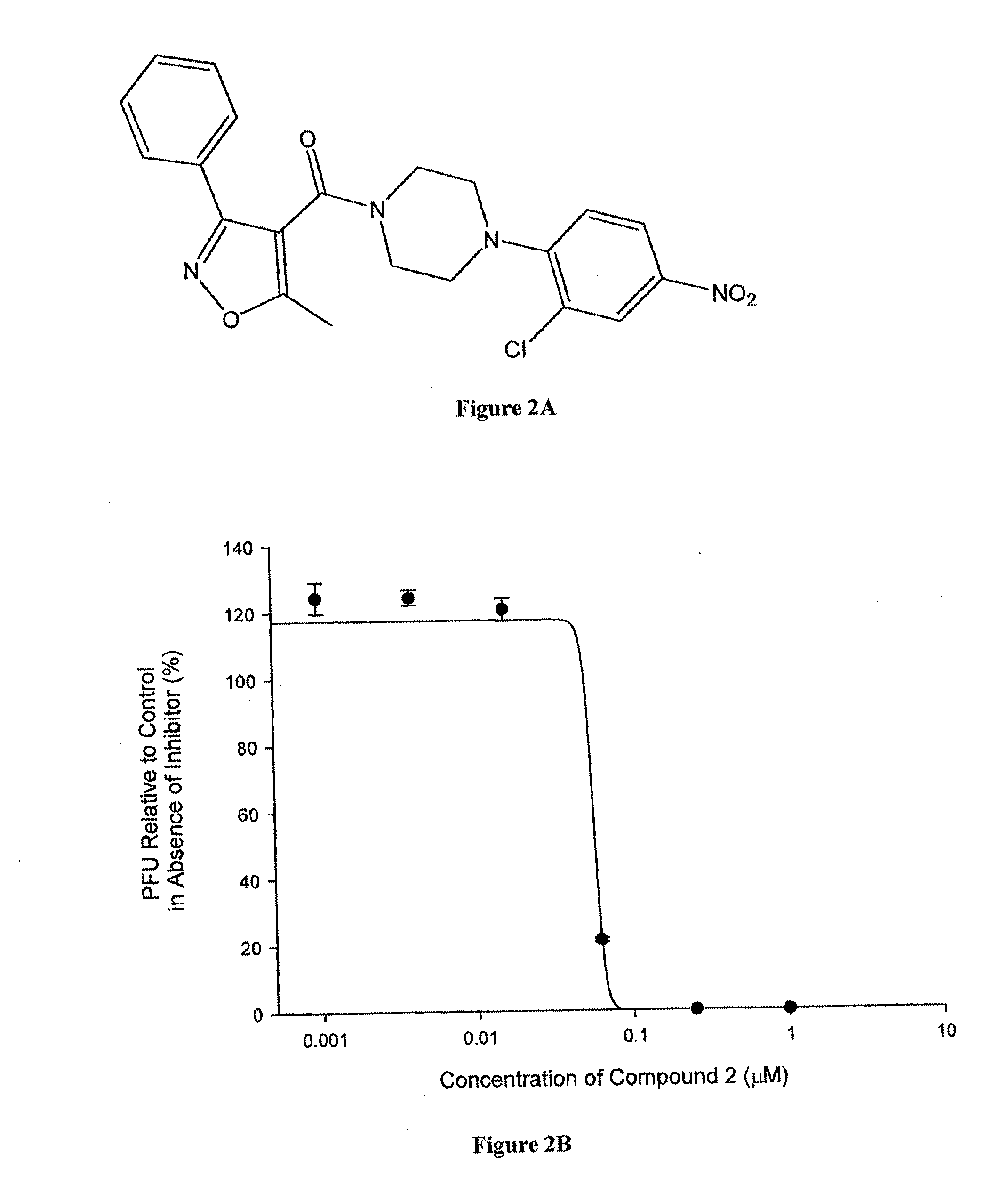
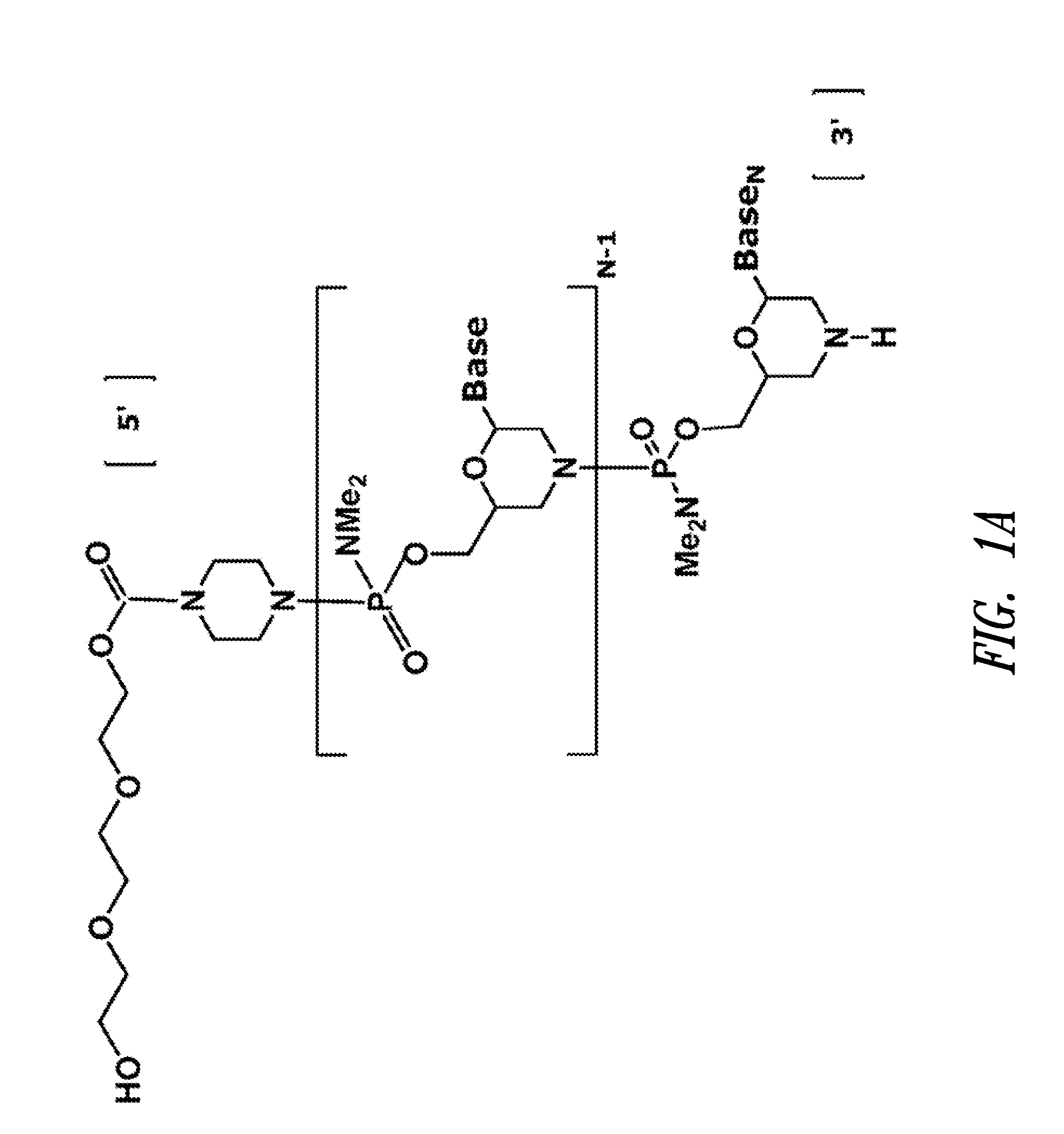
ActiveUS20110212975A1Organic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPiperazinePharmaceutical preservatives
Compounds which exhibit antiviral activity, particularly against influenza virus, and methods of making and using thereof are described herein. In one embodiment, the compounds are heterocyclic amides containing piperazine and isozazole rings and optionally substituted with one or more substituents. The compounds can be formulated with one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients to form compositions suitable for enteral or parenteral administration. The compounds are preferably used to treat or prevent Influenza A infections, such as H1N1, H2N2, H3N2, H5N1, H7N7, H1N2, H9N2, H7N2, H7N3, and H10N7.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Antisense antiviral compound and method for treating influenza viral infection
InactiveUS20060148747A1Inhibition of replicationPromote absorptionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideInfluenzavirus CInfluenzavirus B
The invention provides antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Orthomyxoviridae family and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of influenza virus infection in a mammal. The antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged morpholino oligonucleotides having 1) a nuclease resistant backbone, 2) 12-40 nucleotide bases, and 3) a targeting sequence of at least 12 bases in length that hybridizes to a target region selected from the following: a) the 5′ or 3′ terminal 25 bases of the negative sense viral RNA segment of Influenzavirus A, Influenzavirus B and Influenzavirus C; b) the terminal 25 bases of the 3′ terminus of the positive sense cRNA and; and c) the 50 bases surrounding the AUG start codon of an influenza viral mRNA.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
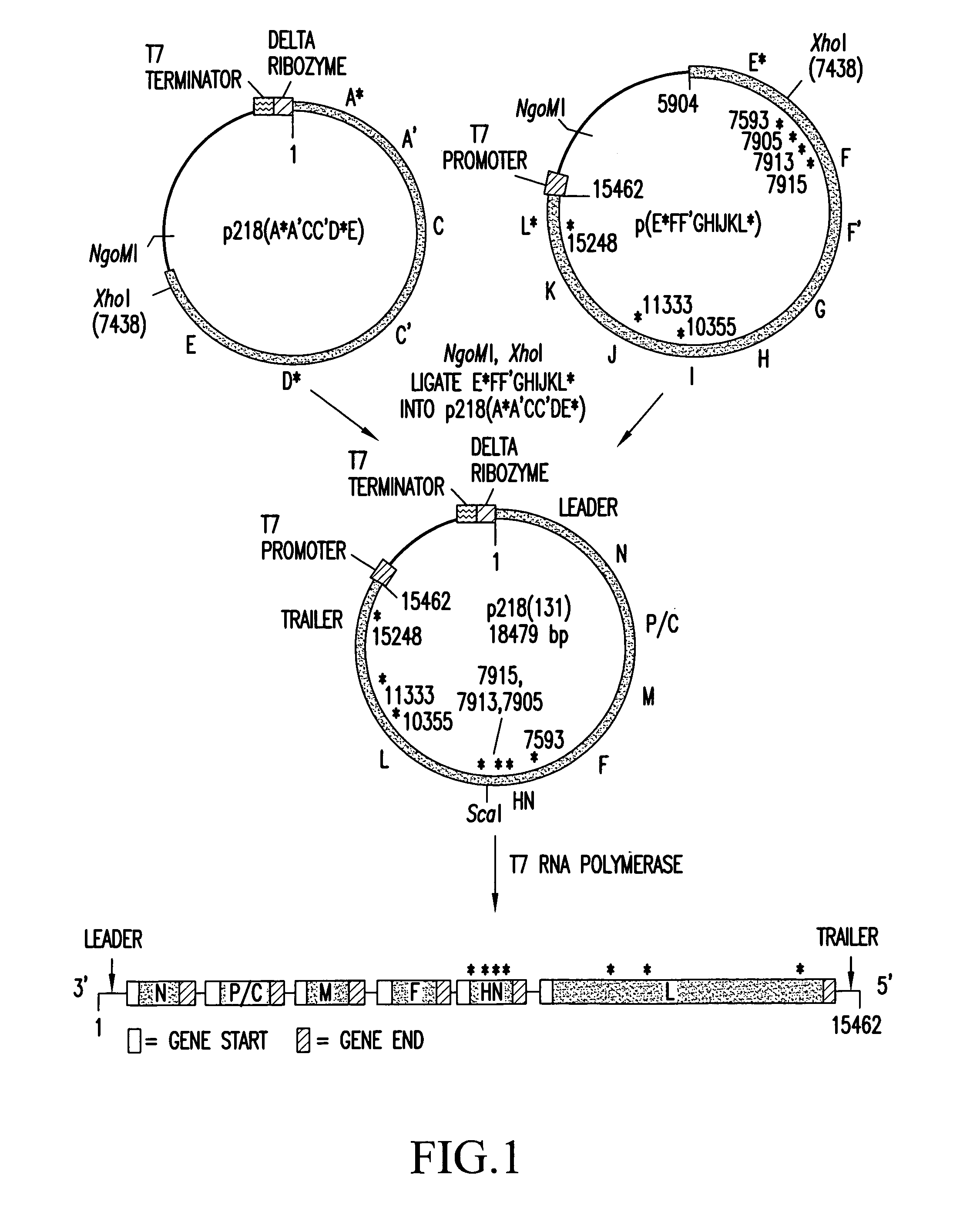
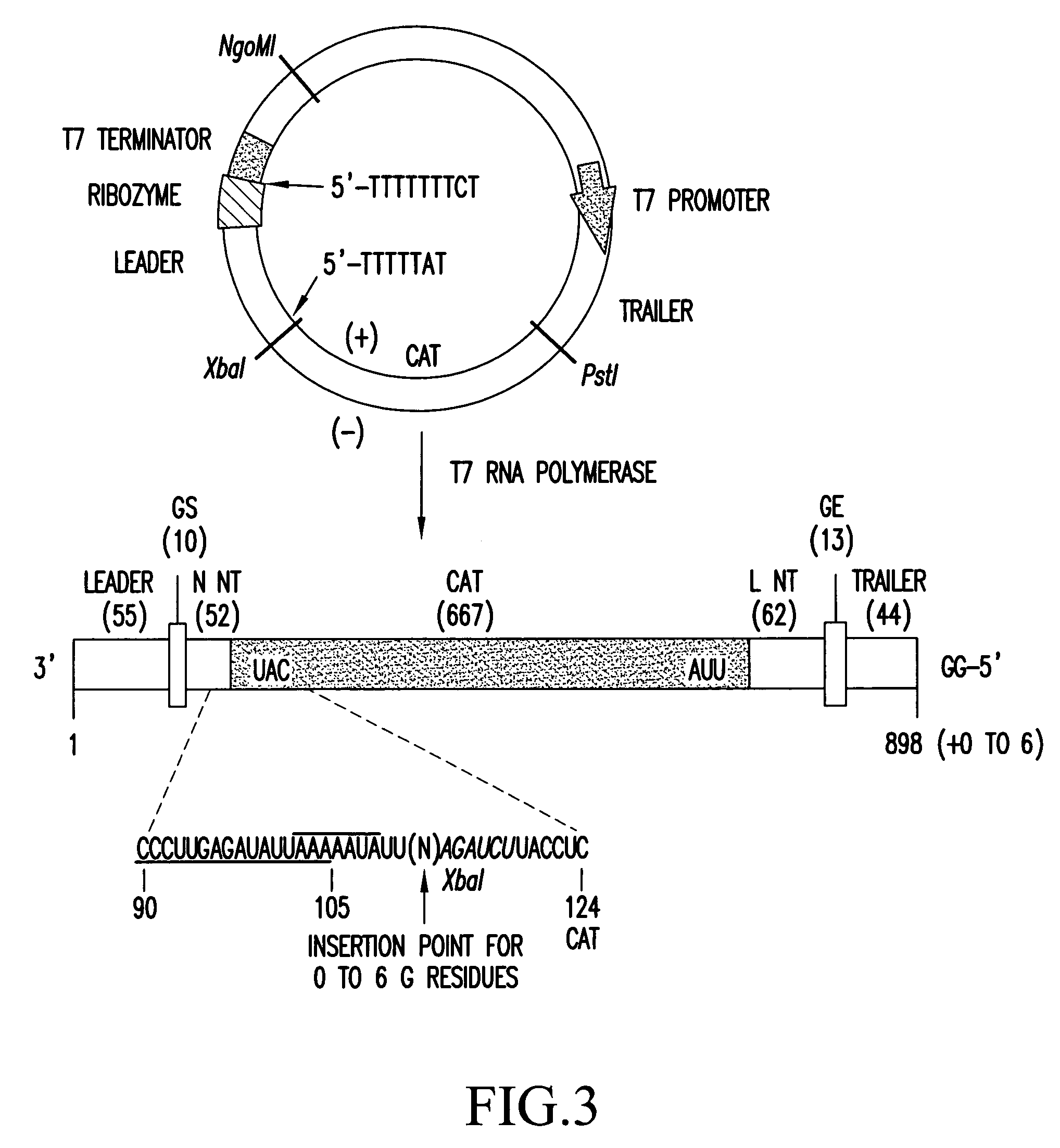
Recombinant influenza vectors with a PolII promoter and ribozymes for vaccines and gene therapy
InactiveUS20050037487A1Easy to operateEnhances these viruses as vaccine vectorsSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesHelper virusViral vector
The invention provides a composition useful to prepare influenza viruses, e.g., in the absence of helper virus, using vectors which include Po1II promoters and multiple ribozyme sequences.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Influenza vaccine
The present invention relates to monovalent influenza vaccine formulations and vaccination regimes for immunising against influenza disease, their use in medicine, in particular their use in augmenting immune responses to various antigens, and to methods of preparation. In particular, the invention relates to monovalent influenza immunogenic compositions comprising an influenza antigen or antigenic preparation thereof from an influenza virus strain being associated with a pandemic outbreak or having the potential to be associated with a pandemic outbreak, in combination with an oil-in-water emulsion adjuvant comprising a metabolisable oil, a sterol or a tocopherol such as alpha tocopherol, and an emulsifying agent.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BEECHAM PHARMA GMBH +1
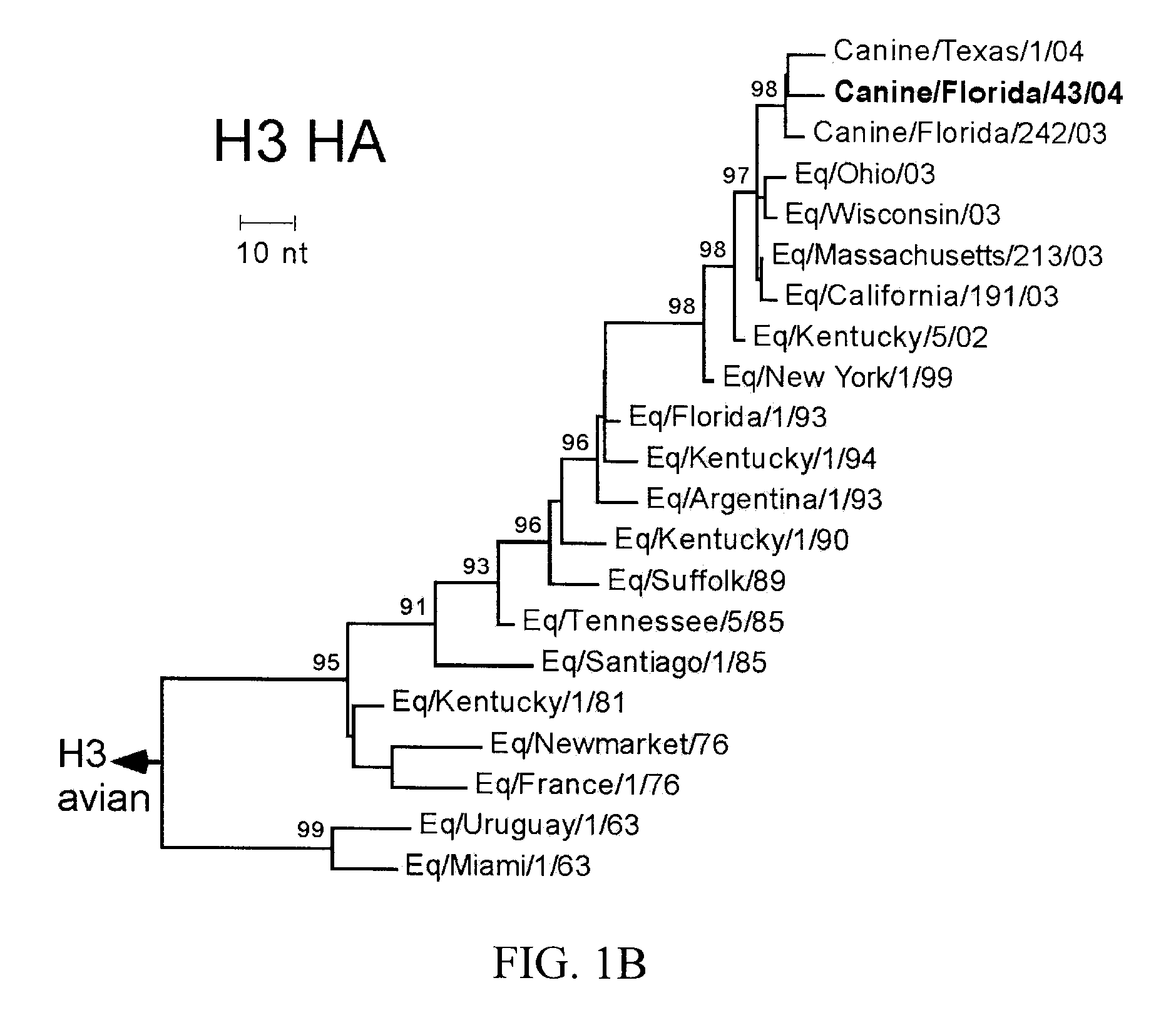
Materials and methods for respiratory disease control in canines
ActiveUS7959929B2Reduce riskPrevent and reduce riskVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseasePulmonary circulation diseases
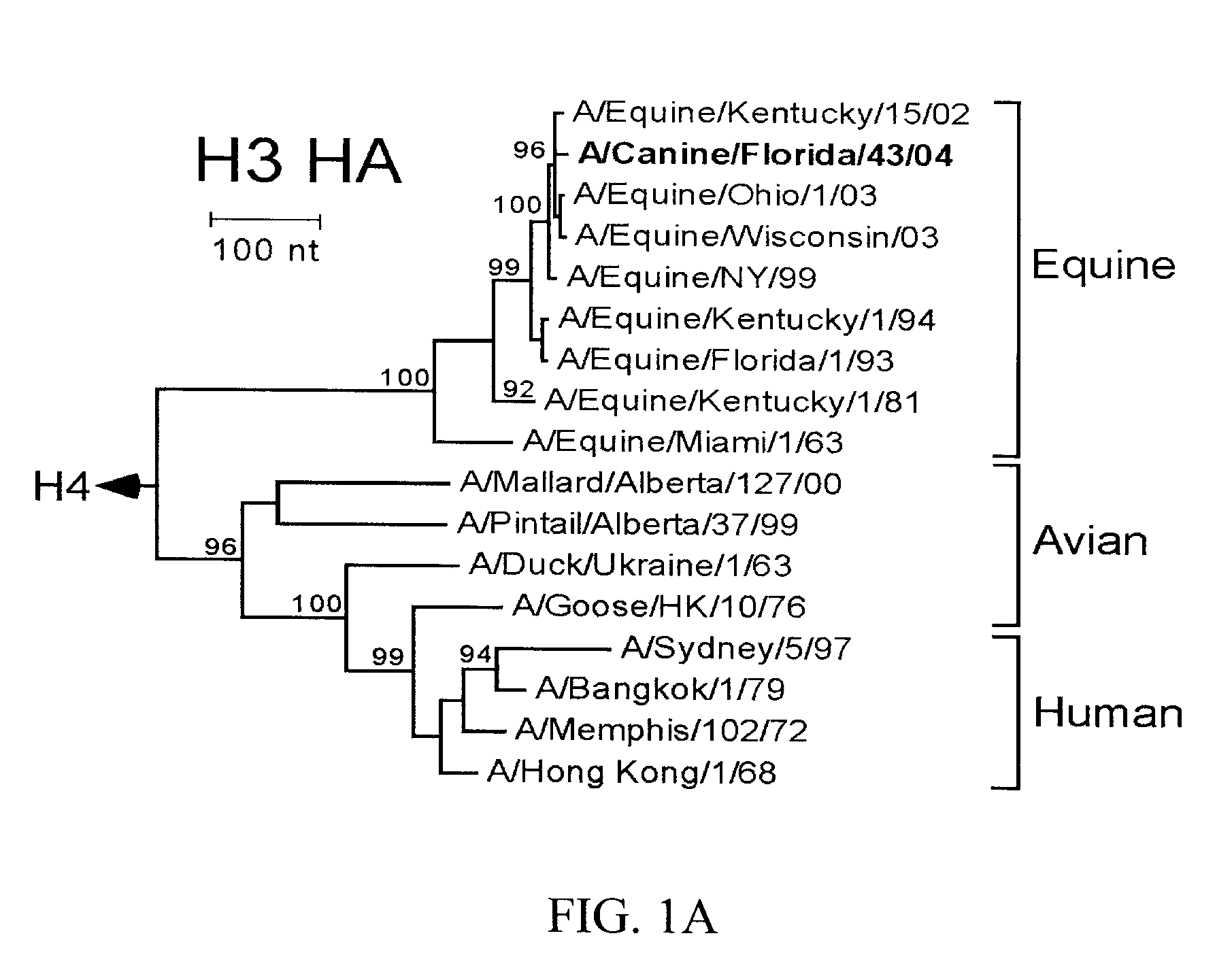
The subject invention pertains to isolated influenza virus that is capable of infecting canids and causing respiratory disease in the canid. The subject invention also pertains to compositions and methods for inducing an immune response against an influenza virus of the present invention. The subject invention also pertains to compositions and methods for identifying a virus of the invention and diagnosing infection of an animal with a virus of the invention.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +2
Recombinant parainfluenza virus expression systems and vaccines comprising heterologous antigens derived from metapneumovirus
Owner:VIRONOVATIVE
Peptide-based vaccine for influenza
A human synthetic peptide-based influenza vaccine for intranasal administration comprises a mixture of flagella containing at least four epitopes of influenza virus reactive with human cells, each expressed individually in Salmonella flagellin, said influenza virus epitopes being selected from the group consisting of: (i) one B-cell hemagglutinin (HA) epitope; (ii) one T-helper hemagglutinin (HA) or nucleo-protein (NP) epitope that can bind to many HLA molecules; and (iii) at least two cytotoxic lymphocyte (CTL) nucleoprotein (NP) or matrix protein (M) epitopes that are restricted to the most prevalent HLA molecules in different human populations.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Antisense antiviral compound and method for treating influenza viral infection
ActiveUS20110118334A1Improve throughputLimit deliveryAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesInfluenzavirus CStart codon
The present invention relates to antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Orthomyxoviridae family and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of influenza virus infection in a mammal. Exemplary antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged, or partially positively charged, morpholino oligonucleotides having 1) a nuclease resistant backbone, 2) 12-40 nucleotide bases, and 3) a targeting sequence of at least 12 bases in length that hybridizes to a target region selected from the following: a) the 5′ or 3′ terminal 25 bases of the negative sense viral RNA segment of Influenzavirus A, Influenzavirus B and Influenzavirus C; b) the terminal 30 bases of the 5′ or 3′ terminus of the positive sense vcRNA; c) the 45 bases surrounding the AUG start codon of an influenza viral mRNA and; d) 50 bases surrounding the splice donor or acceptor sites of influenza mRNAs subject to alternative splicing.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
siRNA silencing of influenza virus gene expression
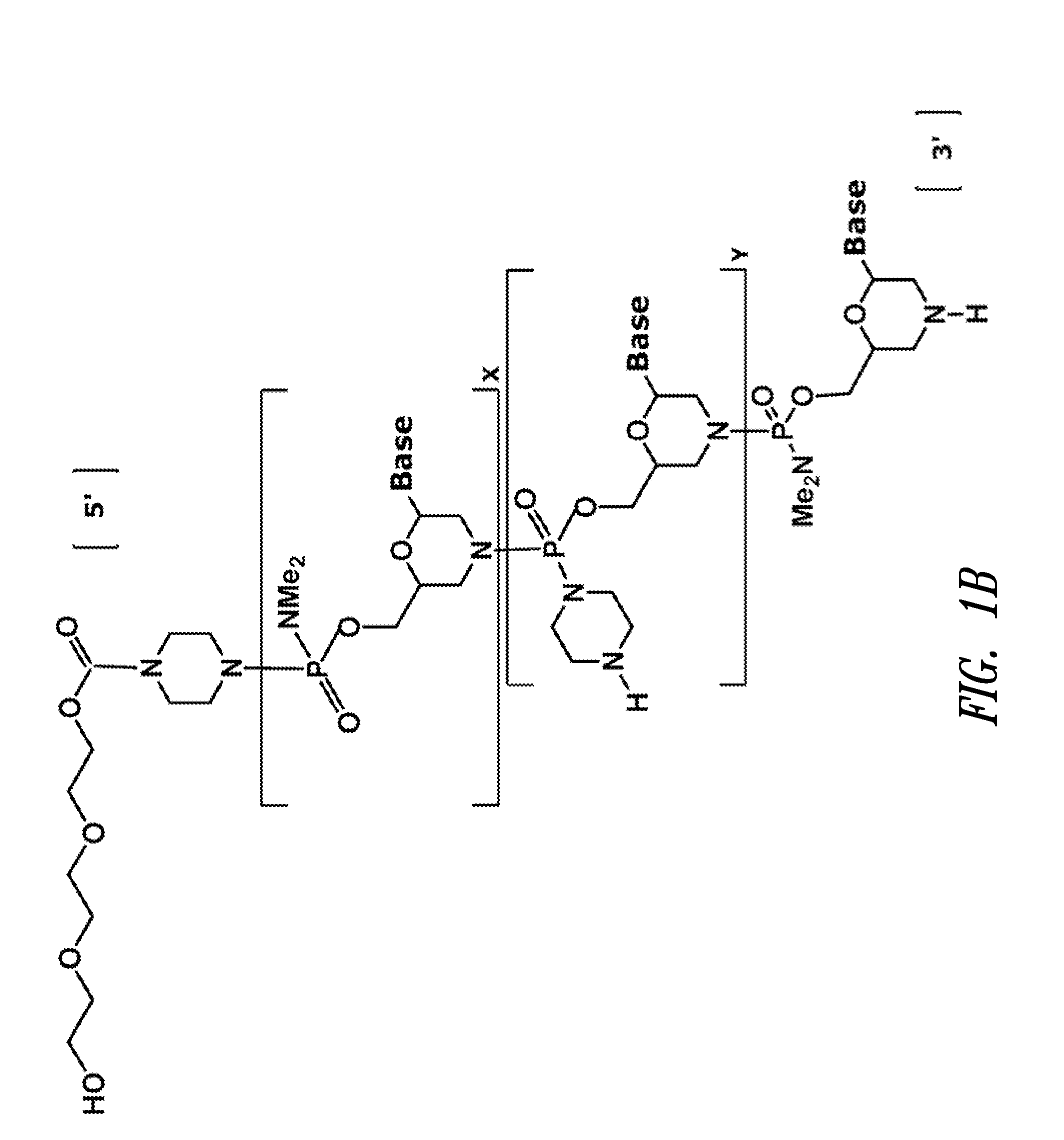
InactiveUS20070218122A1Reduce the amount requiredSsRNA viruses negative-sensePowder deliveryLipid formationSirna silencing
The present invention provides siRNA molecules that target influenza virus gene expression and methods of using such siRNA molecules to silence influenza virus gene expression. The present invention also provides nucleic acid-lipid particles that target influenza virus gene expression comprising an siRNA that silences influenza virus gene expression, a cationic lipid, and a non-cationic lipid.
Owner:PROTIVA BIOTHERAPEUTICS
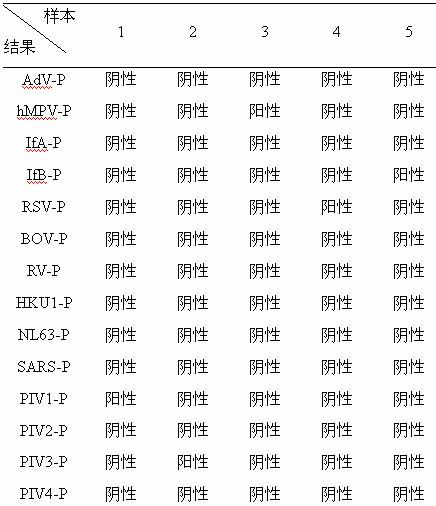
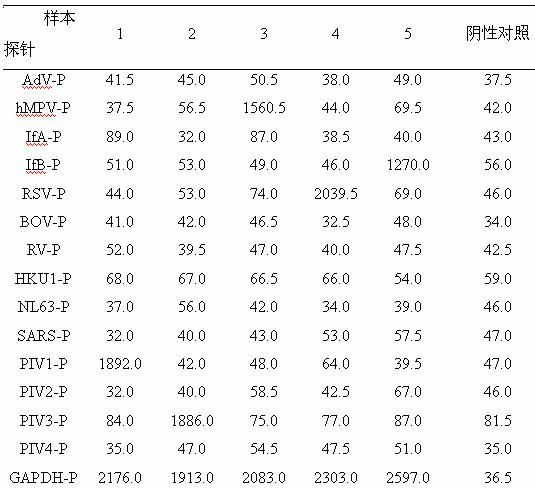
Method for detecting various respiratory viruses and primers and probes thereof
InactiveCN101985665AEasy to operateStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicrosphereNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical fields of biochips and diagnostic reagents, and discloses a method for detecting various respiratory viruses, and primers and probes thereof. In the invention, nucleotide sequences of 14 respiratory viruses, namely adenovirus, human metapneumovirus, influenza virus A, influenza virus B, respiratory syncytial virus, bocavirus, rhinovirus, coronavirus (HKU1, NL63 and SARS), and parainfluenza virus (type I, type II, type III and type IV) are analyzed, and corresponding reverse transcription primers, PCR primers and specific probes are designed. Specific gene segments are amplified by reverse transcription and multiple asymmetric PCR methods; a fluorescence-coded microsphere group coupled with the virus specific probes and the PCR amplification product are incubated and hybridized by liquid phase chip technology; and finally the Bio-PlexTM200 is used for detection. The detection method has the advantages of high flux, high specificity and sensitivity, stable results and good repeatability, the detection method is easy to operate, and the detection speed is high.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
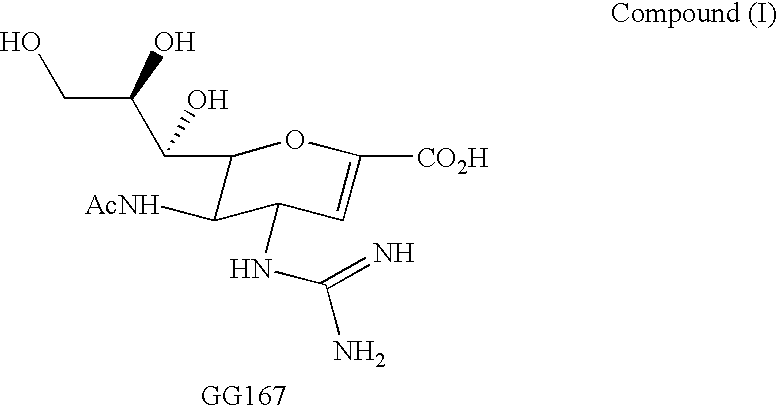
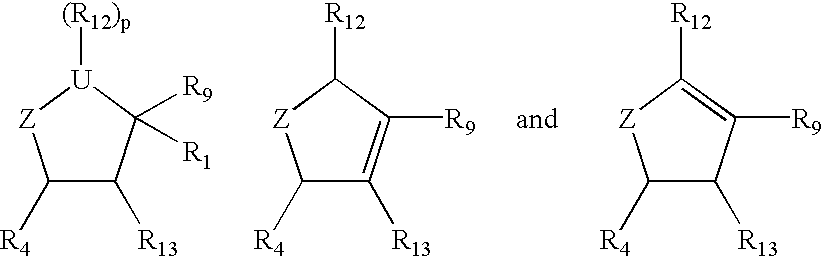
Cyclopentane and cyclopentene compounds and use for detecting influenza virus
New cyclopentane and cyclopentene compounds are provided along with their use in method for detecting influenza virus.
Owner:BIOCRYST PHARM INC
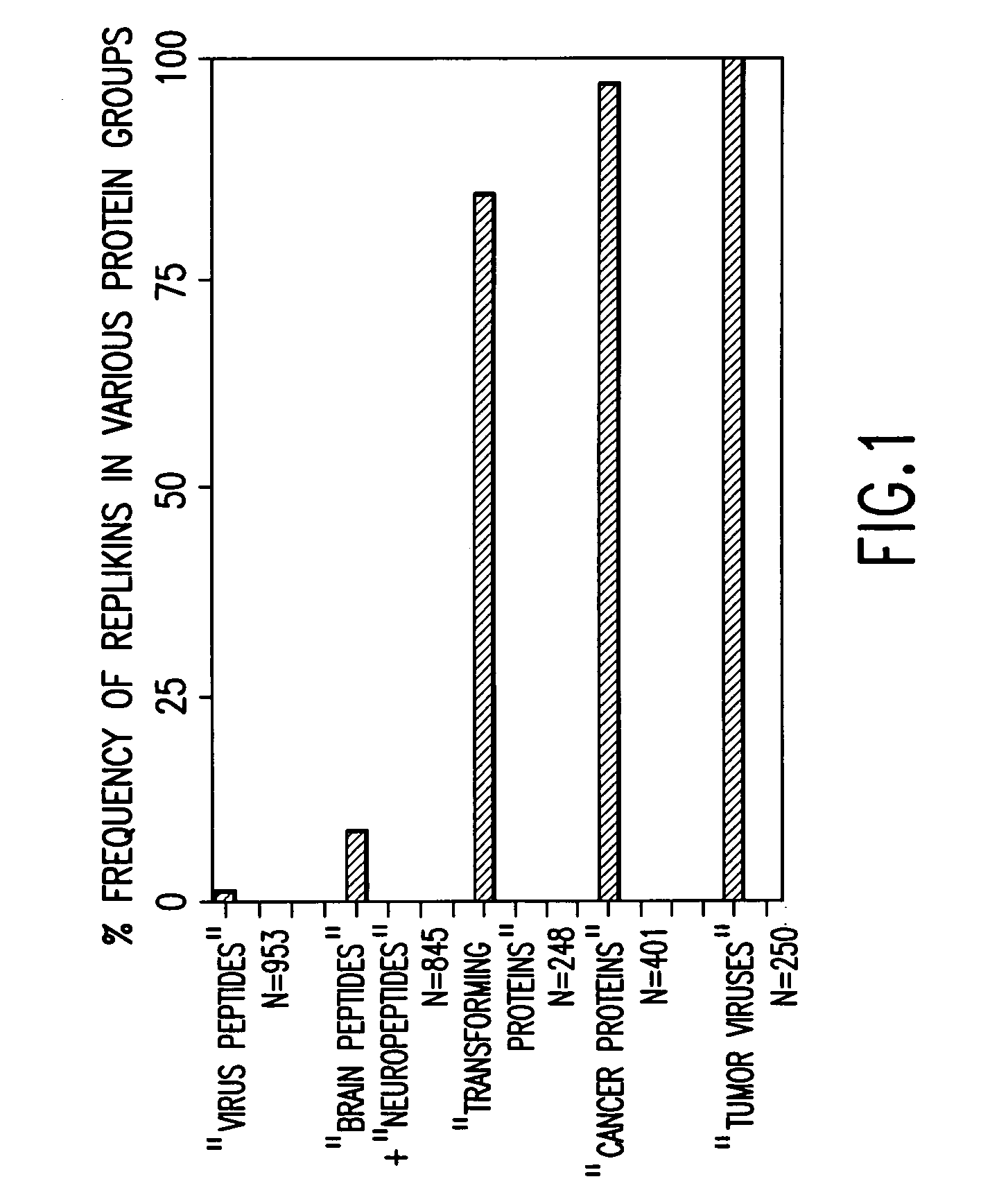
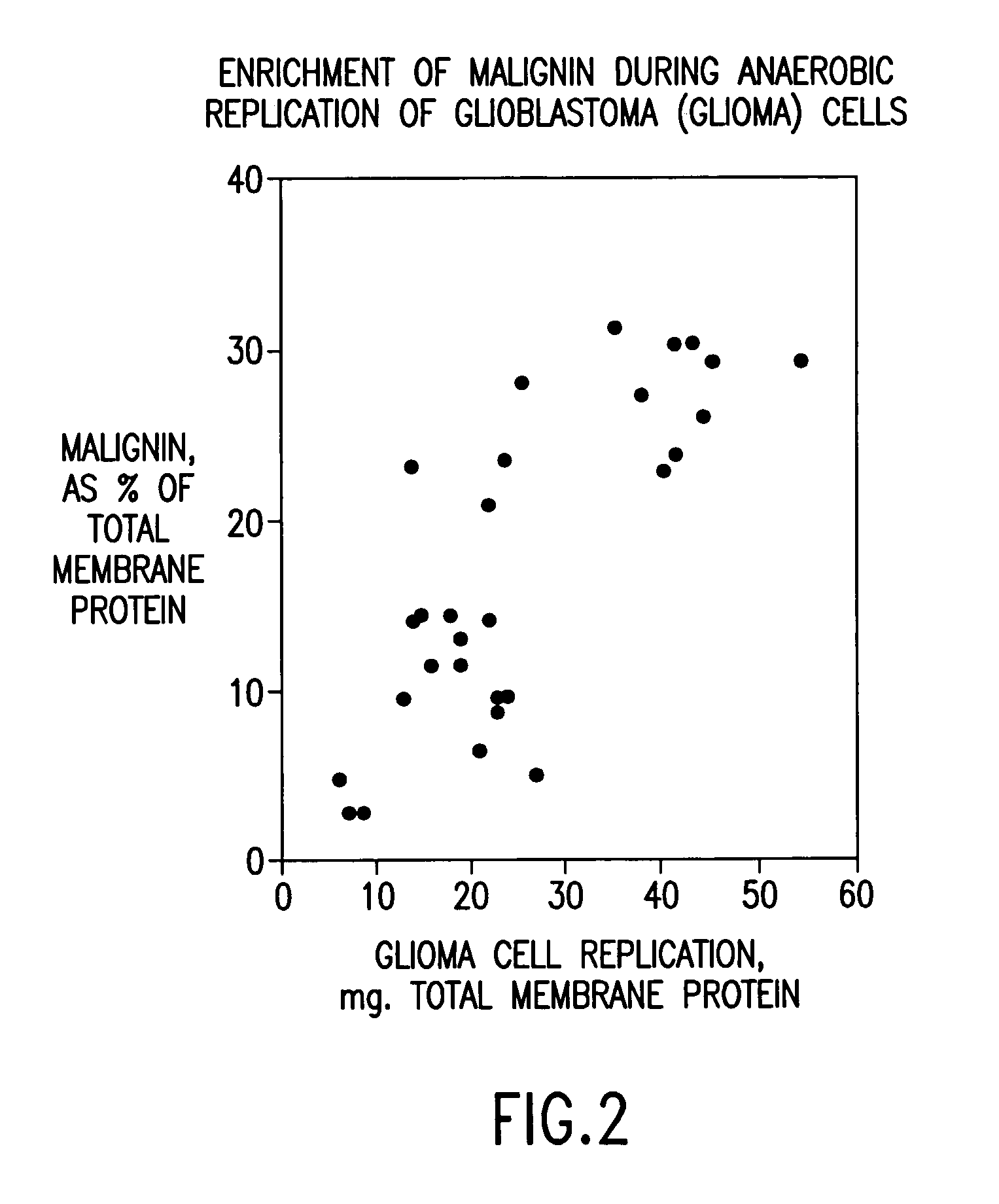
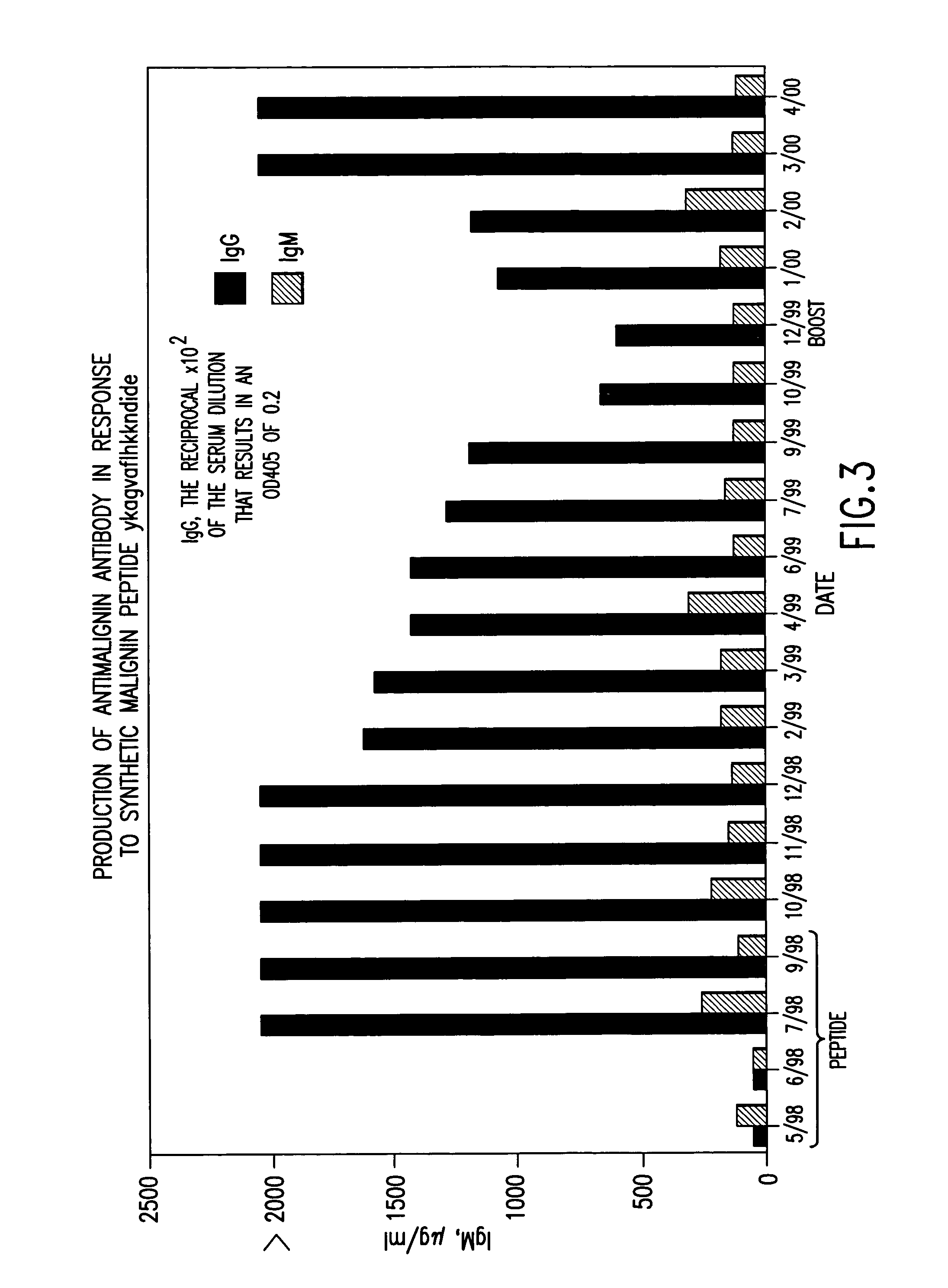
Replikin peptides in rapid replication of glioma cells and in influenza epidemics
Peptides of influenza virus hemagglutinin protein and Plasmodium falciparum malaria antigen, antibodies specific for the peptides, influenza vaccines, malaria vaccines and methods of stimulating the immune response of a subject to produce antibodies to influenza virus or malaria are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for formulating vaccines for influenza virus.
Owner:BOGOCH SAMUEL +1
Compounds and methods for treating influenza
ActiveUS20100330173A1Eliminate side effectsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCancer researchMaturation process
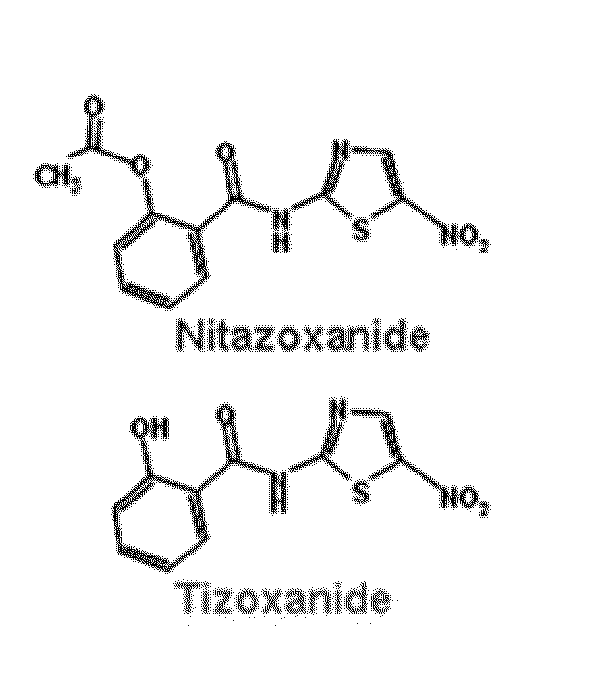
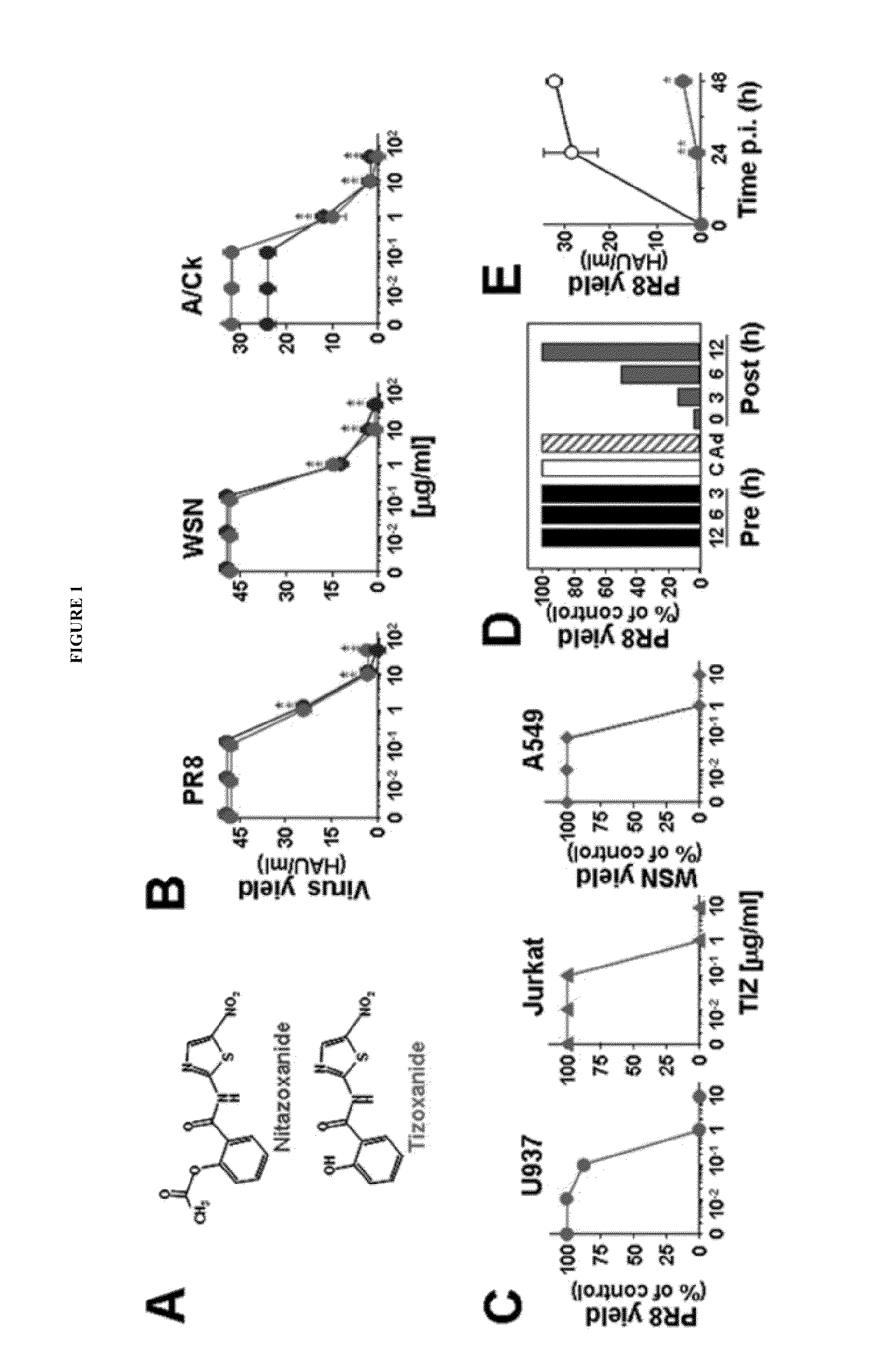
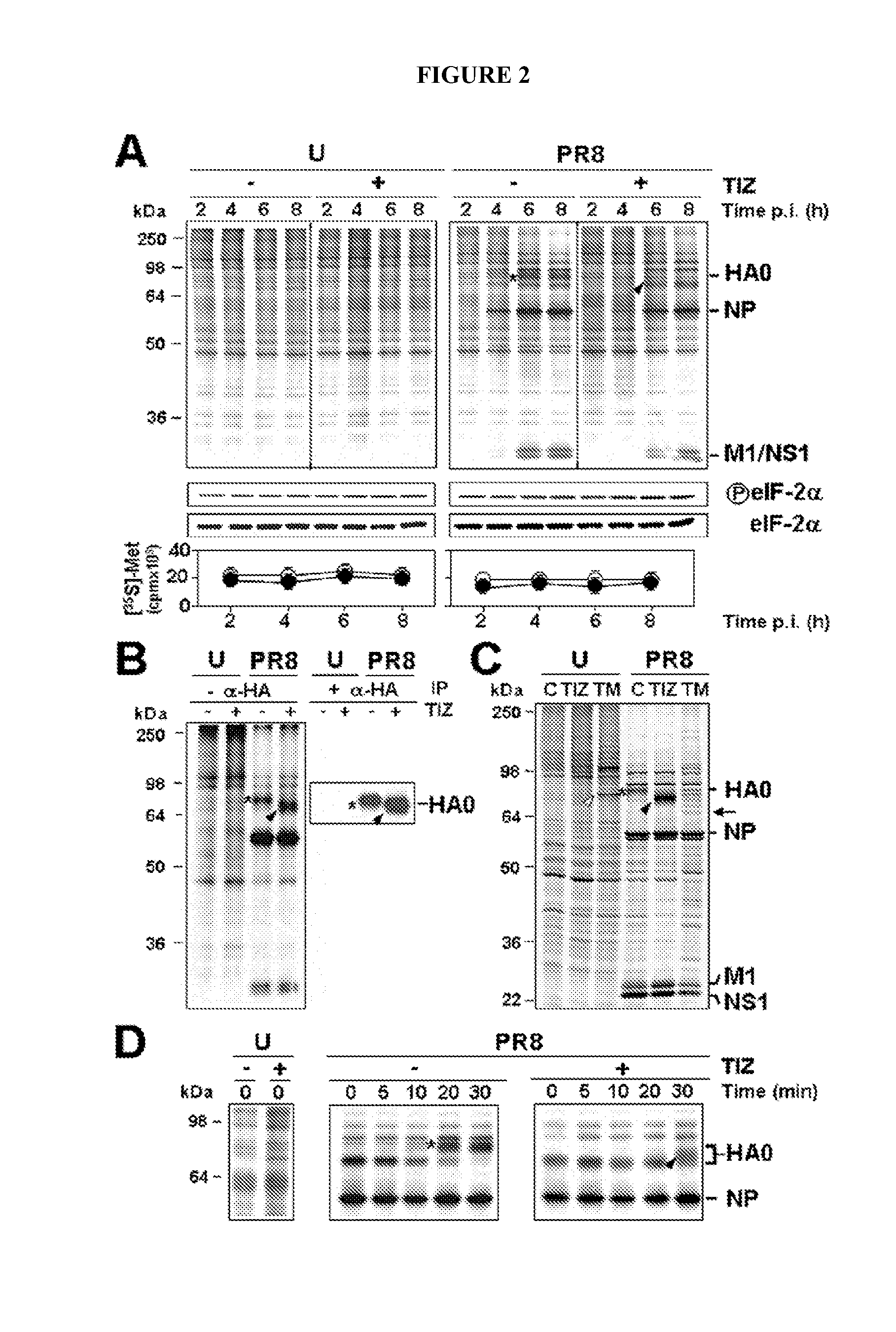
This invention is directed to methods for treating and preventing influenza infection by inhibiting influenza virus HA maturation processes employing compounds of formula I. It is also directed to combinations for treating and preventing influenza infection comprising compounds of formula I and other agents.
Owner:ROMARK LAB L C
Production of attenuated parainfluenza virus vaccines from cloned nucleotide sequences
InactiveUS7208161B1SsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesPolymerase LParainfluenza virus vaccine
Isolated polynucleotide molecules provide recombinant PIV genomes and antigenomes for production of recombinant PIV vaccines. The recombinant genome or antigenome can be expressed with a nucleoprotein (N), phosphoprotein (P), and a large (L) polymerase protein to produce isolated infectious PIV particles. The recombinant PIV genome and antigenome can be modified to produce desired changes, for example to incorporate attenuating mutations from biologically derived PIV mutants or to create chimeric PIV clones, to generate attenuated, immunogenic viruses for vaccine use.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF
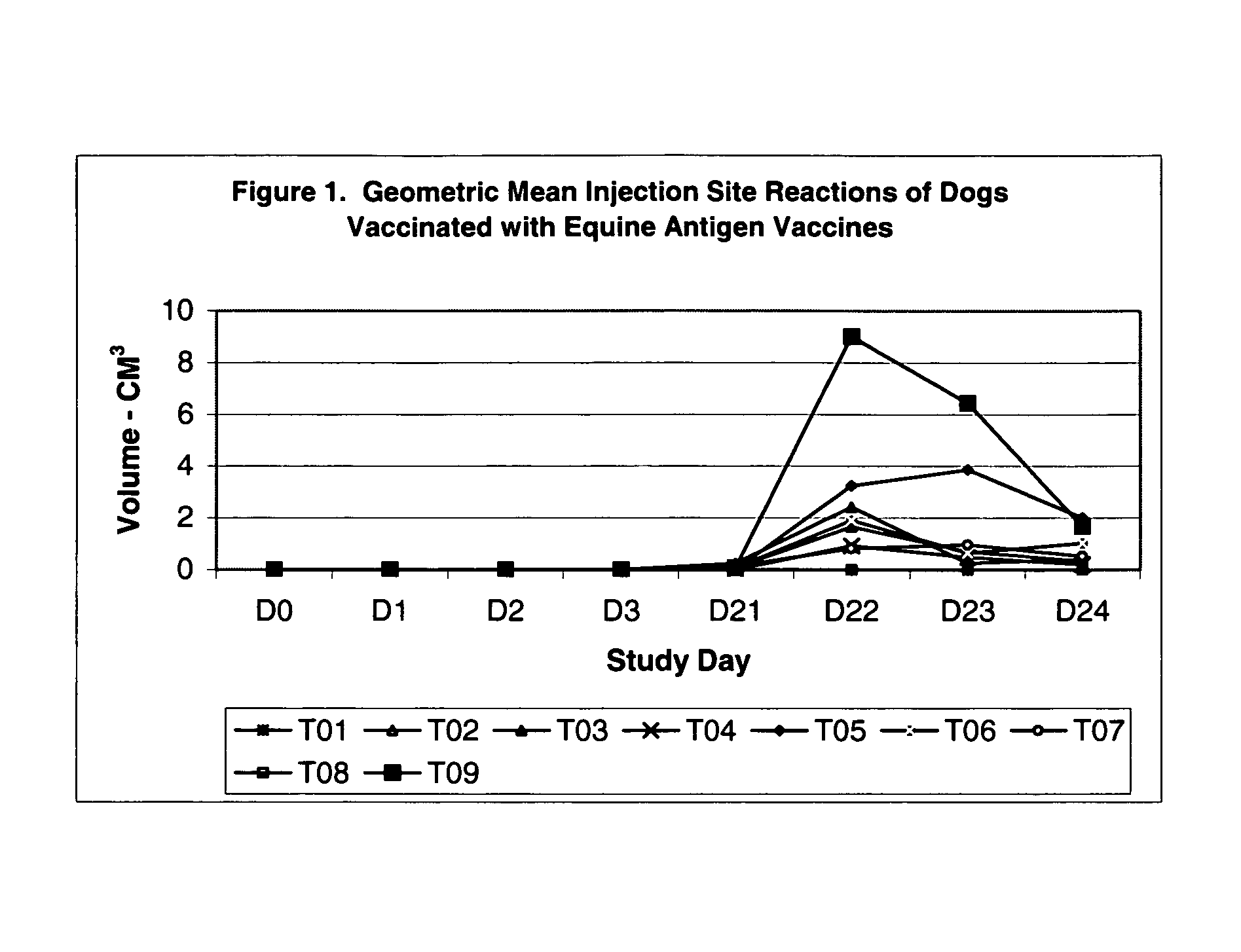
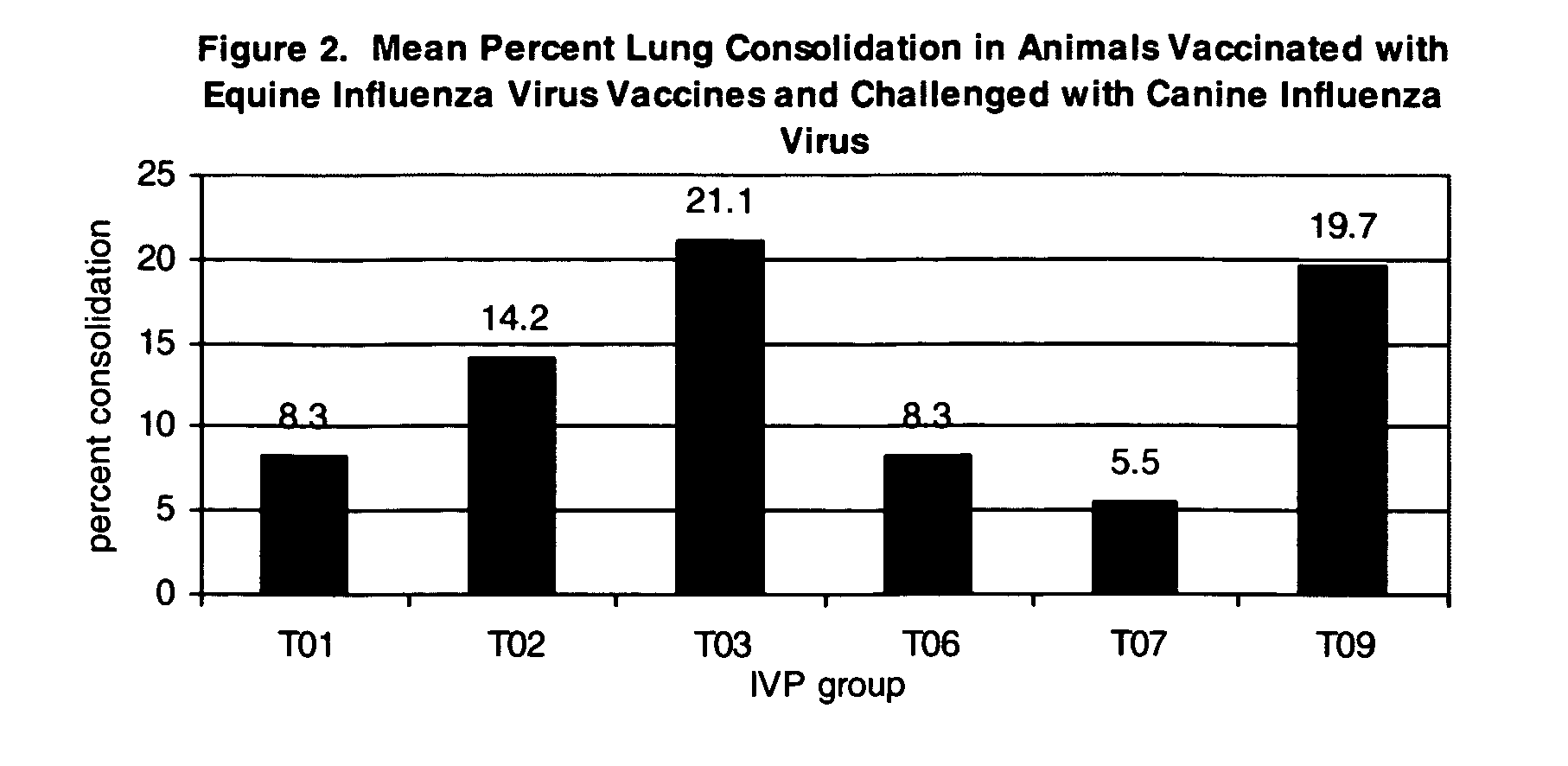
Vaccines and methods to treat canine influenza
The present invention relates to providing new vaccines and treatments for the diseases related to canine influenza virus. It discloses influenza viral antigens, and methods of presenting these antigens to canines, especially dogs. It relates to attenuated and killed vaccines. The present invention relates to experimentally generated canine and equine influenza viruses. The invention also includes influenza A, including H3, N8, H3N8, H7N7 and viruses which contain at least one genome segment from an canine or equine influenza virus. The present invention also relates to the use of these viruses in therapeutic compositions to protect canines, dogs in particular, from diseases caused by influenza viruses.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Antisense antiviral compound and method for treating influenza viral infection
ActiveUS8697858B2Improve throughputLimit deliveryAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesInfluenzavirus CBase J
The present invention relates to antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Orthomyxoviridae family and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of influenza virus infection in a mammal. Exemplary antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged, or partially positively charged, morpholino oligonucleotides having 1) a nuclease resistant backbone, 2) 12-40 nucleotide bases, and 3) a targeting sequence of at least 12 bases in length that hybridizes to a target region selected from the following: a) the 5′ or 3′ terminal 25 bases of the negative sense viral RNA segment of Influenzavirus A, Influenzavirus B and Influenzavirus C; b) the terminal 30 bases of the 5′ or 3′ terminus of the positive sense vcRNA; c) the 45 bases surrounding the AUG start codon of an influenza viral mRNA and; d) 50 bases surrounding the splice donor or acceptor sites of influenza mRNAs subject to alternative splicing.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com