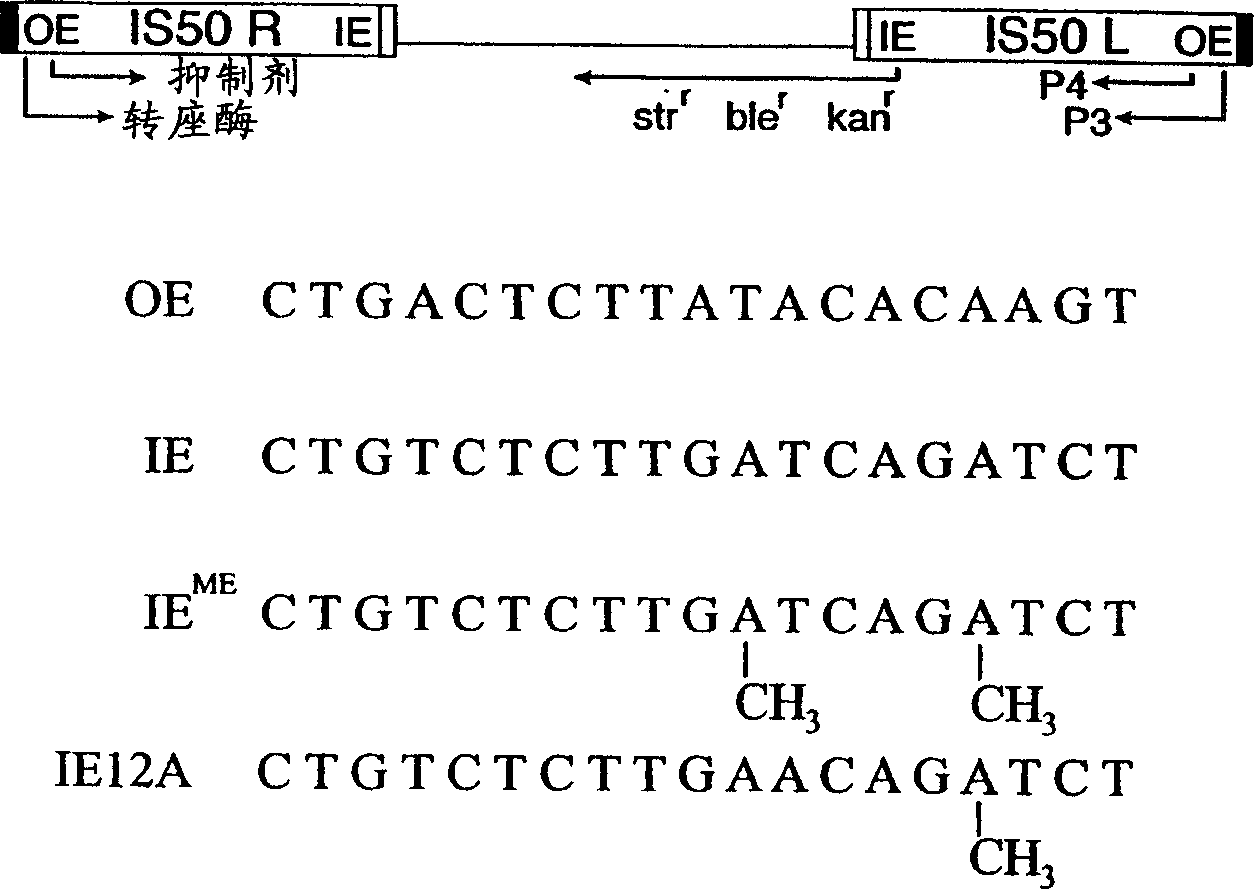Mutant TN5 transposase enzymes and method for their use
A transposase and mutant technology, applied in the direction of transferase, other methods of inserting foreign genetic materials, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of inactivity of wild-type Tnp
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0031] review
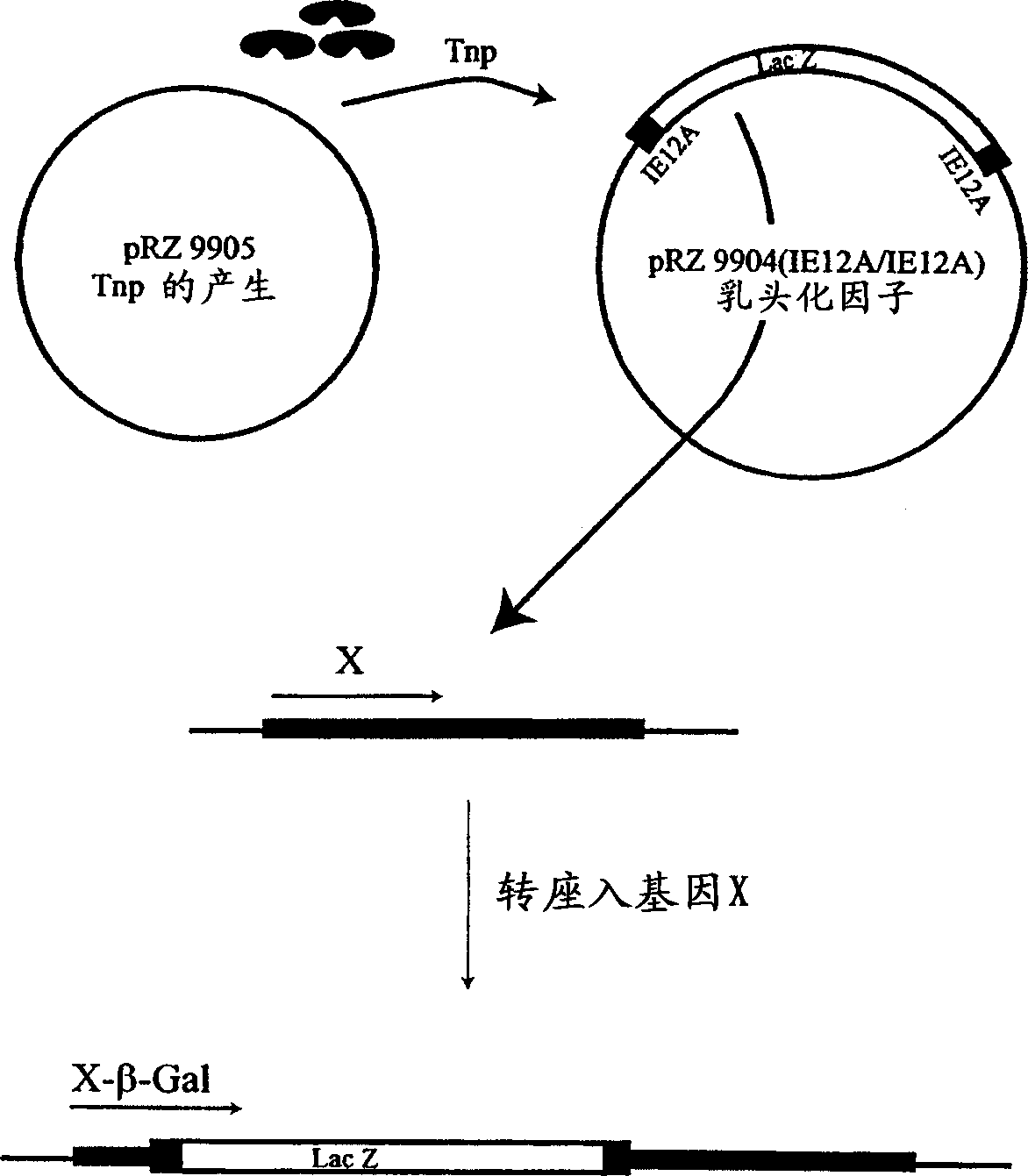
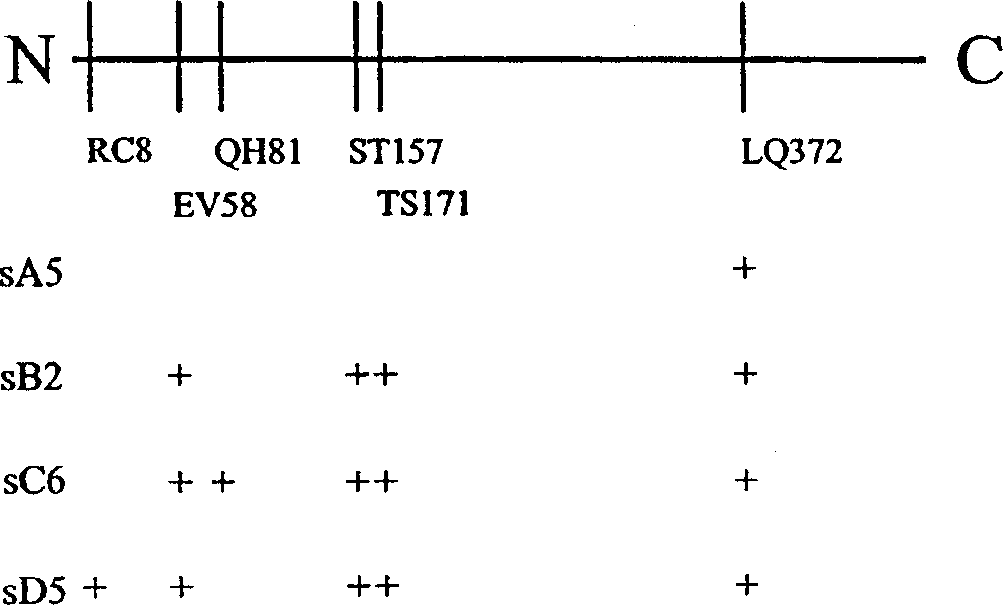
[0032] The families of mutants disclosed herein can be obtained in a number of related ways. In the first approach, Applicants generated mutants that reverted transposition activity in vivo to an end-binding sequence that the mutant wild-type transposase did not recognize as a substrate. In the second approach, Applicants introduced directed mutations into the product of the first approach to determine the preferred structure of the mutant transposases of the invention.
[0033] In the first approach, the IE end-binding sequence was mutated to contain an adenine in place of thymine at position 12 ("IE12A"; SEQ ID NO: 5). The thymine-to-adenine change in IE12A disrupts one of the two methylation sites in wild-type IE. Applicants used sPCR, a method of combinatorial random site-directed mutagenesis, to obtain a modified transposase protein capable of restoring transposition activity to polynucleotides flanked by IE12A. Stemmer, W.P., "Rapid protein evolution i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com