Semiconductor laser element
A technology of laser components and semiconductors, applied in semiconductor lasers, laser parts, lasers, etc., can solve problems such as reducing the quality of recording signals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
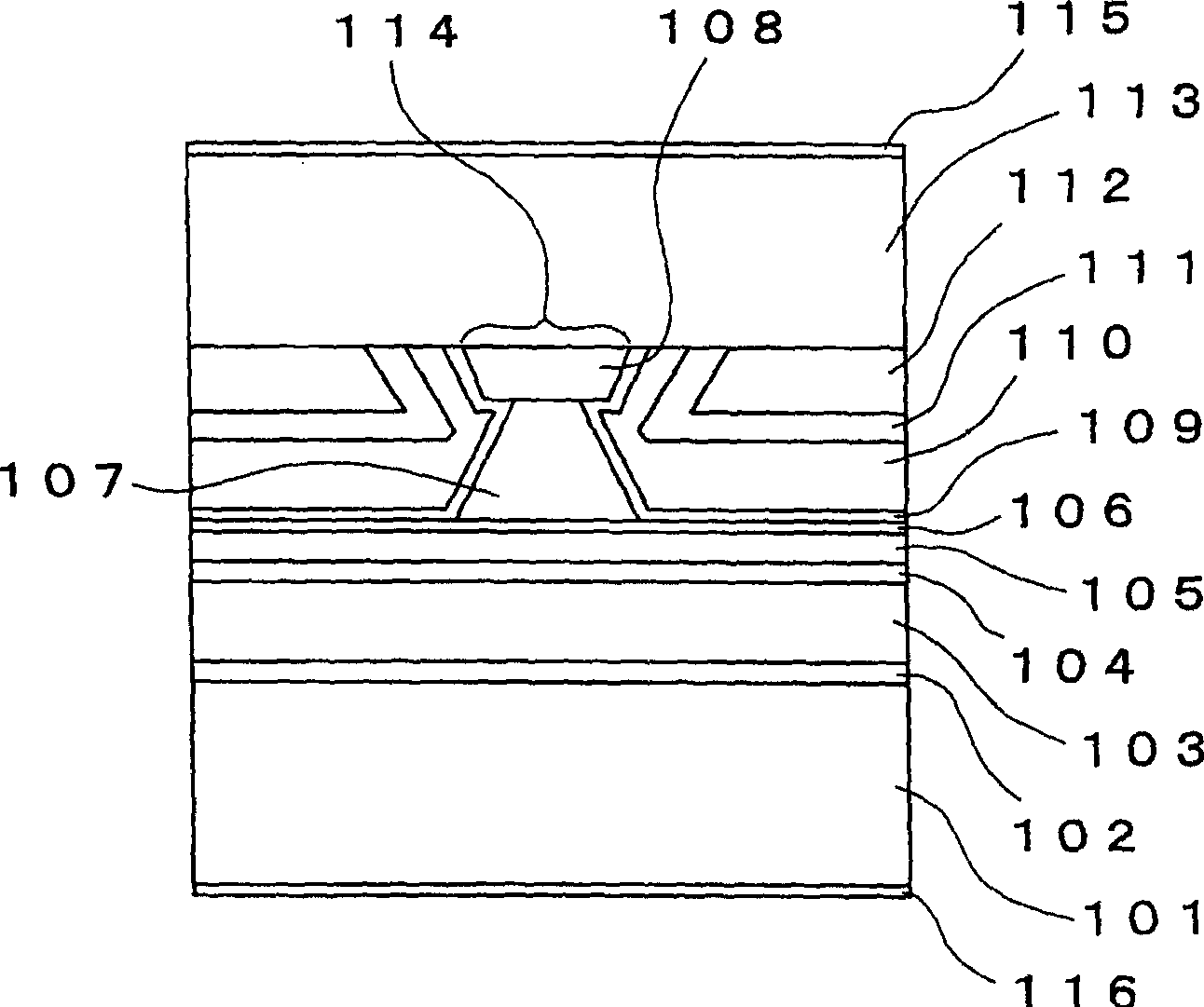
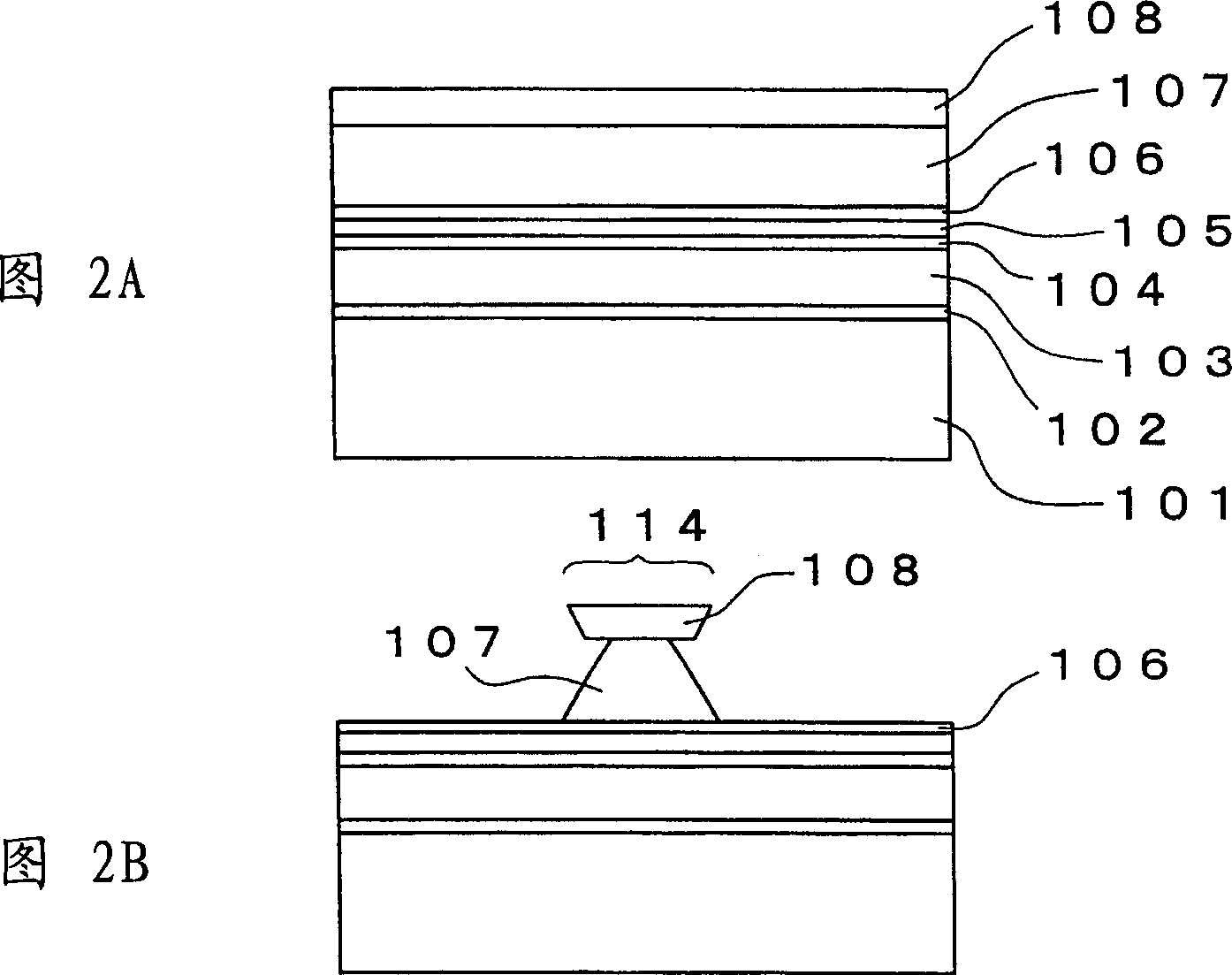
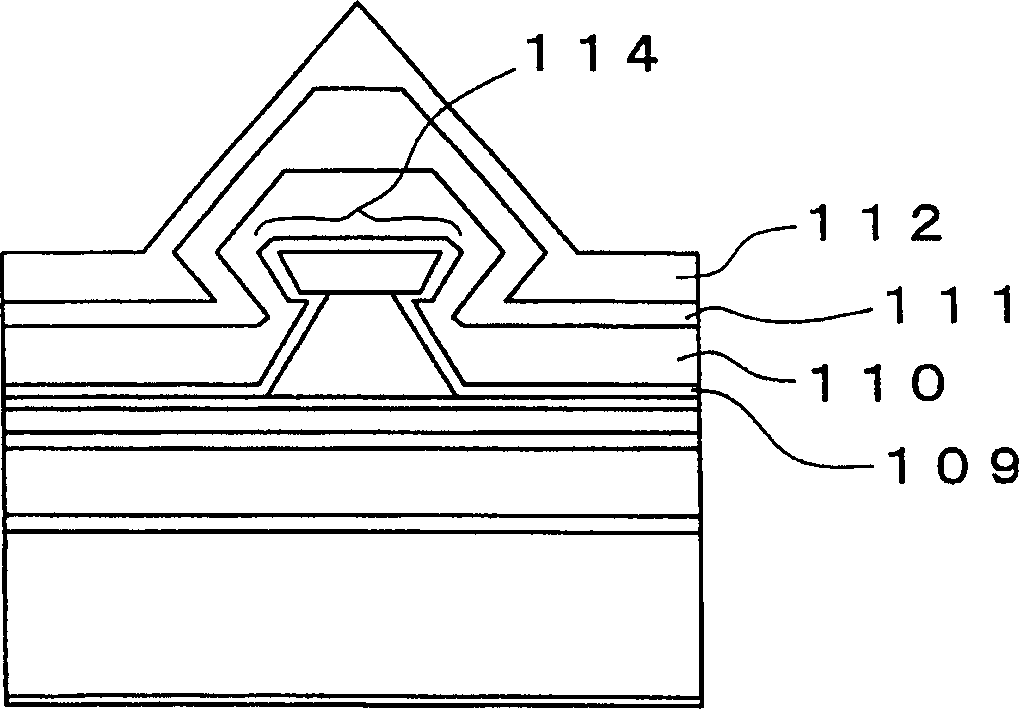
[0077] figure 1 is a view of the semiconductor laser element according to the first embodiment of the present invention. In this semiconductor laser element, an n-type GaAs buffer layer 102, an n-type Al 0.5 Ga 0.5 As first cladding layer 103, one MQW active layer 104, one p-type Al 0.5 Ga 0.5 As second cladding layer 105, and a p-type GaAs etch stop layer 106. A ridge p-type Al 0.5 Ga 0.5 An As third cladding layer 107 and a p-type GaAs protective layer 108 are disposed on the etch stop layer 106 . The ridge p-type Al 0.5 Ga 0.5 The As third cladding layer 107 and the p-type GaAs protective layer 108 constitute a ridge 114 extending along the direction of the resonant cavity. a p-type Al 0.7 Ga 0.3 As spacers 109 are provided on both sides of the ridge 114 in the width direction. an n-type Al 0.7 Ga 0.3 An As photoelectric confinement layer 110 , an n-type GaAs current confinement layer 111 and a p-type GaAs planarization layer 112 are stacked on the spacer lay...
no. 2 example
[0101] Figure 5 is a view showing a second embodiment of the semiconductor laser element of the present invention. This semiconductor laser element is different from the semiconductor laser element of the first embodiment only in terms of the carrier concentration of the substrate, the thickness of the second cladding layer, the main impurities contained in the second cladding layer, and the concentration of impurities contained in the etching stop layer. The main impurity, the dopant of the spacer layer, the layer thickness and carrier concentration, the carrier concentration of the photoelectric confinement layer and the layer thickness of the current confinement layer are different. The same parts as those of the semiconductor laser element of the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals, and no detailed description thereof will be given.
[0102] In the semiconductor laser element of this embodiment, the concentration of carriers in the n-type GaAs sub...
no. 3 example
[0108] Figure 6 is a view showing a third embodiment of the semiconductor laser element of the present invention. In this semiconductor laser element, an n-type GaAs buffer layer 302 is sequentially stacked on an n-type GaAs substrate 301, and an n-type (Al 0.7 Ga 0.3 ) InP first cladding layer 303, a MQW active layer 304, a p-type (Al 0.7 Ga 0.3 ) InP second cladding layer 305 . On the p-type second cladding layer 305 is formed a p-type GaInP etching stopper layer 306 having a predetermined width at the center in the width direction. A ridge p-type (Al 0.7 Ga 0.3 ) InP third cladding layer 307 and a p-type GaAs protective layer 308 are disposed on the etch stop layer 306 . The etch stop layer 306, the third cladding layer 307 and the protective layer 308 form a ridge 314 extending along the direction of the resonant cavity. A p-type AlInP spacer layer 309 is provided on both sides in the width direction of the ridge 314 . An n-type AlInP photoelectric confinement la...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com