Laser quench controlling method and laser quencher
A technology of laser quenching and control method, applied in quenching device, laser welding equipment, heat treatment process control and other directions, can solve problems such as low irradiation energy, inability to quench action, and inability to quench
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings.
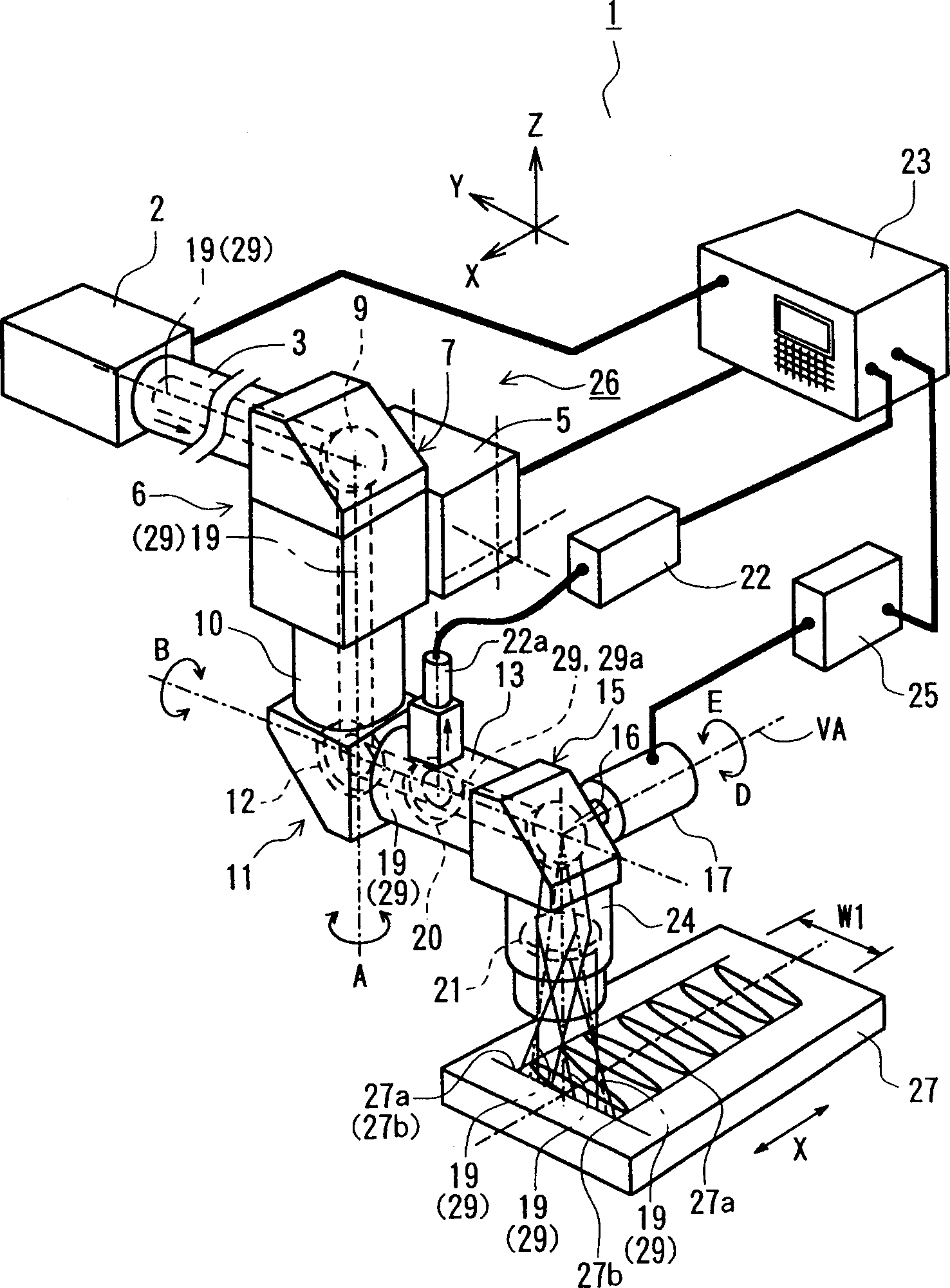
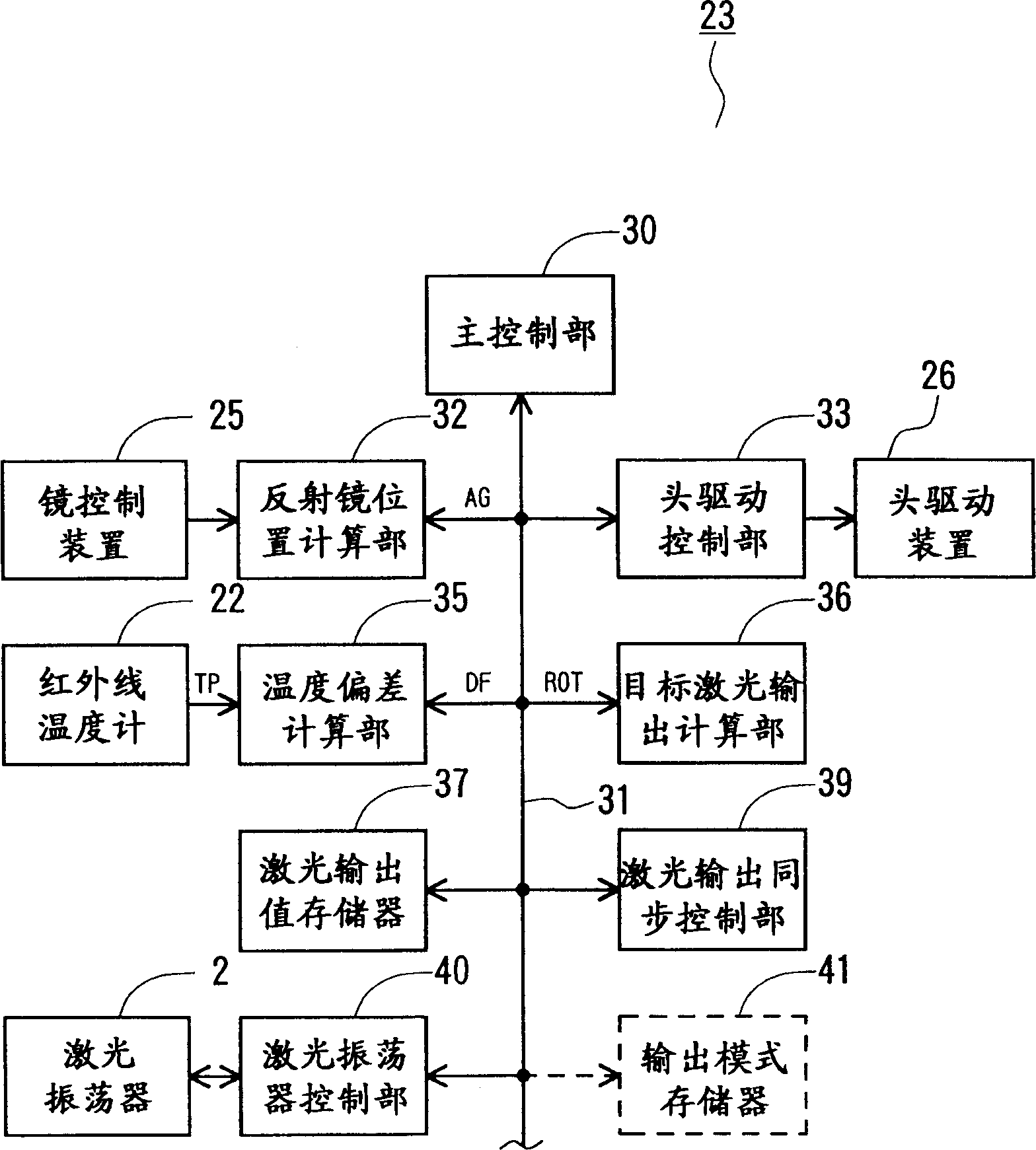
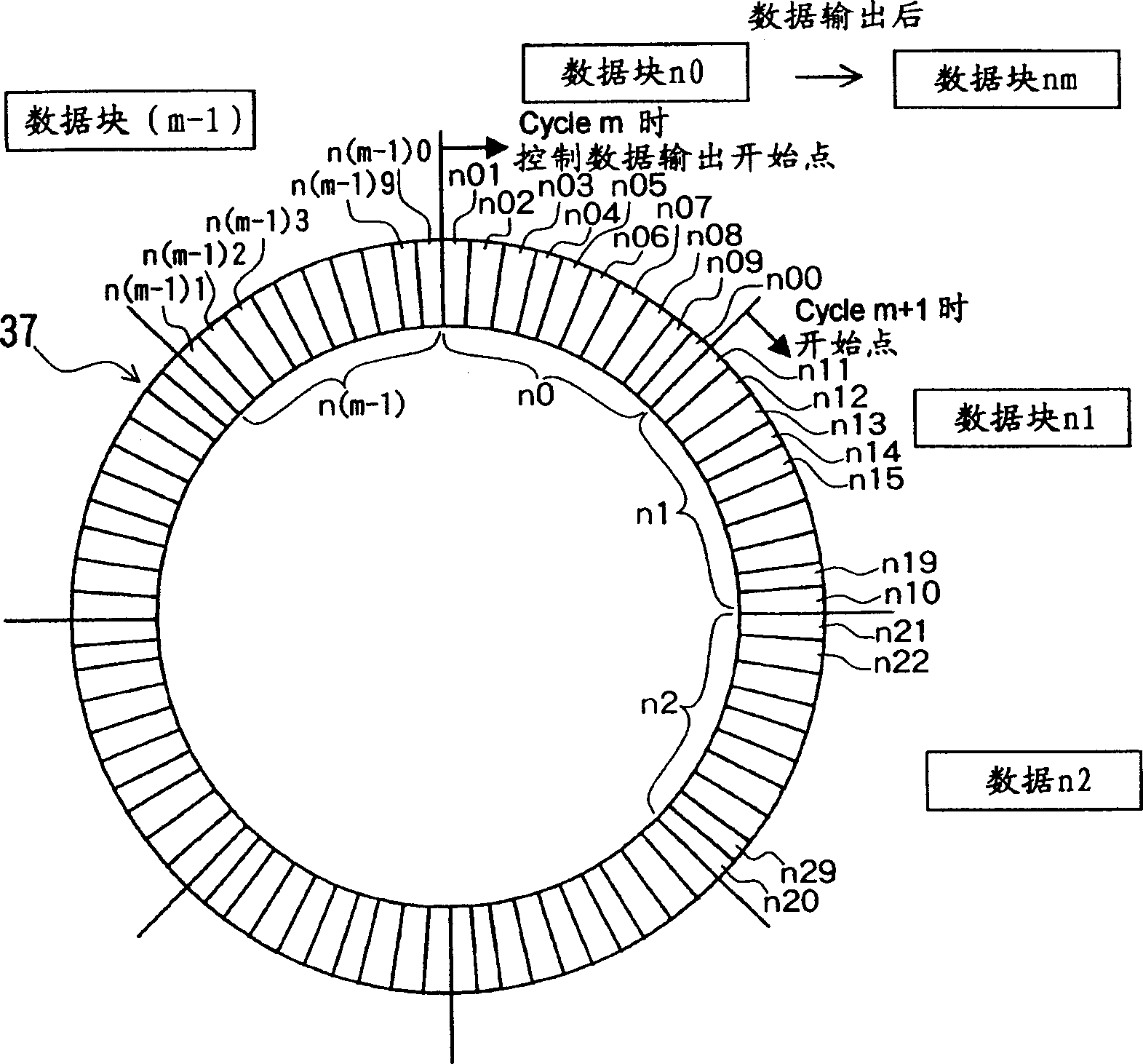
[0044] figure 1 It is a schematic perspective view showing the main part of the laser hardening device applicable to the present invention, figure 2 is a block diagram showing the main parts of the NC device, image 3 is a pattern diagram showing the contents of the laser output value memory, Figure 4 is the schematic diagram of the quenching trajectory of the laser beam, Figure 5 is a schematic diagram showing the contents of each data block in the laser output value memory, Image 6 (a) is a graph showing the trajectory of the laser beam (quenching cycle); (b) is a graph showing the velocity of the laser beam relative to the workpiece corresponding to (a); (c) is an example of a laser output pattern corresponding to (a) (d) is a graph showing another example of the laser output mode corresponding to (a).
[0045] like figure 1 As shown, the laser quenching device 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com