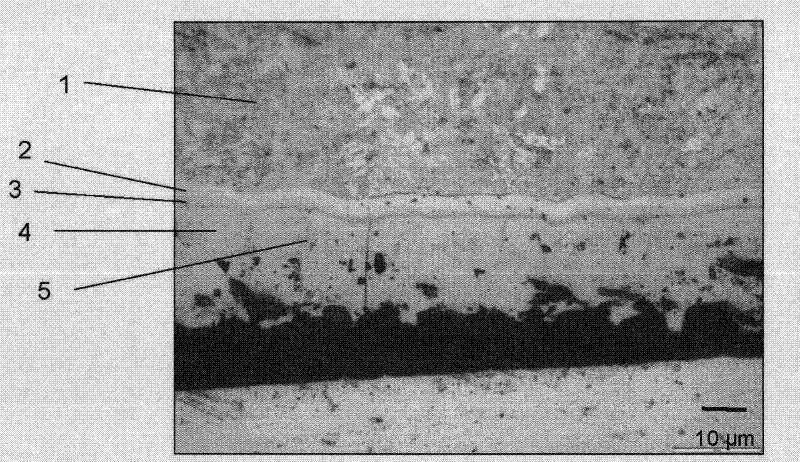
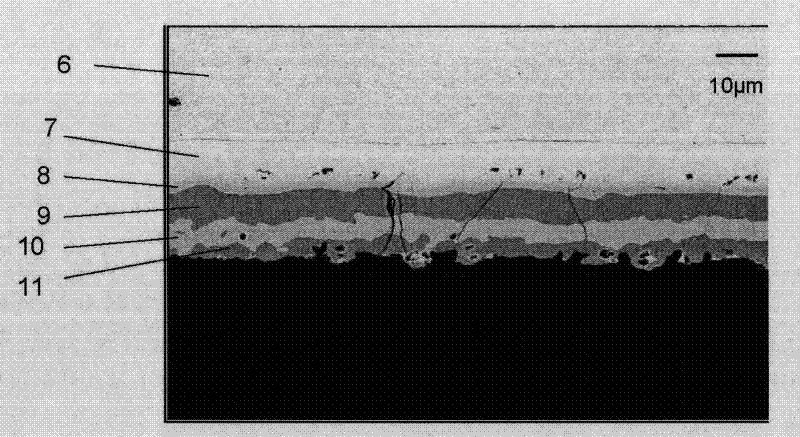
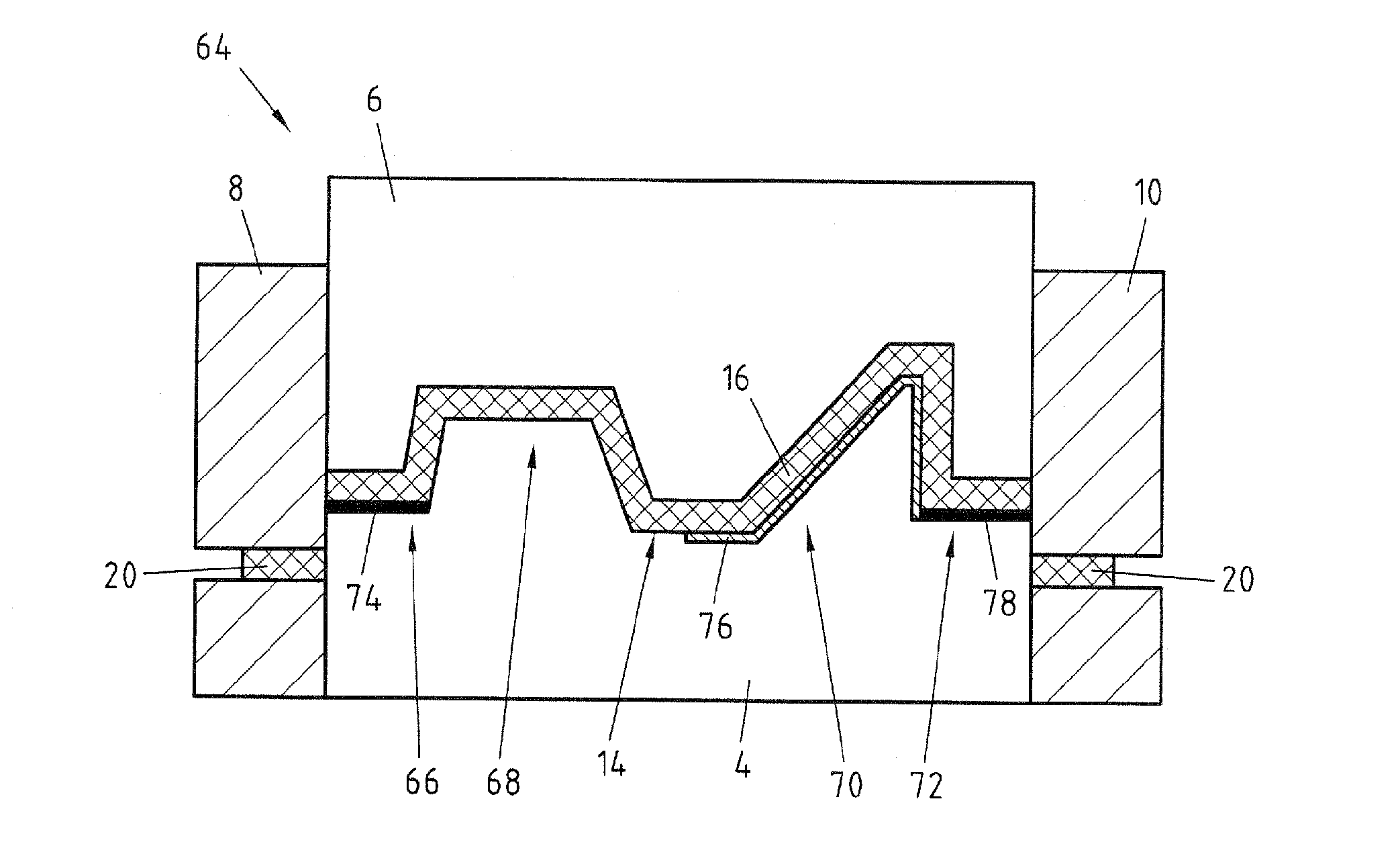
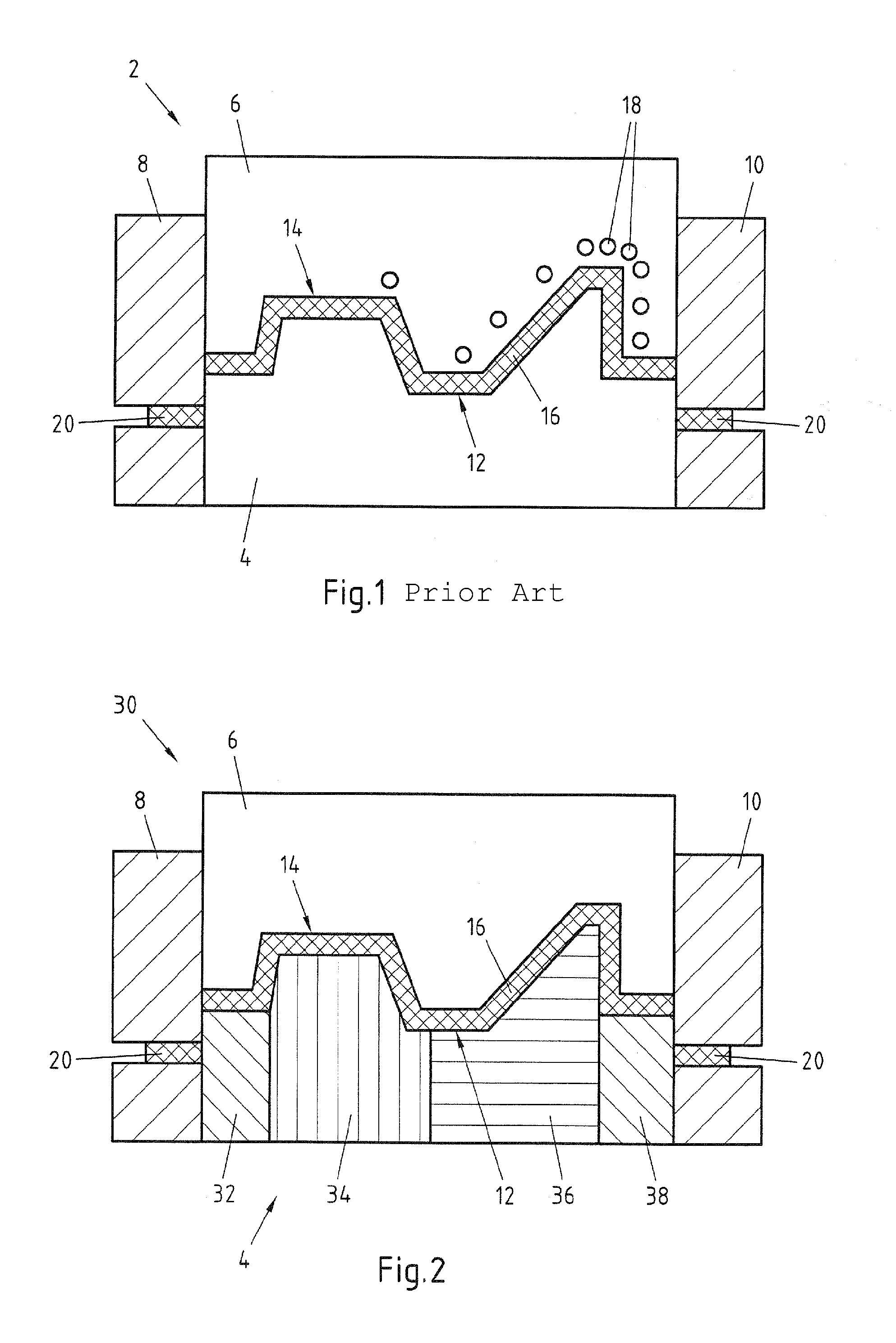
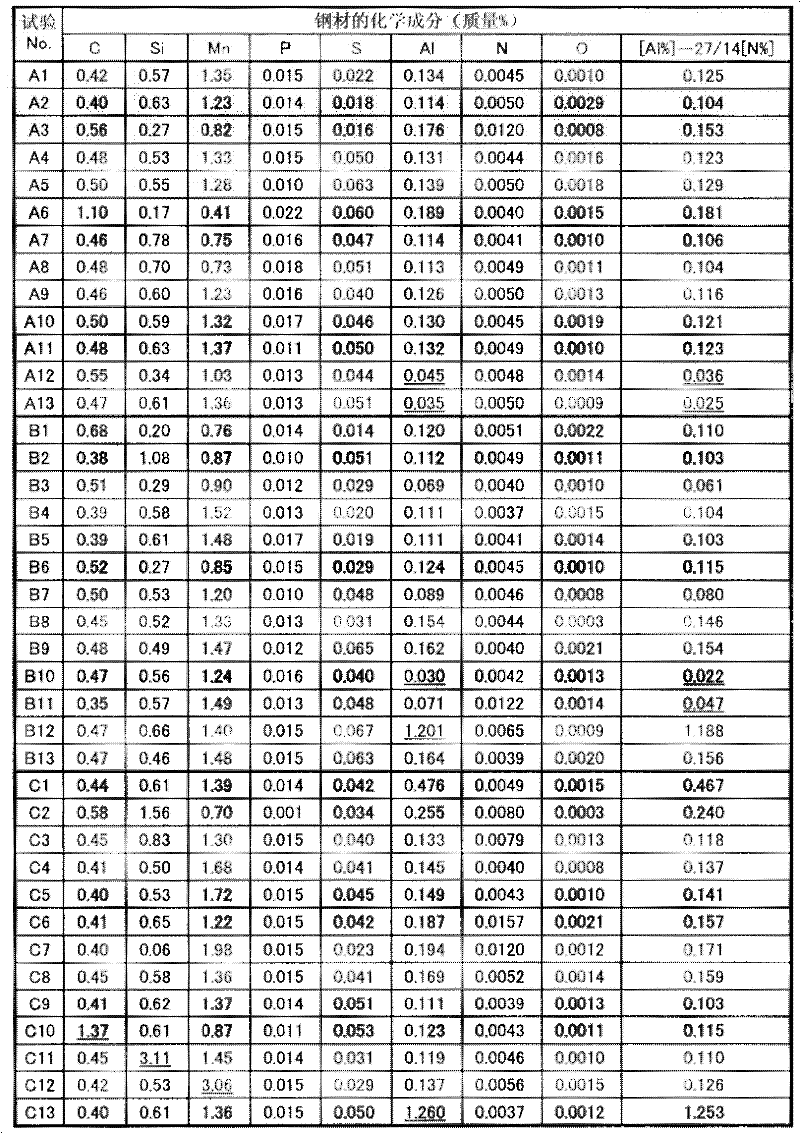
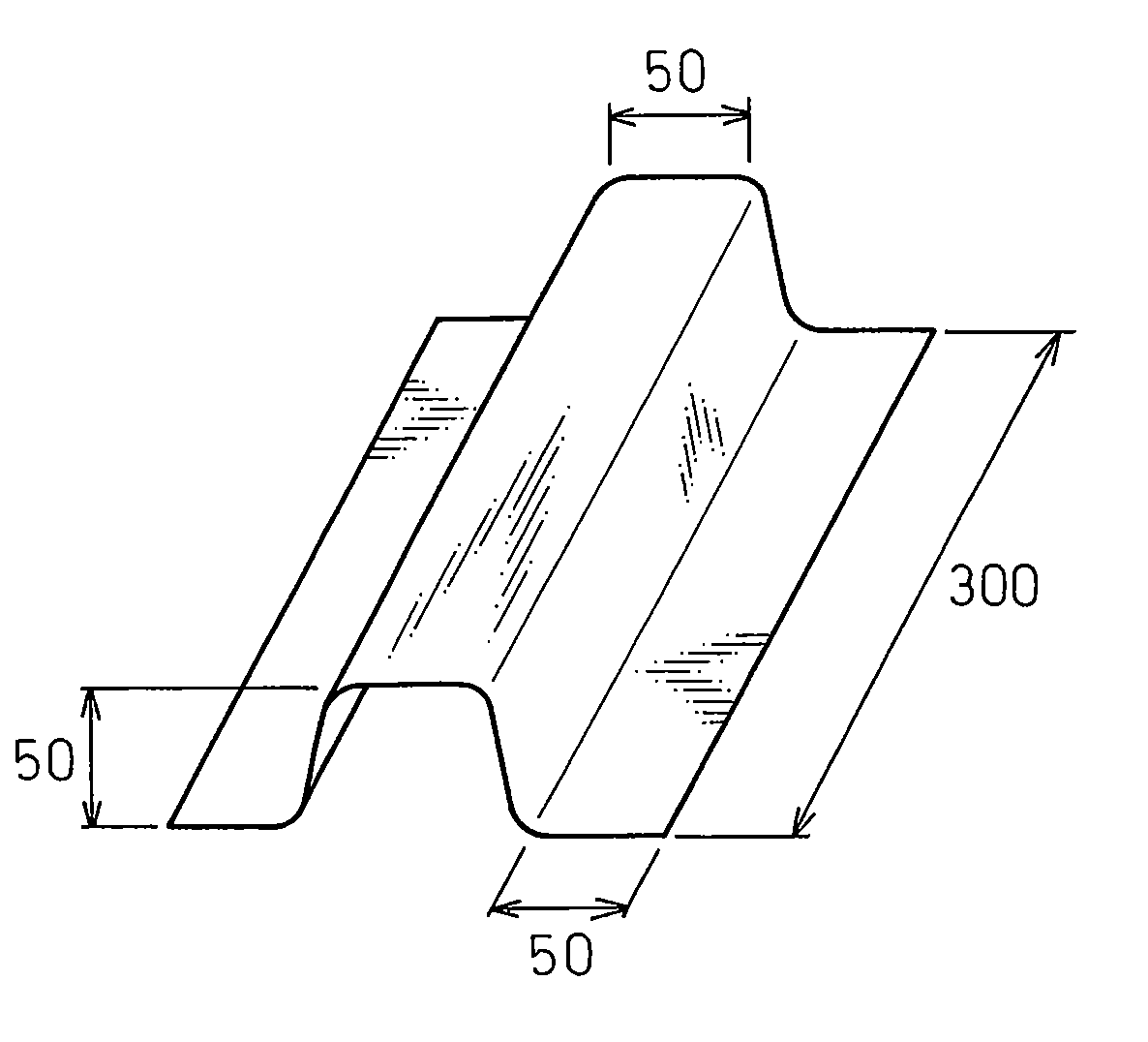
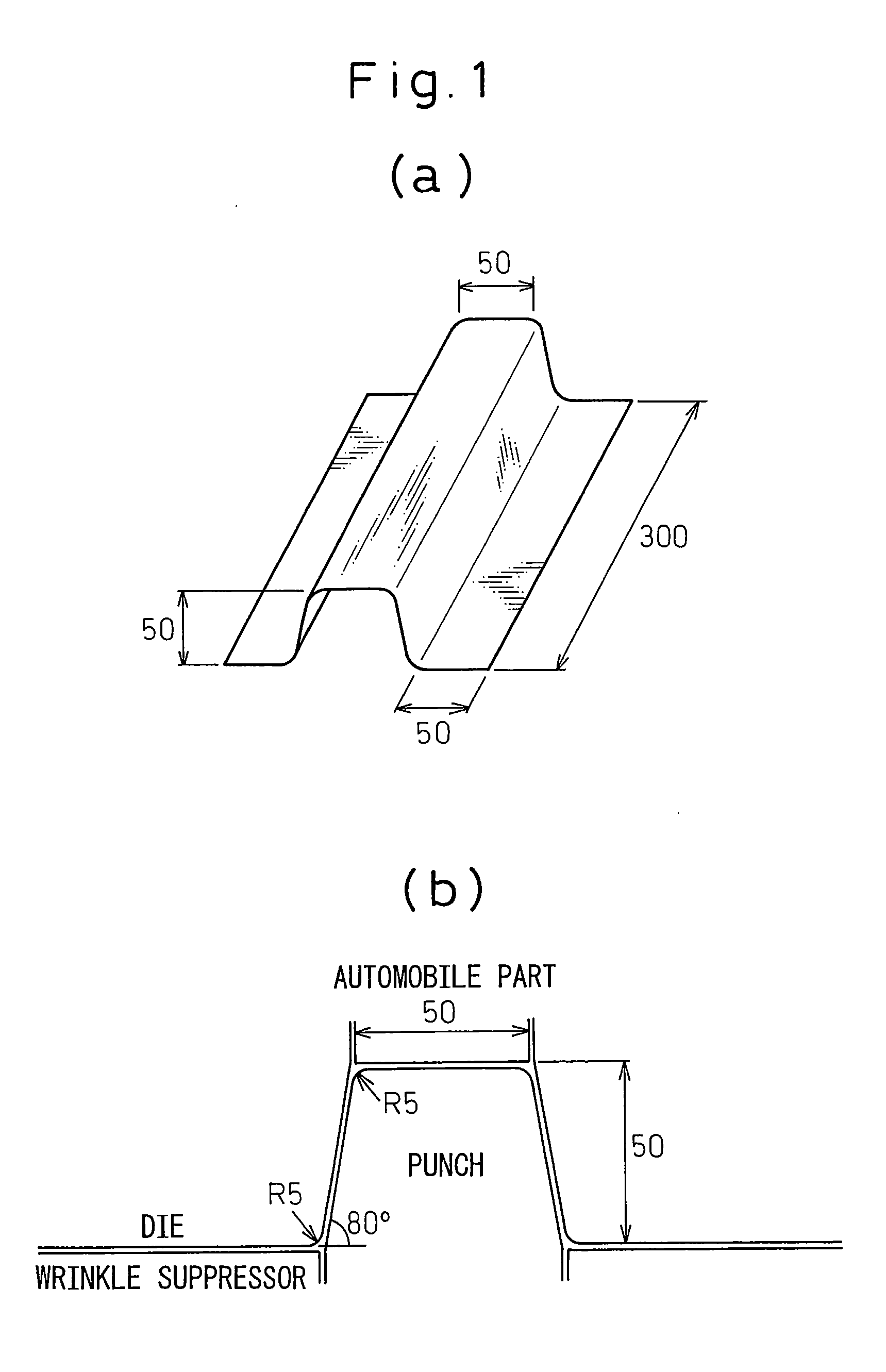
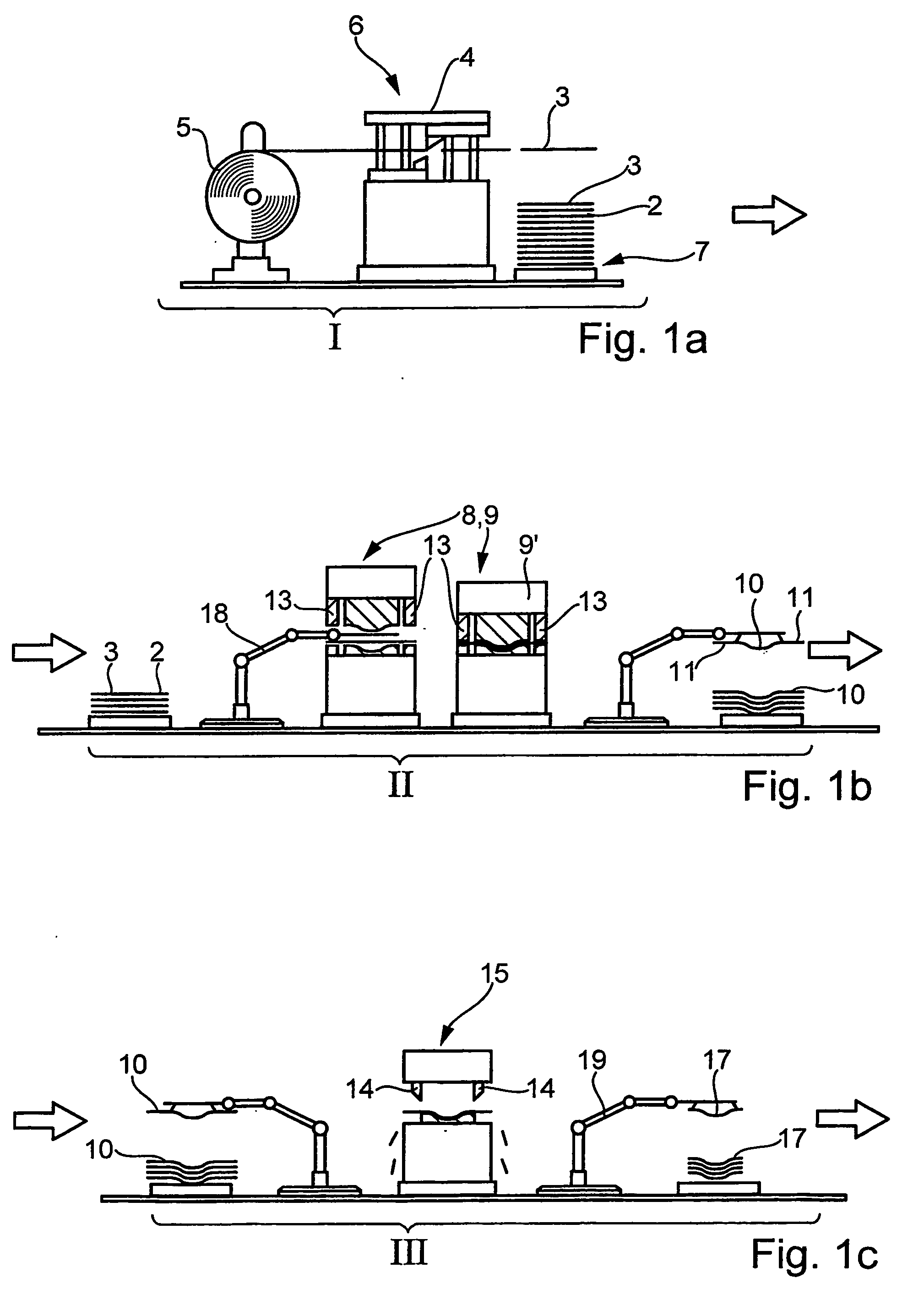
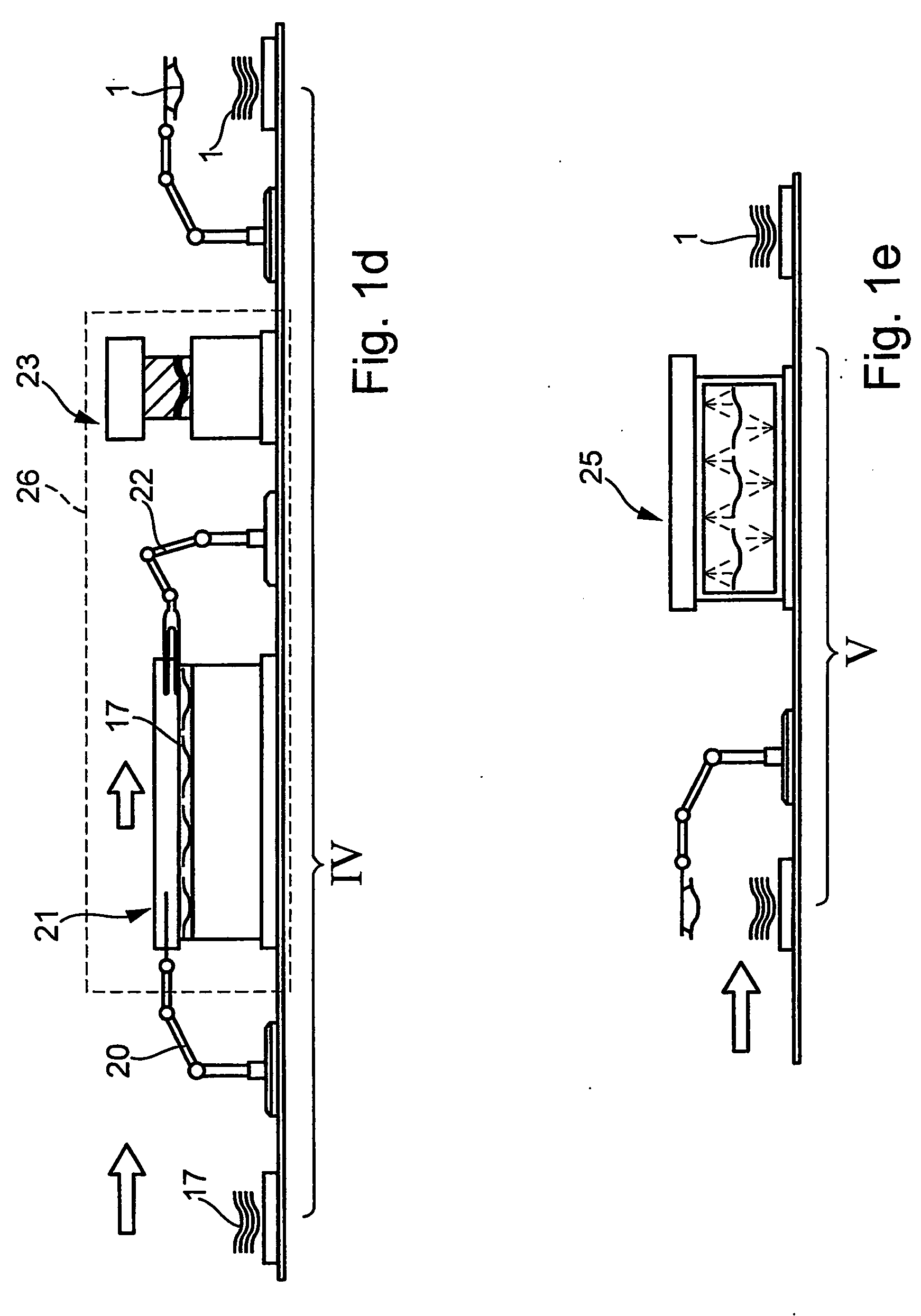
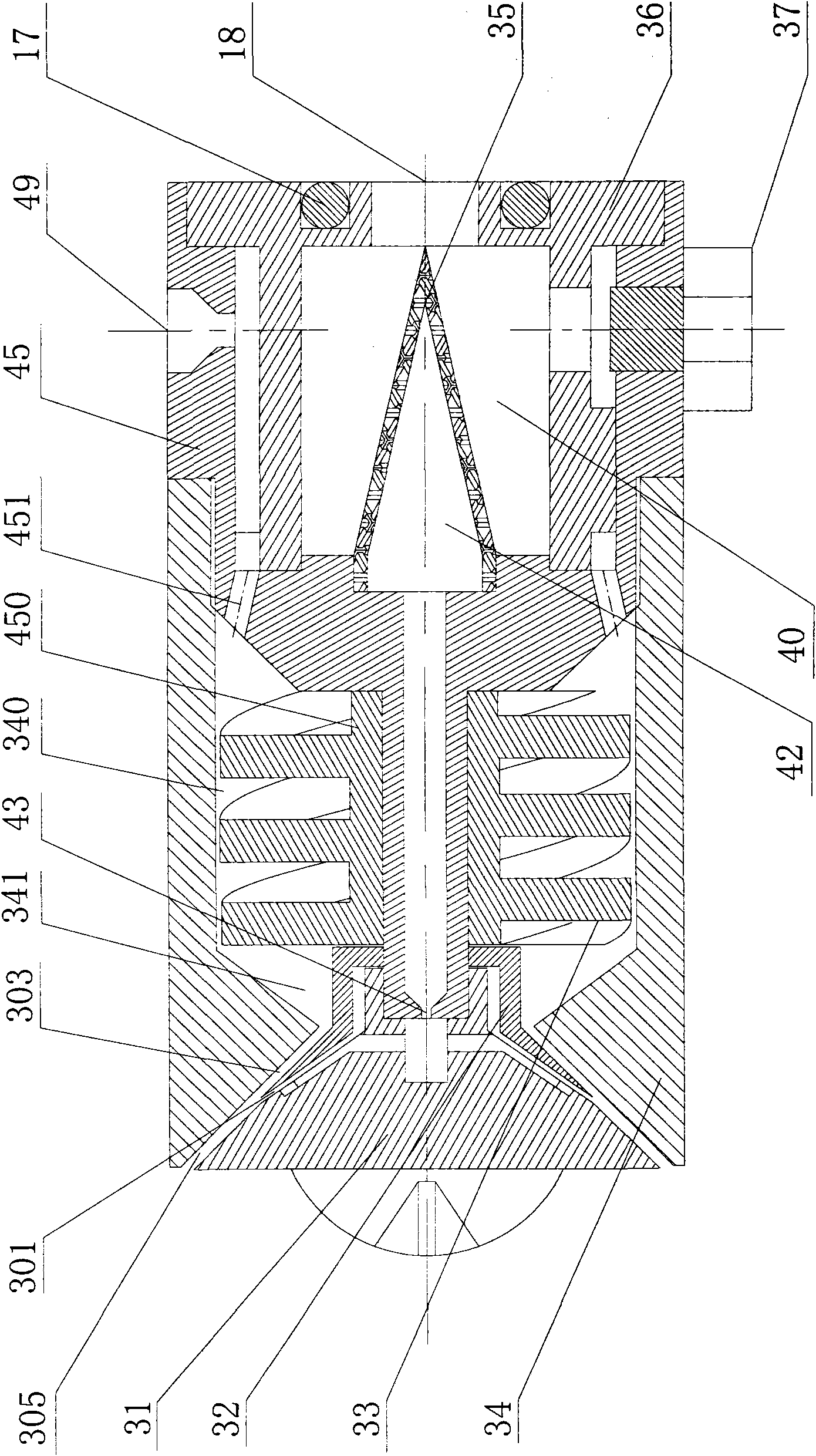
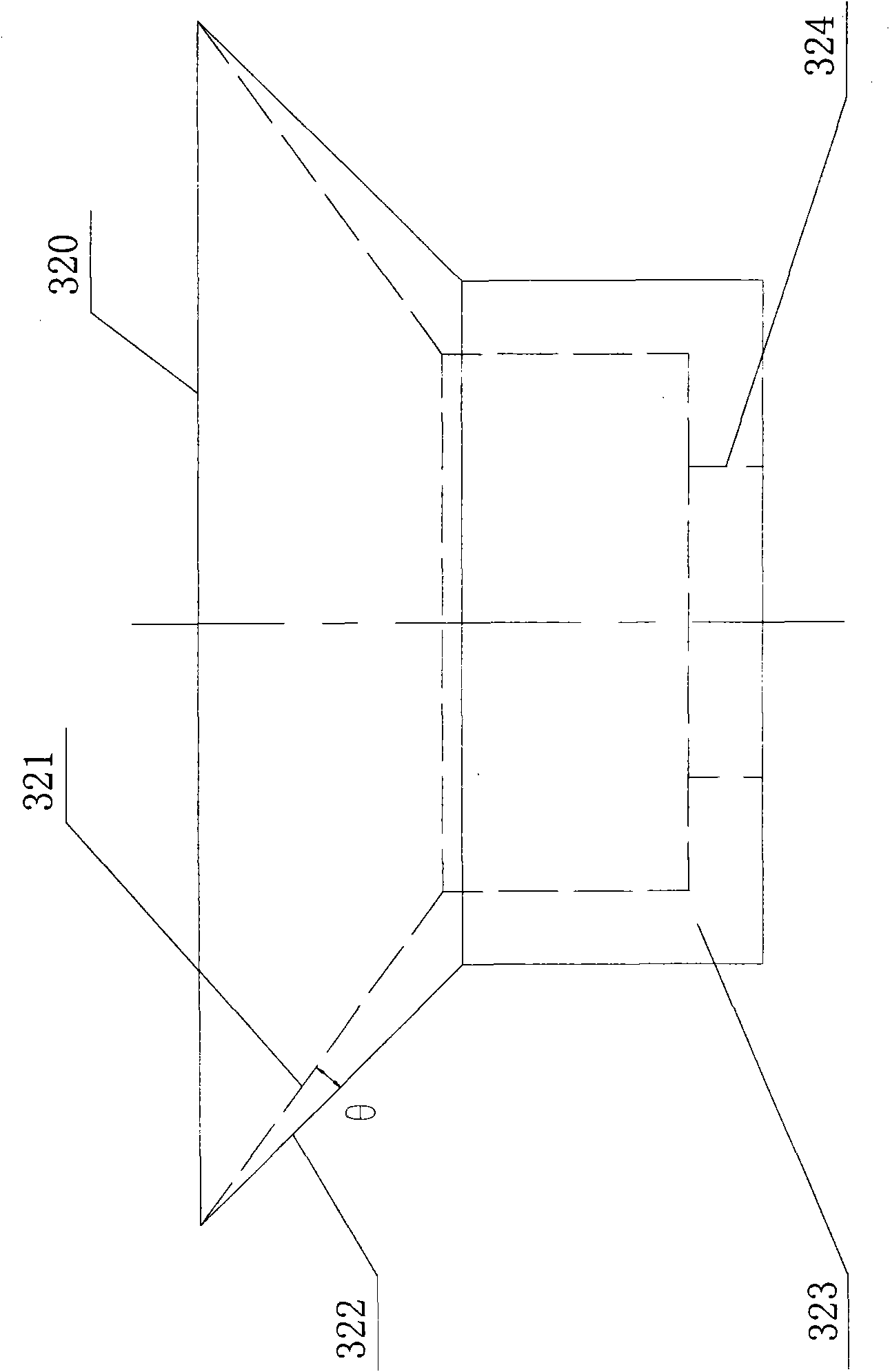
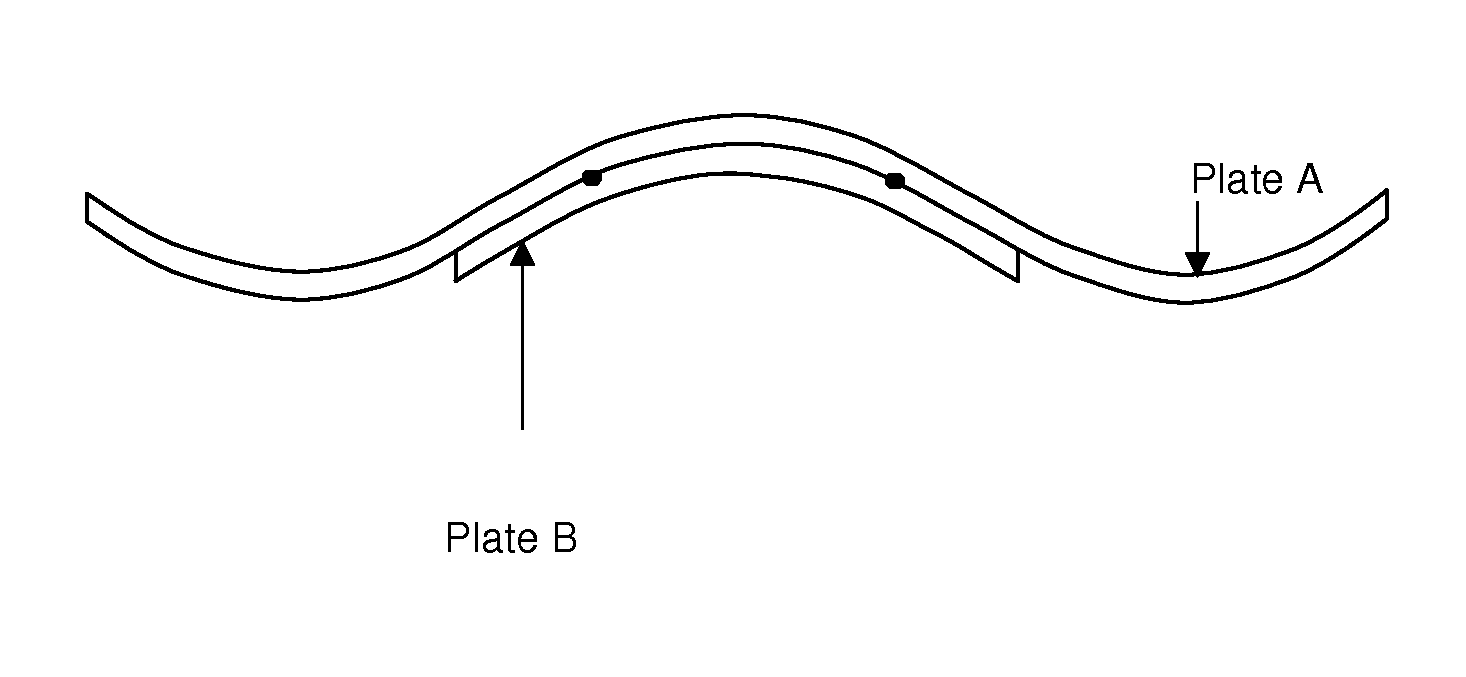
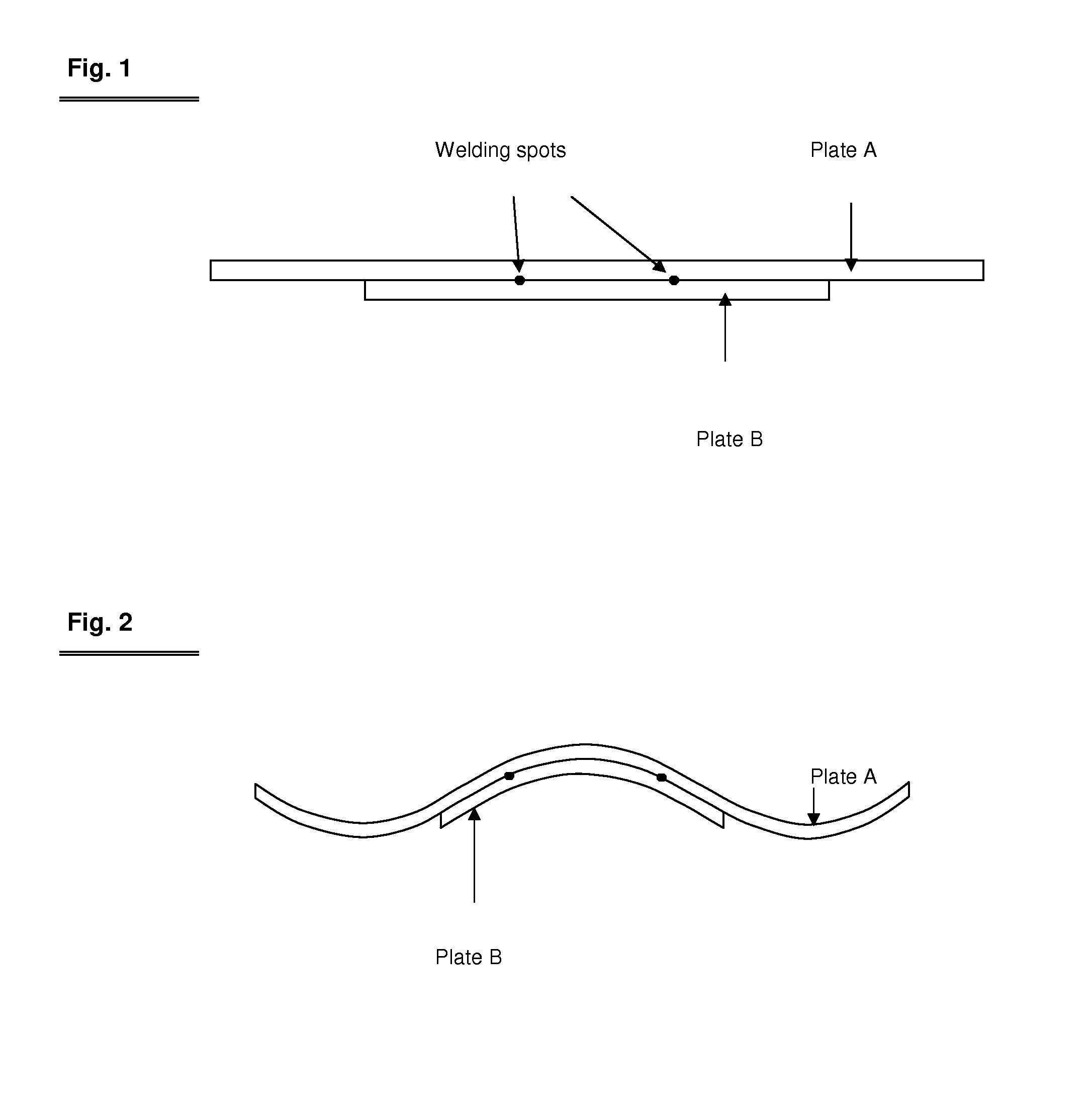
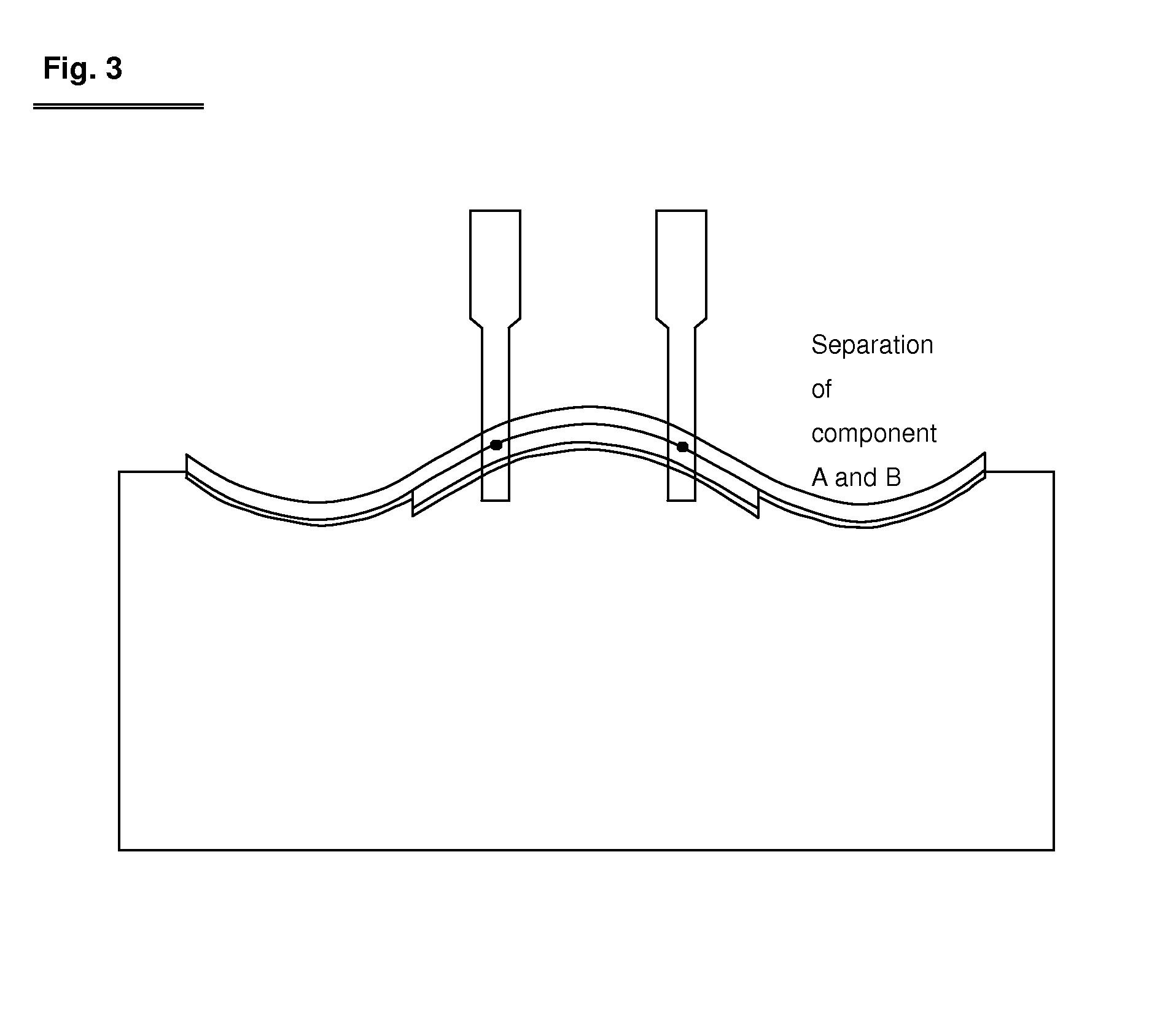
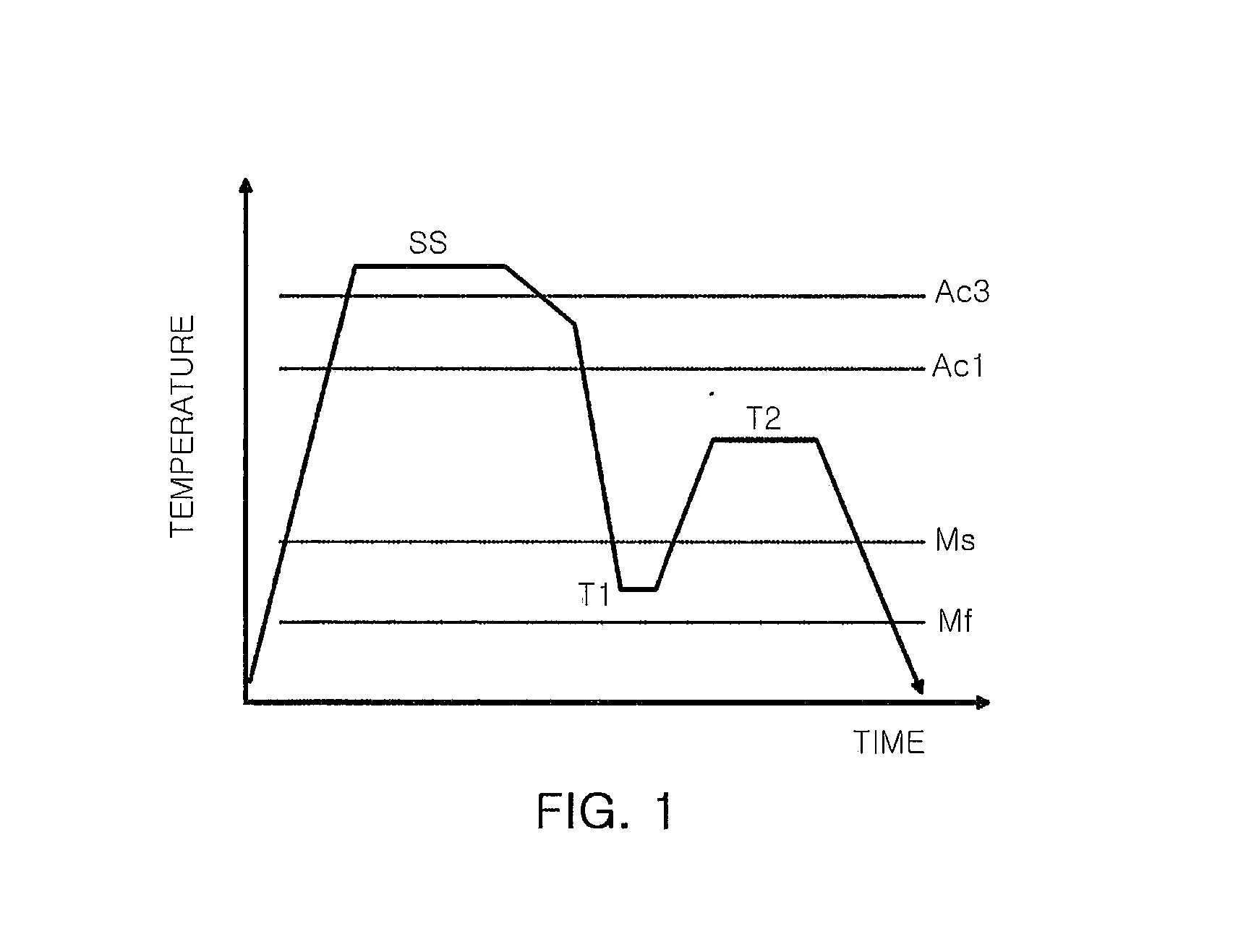
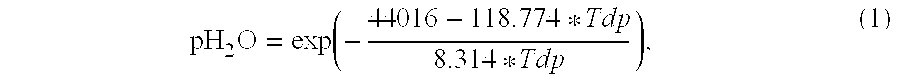Patents
Literature
6168results about "Quenching devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thermal deposition coating method
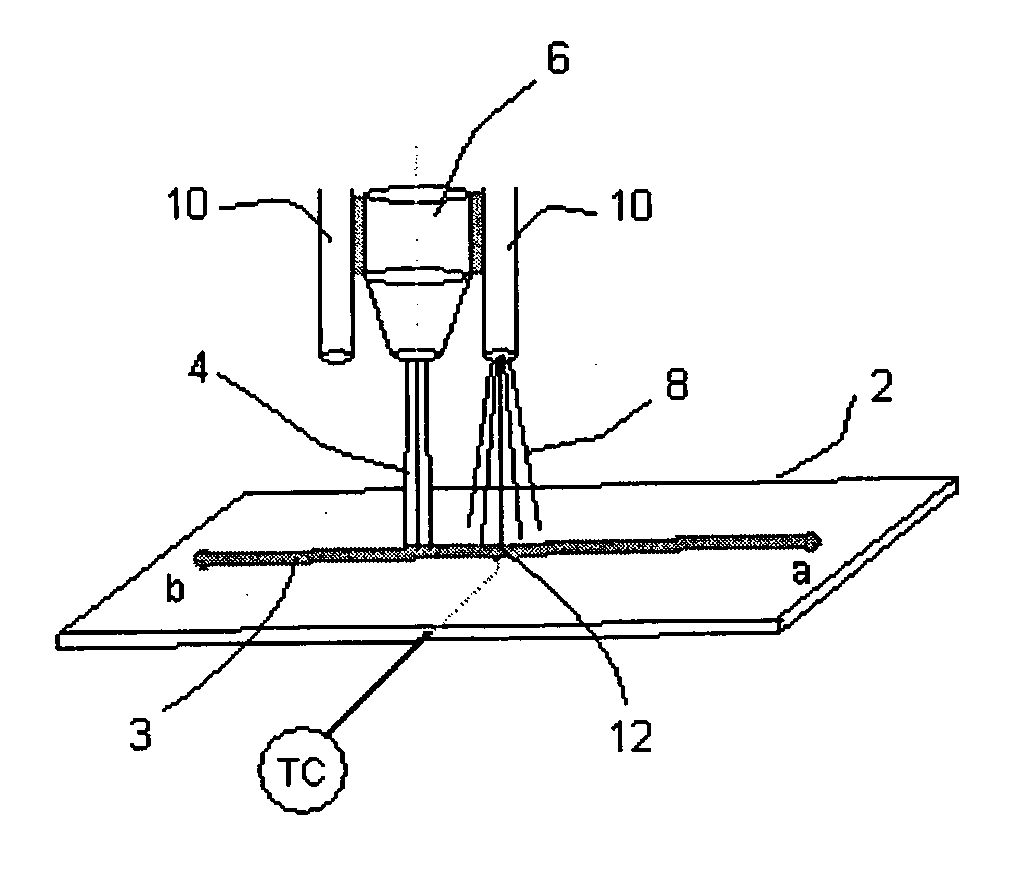
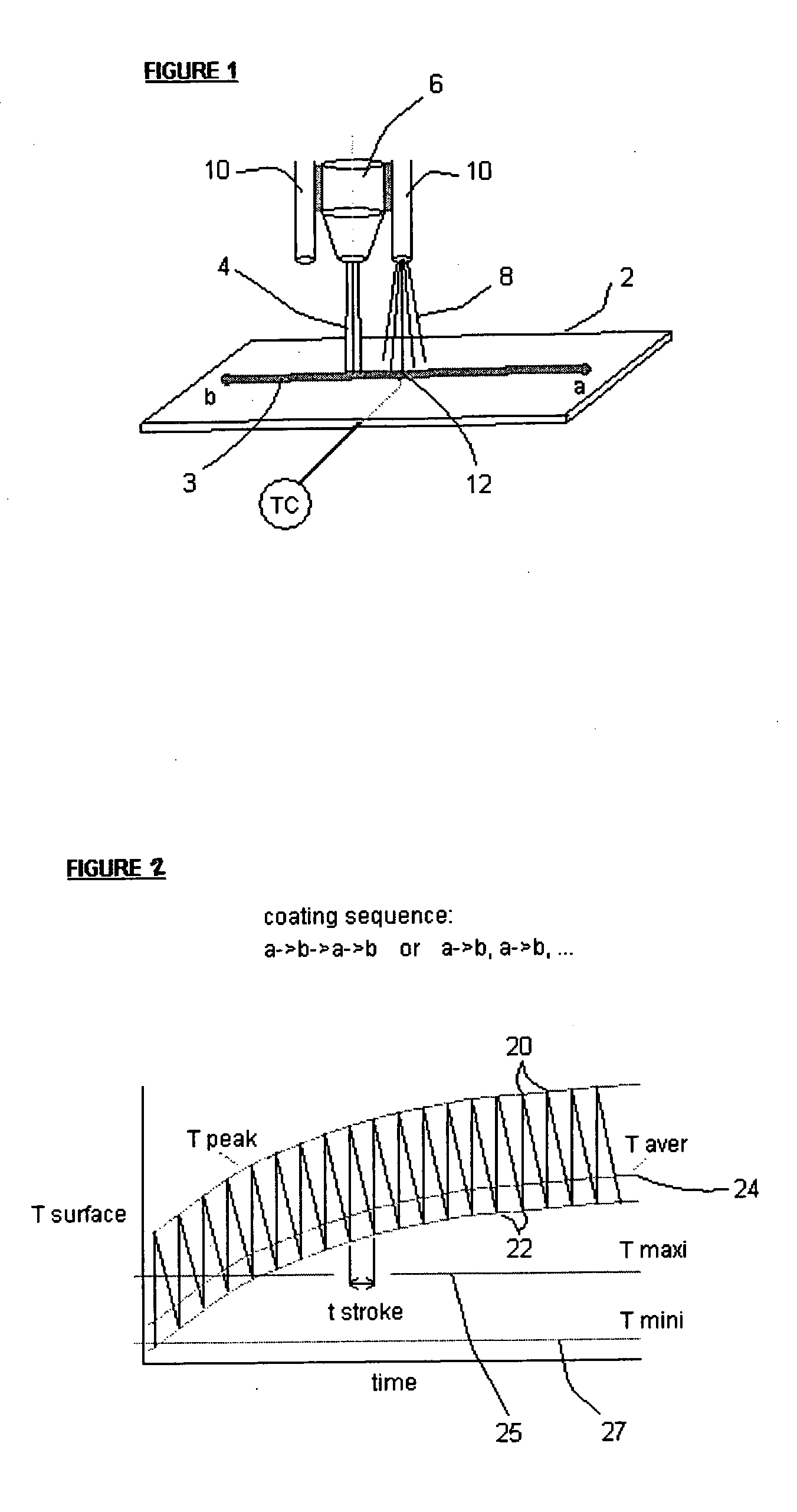
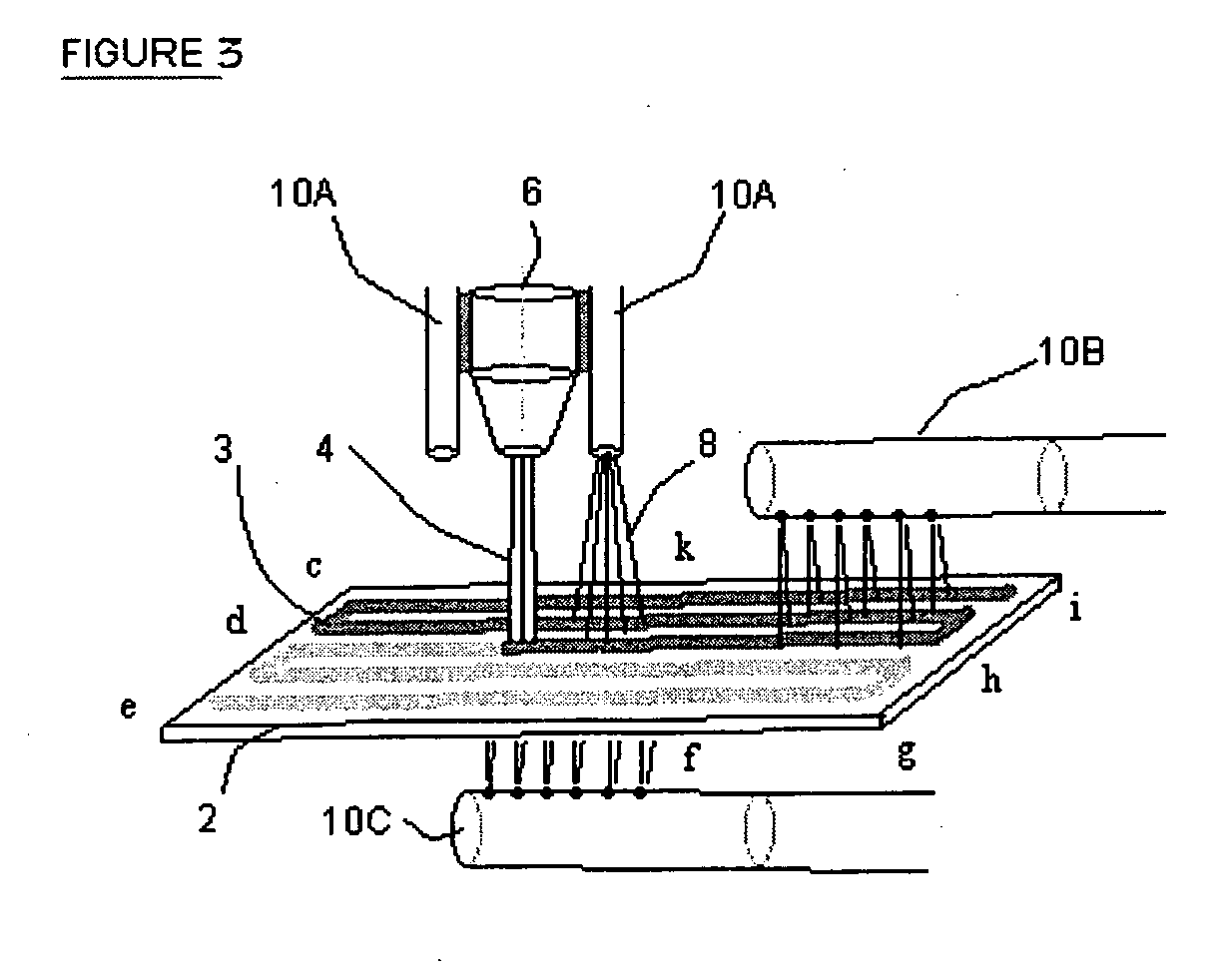
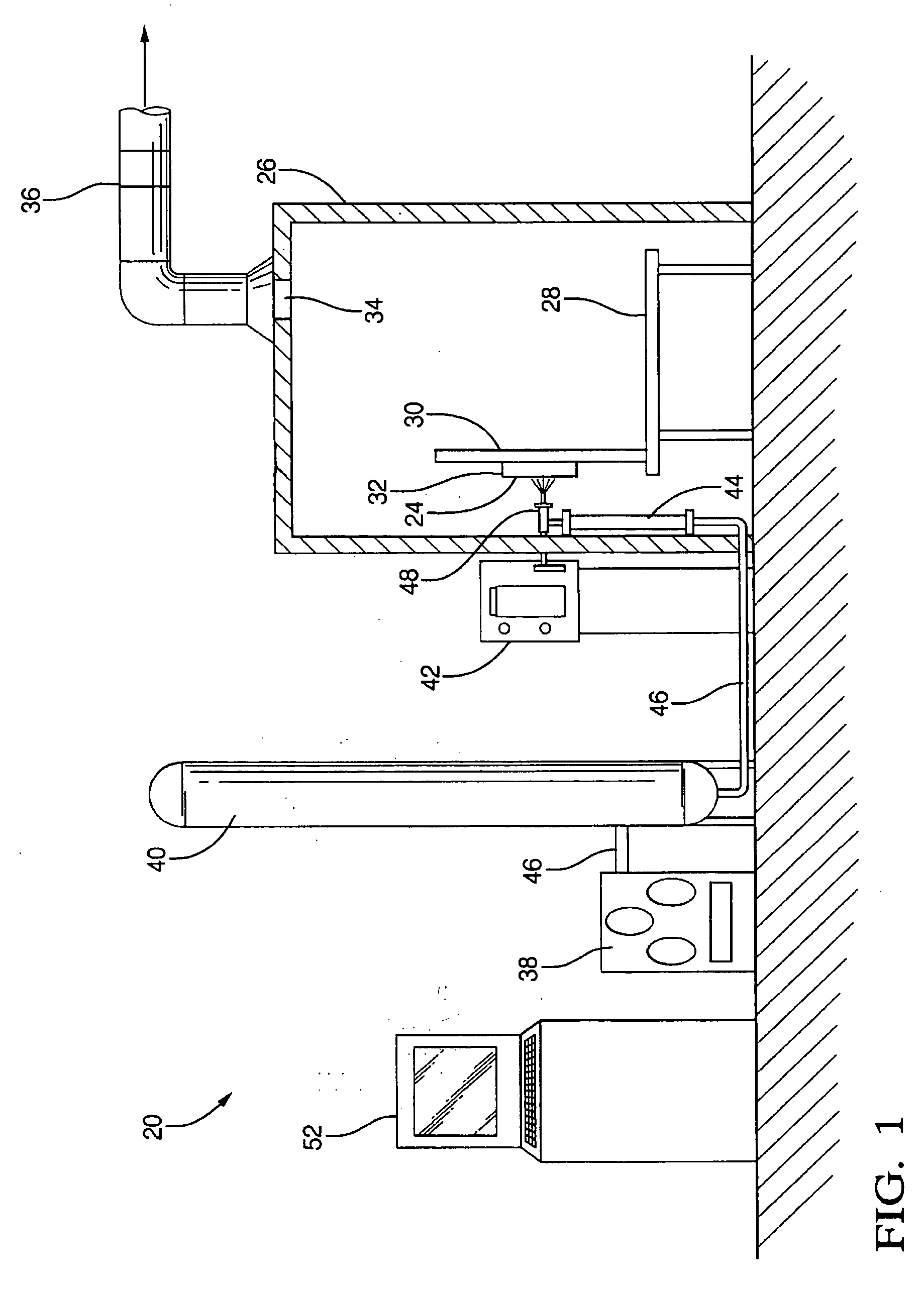
ActiveUS20060228465A1Excellent coating production rateDamaging internal stressLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingThermal depositionRelative motion
A process for the thermal deposition coating of a workpiece, said process comprising the steps of: (c) thermally depositing a coating on a metallic surface of a workpiece from a deposition head wherein at least one condition selected from the group of: coating deposition rate onto said surface, relative motion between the surface and said deposition head, and cryogenic coolant application rate onto said workpiece is controllable; (d) substantially simultaneously measuring temperatures at a plurality of locations over the metallic surface of the workpiece; (c) determining an average temperature of the temperatures measured in step (b); (d) comparing the average temperature to a preselected minimum temperature and a preselected maximum temperature for the workpiece; and (e) adjusting at least one of the controllable conditions if said average temperature is not between the preselected minimum temperature and the preselected maximum temperature for the workpiece. Standard deviations of all temperature readings and controlling the relative motion speed between the thermal coating deposition head and the workpiece provide another improvement for obtaining temperature uniformity over the workpiece surface.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
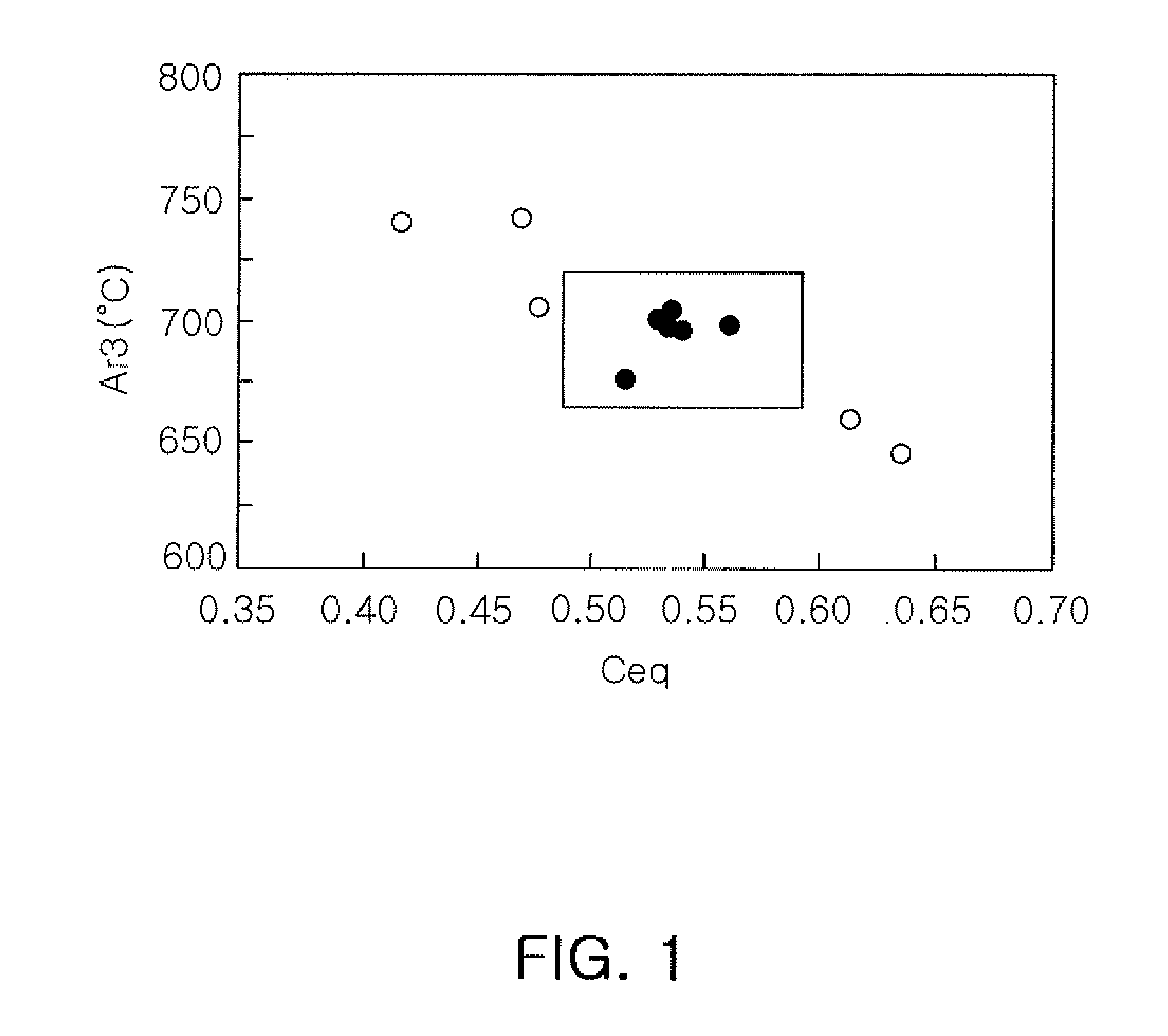
Steel sheet for hot press forming having low-temperature heat treatment property, method of manufacturing the same, method of manufacturing parts using the same, and parts manufactured by the same
ActiveUS20090238715A1Reduced strengthHigh yield strengthMetal rolling stand detailsFurnace typesManganeseHeat treated
A steel sheet for forming having low-temperature heat treatment property, in which heat treatment is performed within a range of lower temperature than a conventional steel sheet in the event of hot press forming or post-heat treatment after cold forming, a method of manufacturing the same, and a method of manufacturing parts using the same. The steel sheet has a composition of, by weight, carbon (C): 0.15 to 0.35%, silicon (Si): 0.5% or less, manganese (Mn): 1.5 to 2.2%, phosphorus (P): 0.025% or less, sulfur (S): 0.01% or less, aluminum (Al): 0.01 to 0.05%, nitrogen (N): 50 to 200 ppm, titanium (Ti): 0.005 to 0.05%, tungsten (W): 0.005 to 0.1%, and boron (B): 1 to 50 ppm, wherein Ti / N: less than 3.4, where Ti / N is the atomic ratio of the corresponding elements, Ceq expressed by the following formula ranges from 0.48 to 0.58, and temperature Ar3 ranges from 670° C. to 725° C. Wherein Ceq=C+Si / 24+Mn / 6+Ni / 40+Cr / 5+V / 14 where C, Si, Mn, Ni, Cr and V indicate the contents (wt %) of the respective elements.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Steel plate for hot stamping, hot stamping process and hot-stamped member
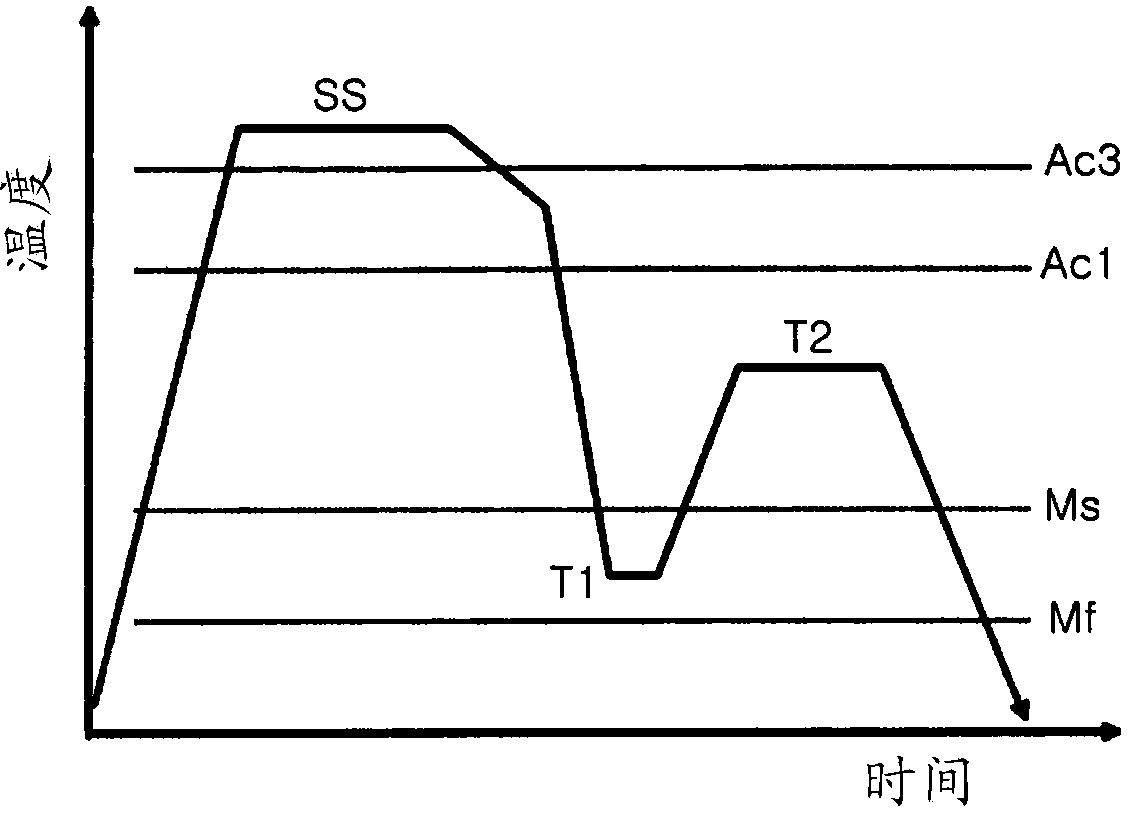
ActiveCN104846274ALow austenitizing temperatureQuenching temperature is lowShaping toolsFurnace typesHot stampingMartensite transformation
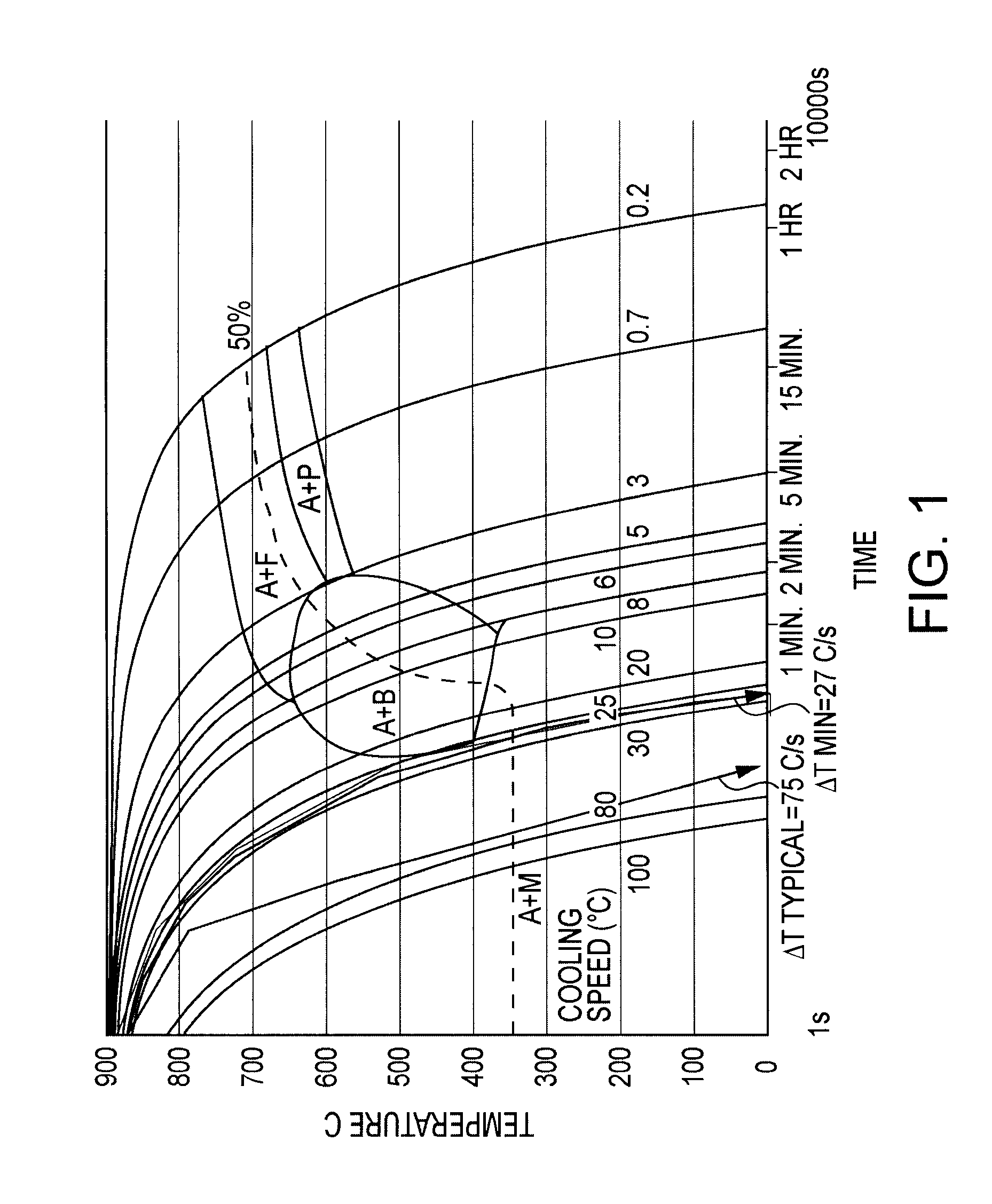
The invention relates to a steel plate for hot stamping, a hot stamping process and a hot-stamped member. The steel plate for hot stamping is characterized by comprising, by weight, 0.18 to 0.42% of C, 4 to 8.5% of Mn and 0.8 to 3.0% of Si and Al, with the balance being Fe and avoidable impurities, wherein the alloy component of the steel plate satisfy the condition that the actual measured value of martensite phase transformation beginning temperature is no more than 280 DEG C. A manufacturing method for the hot-stamped member comprises the following steps: heating a material to 700 to 850 DEG C and carrying out stamping; then carrying out cooling in a die or air cooling or cooling in other manners to 150 to 260 DEG C below the martensite phase transformation beginning temperature; and heating the stamped member to 160 to 450 DEG C, maintaining the temperature for 1 to 100,000 s, carrying out tempering heat treatment and cooling the stamped member to room temperature. The hot-stamped member prepared in the invention has yield strength of no less than 1200 MPa, tensile strength of no less than 1600 MPa and total elongation percentage of no less than 10%.
Owner:EASYFORMING STEEL TECH CO LTD
High-strength alloyed aluminum-system plated steel sheet and high-strength automotive part excellent in heat resistance and after-painting corrosion resistance
InactiveCN1531604AImprove heat resistanceHot-dipping/immersion processesSuperimposed coating processSheet steelCorrosion
The present invention provides a hot press method used for producing a high-strength member for an automobile and, in particular, a part which requires high-strength, such as an undercarriage component of an automobile. More specifically, the present invention provides an aluminum plated steel sheet or an aluminum-zinc plated steel sheet suitable for high temperature forming (hot forming) wherein high strength is obtained after high temperature forming, and a method of producing the same. Also, the present invention provides a hot dip aluminum plated steel sheet which suppresses the alloying reaction of a plated layer during press forming and has beautiful appearance, and an aluminum-system plated steel sheet for hot press having excellent after-painting corrosion resistance. Concretely, the present invention is a high-strength aluminum-system plated steel sheet excellent in heat resistance and after-painting corrosion resistance, characterized by having an Fe-Al-system coating containing, in mass, Mn and Cr of more than 0.1% in total on the surface of the steel containing, in mass, C: 0.05 to 0.7%, Si: 0.05 to 1%, Mn: 0.5 to 3%, P: not more than 0.1%, S: not more than 0.1% and Al: not more than 0.2%, and, in addition, one or more element(s) selected from among Ti: 0.01 to 0.8%, Cr: not more than 3% and Mo: not more than 1%, so as to satisfy the following expression (1): Ti + 0.5xMn + Cr + 0.5xMo > 0.4 ... 1
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
High performance kinetic spray nozzle
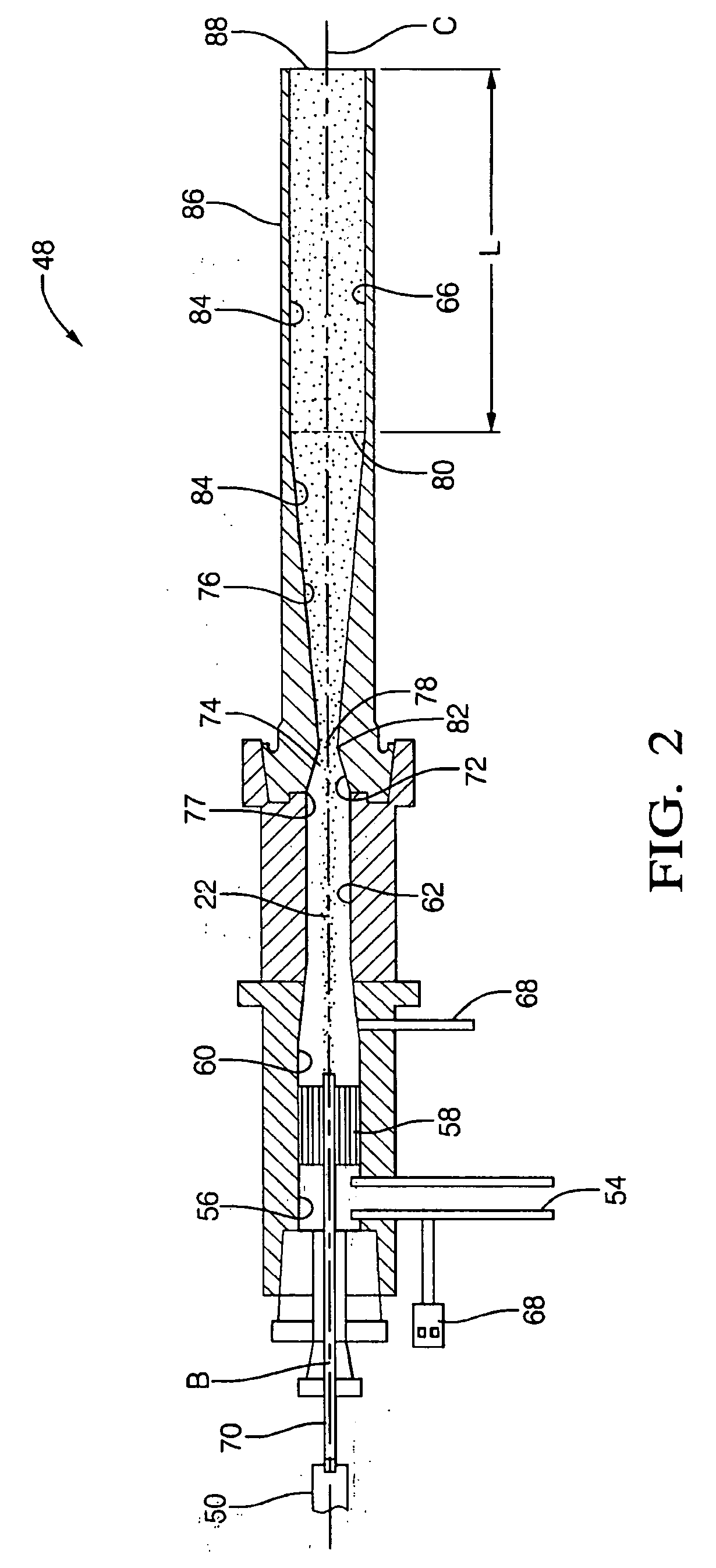
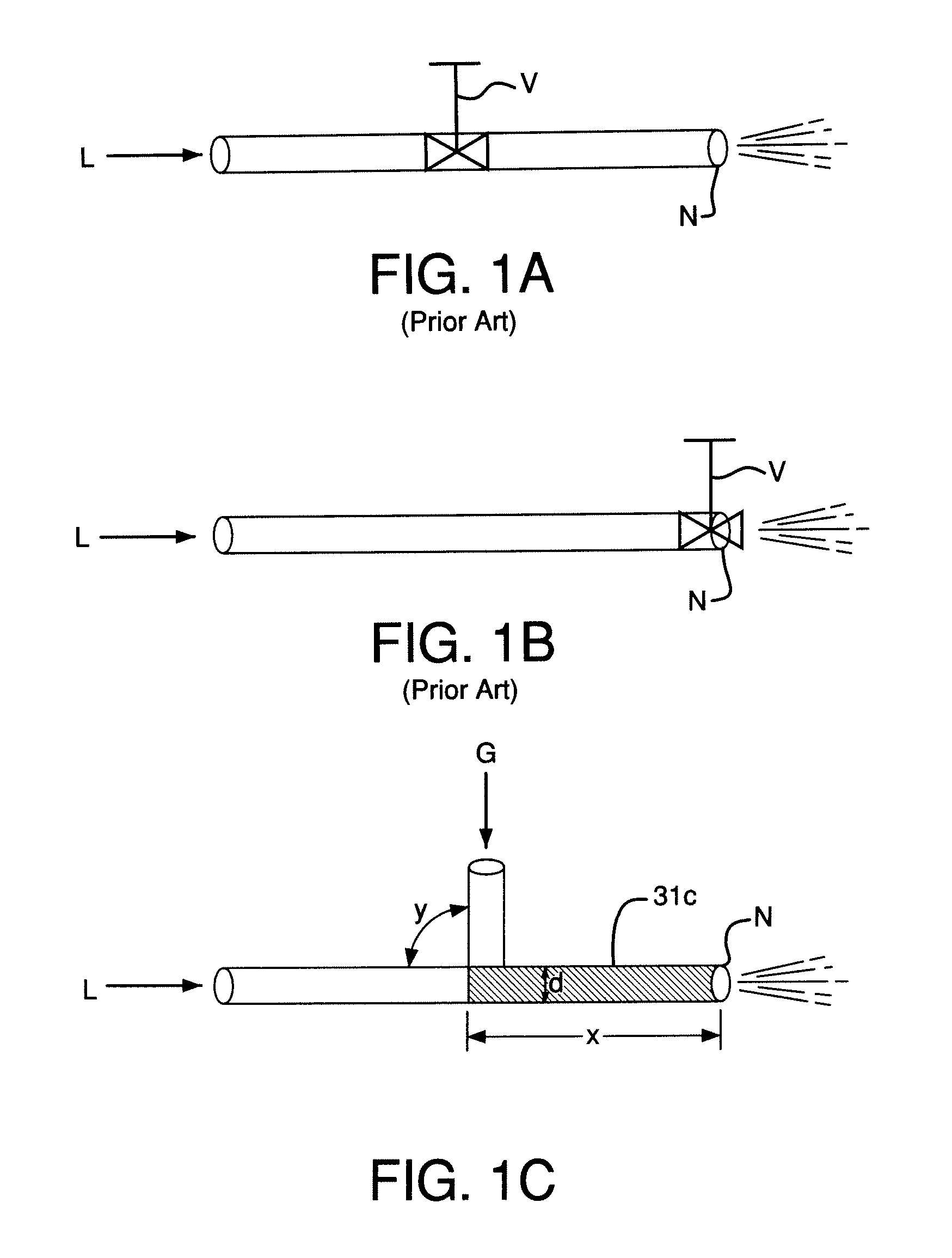
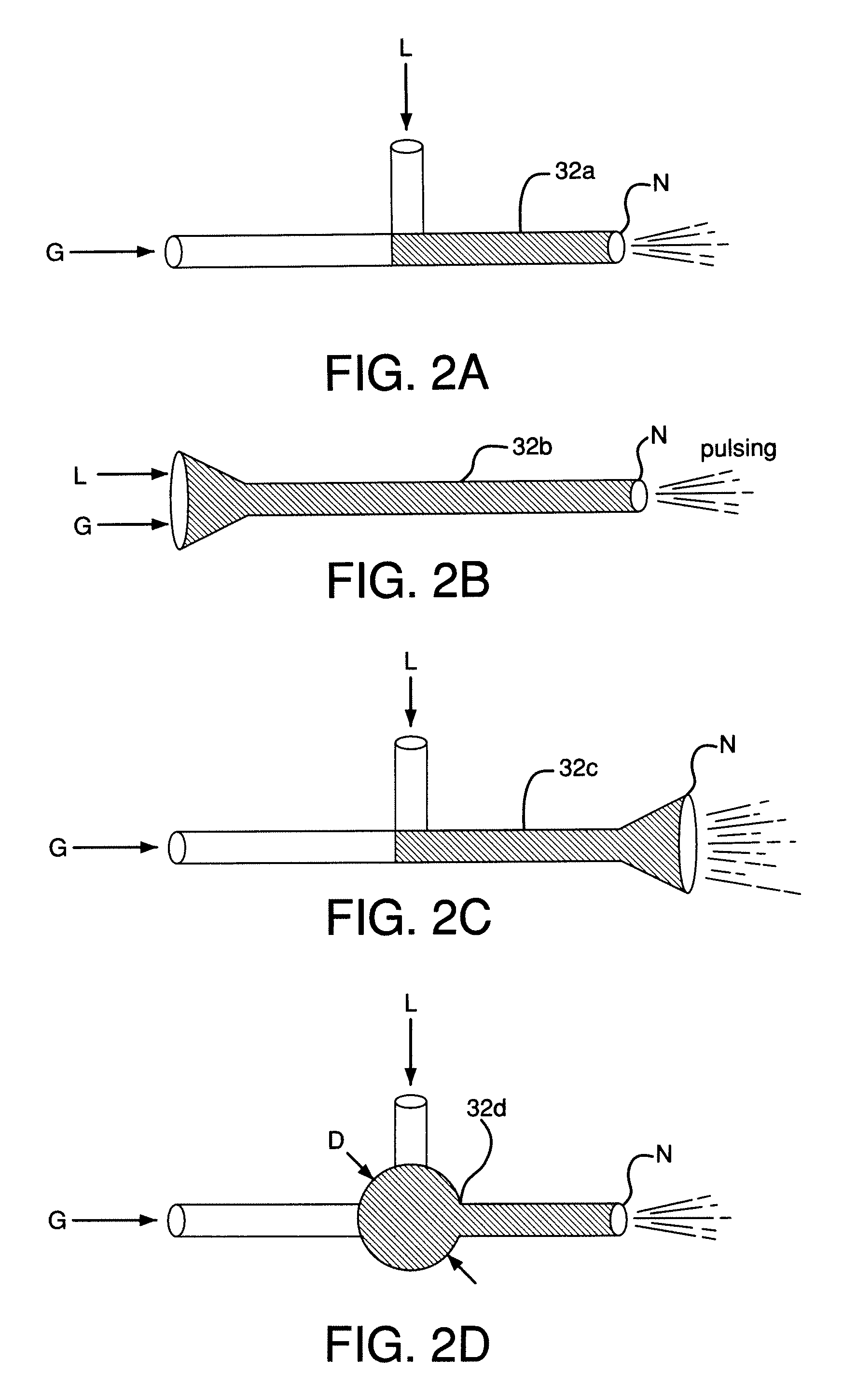
InactiveUS20060275554A1Increase the lengthAvoid negative effectsLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingSpray nozzleHigh pressure
A nozzle assembly for a kinetic spray system includes a convergent portion, a throat portion, and a divergent portion, each cooperating together to define a passage therethrough for passing a mixture of powder particles suspended in a flow of a high pressure heated gas. The nozzle assembly further includes an extension portion attached to the divergent portion and extending to a distal end a pre-determined length from the divergent portion of the nozzle assembly. The extension portion permits a dragging force exerted on the powder particles by the flow of high pressure heated gas to act upon the powder particles for a longer duration of time, thereby permitting the powder particles to accelerate to a greater velocity than has been previously achievable.
Owner:F W GARTNER THERMAL SPRAYING
Steel sheet having enhanced ductility for a molding member, molding member, and method for manufacturing same
ActiveCN103392022AHigh strengthImprove ductilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesUltimate tensile strengthImpurity
Owner:浦项股份有限公司
Microtreatment of Iron-Based Alloy, Apparatus and Method Therefor, and Articles Resulting Therefrom
ActiveUS20100132854A1Minimum of costMinimum of timeFurnace typesIncreasing energy efficiencyHigh carbonQuenching
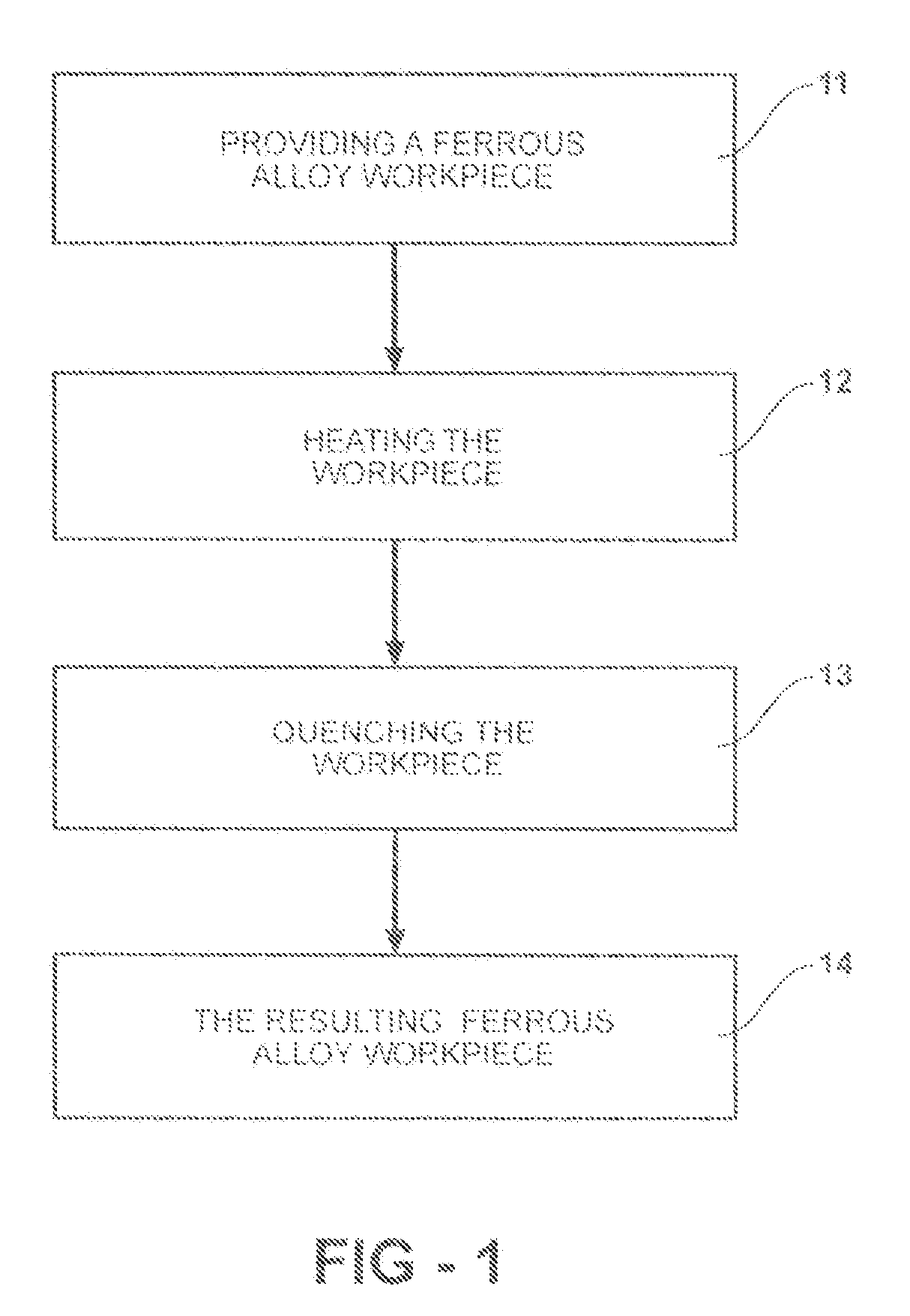
Iron-based alloys and articles in strips, sheets, workpieces and the like are converted into high strength steel with a minimum of cost, time and effort, including producing dual phase materials. This is achievable by extremely rapid micro-treating of low, medium, and high carbon iron-based alloys and articles by rapid heating and rapid cooling at least a portion of the alloy / article. This heating step involves nearly immediately heating the iron-based alloy to a selected temperature above its austenite conversion temperature. Then, the alloy is immediately quenched, also at an extremely fast rate, on at least a portion of the iron-based alloy in a quenching unit adjacent the heating unit. This procedure forms high strength alloy in a desired area, depending upon where the treatment was performed.
Owner:COLA JR GARY M
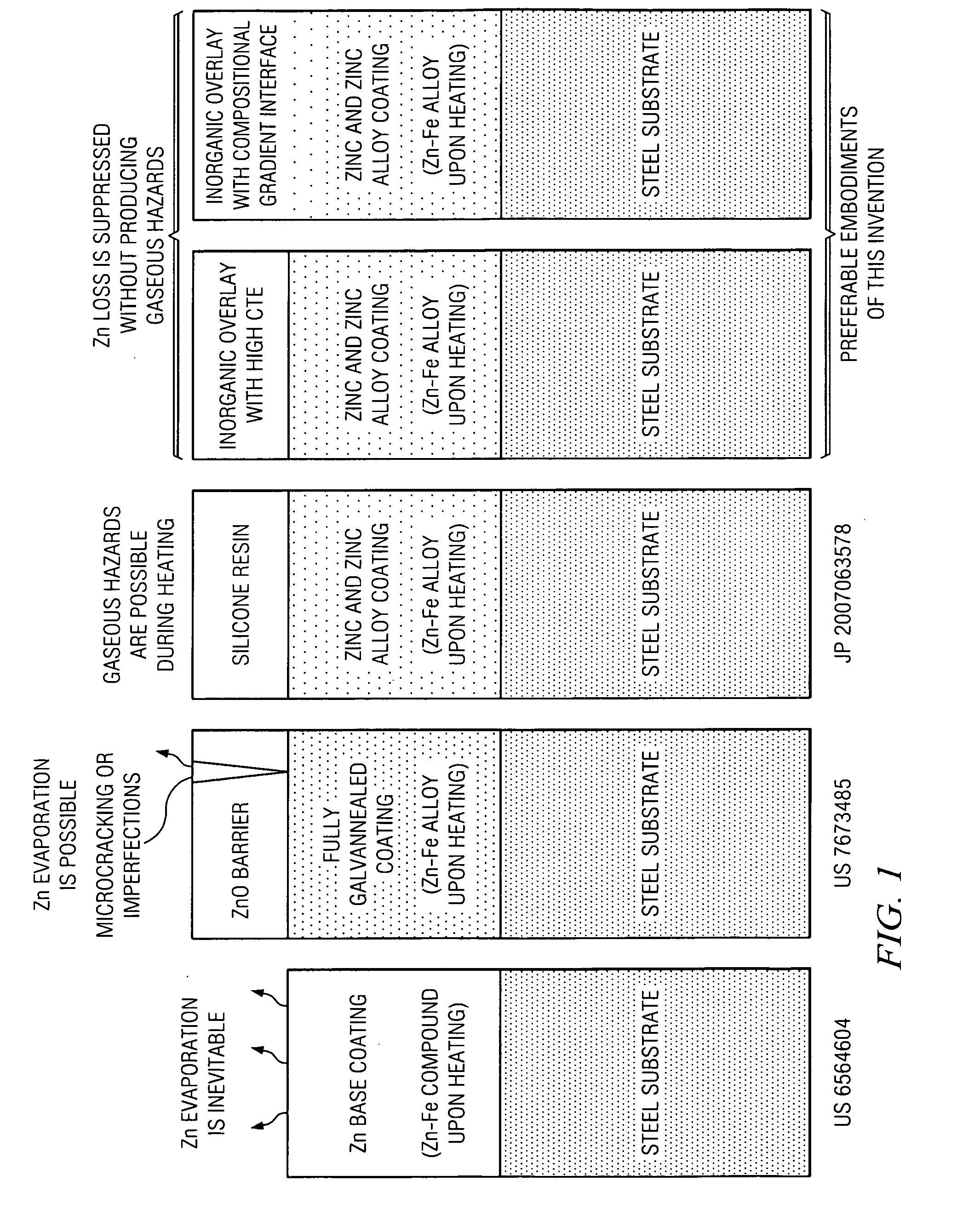
Zinc coated steel with inorganic overlay for hot forming
InactiveUS20120118437A1Retard and restrict lossReduce hardnessHot-dipping/immersion processesPretreated surfacesTungstatePhosphate
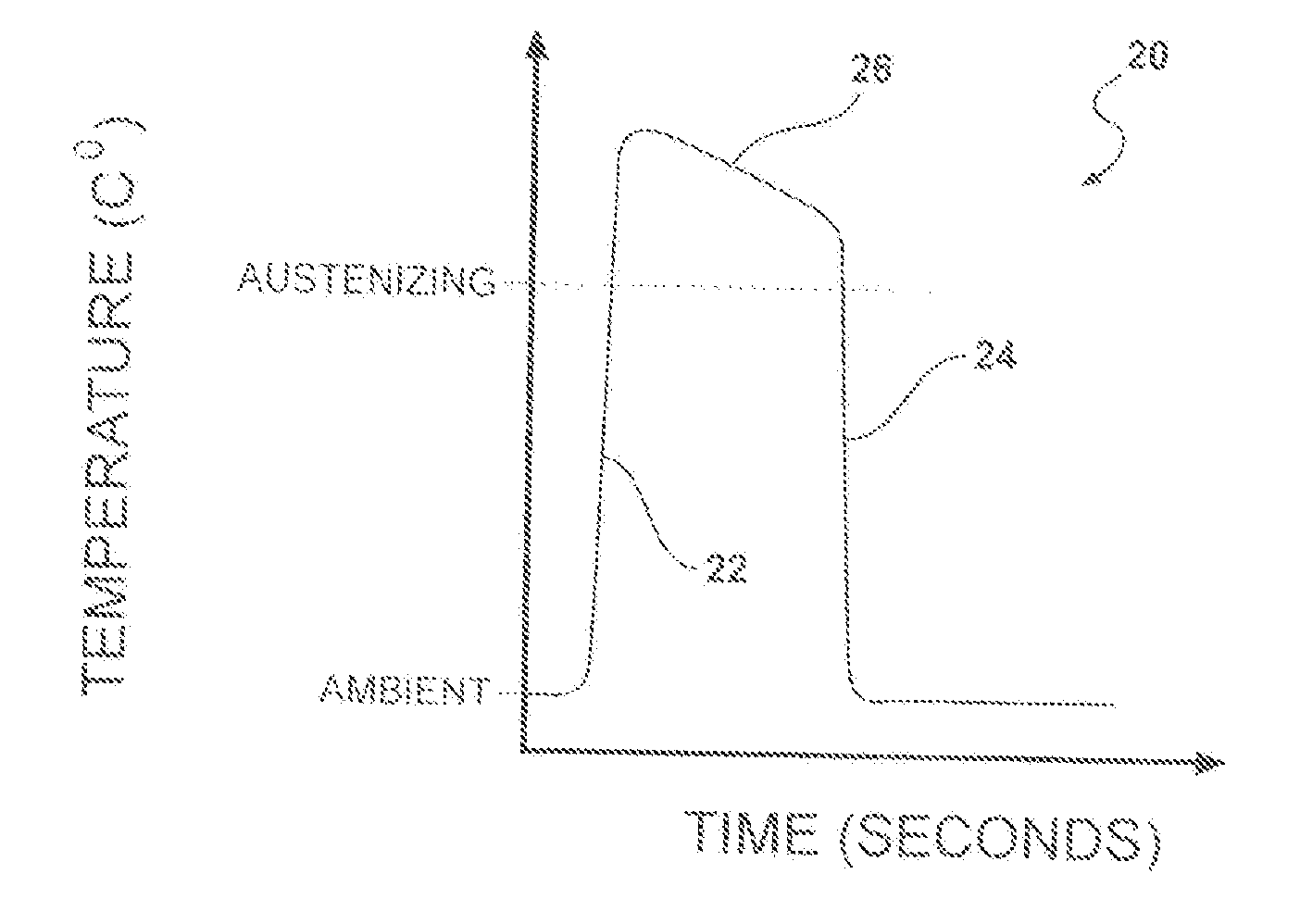
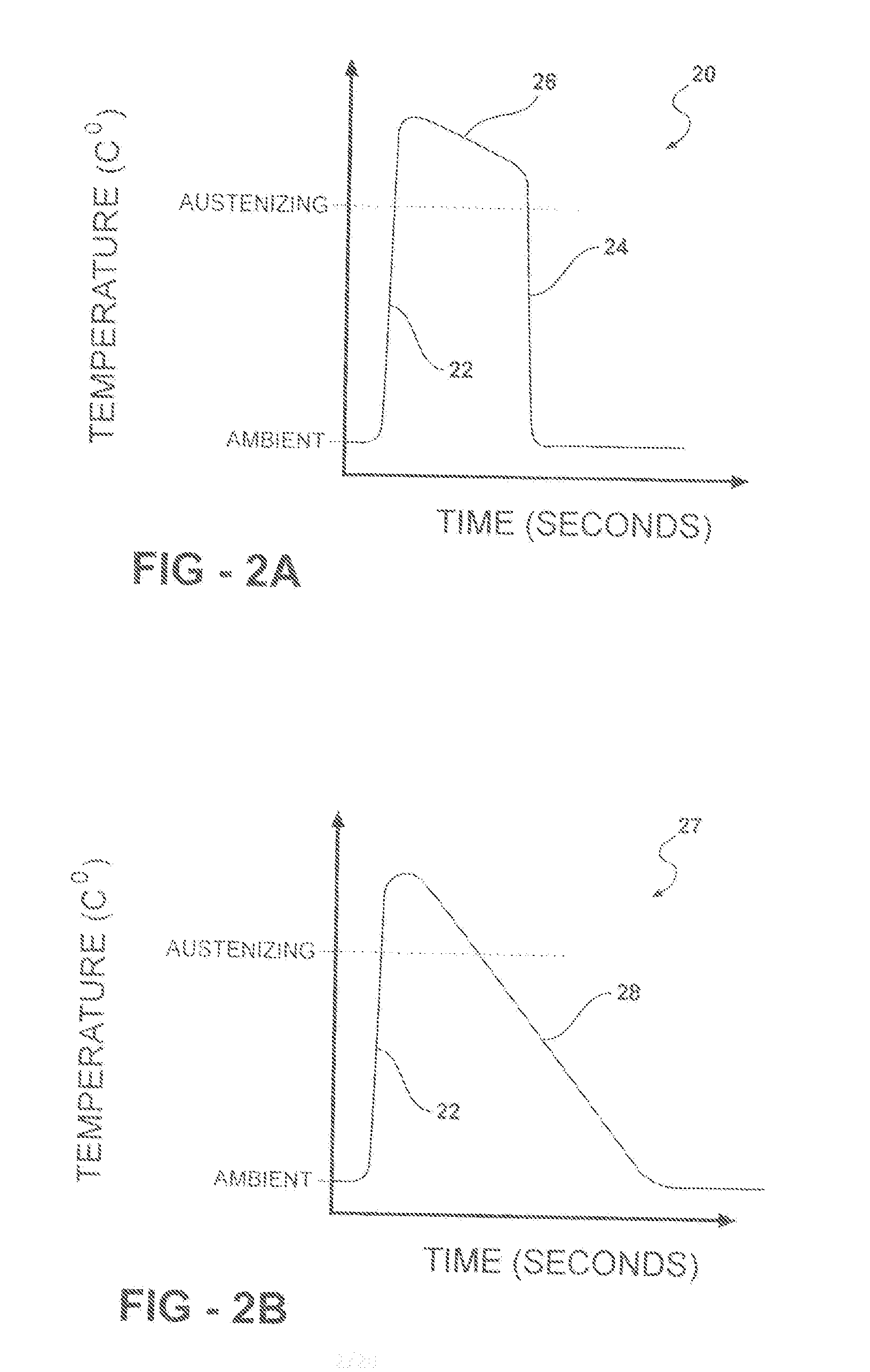
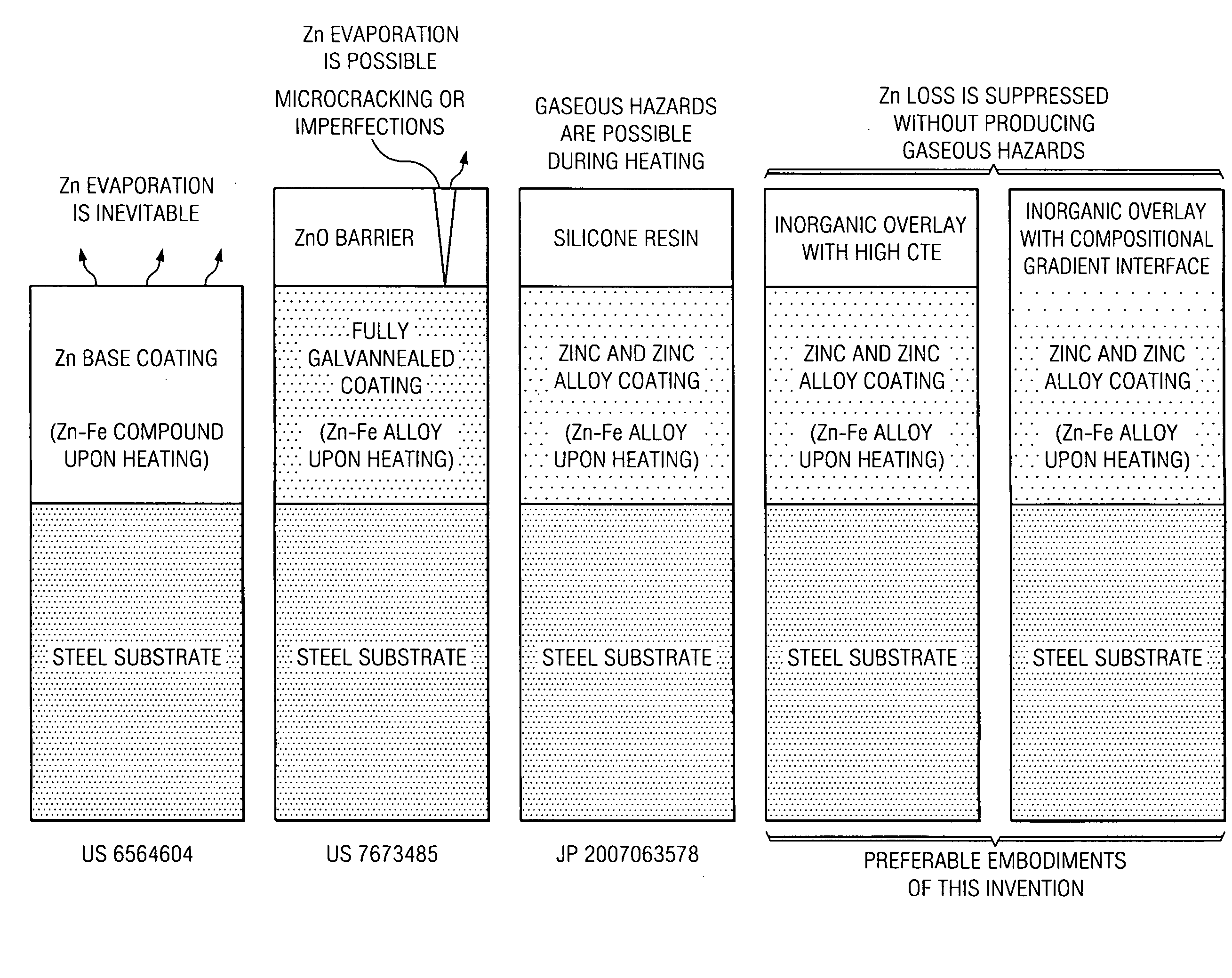
The present invention is of zinc or zinc alloy coated steel for hot forming having an inorganic overlay covering the zinc or zinc alloy coating to prevent loss of zinc during heating and hot forming. In one embodiment, the inorganic overlay has a coefficient of thermal expansion greater than the coefficient of thermal expansion of zinc oxide. In another embodiment, the inorganic overlay has a compositional gradient interface with the zinc or zinc alloy coating. Preferably the inorganic overlay may be comprised of material selected from phosphates, oxides, nitrates, carbonates, silicate, chromate, molybdate, tungstate, vanadate, titanate, borate, fluoride and mixtures thereof. A method of preparing the steel for hot forming and a method for hot forming the steel are provided.
Owner:WANG JIAN +1
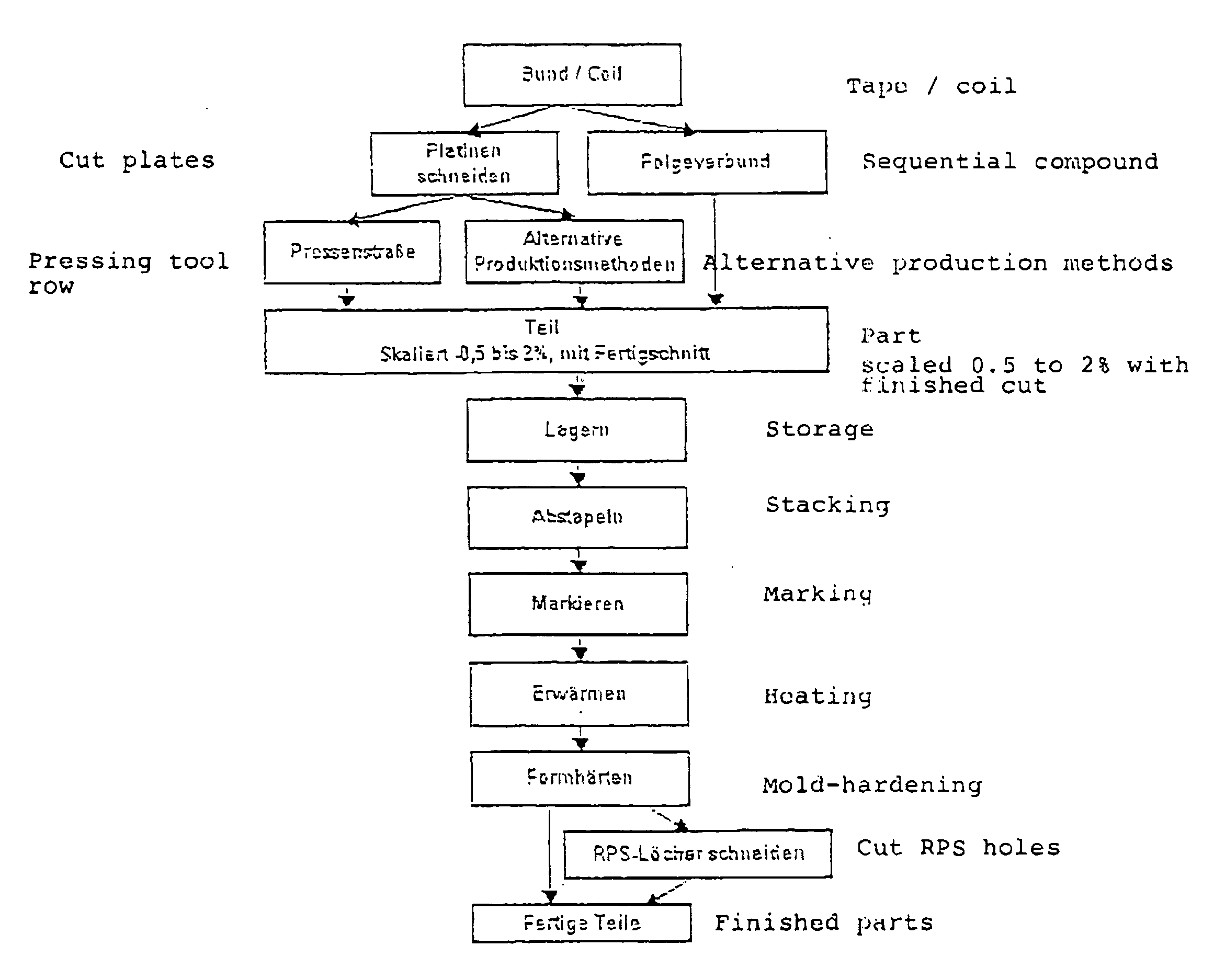
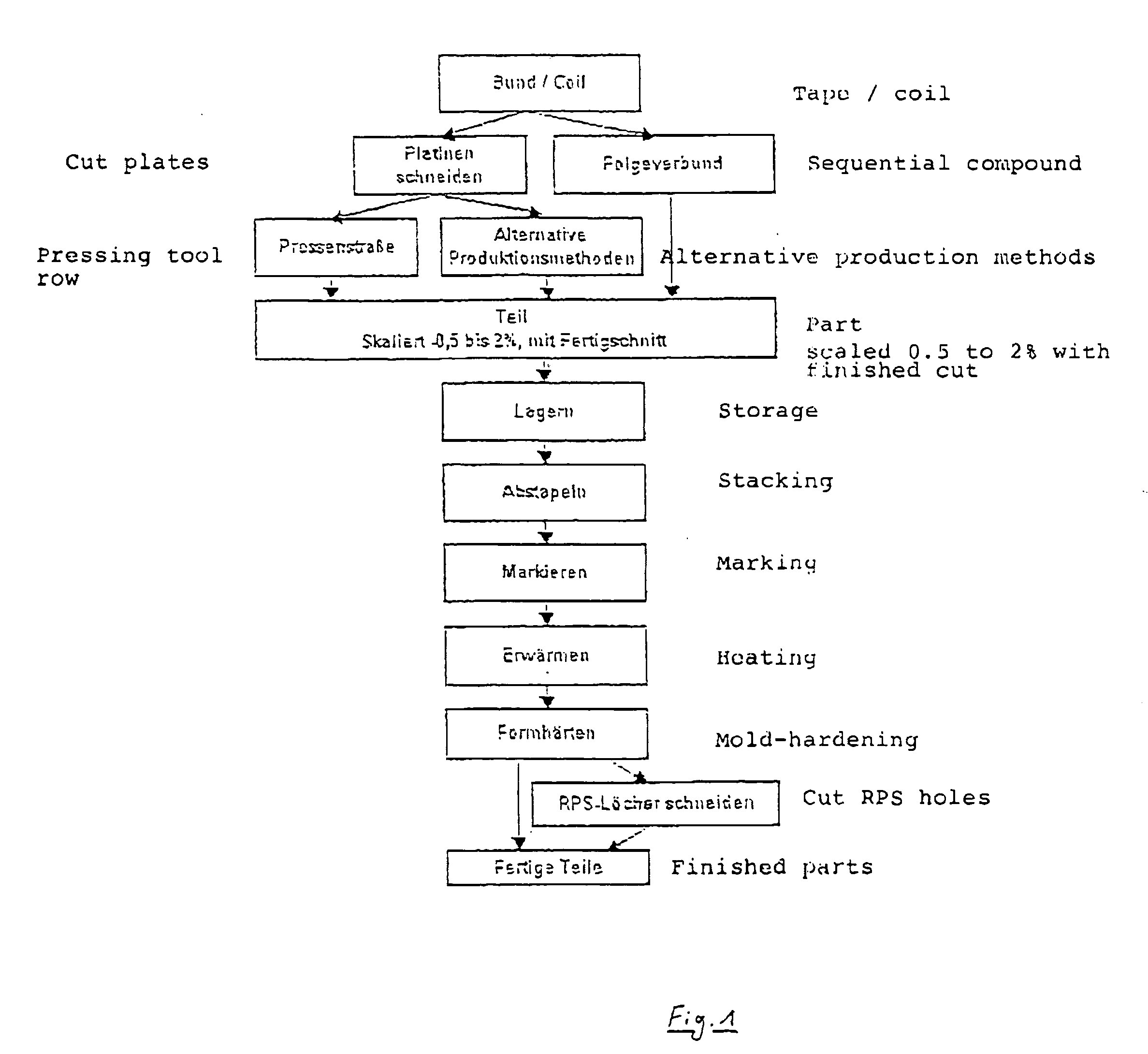
Method for producing hardened parts from sheet steel
ActiveUS20070000117A1Fast coolingEasy to integrateHot-dipping/immersion processesMetal rolling stand detailsPunchingSheet steel
The invention relates to a method for producing hardened structural parts from sheet steel. The method includes shaping at least one shaped part made of sheet steel provided with a cathodic corrosion protection coating, performing any required final trim of the shaped part and possibly any required punching, or the creation of a perforation pattern, subsequently heating the shaped part, at least over partial areas, under the admission of atmospheric oxygen to a temperature which permits austenizing of the steel material, and thereafter transferring the structural part to a mold-hardening tool and performing mold-hardening in the mold-hardening tool, wherein the structural part is cooled by the contact with and pressing by the mold-hardening tool and is hardened thereby.
Owner:VOESTALPINE STAHL GMBH
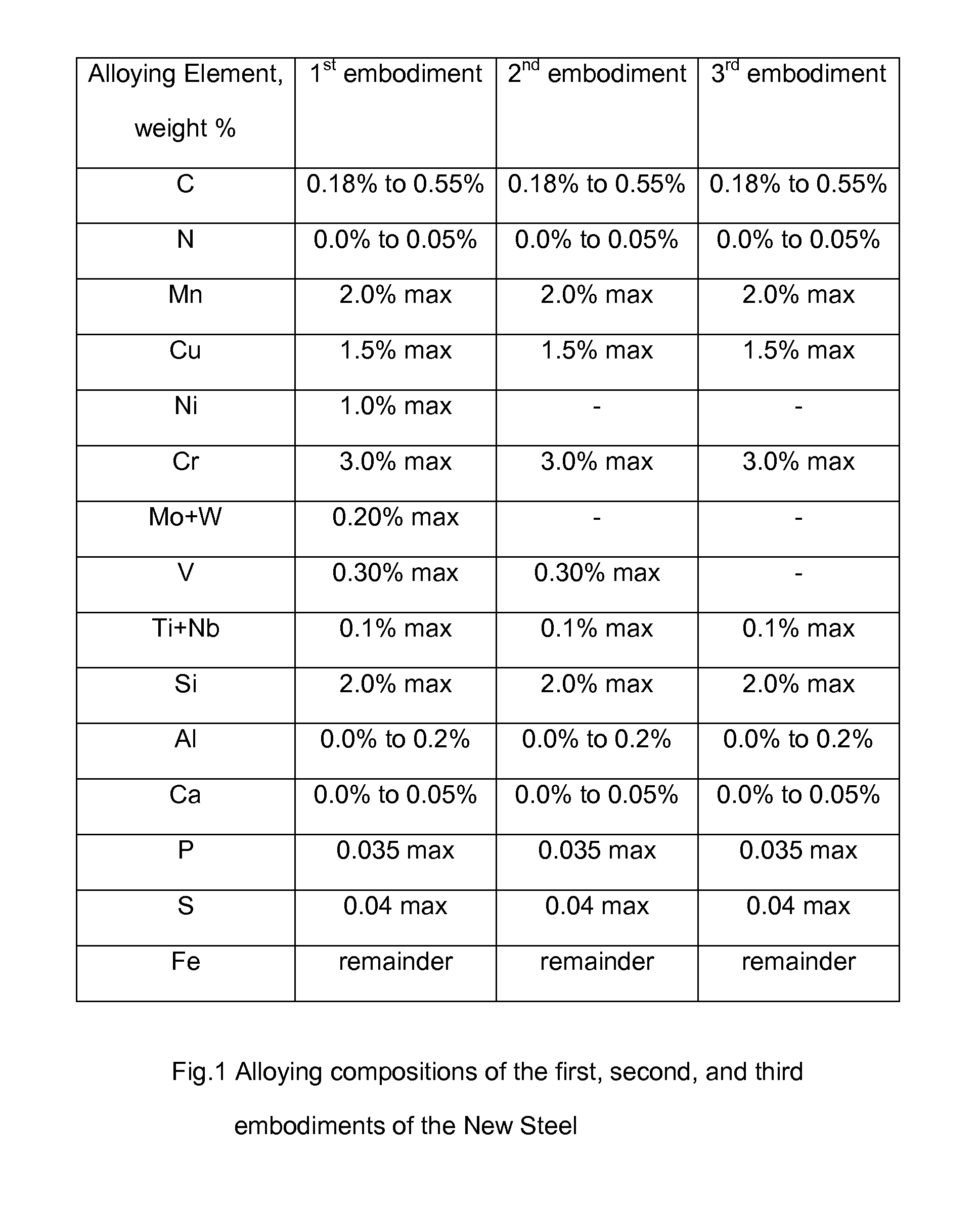
High Strength Low Alloy Steel and Method of Manufacturing
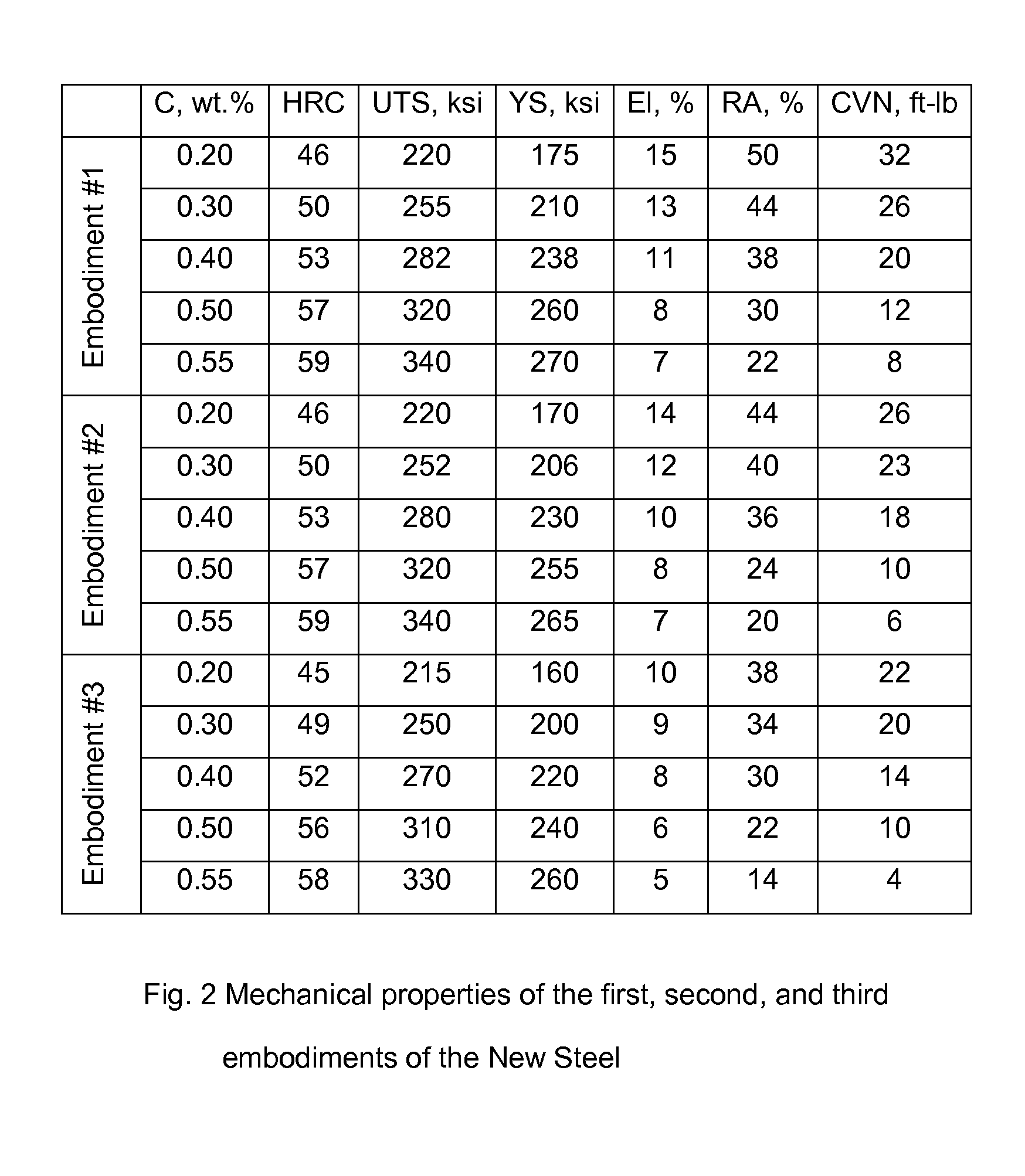
The present invention relates to a wrought, quenched and tempered, fine-grained, with deep hardenability, high strength and low alloy steel having a sum of the alloying elements: nickel, molybdenum, tungsten, vanadium, titanium, and niobium in weight percentage of 1.60% maximum in the first embodiment; vanadium, titanium, and niobium in weight percentage of 0.40% maximum in the second embodiment; titanium and niobium in weight percentage of 0.10% in the third embodiment. The air melted and hot forged steel of the first embodiment has hardness of HRC 55, an ultimate tensile strength of 300 ksi, a yield strength of 257 ksi, a total elongation of 9%, a reduction of area of 32%, and Charpy v-notch impact toughness energy of 15 ft-lb after normalizing, gas quenching, and tempering at 450° F.
Owner:VARTANOV GREGORY
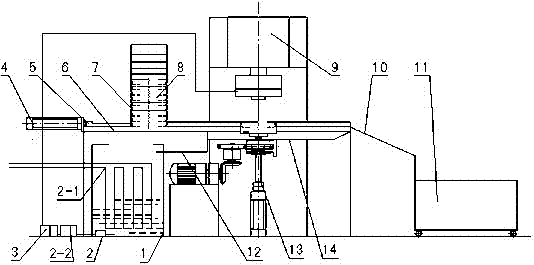
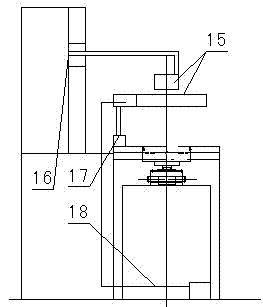
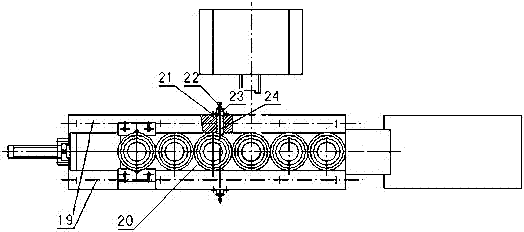
Rotary lifting-type gear sleeve automatic high frequency quenching device
InactiveCN102382953ARealize the heating effectReduce labor intensityIncreasing energy efficiencyFurnace typesGear wheelElectric machinery
The invention discloses a rotary lifting-type gear sleeve automatic high frequency quenching device, which is composed of a bed, a pushing mechanism, a left and right guide rails component, an automatic rotating and elevating component, high frequency induction quenching, a liquid cooling device, a discharging mechanism and PLC; a piston rod end of a pushing cylinder (4) arranged on an end-face at one side of the bed (6) is connected to a pushing plate (5), and the pushing plate (5) is supported against a workpiece circumcircle in a storing rack (7) arranged in the left and right guide rails component; elastic fixed mounts (21) are symmetrically arranged at the outboard of the left and right guide rails at a third material groove station formed between the left and right guide rails (19),a spring pin (24) passes through an adjusting bolt (22), a spring of the spring pin (23) and the left and right guide rails to form inner apertures which are supported against the workpiece circumcircle in the material groove station; a spline shaft controlled by a motor through a gear and a cylinder is provided at the lower part of a fourth material groove station, the end of the spline shaft isconnected with a workpiece positioning seat; a high frequency induction coil and a spray liquid loop supported by a coil pedestal and a cooling rack supporter are provided over the fourth material groove station. The rotary lifting-type gear sleeve automatic high frequency quenching device realizes the purposes of automatic quenching and cooling workpiece.
Owner:ANHUI MINGYAN GEAR
Method of making coated stamped parts and parts made therefrom
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing hot stamped coated parts, which method includes the following consecutive steps, in order: providing a hot-rolled or cold-rolled steel plate including a steel substrate and an aluminum-silicon alloy precoat, the precoat containing Greater than 50% free aluminum and with a thickness of 15 to 50 microns; the steel plate is then cut to obtain a pre-coated steel blank; the blank is then heated in a non-protective atmosphere to a temperature Ti of Te-10°C to Te, Te is the eutectic or solidus temperature of the precoat; the billet at temperature Ti is then heated to 840 to 950°C in a non-protective atmosphere at a heating rate V of 30°C / s to 90°C / s The temperature Tm of the coated heated blank is obtained, and V is the heating rate from the temperature Ti to the temperature Tm; then the coated heated blank is soaked at the temperature Tm for a time tm of 20s to 90s; and then hot stamped. The blank is obtained to obtain a hot stamped coated part; the stamped part is then cooled at a cooling rate to form a microstructure including at least one component selected from martensite or bainite in the steel substrate.
Owner:安赛乐米塔尔研究发展有限公司 +2
Method and Device for Producing a Metal Component
The invention relates to a method for producing a metal structural component, in particular a vehicle structural component, in which a steel part is hot formed and is hardened at least over sections by contact with a tool surface, in which the steel part is during the hardening cooled in at least two partial regions at different cooling rates, so that the partial regions after the hardening differ in their microstructure, wherein the cooling rates differing from one another are produced by sections of the tool surface corresponding to the partial regions of the steel part, which differ from one another as regards their thermal conductivities. The invention also relates to a further method for producing a metal structural component, as well as a tool and a batch furnace.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP STEEL EURO AG
Water quenching and cooling method and device for ultrahigh-strength strip steel
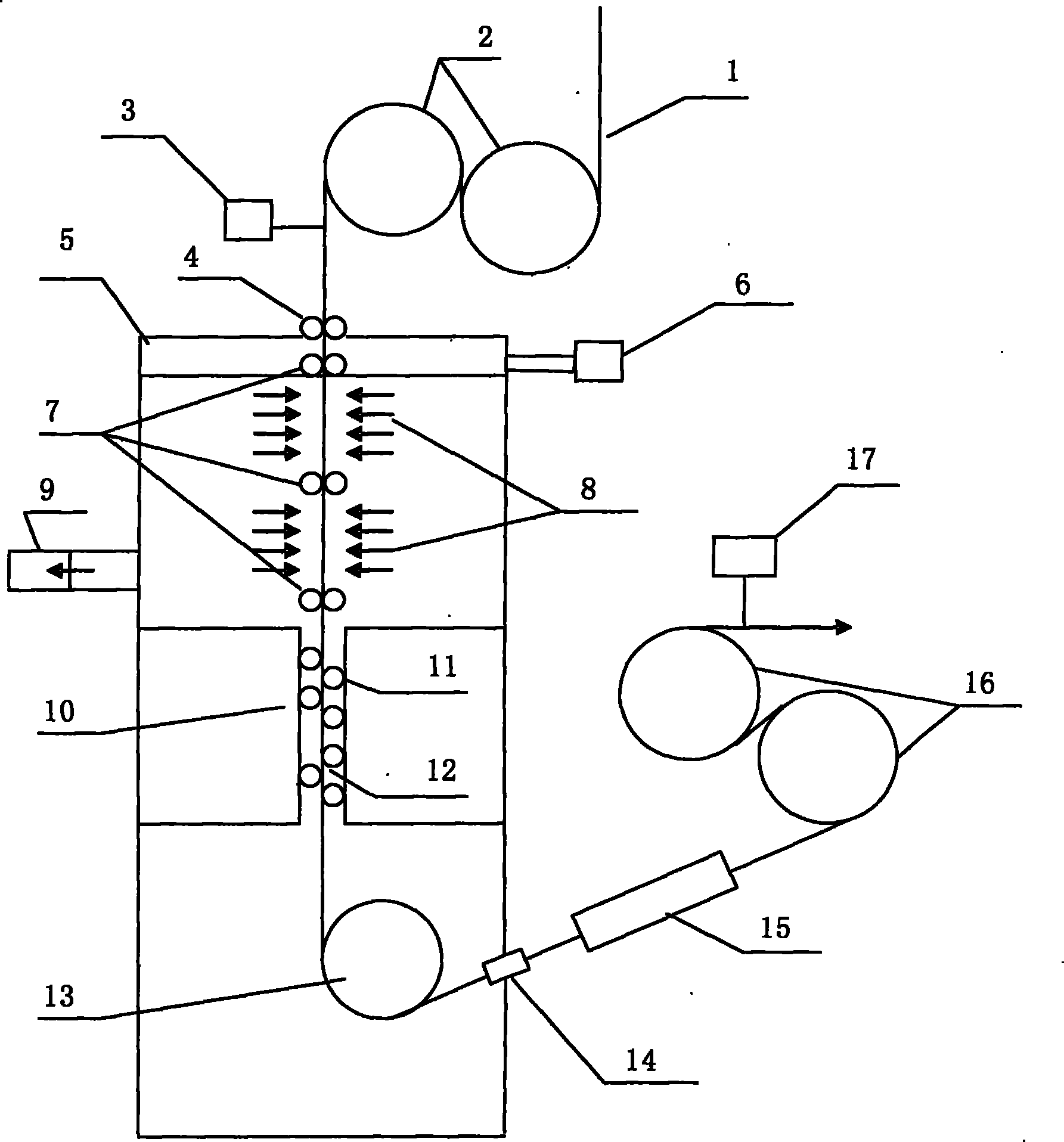
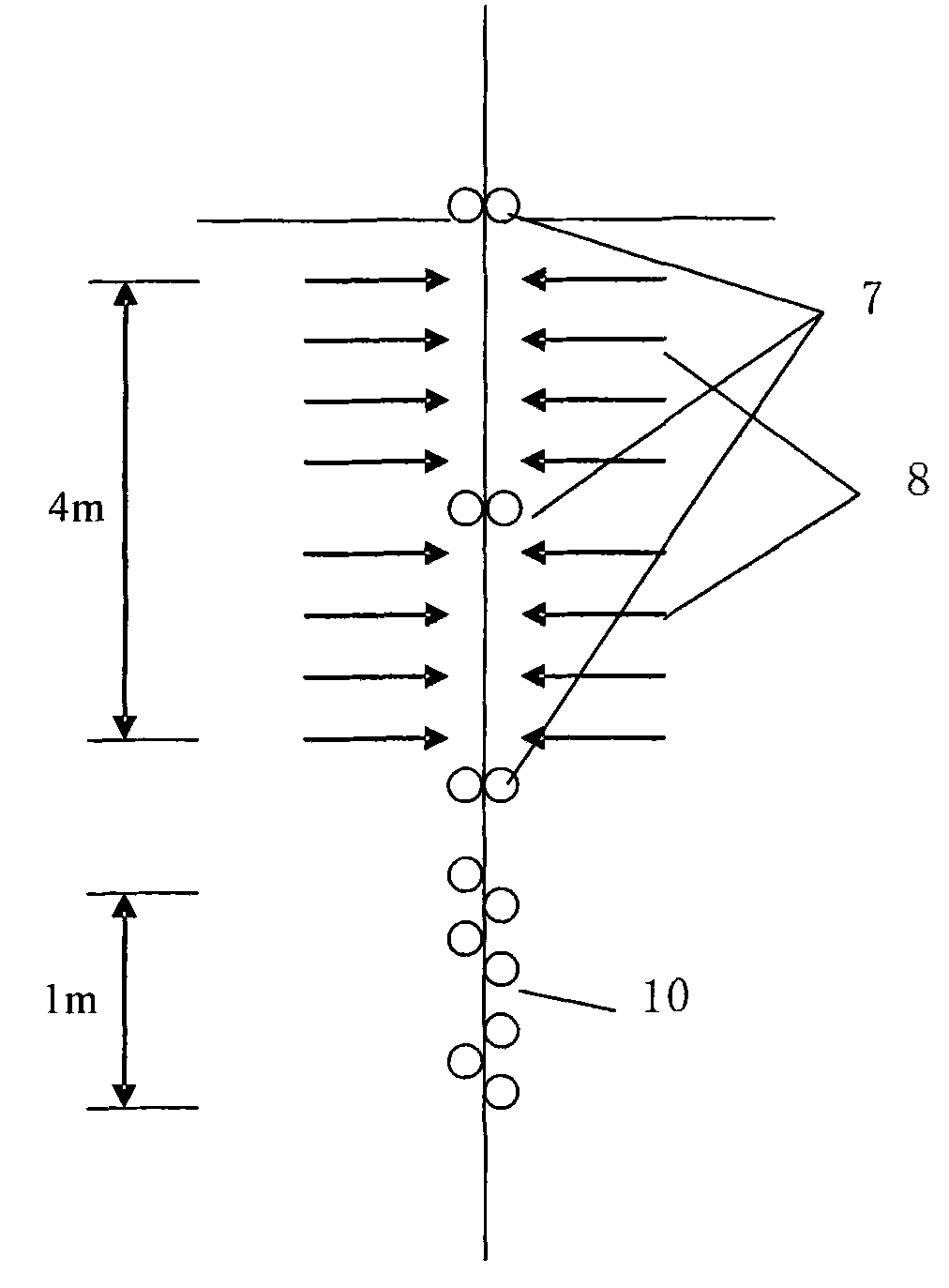
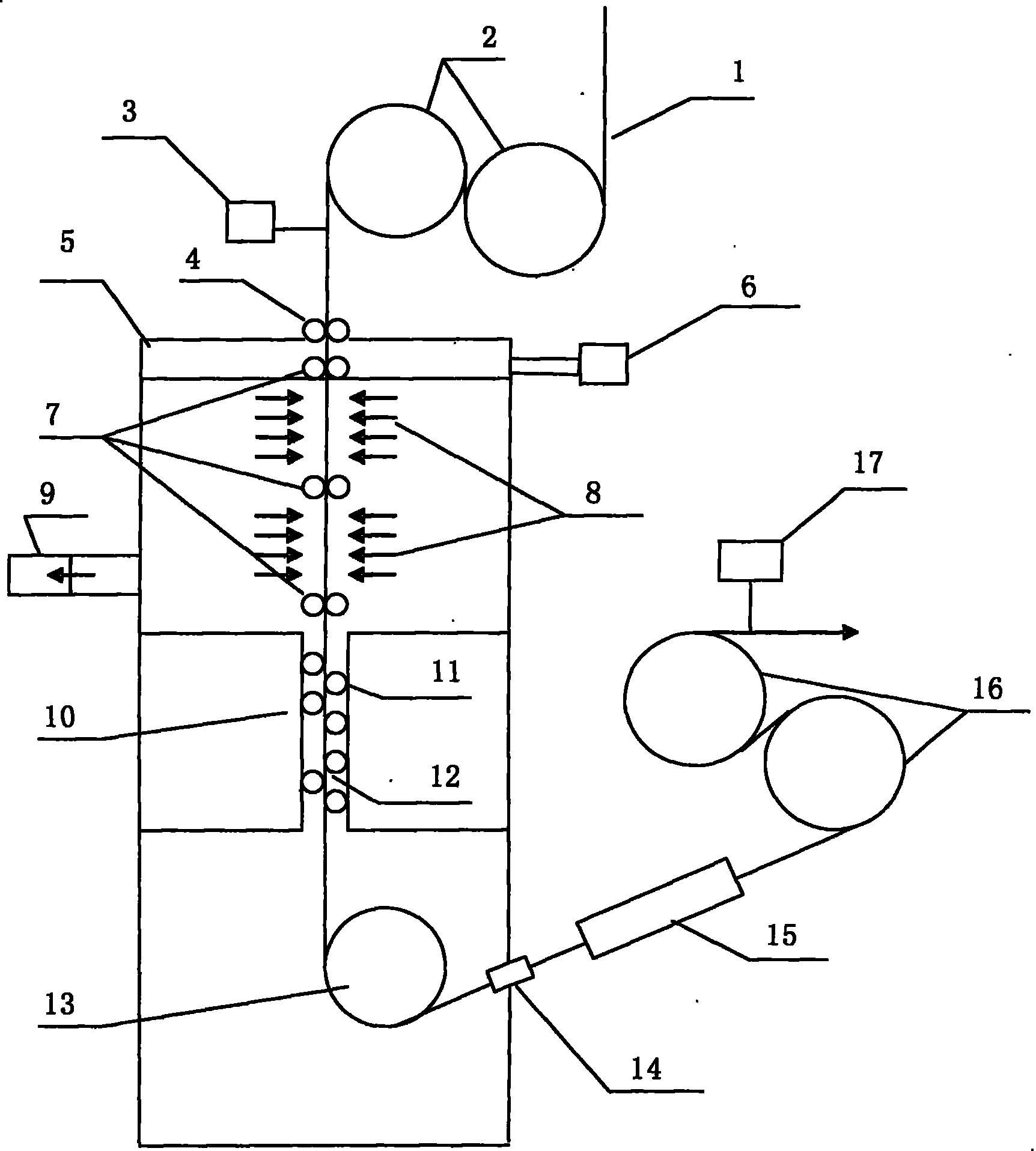
ActiveCN101993995ARapid coolingGood effectFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesSpray nozzleStrip steel
The invention has the purpose of providing a water quenching and cooling method and device for ultrahigh-strength strip steel. The device comprises an inlet tension roll (2), an outlet tension roll (16), and a water quenching and cooling tank (5), wherein water quenching nozzles (8) and a withdrawing and straightening machine (10) are arranged in the cooling tank; the cooling tank is connected with a gas sealing device (4), a gas circulating device (6), a water circulating device (9), a water sealing device (14), a drying device (15), a strip steel operating line centering device (3) and a tension control system (17); the multiple water quenching nozzles (8) in the front section of the water quenching and cooling tank eject high-pressure water to cool the strip steel when the strip steel to be cooled enters the water quenching and cooling tank (5) through the inlet tension roll (2); the steel plate passes through the withdrawing and straightening machine (10) arranged on the lower part of the water quenching and cooling tank (5) after being cooled to 250 to 350 DEG C; the shape of the strip steel plate is straightened by a mild straightening mode; the strip steel after being cooled and straightened is transferred out of the water quenching and cooling device through the outlet tension roll (16); and the rapid cooling can be realized and the ultrahigh-strength steel plate with a good shape can be obtained at the same time.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
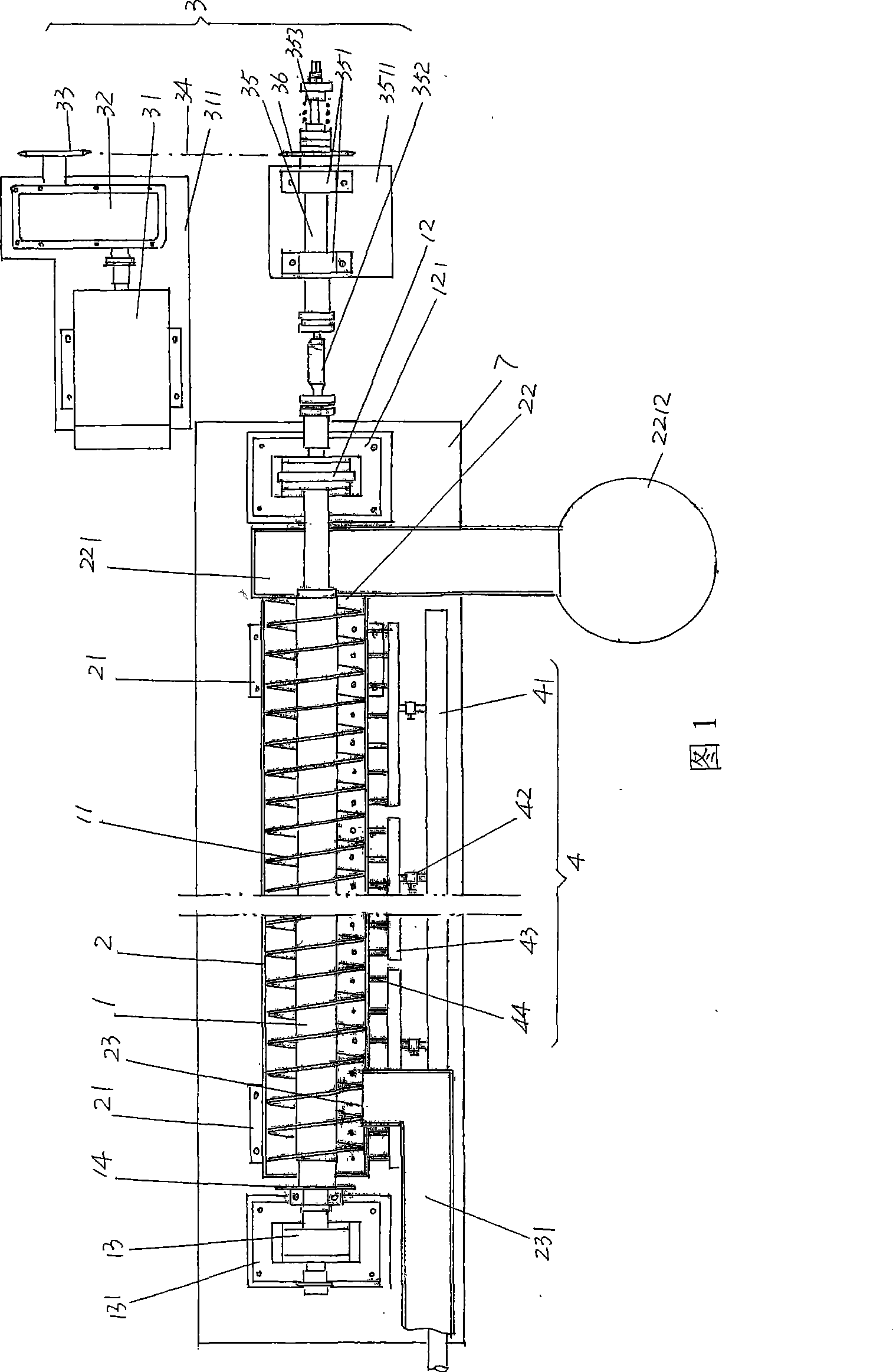
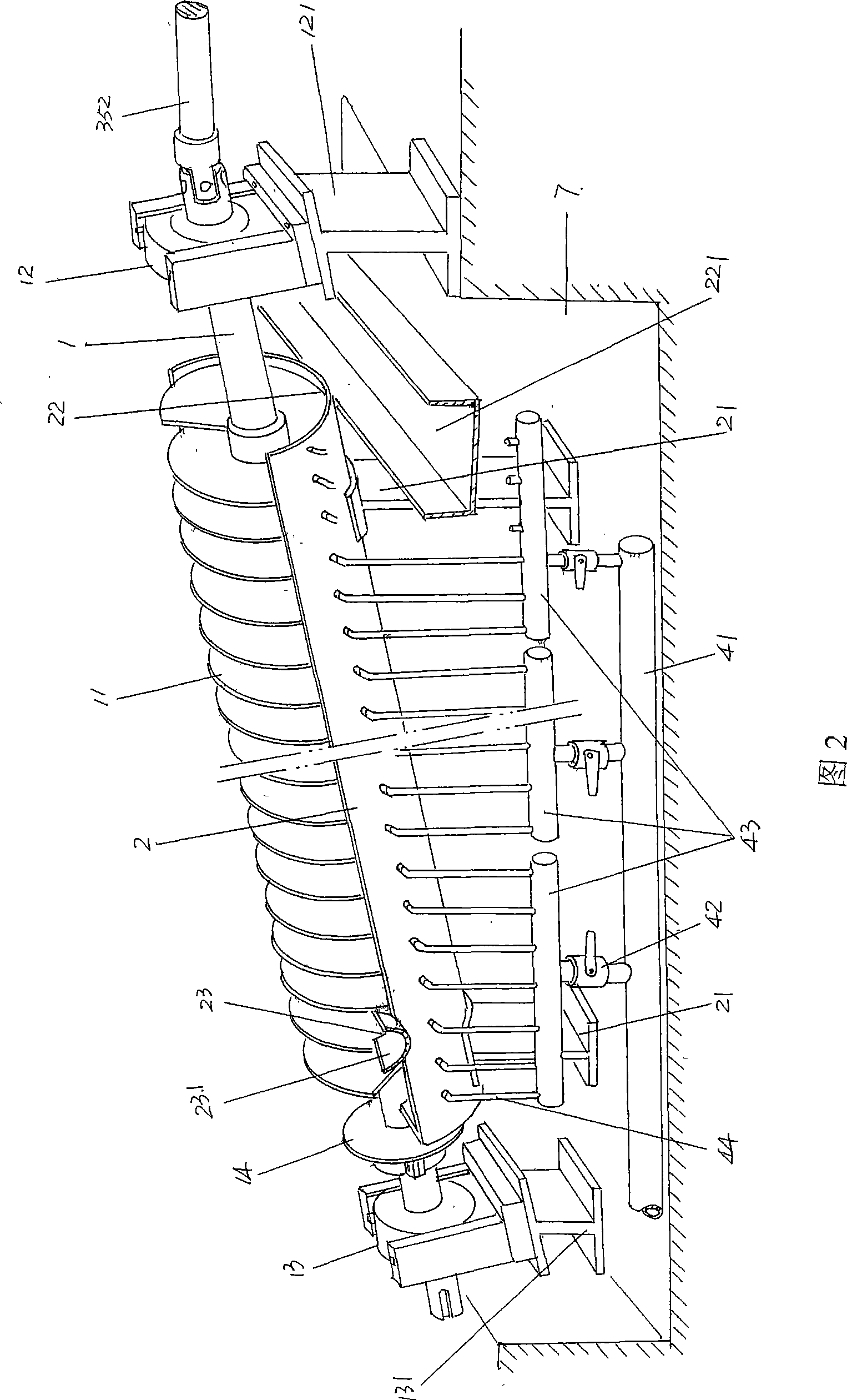
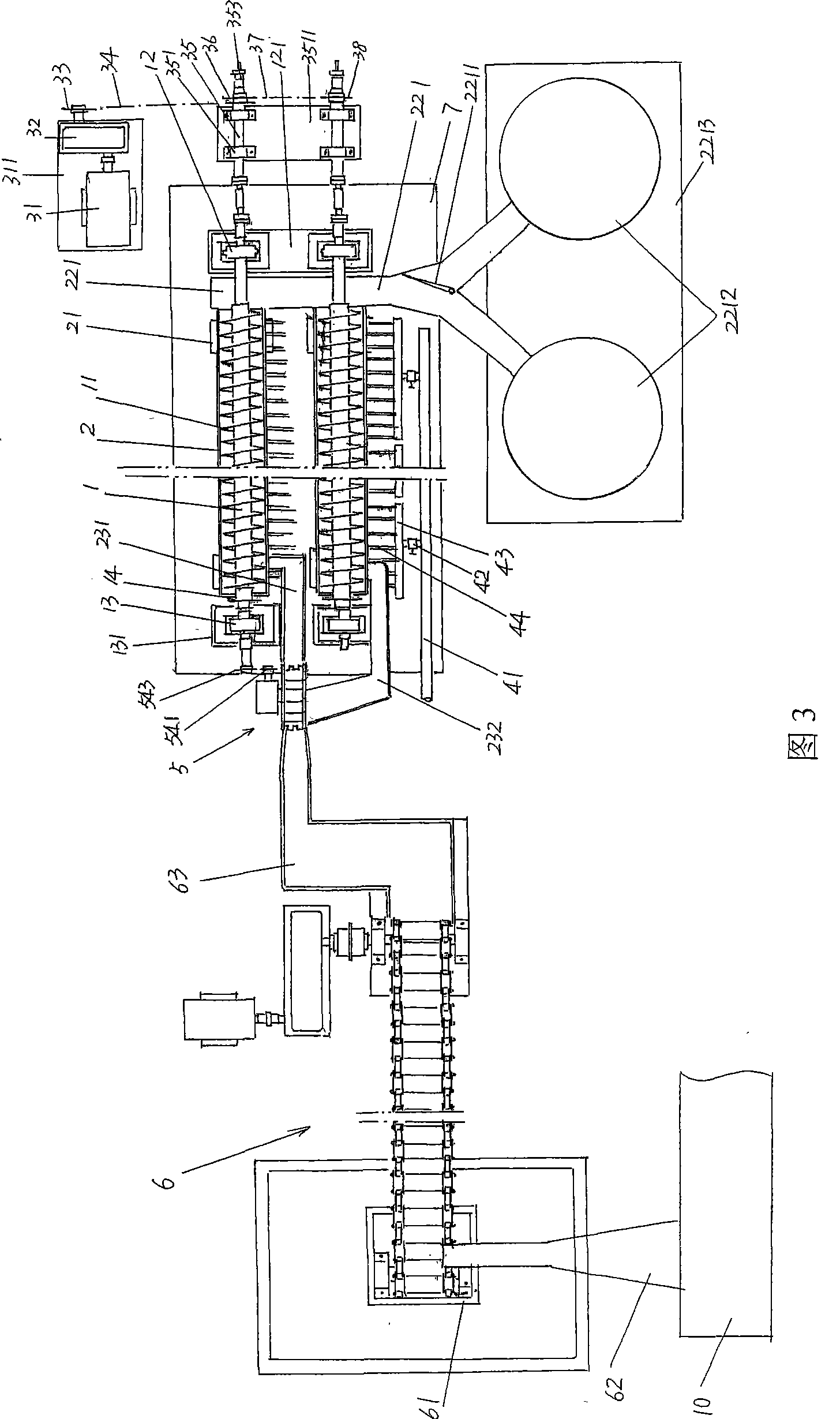
Quenching mechanism of steel ball quenching machine
InactiveCN100497667CSame quenching timeUniform quenching effectFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesSteel ballHardness
Owner:CHANGSHU FEIFAN METALWORK
Method and apparatus for hot forming and hardening a blank
InactiveUS20120006089A1Better withstandInhibition formationShaping toolsFurnace typesSteel beltDuctility
A blank cut from a strip of hardenable hot-formed steel is heated in a furnace to a temperature which is smaller than an Ac3 transformation point in an iron carbon diagram. A first region of the blank is then heated in a conductive heating station to a temperature above the Ac3 transformation point and subsequently hardened in a hot forming and hardening tool to produce a steel part with at least two microstructured regions of different ductility.
Owner:BENTELER AUTOMOBILTECHNIK GMBH
Cutting method for steel for use in machine structure
InactiveCN102470502AImprove overall lifespanMilling cuttersWorkpiecesMechanical engineeringGas mixing
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Hot pressing method for high strength member using steel sheet and hot pressed parts
ActiveUS20070163685A1Little riskImprove hydrogen embrittlement resistanceHot-dipping/immersion processesThin material handlingHydrogen concentrationHigh intensity
The present invention provides a method of hot pressing using hot rolled and cold rolled steel sheet or Al-based plated steel sheet or Zn-based plated steel sheet enabling a strength of at least 1200 MPa to be obtained after high temperature forming and with extremely little possibility of hydrogen embrittlement and such hot pressed parts, that is, a method of hot pressing a high strength automobile parts comprising using steel sheet containing as steel compositions by wt % C:0.05 to 0.5% or steel sheet plated mainly with Al or Zn to produce automobile members by hot pressing during which making the heating temperature before pressing Ac3 or more to 1100° C. or less, making the hydrogen concentration in the heating atmosphere 6 vol % or less, and making the dew point 10° C. or less and such hot pressed parts.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP +1
Production method of warm- or hot-formed product
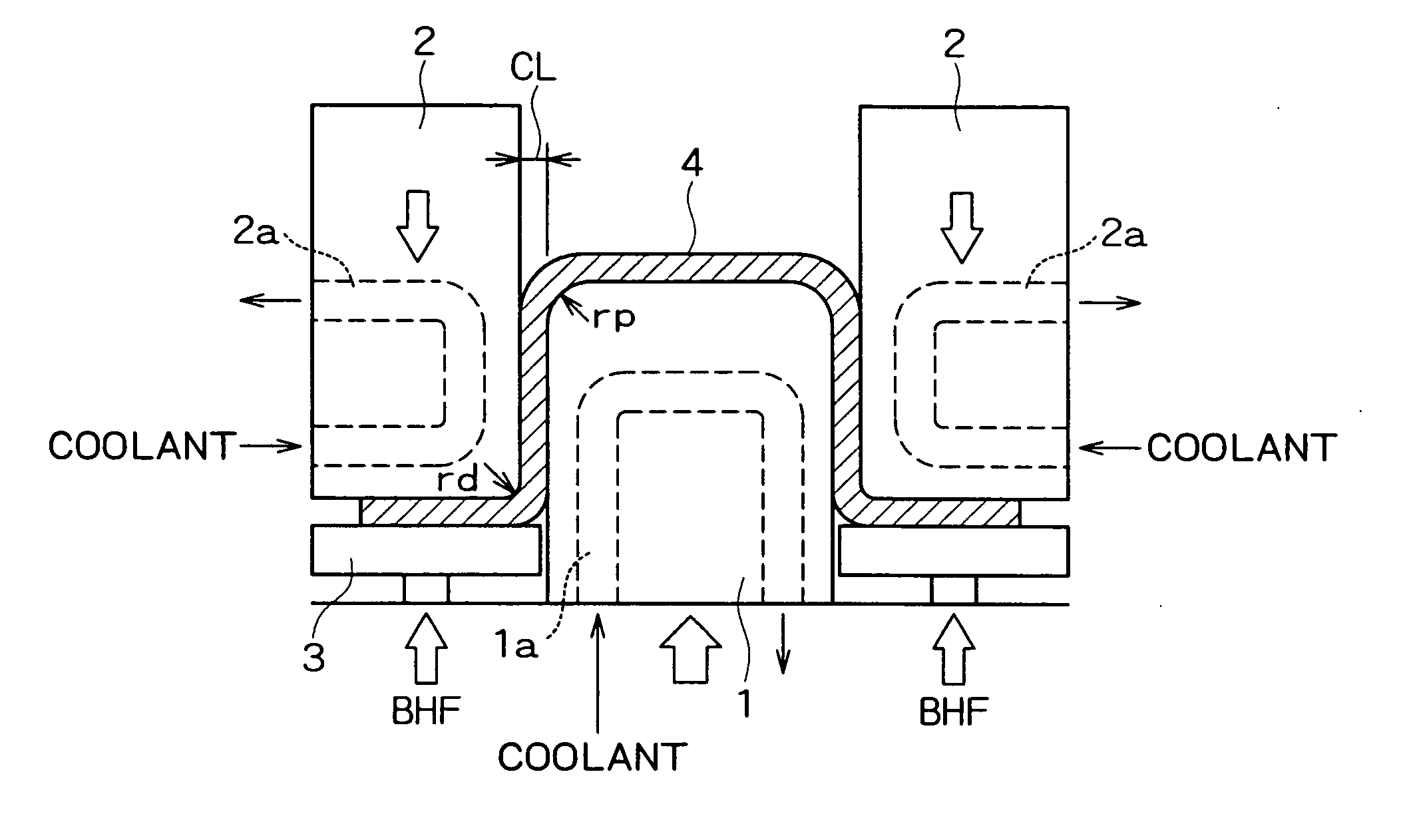
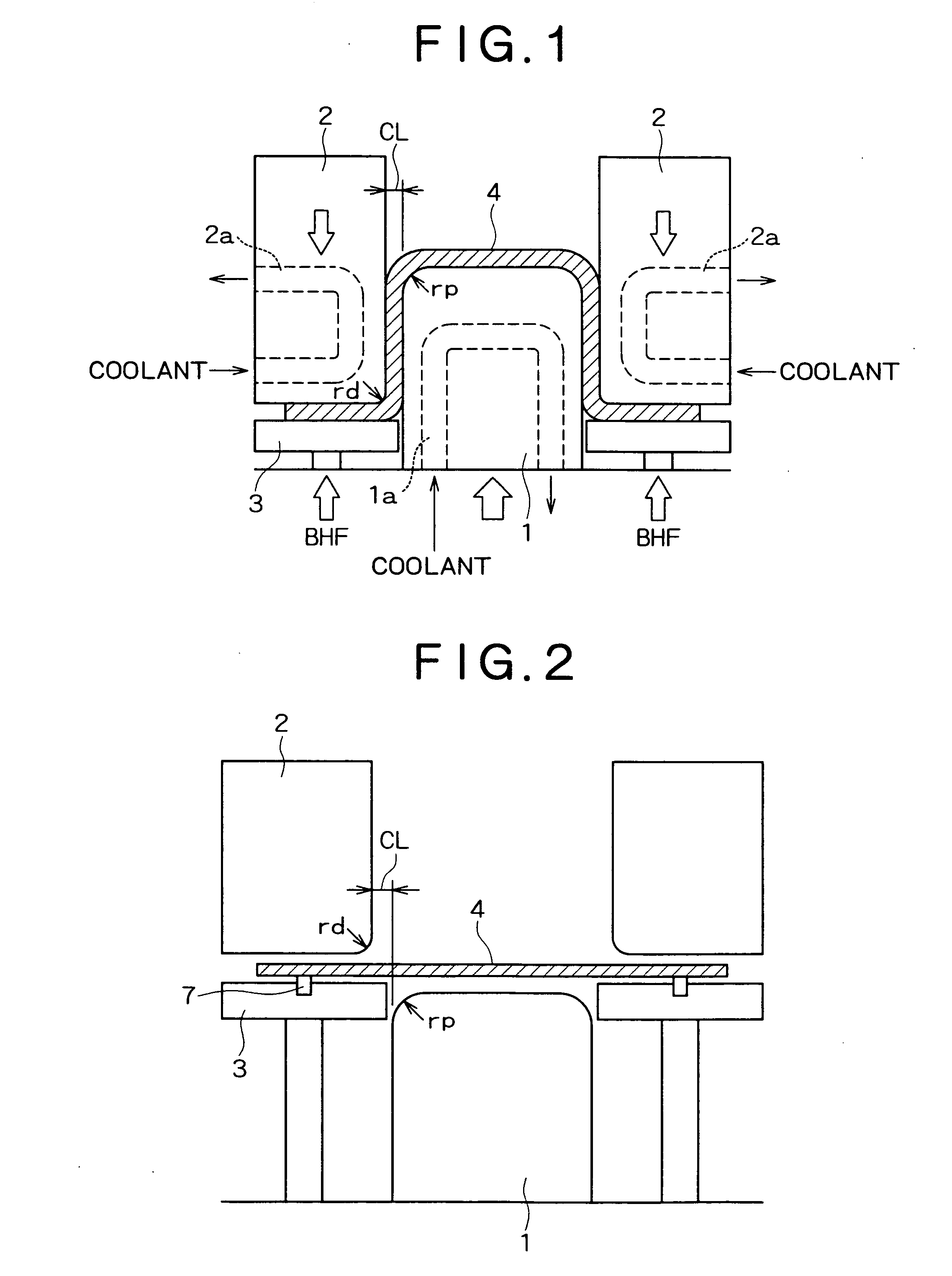
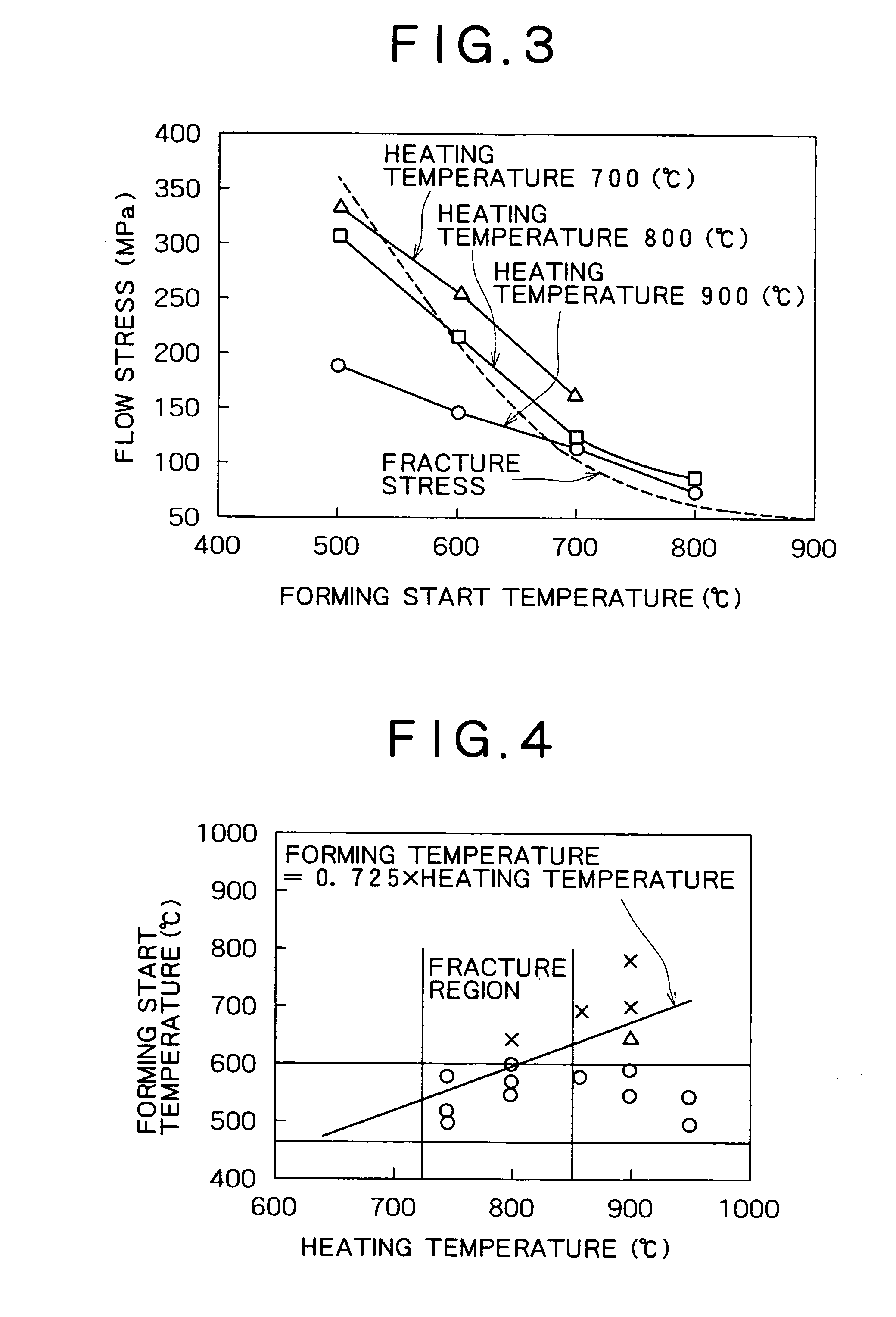
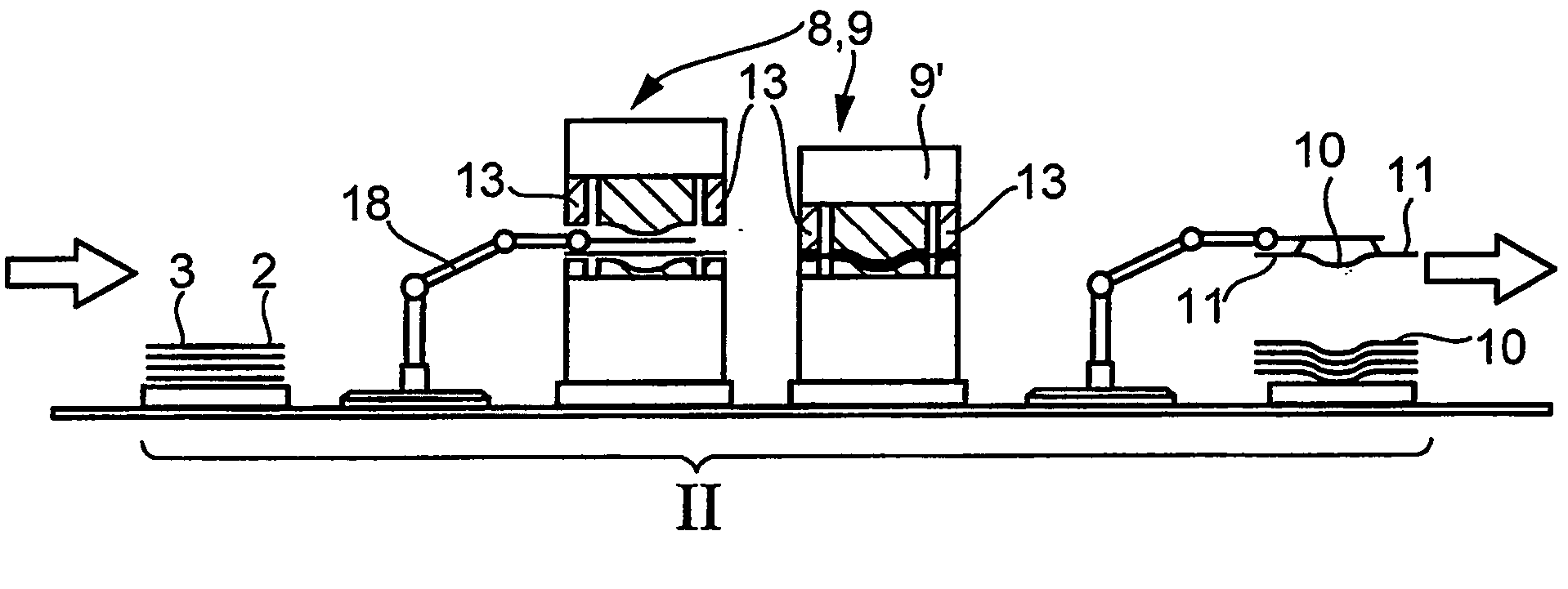
InactiveUS20050257862A1Good molding effectImprove ductilityMetal-working apparatusVehicle componentsHeating temperatureFormability
Disclosed is a method wherein when a steel sheet is subjected to warm or hot forming to produce a formed product by drawing with a punch and a die, the steel sheet is formed while the forming start temperature is controlled in accordance with the heating temperature of the steel sheet. By this method, when a steel sheet is subjected to warm or hot forming, good formability is obtained without the occurrence of fracture, cracking or the like during forming and also a formed product having good ductility is obtained.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Press-hardened part and method for the production thereof
ActiveUS20060137779A1Optimization orderShorten the lengthFurnace typesVehicle componentsCycle timeMetal
Owner:DAIMLER AG
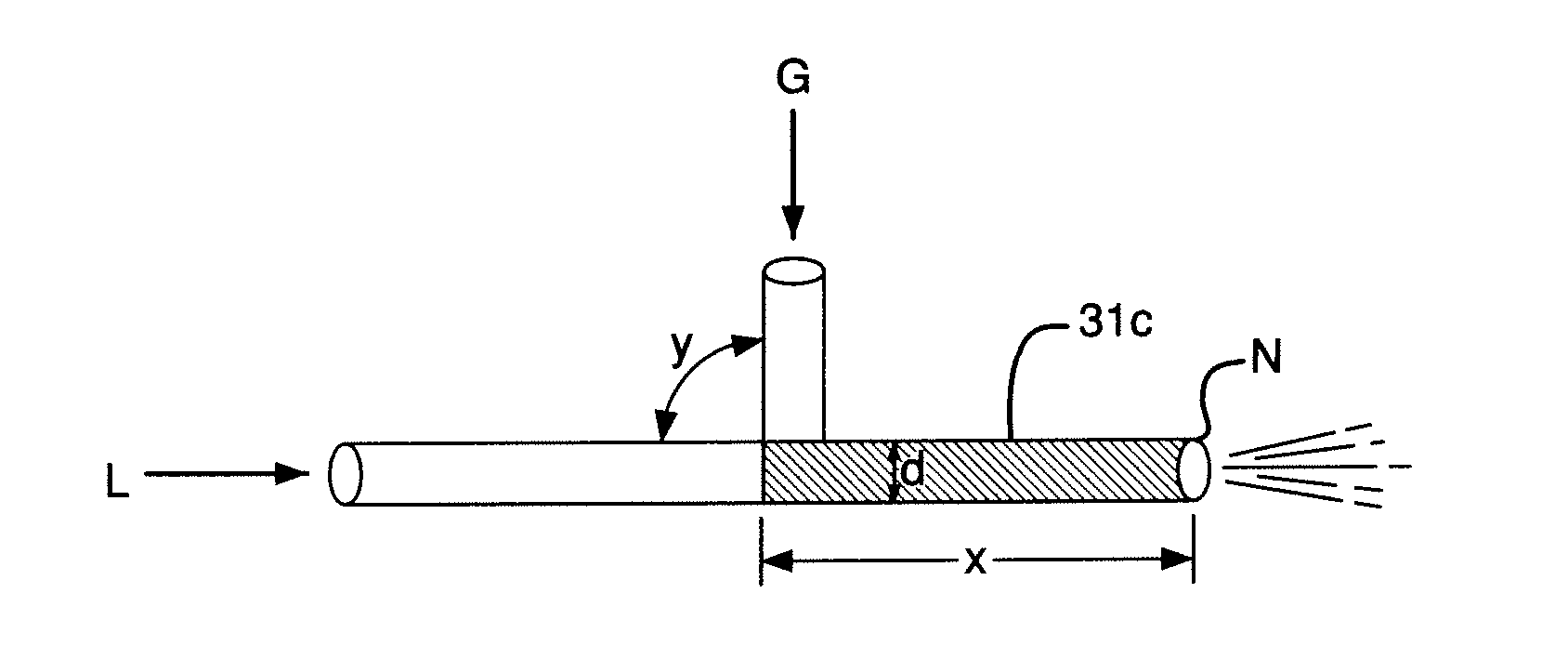
Conical-face spray nozzle without blockage or air resistance and method for forming conical-face aerial fog
ActiveCN101884962ANo air lockWell mixedSpray nozzlesLiquid spraying apparatusSpray nozzleEngineering
The invention relates to a conical-face spray nozzle without blockage or air resistance and a method for forming conical-face aerial fog. The conical-face spray nozzle comprises a fluid mixing ejector, wherein the ejector is provided with a first conical-face fluid slit, a second conical-face fluid slit and a conical-face mixing ejection slit; the first fluid slit and the second fluid slit are partitioned with a certain angle and converged into the mixing ejection slit at the tail end; first fluid and second fluid which are converged into the mixing ejection slit by the first fluid slit and the second fluid slit are fully mixed and atomized by the mechanical synergism of a floating ring machine rotating at high speed and ejected in a conical face along the mixing ejection slit; and accordingly, the conical-face spray nozzle of the invention prevents an ejecting shape and angle of an ejecting medium from the influence of air pressure and flow and can eject according to the design shapeand angle.
Owner:MCC CAPITAL ENGINEERING & RESEARCH
Steel ball quenching machine
ActiveCN101177726AThere will be no crowdingUniform quenching performanceFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesMetallic materialsHardness
The invention relates to a quenching machine of a steel ball, which pertains to the technical field of quenching facilities of metal materials. The quenching machine of the steel ball comprises: a steel ball lifting mechanism which is used for conveying the rolling-formed steel balls; a ball-feeding mechanism which is used for accepting the steel balls conveyed by the steel ball lifting mechanism and is connected with the steel ball lifting mechanism; at least one set of steel ball spiral separating quenching mechanisms which are used for conducting a quenching treat to the steel balls fed by the ball-feeding mechanism and is connected with the ball-feeding mechanism; conveying mechanisms of quenching mediums which have the same quantity with the steel ball spiral separating quenching mechanisms and are used for providing the quenching mediums to the steel ball spiral separating quenching mechanisms and connected with the steel ball spiral separating quenching mechanisms. The invention has the advantages that: the steel balls can obtain inside and outside uniform quenching effects and the hardness (HRC) thereof can reach 60-70; the steel ball lifting mechanism, the ball-feeding mechanism, the steel ball spiral separating quenching mechanisms and the conveying mechanisms of the quenching mediums can be coordinated with each other, thus improving the quenching efficiency in unit time by more than 5 times than the prior art.
Owner:CHANGSHU FEIFAN METALWORK
Warm press forming method and automobile frame component
ActiveCN104159681ASuppresses shape changeHigh dimensional accuracyHot-dipping/immersion processesRailway componentsSheet steelShape change
By the present invention, during forming of a steel sheet having a tensile strength of 400 MPa or greater into a press-formed part comprising a flange part and other portions by press forming, by heating the steel sheet to a temperature range of 400-700°C and then press forming the heated steel sheet using draw forming, at which time this state is maintained for 1 to 5 seconds at the bottom dead center of forming, shape changes such as springback can be suppressed, the dimensional precision of a panel can be enhanced, and the desired mechanical characteristics can easily be obtained in the press-formed part.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Cryogenic Nozzle
ActiveUS20080048047A1Easy to controlMolten spray coatingContainer filling methodsProduct gasProcess engineering
A nozzle and process are set forth for contacting a cryogenic liquid and a gas, and discharging the resulting fluid through the nozzle. In one embodiment, the ratio of the discharged fluid's liquid component to its gaseous component is controlled as a function of the gas pressure.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
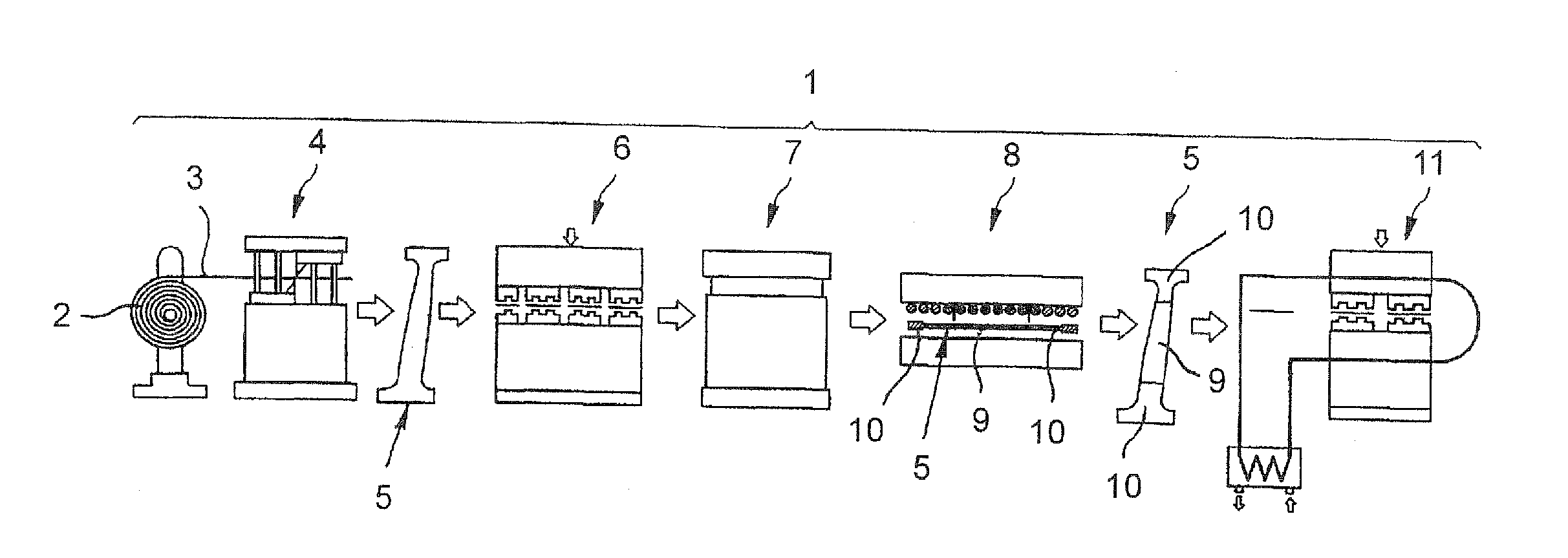
Apparatus for heat treatment of structural body parts in the automobile industry
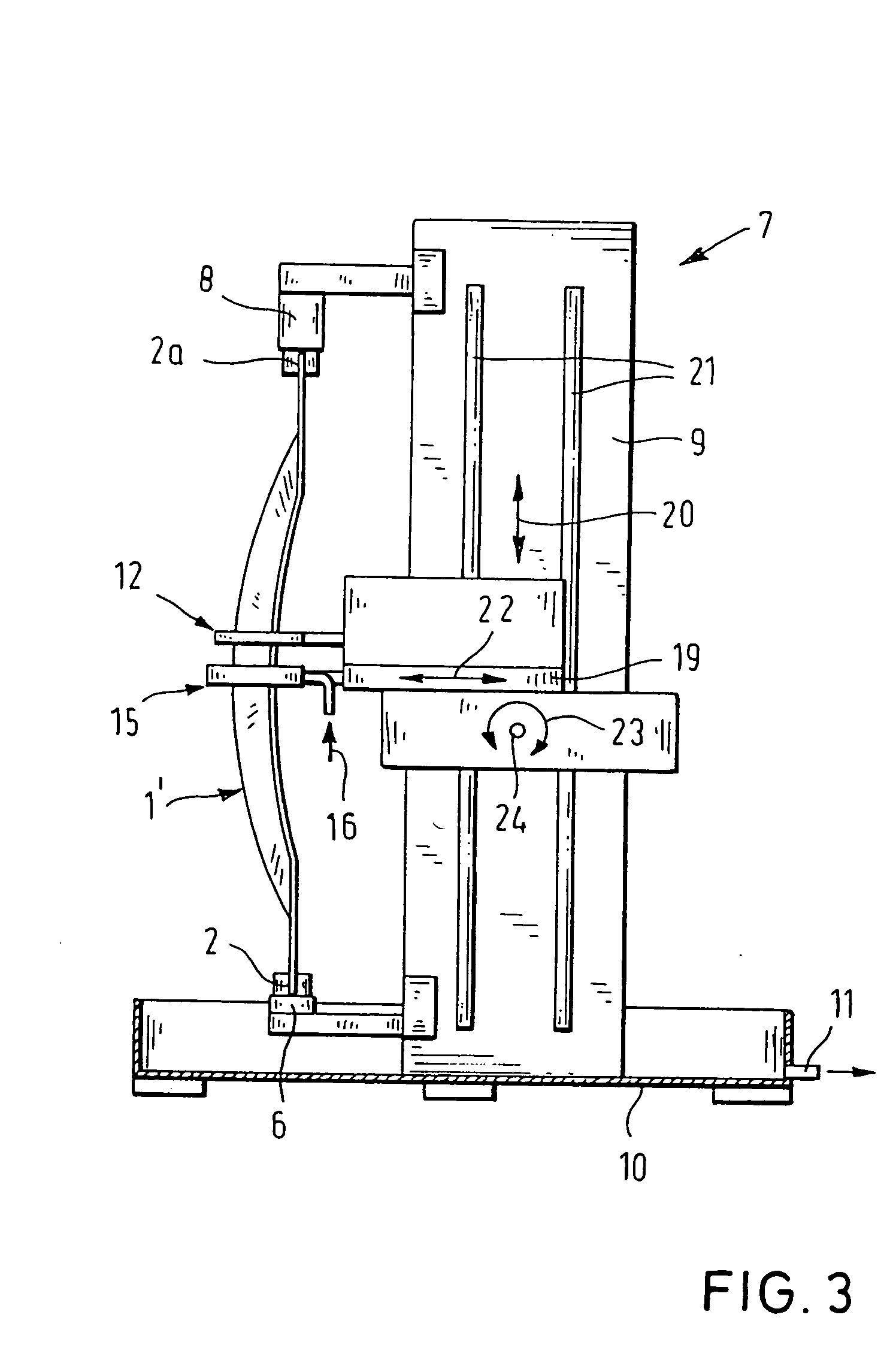
InactiveUS20050006828A1Reduce maintenanceReduce wearFurnace typesIncreasing energy efficiencySheet steelHorizontal axis
Apparatus for heat-treating an elongate structural body part made from a blank compressed while being soft or from steel strip of hardenable 22 Mn B5 mod. steel sheet with a thickness of 1 mm to 3 mm, includes an apparatus for positioning the structural body part in substantially upright disposition. Placed in surrounding relationship to the structural body part is an induction element which can move from bottom to top, thereby being able to follow a contour of the structural body part and allowing to at least partially heat the structural body part to an austenitizing temperature suitable for hardening. Disposed adjacent to the induction element is a cooling unit which follows the induction element in movement direction. The induction element and the cooling unit are moveable relative to one another and connected to a tool carriage which is mounted to a column for movement in a vertical direction, in a transverse direction to the column and about a horizontal axis.
Owner:BENTELER AKTIENGES
Microstructural optimization of automotive structures
A process for hot stamping a steel component is described. The hot stamping process enables the formation of one or more regions of the component to exhibit specific physical properties different than other regions of the component. The various processes are particularly well suited for forming a variety of automobile structural members.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Process for producing components having regions of differing ductility
The invention relates to a process for producing sheet steel components having regions of differing ductility, in which either a sheet metal plate composed of a hardenable steel alloy is used to produce a component by deep-drawing and the deep-drawn component is then at least partially austenitized by a heat treatment and subsequently quench hardened in a die or the plate is at least partially austenitized by a heat treatment and shaped in the hot state, and is quench hardened during or after this, with the sheet metal plate having a zinc-based cathodic corrosion protection coating, characterized in that in regions of a desired higher ductility of the component, at least one additional sheet is attached to the plate, situated so that during the heat treatment, the plate is heated to a lesser degree there than in the remaining region.
Owner:VOESTALPINE METAL FORMING
Steel Sheet for Formed Member Having Enhanced Ductility, Formed Member, and Method for Manufacturing the Formed Member
InactiveUS20130295402A1High strengthImprove ductilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelImpurity
Provided is a steel sheet for a formed member having enhanced ductility, a formed member, and a method for manufacturing the formed member, and more particularly, to a steel sheet for making a formed member having high strength and ductility such as an automotive structural member and a reinforcing member, a formed member, and a method for manufacturing the formed member. The steel sheet for a formed member has enhanced ductility, and includes, by weight %, C: 0.1% to 1.0%, Si+Al: 0.4% to 3.0%, Mn: 0.1% to 5.0%, P: 0.0001% to 0.1%, S: 0.0001% to 0.03%, N: 0.03% or less (but not 0%), and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The formed member having high strength and ductility that can be used for forming an automotive structural member, a reinforcing member, etc. In addition, the formed member can be used for a heat-treatable impact resistant member.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Steel ball quenching machine
ActiveCN100497666CThere will be no crowdingUniform quenching performanceFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesMetallic materialsHardness
The invention relates to a quenching machine of a steel ball, which pertains to the technical field of quenching facilities of metal materials. The quenching machine of the steel ball comprises: a steel ball lifting mechanism which is used for conveying the rolling-formed steel balls; a ball-feeding mechanism which is used for accepting the steel balls conveyed by the steel ball lifting mechanism and is connected with the steel ball lifting mechanism; at least one set of steel ball spiral separating quenching mechanisms which are used for conducting a quenching treat to the steel balls fed by the ball-feeding mechanism and is connected with the ball-feeding mechanism; conveying mechanisms of quenching mediums which have the same quantity with the steel ball spiral separating quenching mechanisms and are used for providing the quenching mediums to the steel ball spiral separating quenching mechanisms and connected with the steel ball spiral separating quenching mechanisms. The invention has the advantages that: the steel balls can obtain inside and outside uniform quenching effects and the hardness (HRC) thereof can reach 60-70; the steel ball lifting mechanism, the ball-feeding mechanism, the steel ball spiral separating quenching mechanisms and the conveying mechanisms of the quenching mediums can be coordinated with each other, thus improving the quenching efficiency in unit time by more than 5 times than the prior art.
Owner:CHANGSHU FEIFAN METALWORK
Warm press forming method and automobile frame component
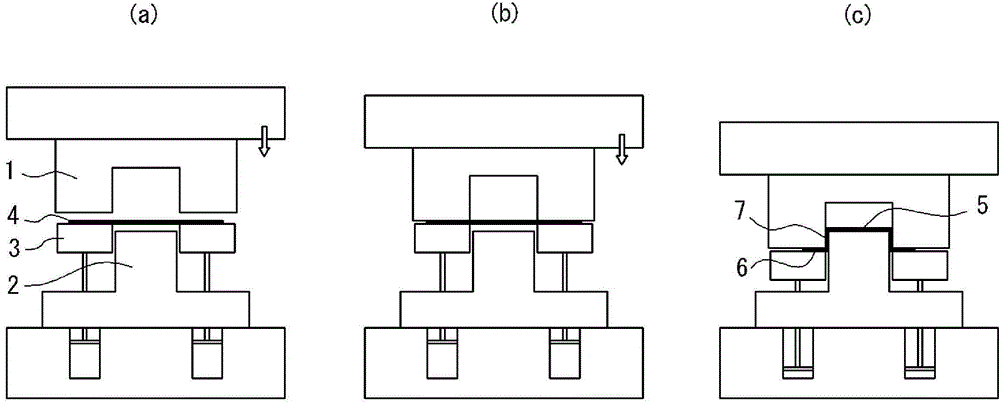
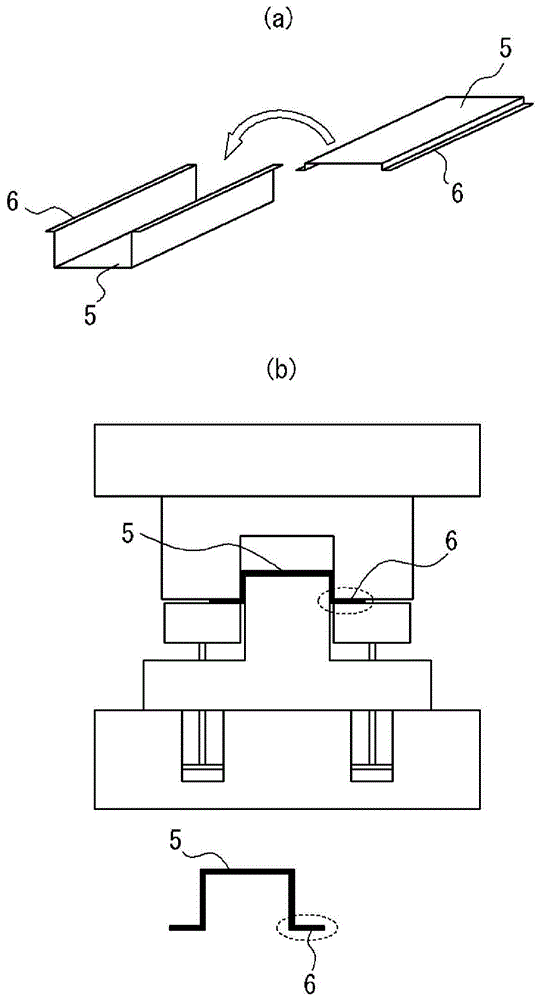
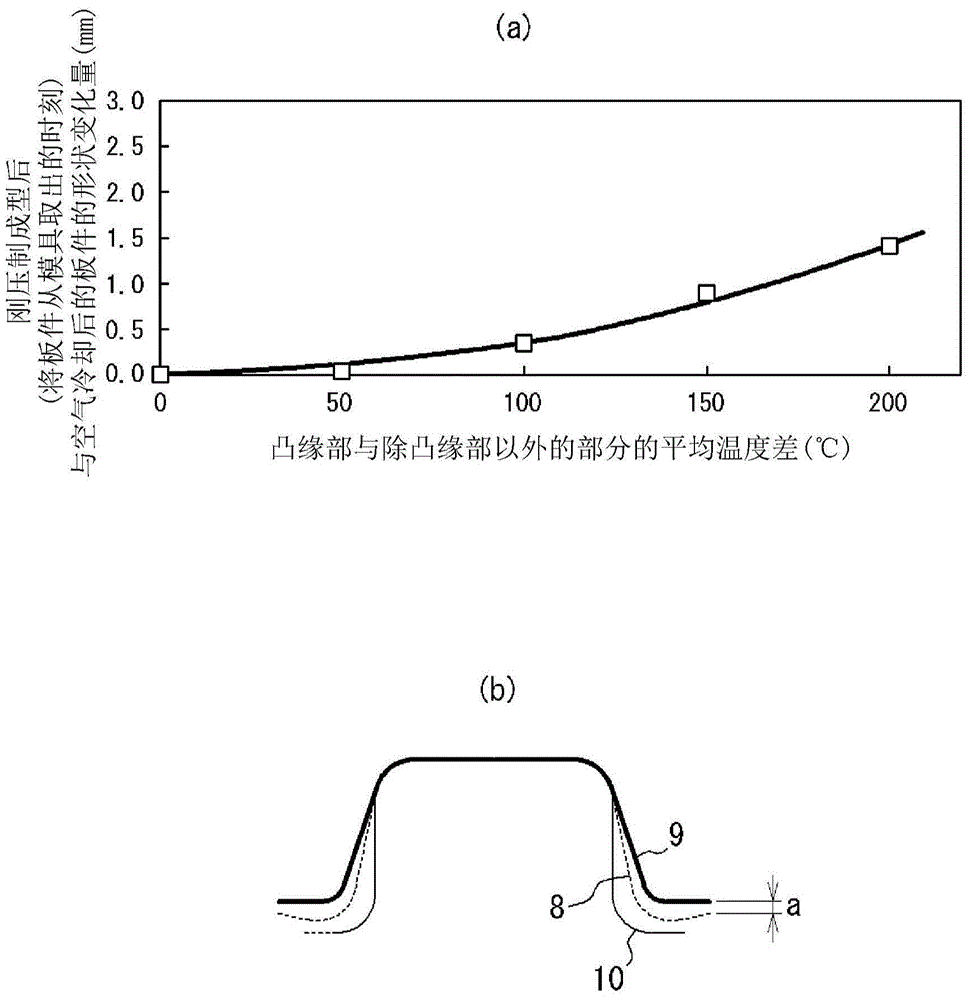
ActiveCN104159680ASuppresses shape changeHigh dimensional accuracyFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesShape changeTemperature difference
By the present invention, during forming of a steel sheet having a tensile strength of 400 MPa or greater into a press-formed part comprising a flange part and other portions by press forming, by heating the steel sheet to a temperature range of 400-700°C and then press forming the heated steel sheet using crash forming, at which time the average temperature difference between the flange part and the other portions of the press-formed part immediately after forming is kept to within 100°C, shape changes such as springback can be suppressed, the dimensional precision of a panel can be enhanced, and the desired mechanical characteristics can easily be obtained in the press-formed part.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com