Recombinant intracellular pathogen vaccines and methods for use
A pathogenic and pathogenic technology, applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, chlamydia antigen components, drug combinations, etc., can solve the problems of no indication of prevention of mammalian intracellular pathogenic diseases, no disclosure, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
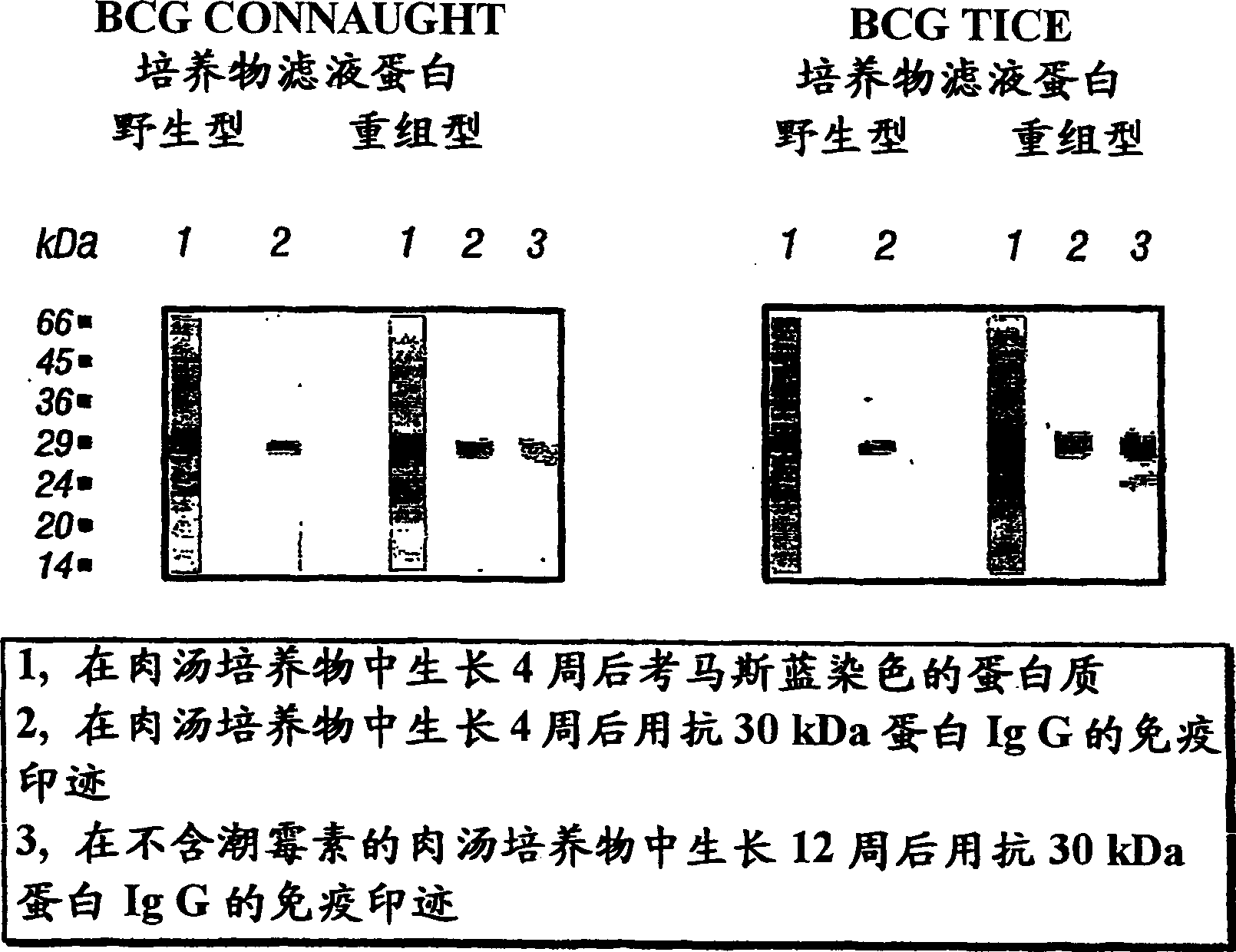
[0060] To determine the effect of pathogen strain variation on vaccination, various embodiments of the invention were prepared using two different BCG strains: BCG Tice and BCG Connaught. Wild-type M. bovis BCG Tice was purchased from Organon, and wild-type M. bovis BCG Connaught was obtained from Connaught Laboratories, Toronto, Canada. The strains were grown in 7H9 medium pH 6.7 (Difco) at 37°C with 5% CO 2 A -95% air atmosphere was maintained as a non-shaking culture. Cultures were sonicated for 5 min in a sonication water bath once or twice a week to reduce bacterial colony clumps.
[0061] Recombinant BCG TICE (rBCG30 Tice) expressing the 30 kDa major extracellular non-fusion protein of M. tuberculosis was prepared as follows. The recombinant construct plasmid pMTB30 of a kind of Escherichia coli / mycobacterium shuttle plasmid pSMT3 prepares as the method that the inventor introduces previously in following document: Harth, G., B.-Y.Lee and M.A.Horwitz.1997, in fast Hig...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Example 2 demonstrates that using mycobacteria closely related to BCG but unable to replicate in mammalian hosts, in vivo expression of the immunogens of the invention does not induce significant levels of protection against challenge with M. tuberculosis. Examples 3 and 4 demonstrate that slow release of the immunogen of the invention by synthetic vaccine microcarriers also fails to induce significant levels of protection against challenge with M. tuberculosis.
[0113] Thus, the following examples serve to emphasize that the intracellular pathogen vaccines of the present invention represent a completely unexpected and significant advance in the field of infectious disease immunology.
Embodiment 1
[0116] Immunization with BCG plus recombinant Mycobacterium tuberculosis 30kDa major extracellular protein (r30) Guinea pigs fail to induce high levels of protection against challenge with Mycobacterium tuberculosis
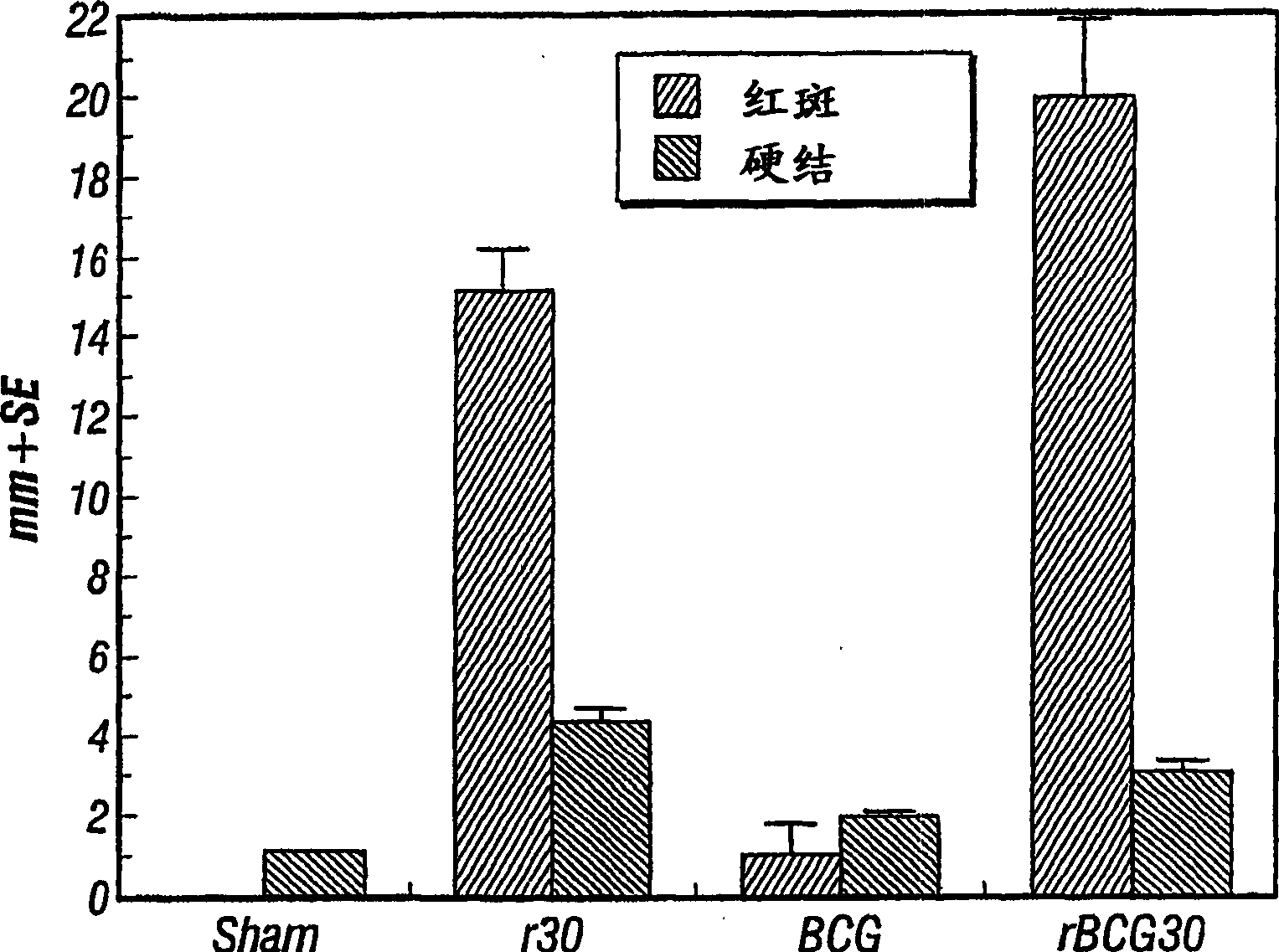
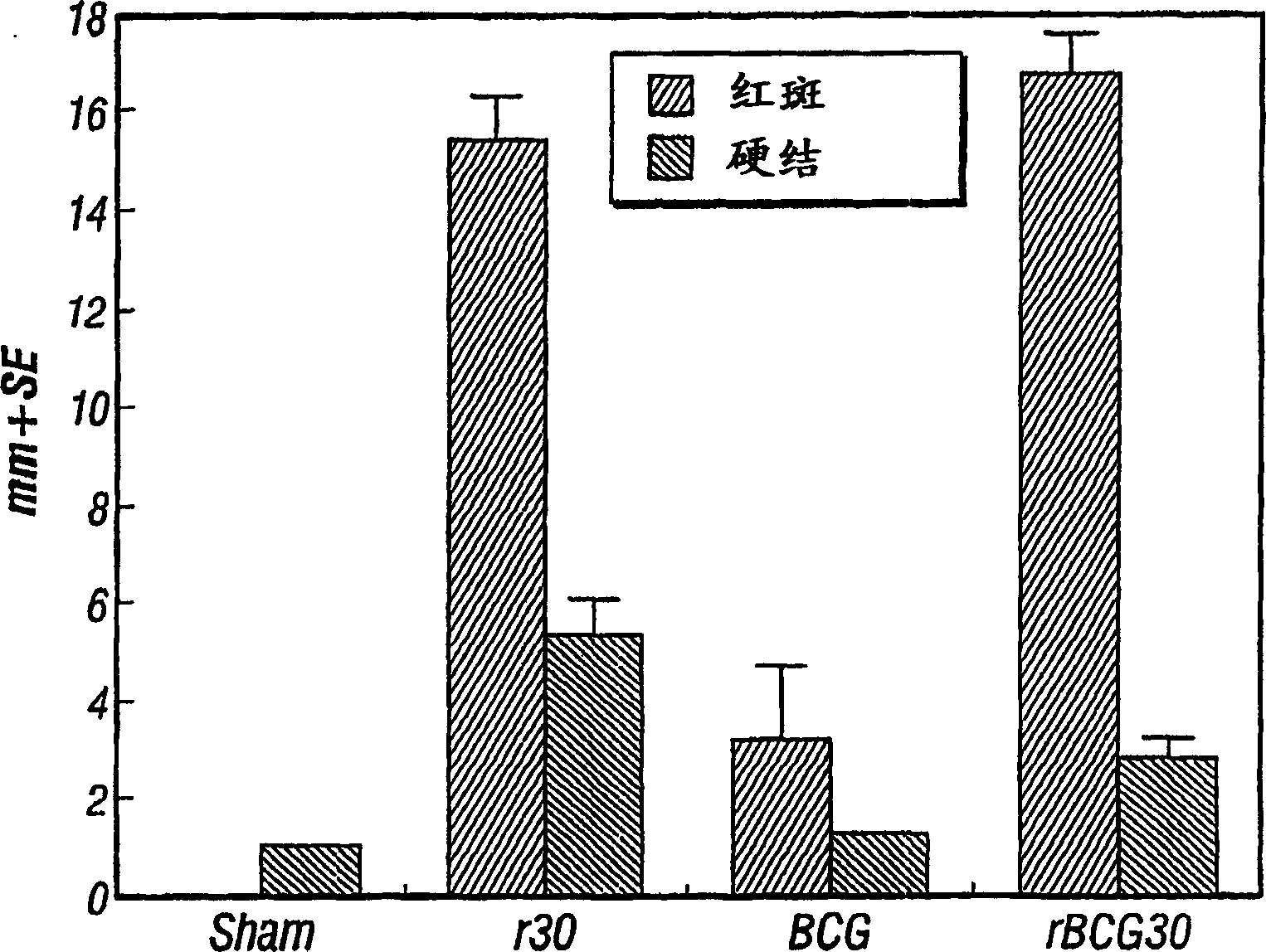
[0117] We have previously immunized guinea pigs with a highly potent adjuvant (SAF, Syntex adjuvant formulation) of BCG plus r30. The r30 protein (100 μg per immunization) was intradermally administered three times. This induces a strong cutaneous delayed-type hypersensitivity (C-DTH) response to r30 ( Figure 5 ). In fact, the C-DTH response was comparable to that induced by recombinant BCG expressing r30. Nevertheless, immunization with both BCG and r30 did not induce high levels of protection against challenge with M. tuberculosis (Table 5). CFU levels in the lungs and spleens of animals immunized with both BCG and r30 were not lower than those of animals immunized with BCG alone. This result is in direct contrast to the above results in which animals ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com