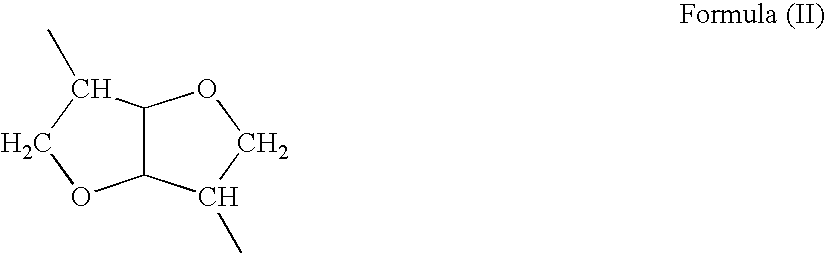Patents
Literature
32 results about "Synthetic vaccine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A synthetic vaccine is a vaccine consisting mainly of synthetic peptides, carbohydrates, or antigens. They are usually considered to be safer than vaccines from bacterial cultures. Creating vaccines synthetically has the ability to increase the speed of production. This is especially important in the event of a pandemic.
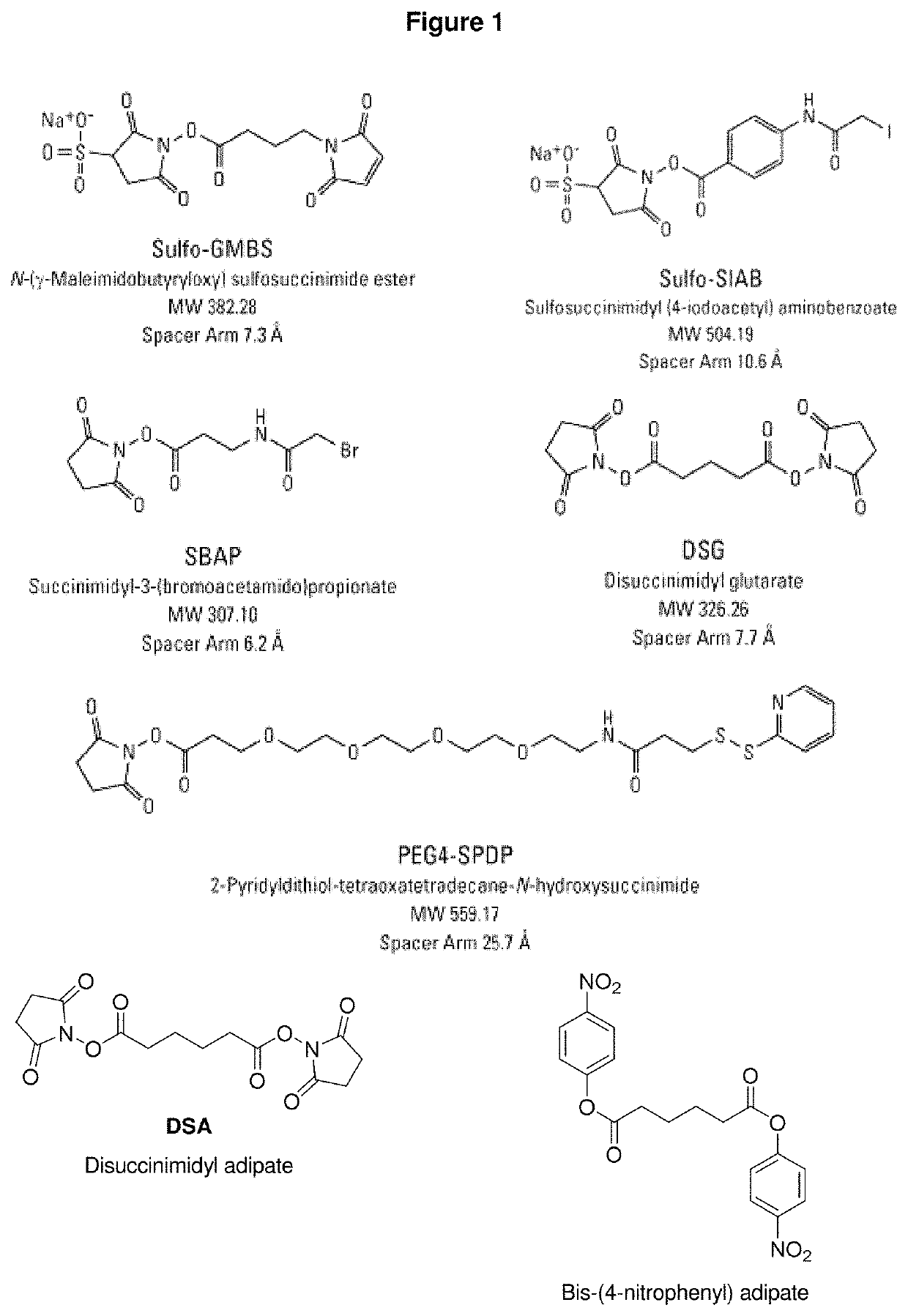
Vaccine delivery compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20080160089A1Easy to produceImprove efficiencySsRNA viruses negative-sensePowder deliveryPolyesterMHC class I
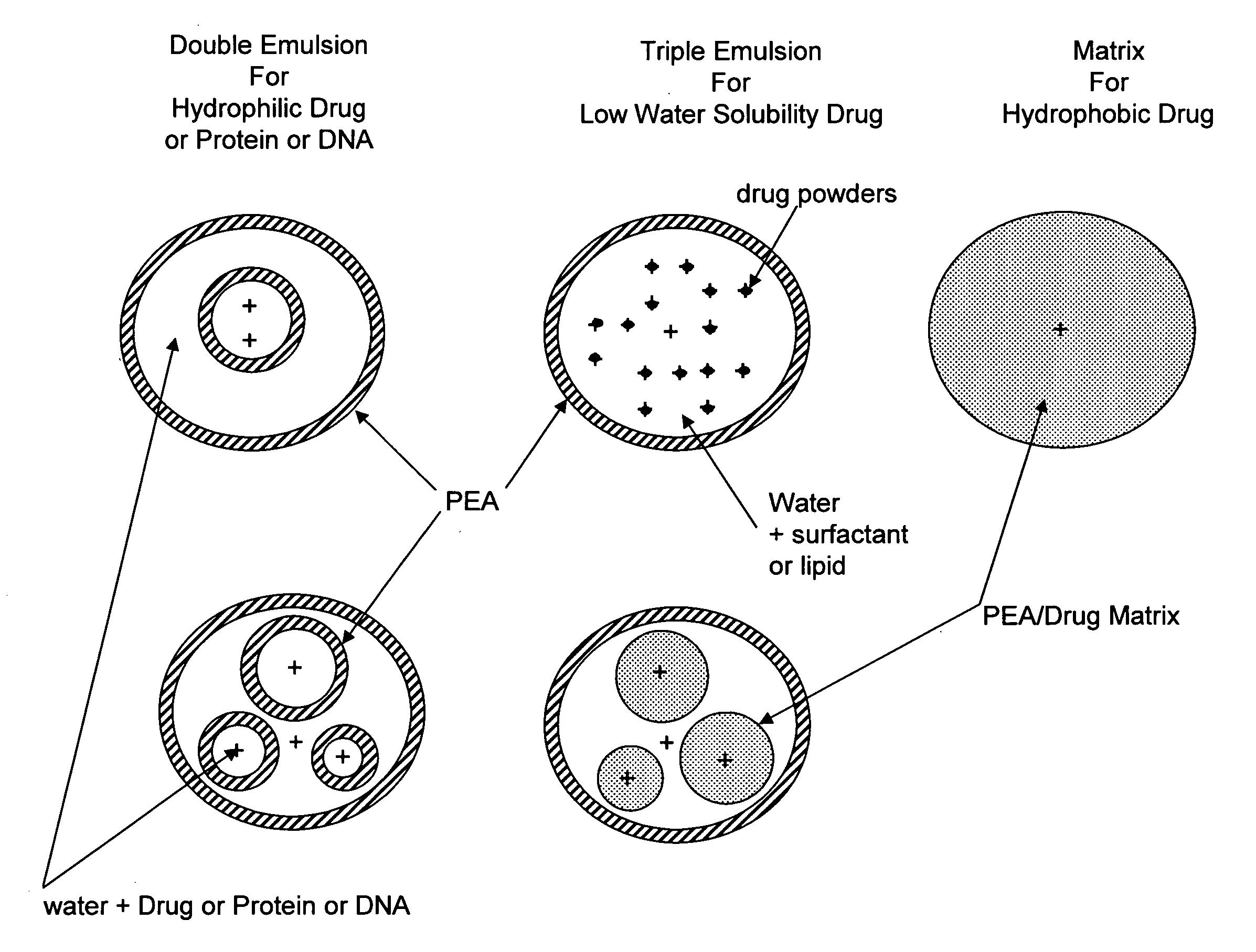
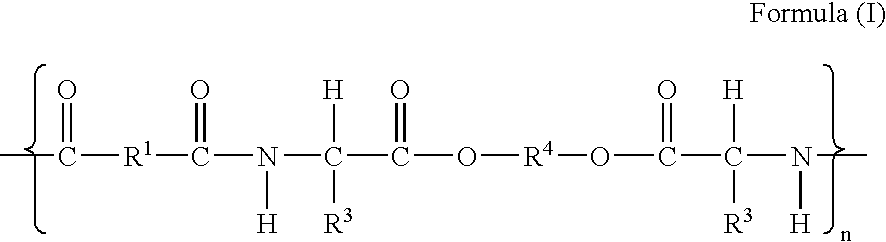
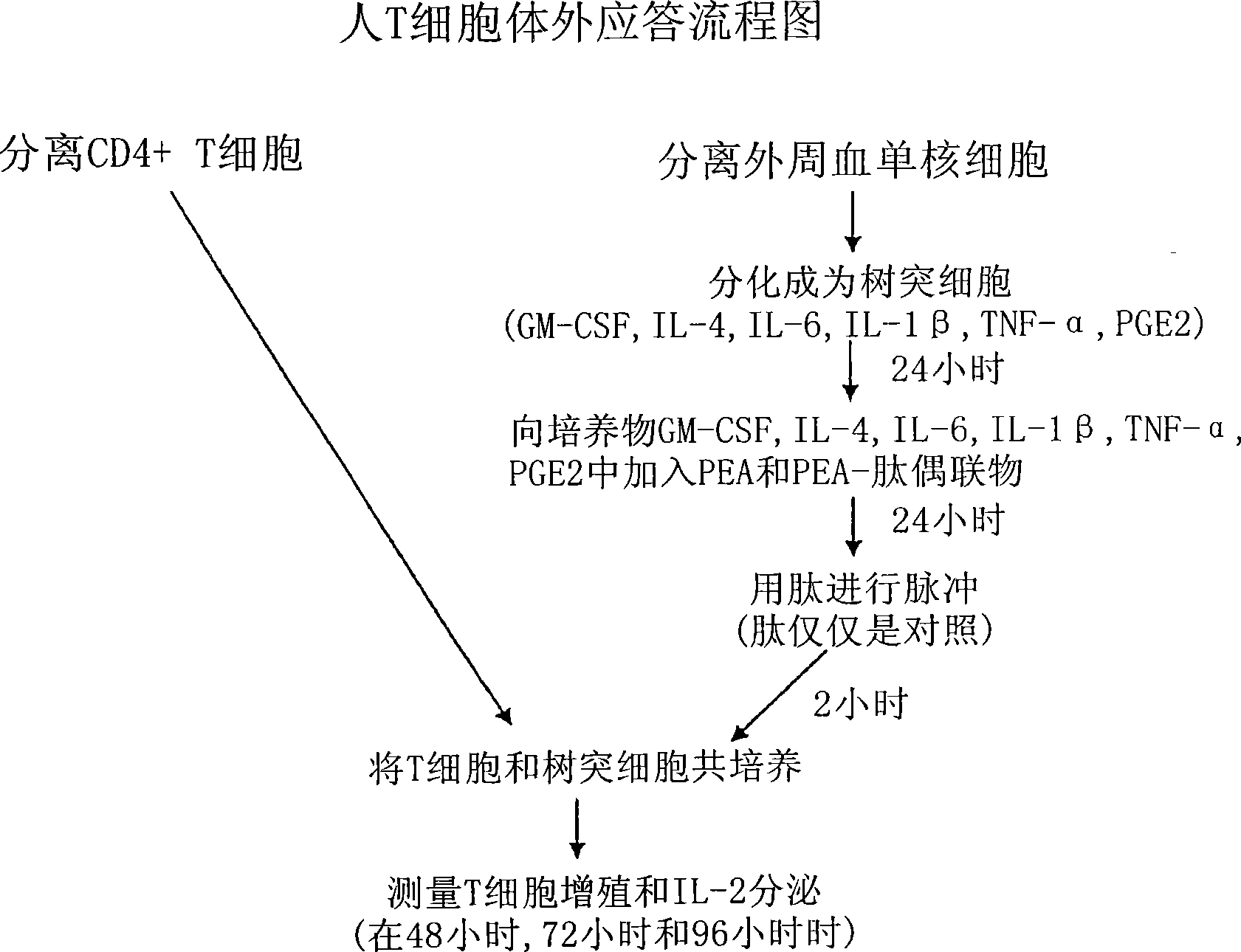
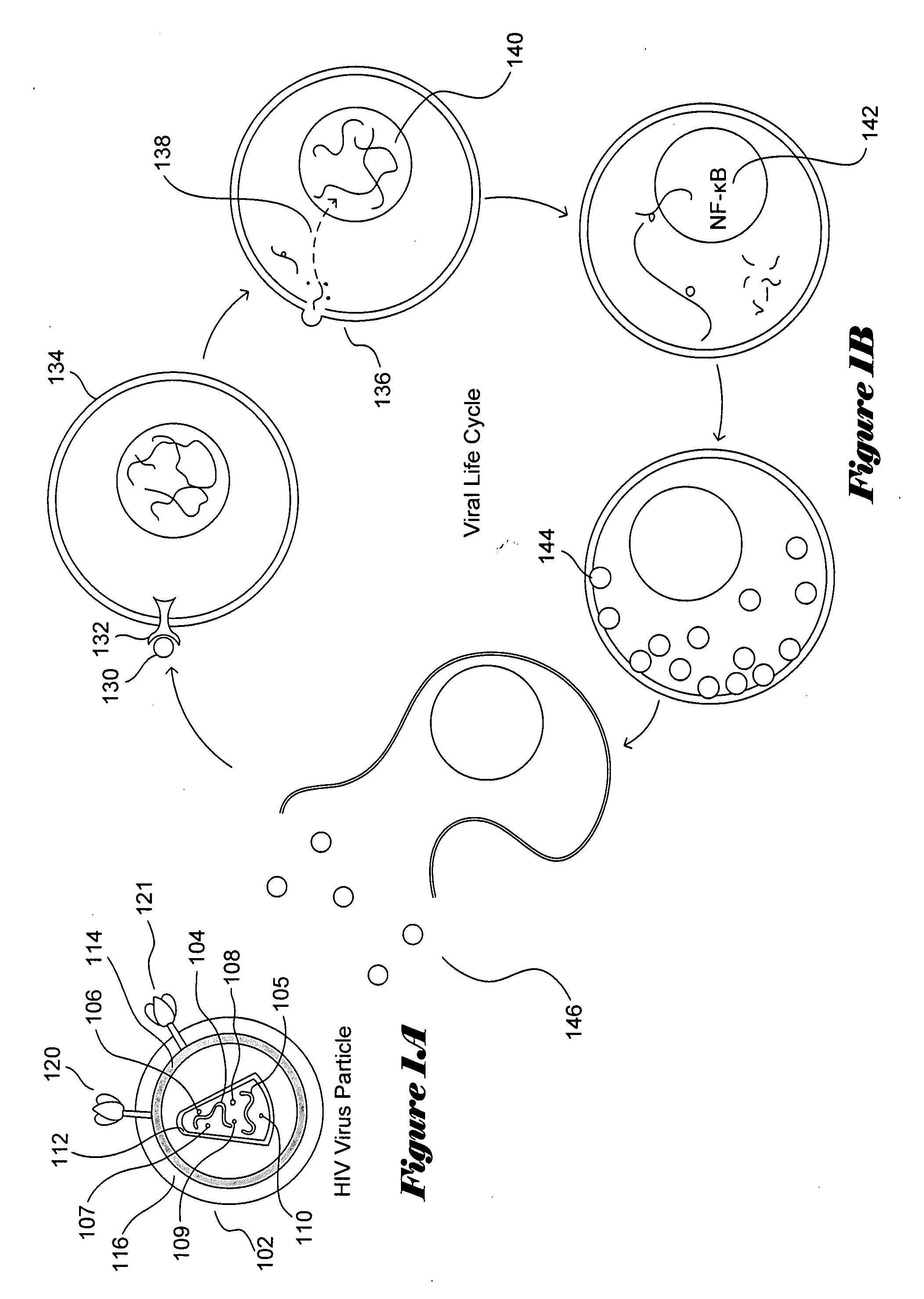
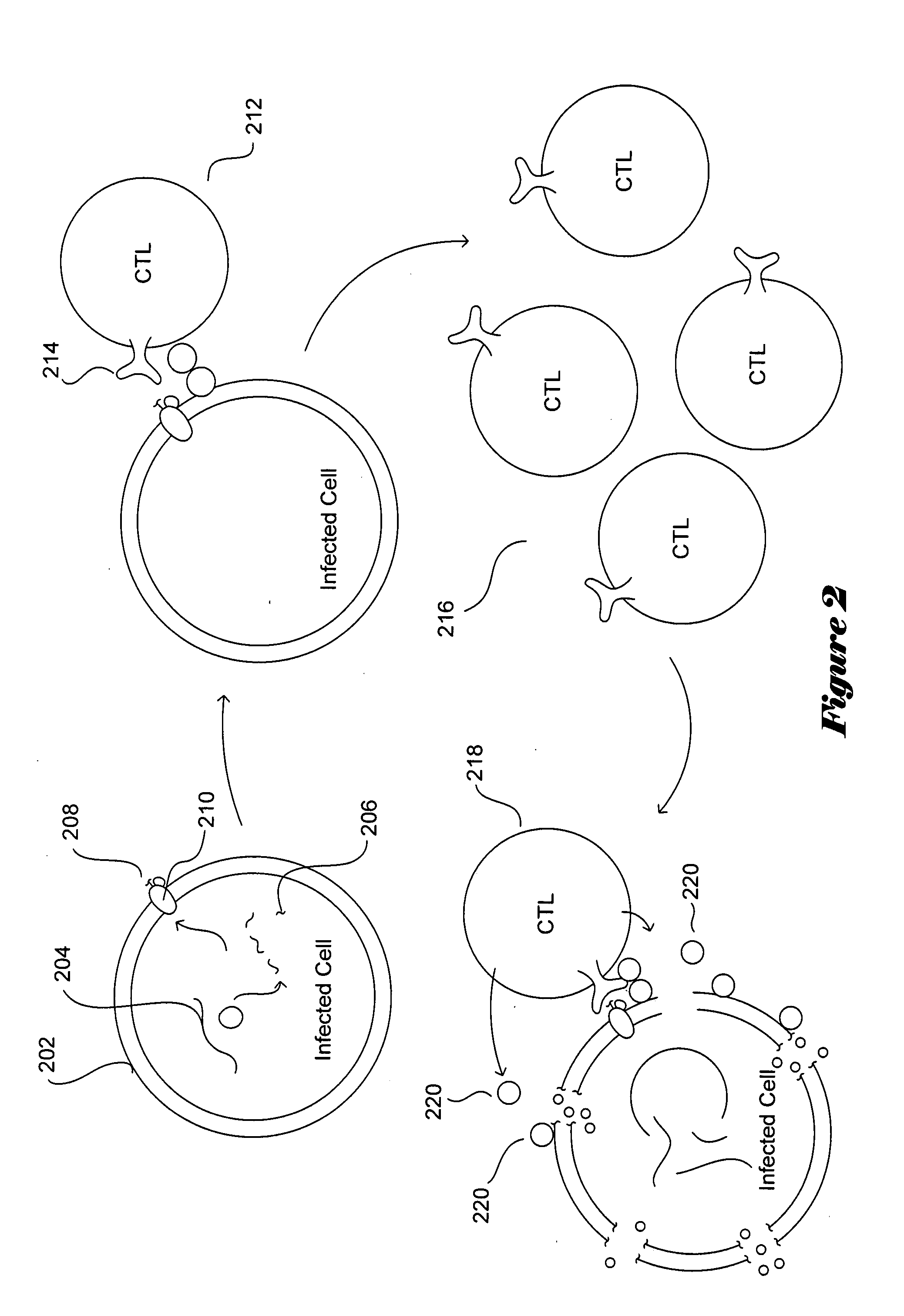
The present invention provides synthetic vaccines against a variety of pathogenic organisms and tumor cells in humans and other mammals based on biodegradable polymers containing polyester amide (PEA), polyester urethane (PEUR), and polyester urea (PEU) and immunostimulatory adjuvants. The vaccines can be formulated as a liquid dispersion of polymer particles or molecules in which are dispersed an immunostimulatory adjuvant, such as a TLR agonist, and whole protein or peptidic antigens containing MHC class I or class II epitopes derived from organism or tumor cell proteins. Methods of inducing an immune response via intracellular mechanisms to the pathogenic organism or tumor cells specific for the antigen in the invention compositions are also included.
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
Synthetic vaccine agents
InactiveUS7097837B2Promote absorptionImprove responsePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCtl epitopeHelper epitope
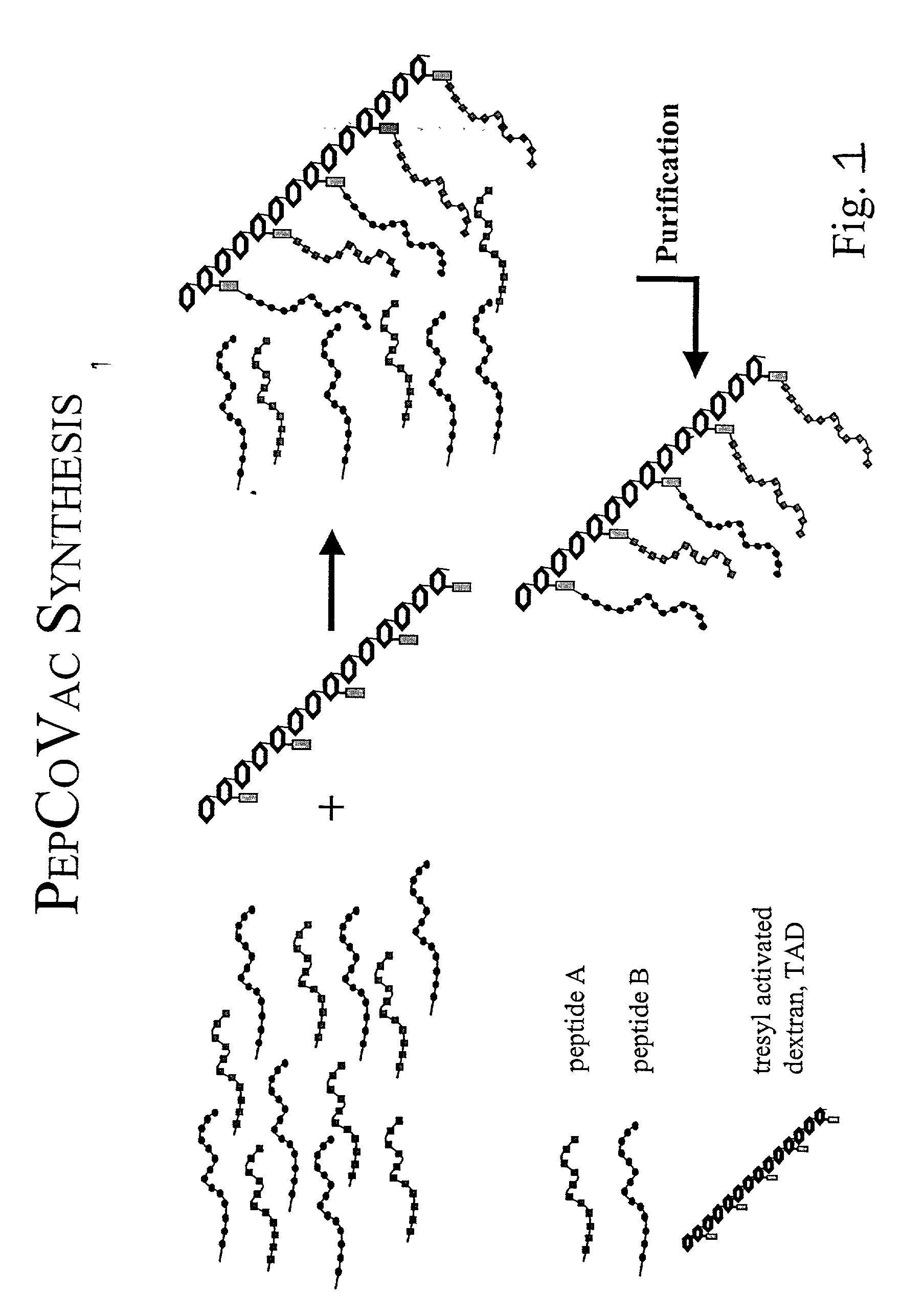
The present invention provides for novel immungens that are comprised of an activated polyhydroxypolymer backbone to which is attached 2 separate antigenic determinants. The 1st antigenic determinant includes a B-cell or CTL epitope and the 2nd antigenic determinant includes a T-helper epitope. In preferred embodiments, the antigenic determinants are derived from different molecules and species. Exemplary immunogens of the invention are constituted of a linear tresyl-activated dextran backbone to which is coupled B-cell or CTL epitopes of an antigen and to which is also coupled universal T-helper epitopes. Also disclosed are immunogenic compositions comprising the immunogens, methods of immunization and a method for identification of suitable immunogens of the invention.
Owner:BEALE STREET 143 INVEST APS
Synthetic vaccine agents
InactiveUS20040191264A1Promote absorptionImprove responseBacterial antigen ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsCtl epitopeHelper epitope
The present invention provides for novel immungens that are comprised of an activated polyhydroxypolymer backbone to which is attached 2 separate antigenic determinants. The 1st antigenic determinant includes a B-cell or CTL epitope and the 2nd antigenic determinant includes a T-helper epitope. In preferred embodiments, the antigenic determinants are derived from different molecules and species. Exemplary immunogens of the invention are constituted of a linear tresyl-activated dextran backbone to which is coupled B-cell or CTL epitopes of an antigen and to which is also coupled universal T-helper epitopes. Also disclosed are immunogenic compositions comprising the immunogens, methods of immunisation and a method for identification of suitable immunogens of the invention.
Owner:PHARMEXA
Vaccine delivery compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20060188469A1Easy to produceSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsPolyesterOrganism
The present invention provides synthetic vaccine delivery compositions based on polyester amide (PEA), polyester urethane (PEUR), and polyester urea (PEU) polymers for stimulating an immune response to a variety of pathogenic organisms and tumor cells in humans and other mammals. The vaccine delivery compositions are formulated as a liquid dispersion of polymer particles or molecules including class I or class II antigen peptides derived from organism or tumor cell proteins, which are taken up by antigen presenting cells of the mammal to induce an immune response in the mammal. Methods of inducing an immune response to the pathogenic organism or tumor cells in the invention compositions are also included.
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
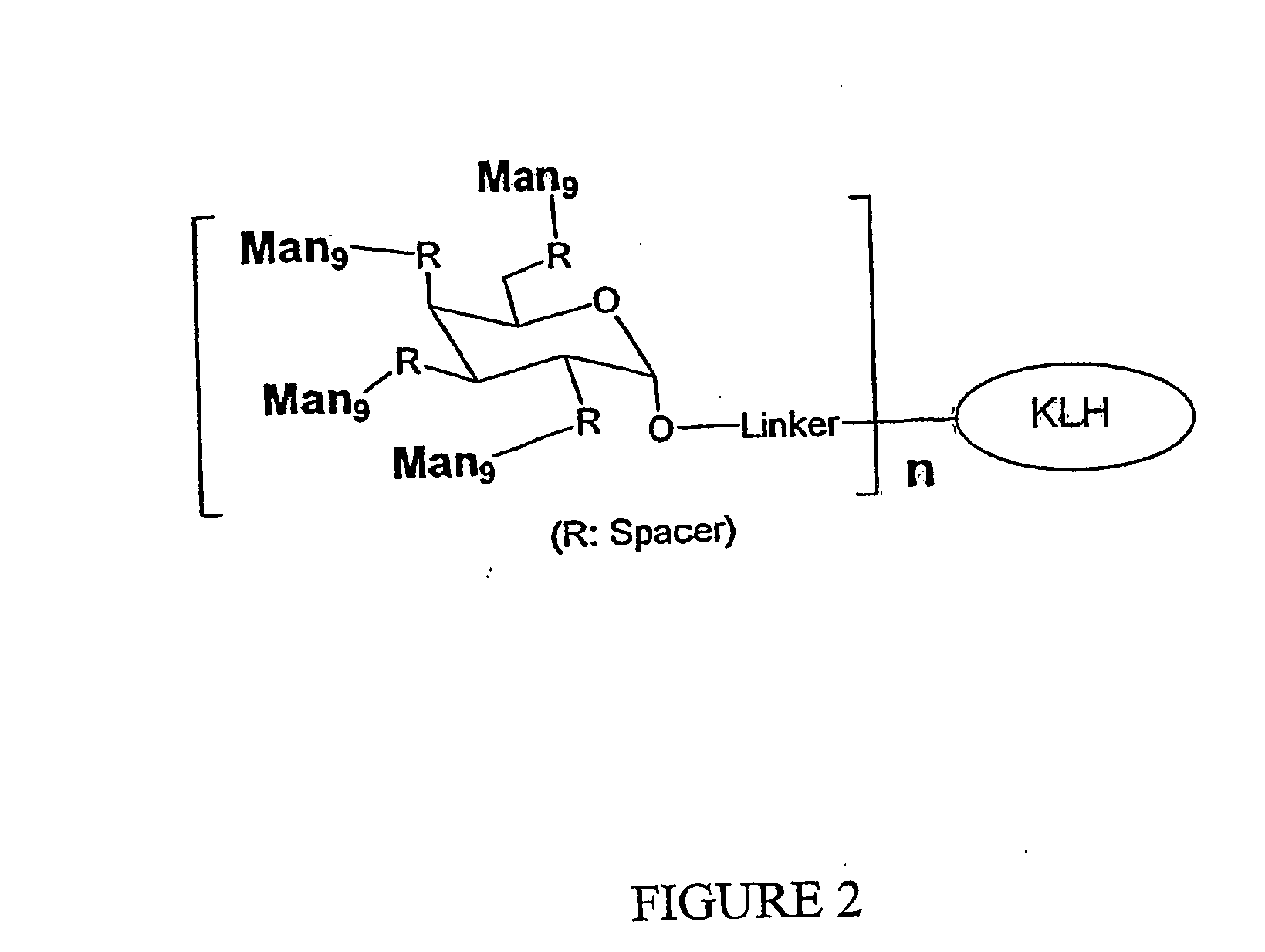
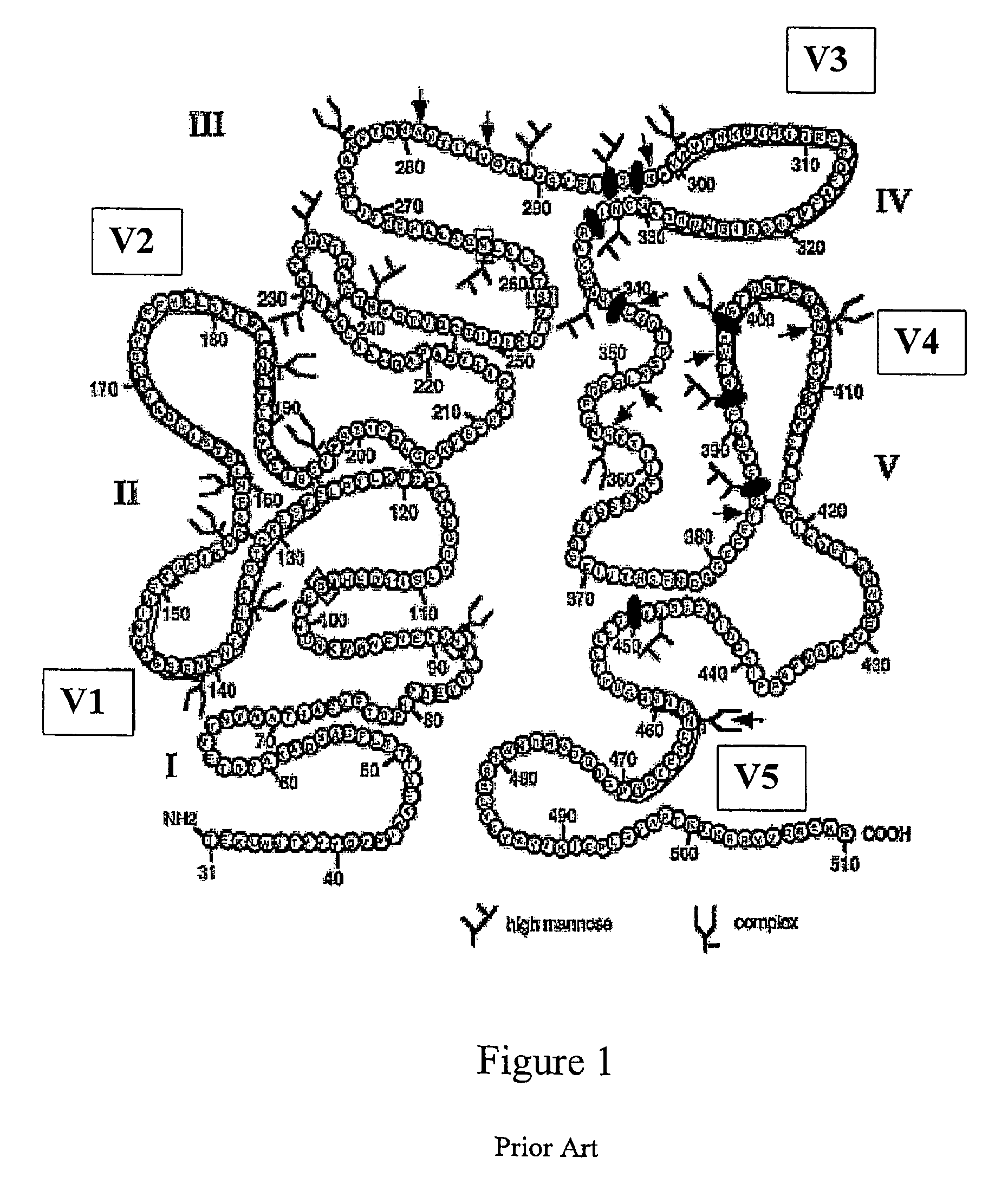
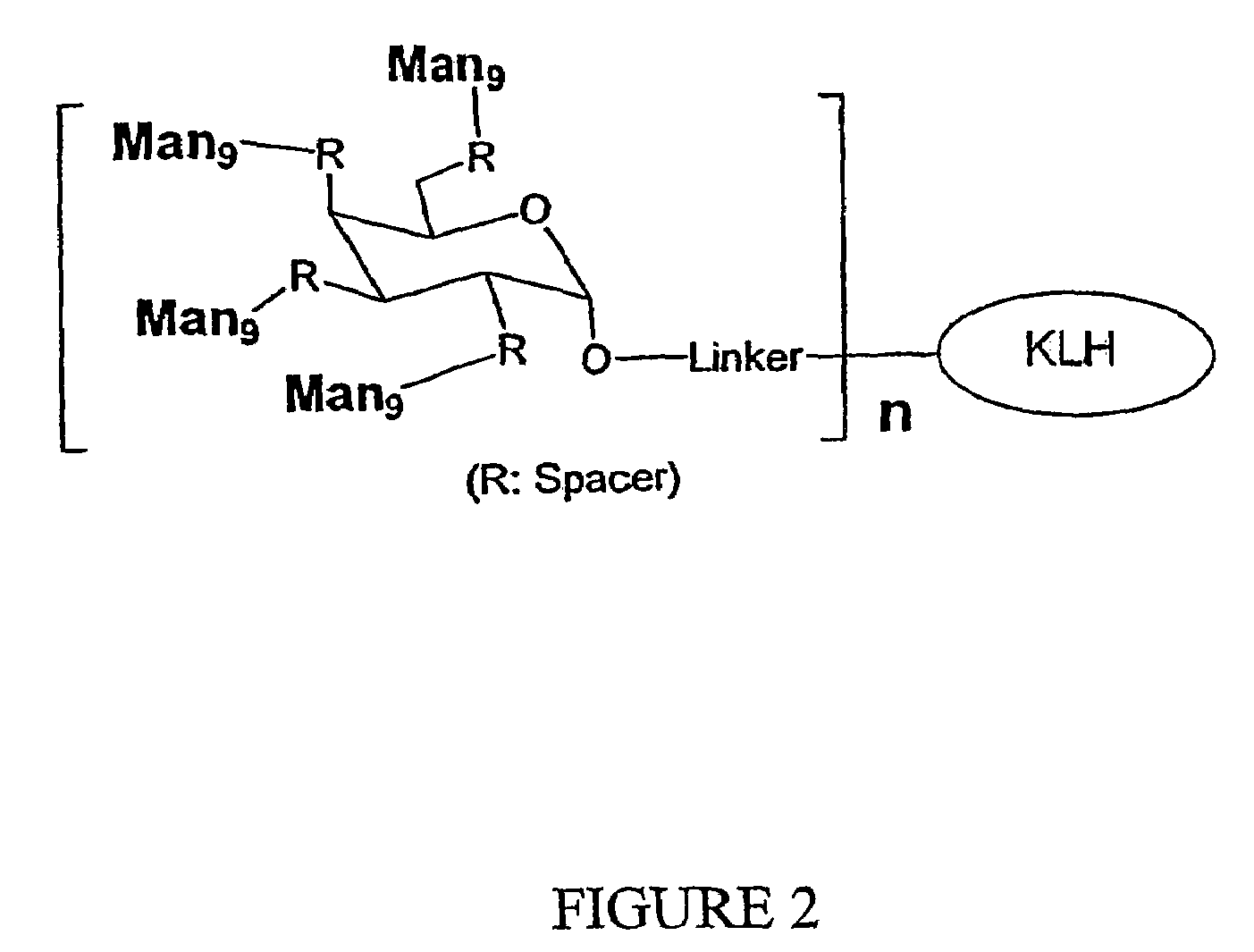
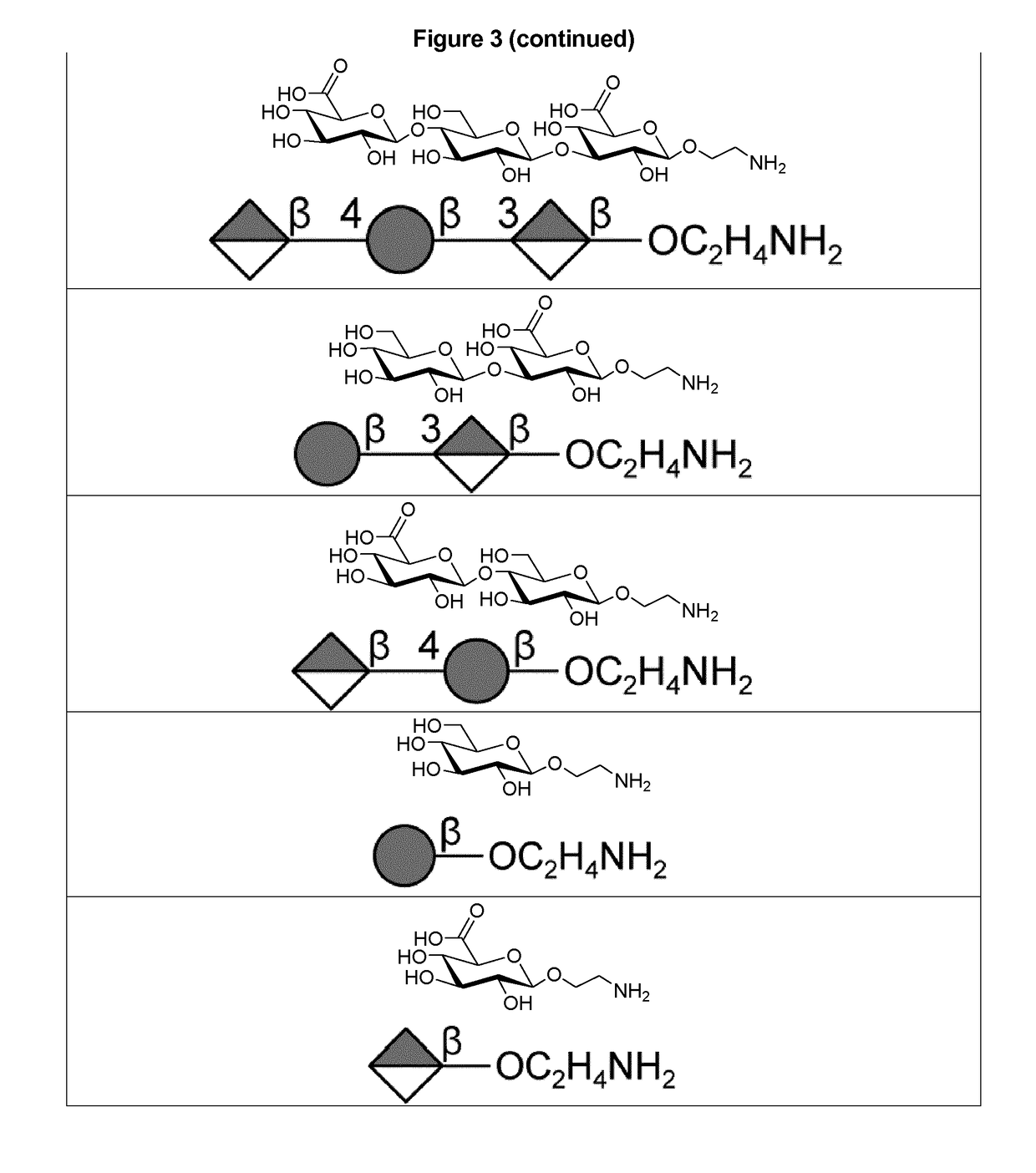
Carbohydrate-based synthetic vaccines for hiv
InactiveUS20050244424A1Increase productionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsHigh mannoseReactive site
The present invention relates to a constructed to oligosaccharide cluster, optionally bonded to an immunogenic protein, that can be administered to a subject to induce an immune response for increasing production of 2G12 and / or used in assays as reactive sites for determining compounds that inactivate and / or bind the high-mannose oligosaccharide cluster. Compositions comprising these clusters, methods of using these clusters and compositions are disclosed.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
Carbohydrate-based synthetic vaccines for HIV
The present invention relates to a constructed oligosaccharide cluster, optionally bonded to an immunogenic protein, that can be administered to a subject to induce an immune response for increasing production of 2G12 and / or used in assays as reactive sites for determining compounds that inactivate and / or bind the high-mannose oligosaccharide cluster. Compositions comprising these clusters, methods of using these clusters and compositions are disclosed.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
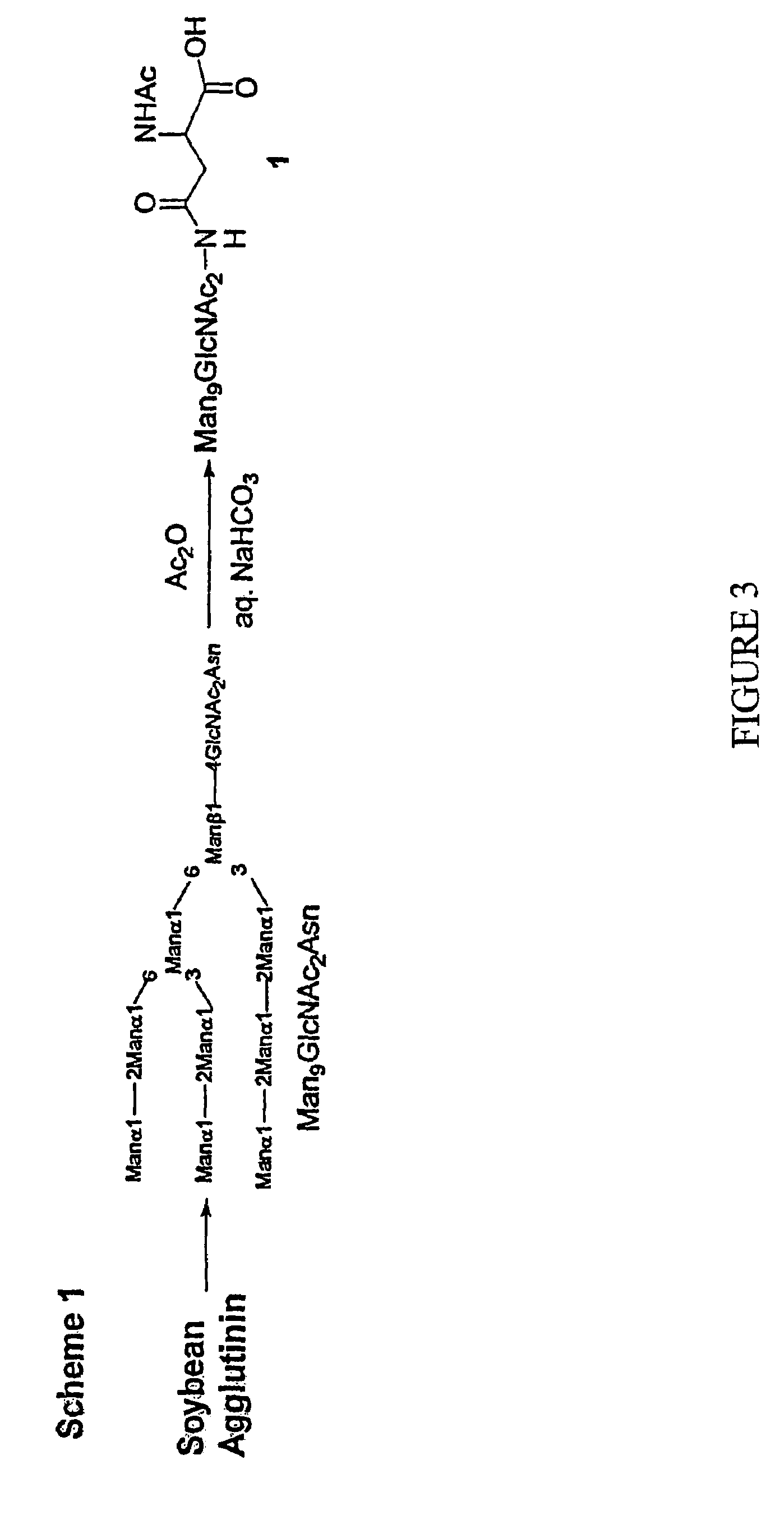
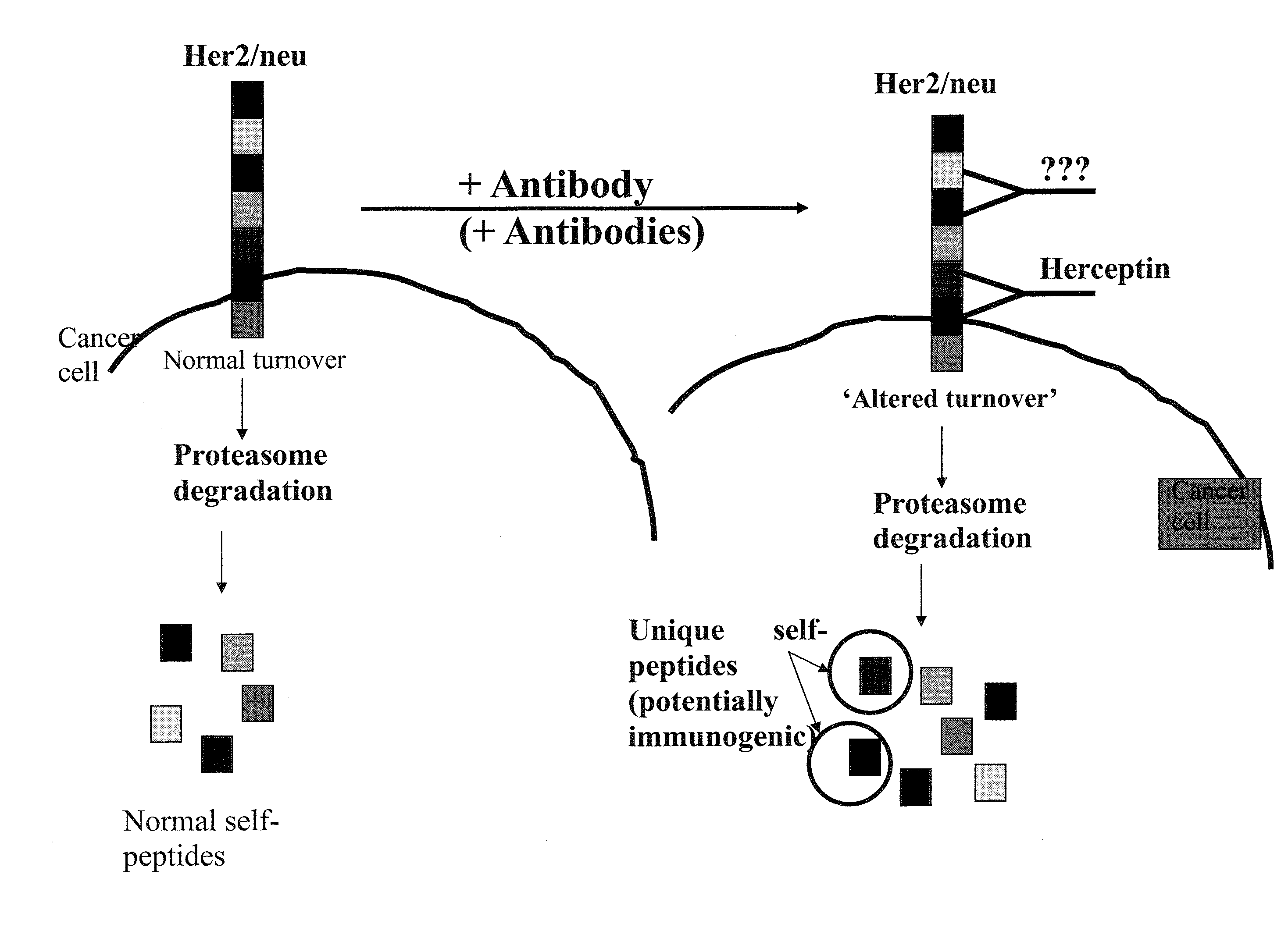
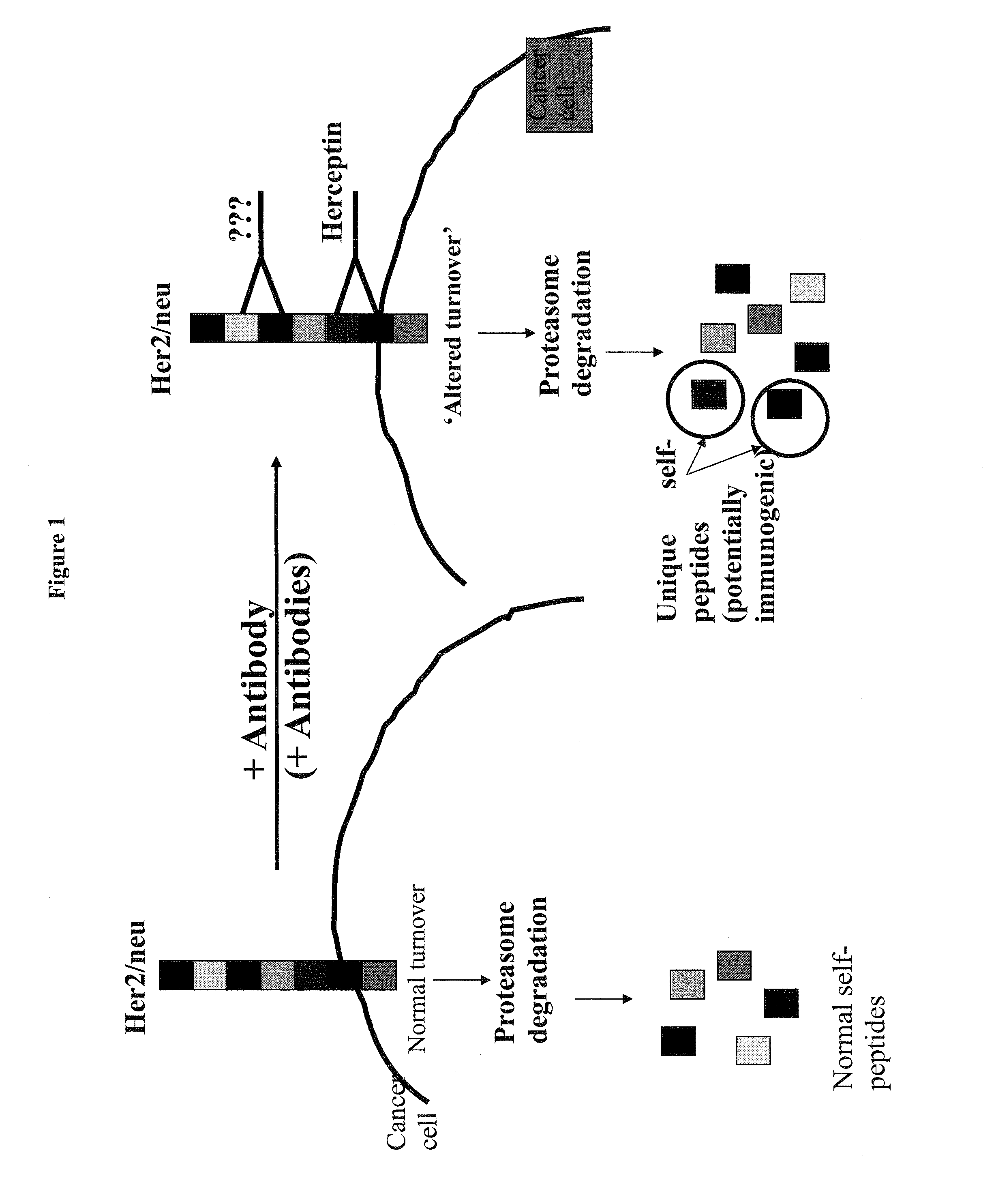
Targeted identification of immunogenic peptides
This invention relates generally to identifying peptide sequences involved in antibody binding to any protein for synthesis of vaccine treatments. This novel method allows for a more manageable vaccine peptide discovery and specific generation of unique immunogenic peptides from self-tumor associated proteins and / or foreign proteins from infectious organisms for specific and / or enhanced expression only in the presence of the antibody.
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC
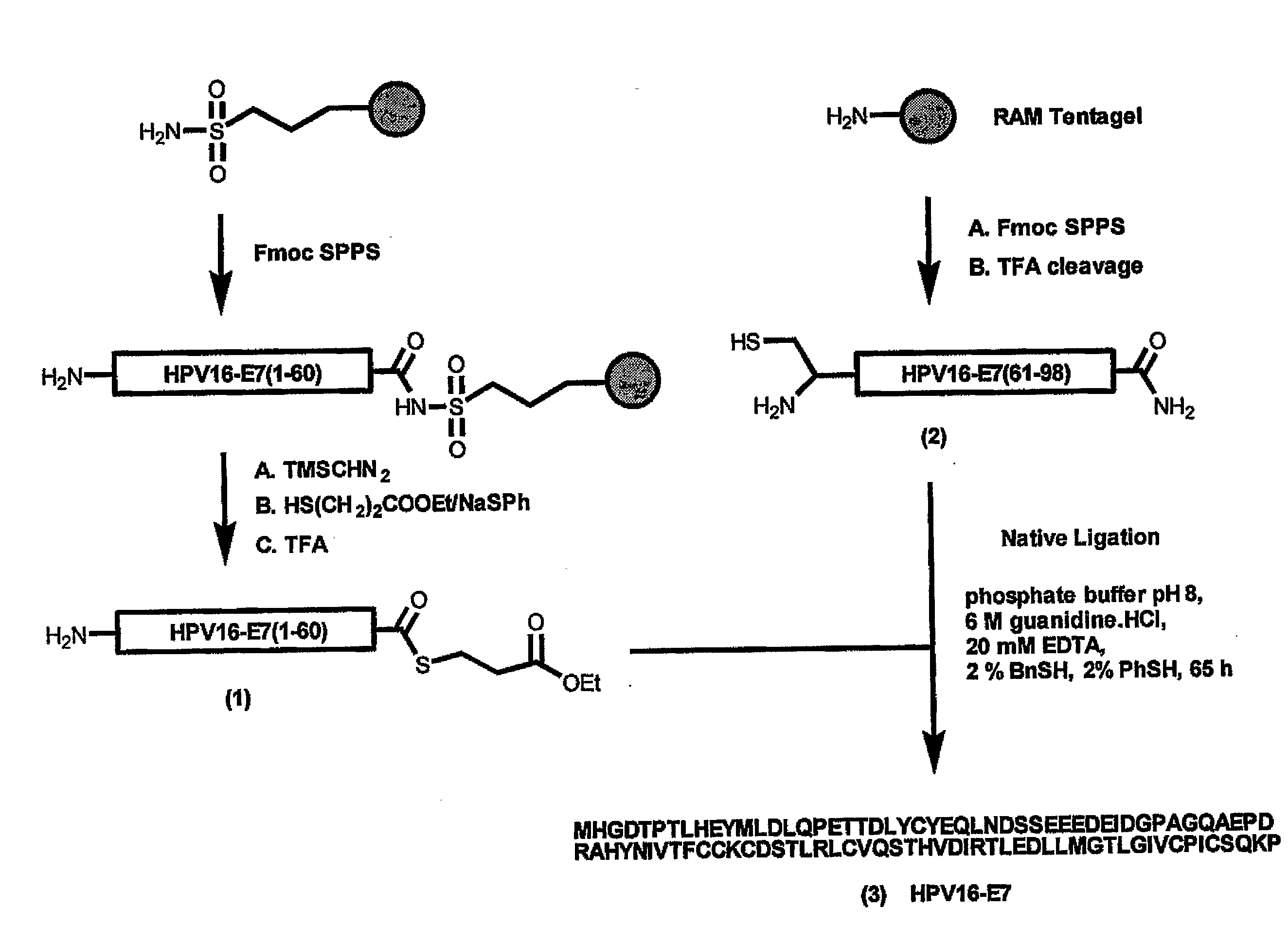
Synthetic Protein as Tumor-Specific Vaccine
InactiveUS20090028874A1Improve quality controlMaximizing numberPeptide/protein ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsChemical synthesisAntigen
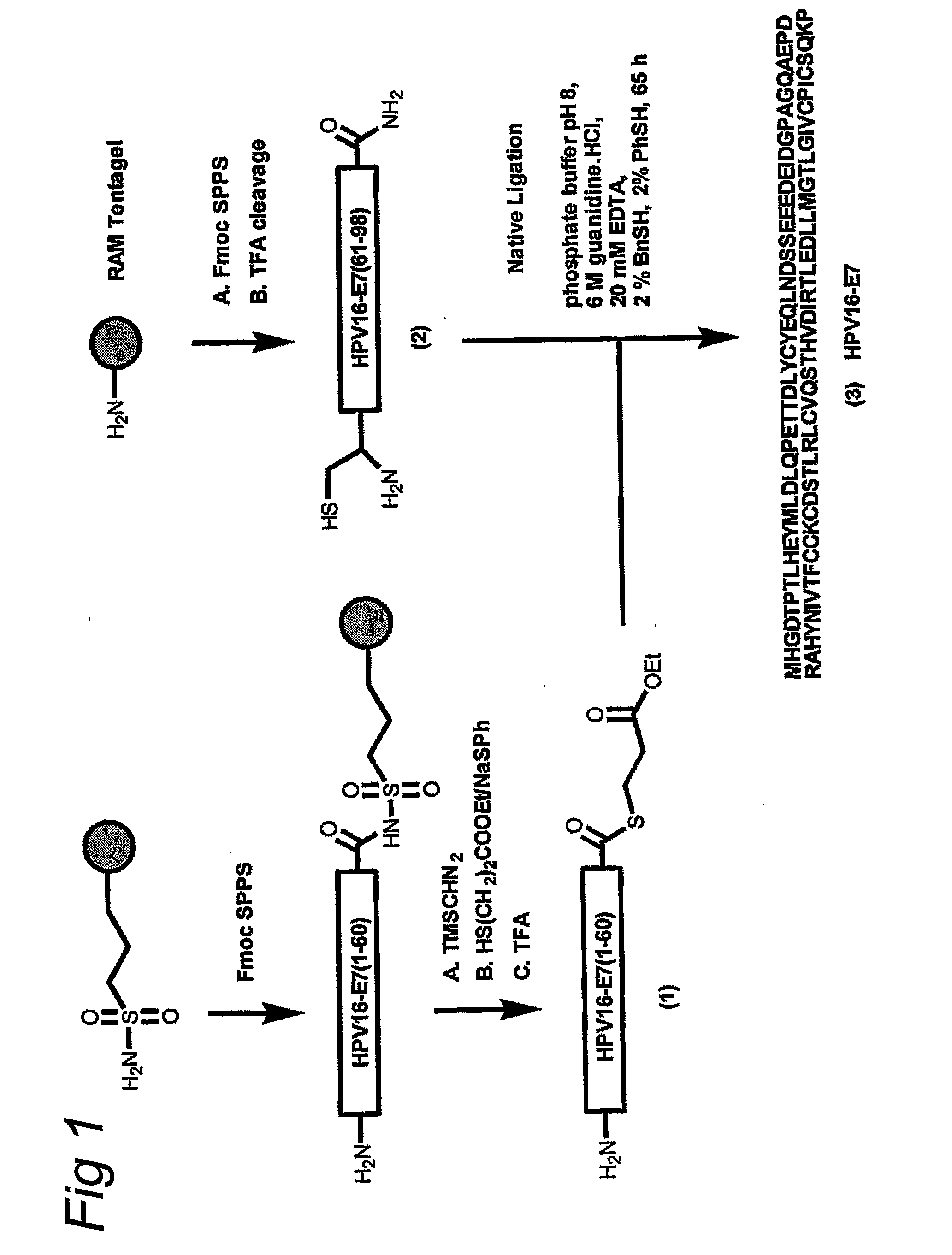
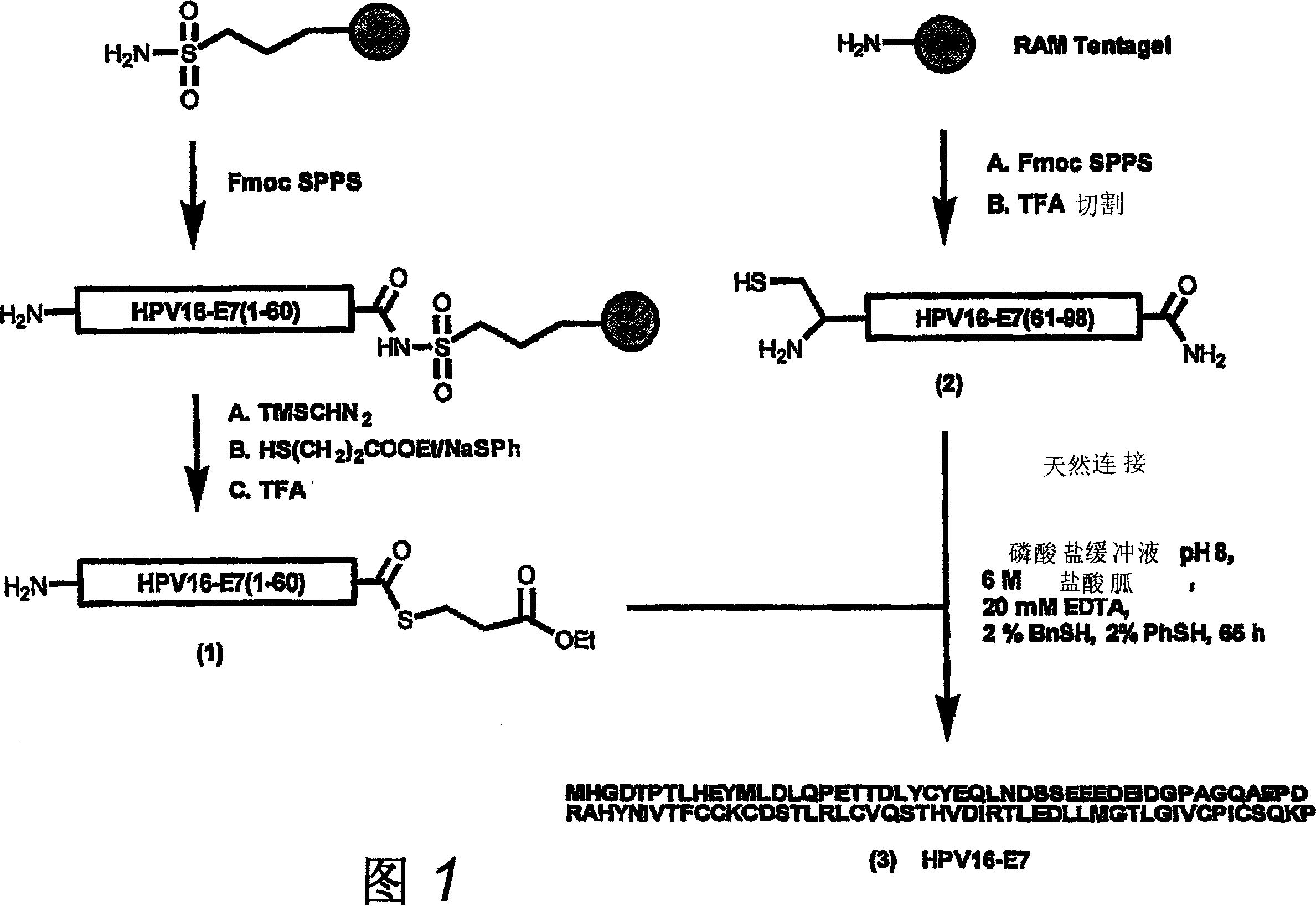
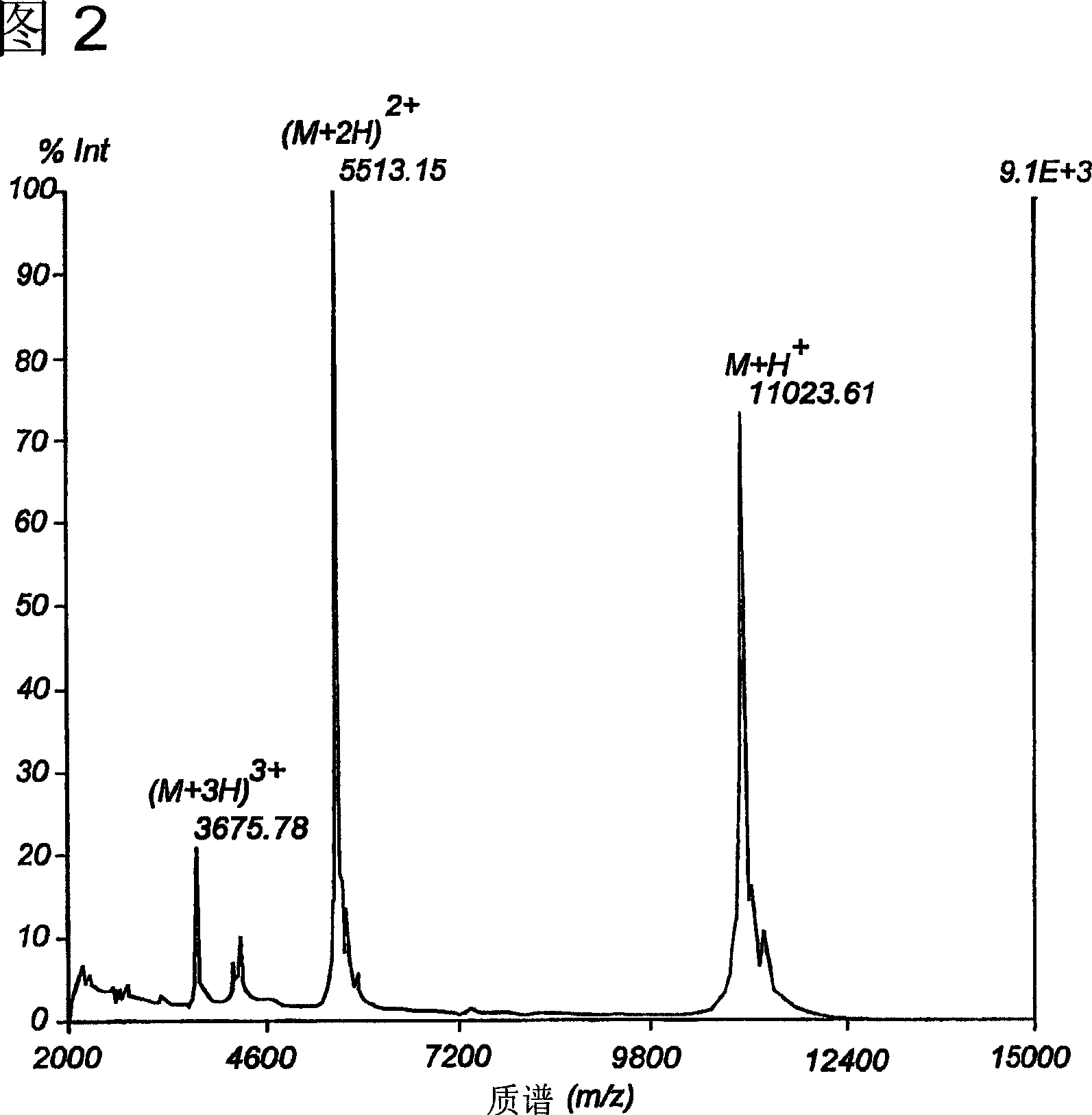
The invention provides a GMP compatible method to chemically synthesize proteins which may be advantageously used in compositions for vaccination that are free of biological contaminants. The method uses conventional synthesis of peptides and linking these to yield synthetic proteins that preferably comprise all T cell epitopes for an antigen. Preferably an adjuvant is covalently attached to a synthetic protein to yield a fully synthetic vaccine. The invention is illustrated mainly by using HPV protein directed immunity as a model.
Owner:LEIDEN UNIV (MEDICAL CENT)
Vaccine delivery compositions and methods of use
The present invention provides synthetic vaccine delivery compositions based on polyester amide (PEA), polyester urethane (PEUR), and polyester urea (PEU) polymers for stimulating an immune response to a variety of pathogenic organisms and tumor cells in humans and other mammals. The vaccine delivery compositions are formulated as a liquid dispersion of polymer particles or molecules including class I or class II antigen peptides derived from organism or tumor cell proteins, which are taken up by antigen presenting cells of the mammal to induce an immune response in the mammal. Methods of inducing an immune response to the pathogenic organism or tumor cells in the invention compositions are also included.
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
Conserved-element vaccines and methods for designing conserved-element vaccines
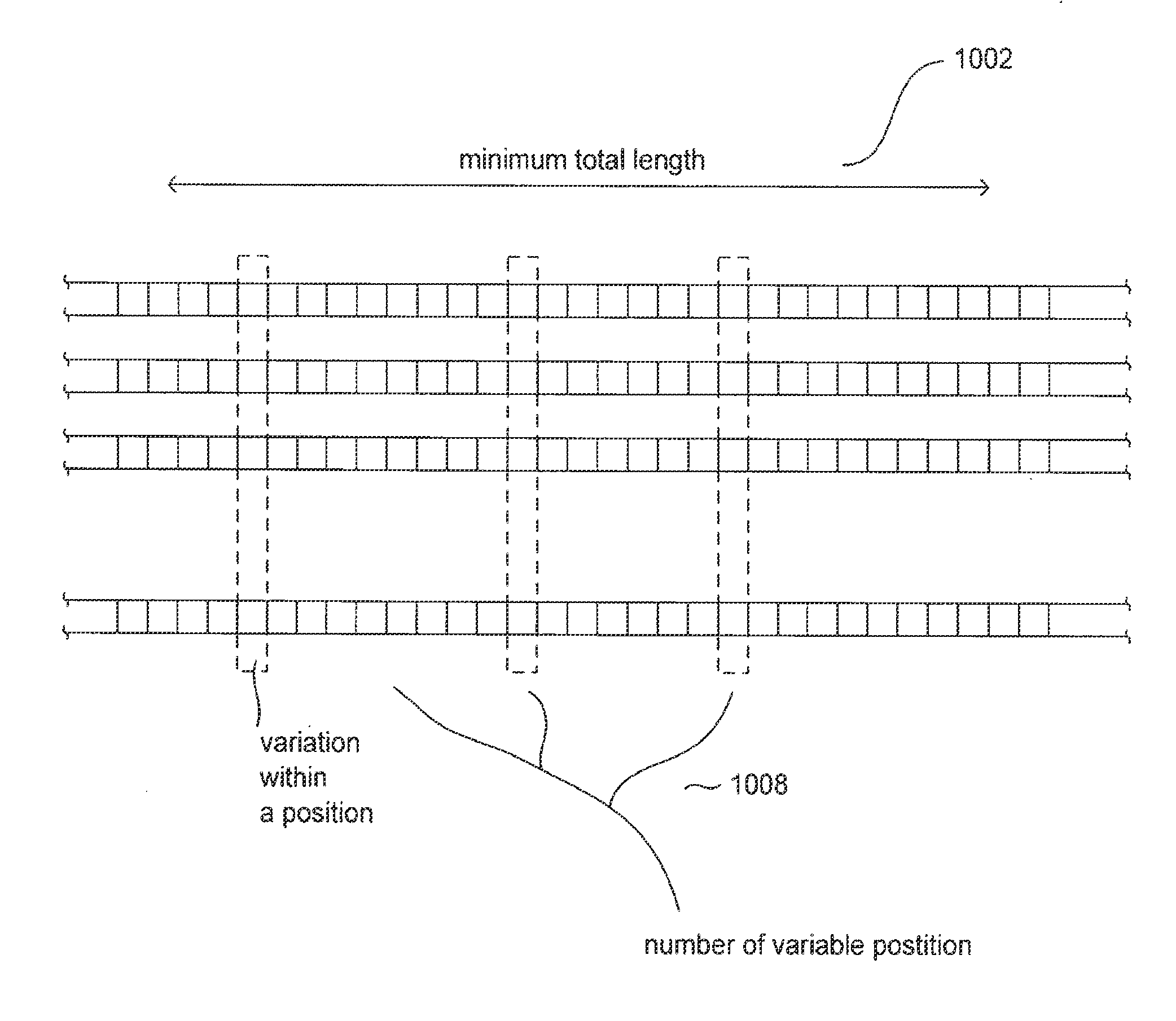
Embodiments of the present invention include conserved-element vaccines and methods for designing and producing conserved-element vaccines. A conserved-element vaccine (“CEVac”) is a recombinant and / or synthetic vaccine that incorporates only highly conserved epitopes from an observed set of pathogen variants. The conserved epitopes are identified computationally by aligning biopolymer sequences, such as concatenated polypeptide sequences that together represent a pathogen proteome, corresponding to an observed set of pathogen variants, and computationally selecting conserved subsequences according to a number of subsequence-selection criteria. These subsequence-selection criteria may include a minimum conserved-subsequence length, a threshold frequency of occurrence of a particular monomer at each conserved, single-monomer position within a conserved subsequence, a threshold combined occurrence for a set of allowable variant monomers at a particular conserved, variable position within a conserved subsequence, and a maximum number of variable positions within a subsequence. A set of conserved subsequences identified according to the subsequence-selection criteria are then filtered to remove subsequences identical to, or too similar to, naturally-occurring host subsequences, and are then assembled into expression vectors for incorporation into microbial hosts for biosynthesis of a recombinant CEVac or assembled into one or more synthetic constructs for a synthetic CEVac.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Conserved-Element Vaccines and Methods for Designing Conserved-Element Vaccines
Embodiments of the present invention include conserved-element vaccines and methods for designing and producing conserved-element vaccines. A conserved-element vaccine (“CEVac”) is a recombinant and / or synthetic vaccine that incorporates only highly conserved epitopes from an observed set of pathogen variants. The conserved epitopes are identified computationally by aligning biopolymer sequences, such as concatenated polypeptide sequences that together represent a pathogen proteome, corresponding to an observed set of pathogen variants, and computationally selecting conserved subsequences according to a number of subsequence-selection criteria. These subsequence-selection criteria may include a minimum conserved-subsequence length, a threshold frequency of occurrence of a particular monomer at each conserved, single-monomer position within a conserved subsequence, a threshold combined occurrence for a set of allowable variant monomers at a particular conserved, variable position within a conserved subsequence, and a maximum number of variable positions within a subsequence. A set of conserved subsequences identified according to the subsequence-selection criteria are then filtered to remove subsequences identical to, or too similar to, naturally-occurring host subsequences, and are then assembled into expression vectors for incorporation into microbial hosts for biosynthesis of a recombinant CEVac or assembled into one or more synthetic constructs for a synthetic CEVac.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Synthetic vaccine agents
InactiveUS20020119162A1Promote absorptionImprove responsePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCtl epitopeHelper epitope
The present invention provides for novel immungens that are comprised of an activated polyhydroxypolymer backbone to which is attached 2 separate antigenic determinants. The 1st antigenic determinant includes a B-cell or CTL epitope and the 2nd antigenic determinant includes a T-helper epitope. In preferred embodiments, the antigenic determinants are derived from different molecules and species. Exemplary immunogens of the invention are constituted of a linear tresyl-activated dextran backbone to which is coupled B-cell or CTL epitopes of an antigen and to which is also coupled universal T-helper epitopes. Also disclosed are immunogenic compositions comprising the immunogens, methods of immunization and a method for identification of suitable immunogens of the invention.
Owner:BEALE STREET 143 INVEST APS
Ultrasonic microvesicle as immuno adjuvant and vaccine carrier
ActiveCN100546649CImprove expression levelImprove immune activityPeptide/protein ingredientsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsVaccine antigenPeptide vaccine
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical engineering, and more specifically, the invention relates to a new type of ultrasonic microbubble used as an immune adjuvant and vaccine carrier. Ultrasound microbubbles carrying vaccine antigens are synthesized by adhering the vaccine antigen material to the surface of the microbubbles and / or wrapping them in the microbubbles; when used, the microbubbles carrying the vaccine antigens are applied to the target tissue through the system and locally, and ultrasonic waves are used to destroy the target tissue. The microbubbles in the tissue area release vaccine antigen substances in a localized manner and enhance the immune activity of the antigens. It is expected to be developed into a new immune adjuvant and vaccine carrier, especially new adjuvants and carriers suitable for peptide vaccines, nucleic acid vaccines, viral and bacterial vaccines.
Owner:许川山 +2
A-type clostridium perfringens populus skin lipoid inactivated vaccine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101695568AMorphological integrityExtension of timeAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsEnzyme digestionBacillus perfringens
The invention discloses an A-type clostridium perfringens populus skin lipoid inactivated vaccine which is synthesized by taking populus skin lipoid as an aduvant and mixing A-type clostridium perfringens toxin subjected to inactivation and detoxication and the populus skin lipoid aduvant. The concrete method comprises the following steps: aseptically inoculating A-type clostridium perfringens in liver and gastric enzyme digestion soup, anaerobically culturing at 37 DEG C for 15-20h, selecting typical colonies to be inoculated on a blood inclined plane, and anaerobically culturing at 37 DEG C for 20-24h; then inoculating in the liver and gastric enzyme digestion soup according to a proportion of 1 percent of the total weight of a culture medium, culturing at a constant temperature of 35 DEG C for 7-8h, centrifuging to obtain the toxin, adding formaldehyde which is 0.3-0.5 percent of the total weight of the toxin, and carrying out inactivation and detoxication at 37 DEG C for 5d; mixing the toxin subjected to inactivation and detoxication with the populus skin lipoid aduvant according to the weight ratio of 4:1 and stirring at high speed to synthesize the vaccine. The A-type clostridium perfringens populus skin lipoid inactivated vaccine has long immunity time, no vaccination reaction after being injected and small stress.
Owner:王靖
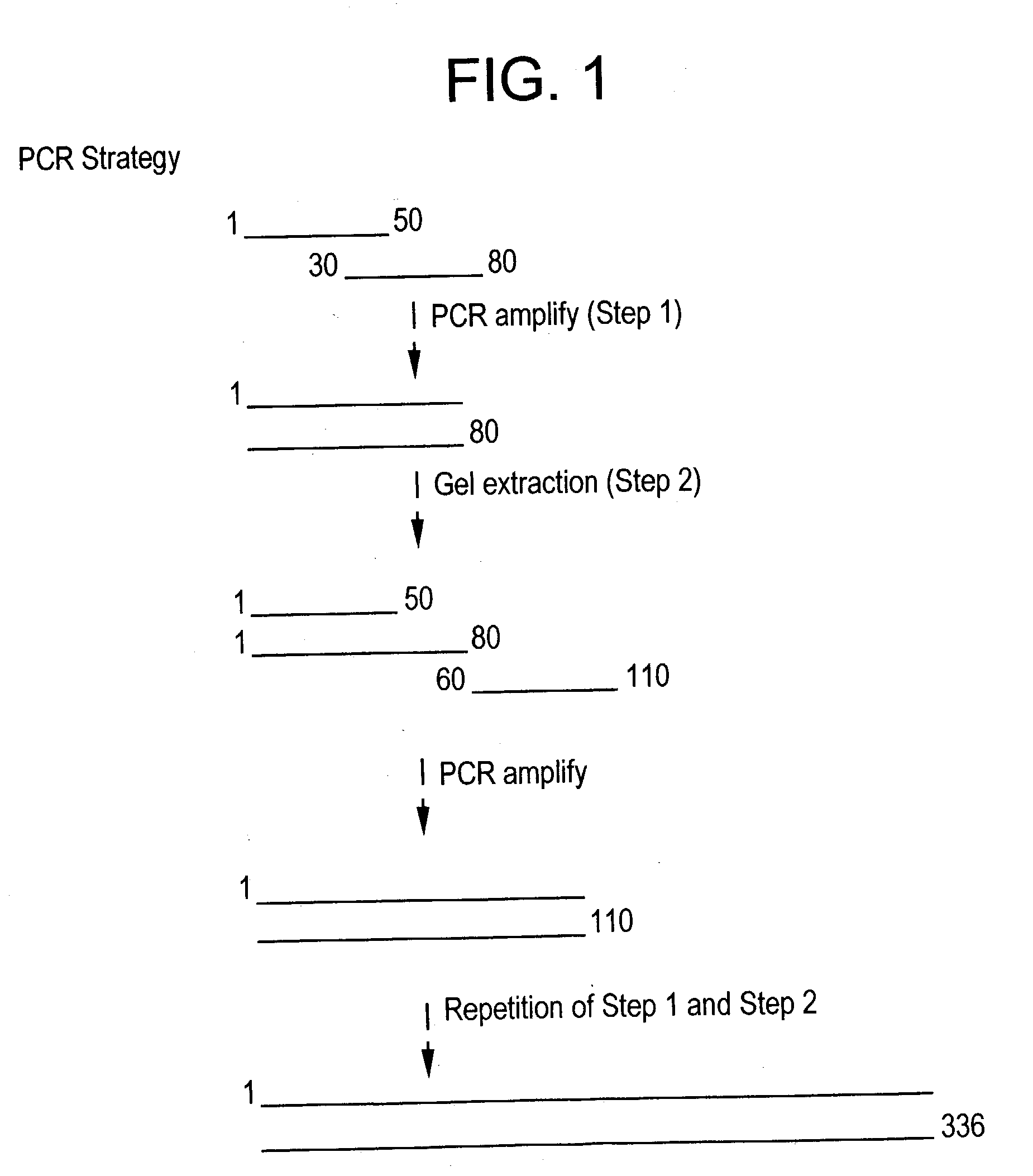
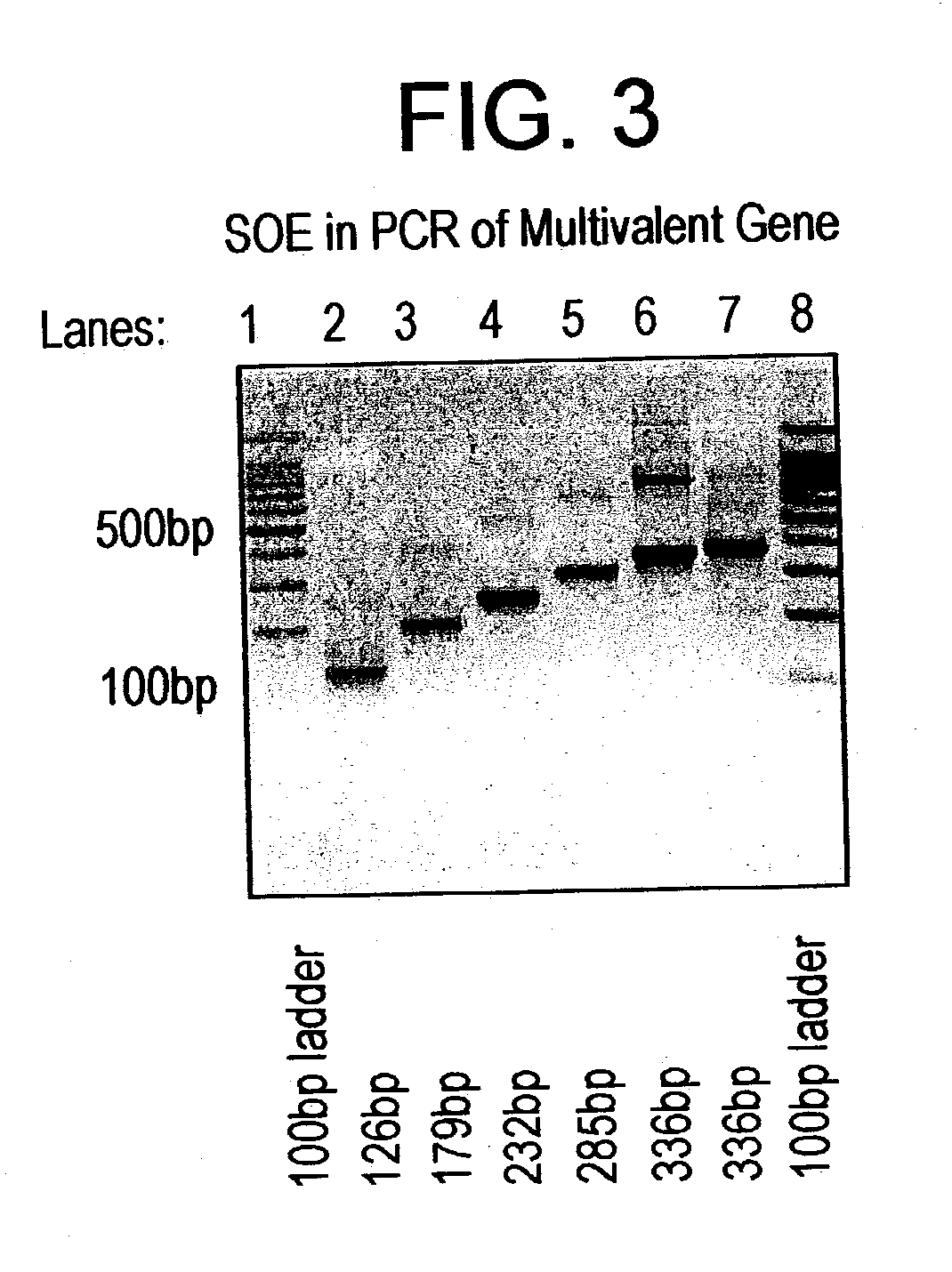
Multivalent synthetic vaccine for cancer
InactiveUS20030082201A1Preventing, inhibiting, or modulating the hypersecretion of VIPBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBombesinVasoactive intestinal peptide
Multivalent vaccine comprising peptides from vasoactive intestinal peptide, bombesin, Substance P and epidermal growth factor are described. A method of constructing a multivalent gene for use in various expressions vectors and the protein recombinantly expressed in the prokaryotic expression systems are also described.
Owner:DABUR RESEARCH FOUNDATION
Porcine pseudorabies virus, vaccine composition and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveUS20160114029A1Enhance immune functionAvoid infectionSugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsRabiesEngineered genetic
Provided in the embodiments of the present invention is a vaccine composition including an immune amount of attenuated live vaccine, inactivated vaccine, subunit vaccine, synthetic vaccine, or genetically engineered vaccine of the porcine pseudorabies virus strain. The vaccine composition can effectively induce antibody generation, and prevent infections of virulent strains of the porcine pseudorabies virus, and provides effective protection for pigs.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Typhoid, paratyphoid ectoblast protein vaccine
ActiveCN1911444AImprove securityImprove protectionAntibacterial agentsAntibody medical ingredientsMicrobiologyThallus
An outer membrane vaccine for preventing the infection of typhoid bacillus and paratyphoid bacillus A and B is disclosed. Its preparing process includes such steps as culturing said bacilli in culture liquid, getting their thallus, and preparing vaccine.
Owner:BEIJING ZHIFEI LVZHU BIOPHARM
Method for Rapid High Volume Production of Synthetic Vaccines
PendingUS20180340202A1Improve stabilityIncrease doseApparatus sterilizationVirus peptidesModularitySynthetic vaccine
The present invention features an on demand programmable machine and process for producing synthetic vaccine or other protein product(s). This system includes modular machine components with programmable inputs to responsively and rapidly synthesize selected protein product(s) in desired amounts. When the device is programmed to produce multiple proteins in a single run, the amount of each protein produced is independently controlled. The programmability and modularity is scalable permitting e.g., low volume output to manage an incipient local outbreak, and in cases where higher production volumes are necessary to prevent epidemic or pandemic events, high levels of production can be planned at the outset or scaled up as greater need is recognized.
Owner:POSTREL RICHARD
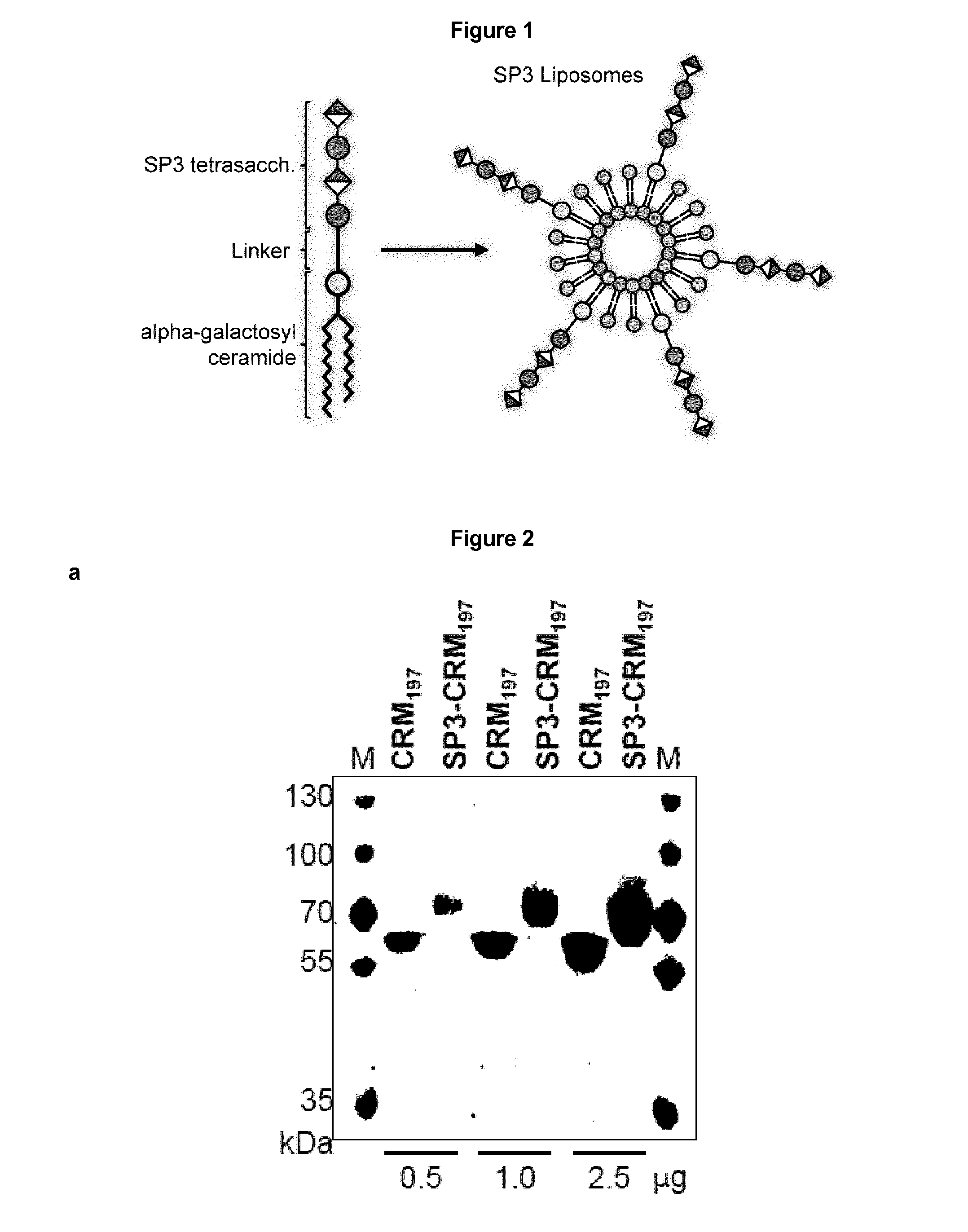
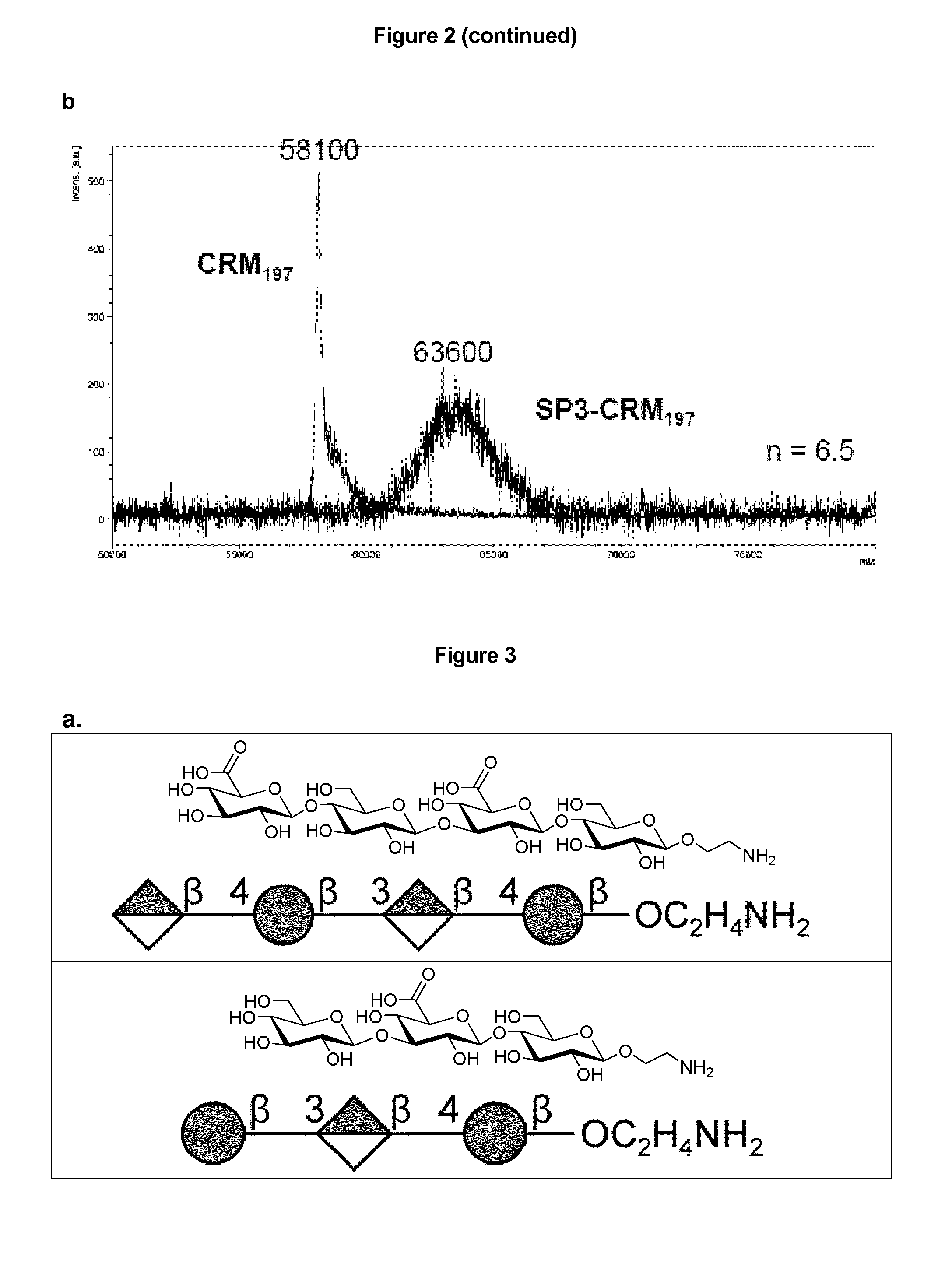
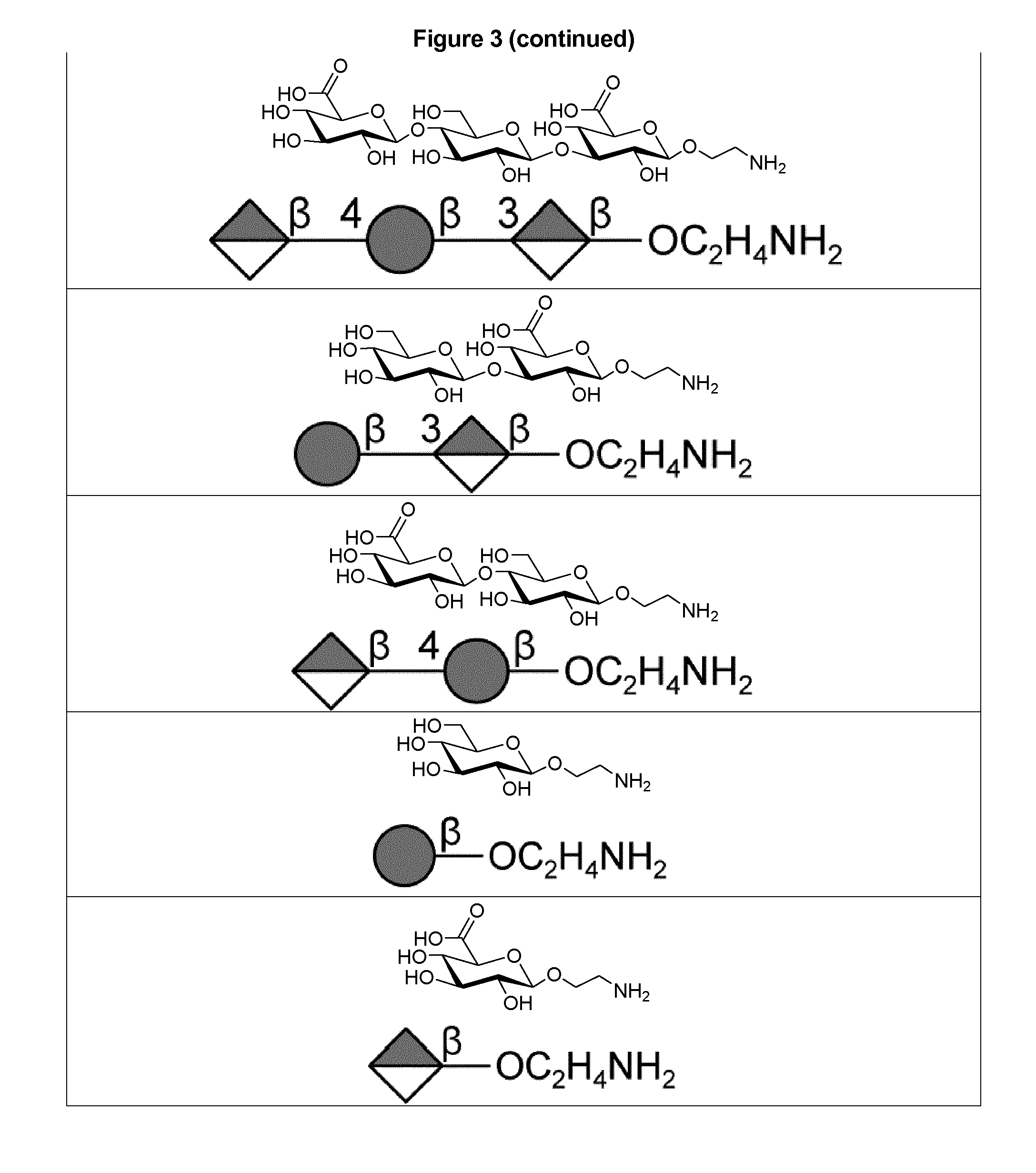
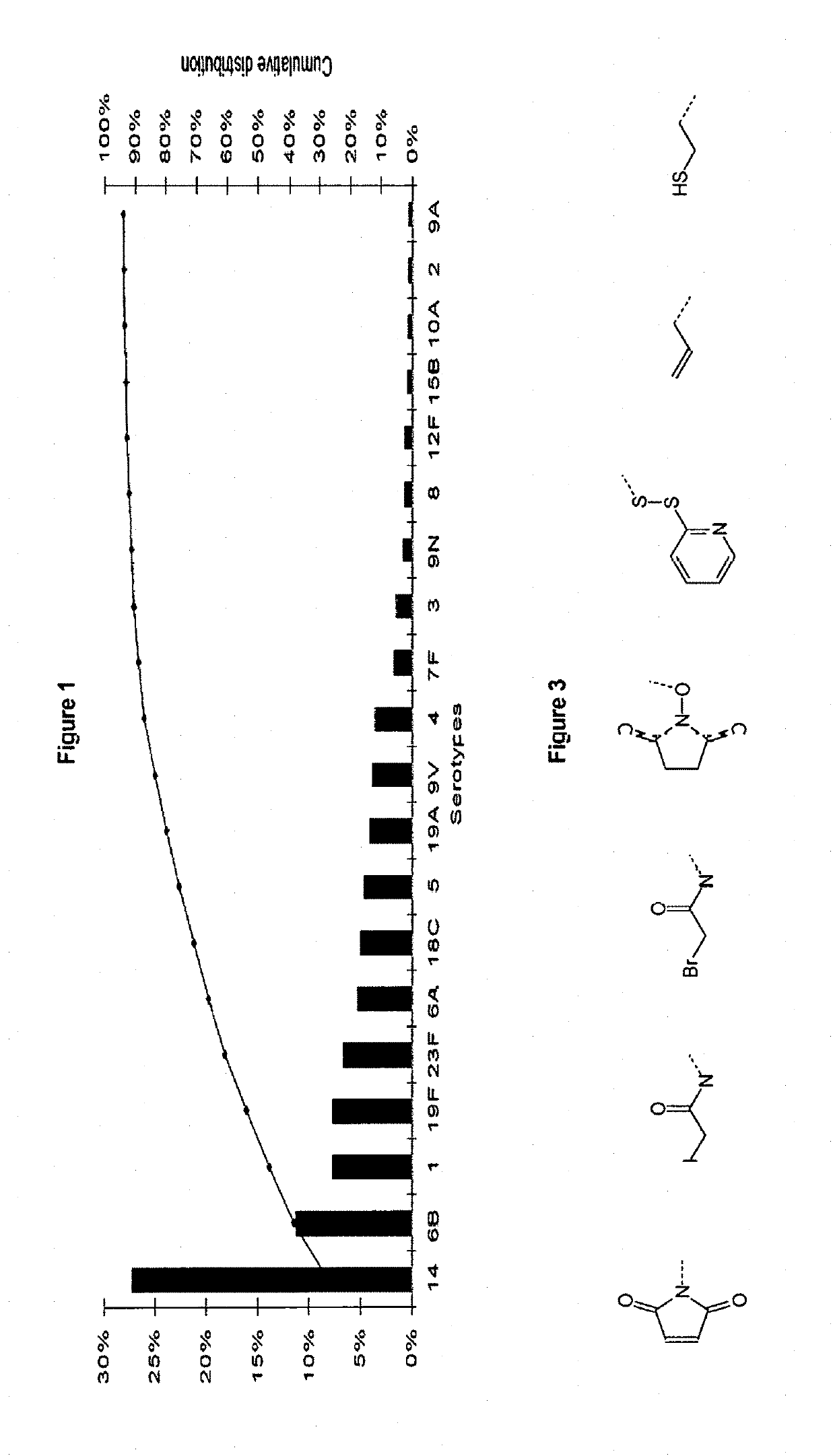
Protein and peptide-free synthetic vaccines against streptococcus pneumoniae type 3
InactiveUS20160279224A1Extraordinary stability at room temperatureEffectively and continuously immunizing against <Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseStreptococcus constellatus
The present invention provides a protein- and peptide-free conjugate comprising a synthetic carbohydrate and a carrier molecule, wherein the synthetic carbohydrate is a Streptococcus pneumoniae type 3 capsular polysaccharide related carbohydrate and the carrier molecule is a glycosphingolipid. Said conjugate and pharmaceutical composition thereof are useful for immunization against diseases associated with Streptococcus pneumoniae, and more specifically against diseases associated with Streptococcus pneumoniae type 3.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Synthetic vaccines against Streptococcus pneumoniae type 1
ActiveUS10328141B2Improving immunogenicityAdd supportAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsStreptococcus pneumoniaeDisease
The present invention relates to the total synthesis of saccharide structures contained in the capsular polysaccharide of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 1, to glycoconjugates containing said saccharide structures obtained by total synthesis and to use of such glycoconjugates and pharmaceutical compositions thereof in the immunization against diseases associated with bacteria containing said saccharide structures in their capsular polysaccharide, and more specifically associated with Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Typhoid, paratyphoid envelope protein vaccine
ActiveCN100571774CImprove securityImprove protectionAntibacterial agentsAntibody medical ingredientsBacillus typhosusTyphoid/paratyphoid fevers
An outer membrane vaccine for preventing the infection of typhoid bacillus and paratyphoid bacillus A and B is disclosed. Its preparing process includes such steps as culturing said bacilli in culture liquid, getting their thallus, and preparing vaccine.
Owner:BEIJING ZHIFEI LVZHU BIOPHARM
Synthetic vaccine for tick control
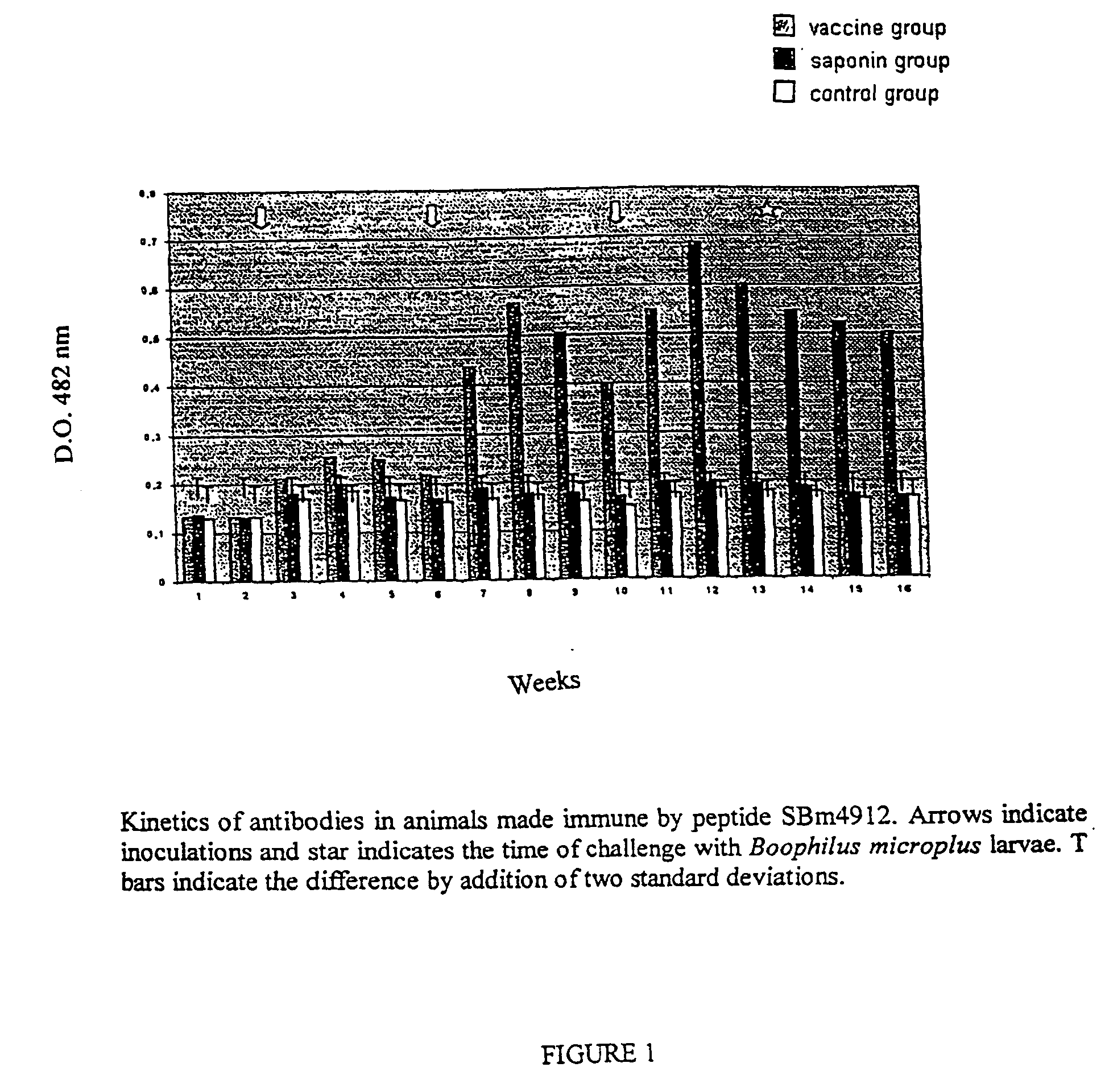
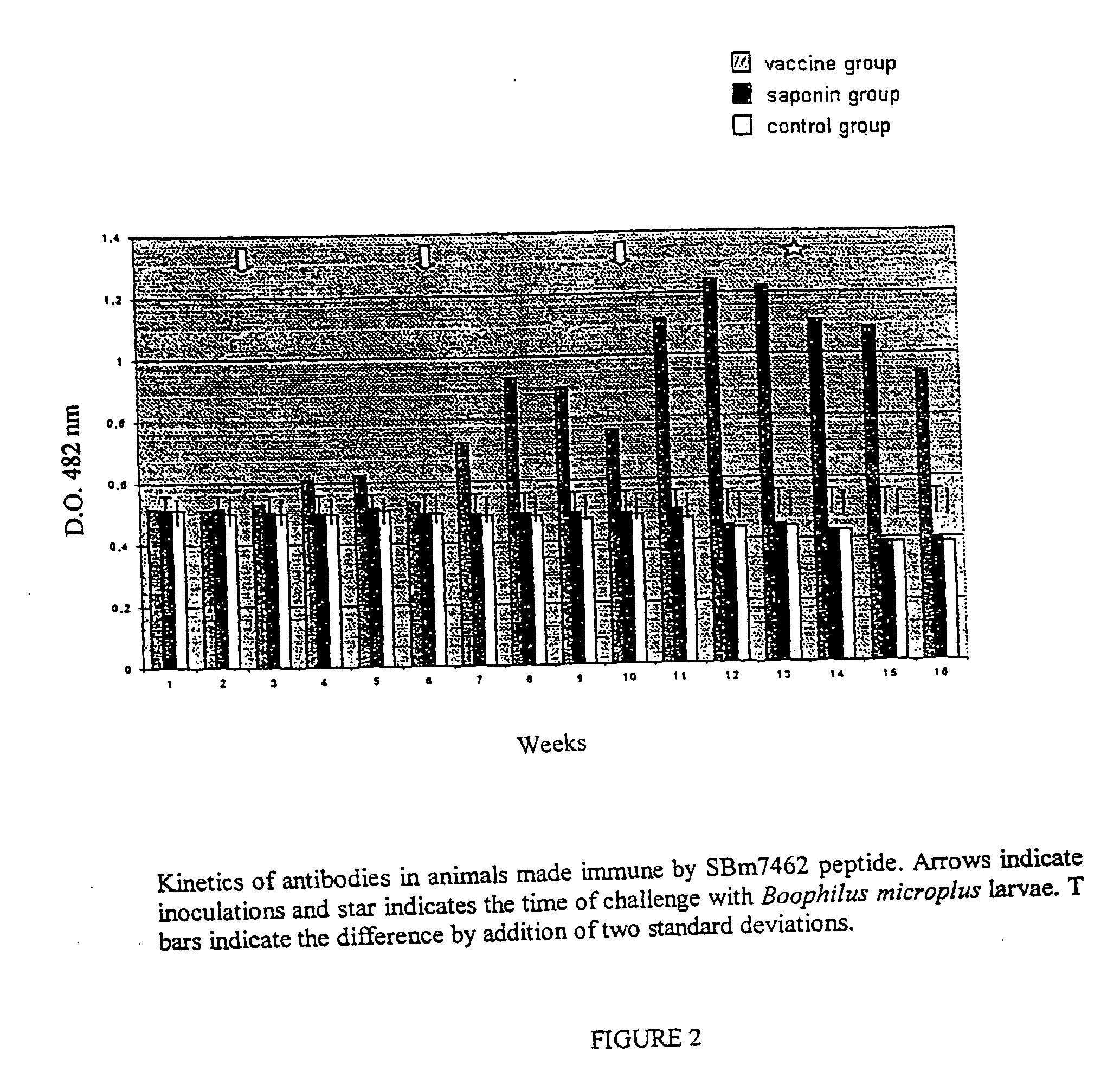
InactiveUS8110202B2Protozoa antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSynthetic ImmunogensTick Control
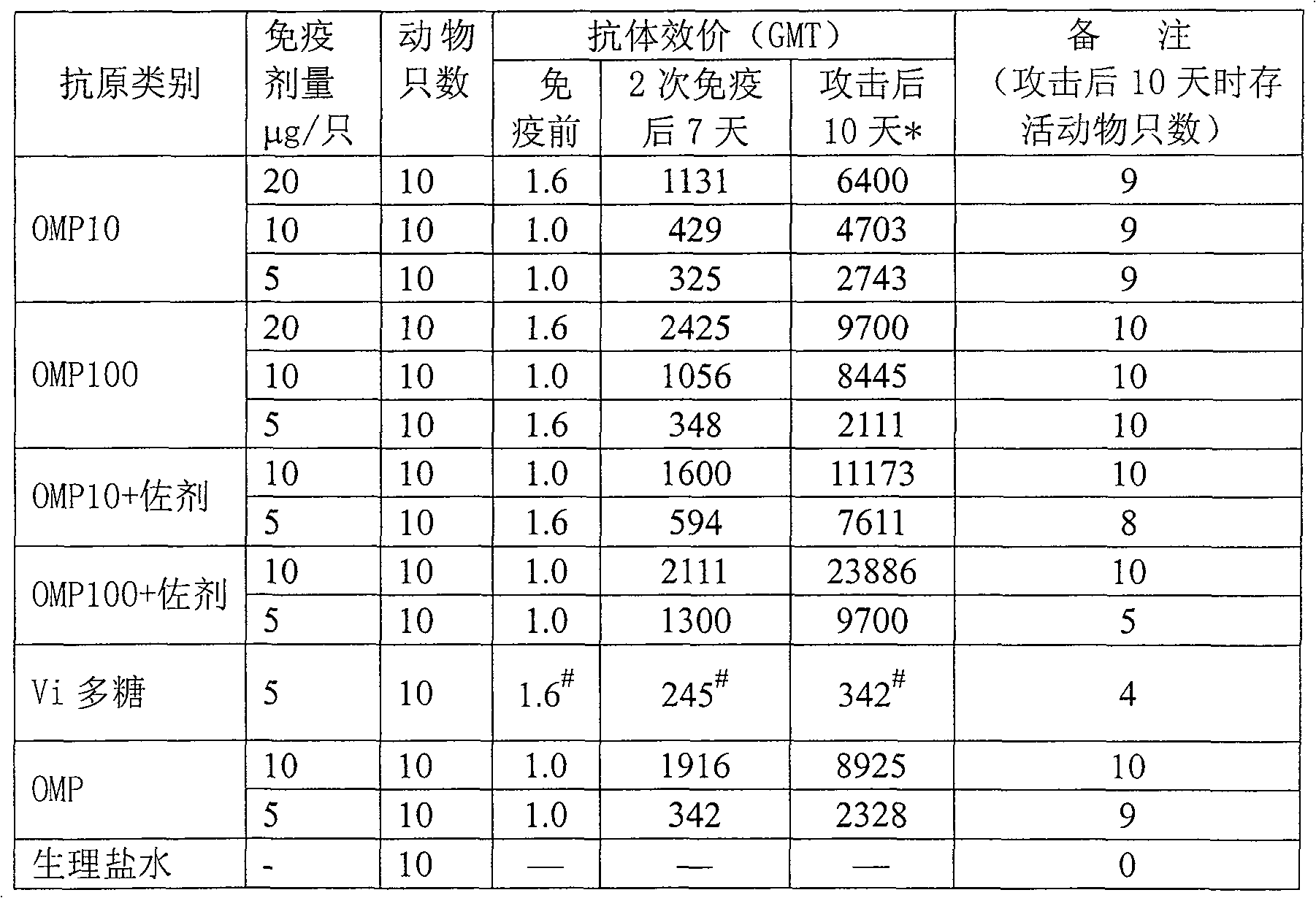
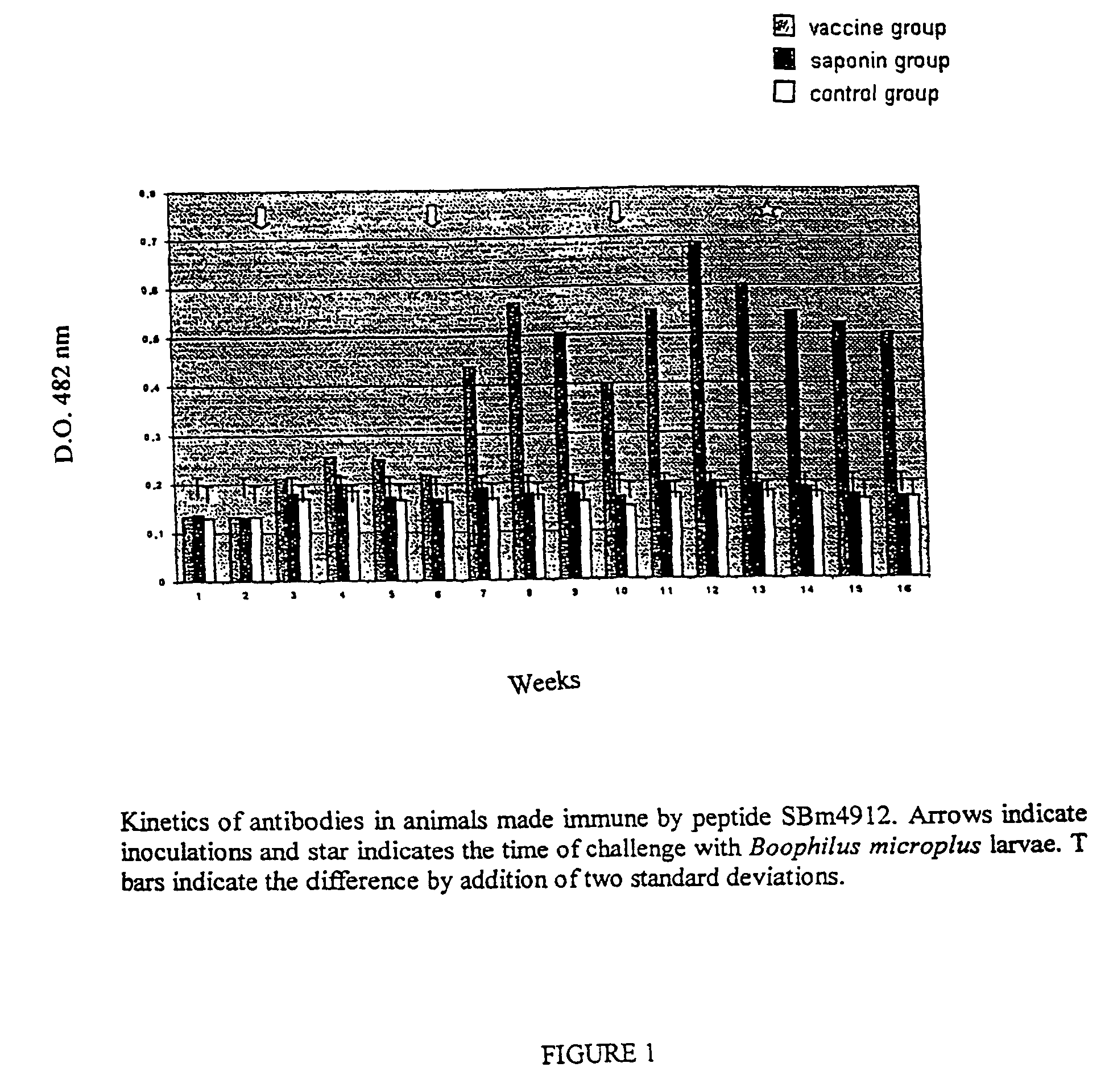
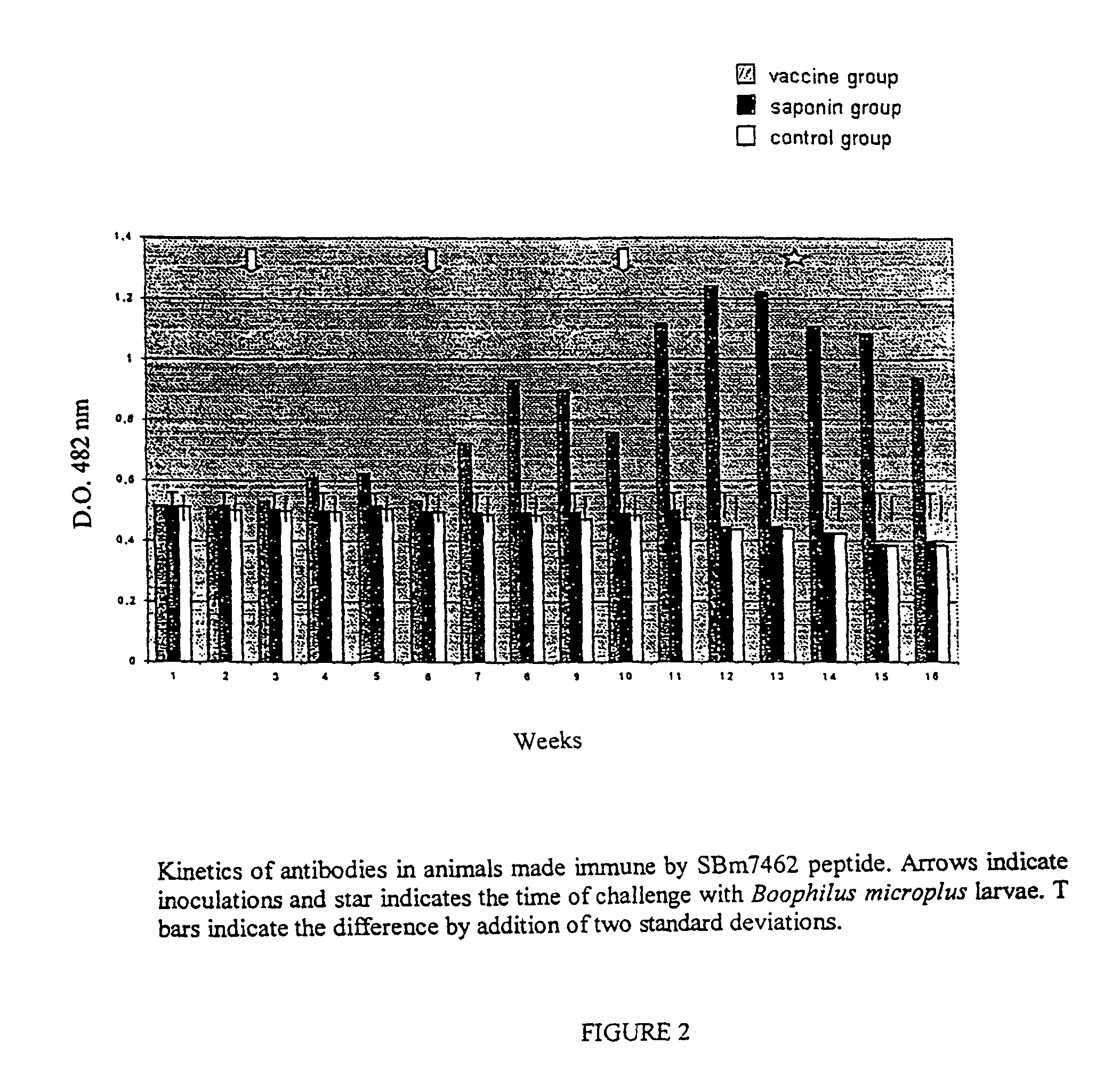
This invention is related to the field of immunology of protein biotechnology and particularly to the construction of synthetic immunogens which result, where inoculated, in the production by cattle of an immune response capable of lesion to the ticks feeding on the inoculated bovines, reducing their number, their weight and their reproductive capacity to such an extent that the constructed immunogen can be used as an effective vaccine for tick control on bovines. The technical object of the invention consists of the design and construction of two synthetic immunogens constituted of a continuous and defined sequence with forty-three (43) amino acids, found in different positions in the sequence of protein Bm86, their polymerization with cysteine in the N-terminal and in the C-terminal, the medicamentous composition based on said peptide(s) and the synthetic vaccine obtained thereby.
Owner:FUNDACAO UNIVE FEDERAL DE VICOSA +1
Synthetic protein as tumor-specific vaccine
The invention provides a GMP compatible method to chemically synthesize proteins which may be advantageously used in compositions for vaccination that are free of biological contaminants. The method uses conventional synthesis of peptides and linking these to yield synthetic proteins that preferably comprise all T cell epitopes for an antigen. Preferably an adjuvant is covalently attached to a synthetic protein to yield a fully synthetic vaccine. The invention is illustrated mainly by using HPV proteins directed immunity as a model.
Owner:LEIDEN UNIV (MEDICAL CENT)
Protein and peptide-free synthetic vaccines against Streptococcus pneumoniae type 3
InactiveUS10052373B2Extraordinary stabilityEffectively and continuously immunizing against <Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseStreptococcus constellatus
The present invention provides a protein- and peptide-free conjugate comprising a synthetic carbohydrate and a carrier molecule, wherein the synthetic carbohydrate is a Streptococcus pneumoniae type 3 capsular polysaccharide related carbohydrate and the carrier molecule is a glycosphingolipid. Said conjugate and pharmaceutical composition thereof are useful for immunization against diseases associated with Streptococcus pneumoniae, and more specifically against diseases associated with Streptococcus pneumoniae type 3.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Synthetic vaccines against Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 2
ActiveUS10864261B2Improving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticStreptococcus pneumoniae conjugatedAssay
The present invention relates to a synthetic saccharide of general formula (I) that is related to Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 2 capsular polysaccharide, a conjugate thereof and the use of said saccharide and conjugate for raising a protective immune response in a human and / or animal host. Furthermore, the synthetic saccharide of general formula (I) is useful as marker in immunological assays for detection of antibodies against Streptococcus pneumoniae type 2 bacteria.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
A rapid qualitative and quantitative detection method for oil adjuvant vaccines
ActiveCN107064492BStrong demulsification abilityAchieve complete suppressionMaterial analysisN-ButanolPeptide vaccine
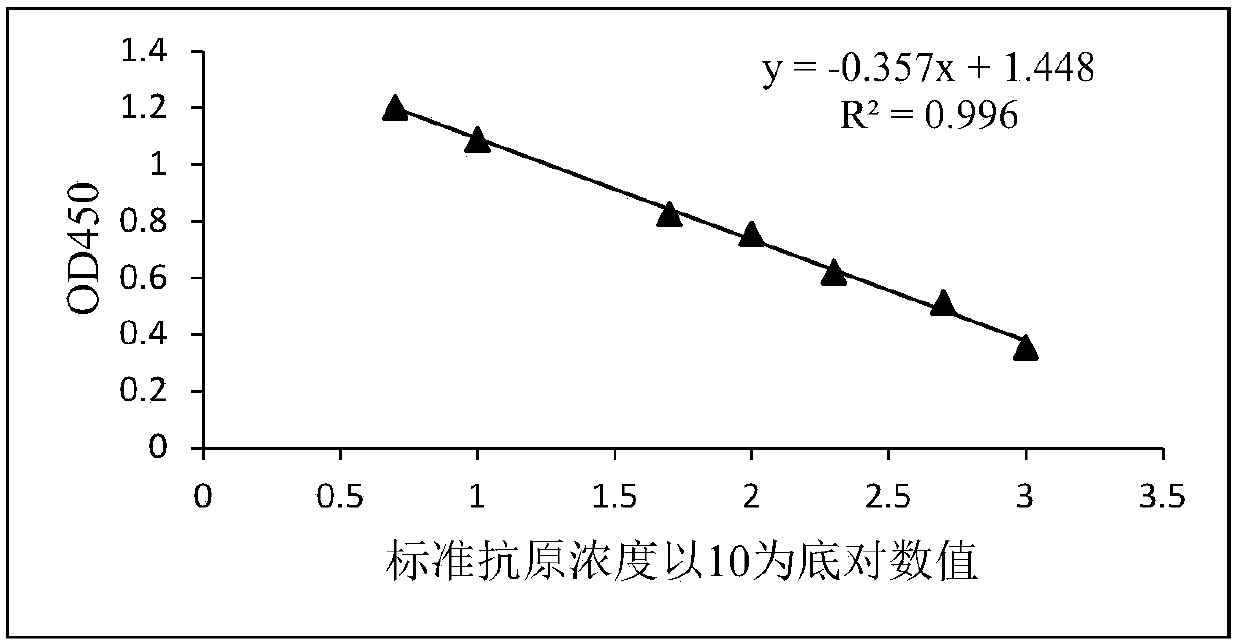
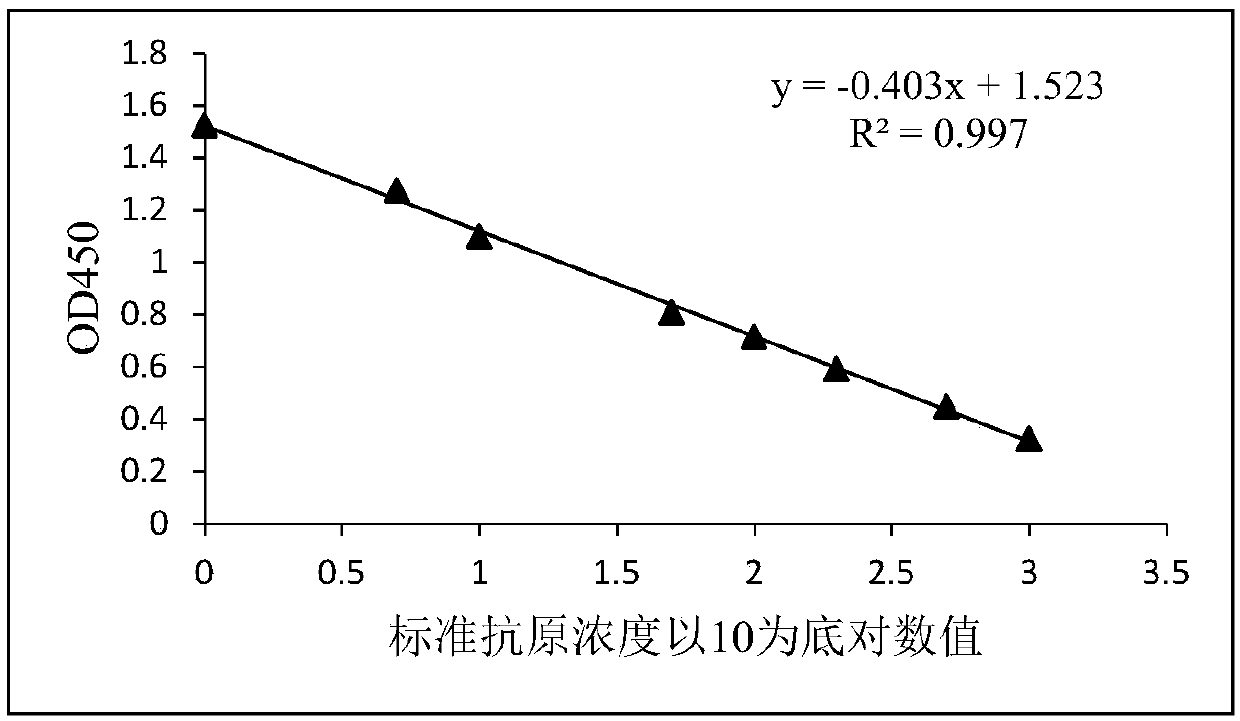
The present invention provides a rapid qualitative and quantitative detection method for an oil adjuvant vaccine. The rapid qualitative and quantitative detection method comprises: demulsifying a foot-and-mouth disease synthetic peptide vaccine, and carrying out qualitative and quantitative detection on the demulsified antigen sample by using a competitive ELISA method, wherein the demulsifying method comprises: mixing a foot-and-mouth disease synthetic vaccine and a demulsifying agent, and layering to obtain a water phase antigen sample, the demulsifying agent comprises the mixture of an organic solvent and an acid, the organic solvent is one selected from acetonitrile, n-butanol, benzyl alcohol, butyl diethylene glycol and ethanol, and the acid is one selected from hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, formic acid and trifluoroacetic acid. According to the present invention, the demulsifying ability of the demulsifying method is strong, wherein the sample can be determined without the purification treatment so as to shorten the detection time; and the antigen concentration is subjected to qualitative and quantitative detection by using the competitive ELISA method, such that the slope of the obtained standard curve can be greater than the slope of the standard curve obtained through the conventional indirect competition method so as to substantially improve the detection sensitivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHEN LIAN BIOMEDICAL CORP
Synthetic vaccines against streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 2
The present invention relates to a synthetic saccharide of general formula (I) that is related to Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 2 capsular polysaccharide, a conjugate thereof and the use of said saccharide and conjugate for raising a protective immune response in a human and / or animal host. Furthermore, the synthetic saccharide of general formula (I) is useful as marker in immunological assays for detection of antibodies against Streptococcus pneumoniae type 2 bacteria.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Synthetic vaccine for tick control
InactiveUS20050281836A1Protozoa antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSynthetic ImmunogensCysteine thiolate
This invention is related to the field of immunology of protein biotechnology and particularly to the construction of synthetic immunogens which result, where inoculated, in the production by cattle of an immune response capable of lesion to the ticks feeding on the inoculated bovines, reducing their number, their weight and their reproductive capacity to such an extent that the constructed immunogen can be used as an effective vaccine for tick control on bovines. The technical object of the invention consists of the design and construction of two synthetic immunogens constituted of a continuous and defined sequence with forty-three (43) amino acids, found in different positions in the sequence of protein Bm86, their polymerization with cysteine in the N-terminal and in the C-terminal, the medicamentous composition based on said peptide(s) and the synthetic vaccine obtained thereby.
Owner:FUNDACAO UNIVE FEDERAL DE VICOSA +1
Porcine pseudorabies virus, vaccine composition and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveUS9650424B2Avoid infectionSlow onsetSugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsGenetically engineeredSynthetic vaccine
Provided in the embodiments of the present invention is a vaccine composition including an immune amount of attenuated live vaccine, inactivated vaccine, subunit vaccine, synthetic vaccine, or genetically engineered vaccine of the porcine pseudorabies virus strain. The vaccine composition can effectively induce antibody generation, and prevent infections of virulent strains of the porcine pseudorabies virus, and provides effective protection for pigs.
Owner:PULIKE BIOLOGICAL ENG INC
Preparation and application of cationic epitope vaccine
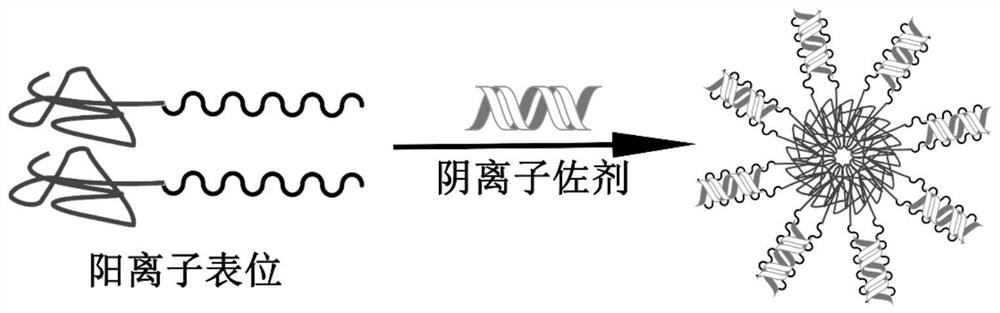
PendingCN112023036APromote maturation and activationImprove cross presentationCancer antigen ingredientsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsAntigenAdjuvant
The invention relates to a self-assembled nano epitope vaccine and application thereof. A T cell epitope peptide is subjected to cationization modification, so that the T cell epitope peptide and an anionic adjuvant are self-assembled in an aqueous solution to form a nano composite vaccine through electrostatic interaction. The vaccine can prevent or treat tumors or serve as a combined preparationof an anticancer active preparation. The epitope vaccine has the advantages of clear components, easiness in preparation, specificity cavity, high safety and good clinical transformation and practical application prospects. The problems of low synthetic efficiency, difficulty in separation and purification and the like of a synthetic vaccine are solved. Compared with other vaccines, the epitope vaccine has the advantages that a preparation method is simple, the size of formed vaccine nanoparticles is favorable, an additional delivery carrier is not needed, self-delivery of an antigen and theadjuvant is realized, activation of antigen presenting cells is promoted, an antitumor immune response is induced, tumor growth is inhibited, and tumor prevention and treatment functions can be realized.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com