Transmission-type screen and back-type projector
A transmission type, projector technology, used in projectors, instruments, lenses, etc. with built-in screens/external screens, can solve problems such as easy occurrence of ripples and easy occurrence of diffracted light, and achieves reduction of flicker, suppression of diffracted light, and suppression of Contrast drop effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
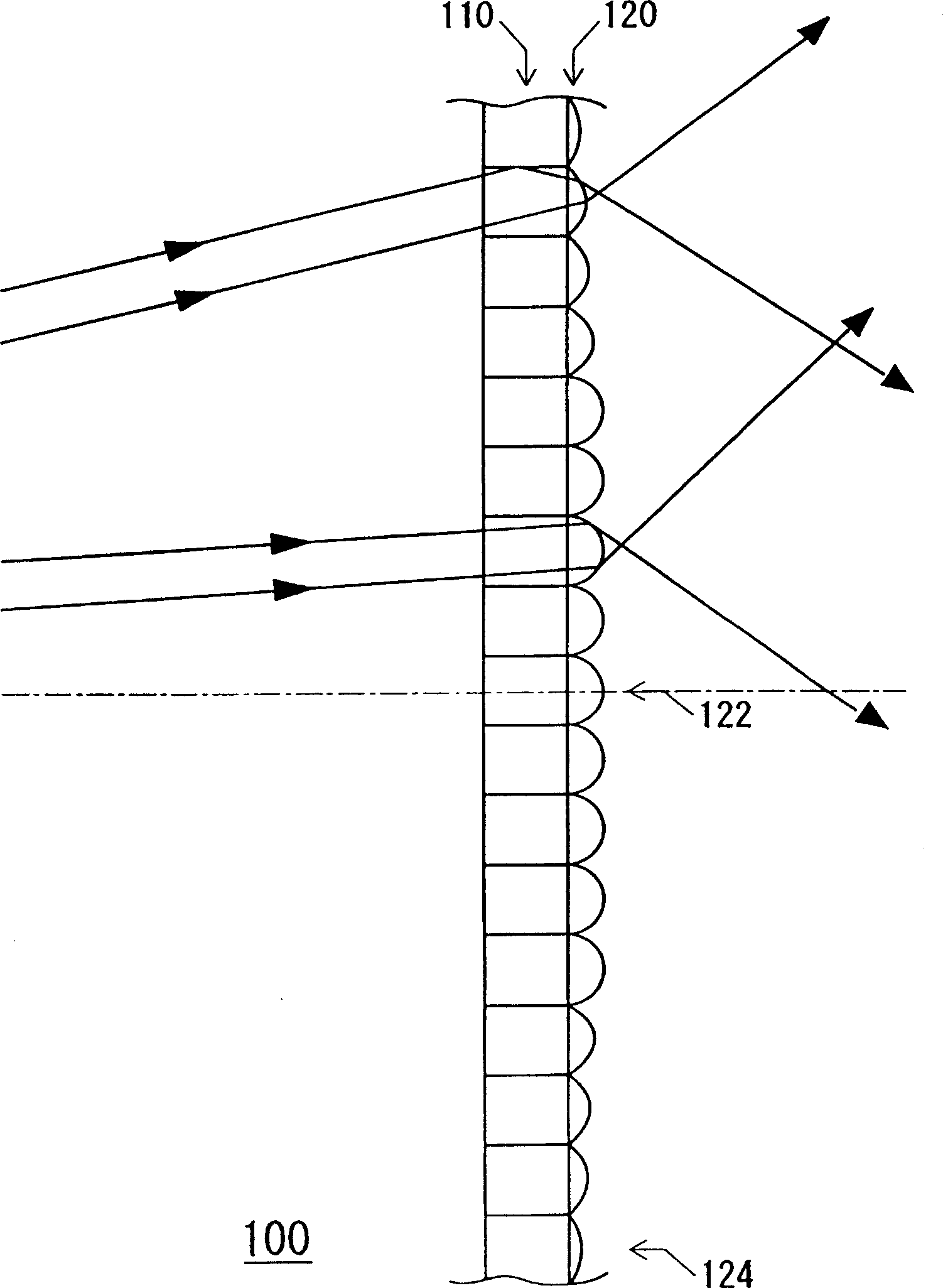
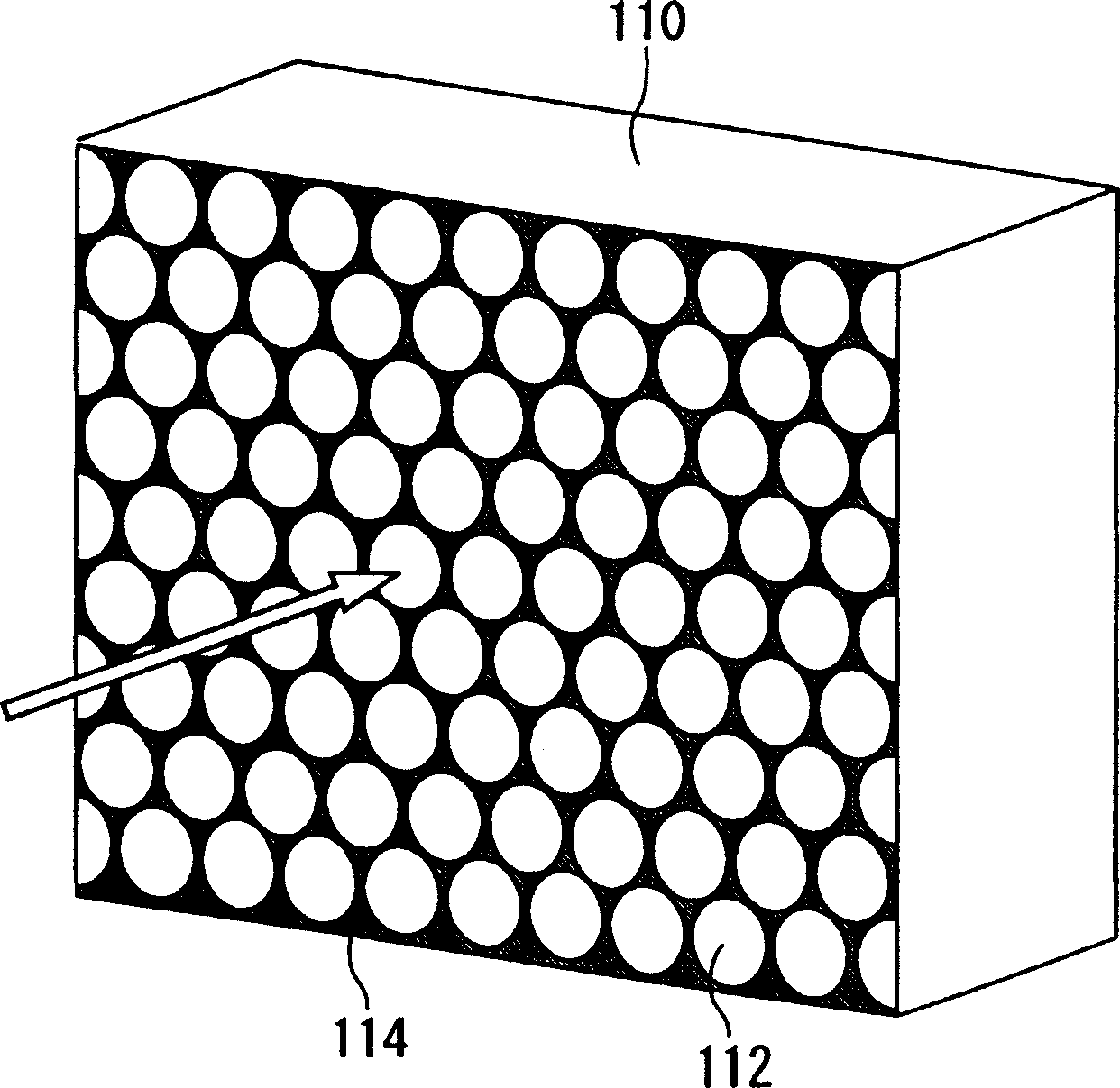
[0073] The transmissive screen of Embodiment 1 is a transmissive screen used for a rear projector. figure 1 It is a figure which shows the optical system of the transmissive screen of Example 1. also, figure 2 It is a perspective view of a light guide plate constituting a part of the transmissive screen of the first embodiment. Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown in , the transmissive screen 100 has: a light guide plate 110, the light guide plate is arranged as a plurality of substantially cylindrical light guide spaces with optical fibers 112; The side is used as an emission angle distribution uniformizing device for uniforming the emission angle distribution of the optical fiber emitted from the light guide plate 110 within the screen.
[0074] The microlens array 120 has a plurality of microlenses provided corresponding to the optical fibers 112 of the light guide plate 110 , and the curvature radius of these microlenses gradually increases from the center of the...
Embodiment 2
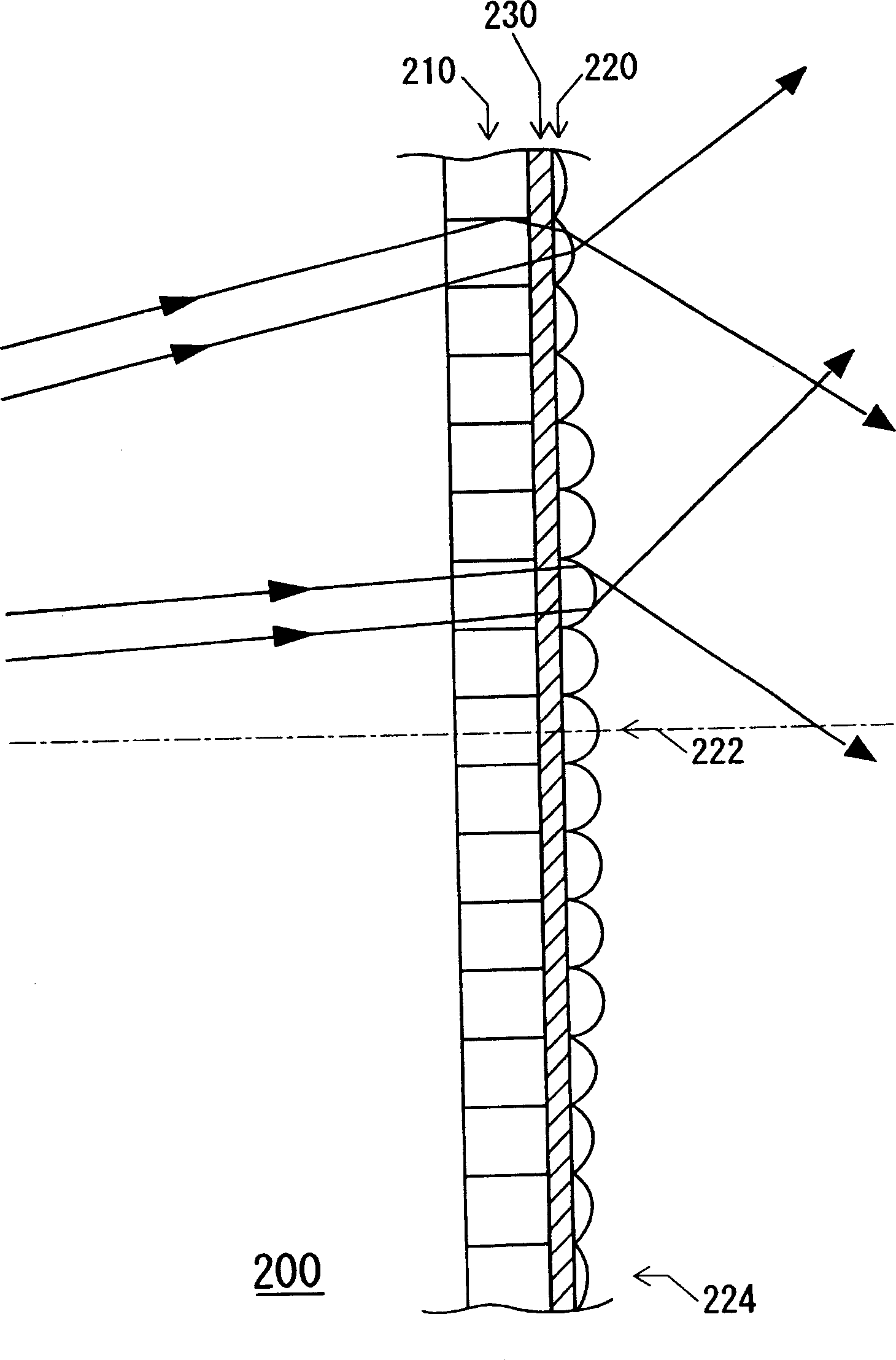
[0083] image 3 It is a figure which shows the optical system of the transmissive screen of Example 2 of this invention. Such as image 3 As shown in , the difference between the transmissive screen 200 of Embodiment 2 and the transmissive screen 100 of Embodiment 1 is that it has a light diffusion layer 230 .
[0084] That is, in the transmissive screen 100 of the first embodiment, the microlens array 220 is disposed on the exit surface of the light guide plate 110, whereas in the transmissive screen 200 of the second embodiment, only the microlens array 220 is disposed on the exit surface of the light guide plate 110. A light-diffusing layer 230 is disposed on the central portion of the surface, and a microlens array 220 is also disposed on the light-diffusing layer 230 .
[0085]Therefore, in the transmissive screen 200 of the second embodiment, since the light passing through the light guide plate 110 is diffused by the light-diffusing layer 230, it is incident on the mi...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Figure 4 It is a figure which shows the optical system of the transmissive screen of Example 3 of this invention. Such as Figure 4 As shown in , the difference between the transmissive screen of Embodiment 3 and the transmissive screen of Embodiment 1 lies in the structure of the microlens array. That is, in the transmissive screen 100 of the first embodiment, it is a microlens array in which the radius of curvature of the microlens gradually increases from the screen center to the screen periphery of the transmissive screen. That is, it is a microlens array in which the radius of curvature of the microlenses at the center of the screen is at least smaller than that of the microlenses at the periphery of the screen. In contrast, in the transmissive screen 300 of Example 3, the curvature of the microlenses is constant, and the refractive index of the base material constituting the microlens array gradually decreases from the center of the screen to the periphery of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com