Semiconductor storage
A memory and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, static memory, digital memory information, etc., to achieve the effects of preventing damage, low current consumption, and preventing misoperation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment
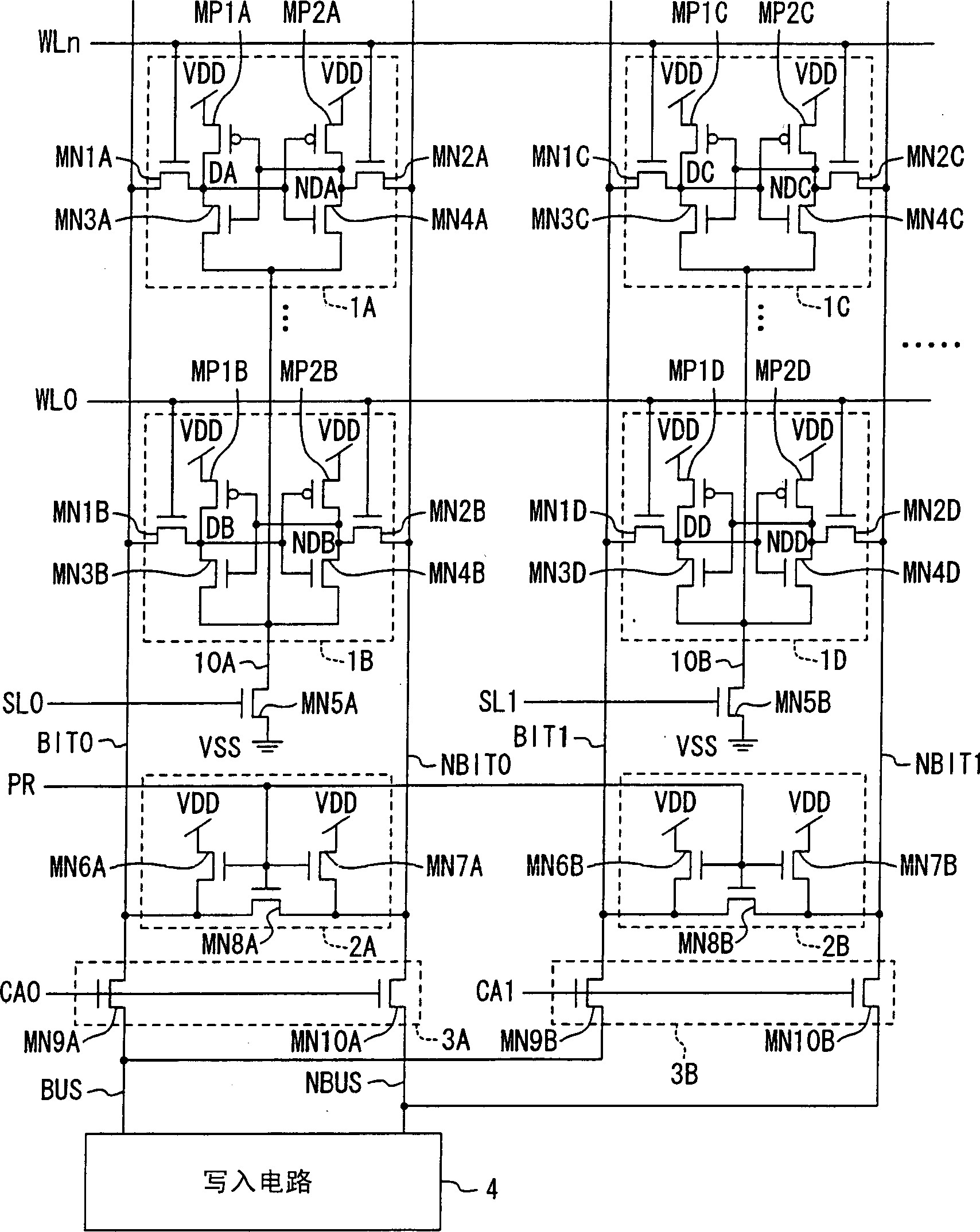
[0041] figure 1 A configuration diagram of a semiconductor memory device according to a first embodiment of the present invention is shown.
[0042] In this figure, a plurality of memory cells 1A to 1D are arranged in an array. The memory cell 1A will be described below as a representative. Since the other memory cells 1B to 1D have the same internal structure, they are attached with reference numerals B, C, and D, respectively, and their descriptions are omitted.
[0043] The memory cell 1A is composed of two P-type load transistors MP1A and MP2A, two N-type transfer transistors MN1A and MN2A, and two N-type drive transistors MN3A and MN4A. The sources of the two load transistors MP1A and MP2A are connected to the high-voltage power supply VDD and supplied with a high potential (first potential), and the drains are connected to the sources of the two transfer transistors MN1A and MN2A and the two drive On the drains of transistors MN3A and MN4A. The gates of the two load...
no. 2 Embodiment
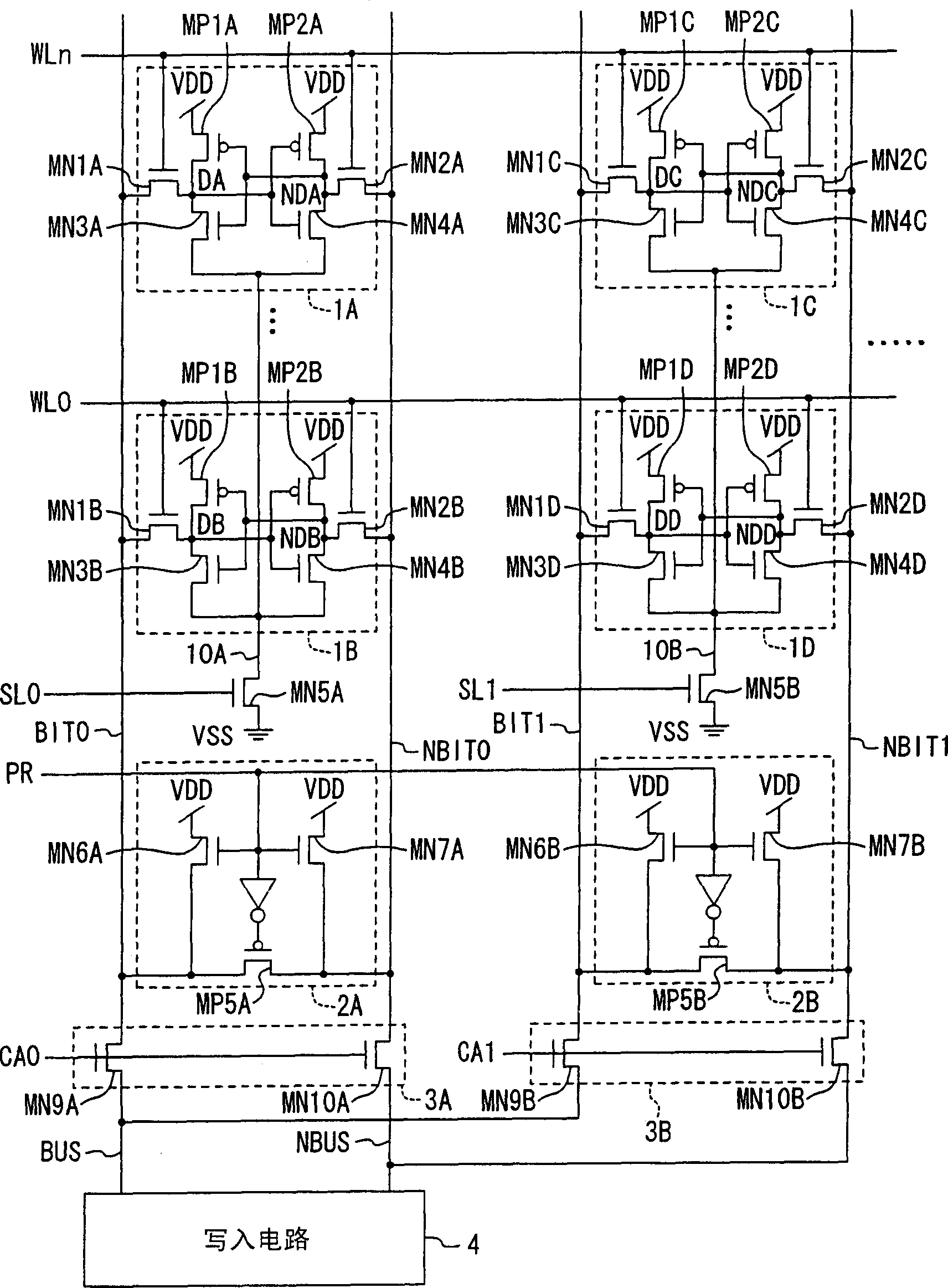
[0056] Next, a semiconductor memory device according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0057] exist image 3 The semiconductor memory of this embodiment is shown in . In this figure, with figure 1 Compared with semiconductor memory, it is only different in the following aspects. That is, the balance transistors of the precharge and balance circuits 2A and 2B are composed of P-type transistors MP5A and MP5B, and the inverted signal of the precharge signal PR is input to the gates of these transistors.
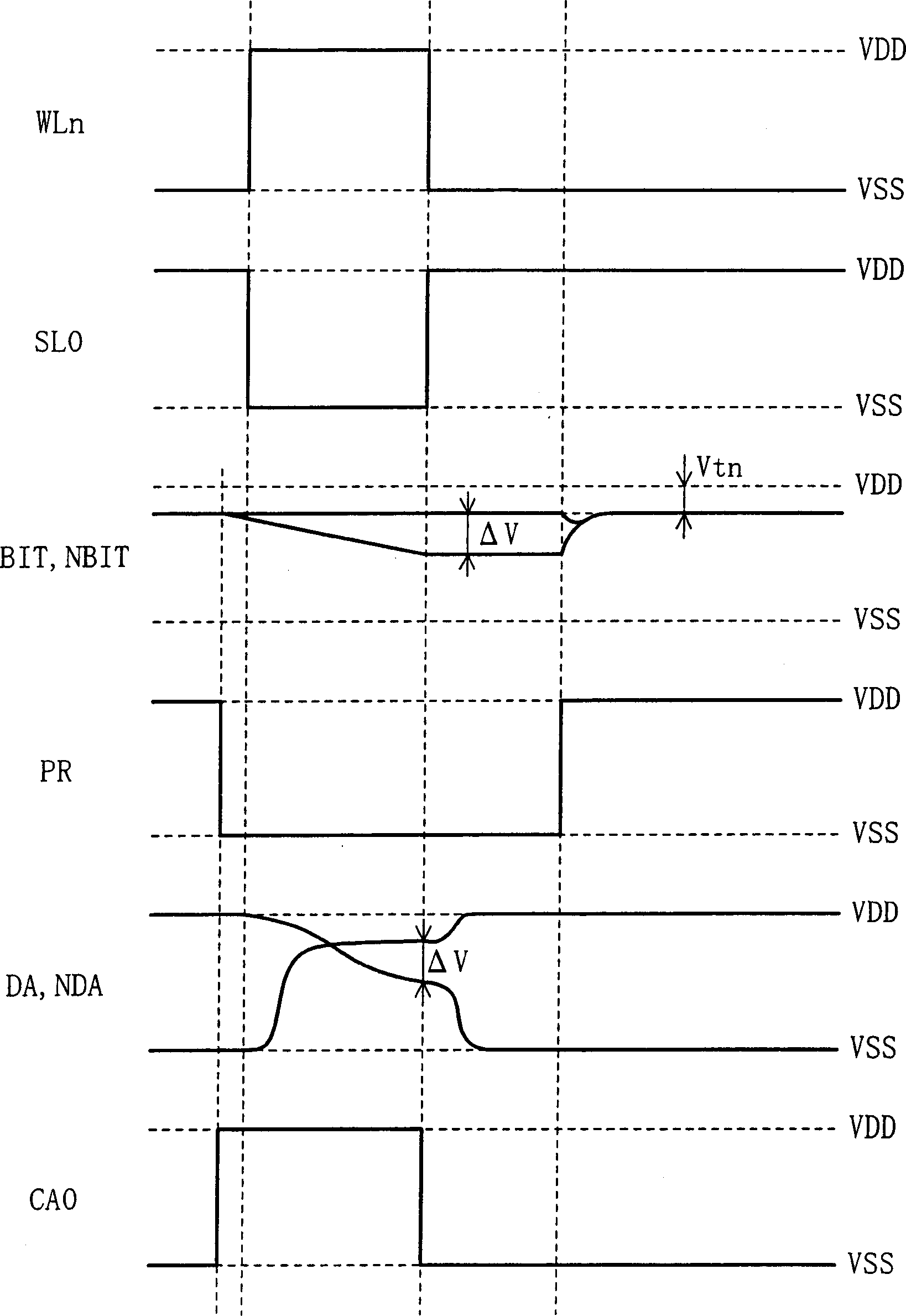
[0058]In this embodiment, even if the potentials of the bit lines BITO, NBITO, BIT1, and NBIT1 are higher than the precharge potential VDD-Vtn, since the write circuit 4 is used to write data to the selected bit line (such as BITO, NBITO) The potential of one of the storage nodes DA and NDA in the memory cell 1A is pulled down to the ground potential VSS, and the data of the bit lines BITO and NBITO are transmitted to the memory cell 1A. Th...
no. 3 Embodiment
[0061] Next, a semiconductor memory device according to a third embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0062] Figure 4 The semiconductor memory of this embodiment is shown in . The figure of semiconductor memory with figure 1 The semiconductor memory device of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 10 differs only in the following structure.
[0063] That is, in each of the memory cells 1A to 1D, the transfer transistors are composed of P-type transistors (MP3A and MP4A), (MP3B and MP4B), (MP3C and MP4C), (MP3D and MP4D), and word Inversion signal of line selection signals WLn to WL0. In addition, in the precharge and balance circuits 2A and 2B, the precharge transistors are composed of P-type transistors (MP5A and MP6A), (MP5B and MP6B), and the balance transistors are also composed of P-type transistors MP7A and MP7B. The inverted signal of the precharge signal PR is input to the pole. Furthermore, the column selectors 3A and 3B are respectively composed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com