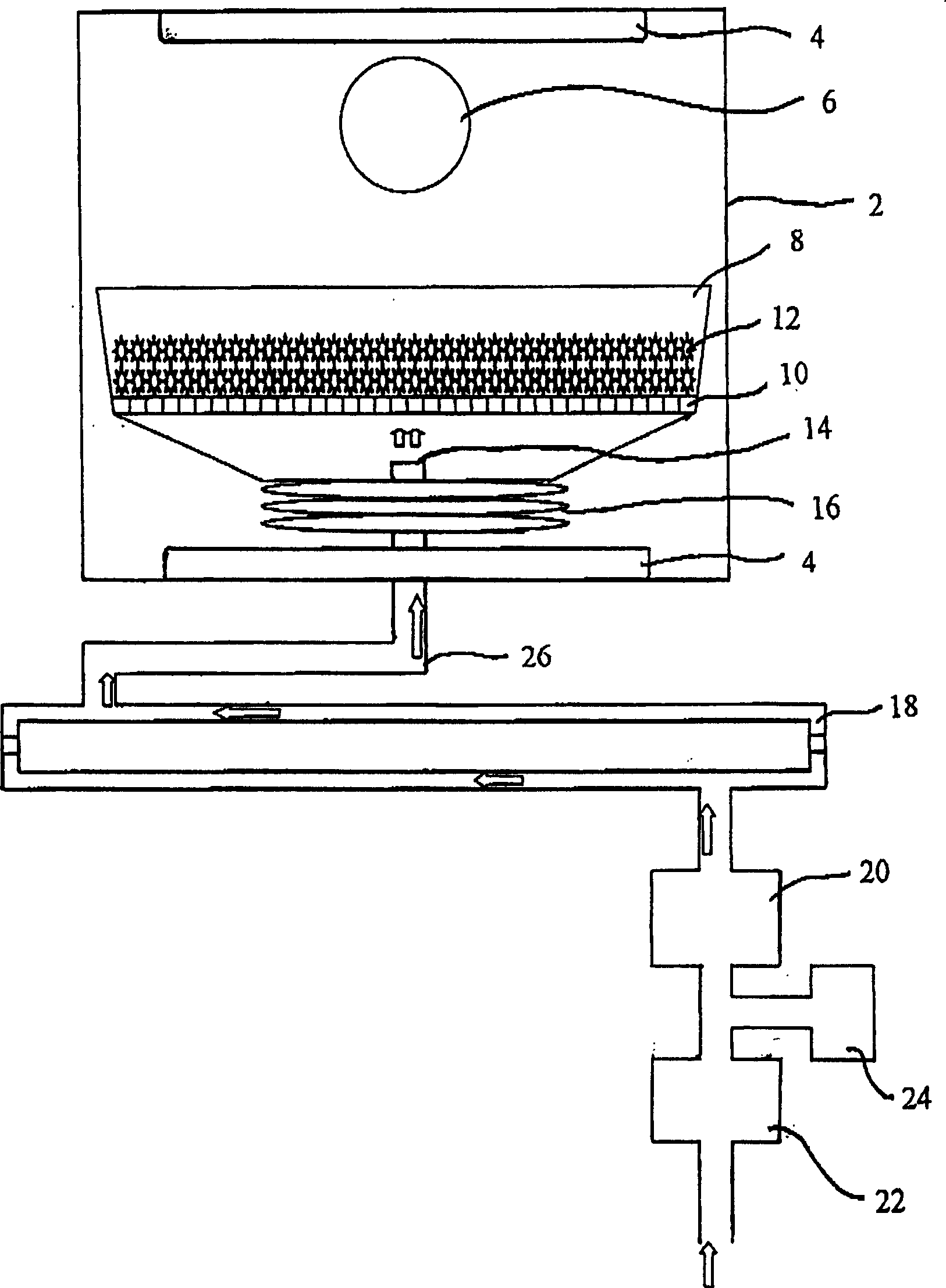
Changing of hydrophilic/hydrophobic characteristics of natural organic substances in oxidation thermo-chemical drying course
A hydrophobic, organic substance technology, applied in other chemical processes, water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of non-biodegradation, limited large-scale industrial application, limited source of raw materials, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0076] Example 1. Various hydrophobic and lipophilic adsorbents prepared under basic oxidation thermochemical drying conditions
[0077] Collect some raw materials, such as wood chips, bamboo chips, grass, peanut shells, bamboo leaves, corn leaves, corn stalks, corn ears, tobacco leaves, rice straw, bagasse, sweet sorghum residues, water bamboo stems, reeds, absorbent cotton, pine needles, cardboard boxes, cloth, Rice husk, bean pods, coconut palm, peat, hair, paper and sponge, without any pretreatment, under the conditions of no air convection, no blast, and no ozone, heated in a preheated oven at 250°F (121°C) for 4~ 7 hours. All materials have a significant improvement in water floating performance after treatment than before treatment. However, the floating rate of these materials on water for a long time has not yet reached a satisfactory effect, and the oil absorption capacity after short-term contact with water has only been improved slightly. For example, after a product m...
example 2
[0078] Example 2. Acid or alkali pretreatment
[0079] The raw materials are soaked in acid or alkali solution for 30 minutes at room temperature. The raw materials were taken out and squeezed dry by hand, and prepared under the conditions of Example 1. The raw materials soaked in 5-10% sodium hydroxide need to be washed with water before heat treatment. The tested raw materials are: sawdust, wood shavings, cardboard boxes, kitchen paper, straw, peat, peanut shells, coconut palm, leaves, bagasse, sweet sorghum residue, bean pods, corn stalks, cotton, grass, etc. The tested acids are: citric acid, acetic acid, lactic acid, oxalic acid, malic acid, formic acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid and phytic acid, with a concentration of 50-250 mM. The alkali tested were: saturated lime water, 5-10% sodium hydroxide. Compared with the corresponding products in Example 1, all tested products have improved water absorption. The acid-pretreated product has a pH of 5-6, and the alkali-pretreate...
example 3
[0080] Example 3. Air convection and higher temperature
[0081] According to the conditions of Example 1, but the raw material was pretreated with 0.2M acetic acid and heated at 350°F (177°C) for 4 to 5 hours under air convection. The tested raw materials are: wood chips, bamboo chips, grass, peanut shells, corn leaves, corn stalks, ears of corn, tobacco leaves, tea, rice straw, garlic husks, bagasse, sweet sorghum residue, rice stems, pine needles, brown, flax, ramie, Carton, cloth, shredded cotton seed, rice husk, bean pods, coconut palm, hair and paper. Compared with the corresponding products in Example 1, all tested products have a certain improvement in oil absorption capacity, a significant improvement in water floating capacity and a significant improvement in oil absorption capacity after being in contact with water for a short time. The most improved products are: wood chips, corn ears, coconut palm, tobacco leaves, grass, bagasse and sweet sorghum residue. For example,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| oil absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| oil absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com