Recombinant human antibody against HBsAg and its preparation method
A surface antigen, human-derived technology, applied in recombinant DNA technology, anti-animal/human immunoglobulin, using vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, etc., can solve the problems of difficult renaturation and low expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0060] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments, but the embodiments are only used to illustrate the present invention rather than limit the present invention.
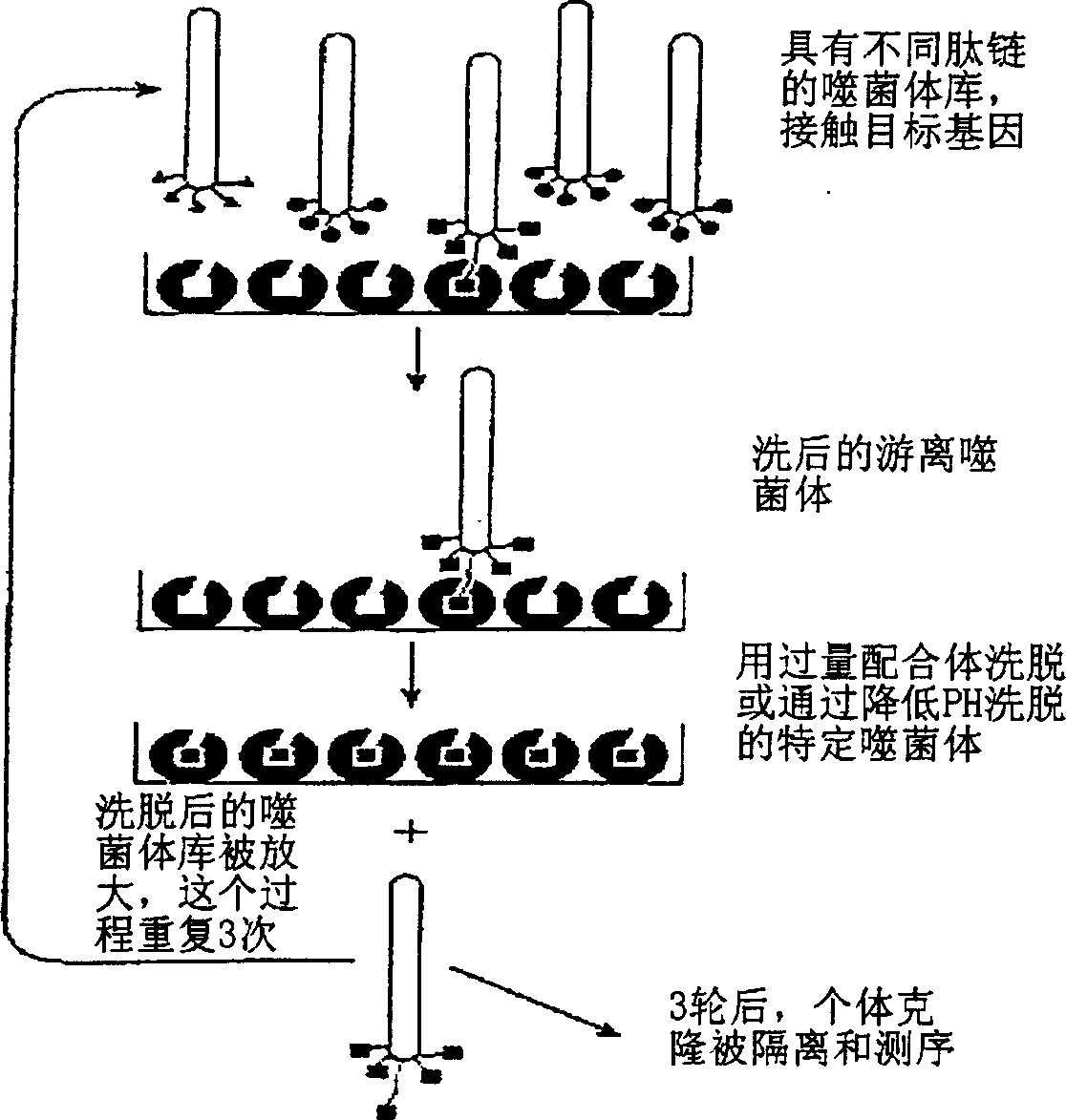
[0061] 1. Obtaining anti-HBsAg Fab antibody fragment gene by phage display technology
[0062] On the fifth day after the booster injection of hepatitis B vaccine volunteers, blood was collected, monocytes were isolated, mRNA was extracted, cDNA was synthesized by reverse transcription, and the light chain gene and heavy chain Fd of the anti-HBsAg antibody were amplified by PCR with the designed primers. The fragment genes were respectively inserted into the corresponding sites of the vector pComb3H (Carlos F.Barbas and Dennis R.Burton, 1994, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Monoclonal Antibodies from combinatorial Libraries) to construct vector plasmids containing antibody light chain and heavy chain Fd segments. Transform the competent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com