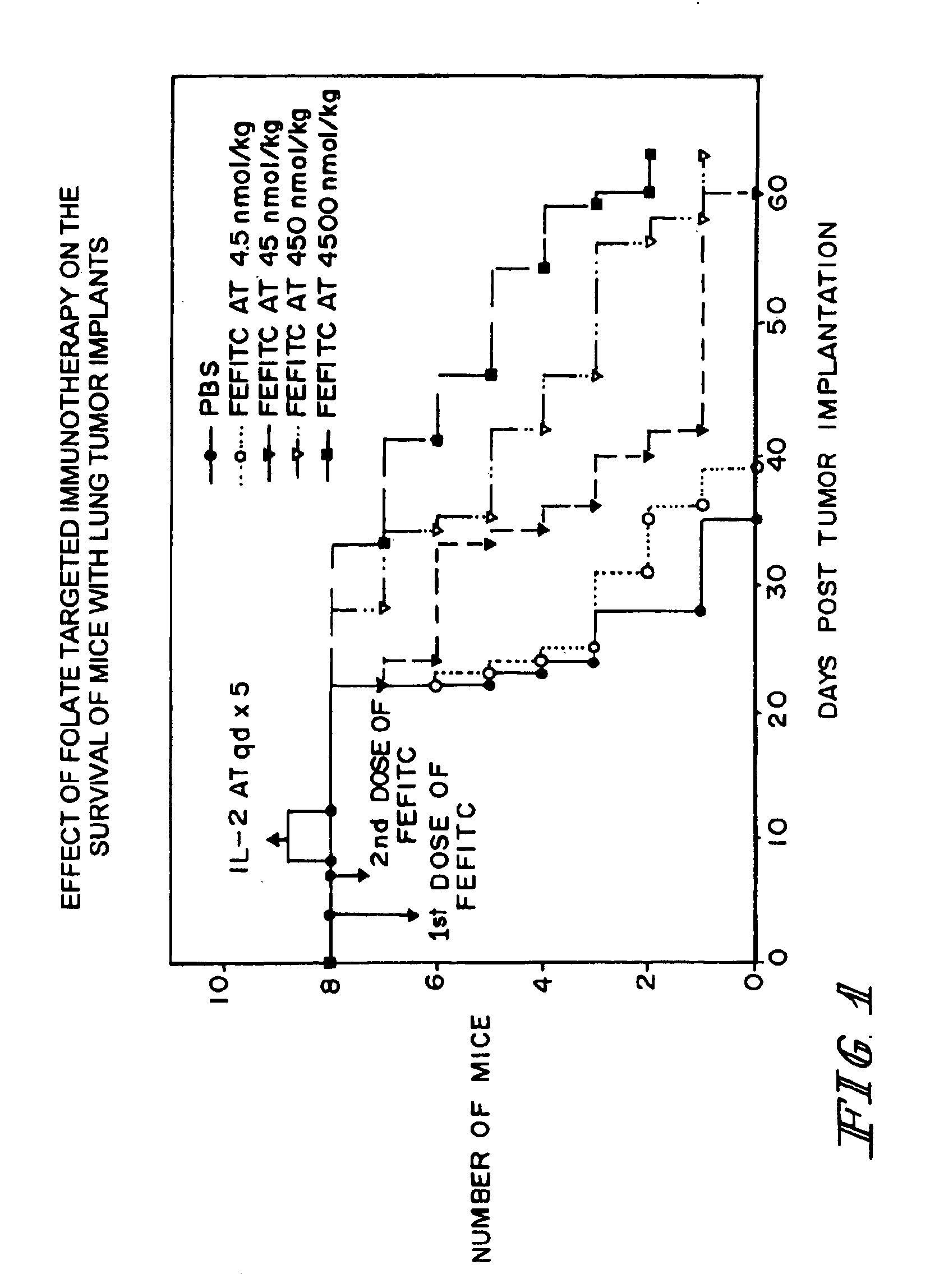
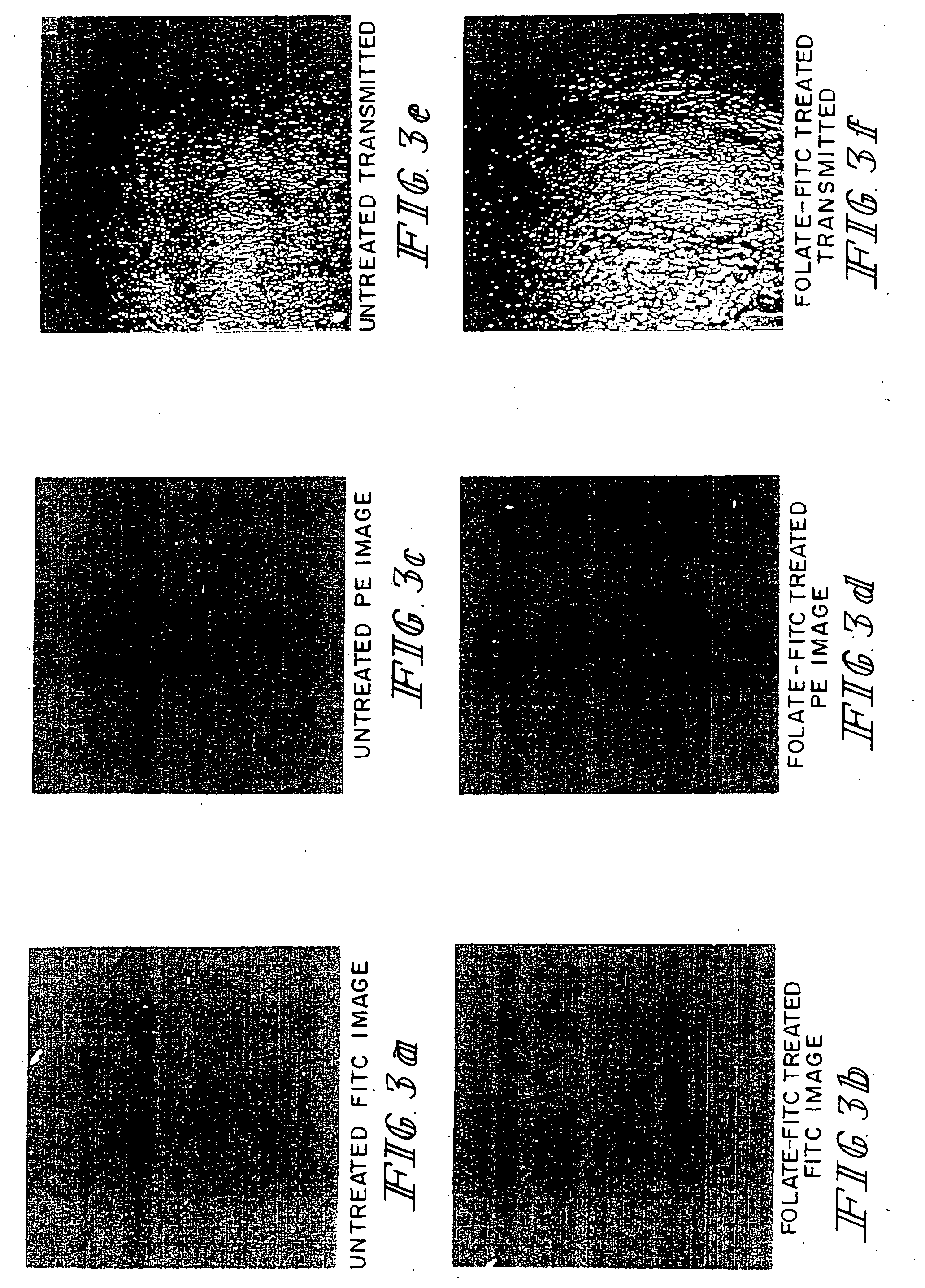
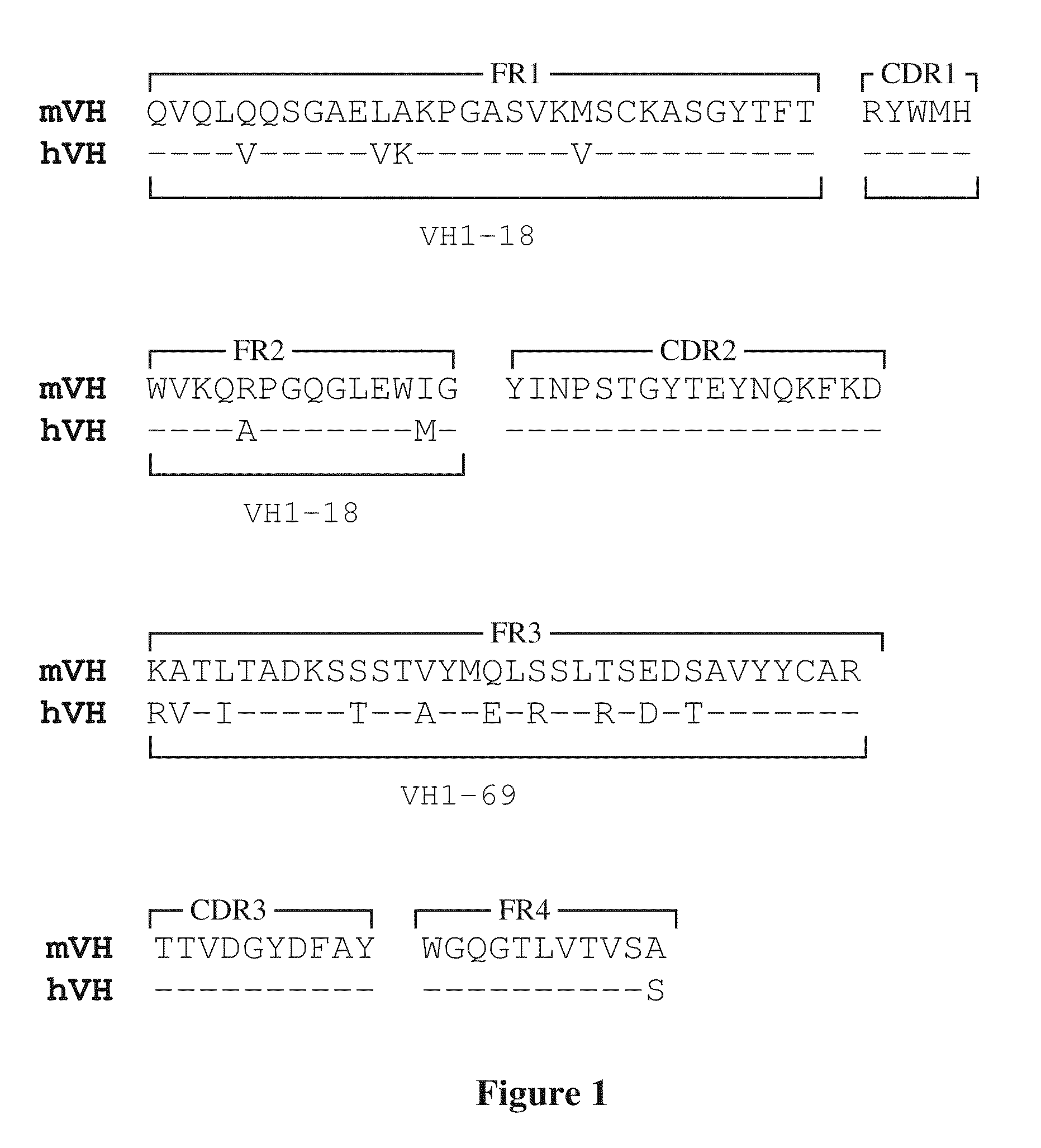
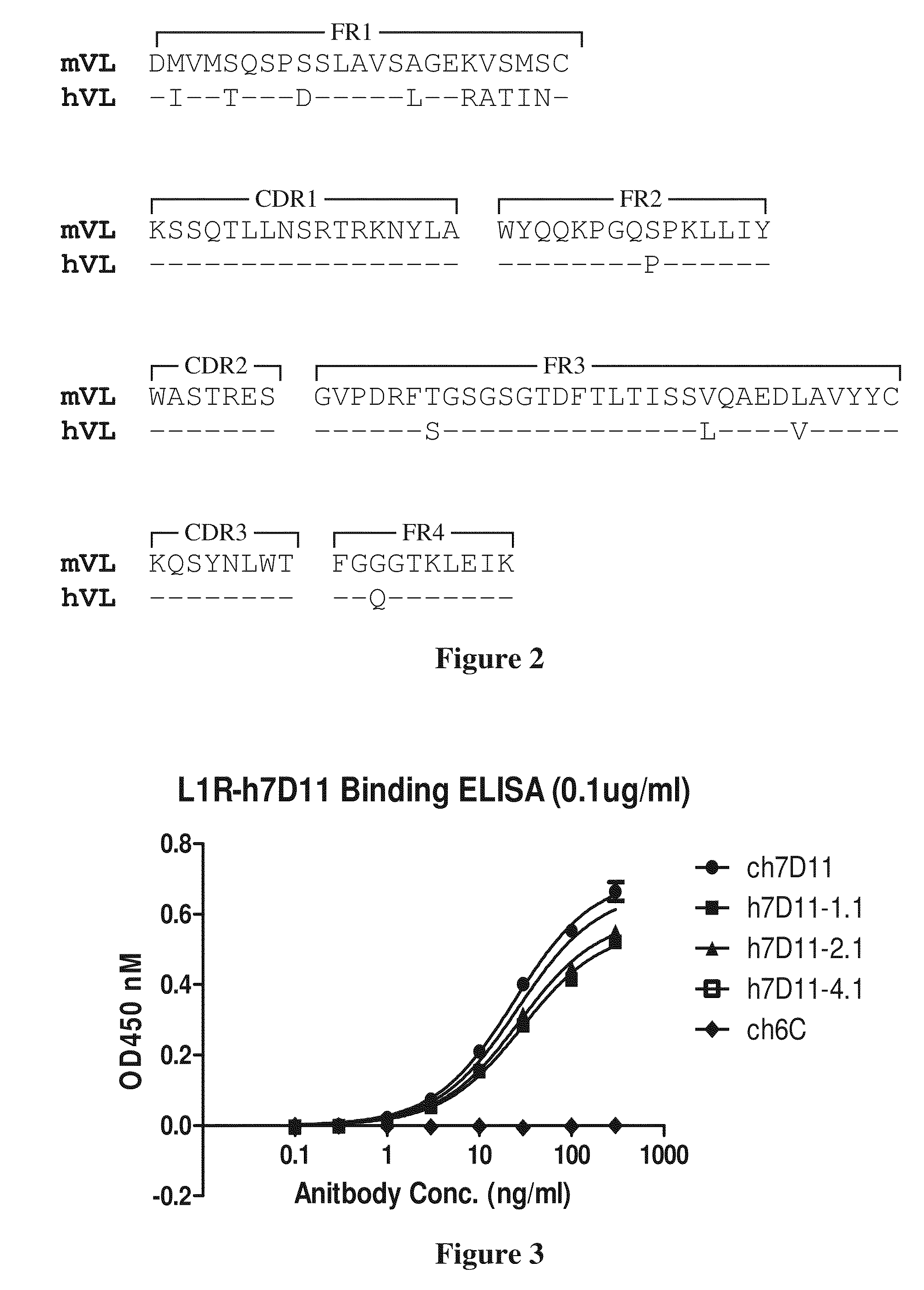
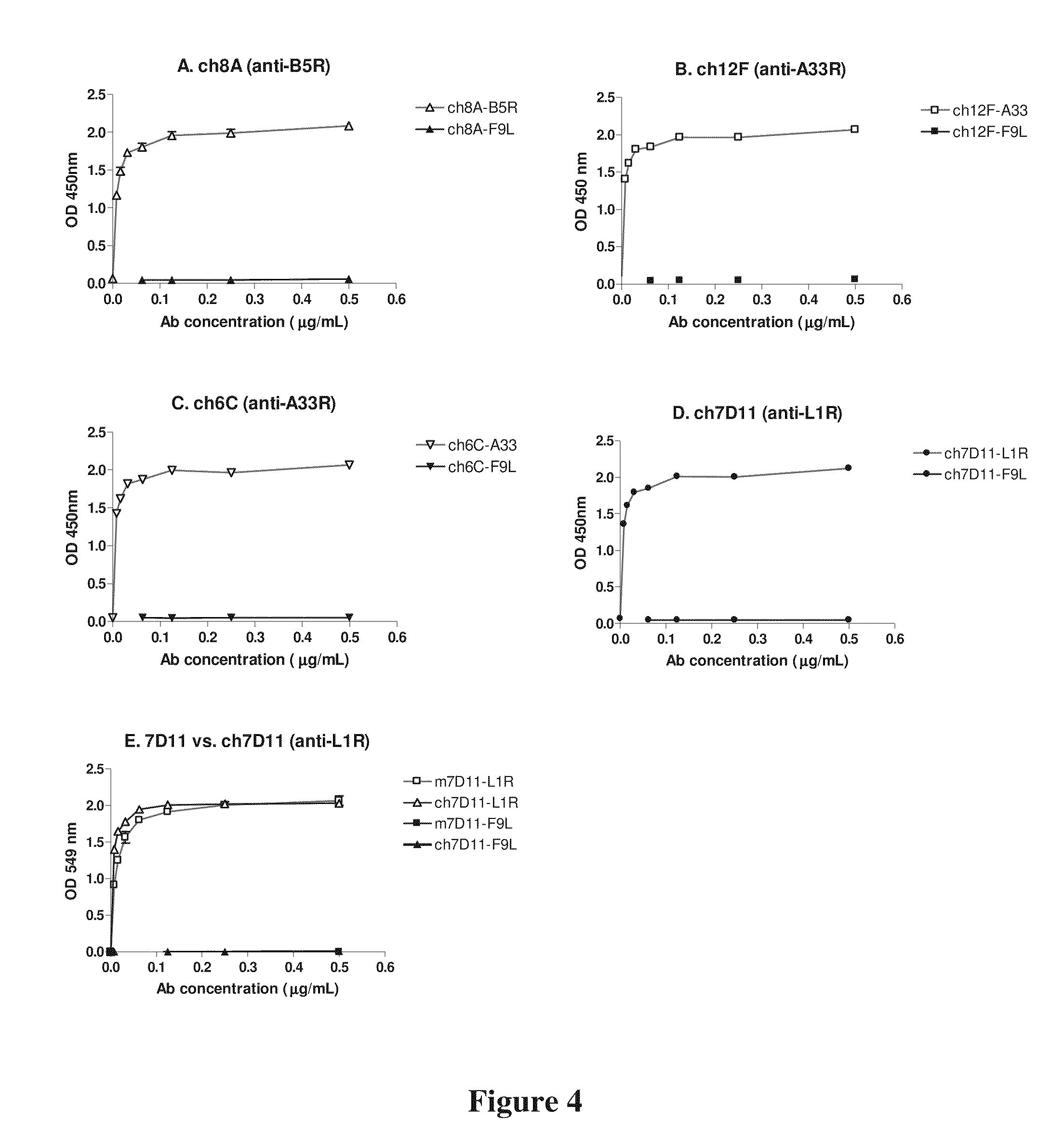
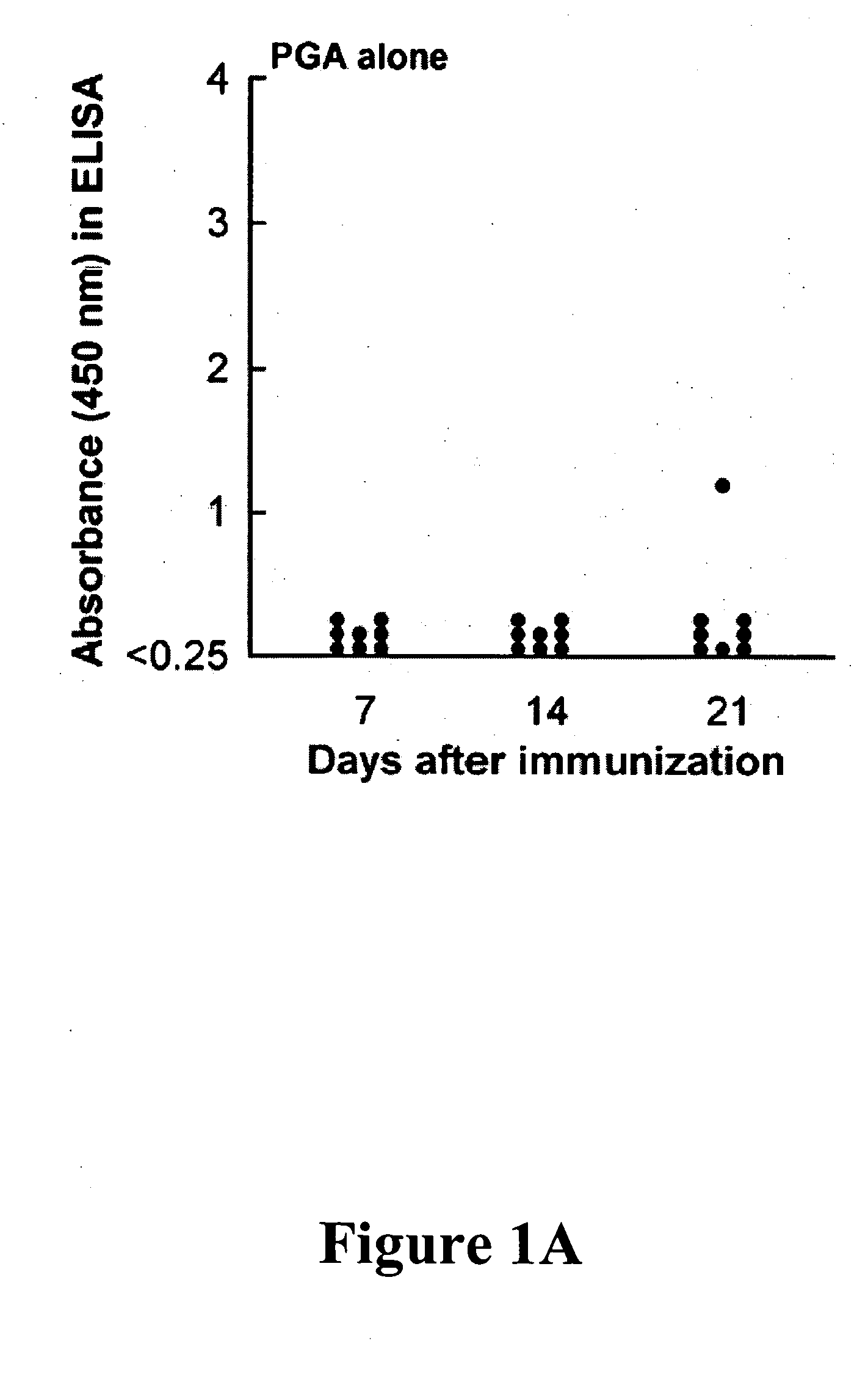
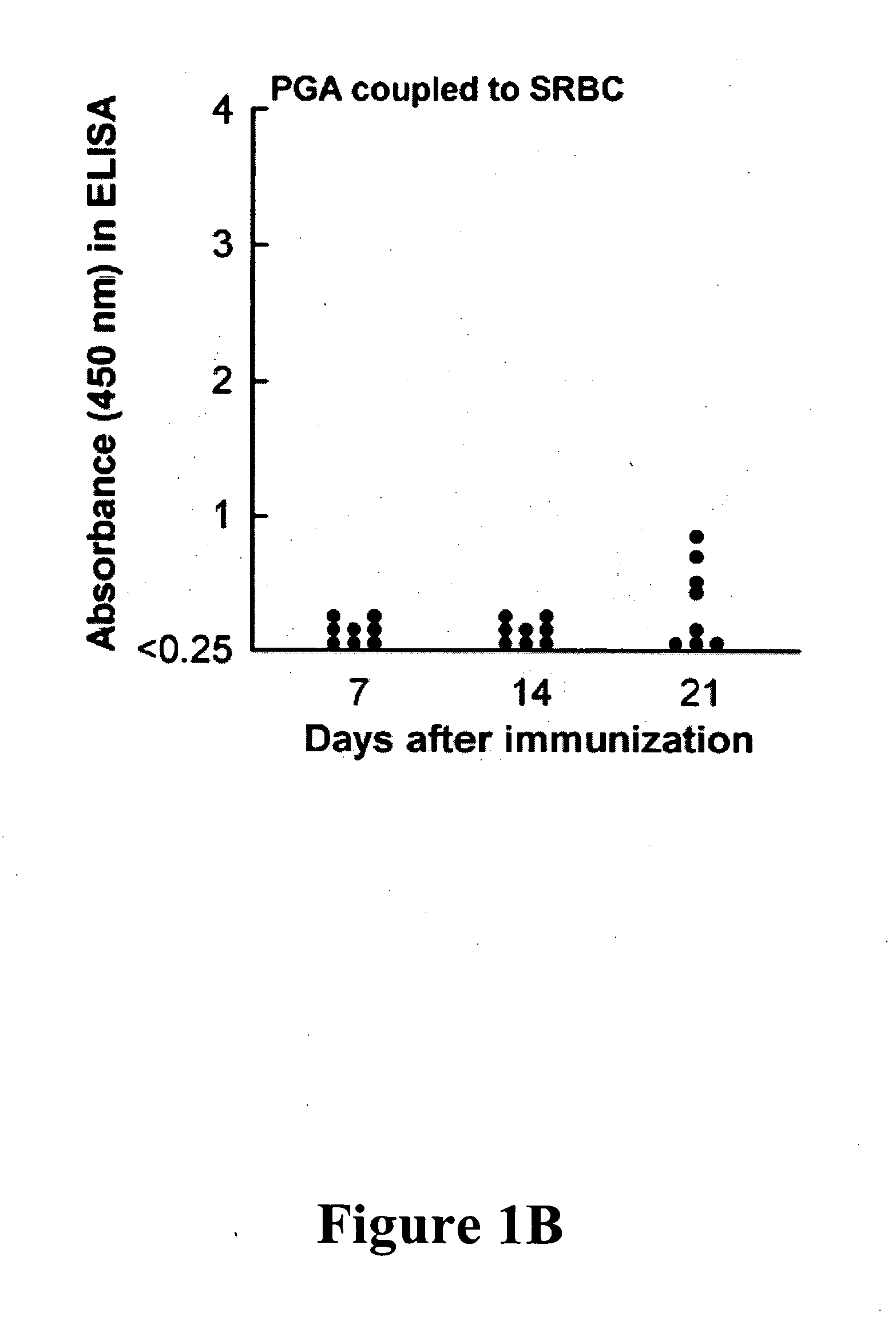
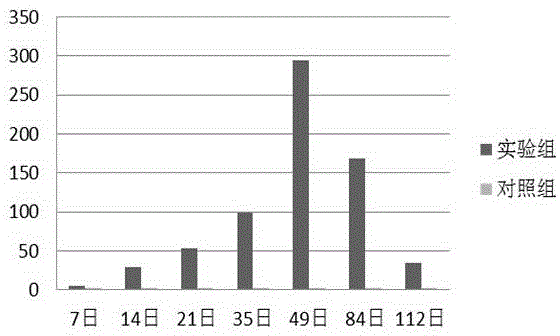
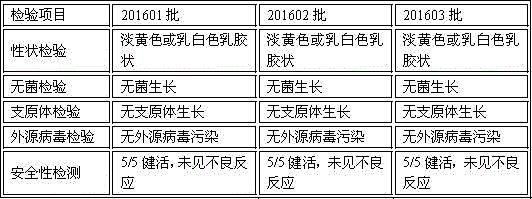
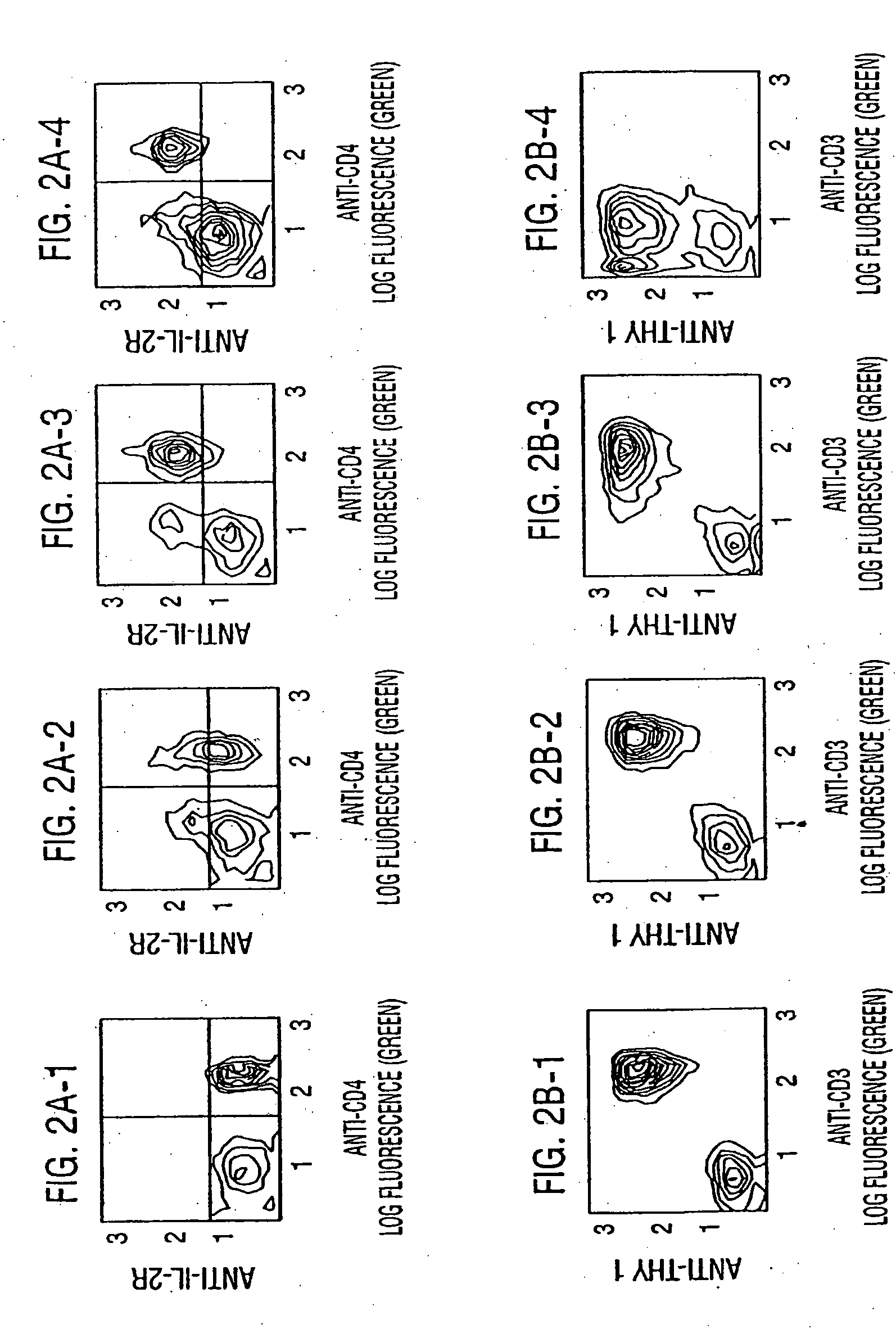
Patents
Literature
79 results about "Acquired Passive Immunity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Maternal passive immunity is a type of naturally acquired passive immunity, and refers to antibody-mediated immunity conveyed to a fetus or infant by its mother. Naturally acquired passive immunity can be provided during pregnancy, and through breastfeeding.
Method of treatment using ligand-immunogen conjugates
InactiveUS7033594B2Improve recognitionEnhance endogenous immune response-mediated eliminationAntibacterial agentsBiocideBinding siteCytotoxicity
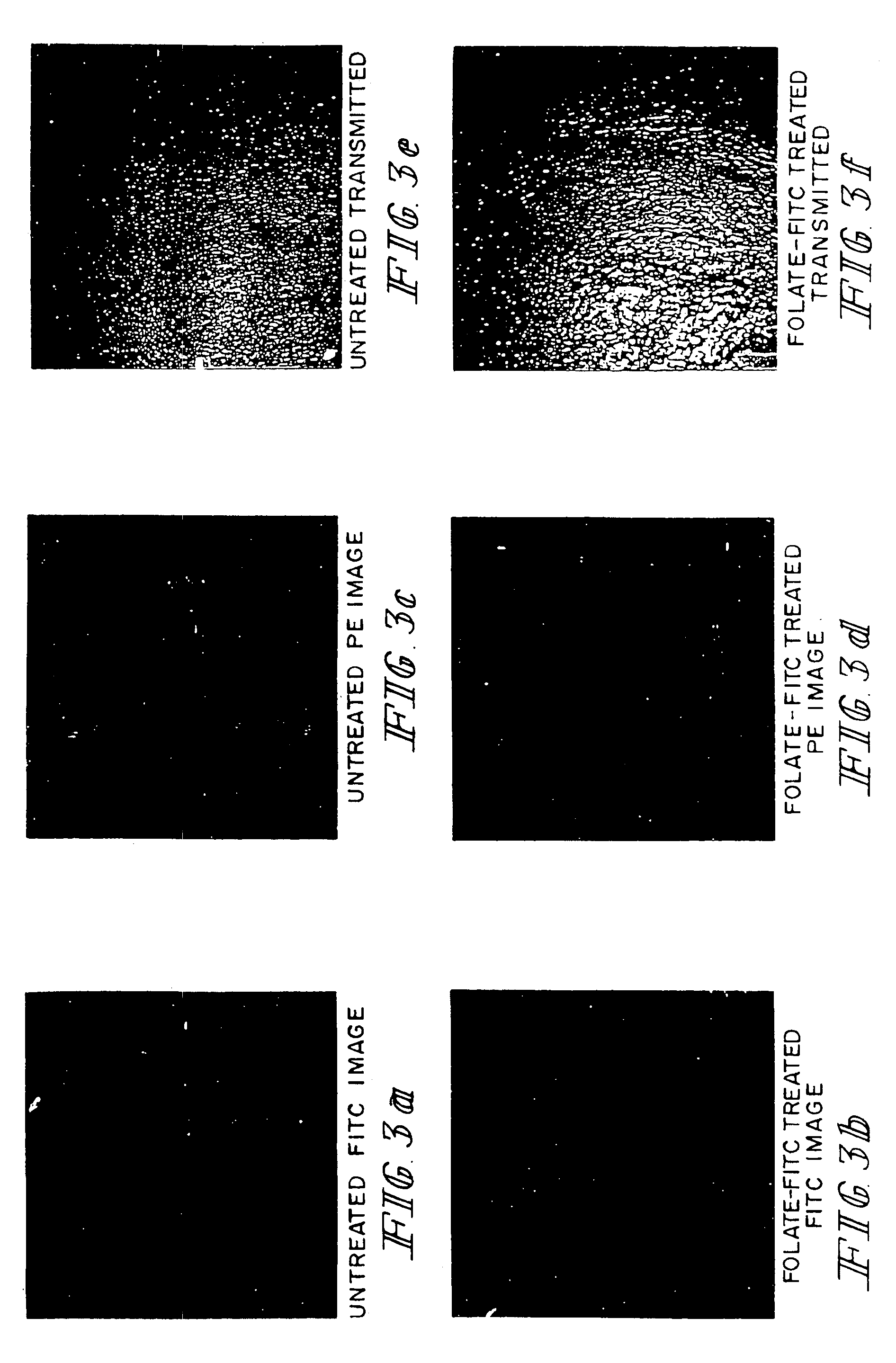
A method and pharmaceutical composition are provided for enhancing the endogenous immune response-mediated elimination of a population of pathogenic cells in a host animal wherein the pathogenic cells preferentially express, uniquely express, or overexpress a binding site for a particular ligand. The invention comprises administering the ligand conjugated to an immunogen to a host animal harboring the population of pathogenic cells. Antibodies, preexisting or administered to the host animal to establish a passive immunity, directed against the immunogen bind to the ligand-immunogen conjugate resulting in elimination of the pathogenic cells by the host's immune response. At least one additional therapeutic factor is administered selected from the group consisting of a cell killing agent, a tumor penetration enhancer, a chemotherapeutic agent, antimicrobial agent, a cytotoxic immune cell, and a compound capable of stimulating an endogenous immune response wherein the compound does not bind to the ligand-immunogen conjugate.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Polysaccharide vaccine for staphylococcal infections
ActiveUS20050118198A1Improving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsNatural sourceIntracellular
The invention relates to compositions of a deacetylated poly N-acetylated glucosamine (dPNAG) of Staphylococci. The dPNAG may be isolated from natural sources or synthesized de novo. The invention also relates to the use of dPNAG as a vaccine for inducing active immunity to infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermidis, other related coagulase-negative or coagulase-positive Staphylococci, and other organisms carrying the ica (intracellular adhesion) locus. The invention further provides methods of use for antibodies directed to dPNAG, particularly for inducing passive immunity to the same class of infections.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Methods for converting or inducing protective immunity
InactiveUS20090214533A1Reduced activityReduce functionAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsRegulatory T cellImmune complex deposition
The invention is based in part on the finding that suppressing regulatory T cell function is needed in order to convert passive immunity into active antigen-specific immunity. Generally, the methods of the invention comprise at least the combination of: (1) increasing the amount of immune complexes in the subject, wherein the immune complex comprises a target antigen and a immunoglobulin molecule comprising (i) a variable region specific to the target antigen and (ii) a Fc receptor binding region; and (2) inhibiting regulatory T cell function or decreasing / depleting the regulatory T cell population in the subject.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method of treatment using ligand-immunogen conjugates
InactiveUS20060067946A1Improve recognitionEnhance endogenous immune response-mediated eliminationAntibacterial agentsBiocideBinding siteCytotoxicity
A method and pharmaceutical composition are provided for enhancing the endogenous immune response-mediated elimination of a population of pathogenic cells in a host animal wherein the pathogenic cells preferentially express, uniquely express, or overexpress a binding site for a particular ligand. The invention comprises administering the ligand conjugated to an immunogen to a host animal harboring the population of pathogenic cells. Antibodies, preexisting or administered to the host animal to establish a passive immunity, directed against the immunogen bind to the ligand-immunogen conjugate resulting in elimination of the pathogenic cells by the host's immune response. At least one additional therapeutic factor is administered selected from the group consisting of a cell killing agent, a tumor penetration enhancer, a chemotherapeutic agent, antimicrobial agent, a cytotoxic immune cell, and a compound capable of stimulating an endogenous immune response wherein the compound does not bind to the ligand-immunogen conjugate.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Compositions for the Prevention and Treatment of Smallpox
The present invention relates to improved compositions for the prevention and treatment of smallpox, and in particular to the use of compositions containing an antibody that binds to an epitope found on the MV form of the smallpox virus and an antibody that binds to an epitope found on the EV form of the smallpox virus. The invention relates to such compositions, especially to non-blood derived antibody compositions, such as chimeric or humanized antibodies, and to methods for their use in imparting passive immunity against smallpox infection to individuals at risk of smallpox virus infection or who exhibit smallpox.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Mutants of clostridium difficile toxin B and methods of use
InactiveUS20080107673A1Antibacterial agentsAnimal cellsHospitalized patientsClostridium difficile infections
An active, or passive vaccine utilizing purified non-toxic mutant TcdB toxins from Clostridium difficile for humans and animals against infections caused by C. difficile and / or C. sordellii. Persons most potentially affected by C. difficile infections include hospitalized patients, infants, and elderly persons. The TcdB toxin mutant of the vaccine preferably lacks the toxicity of a native C. difficile TcdB toxin. A serum comprising antibodies raised to the TcdB toxin mutant is also available for treating humans or animals against C. difficile infections. The serum may be used in a method for conferring passive immunity against C. difficile. Antibodies to the TcdB toxin mutant may be used in diagnostic tests or in treatments to clear TcdB toxin from bodily fluids. The mutant TcdB toxin may be produced by recombinant methods using cDNA encoding the toxin, the cDNA contained for example in a plasmid or host cell.
Owner:BALLARD JIMMY D +1
Foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) resistant monoclonal antibody and identified epitope and application thereof
ActiveCN101724605AGood passive immunityImprove immunityVirus peptidesImmunoglobulins against virusesIn vivoAmino acid
The invention discloses a foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) resistant monoclonal antibody and an identified epitope and application thereof, and belongs to the field of prevention and control of the FMDV. The microbial collection number of a hybridoma cell line, which can secrete the neutralizing monoclonal antibody resisting to Asia-1 FMDV, is CGMCC No.2692; and the microbial collection number of the hybridoma cell line, which can secrete the neutralizing monoclonal antibody resisting to O-type FMDV, is CGMCC No.2691. The invention also discloses amino acid sequences of a conformational neutralizing epitope of the Asia-1 FMDV VP1 protein and a linear neutralizing epitope of the O-type FMDV VP1 protein which are identified by the two monoclonal antibodies respectively. In-vitro neutralization tests and in-vivo animal protection tests show that both the two monoclonal antibodies have excellent passive immunity effect, can be applied to emergency prevention of the FMDV and have excellent immunity effect on the passive immunity of the FMDV.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Device for administration of fluids
The present invention comprises a device for oral administration of a fluid source, preferably administration to an individual in need thereof, and methods for use of said device. In one embodiment of the invention, the device is used to administer colostrum to newborn calves, on order to generate higher levels of passive immunity in the calves than may be gained either from natural suckling or bottle feeding of colostrum. The fluid or liquid source according to the invention is preferably selected from the group consisting of milk, artificial milk substitutes, and colostrum. Liquid obtained from a domestic animal, including a bovine species.
Owner:TRACECO
Compositions for the prevention and treatment of smallpox
The present invention relates to improved compositions for the prevention and treatment of smallpox, and in particular to the use of compositions containing an antibody that binds to an epitope found on the MV form of the smallpox virus and an antibody that binds to an epitope found on the EV form of the smallpox virus. The invention relates to such compositions, especially to non-blood derived antibody compositions, such as chimeric or humanized antibodies, and to methods for their use in imparting passive immunity against smallpox infection to individuals at risk of smallpox virus infection or who exhibit smallpox.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Crucian herpesvirus disease JDORF25 vaccine as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104593388ASimple purification processReduce manufacturing costFungiVirus peptidesAntigenPichia pastoris
The invention discloses a crucian herpesvirus disease JDORF25 vaccine as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The crucian herpesvirus disease vaccine is recombinant protein truncated, optimized and translated by crucian herpesvirus type II immuno-related ORF25 gene, wherein the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2; the gene segment is synthesized, transferred to a yeast expression vector and screened by highly copying and cloning to finally obtain a high-expression recombinant protein pichia pastoris Km71 / CyHV-2-25 Pichia pastoris Km71 / CyHV-2-25, CCTCC NO: M2014570. The protein fermented by the yeast has the characteristics of high activity and high yield. The passive immunity test defines that the antigen protein can effectively prevent crucian herpesvirus disease and can also be mixed with adjuvants for highly effectively preventing crucian herpesvirus disease.
Owner:YANGTZE RIVER FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Preparation method of C-type clostridium perfringens toxin vaccine of piglet red dysentery
ActiveCN103432578AHigh potencyNo side effectsAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseAdjuvant
The invention relates to a preparation method of a C-type clostridium perfringens toxin vaccine of piglet red dysentery. The preparation method comprises the following steps of inoculating strains NCTC (National Collection Of Type Culture) 3180 of the C-type clostridium perfringens into a blood plate culture medium for carrying out anaerobic cultivation for 36 hours at 37 DEG C; carrying out shake cultivation on the culture by adopting a homemade toxin-producing medium (100 ml of PBS (Phosphate Buffer Solution), 2g of peptones, 1g of dextrin, 2g of yeast extracts, and 1.2g of L- arginine) under an anaerobic environment; inactivating the culture, filtering and adding an adjuvant to prepare the C-type clostridium perfringens toxin vaccine of the piglet red dysentery. During a using process, intramuscular injection is respectively adopted once a month and half a month before the delivery of a sow, wherein the dosage is 5-10 ml at a time. The C-type clostridium perfringens toxin vaccine of the piglet red dysentery is used for the sow at the later immunological gestation period, so that piglets obtain passive immunity through colostrums, and therefore, piglet red dysentery can be prevented. Moreover, the C-type clostridium perfringens toxin vaccine of the piglet red dysentery can be used for preventing sheep struck and calf enterotoksemia, so that the popularization of the C-type clostridium perfringens disease can be effectively controlled.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bivalent vaccine for preventing porcine epidemic diarrhea and Escherichia coli
ActiveCN103861098AImprove survival rateImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsDigestive systemEscherichia coliDisease
The invention provides a bivalent vaccine for preventing porcine epidemic diarrhea and Escherichia coli. The bivalent vaccine comprises an antigen and a vaccine adjuvant, wherein the antigen is a fimbriae antigen of porcine epidemic diarrhea bacterium and Escherichia coli K88, K99 and 987P conserved under CGMCC No. 8503. The bivalent vaccine for preventing porcine epidemic diarrhea and Escherichia coli has good immunogenicity, and can quickly produce antibody after immunity, the produced antibody has high titer and long preservation period and can maintain for long time, the immunizing dose is small, and the adjuvant selected is easily injected; the bivalent vaccine can be used for preventing two types of diseases, piglets given birth by pregnant sows which are inoculated with the vaccine before hybridization can obtain better passive immunity and have strong immunity against virulent strains, and therefore the survival rate of the piglets is improved.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
Device for administration of fluids
The present invention comprises a device for oral administration of a fluid source, preferably administration to an individual in need thereof, and methods for use of said device. In one embodiment of the invention, the device is used to administer colostrum to newborn calves, on order to generate higher levels of passive immunity in the calves than may be gained either from natural suckling or bottle feeding of colostrum. The fluid or liquid source according to the invention is preferably selected from the group consisting of milk, artificial milk substitutes, and colostrum. Liquid obtained from a domestic animal, including a bovine species.
Owner:TRACECO
Stabilized liquid egg material for extended shelf life
ActiveUS20110159002A1Extended shelf lifeMaintaining binding activityEgg immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against virusesLiquid productPreservative
The present invention is directed to shelf-stable liquid egg material, methods for making the same, and method of using the same. The present invention is also directed to an animal feed supplement containing a stabilized IgY antibody titer in liquid eggs stored at room temperature for extended periods of time with the use of glycerol and preservatives. The stabilized liquid whole egg or stabilized liquid yolks of the egg containing non-specific or elevated specific IgY titer may be used as animal feed supplements animals to provide passive immunity to these animals. The stabilized nature of the IgY and liquid egg allows for extended shelf life of these liquid products at room temperature.
Owner:R&D LIFESCI
Vaccine to control equine protozoal myeloencephalitis in horses
The present invention provides vaccines and methods for making the vaccines that actively or passively protect an equid or other animal against Sarcocystis neurona. In particular, the present invention provides vaccines that provide active immunity which comprise a polypeptide or DNA vaccine that contains or expresses at least one epitope of an antigen that has an amino acid sequence substantially similar to a unique 16 (±4) kDa antigen and / or 30 (±4) kDa antigen of Sarcocystis neurona. The present invention further provides a vaccine that provides passive immunity to Sarcocystis neurona comprising polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies against at least one epitope of an antigen substantially similar to a unique 16 (±4) kDa antigen and / or 30 (±4) kDa antigen of Sarcocystis neurona.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Compositions and methods for detection, prevention, and treatment of anthrax and other infectious diseases
ActiveUS20090280513A1High molecular weightEasy to produceAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsSerum igeAgonist
Compositions and methods for the detection, prevention, or treatment of anthrax or other infectious diseases. In one aspect, the present invention provides methods of immunizing humans or animals against Bacillus anthracis or other capsulated pathogens. The methods include administering a capsular polypeptide of a pathogen of interest and a CD40 agonist to a human or animal. The capsular polypeptide or the CD40 agonist is administered in such an amount or frequency that an immunoprotective response can be elicited in the human or animal against the pathogen of interest. In another aspect, the present invention provides methods of using passive immunization with anti-capsular polypeptide antibodies to prevent or treat infections caused by Bacillus anthracis or other pathogens. In yet another aspect, the present invention provides methods useful for diagnosis of anthrax by detection of capsular polypeptide in serum or other biological samples.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus variant inactivated vaccine and application thereof
InactiveCN106729691AImproving immunogenicityPassive immunity is goodSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsEpidemic diarrheaNeutralizing antibody
The invention provides a porcine epidemic diarrhea virus variant inactivated vaccine which is prepared after inactivating a diarrhea virus variant PEDV / CH / BJ / 2014. The vaccine is excellent in immunogenicity; after a sow is inoculated with the vaccine before parturition, a neutralizing antibody is rapidly produced, the antibody titer is high, the maintenance time is long, a piglet of the inoculated sow litter acquires better passive immunity, the piglet is effectively protected against the attack of the epidemic diarrhea virus, and the survival rate of the piglet is increased.
Owner:BEIJING DAWEIJIA BIOTECH SHARE CO LTD
Inactivated bovine scours vaccines, processes and method of preventing bovine scours
InactiveUS6974577B2Prevention and control of diseaseBacterial antigen ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseBacteroidesDisease
Inactivated scours vaccines for immunization and protection of bovine animals from disease caused by infection with bovine rotavirus and bovine coronavirus, which comprise and effective amount of at least one inactivated viral strain are described. Polyvalent inactivated vaccines further comprising an effective amount of an antigenic component which is protective against one or more additional pathogenic organisms or viruses are also disclosed. Said vaccines are prepared from one or more strains of rota- and coronavirus, C. perfringens Type C bacteria and E. coli bacteria, and combinations thereof. Preferably, a polyvalent inactivated vaccine is provided for parenteral administration. Passive immunity is achieved in neonatal calves via immunization of pregnant cows prior to birth.
Owner:ELANCO TIERGESUNDHEIT AG
Anti-Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Monoclonal Antibody and Its Recognized Epitope and Application
ActiveCN102277333AGood passive immunityImprove immunityImmunoglobulins against virusesMicroorganism based processesIn vivoNeutralization epitope
The invention discloses a monoclonal antibody resisting the foot and mouth disease virus, epitope identified by the monoclonal antibody, as well as application of the monoclonal antibody, and belongs to the field of prevention and control of the foot and mouth disease. The hybridoma cell line capable of excreting the neutralizing monoclonal antibody resisting O-type FMDV (foot and mouth disease virus) has a microbial preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) 2691. The invention also discloses amino acid sequences of linear neutralization epitope of O-type FMDV VP1 protein identified by the monoclonal antibody respectively. In-vitro neutralization tests and in-vivo animal protection tests prove that: the monoclonal antibody disclosed by the invention has excellent passive immune effect, can be applied to emergency prevention of the foot and mouth disease, and plays an excellent immune effect to the passive immunity of the foot and mouth disease.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Human monoclonal antibodies and methods for producing the same
The present invention provides for methods of producing human monoclonal antibodies against a wide variety of antigens including bacterial and viral antigens, as well as tumor antigens, and various autoantigens. Also provided are the antibodies themselves, nucleic acids encoding such antibodies, cells producing such antibodies, and methods of using such antibodies for diagnostic assays and passive immunity against disease states such as infection and cancer.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Methods and compositions for promoting immunopotentiation
InactiveUS20060078557A1Increasing cell proliferationRapid rise in intracellular calciumImmunoglobulin superfamilyVirus peptidesAbnormal tissue growthFungal microorganisms
This invention discloses immunopotentiating agents which stimulate an immune response. These agents are categorized into single agents that act directly, adjuvants added concurrently with the agents, or heteroconjugates. Heteroconjugate agents elicit or enhance a cellular or humoral immune response which may be specific for an epitope contained within an amino acid sequence. Enhanced hematopoieses by bone marrow stem cell recruitment was also a result of administering some of these agents. Examples of immunopotentiating agents include monoclonal antibodies and proteins derived from microorganisms (e.g., enterotoxins) which activate T cells. One method of treatment disclosed uses only the immunopotentiating agent to stimulate the immune system. Another uses adjuvants in combination with the agent. A third method employs heteroconjugates. Heteroconjugates comprise: (a) an immunopotentiating protein which is characterized as having an ability to stimulate T cells; and (b) a second protein having an amino acid sequence which includes an epitope against which a cellular or humoral response is desired. This invention also relates to a method of preparing the heteroconjugate, and to a method of stimulating the immune system in vivo in a novel way. One route of stimulation is to activate T cells, in some instances, specific subsets of T cells, by administering heteroconjugates containing an immunopotentiating protein and a second protein, to mammals. For this method of treatment, the second protein in the heteroconjugate is derived from abnormal or diseased tissue, or from an infectious agent; alternatively, the second protein is produced synthetically by standard methods of molecular biology. Sources of the second protein include tumors, viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoal or metozoal parasites. Monoclonal antibodies or T cells prepared from mammals whose immune systems have responded to administration of the heteroconjugate may be produced and administered to induce passive immunity. A method of preparing a hybridoma which secretes said monoclonal antibodies and use of these monoclonal antibodies and T cells, are also disclosed. This invention is also directed to a vaccine comprising the heteroconjugate.
Owner:BLUESTONE JEFFERY A
HPV6L1 protein-resisting antibody, preparation method therefor and application thereof
ActiveCN105153302ANo cross reactionStrong specificityImmunoglobulins against virusesTissue cultureHeavy chainCdr3 region
The invention provides an antibody or an antigen bound part which is specifically bound to a human papilloma virus low-risk sub type-type 6 L1 protein and / or VLP. The antibody or the antigen bound part comprises CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 regions of a heavy chain variable region shown in SEQ ID NO. 1-3 and CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 regions of a light chain variable region shown in SEQ ID NO. 4-6. The antibody or the antigen bound part which is specifically bound with the human papilloma virus low-risk sub type-type 6 L1 protein and / or VLP has no cross reactions with most of other HPV sub types such as HPV11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68 and the like, is high in specificity, has a characteristic of neutralizing a HPV6 pseudovirus and blocking infection of the pseudovirus, and is high in affinity. A twin-antibody sandwiched ELISA detection kit established by two antibodies can be used for detecting the presence or level of HPV6L1 protein and the antibody can be further used for treatment of patients and passive immunity of susceptible population and has a good application prospect.
Owner:NAT VACCINE & SERUM INST
Preparation method of gosling plague inactivated vaccines as well as prepared inactivated vaccines
ActiveCN106310247AImprove product qualityLower protein contentMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsYolkEmbryo
The invention relates to a production method of gosling plague inactivated vaccines, and belongs to the technical field of biological products. The method comprises the following steps: (1) screening healthy and susceptible goose embryos; (2) preparing virus liquid for production; (3) determining titer of virus liquid, inactivating virus liquid, preparing vaccines, and carrying out split charging. The breeder geese are immunized, so that specific antibodies of gosling plague virus in serum and hatching egg yolks of breeder geese during egg producing period are at a high level, and after hatched goslings are hatched, the yolks are absorbed in order to produce good passive immunity protection effects. The vaccines have the advantages of high safety without hazardness due to distribution of virus, multitime immunization, substantially reduced human cost, and the like.
Owner:扬州优邦生物药品有限公司
Oral use of specific antibodies for intestinal health
InactiveUS20070154484A1Snake antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaEscherichia coliRotavirus RNA
Methods and compositions are provided to treat enteric disease. The methods and compositions use passive immunity to treat diseases of the gut, including diseases caused by Salmonella sp., E. Coli, Clostridium difficile, Clostridium perfringens A, Clostridium perfringens C, Clostridium perfringens D, canine distemper, feline distemper, Rotavirus, and Parvovirus. Specific antibodies are administered orally to a subject to improve intestinal health.
Owner:MG BIOLOGICS
Preparation method and applications of anti-pseudorabies virus pig origin monoclonal antibody
InactiveCN108203716AMake up for the damageEnhance phagocytosisHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against virusesPig farmsPlasmid dna
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and discloses a preparation method and applications of an anti-pseudorabies virus pig origin monoclonal antibody. The preparation method comprises following steps: positive hybridoma cells capable of realizing stable secretion of anti-pseudorabies virus (PRV) glycoprotein monoclonal antibodies are screened; secretion of the monoclonal antibodies is carried out; enlarge culture is carried out; enrichment, purification, and sequencing are carried out; design of corresponding specific primers is carried out, pig origin modification is carried out, cloning is carried out using a virus gene carrier or a non-virus gene carrier (including plasmid DNA and minicircle DNA), large scale production of different pig origin monoclonal antibodies iscarried out using insect cells or CHO cell fermentation, or the above pig origin monoclonal antibody gene carrier is introduced into pigs; injection, or feeding through nasal feeding and spraying areadopted for neutralization of pseudorabies virus with the anti-pseudorabies virus pig origin monoclonal antibodies, so that passive immunity is adopted for purifying of pseudorabies virus positive pig farms, and preventing and treating of porcine pseudorabies.
Owner:SHENZHEN JASON INTELLIGENT BIOTECH CO LIMLTED PRC
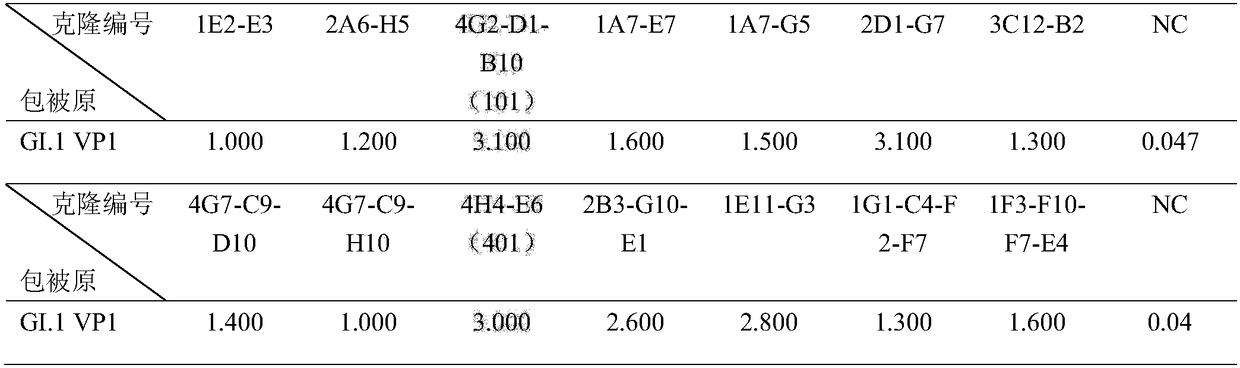
Antibody capable of realizing specific binding with norovirus GI.1 gene type VP1 protein and/or VLP, and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN109180810AStrong specificityHigh affinityBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against virusesHeavy chainNorovirus GI
The invention discloses an antibody capable of realizing specific binding with norovirus GI.1 gene type VP1 protein and / or VLP, and a preparation method and applications thereof. The antibody containsCDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 zones containing heavy chain variable regions represented by SEQ ID NO.1-3, and / or CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 zones containing light chain variable regions represented by SEQ ID NO.4-6.No cross reaction of the norovirus GI.1 gene type VP1 protein and / or VLP antibody or an antigen binding part with GII.4 gene type is caused; the specificity is high; the antibody is capable of blocking binding of norovirus GI.1 gene type VP1 protein and / or VLP with HBGA; the endophilicity is high; the antibody can be used for research and development of kits used for detecting existing or contentof norovirus GI.1 gene type VP1 protein and / or VLP in samples, and treatment on patients and passive immunity on susceptible population, and is promising in application prospect.
Owner:NAT VACCINE & SERUM INST +1
Porcine epidemic diarrhea live vaccine
ActiveCN103933561ALow toxicityImproving immunogenicityDigestive systemAntiviralsAntigenEpidemic diarrhea
The present invention provides a porcine epidemic diarrhea (PED) live vaccine, which contains an antigen and a protection agent, wherein the antigen is a PED virus SD10 strain having the preservation number of CGMCC No.8503. According to the present invention, the used antigen PED virus SD10 strain has characteristics of low toxicity and good immunogenicity, the antibody is rapidly produced after the prepared vaccine is adopted to immunize, the produced antibody has characteristics of high titer, long maintaining time, long storage time and low immune dose, and piglets produced by pregnant sows can achieve good passive immunity through immunization injection before mating, such that the piglets can produce strong immunity and can resist virulent virus attacks so as to improve the piglet survival rate.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
Mimic epitope peptide resistant to IL-6 receptor Tocilizumab and application of mimic epitope peptide
ActiveCN104945485AInhibitory activityIncrease painPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticDiseaseReceptor
The invention discloses mimic epitope peptide resistant to IL-6 receptor Tocilizumab and application of the mimic epitope peptide. The amino acid sequence of the mimic epitope peptide is shown in SEQ ID NO.1-4, the sequence of the mimic epitope peptide may be different from that of an IL-6 receptor, the mimic epitope peptide and the IL-6 receptor are similar in spatial structure, and the mimic epitope peptide and the IL-6 receptor have the same biological activity. Antibodies produced through the mimic epitope immunostimulation body can recognize mimic epitope and can also recognize the IL-6 receptor so that the activity of the IL-6 can be inhibited, the effect same as that of the Tocilizumab is generated, and meanwhile, the problem that passive immunity needs to be performed many times is solved. The mimic epitope peptide resistant to the IL-6 receptor Tocilizumab provides a new drug path for preventing and treating rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases.
Owner:杨麟 +2
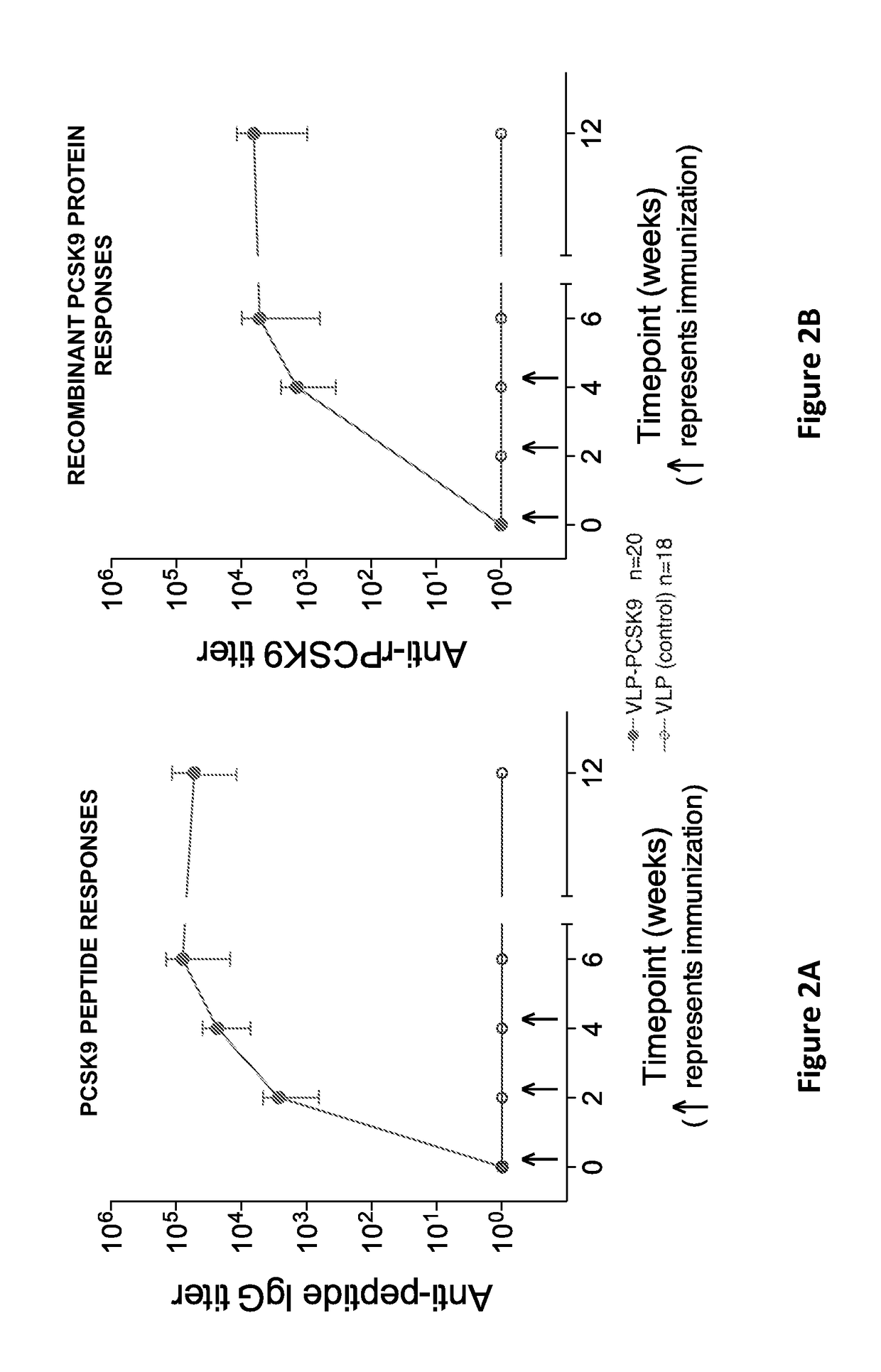
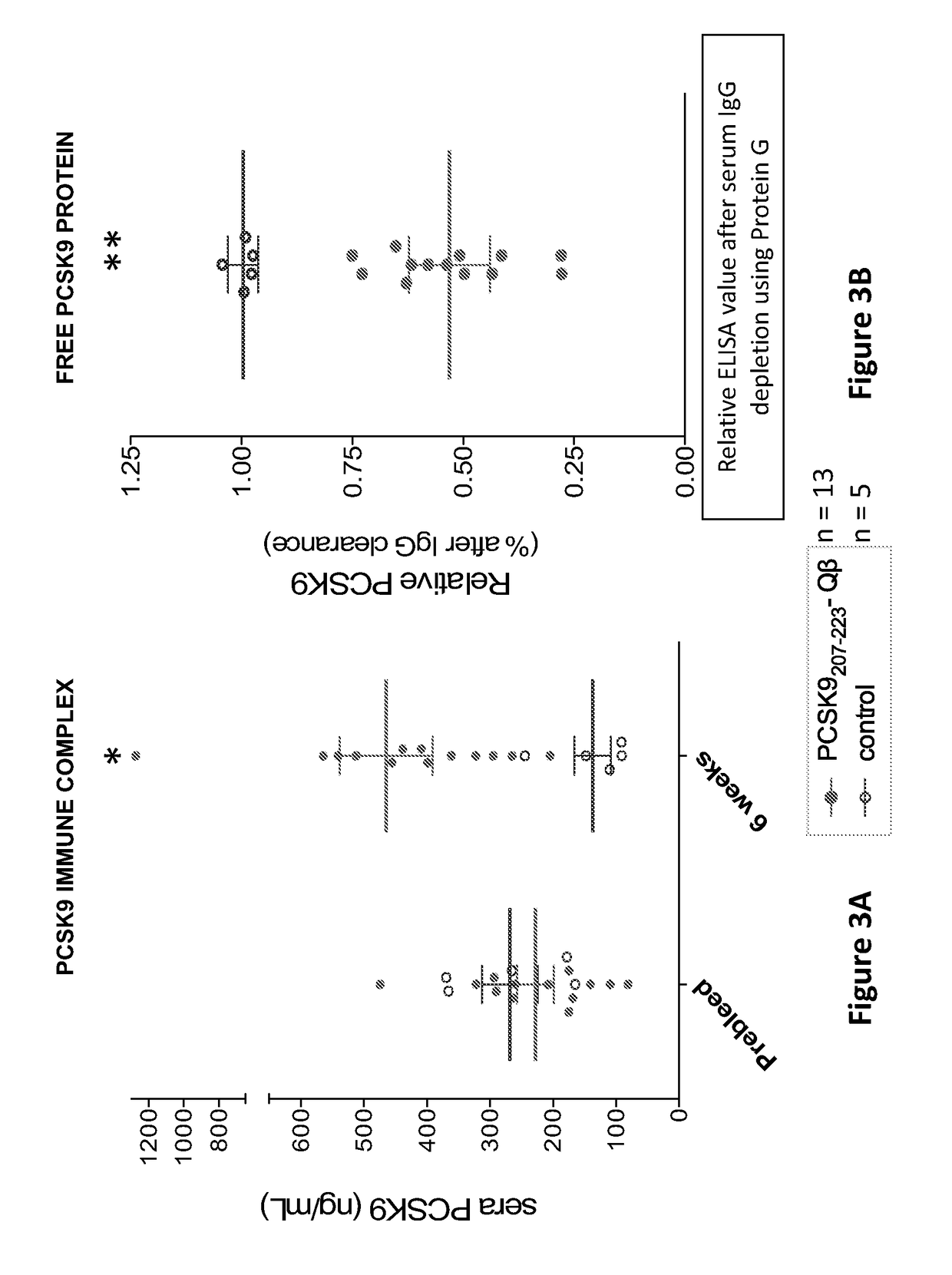
Pcsk9 vaccine and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20170189503A1Preventing and alleviating and treating dyslipidemiaPeptide/protein ingredientsVertebrate antigen ingredientsDyslipidemiaLower blood cholesterol
Owner:STC UNM
Methods and reagents for the detection of antibodies to adenovirus
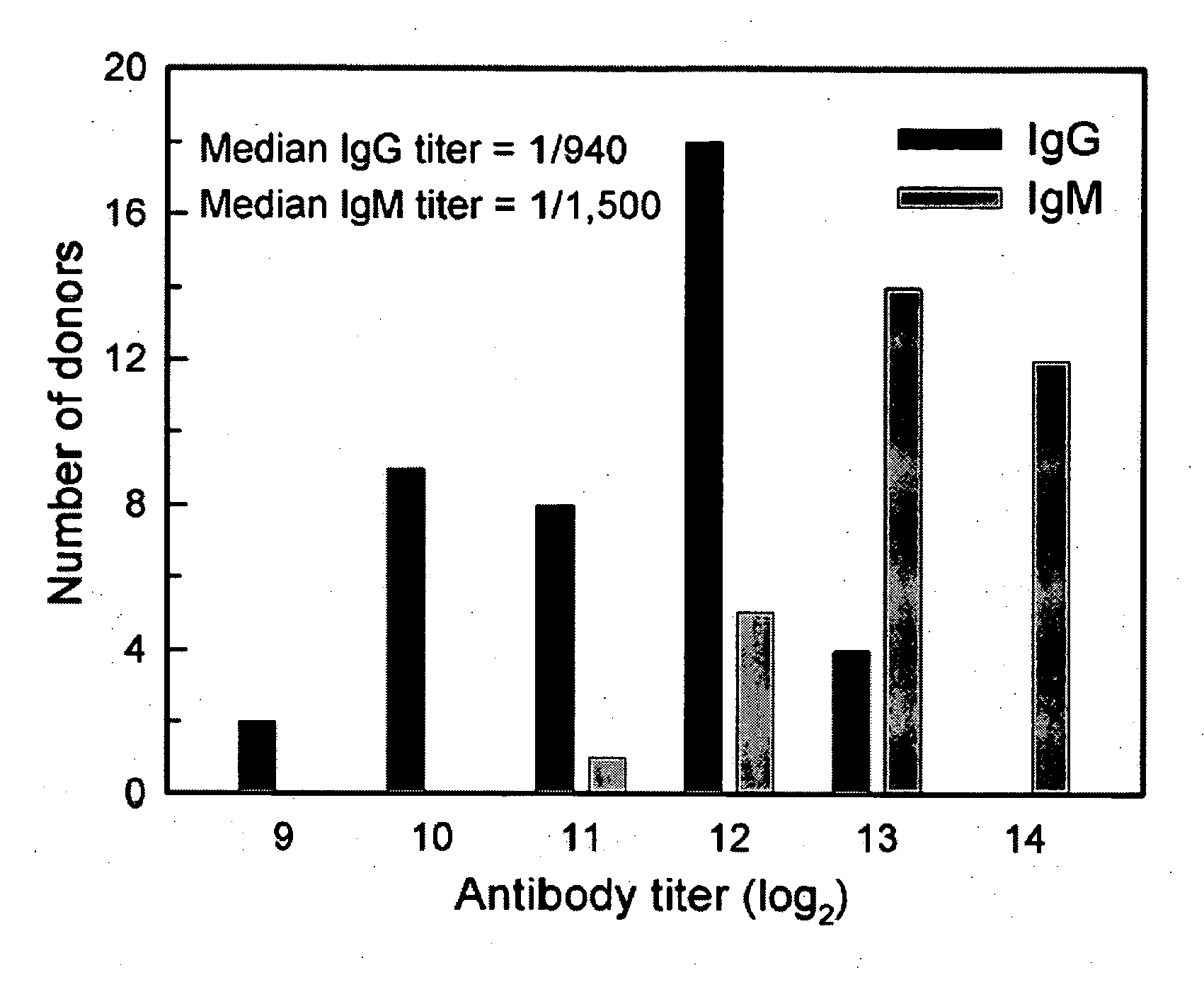
InactiveUS6964843B1Viral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayAdenovirus infection
The present invention provides methods and reagents for detecting antibodies to adenovirus. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention is useful for detecting antibodies to adenovirus serotype 5. In a further preferred embodiment, the present invention can be used in a biosensor-based assay. It is contemplated that the present invention is useful to detect antibodies for ascertaining adenovirus infection, evaluating patient response to gene therapy using adenovirus vectors, developing vaccines to adenovirus infection, developing therapeutics for inducing passive immunity to adenovirus infection, as well as other uses.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com