Preparation method of gosling plague inactivated vaccines as well as prepared inactivated vaccines
An inactivated vaccine and gosling plague technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of infection, epidemic prevention failure, foreign virus contamination, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the content of impurities, increasing the content of viruses, and increasing the loss of antigens
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Screening of healthy susceptible goose embryos
[0025] In view of the limitations of the propagation conditions of gosling plague virus, only non-immune healthy susceptible goose embryos can be selected as the breeding carrier for seed virus preparation, seed virus production and venom production. The screening and detection of non-immune goose embryos has become one of the important tasks in the development and production of vaccines. In this study, the detection of GPV agar antibody in the yolk of non-immune goose embryos and the detection of gosling plague virus in goose embryos before inoculation ensured that non-immune goose embryos The quality of immune goose embryos, the main steps include gosling plague agar diffusion test antigen production and quality standards, detection of gosling plague agar diffusion antibody and gosling plague virus antigen detection method, and at the same time according to the appendix of the 2010 edition of "Chinese Veterinary Pharmaco...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Virus inoculation and culture preparation of virus liquid
[0068] Virus breeding
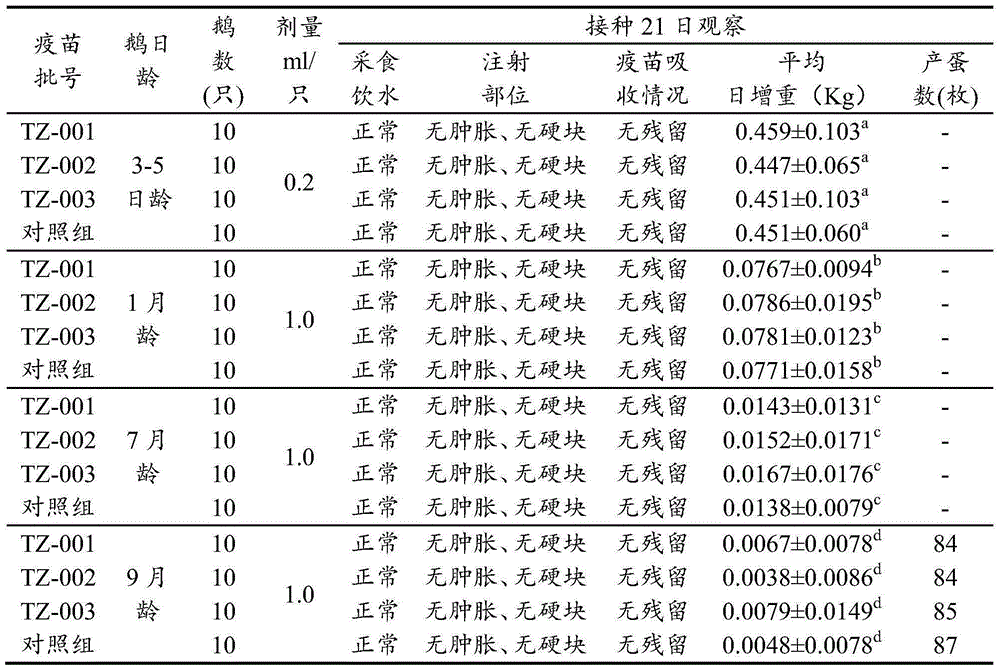
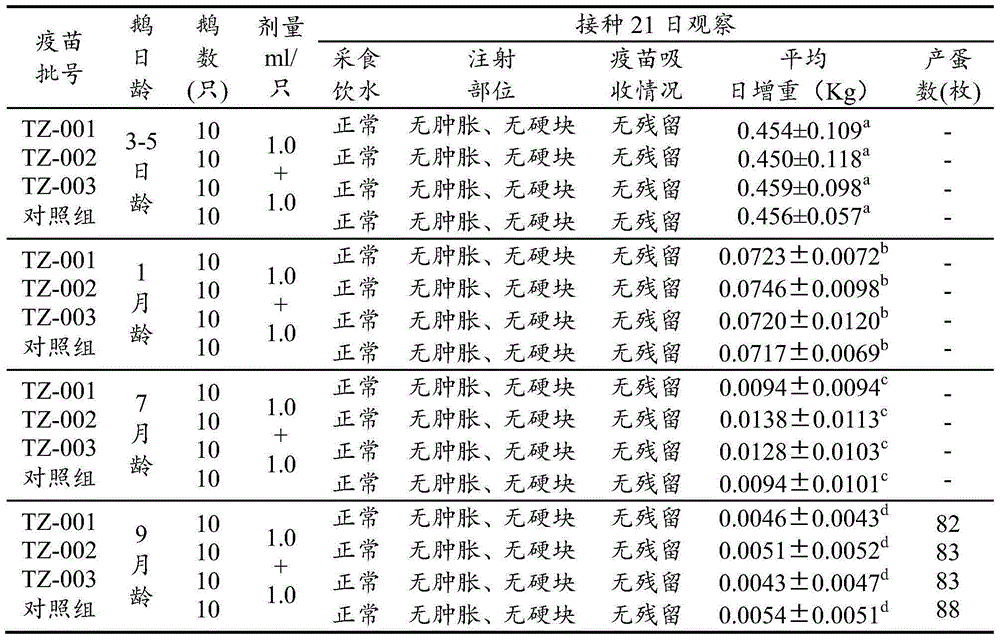
[0069] The seed poison was diluted 1:100 times with sterilized normal saline, and 11-day-old susceptible goose embryos were inoculated into the allantoic cavity, 0.2ml per embryo, and the embryos were irradiated 3-4 times a day after inoculation, and the embryos were selected to die within 48-120 hours For the goose embryos with obvious lesions, the allantoic fluid was harvested separately and placed in a sterilized container. Quantitatively subpackage the samples that have passed the sterility test and are negative for agglutination of 1% chicken erythrocyte suspension, indicate the harvest date, generation of seed virus and other information, and store them in a freezer.
[0070] inoculation
[0071] Dilute the virus seeds used for production 1:100 times with sterile saline, inoculate 11-day-old susceptible goose embryos into the allantoic cavity, 0.2ml per embryo, seal the holes wit...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Purification, concentration and vaccine preparation of virus liquid
[0078] 1 Purification of virus liquid
[0079] The qualified virus liquid is sent to the Alta Laval online disc centrifuge through a sterile pipeline, and after continuous online centrifugation, the purified virus liquid is obtained.
[0080] 2 Concentration of virus liquid
[0081] After the virus is purified, it is sent to the PALL concentrator through a sterile pipeline for concentration, and the concentration is carried out according to the concentration factor determined by the virus content before concentration, so that the virus content in each ml of the concentrated virus liquid is not less than 10 8.0 ELD 50 .
[0082] 3 Virus liquid inactivation and preparation into vaccine products
[0083] 3.1 Inactivation of virus liquid:
[0084] Filter the qualified antigen mixture with 4 layers of sterilized gauze and 1 layer of 80-mesh copper mesh, put it in an inactivation tank, add BEI cyclized...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com