Data transfer apparatus for low voltage differential signaling
A technology for data transmission and differential signals, applied in the field of data transmission equipment for low-voltage differential signals, and can solve the problems of not dealing with common mode noise, increasing the complexity and size of amplifiers, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
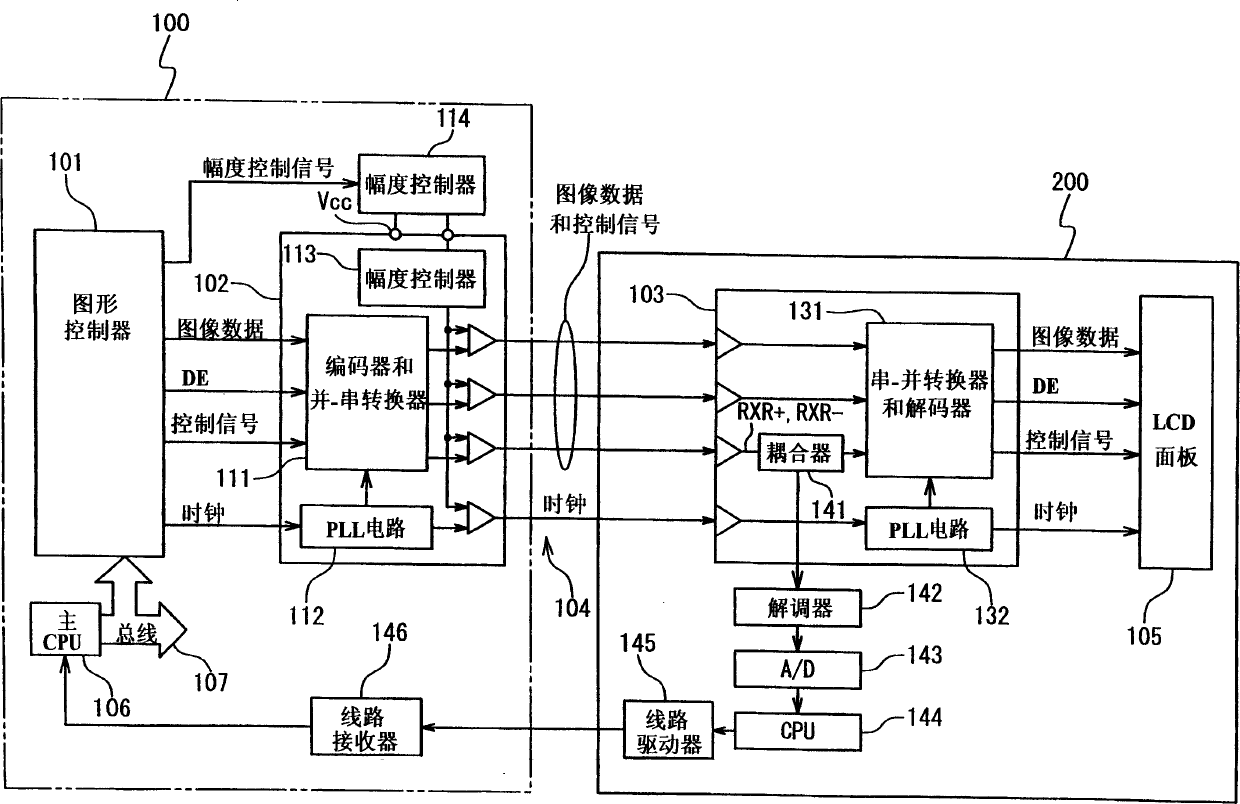
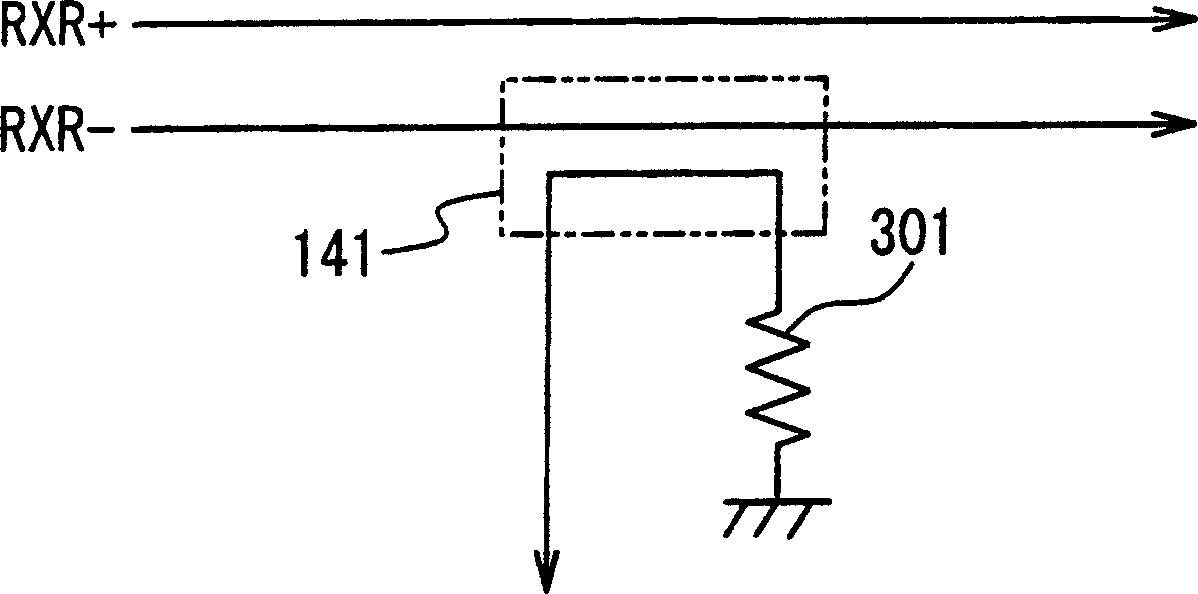
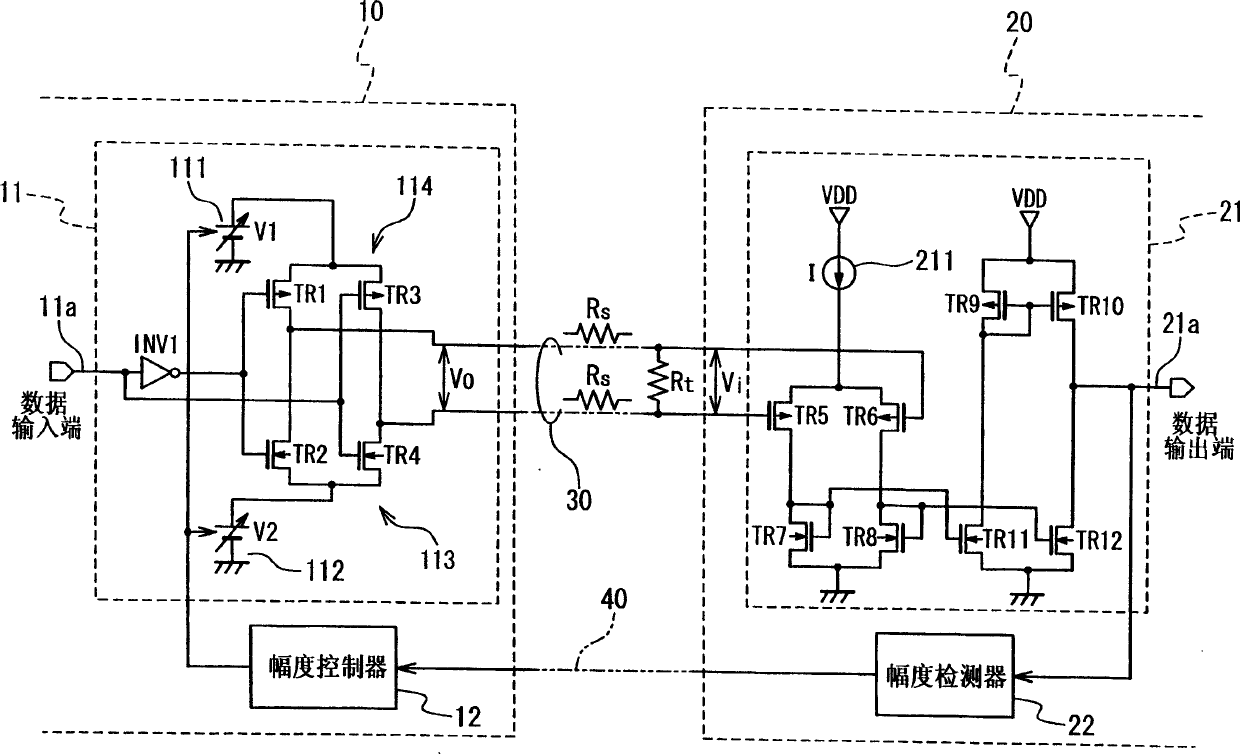
[0038] In the first embodiment shown in FIG. 3 , the data transmission device is composed of a transmitter 10 and a receiver 20 . The transmitter 10 and the receiver 20 are connected by a transmission line 30 comprising a pair of twisted pair signal lines. In addition, a feedback signal line 40 is additionally interposed between the transmitter 10 and the receiver 20 .
[0039] The transmitter 10 includes an output buffer 11 and an amplitude controller 12 . The output buffer 11 generates a differential signal in response to the input transmission data signal 11a. Amplitude controller 12 controls the amplitude of the differential signal generated by output buffer 11 in response to receiving a feedback signal from receiver 20 via feedback signal line 40 .
[0040] The receiver 20 includes an input buffer 21 and an amplitude detector 22 . The input buffer 21 receives the differential signal from the transmitter 10 through the transmission line 30, and converts the received dif...
no. 2 example
[0071] Fig. 7 is a circuit diagram showing the structure of the data transmission device in the second embodiment. The data transmission device in the second embodiment includes a transmitter 10', and the transmitter 10' includes an open-drain output buffer 51 instead of the output buffer 11 shown in FIG. 3 . In addition, the transmitter 10' also includes an amplitude controller 12' which provides the output buffer 51 with a number of amplitude control signals C0 to C2. The output buffer 51 includes first and second drivers 511 and 512, and first and second selectors 513 and 514, which are connected to the first and second drivers 511 and 512, respectively.
[0072]Each driver 511 and 512 is composed of a plurality of n transistors with different driving capabilities, where n is an integer equal to or greater than 2. It should be noted that the term "drive capability" for a particular transistor means the maximum current flowing through the transistor when the transistor is t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com