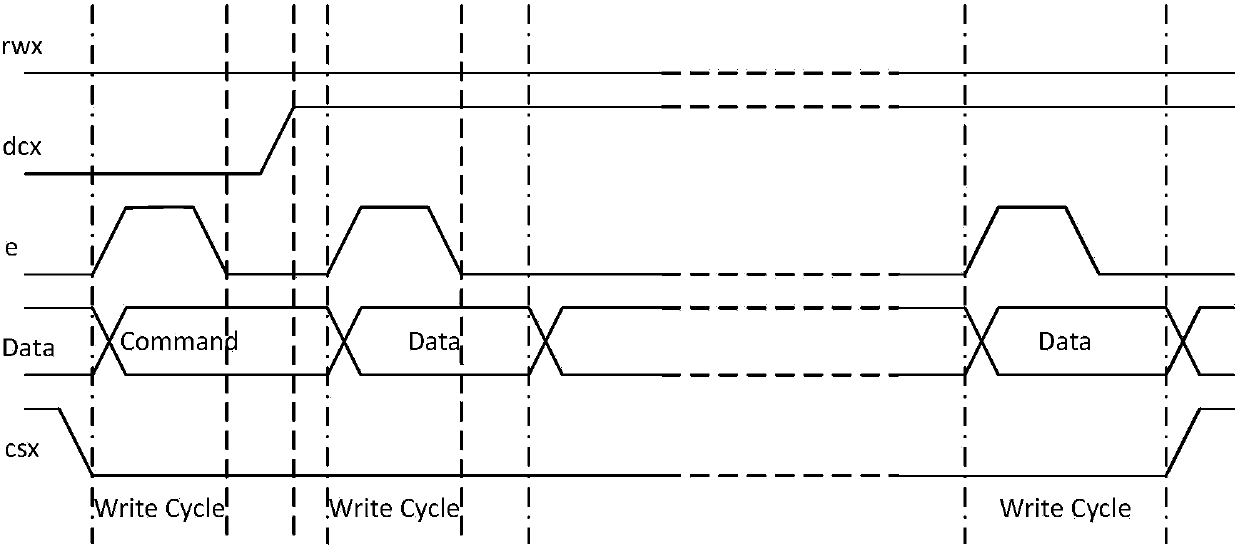
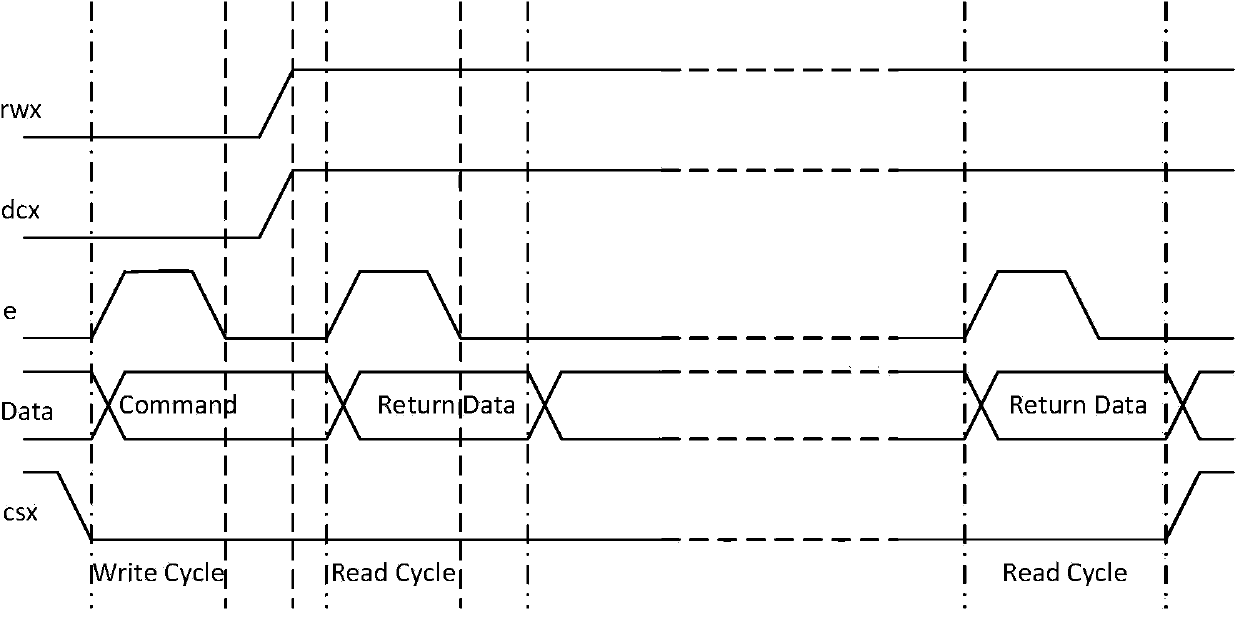
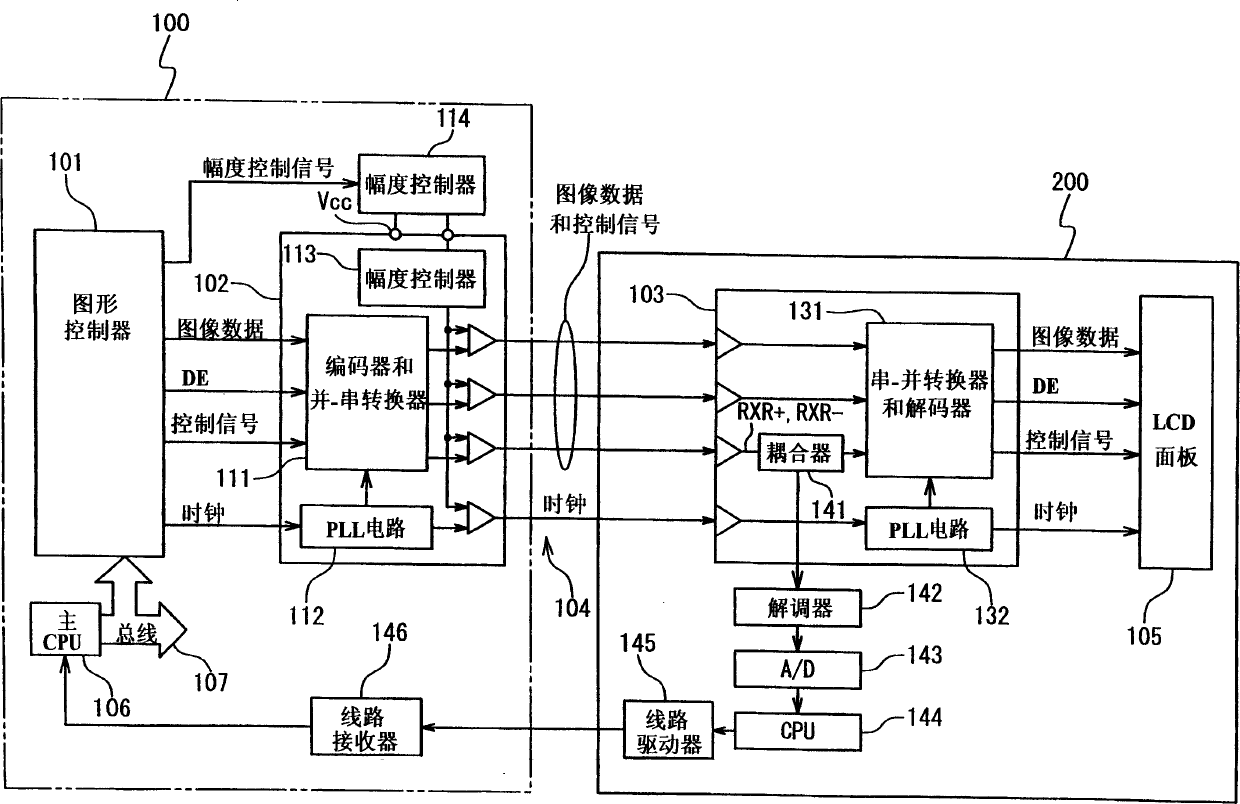
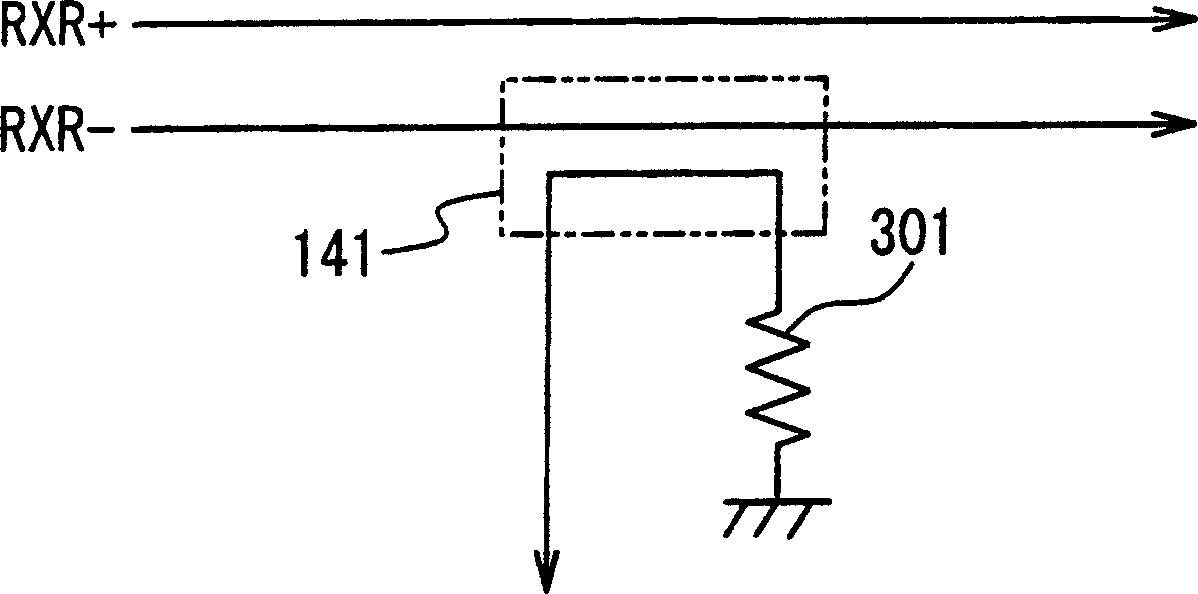
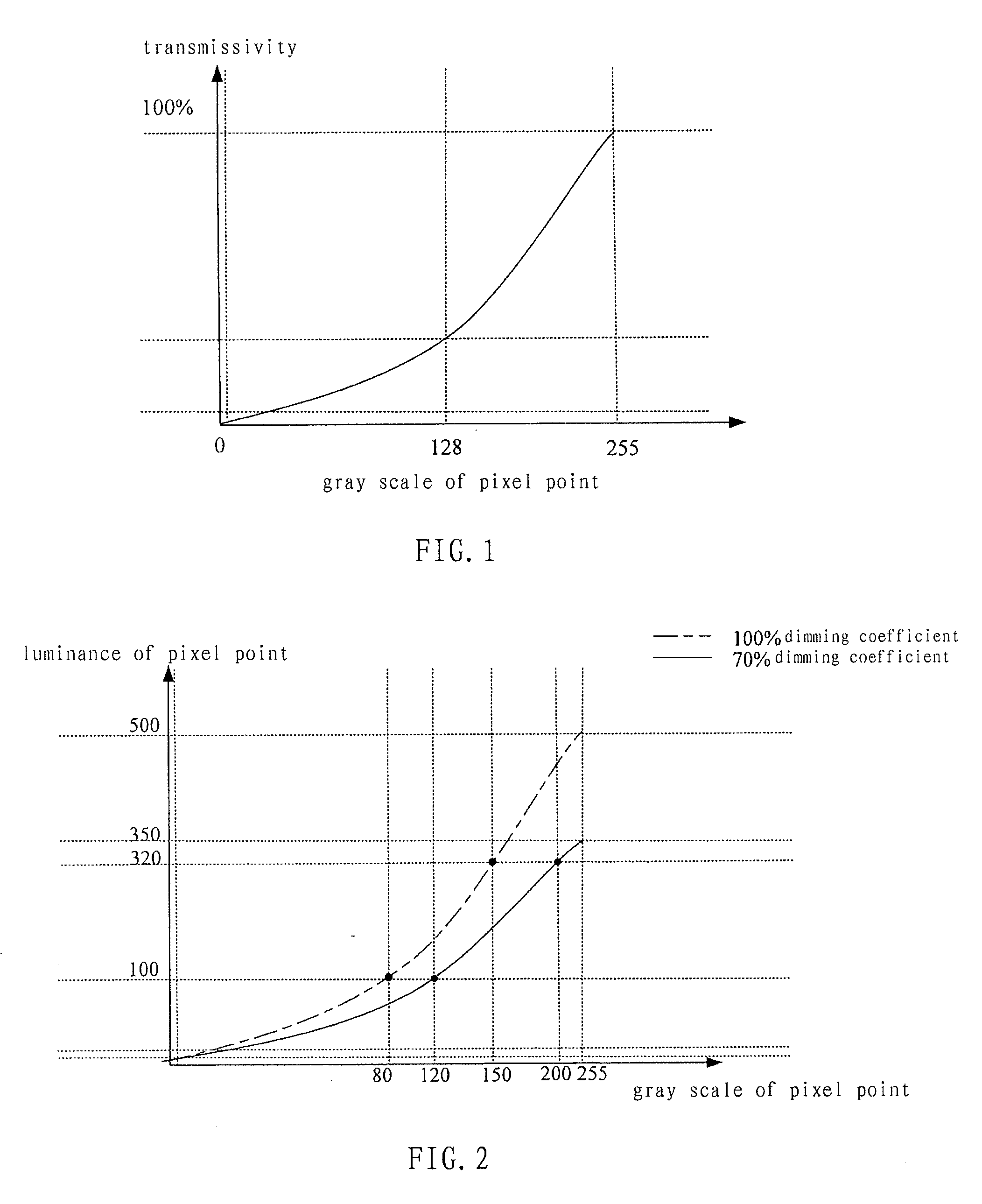Patents
Literature
488 results about "Low-voltage differential signaling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
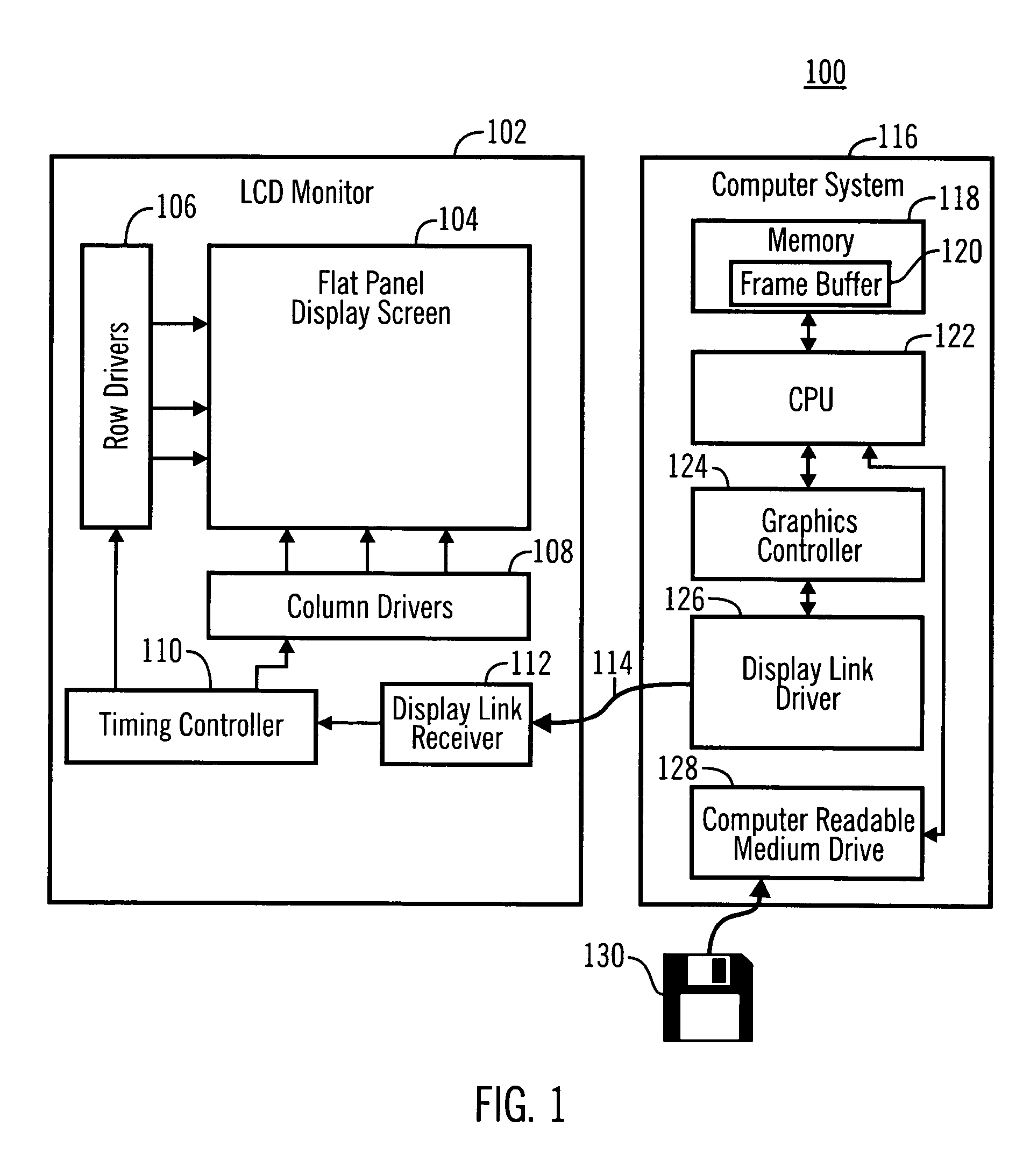
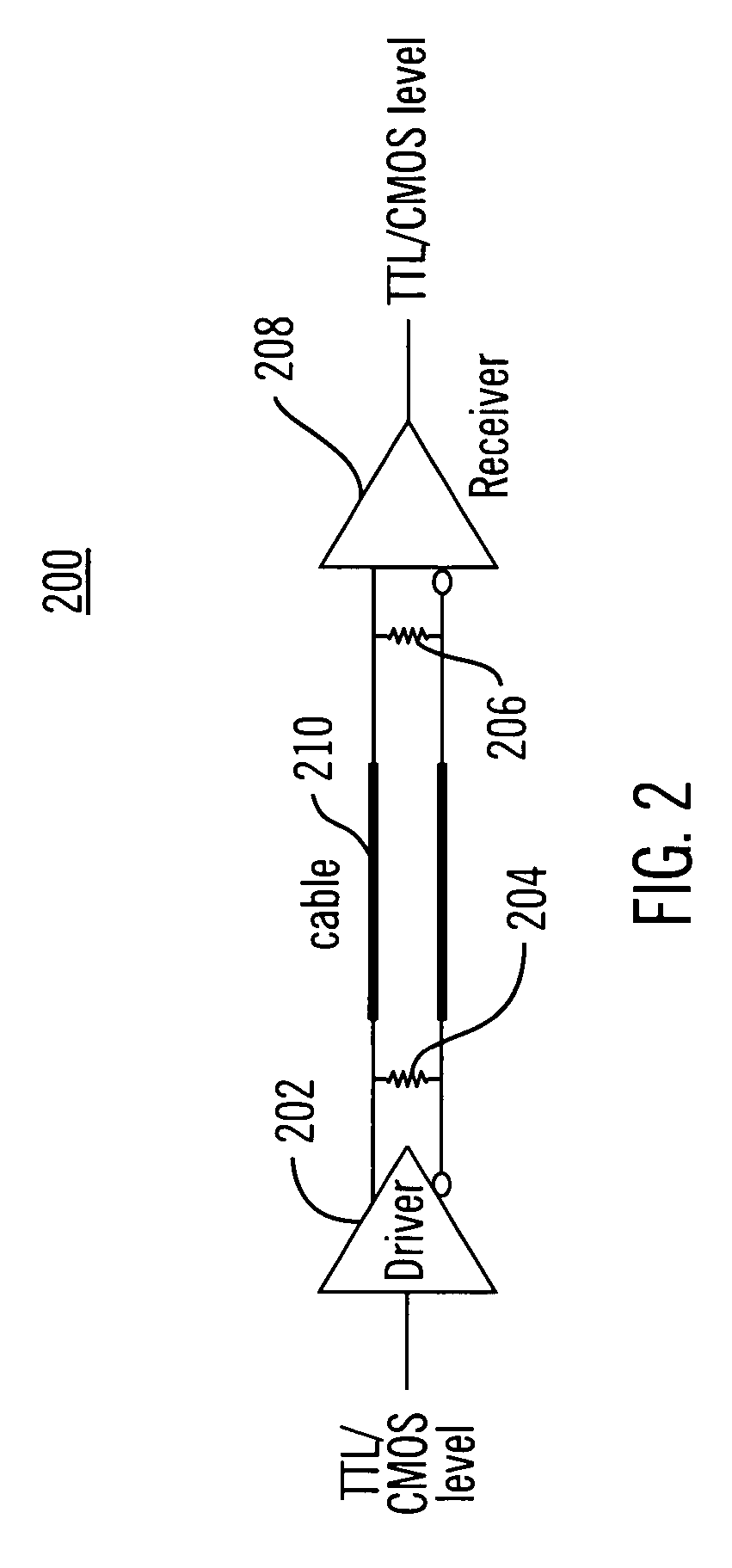
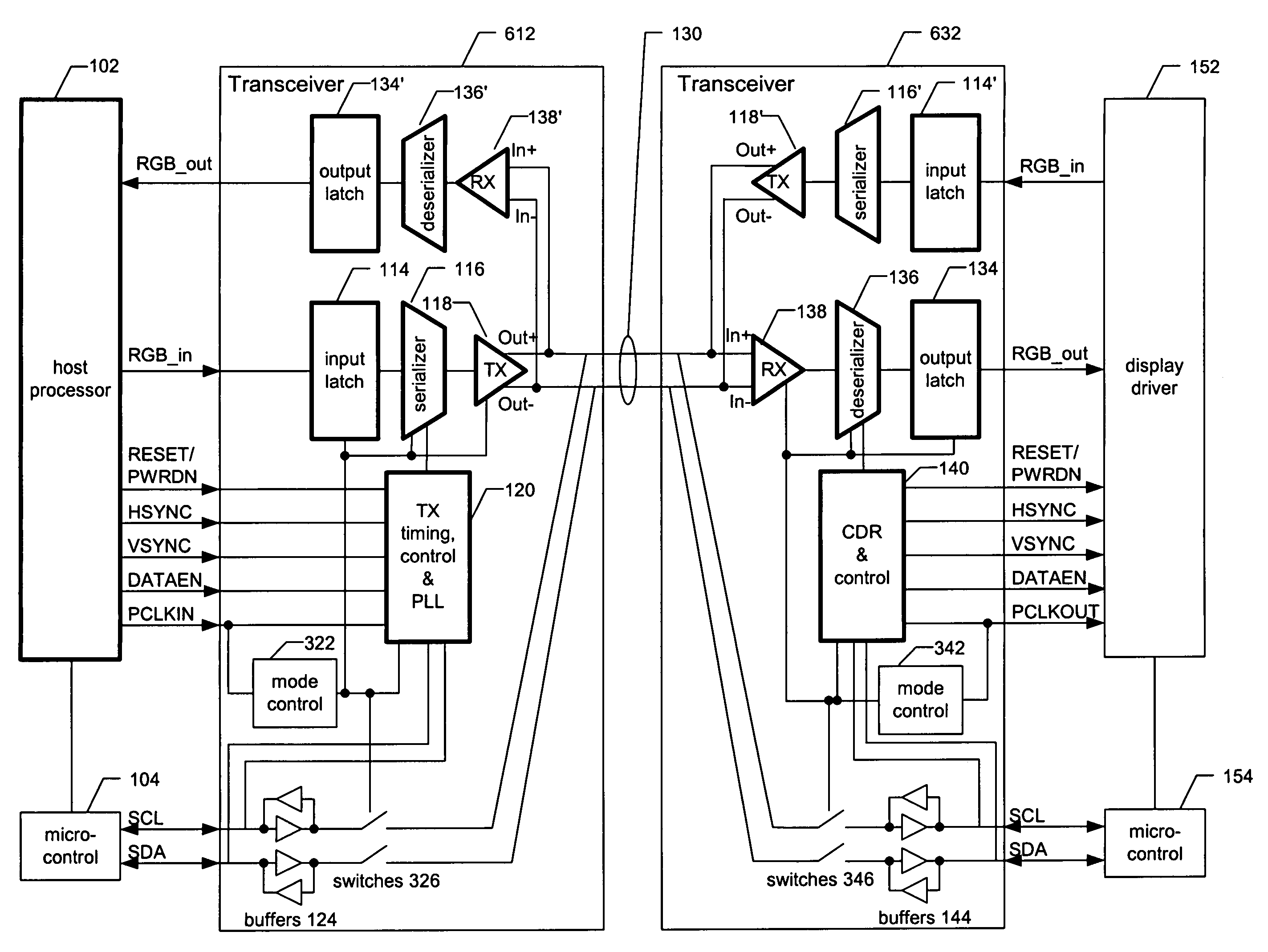
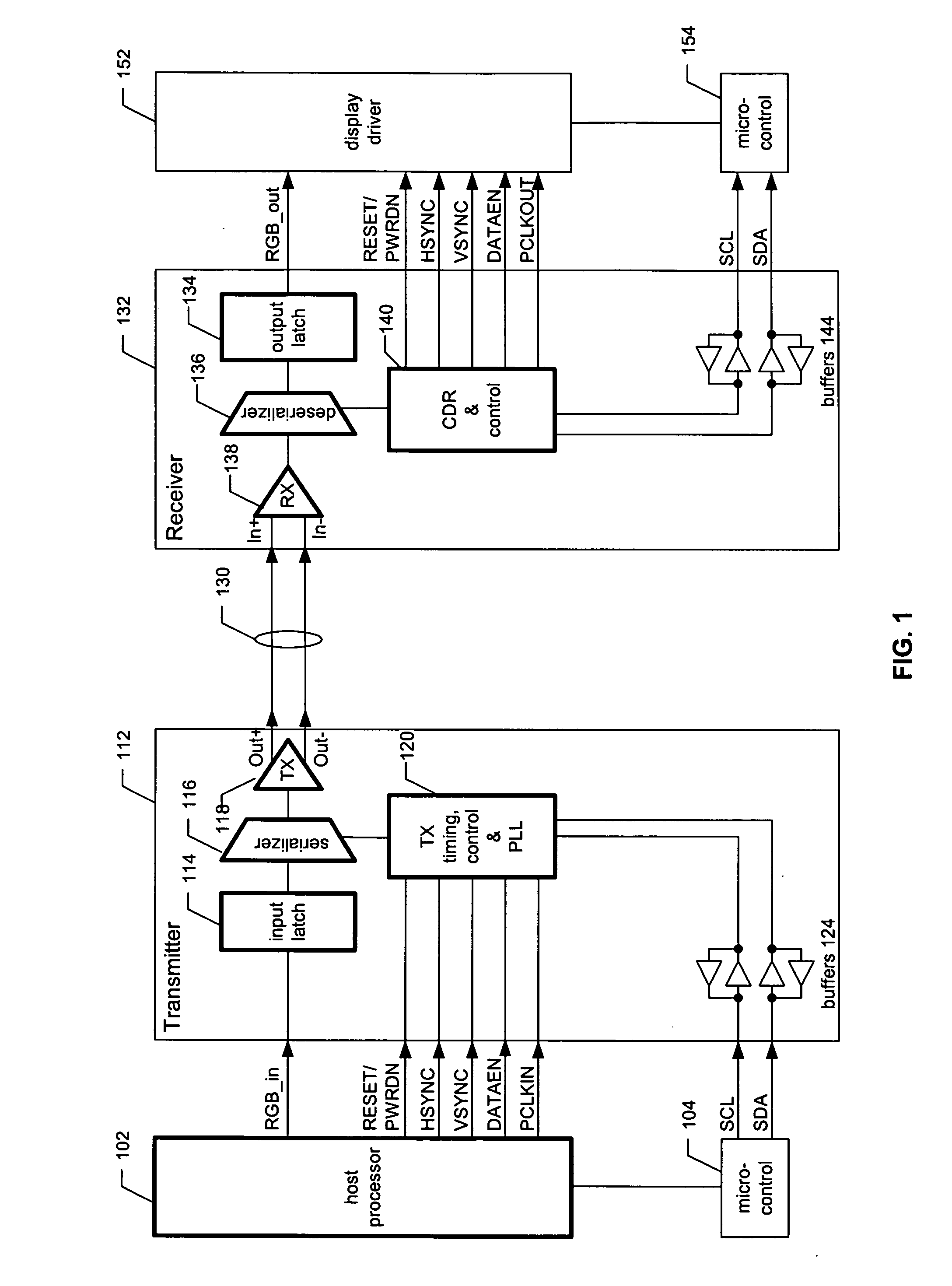
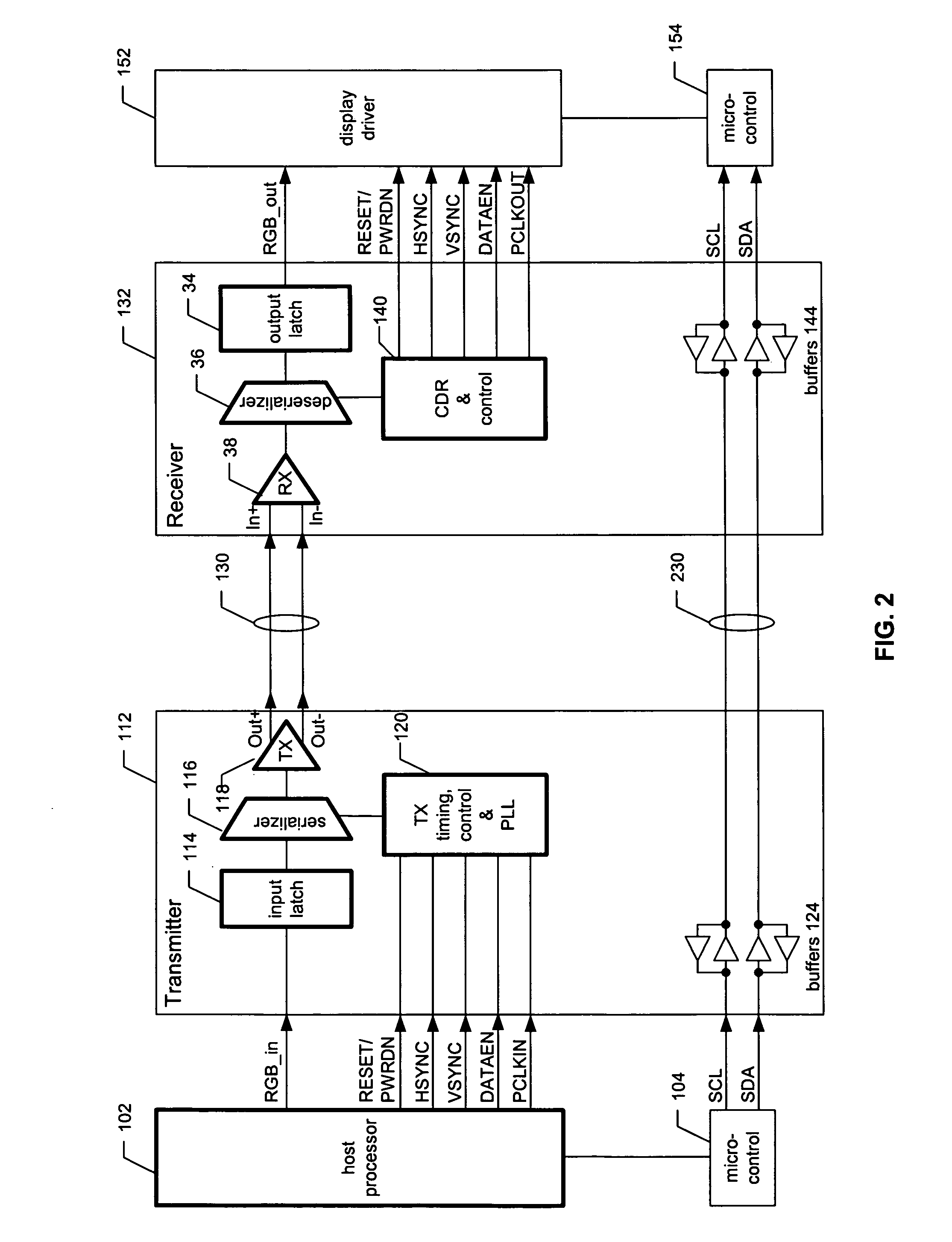
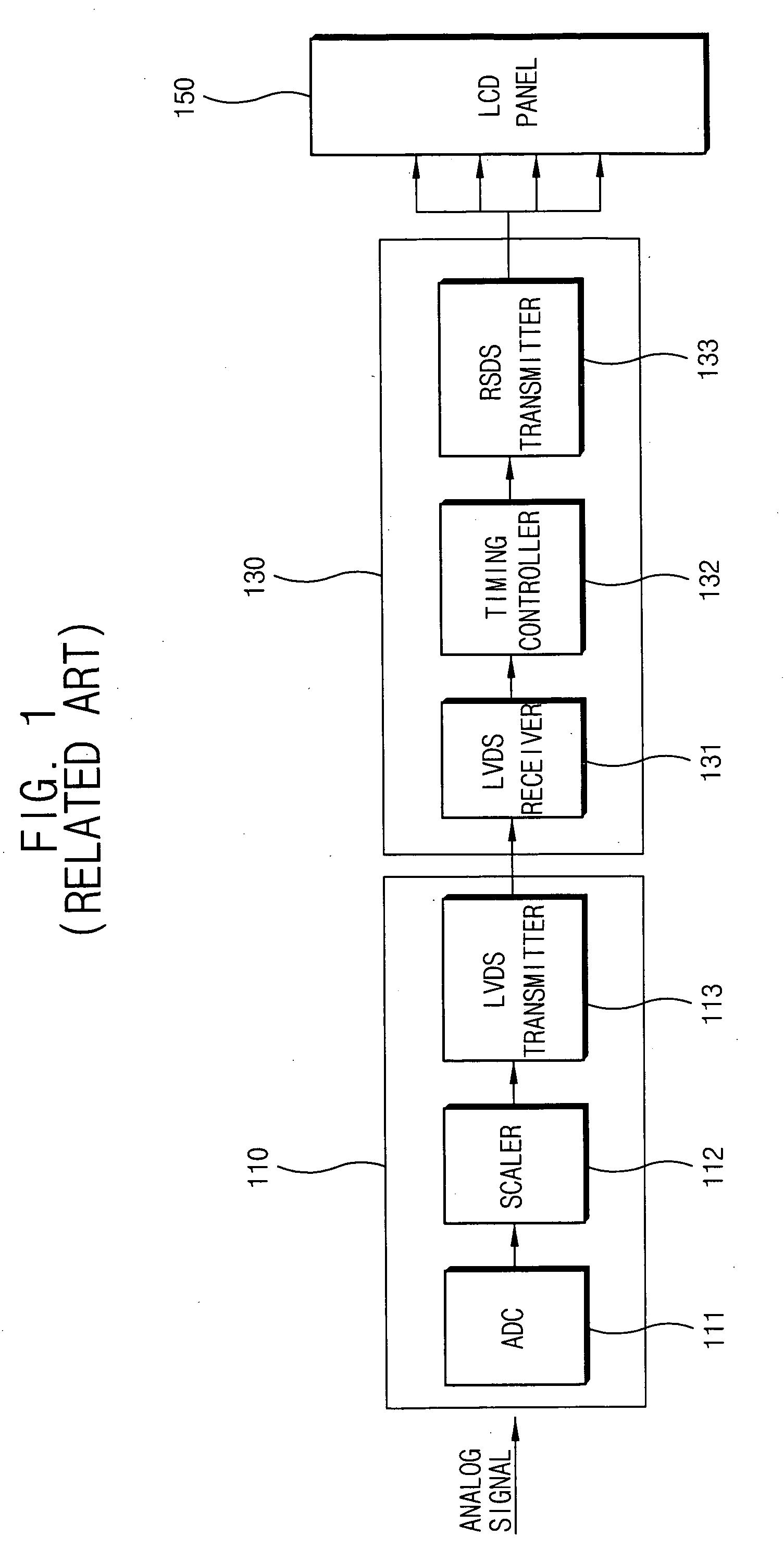
Low-voltage differential signaling, or LVDS, also known as TIA/EIA-644, is a technical standard that specifies electrical characteristics of a differential, serial communication protocol. LVDS operates at low power and can run at very high speeds using inexpensive twisted-pair copper cables. LVDS is a physical layer specification only; many data communication standards and applications use it and add a data link layer as defined in the OSI model on top of it.
Power efficient, high bandwidth communication using multi-signal-differential channels
ActiveUS7358869B1High coding densitySave areaAnalogue conversionIndividual digits conversionPower efficientHigh bandwidth
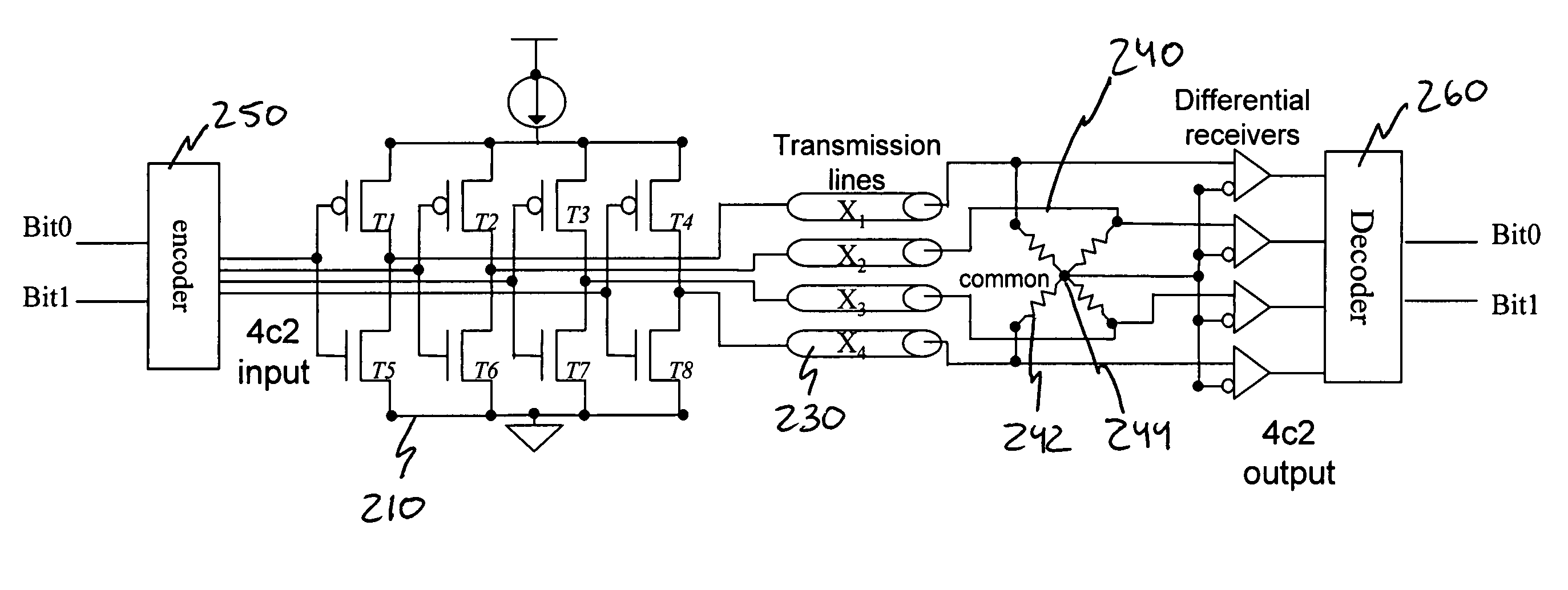
A low-power, area and pin efficient signaling alternative to serial differential links used for chip-to-chip, backplane, optical and other signaling applications. The multi-bit differential signaling (MBDS) generally comprises a driver and link termination network design coupled with a coding system based on n choose M (nCm) coding. MBDS has comparable electrical characteristics to conventional low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) and is fully compatible with existing LVDS receivers in point-to-point and multi-point bus topologies. However, MBDS uses up to 40% less power, with up to 33% fewer I / O pads than equivalent LVDS links.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
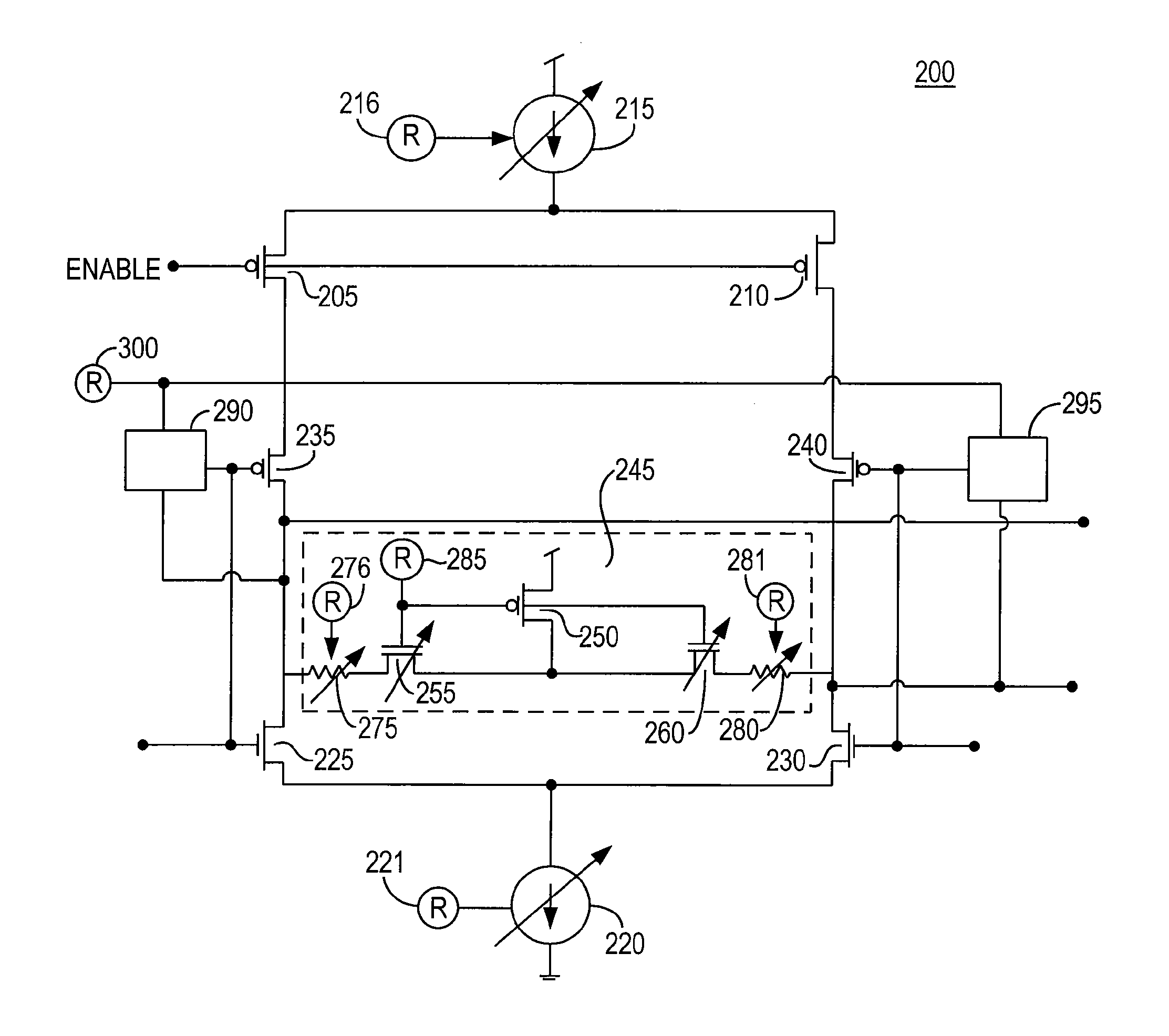
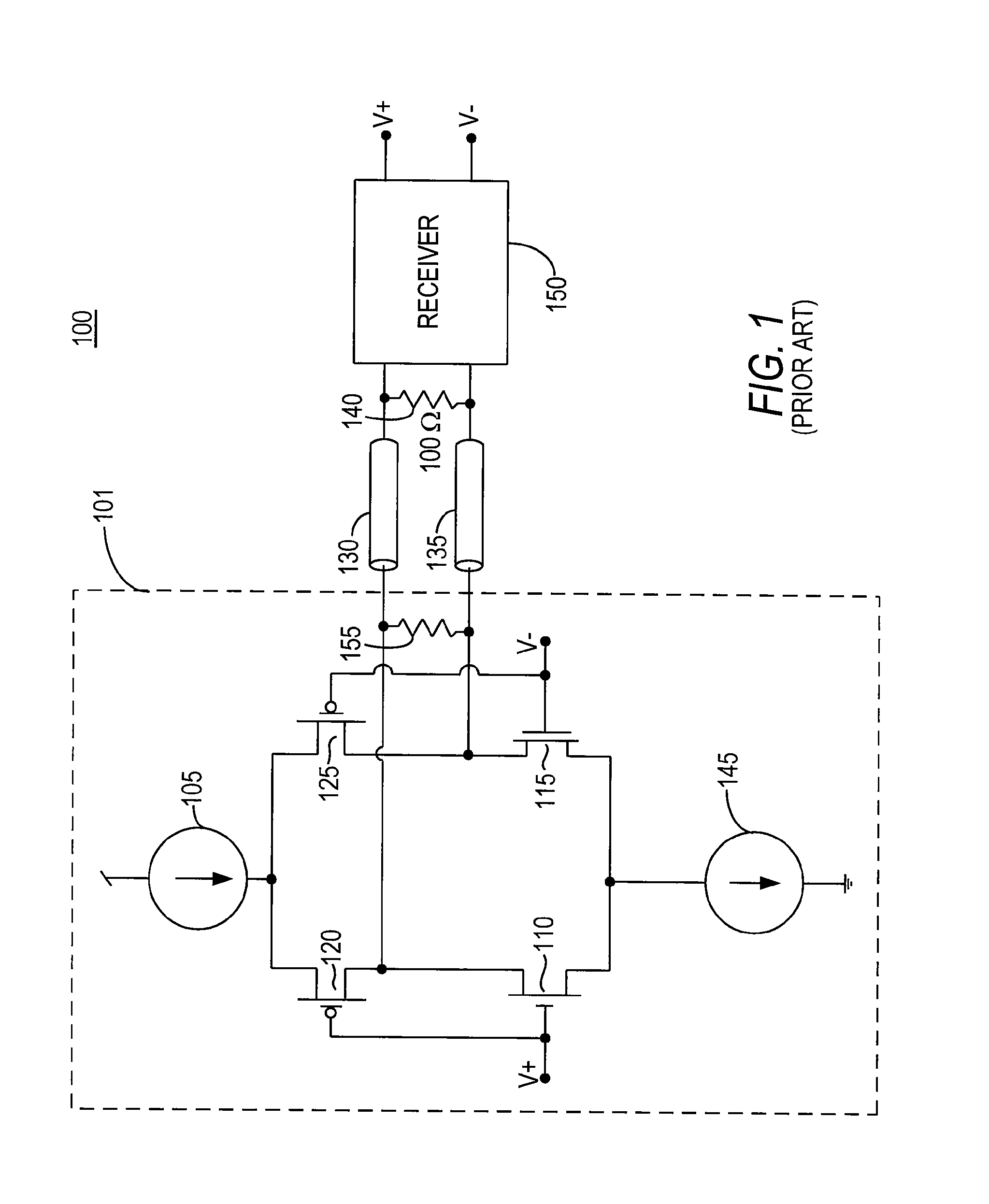
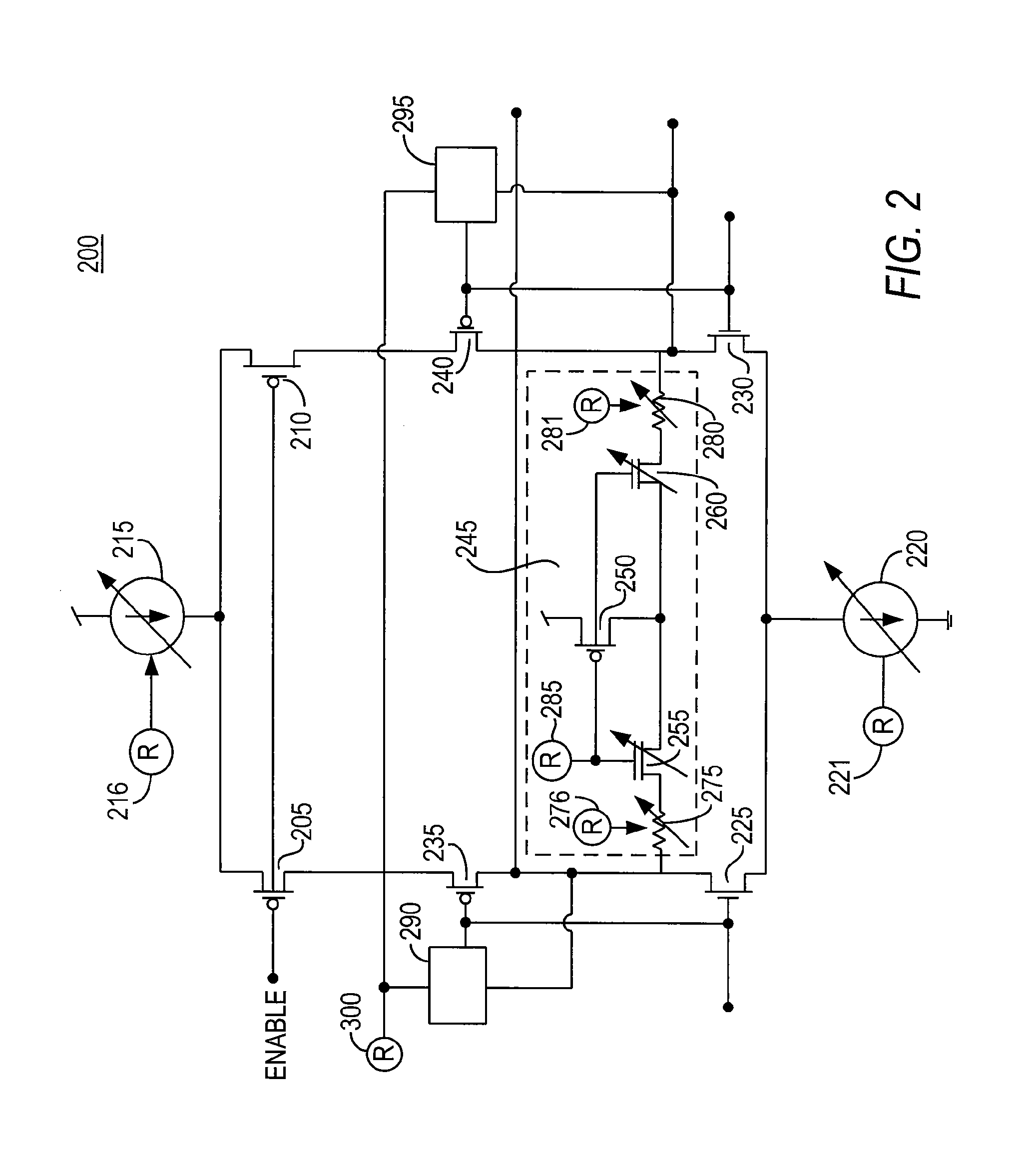
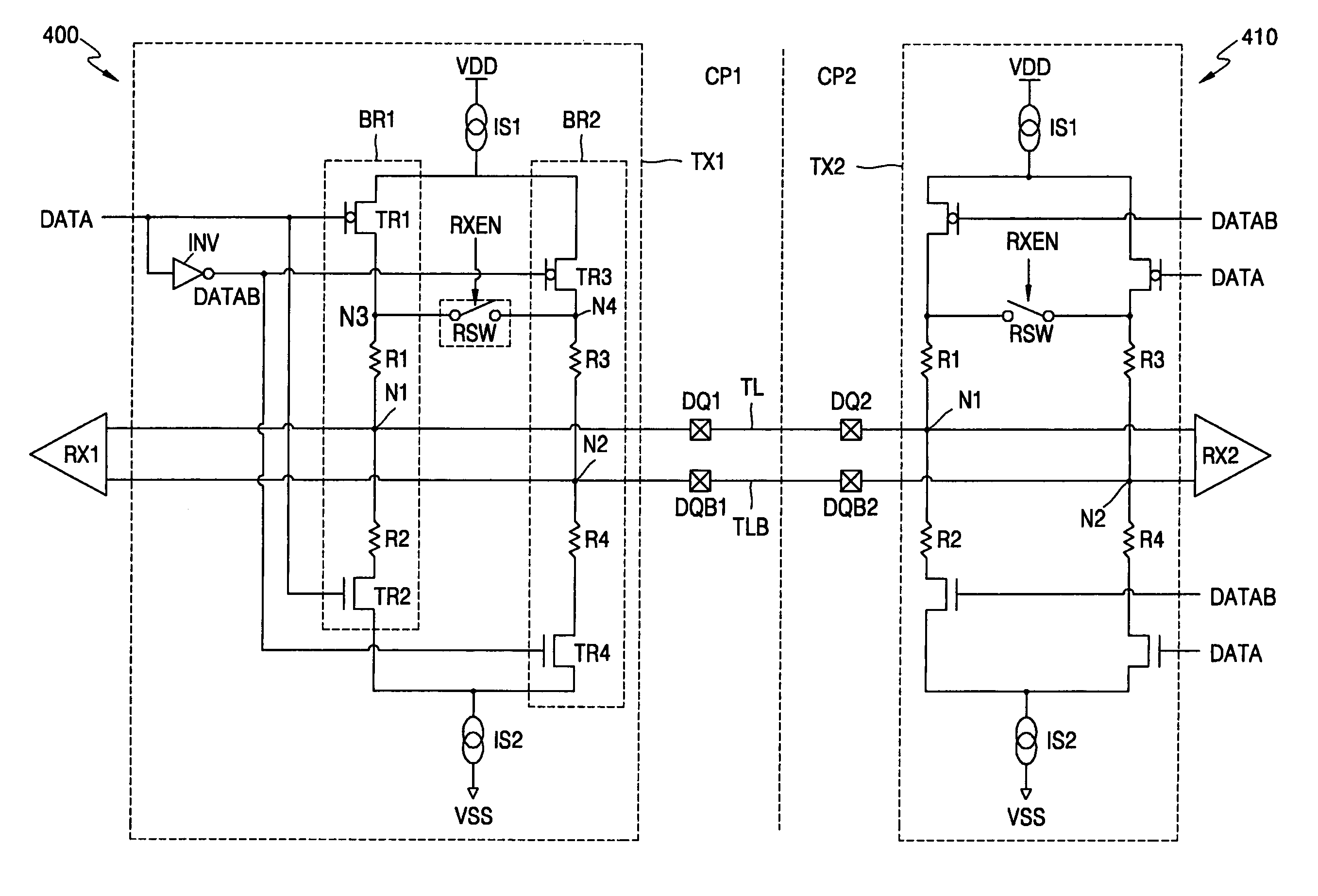
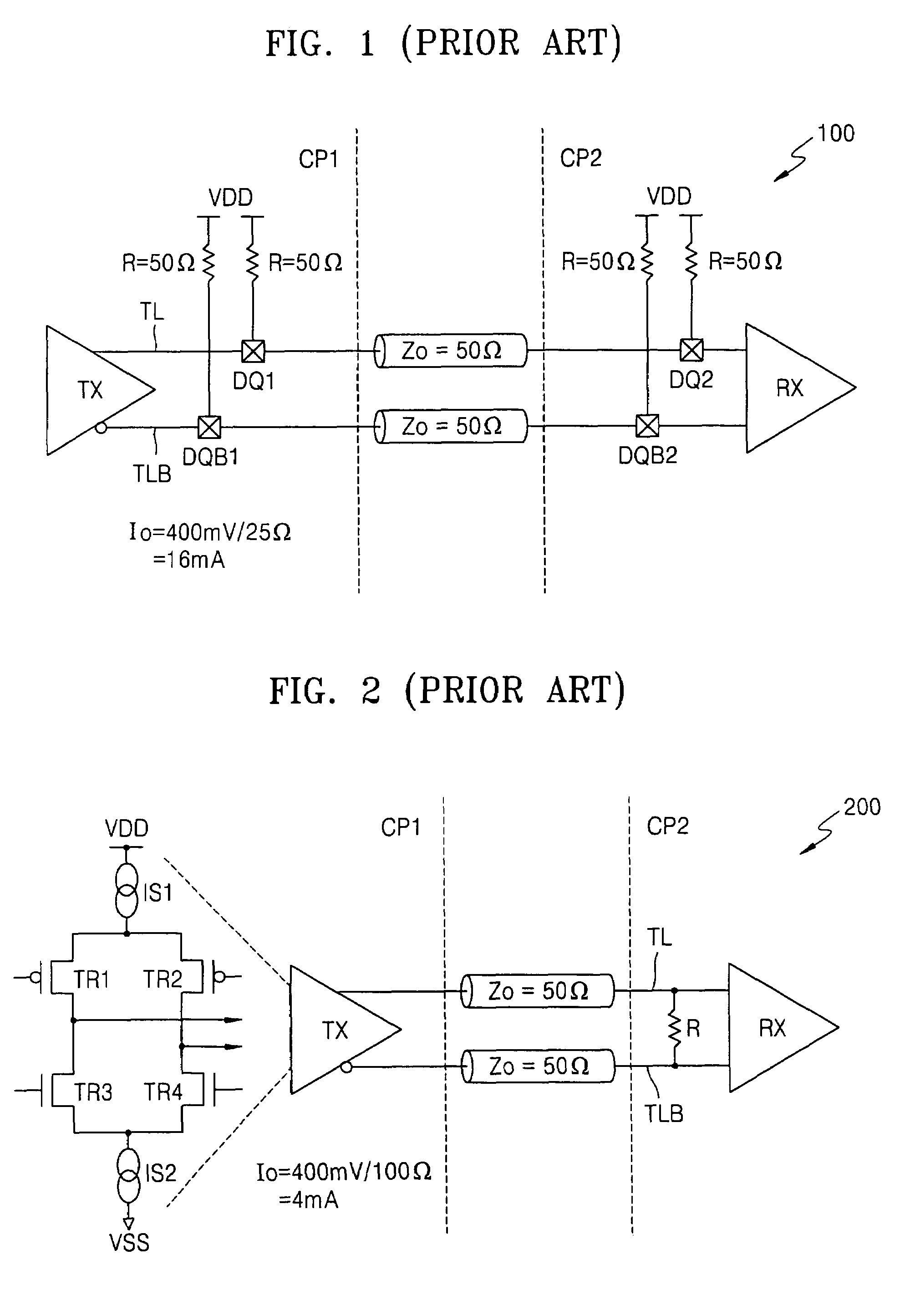
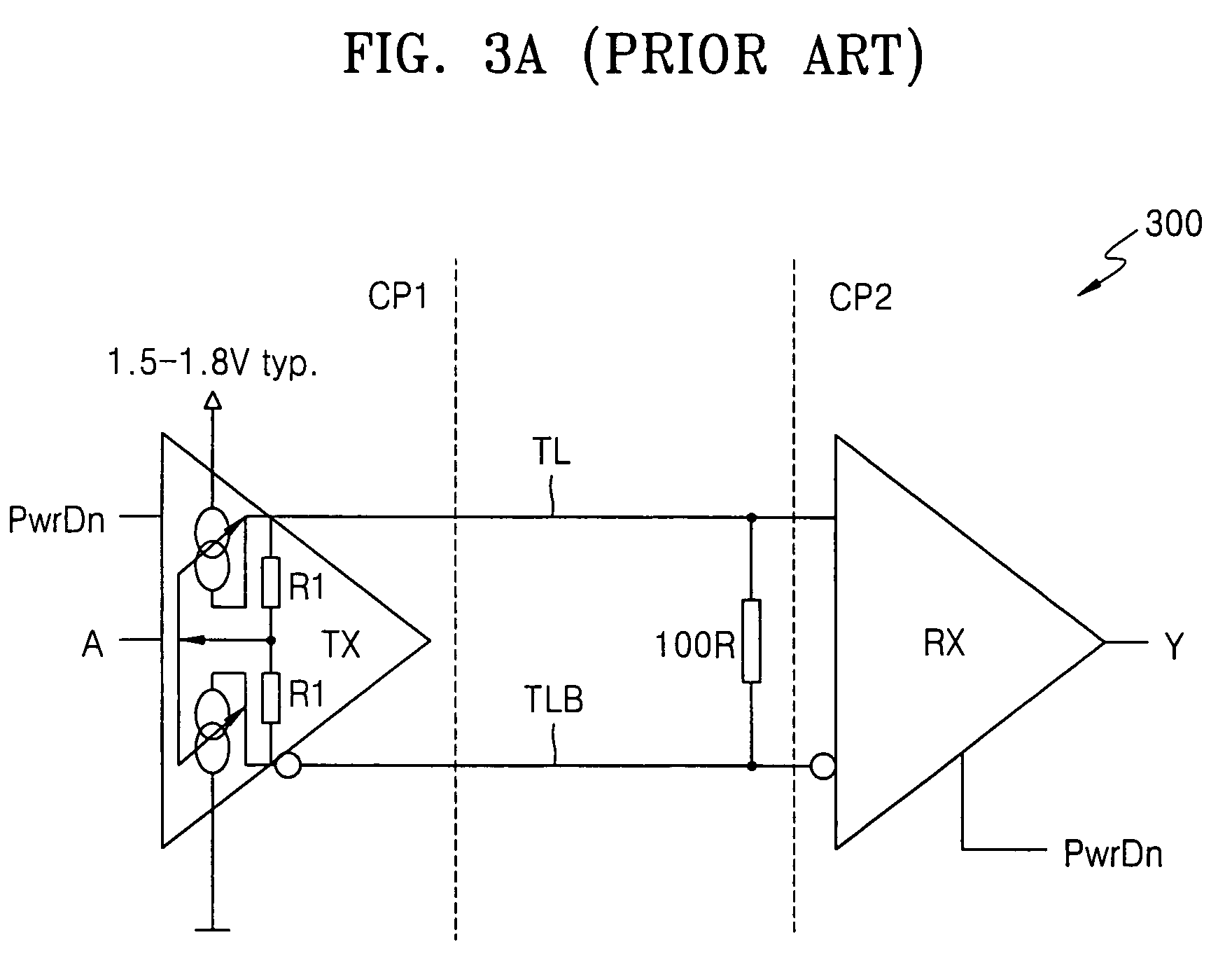
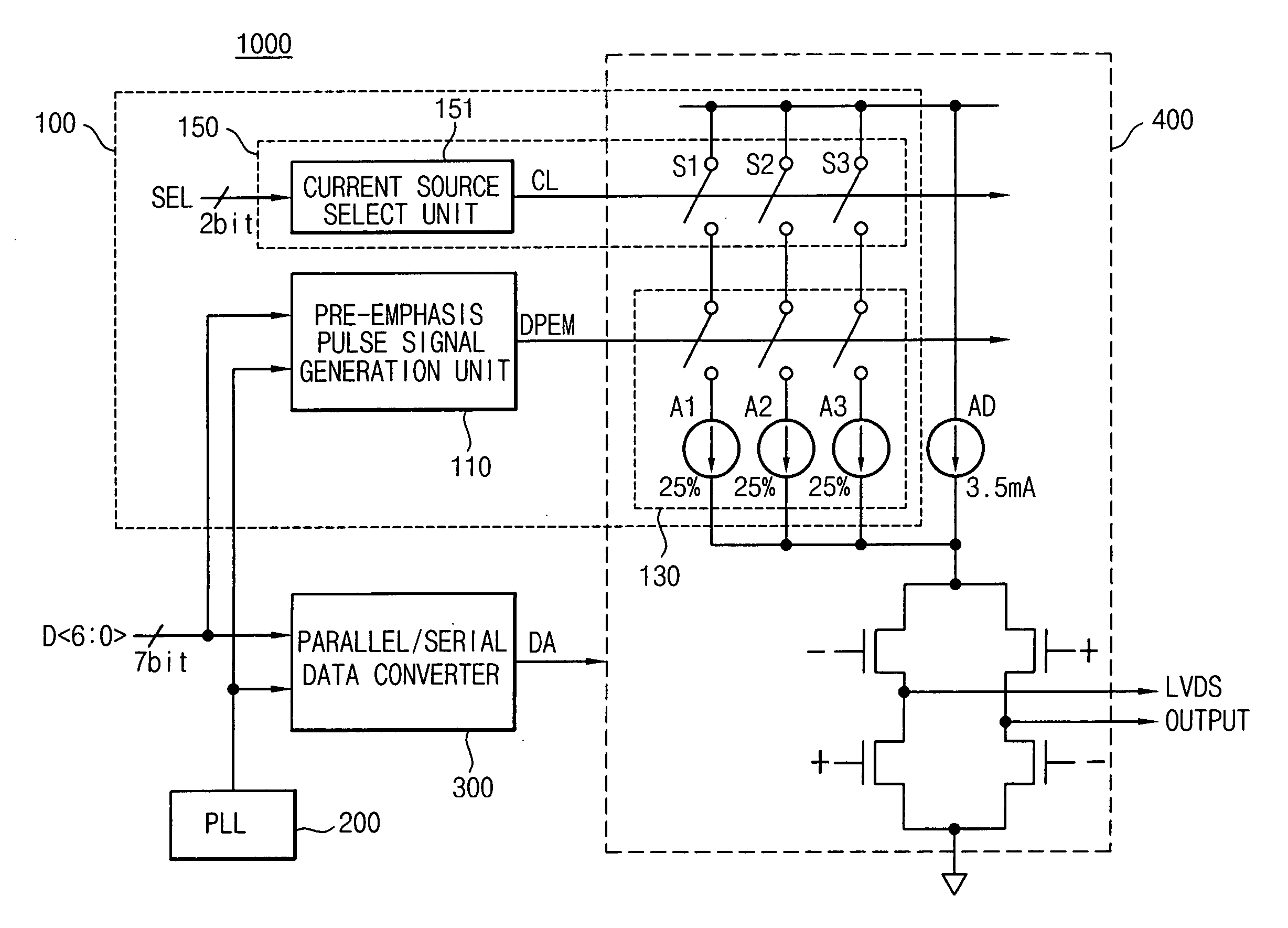
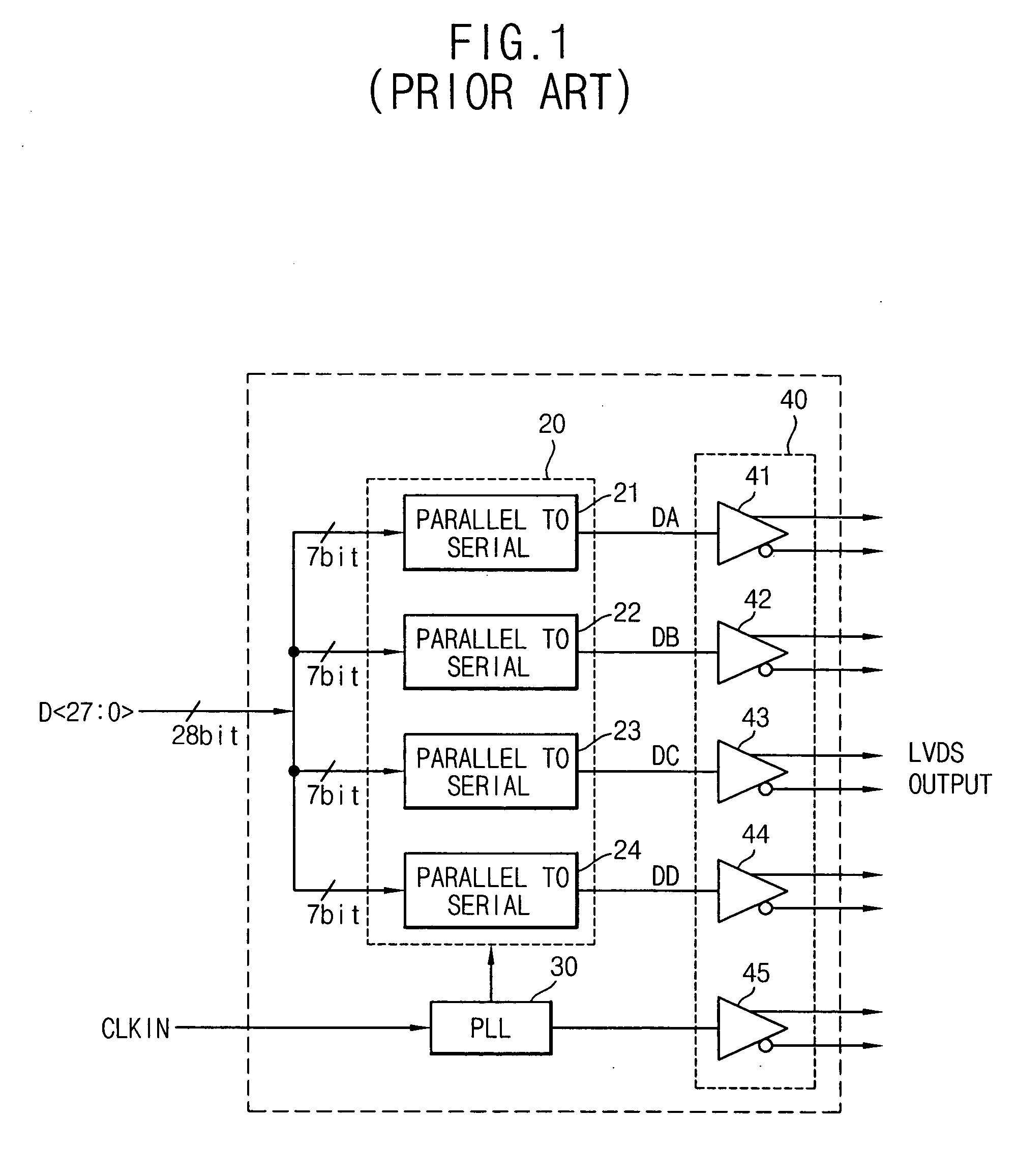
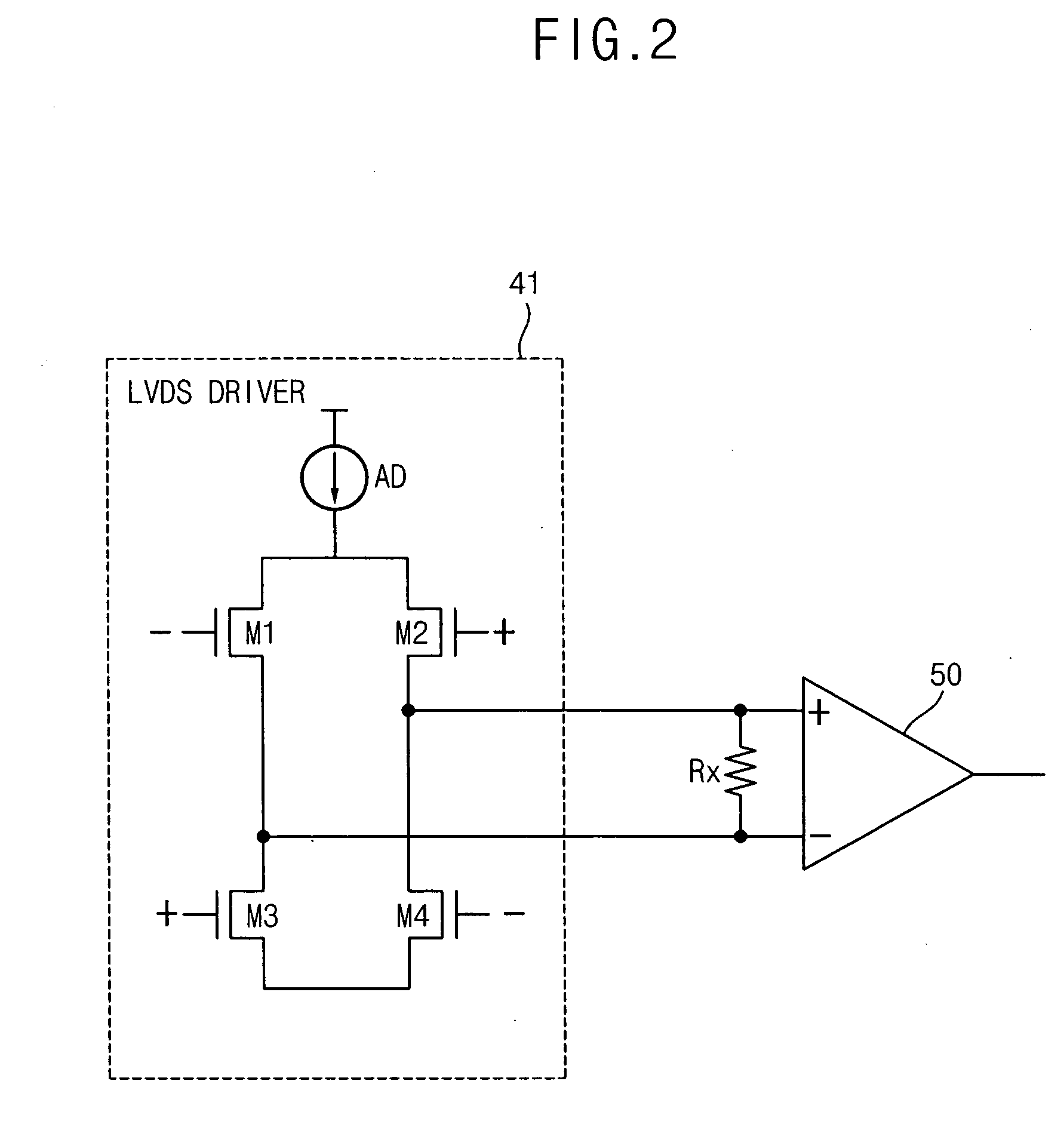
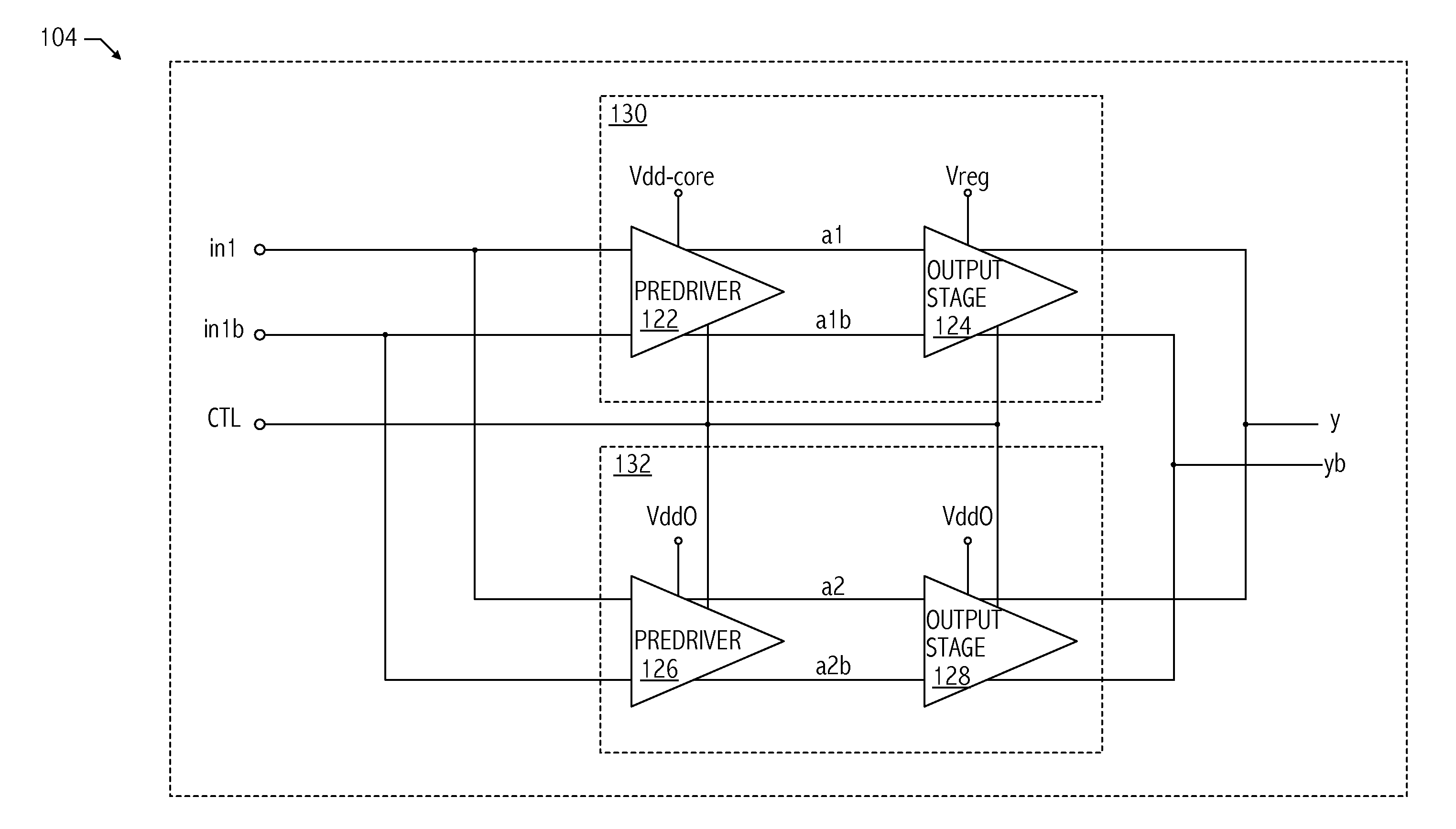
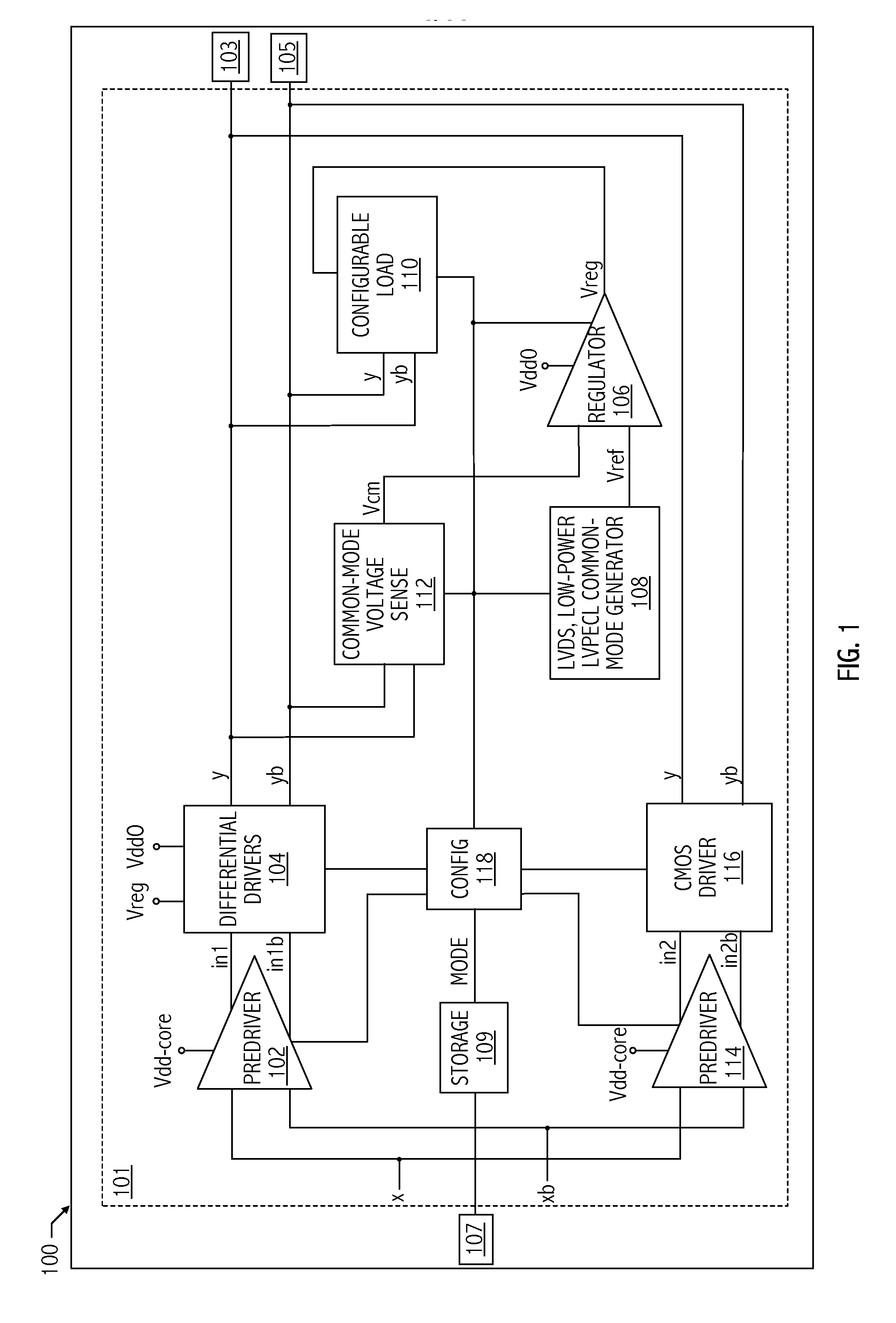
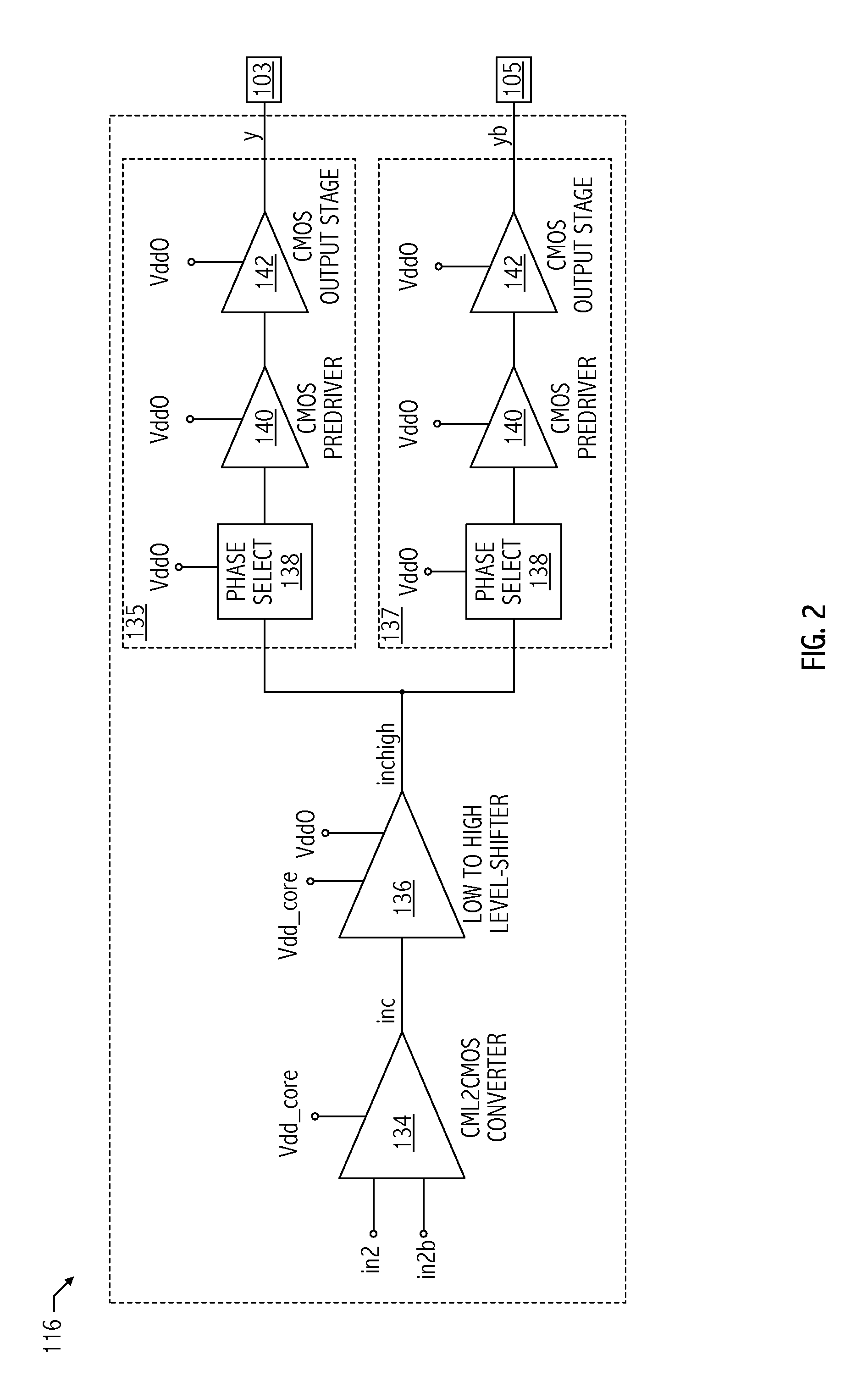
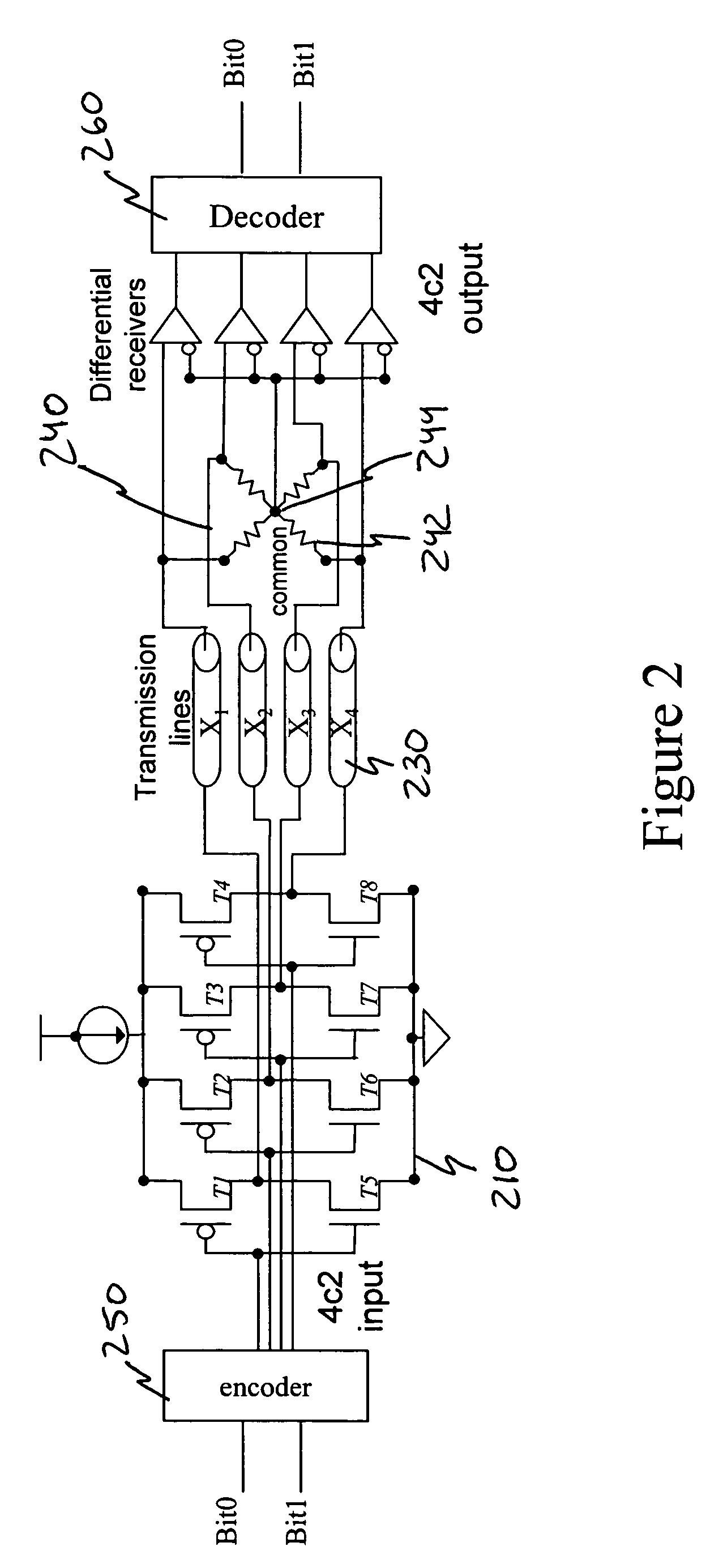
Low voltage differential signaling [LVDS] driver with pre-emphasis
ActiveUS6977534B2Reduce data jitterMultiple input and output pulse circuitsBaseband system detailsControl signalSecondary stage
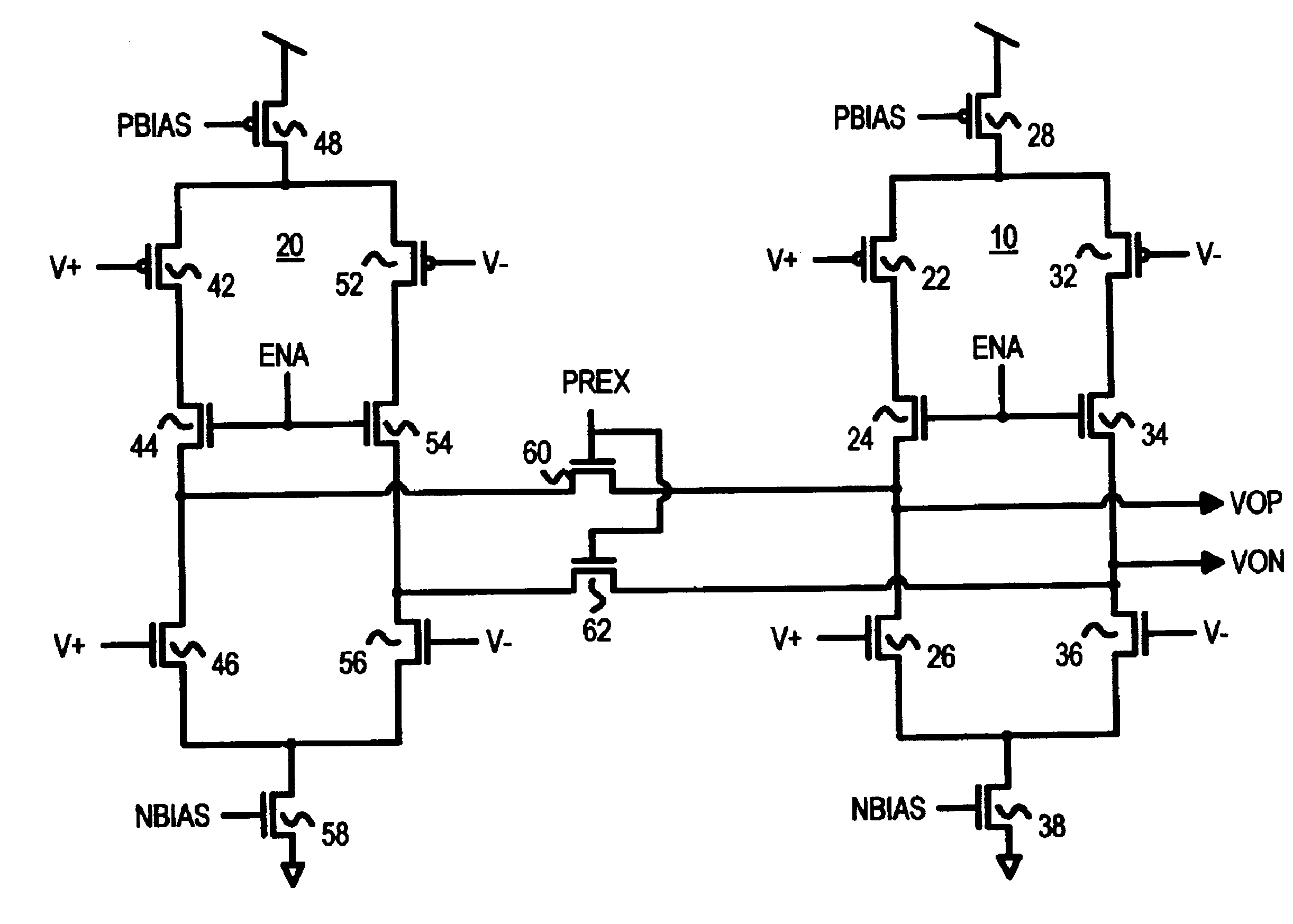
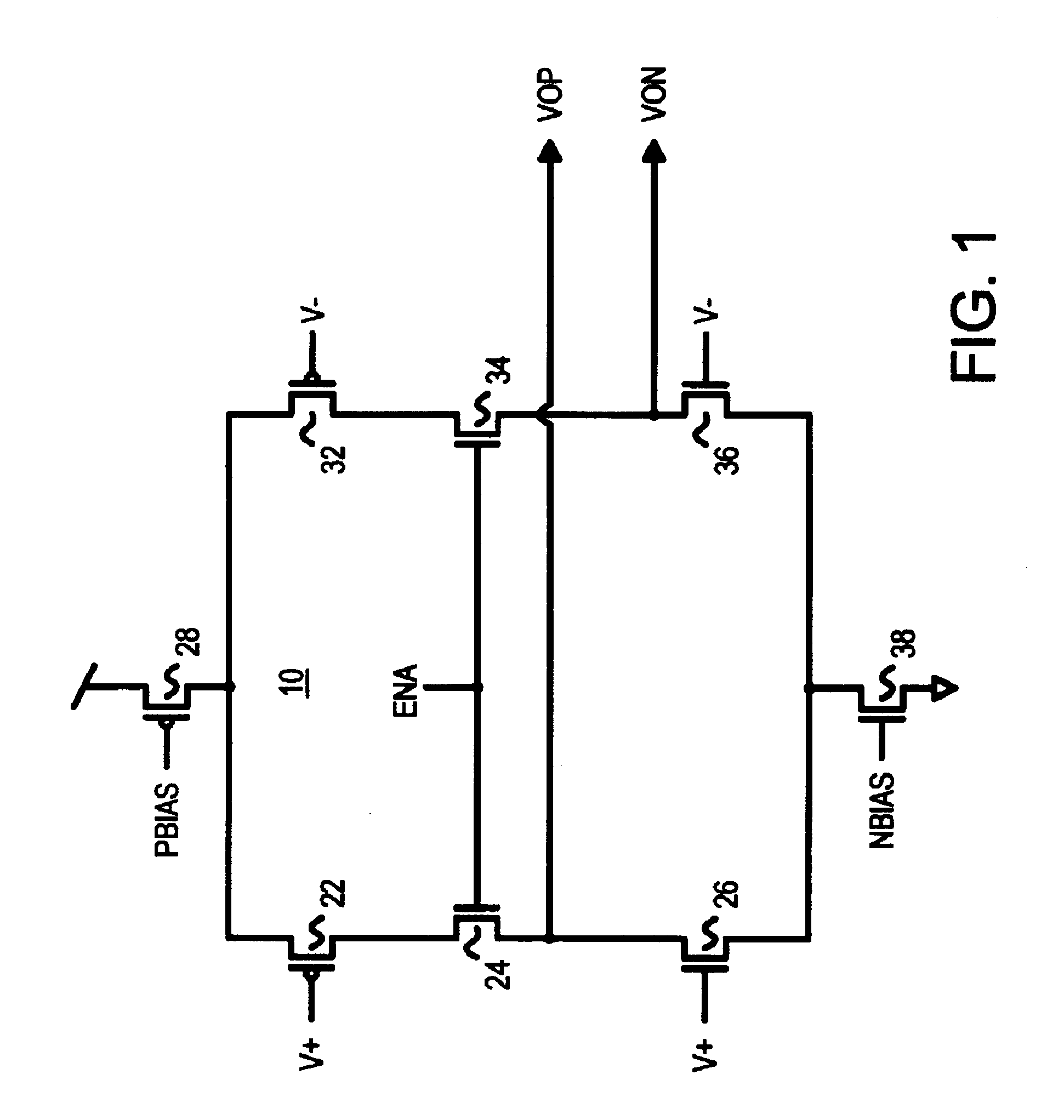
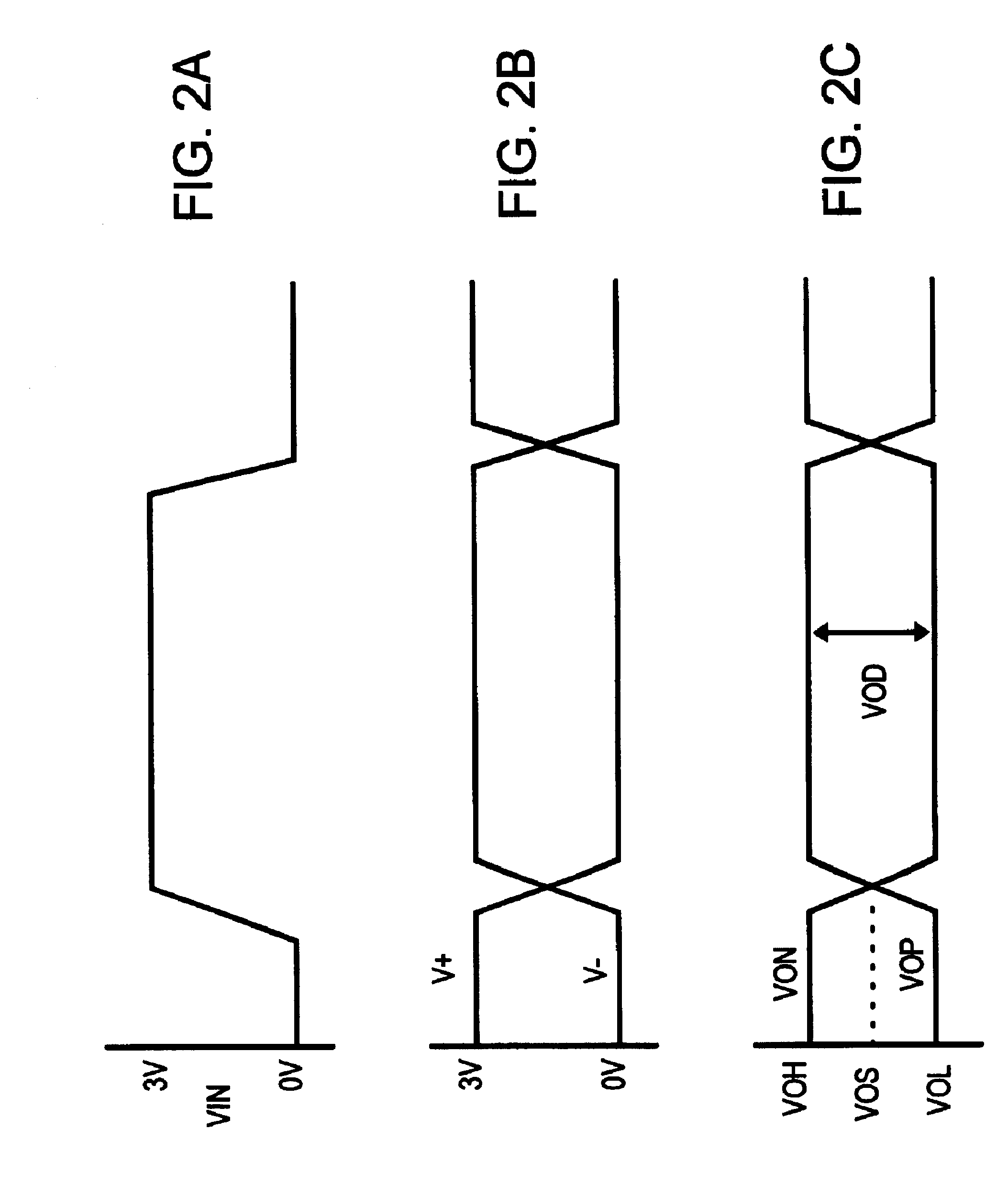
A Low Voltage Differential Signaling Driver with Pre-emphasis and including a primary stage having a first switching circuit providing an output representing a sequence of pulses at a predetermined current level, a secondary stage having a second switching circuit arranged to provide an additional current level for the pulses, and a control circuit arranged to provide control signals for controlling the first and second switching circuits. The control circuit detects a difference in level between two consecutive pulses of the sequence and provides accordingly control signals to the first and second switching circuits. The control signals are such that when two consecutive pulses of the sequence are different, the additional current level is added to the predetermined current level, whilst when two consecutive pulses of the sequence are identical, the additional current level is subtracted from the predetermined current level.
Owner:RPX CORP
Low-voltage differential-signalling output buffer with pre-emphasis
InactiveUS6288581B1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse automatic controlLow voltageEngineering
A low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) output buffer has an improved eye pattern. The LVDS buffer has two parallel stages. A primary stage generates enough current to generate a first voltage drop across a load resistor. At higher frequencies, parasitic capacitive coupling reduces this first voltage drop, closing the eye pattern. A boost stage generates an additional boost current through the load resistor, adding to the voltage drop and opening the eye pattern. The boost stage is coupled to the outputs by link transistors that are enabled by a pre-emphasis signal generated by resetable pulse generators. When outputs switch, the pre-emphasis signal pulses the link transistors on, adding the boost current. At high frequencies, the pulse generators are reset before the pre-emphasis signal ends. The boost current is continuously added at high frequencies, but at low frequencies the boost current only occurs during the pre-emphasis period after outputs switch.
Owner:DIODES INC
Versatile RSDS-LVDS-miniLVDS-BLVDS differential signal interface circuit
InactiveUS6992508B2Logic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDifferential signalingVoltage source
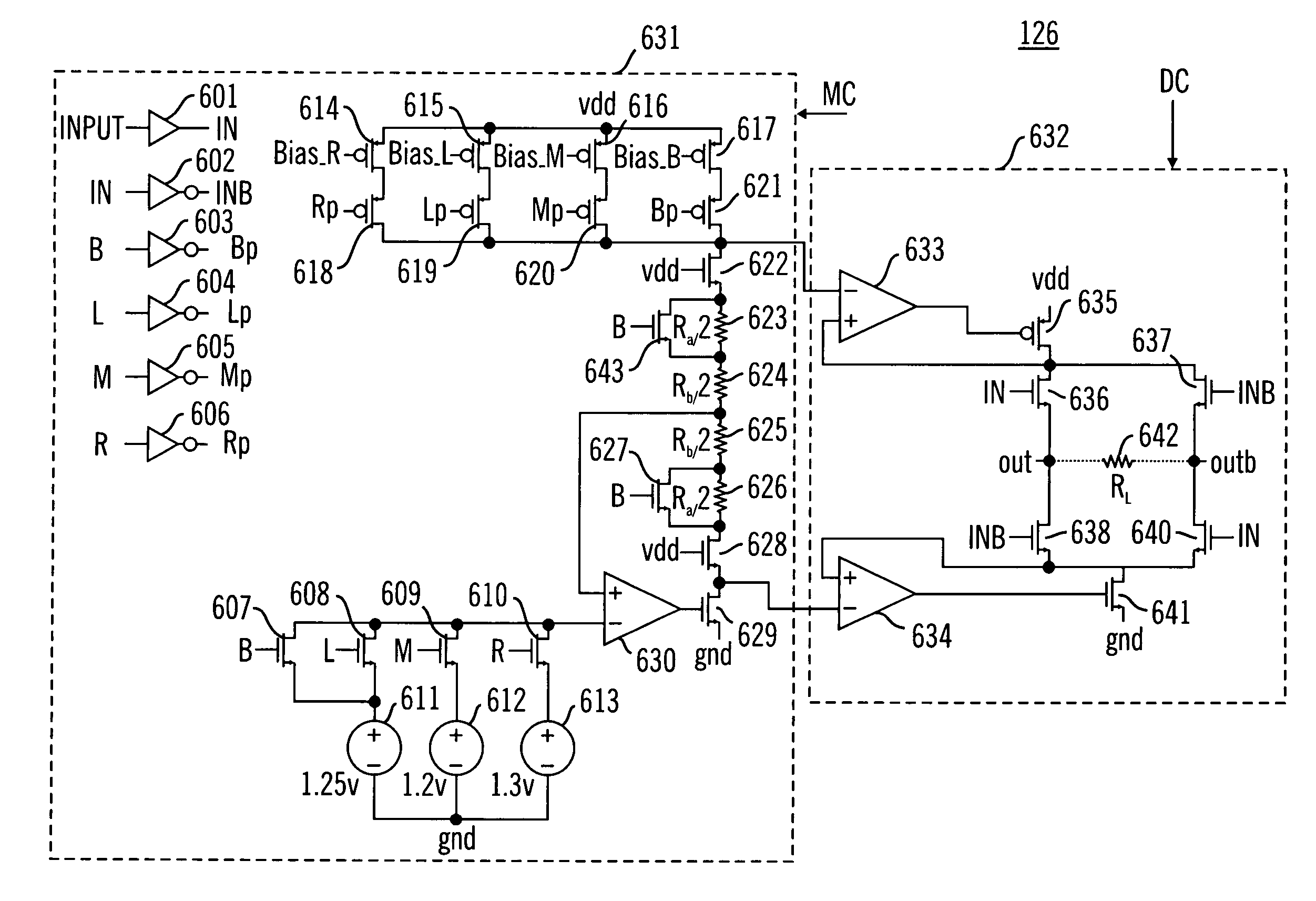
An electronic circuit includes a selectively configurable differential signal interface and a selection control input for selecting one of a plurality of standard differential signal interfaces for configuration of the differential signal interface. The selection control input selects one of the following plurality of standard differential signal interfaces: reduced swing differential signaling (RSDS), low voltage differential signaling (LVDS), mini low voltage differential signaling (mini-LVDS), and bussed low voltage differential signaling (BLVDS), for configuration of the differential signal interface. The electronic circuit may also include a plurality of selectable voltage sources (611, 612, 613) and a plurality of selectable current sources (614, 615, 616, 617), for selecting, in response to an input signal at the selection control input, at least one of an operating D.C. voltage, a standard differential signal voltage, and a standard differential signal current for the differential signal interface.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
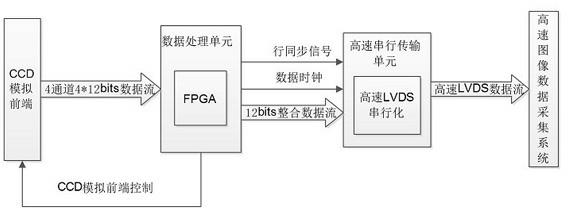
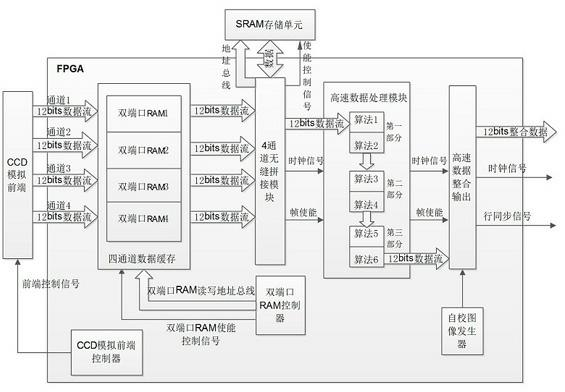
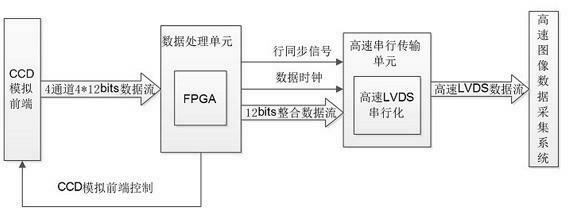
Data processing and transmitting system of high-speed multichannel CCD (charge-coupled device)
InactiveCN102638661AReal-time processingReduce in quantityTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionSerial transferData stream
The invention discloses a data processing and transmitting system of high-speed multichannel CCD (charge-coupled device), which comprises a CCD analog front end, a data processing unit, a high-speed serial transmission unit and a high-speed image data collection system which are sequentially connected. The CCD analog front end is used for converting an analog signal output by a CCD detector and subjected to sampling and pulse control into n channels of digital image data via n A / D (analog / digital) converters, transmitting the digital image data to the data processing unit, and acquiring data of each channel at the same time. The data processing unit is used for transmitting single-channel high-speed data streams, a data transmitter clock and a horizontal synchronizing signal acquired from integration of the digital image data to the high-speed serial transmission unit. The high-speed serial transmission unit is used for converting single-channel high-speed data streams via LVDS (low-voltage differential signaling) serial chips into high-speed LVDS data streams for transmitting. The high-speed image data collection system is used for collecting the high-speed serial LVDS data streams and realizing real-time storing and displaying of the image data.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Programmable low-voltage differential signaling output driver
ActiveUS7236018B1Increase output impedanceInhibit currentGated amplifiersElectric pulse generatorLow voltageEngineering
The present invention relates to a programmable low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) output driver. The programmable LVDS output driver may include circuitry for tri-stating the output to allow several programmable LVDS output drivers to be coupled to a single receiver. The programmable LVDS output driver may also include programmable current sources for varying the output current, as well as providing additional current to circuitry within the driver (e.g., impedance circuitry). The programmable LVDS output driver may also include an impedance circuit for adjusting the output impedance of the output driver, while only diverting a small amount of source current. The current diverted by the impedance circuit may be compensated for by increasing the source current from the programmable current sources. The programmable LVDS output driver may also include pre-emphasis circuitry for boosting the edge rates of output signals.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Use of differential pair as single-ended data paths to transport low speed data
InactiveUS20080117994A1Reduce power consumptionPower managementTransmission systemsLow speedDifferential signaling
Provided herein are systems and methods for transmitting signals across a pair of wires. In accordance with specific embodiments, a differential signal is transmitted across the pair of wires during one period of time, and two single-ended signals are transmitted across the same pair of wires during another period of time. Low voltage differential signaling (LVDS) can be used to transmit the differential signal across the pair of wires. In contrast, non-differential signaling can be used to transfer the two singled-ended signals across the same pair of wires.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
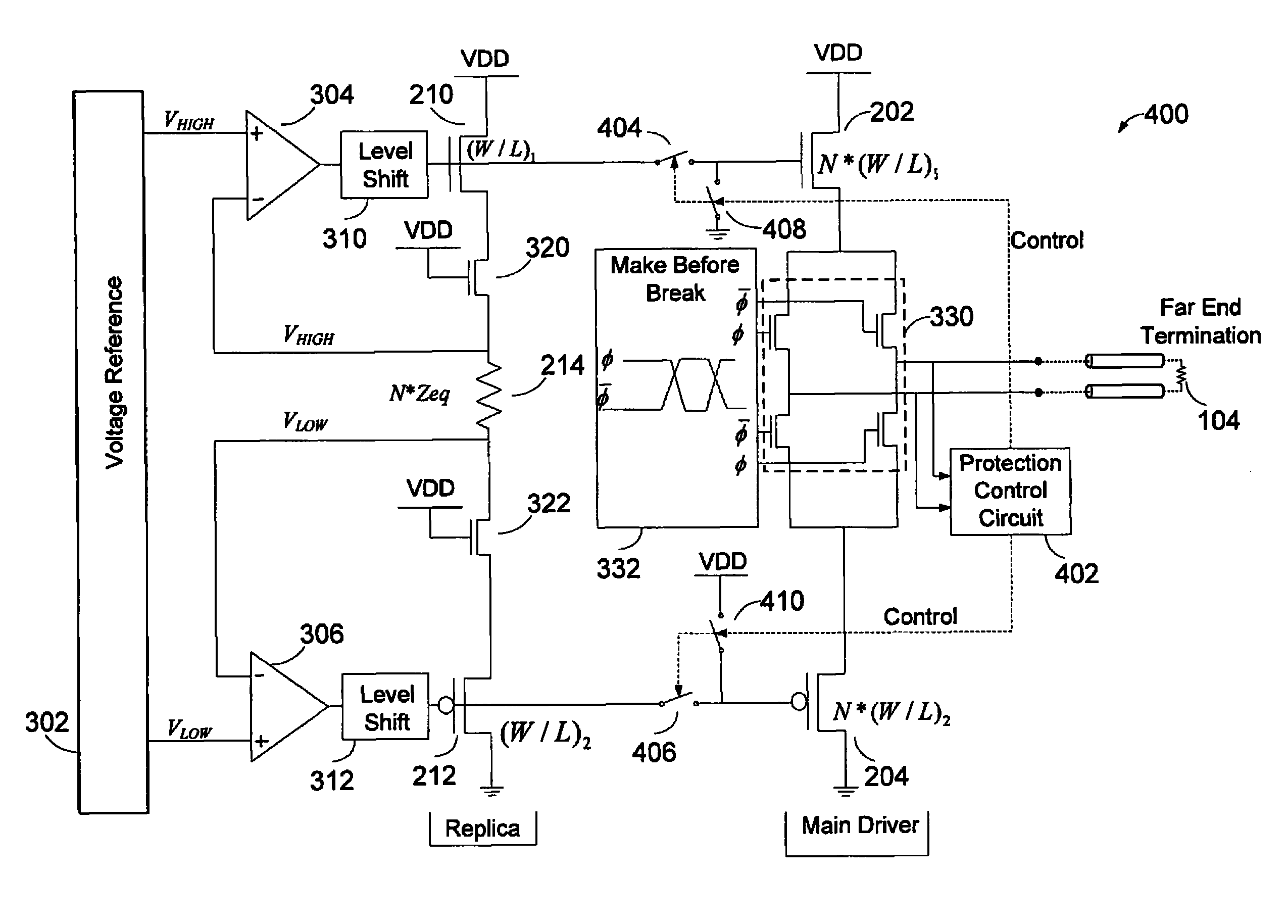
Hot-pluggable differential signaling driver
ActiveUS7898295B1Improve efficiencyReduction in power-off leakage current currentReliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingDifferential signalingEngineering
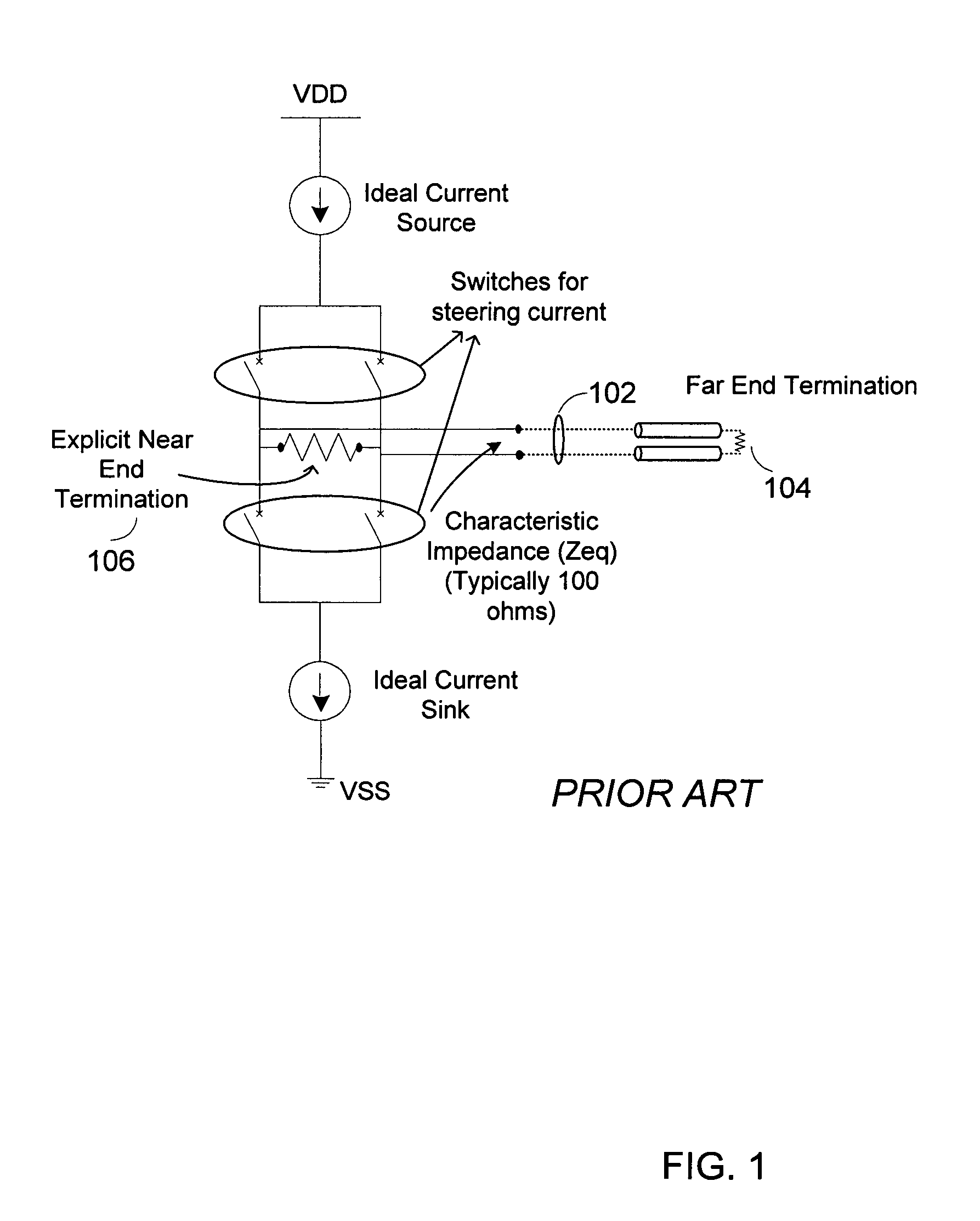
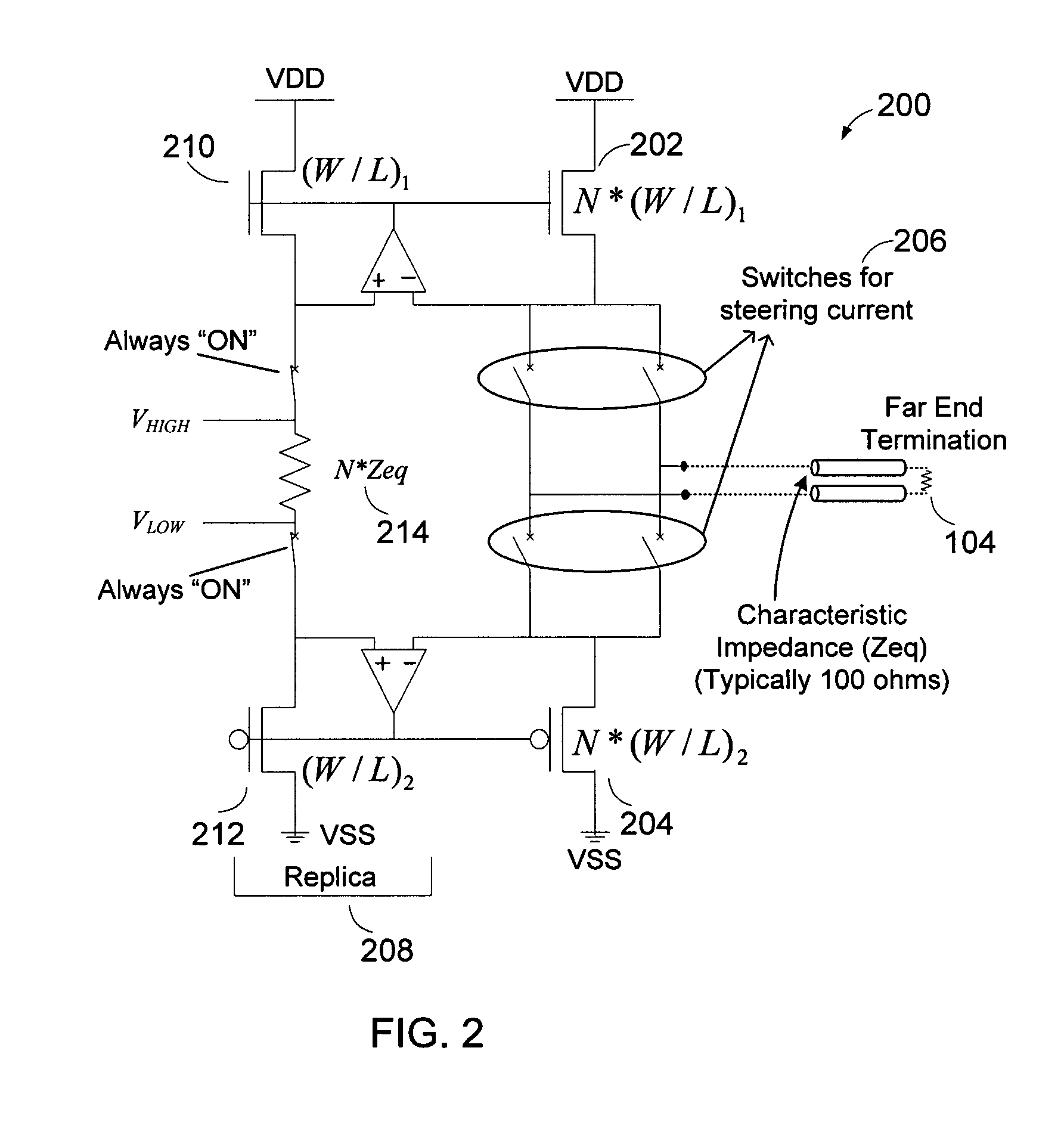
Apparatus and methods provide low voltage differential signaling (LVDS) driver with replica circuit biasing and protection for hot plugging. The replica biasing is non-intrusive in nature, and can control the voltage swing tightly over parametric variations. The absence of an explicit near-end driver termination improves efficiency, while replica biasing controls output voltage swing levels. Hot-pluggable compatibility is achieved by a reduction in power-off leakage current and short circuit current protection.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Low power low voltage differential signaling driver
ActiveUS6927608B1Minimum power consumptionElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorCurrent sourceTransistor
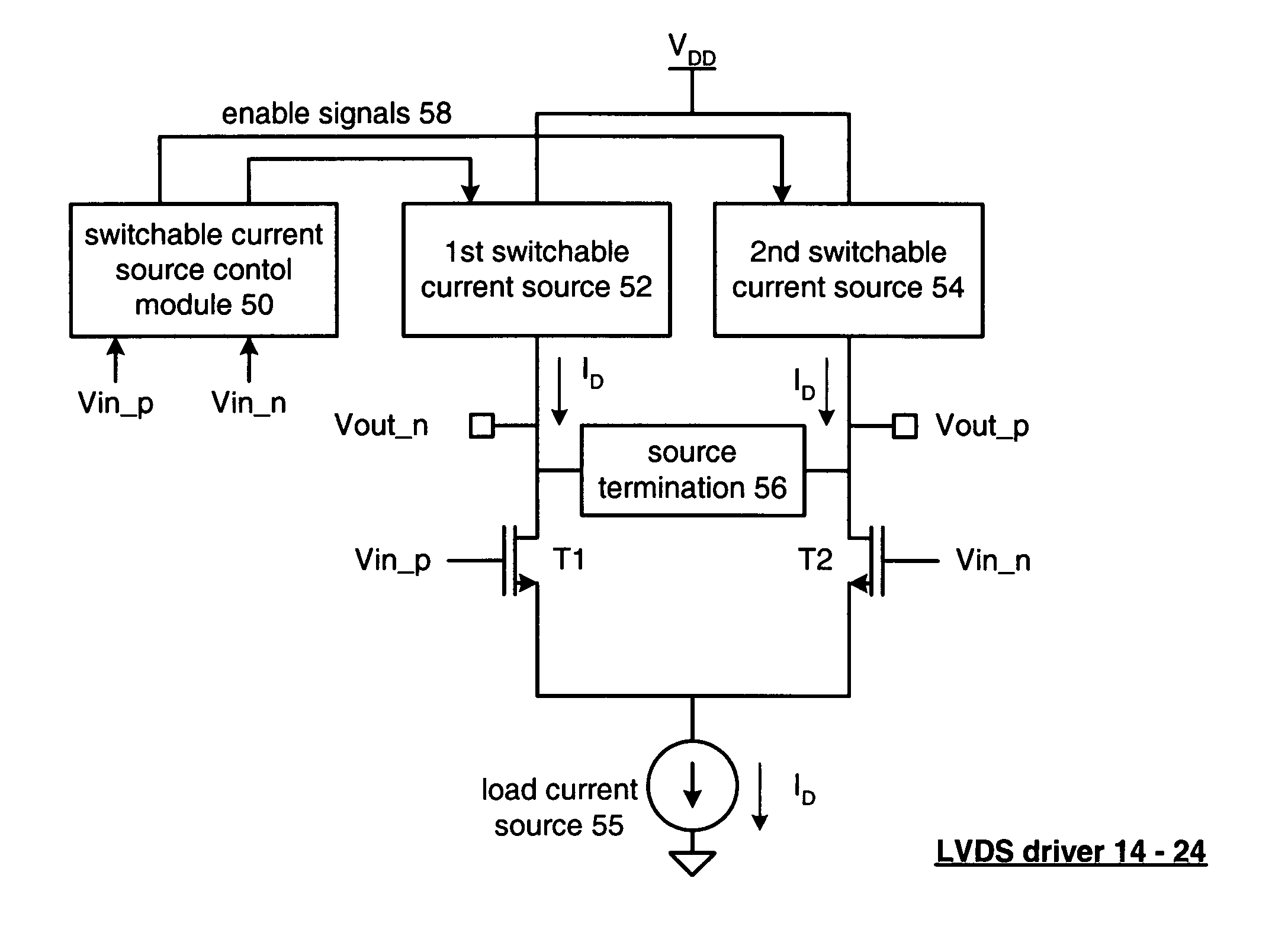
A low power LVDS driver includes a switchable current module, a source termination circuit, a transistor section, and a load current source. The switchable current module is operably coupled to produce a first current when a differential input signal is in a first state and to produce a second current when the differential input signal is in a second state. The source termination circuit is operably coupled in parallel with a load. The transistor section is operably coupled to receive the first and second currents from the switchable current module via at least one of the source termination circuit and the load, wherein the transistor section produces an LVDS output signal based on the first and second currents, the differential input signal, and the source termination circuit. The load current source is operably coupled to sink the first and second currents from the transistor section.
Owner:XILINX INC
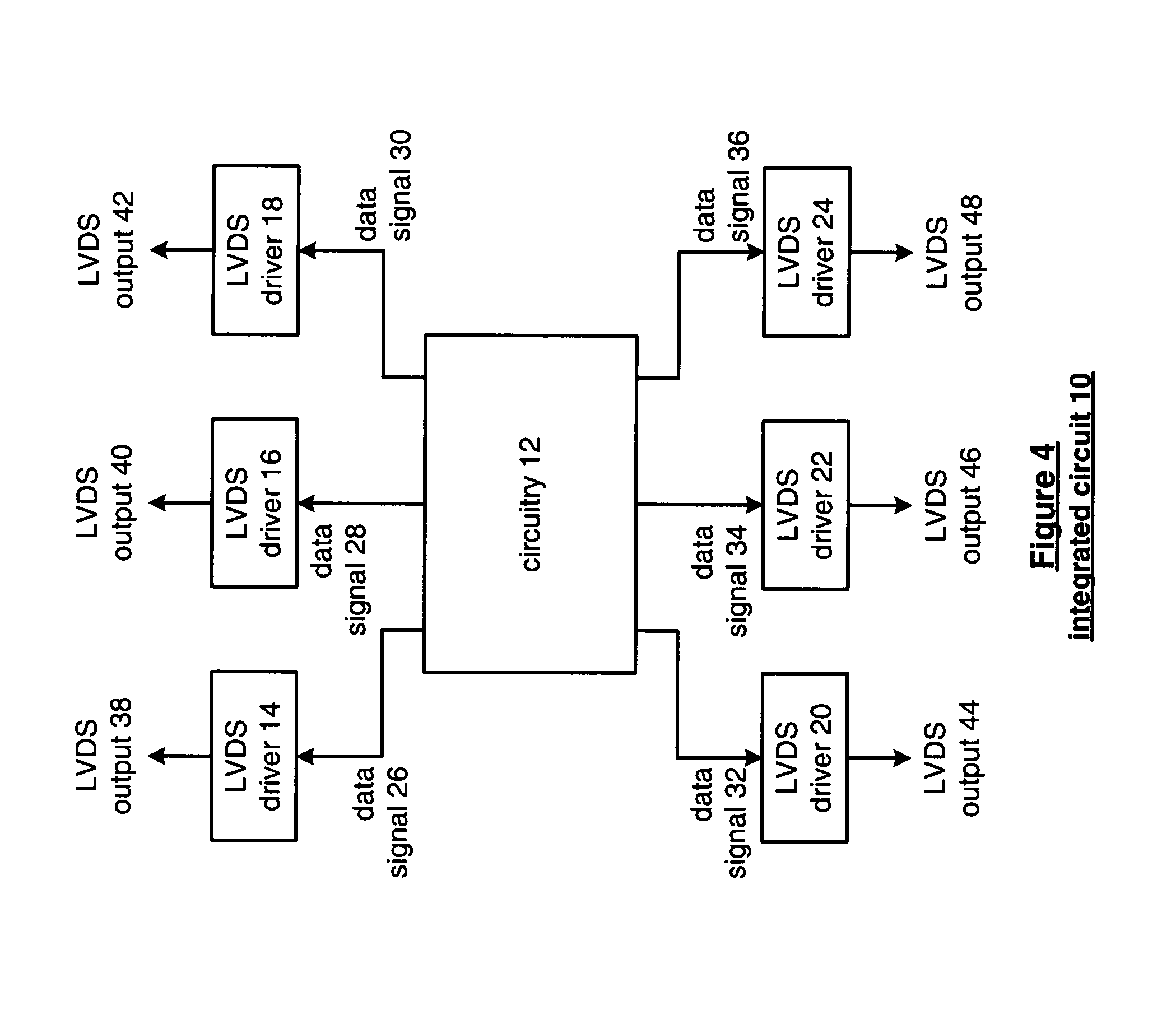
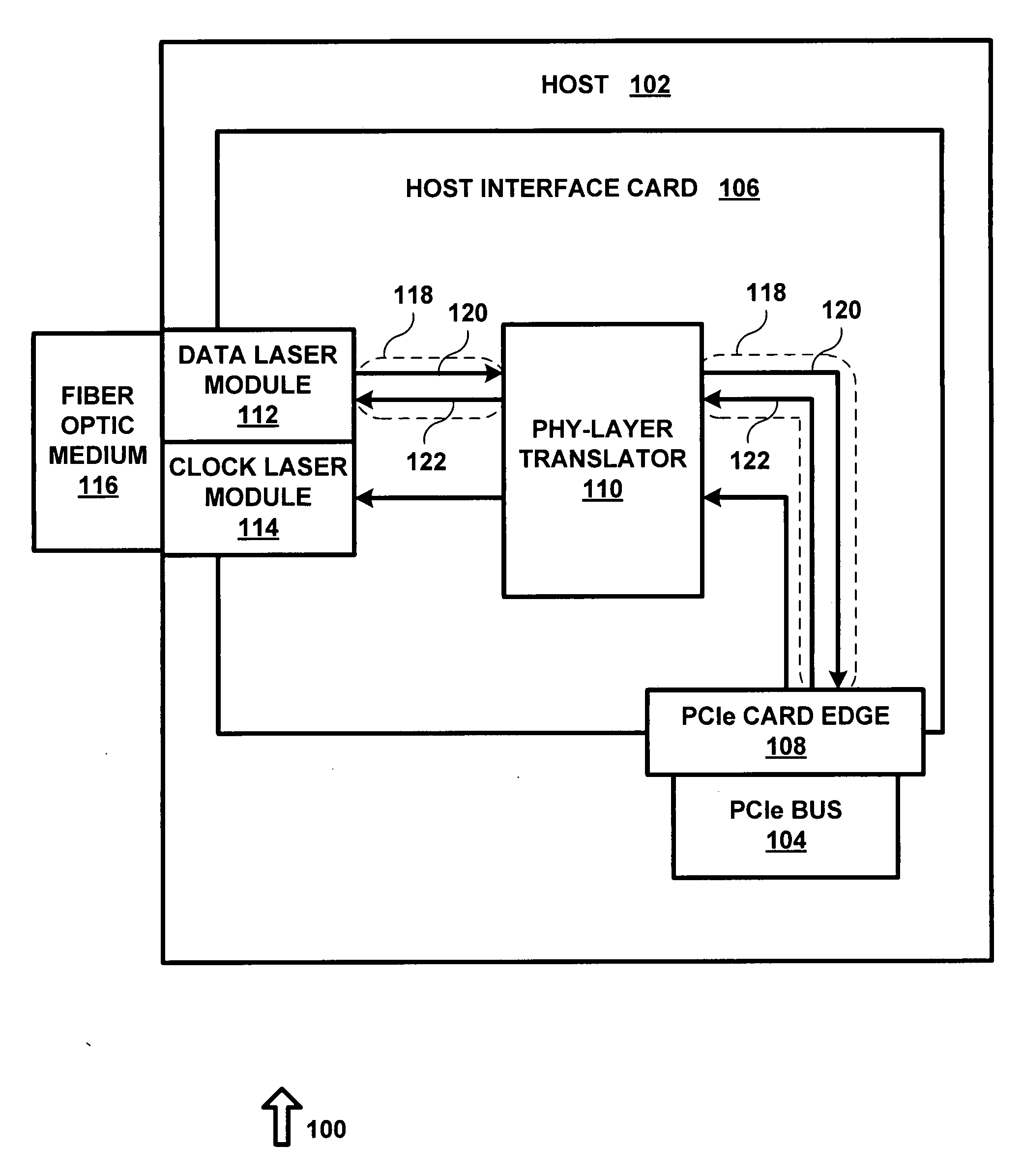
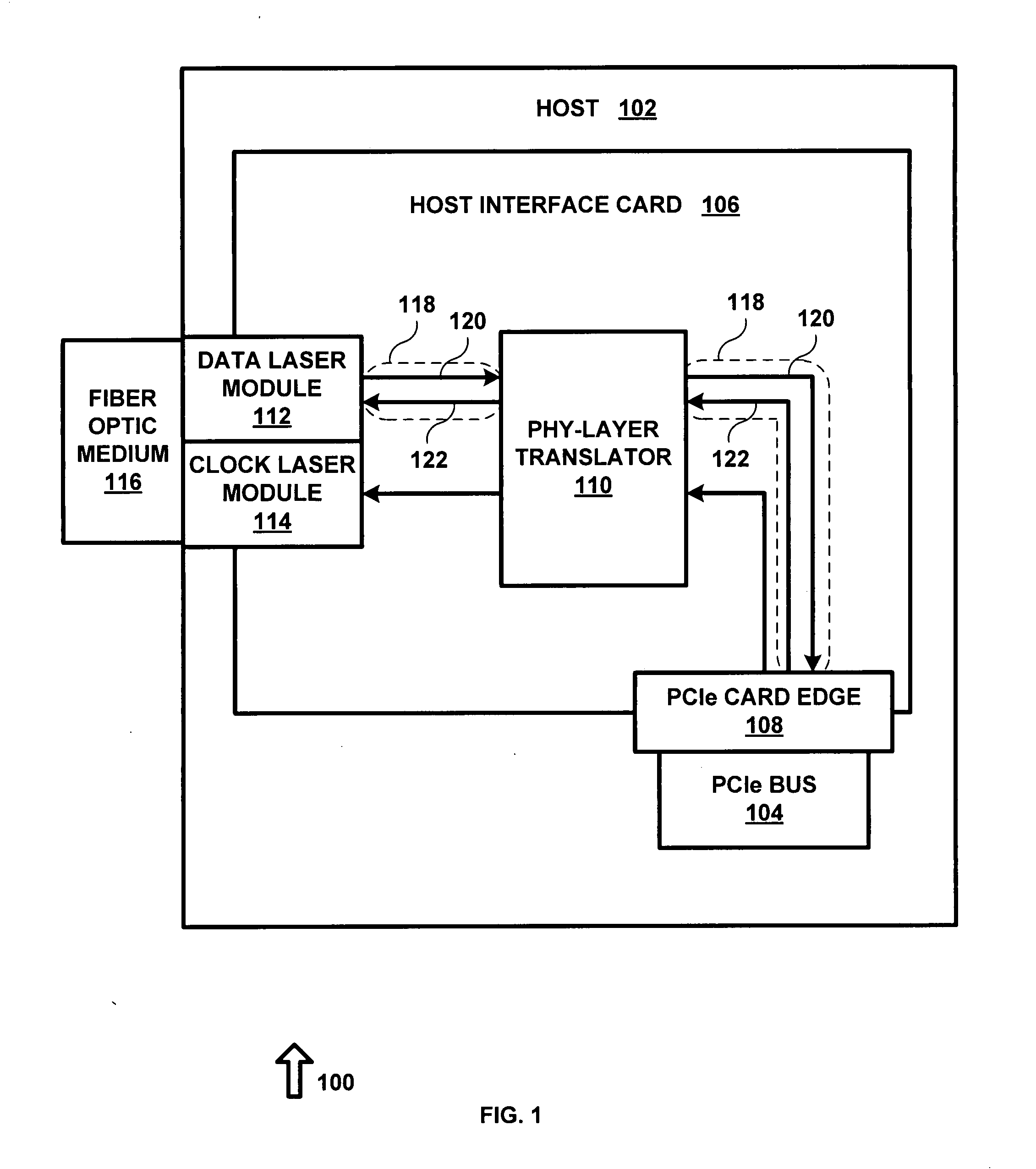
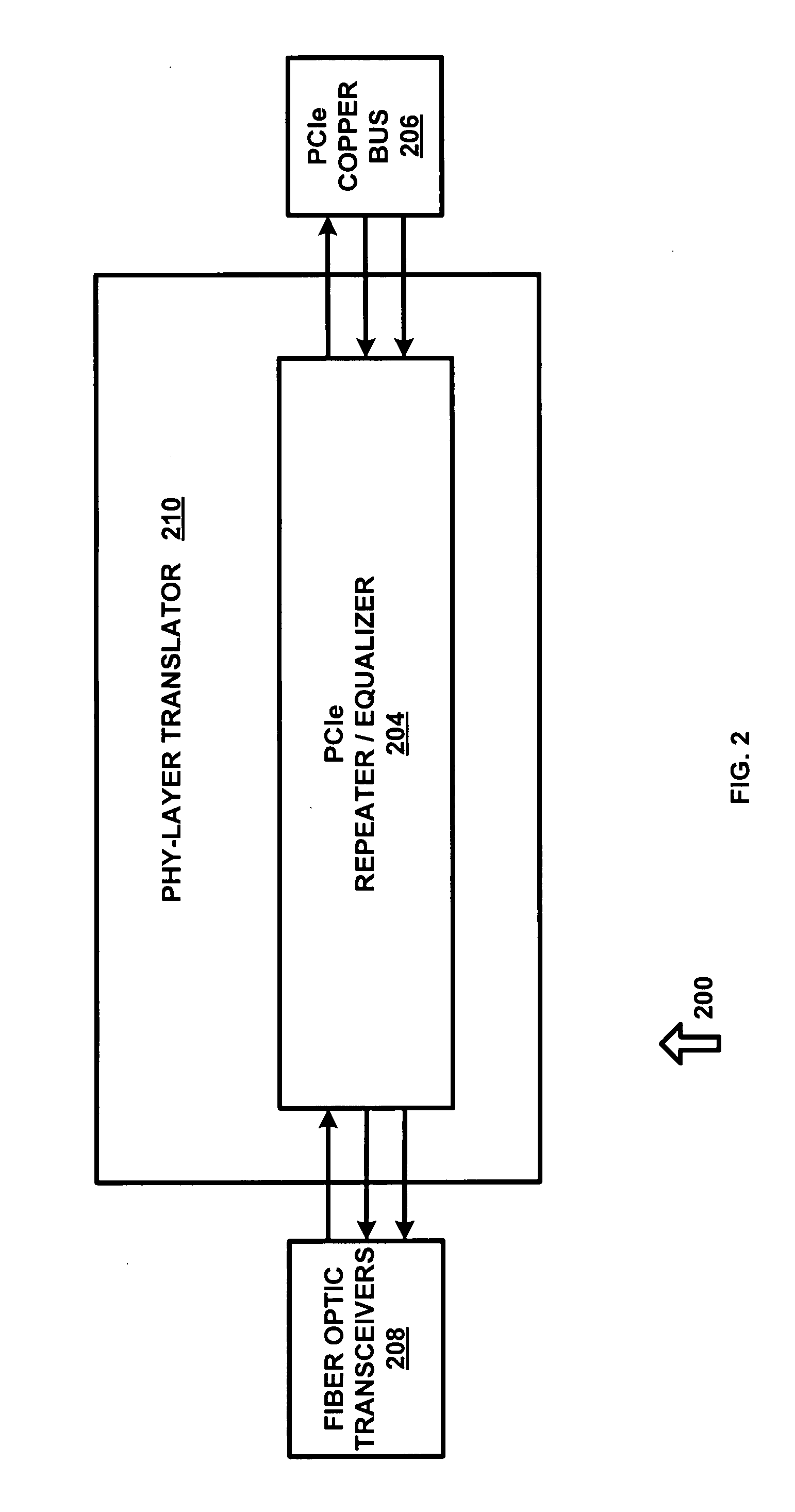
System and method for expanding PCIe compliant signals over a fiber optic medium with no latency
ActiveUS20090052903A1Robust and scalable and economically advantageousImprove scalabilityElectromagnetic transmissionElectric digital data processingFiberTransceiver
A system for expanding PCI Express (PCIe) compliant signals over a fiber optic medium with no latency. A standardized fiber optic transceiver is adapted to provide an optimal PCIe expansion over a fiber optic medium. Signal buffers are utilized to translate and fine-tune standardized PCIe traffic to a level of low voltage differential signaling (LVDS) that is comprehensible to a wide range of fiber optic transceivers over a wide range of interface bandwidths. The intended use for such a high-speed LVDS buffer is to strengthen and enable PCIe signals over metal (copper) cable or metal printed circuit board (PCB) traces for large PCBs, such as backplanes, server motherboards, etc. By disposing the PCIe buffer used for metal (copper) cable between the PCIe bus and the fiber optic transceiver, one can achieve the signal conditioning and translating required to allow PCIe signals to pass over the fiber optic medium.
Owner:RJ INTPROP
Low voltage differential signaling drivers including branches with series resistors
ActiveUS7595661B2Reduce in quantityMinimizes signal reflectionElectric pulse generatorDifferential amplifiersLow voltageResistor
A low voltage differential signal driver includes first and second current sources, a first branch and a second branch. The first branch includes at least two transistors and at least two resistors between them that are all connected in series between the first and second current sources, to define a first node between adjacent resistors that is configured to transmit and receive differential signals. The second branch also includes at least two transistors and at least two resistors between them that also are all connected in series between the first and second current sources, to define a second node between adjacent resistors that is also configured to transmit and receive differential signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Processing device and processing method for high dynamic constrast of liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20090066632A1Improve dynamic contrastQuality improvementStatic indicating devicesPower inverterLiquid-crystal display
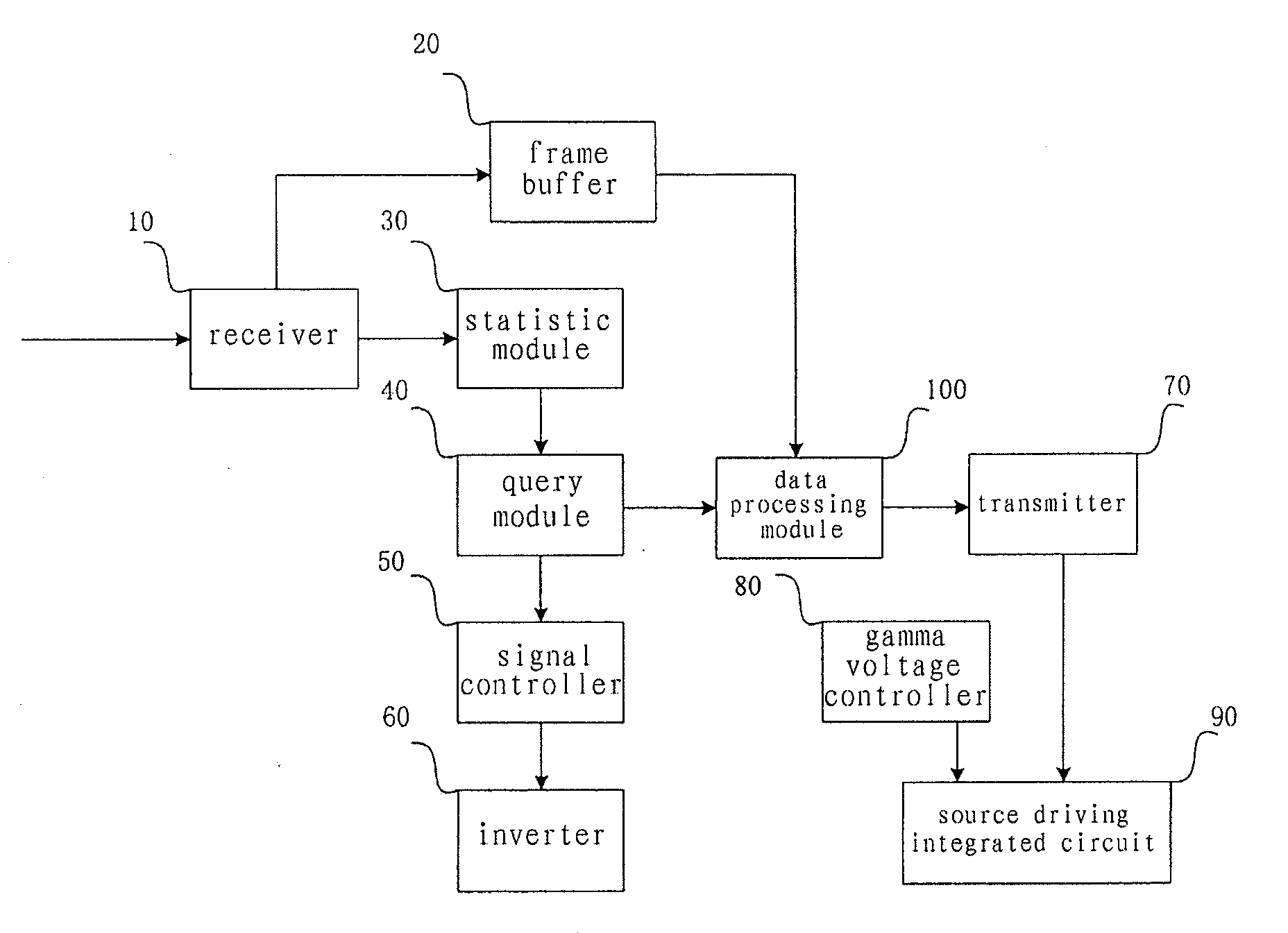
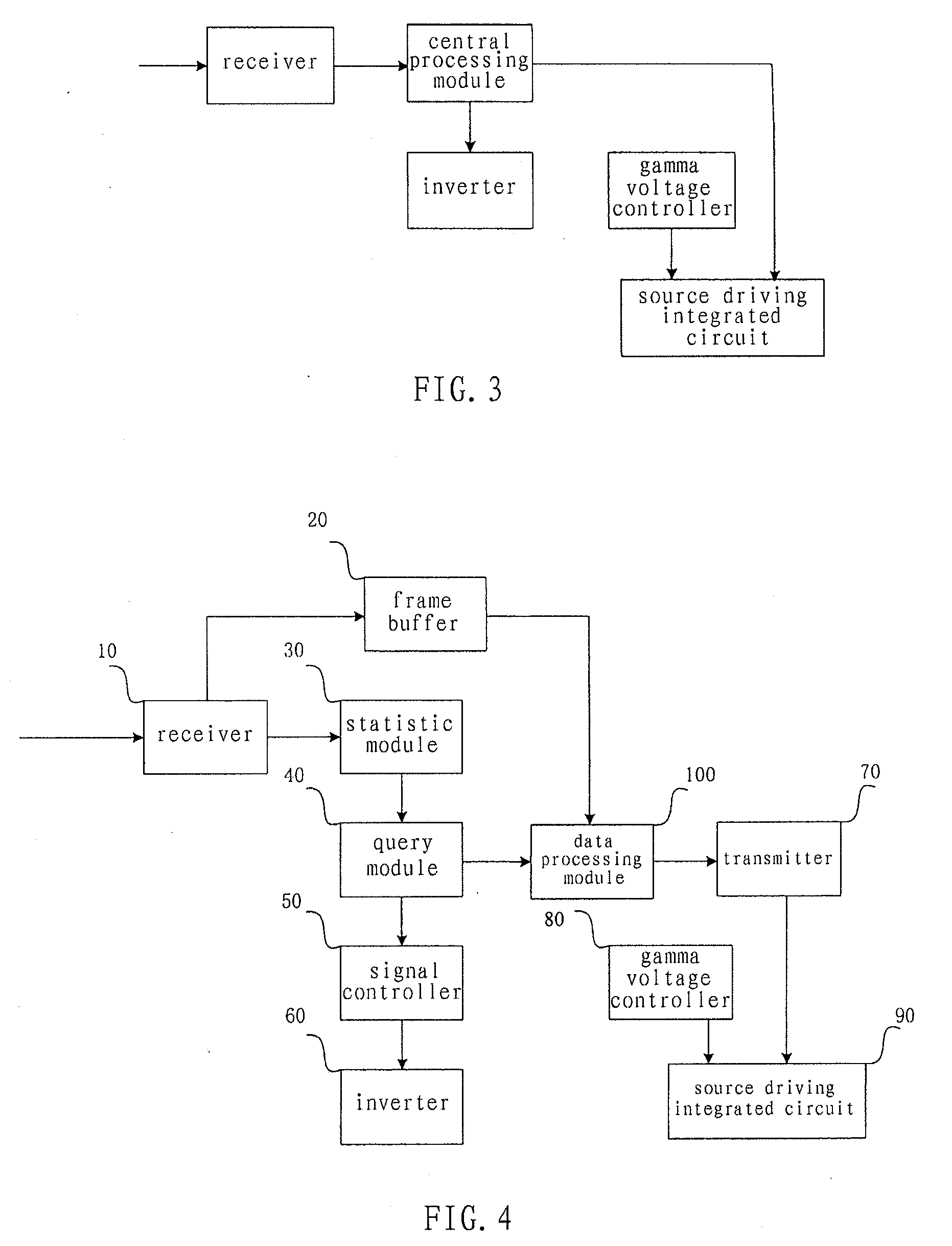
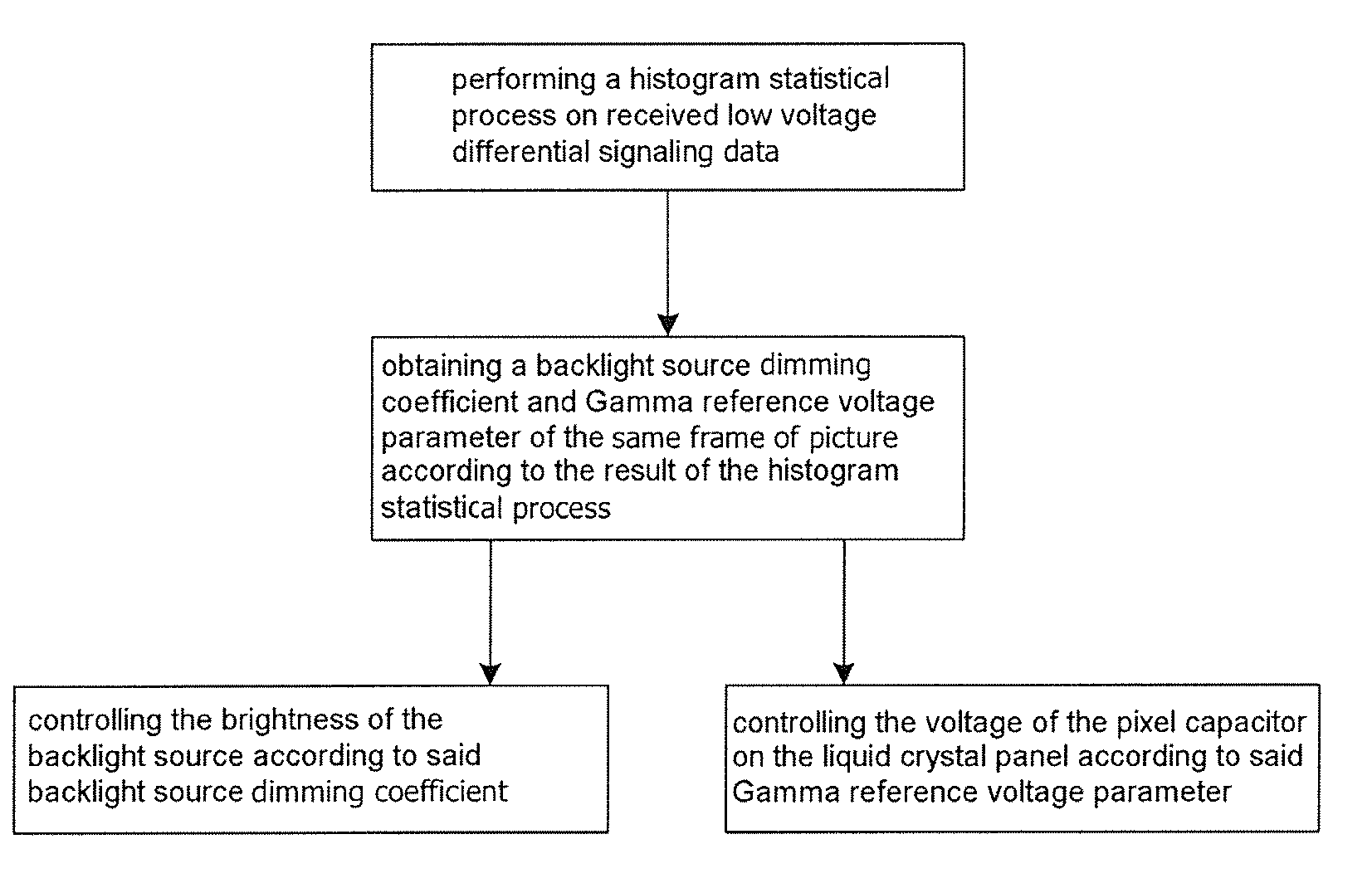
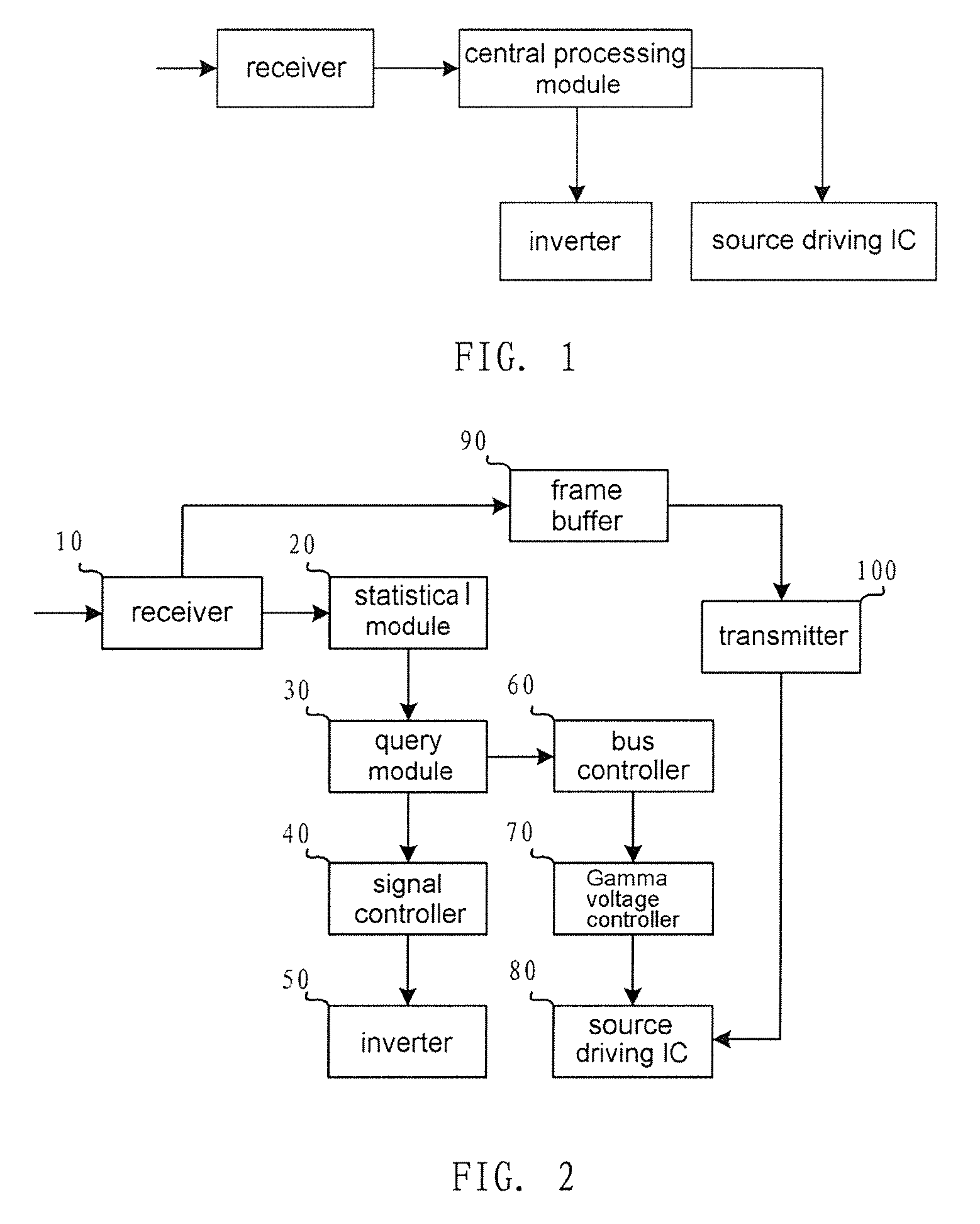
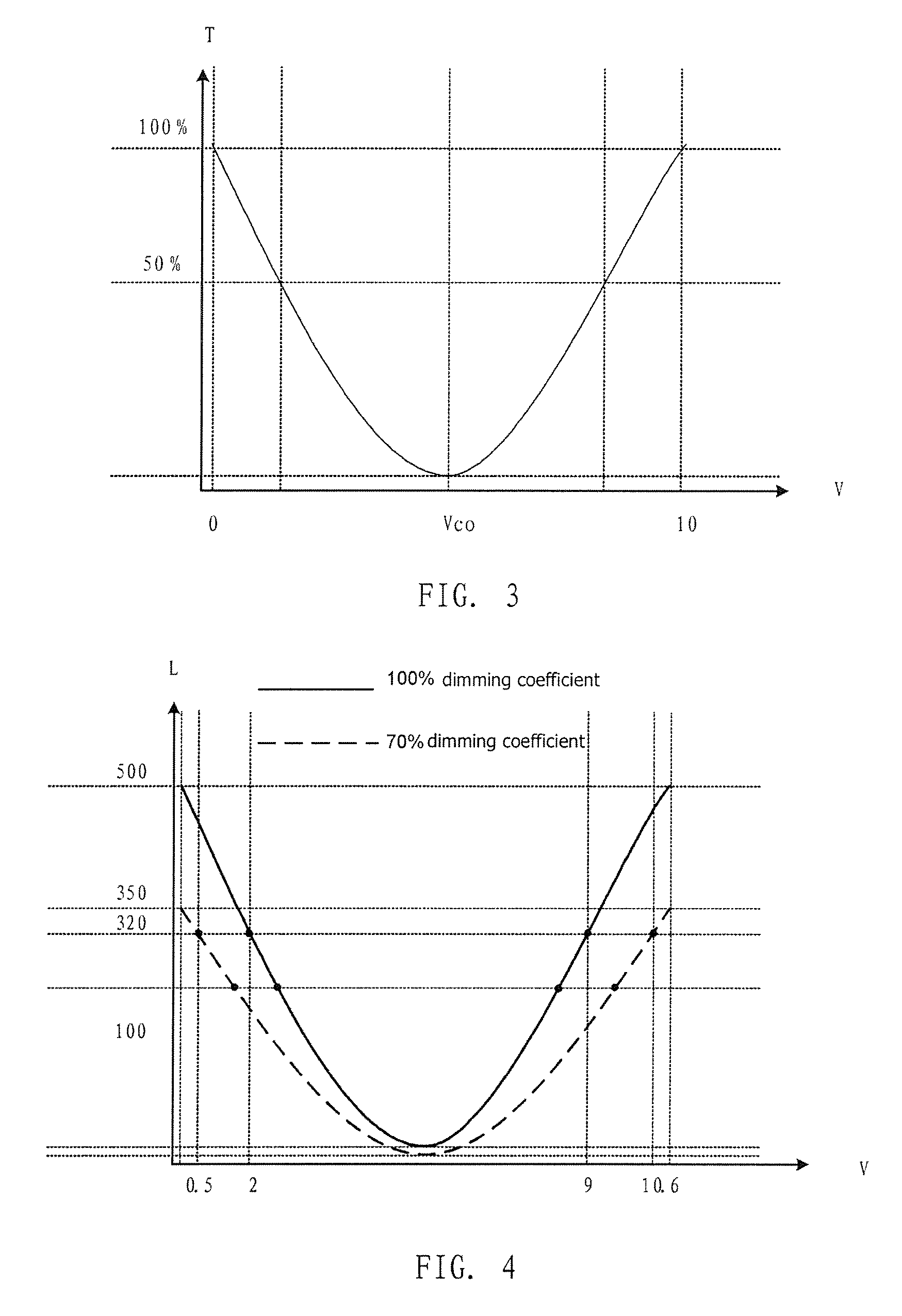
The present invention relates to a processing device and method for high dynamic contrast of a liquid crystal display device. The processing device comprises a receiver, an inverter and a source driving IC connected to a central processing module, a gamma voltage controller connecting to the source driving IC. The process method comprises: performing histogram statistic processing on a received low voltage differential signaling data; obtaining a backlight source dimming coefficient of picture of a same frame and an I / O gray scale mapping table corresponding to the backlight source dimming coefficient according to result of the histogram statistic processing; controlling to adjust data output to a source driving IC according to the I / O gray scale mapping table; and controlling luminance of a backlight source according to the backlight source dimming coefficient. The present invention adjusts the luminance of the backlight source and the output data of the LCD device concurrently, therefore improves dynamic contrast of pictures, mitigates problems of low contrast and flicker in the LCD, and save the power consumption of the backlight source.
Owner:BEIJING BOE OPTOELECTRONCIS TECH CO LTD
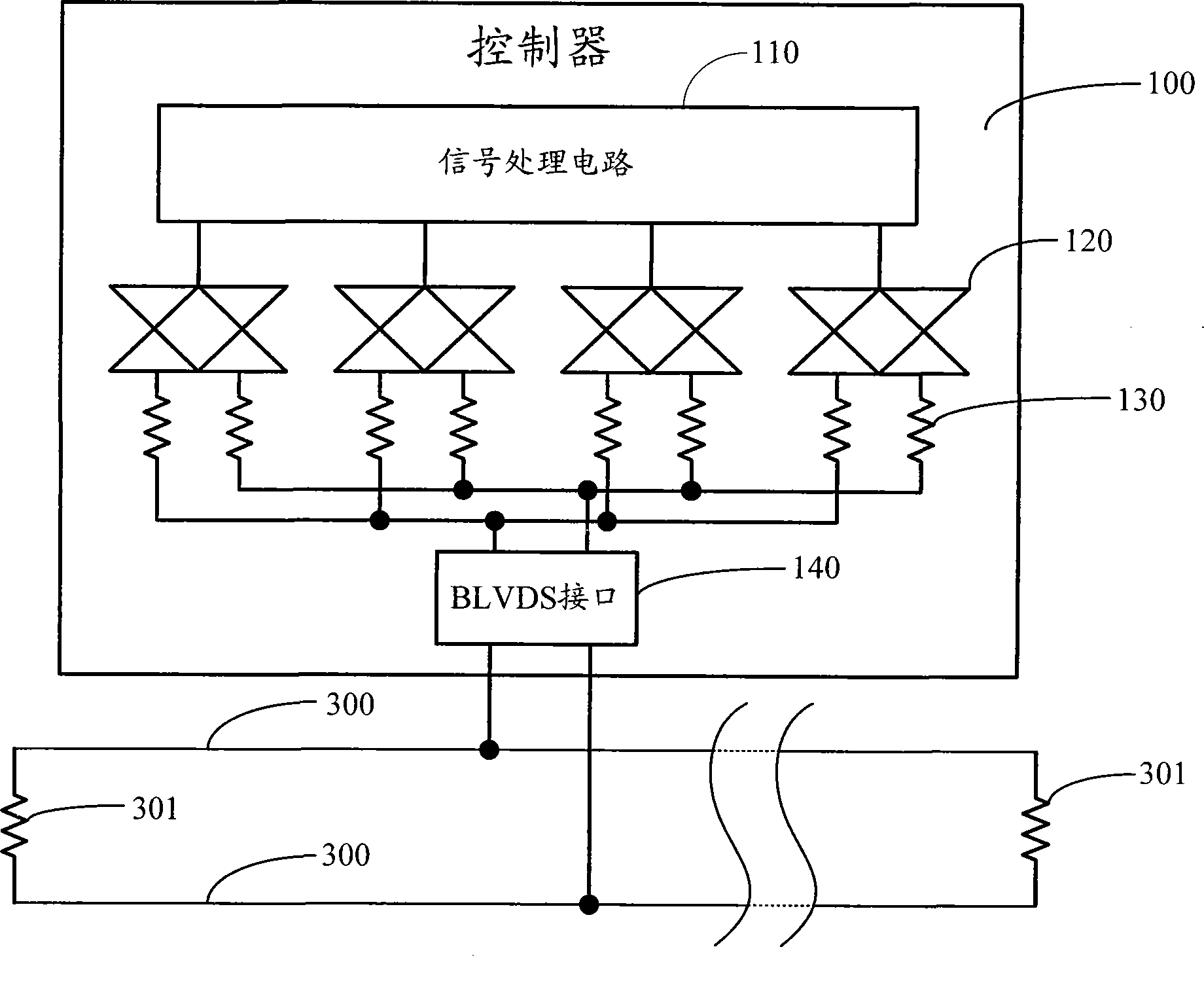
Liquid crystal display splicing wall
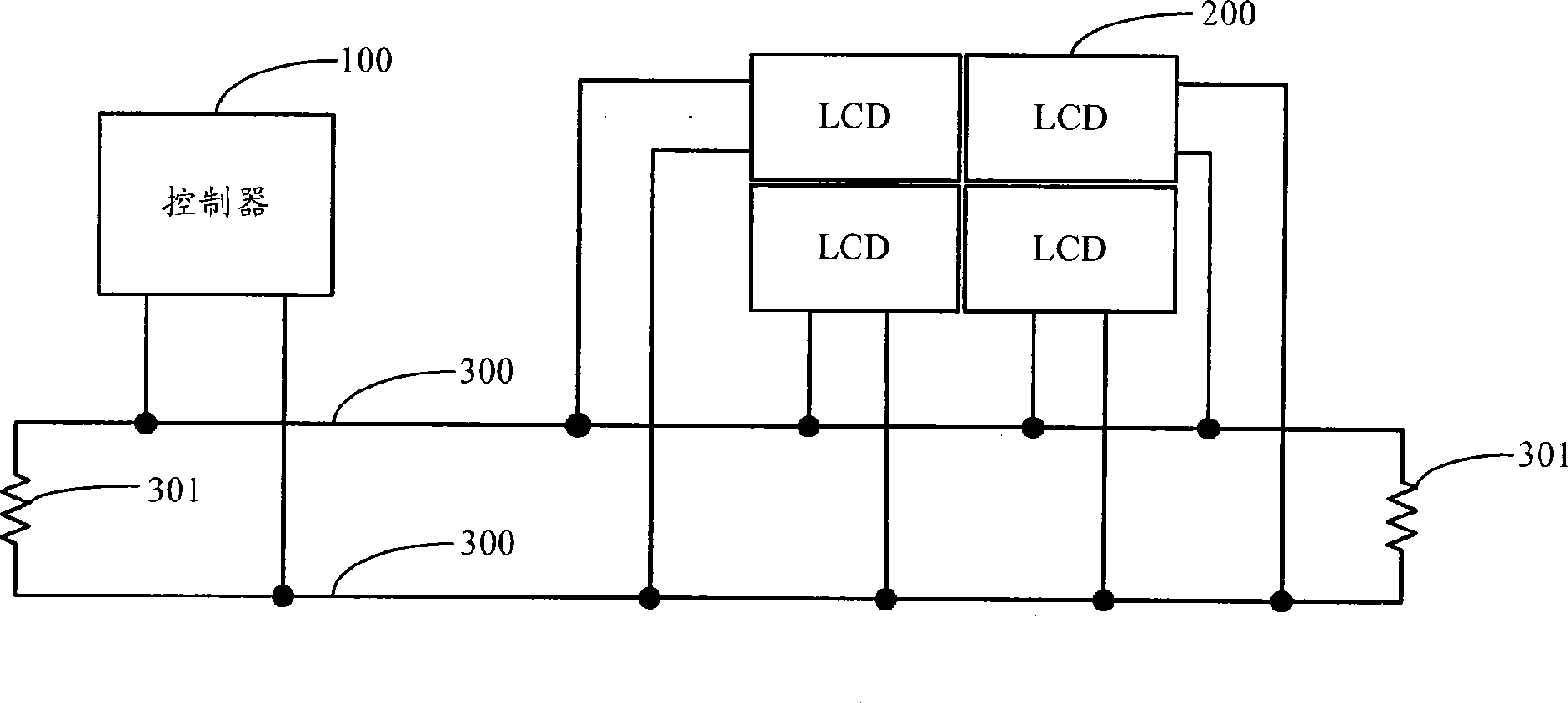
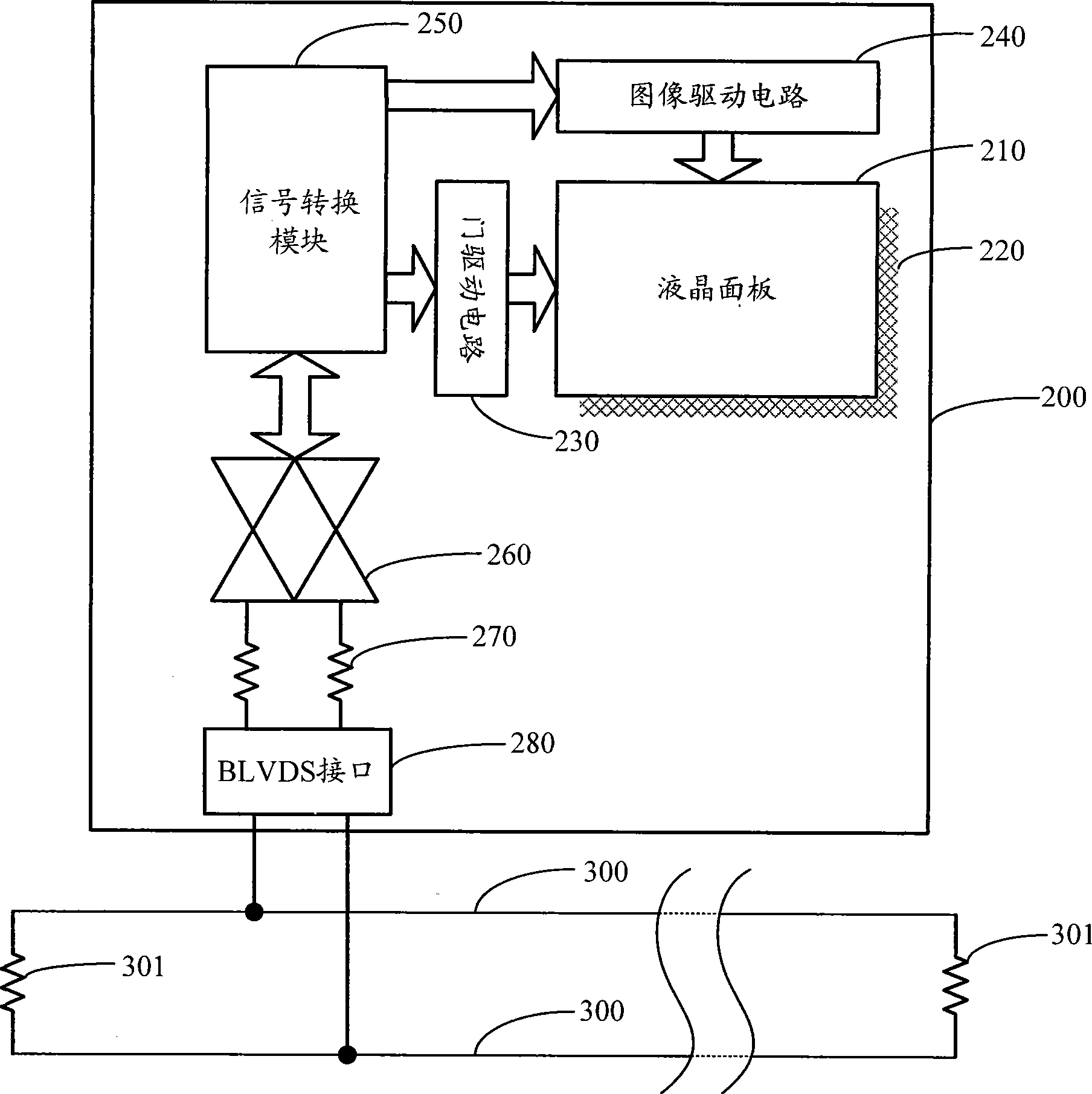
ActiveCN101520997AChange structureIncrease flexibilityStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayNetwork packet
The invention discloses a liquid crystal display splicing wall which comprises a controller (100) and more than two liquid crystal display units (200), wherein the controller (100) and the liquid crystal display units (200) are connected to a BLVDS bus (300) by respective bus low voltage differential signaling (BLVDS) interfaces, and each liquid crystal display unit has an exclusive bus address; the controller (100) distributes an image signal of each liquid crystal display unit, encapsulates the image signal and the bus address of the liquid crystal display unit (200) which corresponds to the image signal into a data packet and sends the data packet to the BLVDS bus (300) by the BLVDS interfaces; the liquid crystal display units (200) judge whether the bus address of the data packet in the BLVDS bus (300) is matched with the bus address of the liquid crystal display units or not, if the bus address of the data packet in the BLVDS bus (300) is matched with the bus address of the liquid crystal display units, the LCD display units receive the data packet and display images according to the image signals in the data packet.
Owner:KUSN INFOVISION OPTOELECTRONICS
Organic light emitting diode display device and driving method thereof
An organic light emitting diode display device is disclosed which includes a data driver configured to transfer a sensing data packet and a timing controller configured to receive the sensing data packet in a bus low voltage differential signaling mode. The timing controller includes an internal clock generator configured to generate at least one internal clock signal and a buffer configured to latch the sensing data packet in synchronization with the internal clock signal.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Liquid crystal module test device with display port (DP) interface and test method thereof
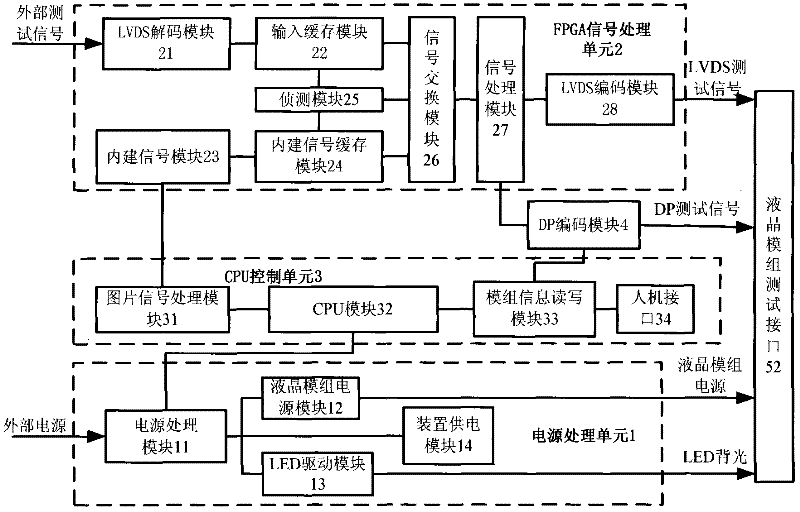
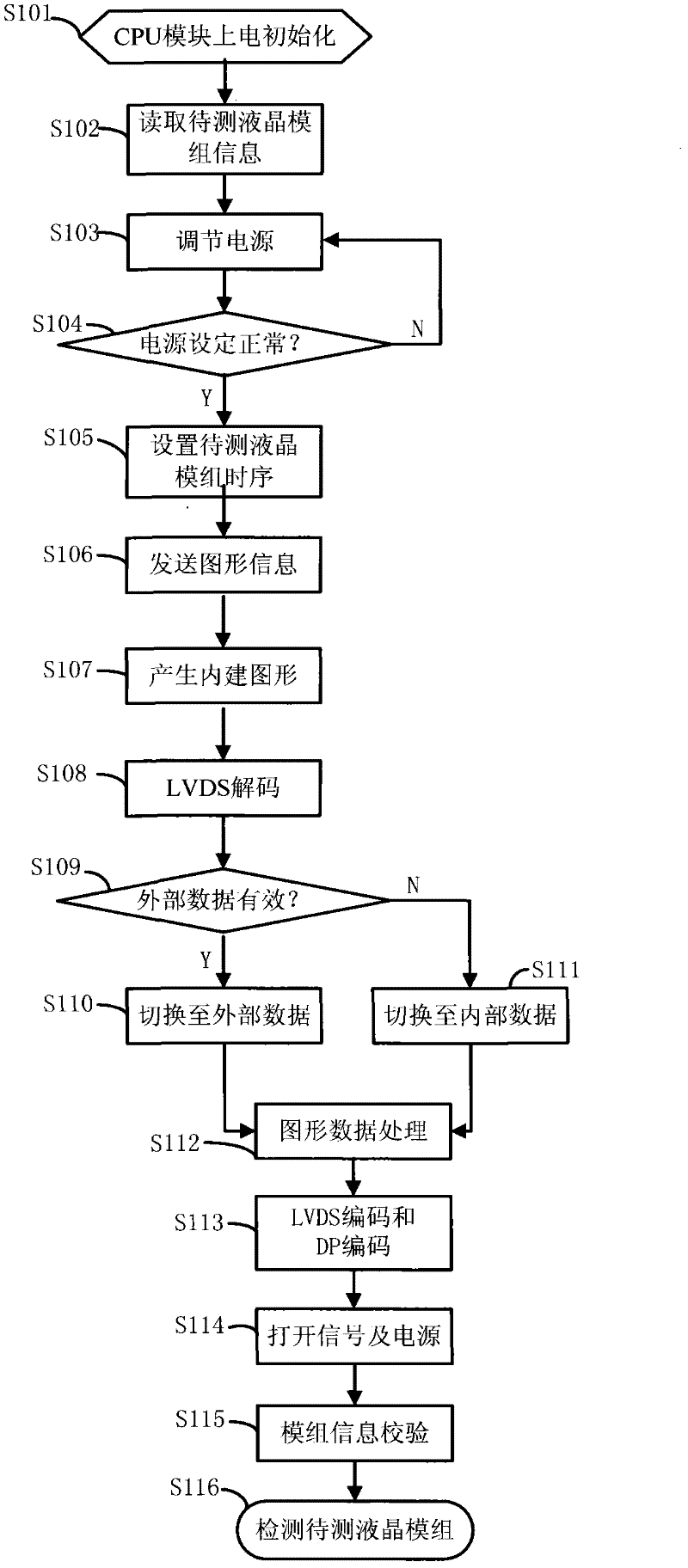
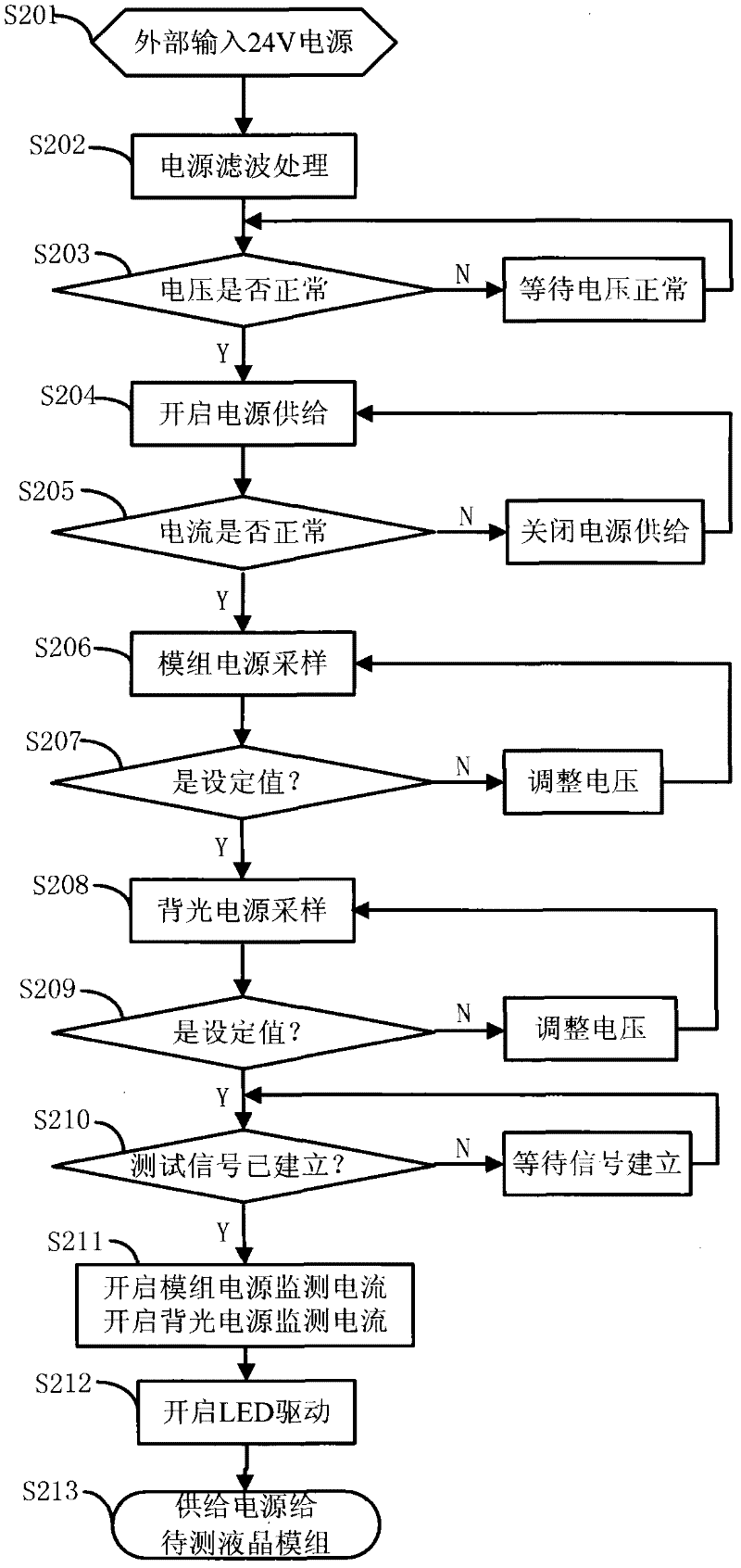
ActiveCN102446477AAuto switchHighly integratedStatic indicating devicesElectrical testingLow voltageEngineering
The invention discloses a liquid crystal module test device with a display port (DP) interface and a test method thereof, which relate to the test field of liquid crystal modules. The liquid crystal module test device with the DP interface comprises a power supply processing unit, a field programmable gate array signal processing unit and a central processing unit (CPU) control unit, wherein the power supply processing unit and the field programmable gate array signal processing unit are connected with one liquid crystal module test interface; the liquid crystal module test interface is connected with a liquid crystal module to be tested; the power supply processing unit comprises a power supply processing module and a light emitting diode (LED) driving module; the CPU control unit and the field programmable gate array signal processing unit are both connected with one DP coding module which outputs a signal to the liquid crystal module to be tested; and the field programmable gate array signal processing unit comprises a built-in signal module, a low-voltage differential signaling decoding module and a low-voltage differential signaling coding module. According to the test device and the test method, a low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) interface and the DP interface are simultaneously provided, an external input test signal and a built-in test signal are simultaneously supported, and LED backlight driving output is provided.
Owner:WUHAN JINGCE ELECTRONICS GRP CO LTD
High-resolution image acquisition and processing device
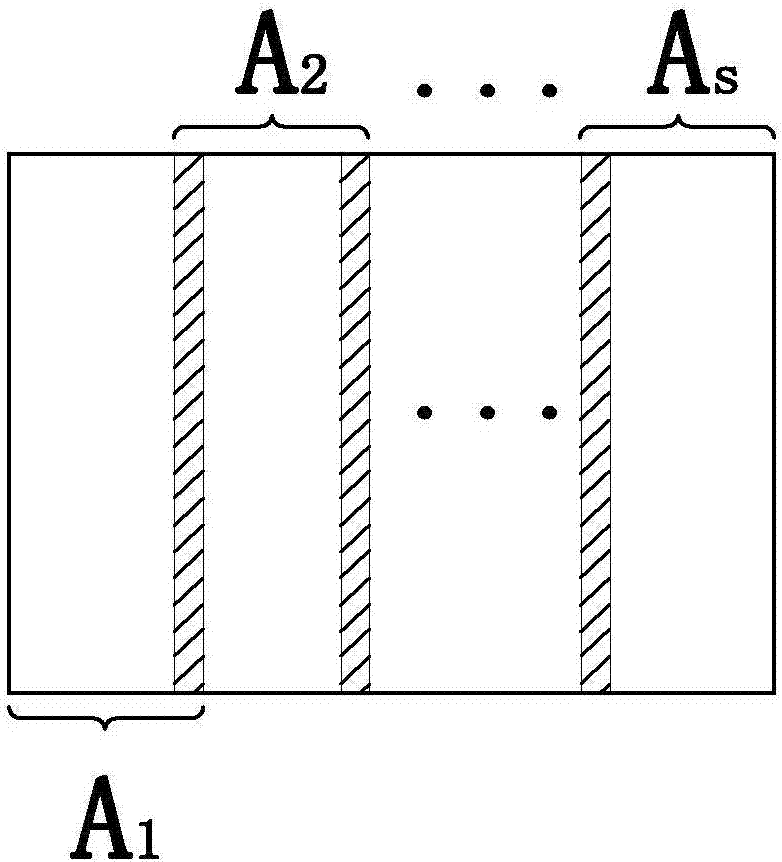
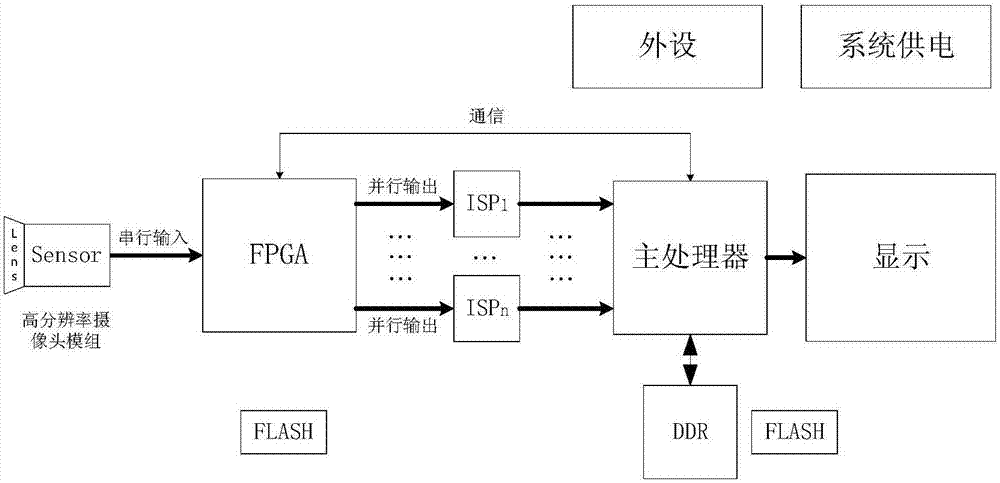
ActiveCN107249101AReal-time processingIncrease flexibilityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsData streamHigh resolution image
The invention relates to a high-resolution image acquisition and processing device. The device includes an image acquisition module, an LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling) serial-to-parallel conversion module, a data mapping module, an image cutting module, a multi-path synchronization module, a communication control module, an image processing module, an output display module and peripherals; the LVDS serial-to-parallel conversion module is used for deserializing the data of each channel of an LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling) interface, recovering clock signals from serial data streams and demodulating the restored data; the data mapping module is used for performing alignment, data frame decoding and combinational mapping operation on bit data which are analyzed from the differential channels; the image cutting module is used for analyzing and cutting high-resolution images and outputting a plurality of paths of small-frame images; and a multi-path synchronization module is used for performing synchronization operation on the plurality of paths of small-frame images and transmitting the synchronized image data to the video input interface of a main processor in parallel at the same time. The high-resolution image acquisition and processing device of the invention has the advantages of real-time processing of high-resolution images, high applicability and high flexibility.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
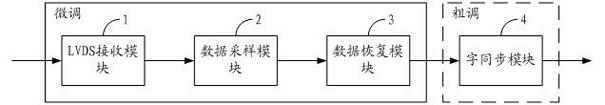
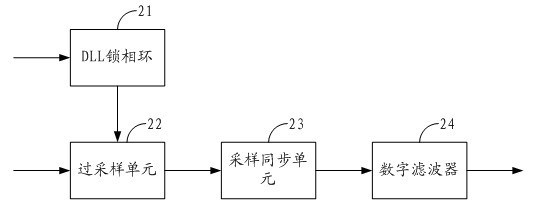
High-speed parallel interface circuit
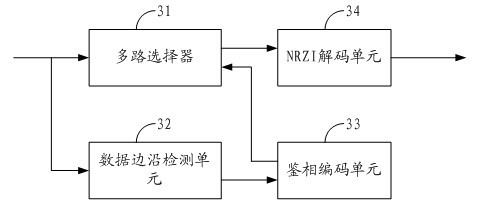
The invention is suitable for the digital communication field, and provides a high-speed parallel interface circuit. The high-speed parallel interface circuit comprises a low voltage differential signaling (LVDS) receiving module, a data sampling module, a data restoring module and a word synchronization module, wherein the LVDS receiving module receives and shapes data; the data sampling module is connected with the LVDS receiving module and samples the data output by the LVDS receiving module under a plurality of phase clocks; the data restoring module is connected with the data sampling module, selects optimal sampling data from oversampling data output from the data sampling module and restores original data by non return to zero inverse (NRZI) decoding; and the word synchronization module is connected with the data restoring module and carries out shift adjustment to the data output by the data restoring module. In the high-speed parallel interface circuit, oversampling and word synchronization are combined to carry out accurate sampling restoration and synchronization to source-synchronous parallel data; and data in the center of an effective window can be dynamically and accurately sampled and restored in real time by dynamically synchronizing, filtering, discriminating phase, selecting the oversampling data and the like.
Owner:成都三零嘉微电子有限公司
Pre-emphasis apparatus, low voltage differential signaling transmitter including the same and pre-emphasis method
InactiveUS20070063739A1Improve reliabilityBaseband system detailsLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsData signalEngineering
A pre-emphasis apparatus of a LVDS transmitter includes a pre-emphasis signaling generation unit and a pre-emphasis current output unit. The pre-emphasis signal generation unit generates a pre-emphasis pulse signal based on N parallel data signals received from an external source and N-phase clock signals received from a phase locked loop, where N is an integer greater than 1. The pre-emphasis current output unit provides an additional current for a pre-emphasis operation to a current source of a LVDS driver in response to the pre-emphasis pulse signal generated by the pre-emphasis pulse signal generation unit. The pulse signal for pre-emphasis is generated based on the parallel data signals received from the external source and the multi-phase clock signals, which are output from the phase locked loop for performing a sampling of the parallel data signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for realizing integration of display image processing and timing control chip
InactiveCN101996544AReduce in quantityLow costStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayImaging processing
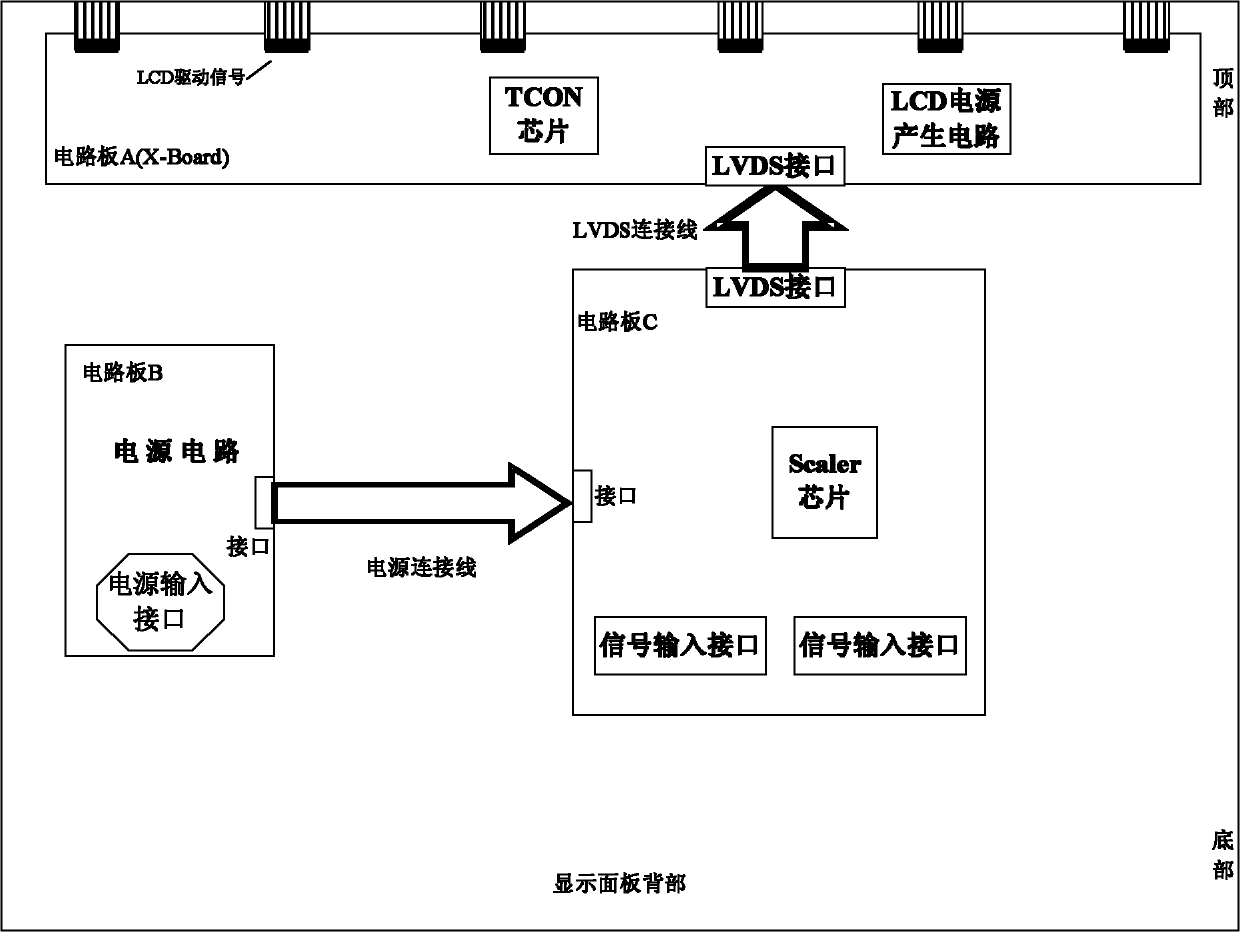
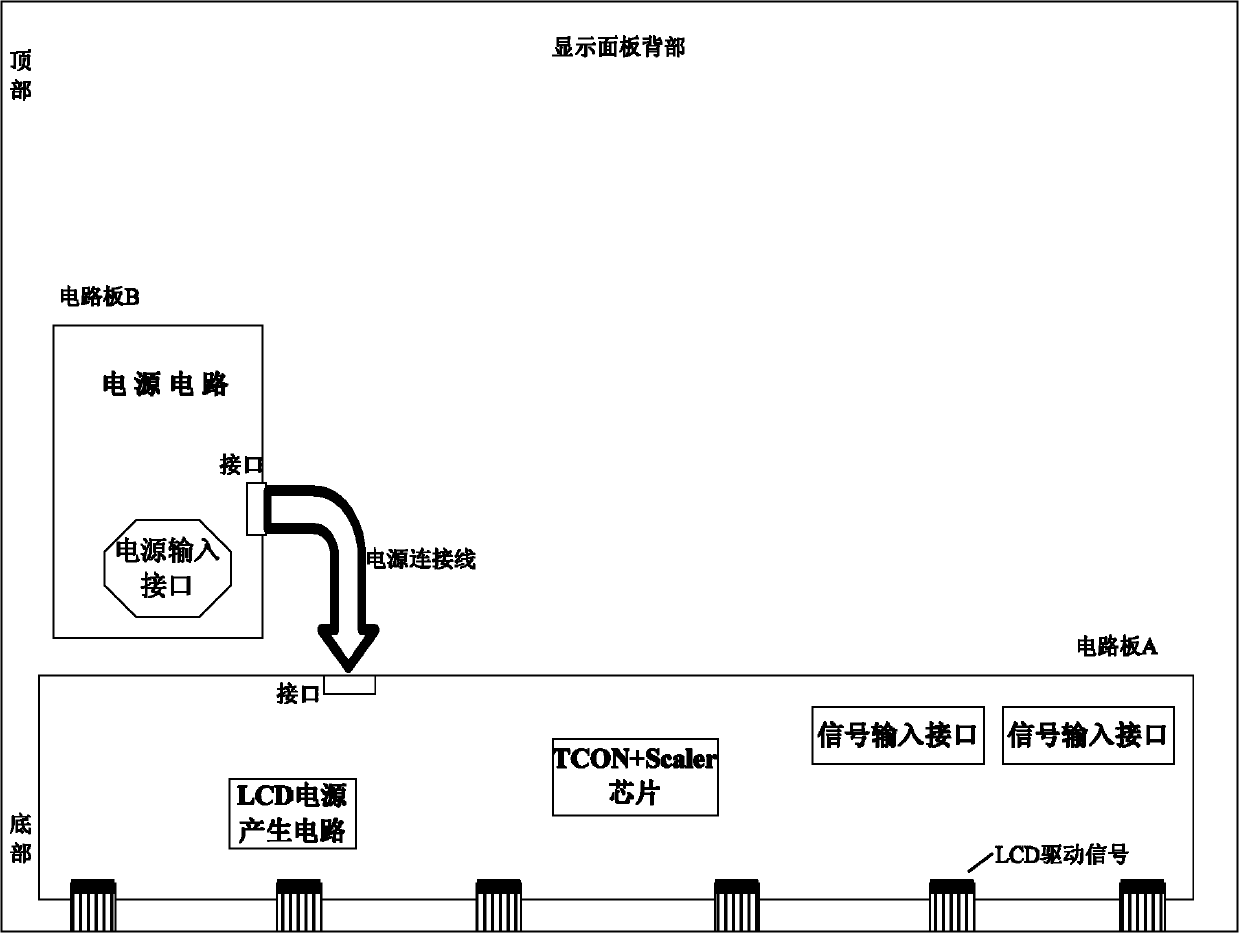
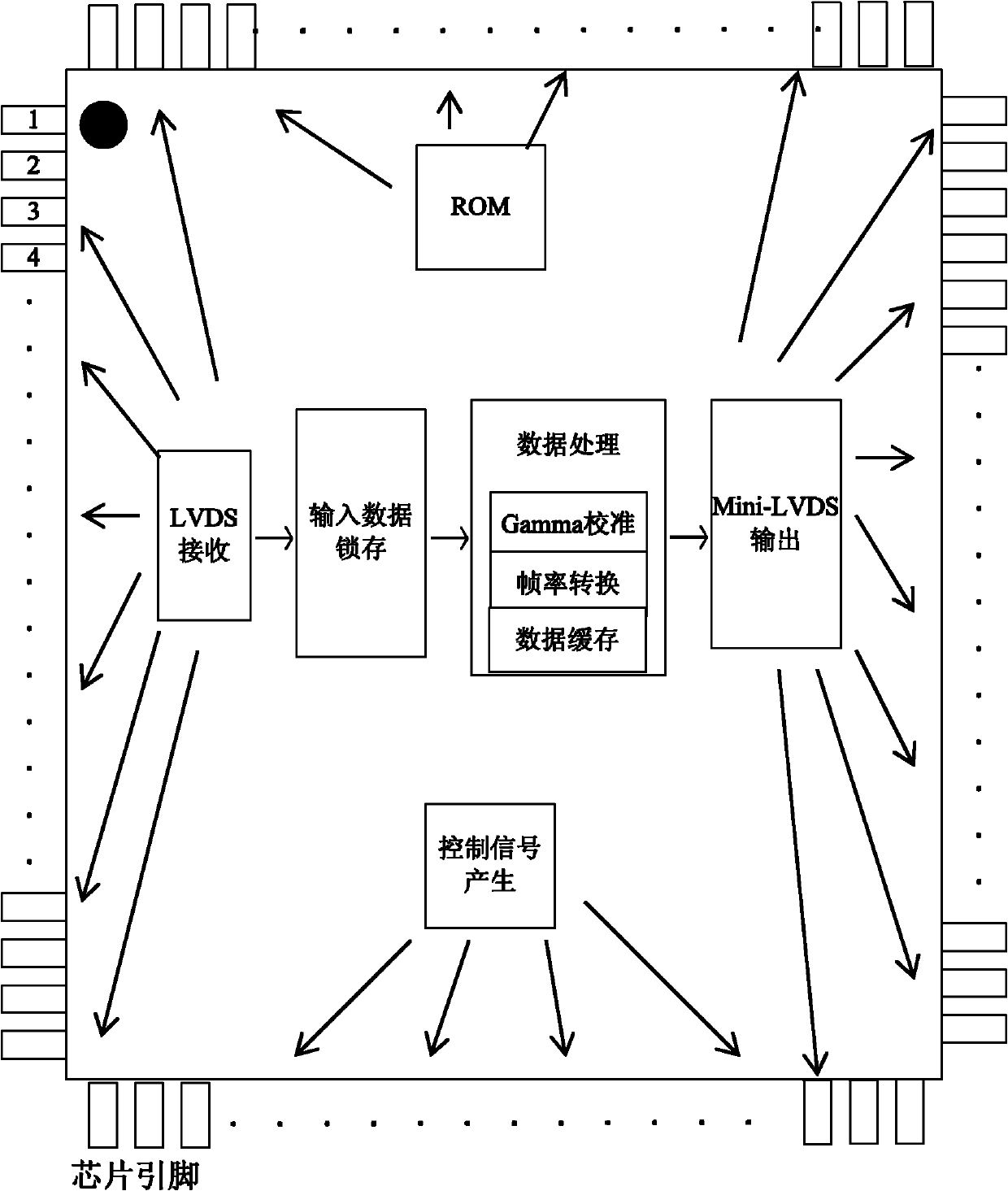
The invention relates to a method for realizing integration of a display image processing and timing control chip, which comprises the following implementation steps: (1) according to a signal flow of a display system, an image processing chip and a timing control chip are arranged in one chip; at the back end of image processing, a low voltage differential signaling (LVDS) signal output from a display control link is directly input into a data latch of a timing control (TCON) module; after data processing, the LVDS signal is output from a Mini-LVDS transmitting module; a source pole and gate pole control signal generating link is embedded into the image processing chip; and the output of the chip is a Mini-LVDS signal and corresponding control signals which are directly received and used by a liquid crystal display (LCD) panel; (2) a circuit board is in an integration structure, and except a power supply circuit board, other function modules are all concentrated on the circuit board; and (3) a power supply interface and an external signal input interface are arranged at the lower end of the back part of a display; and after the integration design of the circuit board is adopted, the liquid crystal panel needs to be flipped up and down. The invention has simplified structure, simple process and reliable performance.
Owner:TIANJIN SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
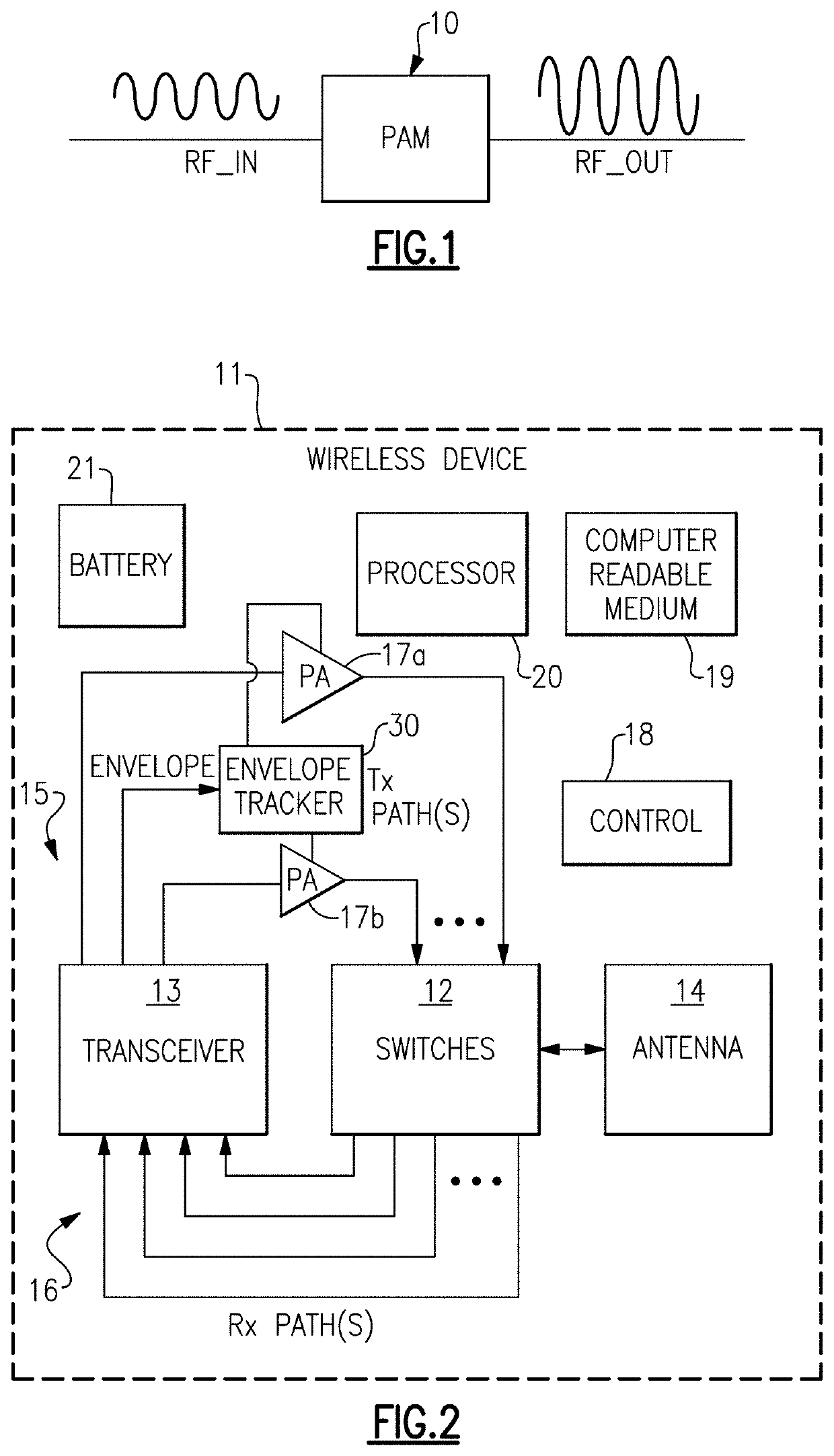
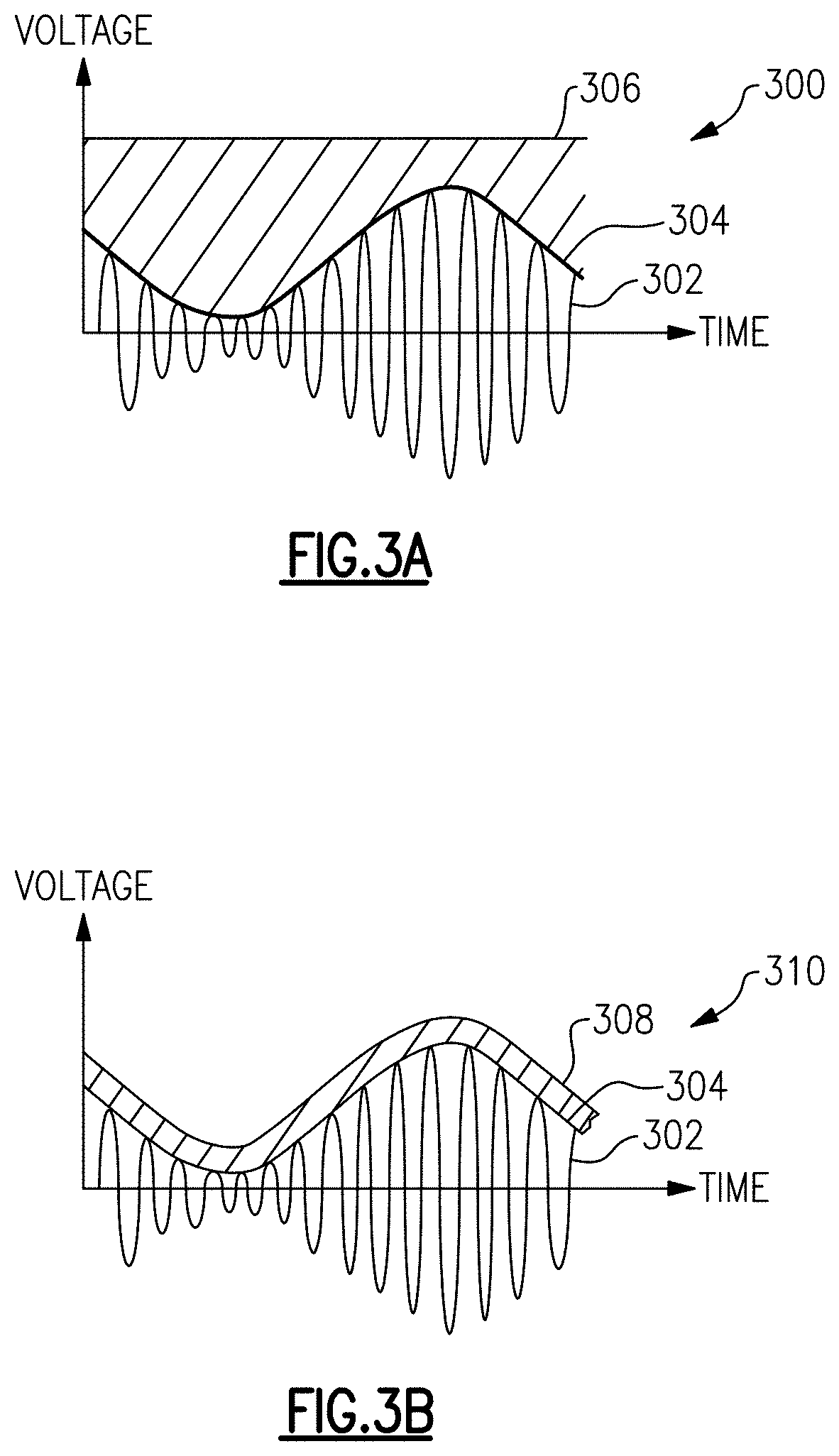
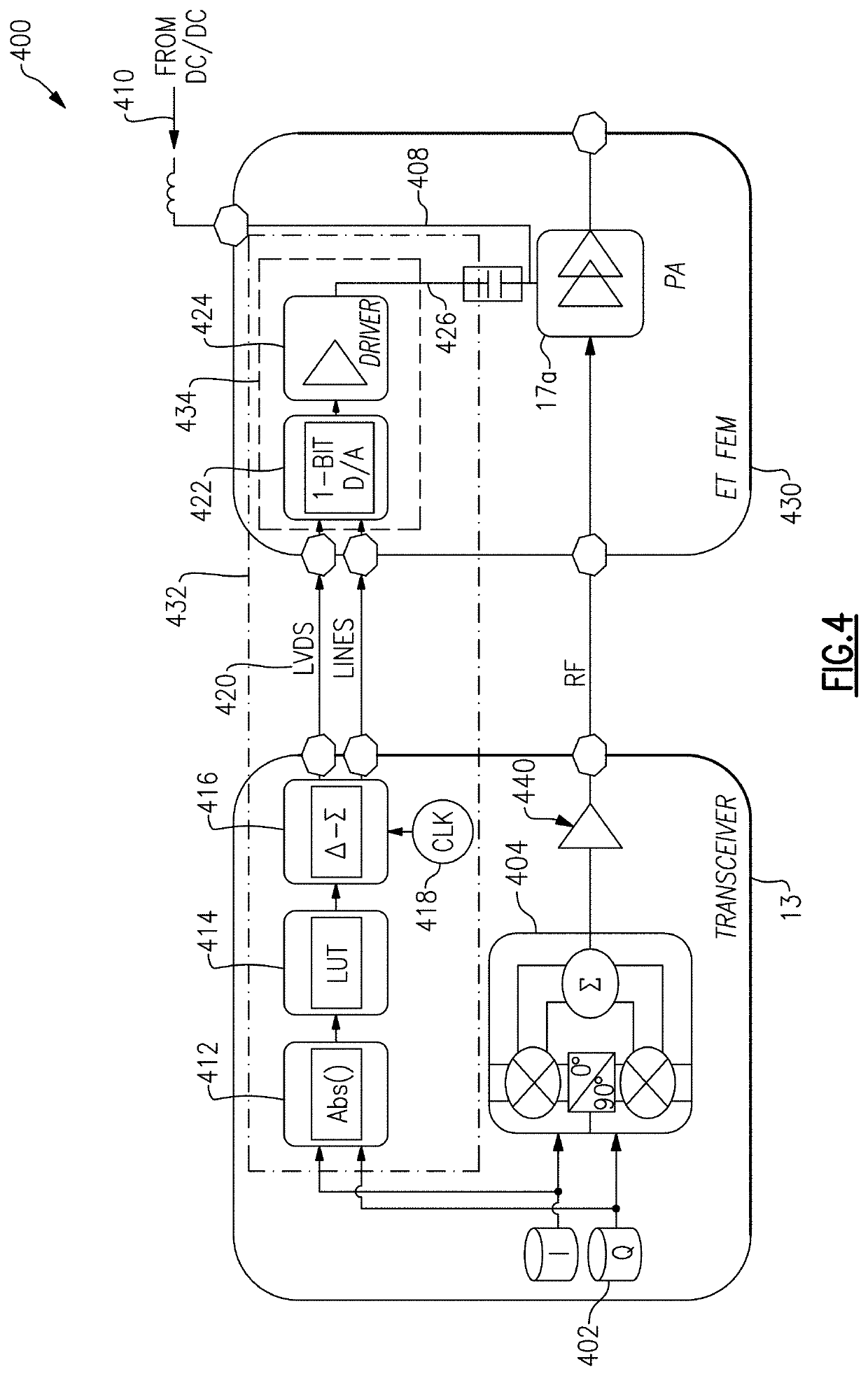
Automated envelope tracking system
ActiveUS20190341888A1Power amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyTransceiverAudio power amplifier
Embodiments described herein relate to an envelope tracking system that uses a single-bit digital signal to encode an analog envelope tracking control signal, or envelope tracking signal for brevity. In certain embodiments, the envelope tracking system can estimate or measure the amplitude of the baseband signal. The envelope tracking system can further estimate the amplitude of the envelope of the RF signal. The system can convert the amplitude of the envelope signal to a single-bit digital signal, typically at a higher, oversample rate. The single-bit digital signal can be transmitted in, for example, a low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) format, from a transceiver to an envelope tracker. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC or A / D) can convert the single-bit digital signal back to an analog envelope signal. Moreover, a driver can increase the power of the A / D output envelope signal to produce an envelope-tracking supply voltage for a power amplifier.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
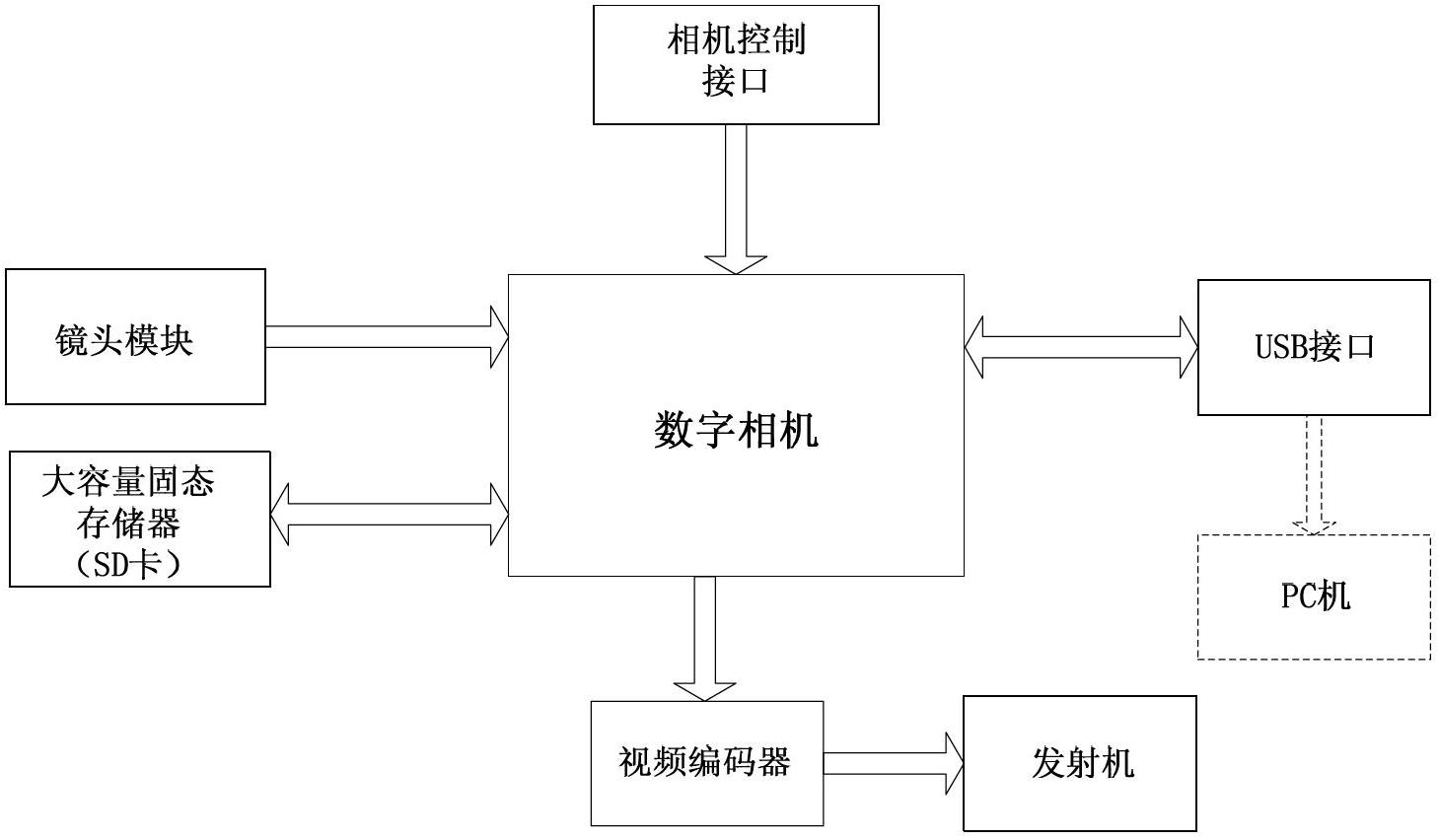
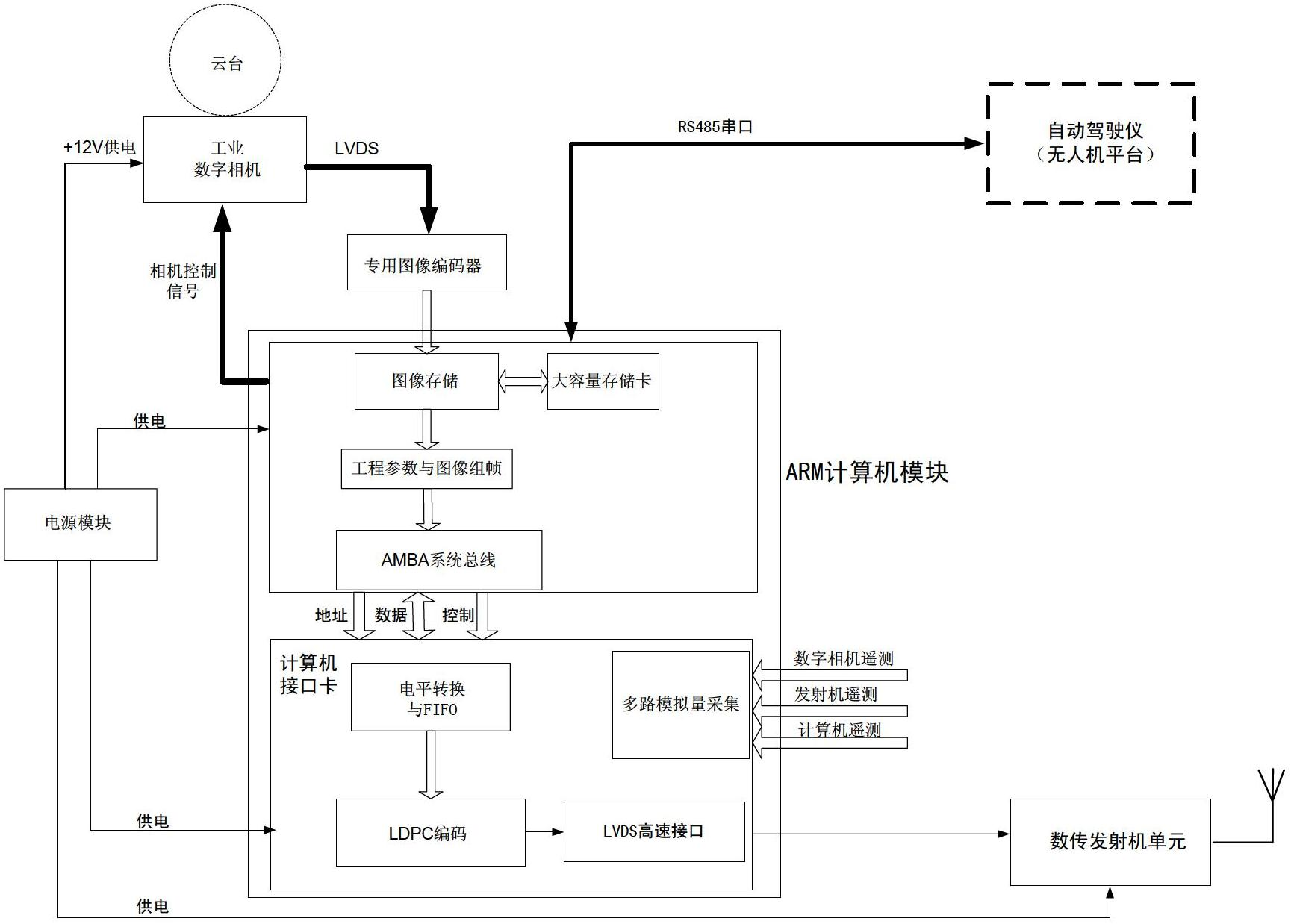
Unmanned plane load device with real-time wireless high resolution image transmission function
InactiveCN102695041AReach remote sensingReach mappingClosed circuit television systemsWireless image transmissionSystem configuration
The invention relates to an unmanned plane load device with a real-time wireless high-resolution image transmission function, which comprises a digital camera module, a control processing module, a power supply module, as well as a high-speed image acquisition and coding module and a data transmission transmitter module, wherein the digital camera module is used for photographing a region to be inspected or mapped; the control processing module is used for completing the management control, data processing and system configuration of each functional module; the power supply module is used for powering devices; the high-speed image acquisition and coding module is used for processing and transmitting high-resolution images, acquiring original image data via a high-speed LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling) interface of the digital camera, compressing and coding images to form an image code stream via a wavelet compression unit, and packing, framing and transmitting to the transmitter module via the control processing module; and the data transmission transmitter module transmits the data processed by the control processing module by adopting microwave to a ground station to increase the bandwidth of data transmission. The device is low in cost, good in real time performance, high in reliability, flexible in configuration, visual and convenient.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
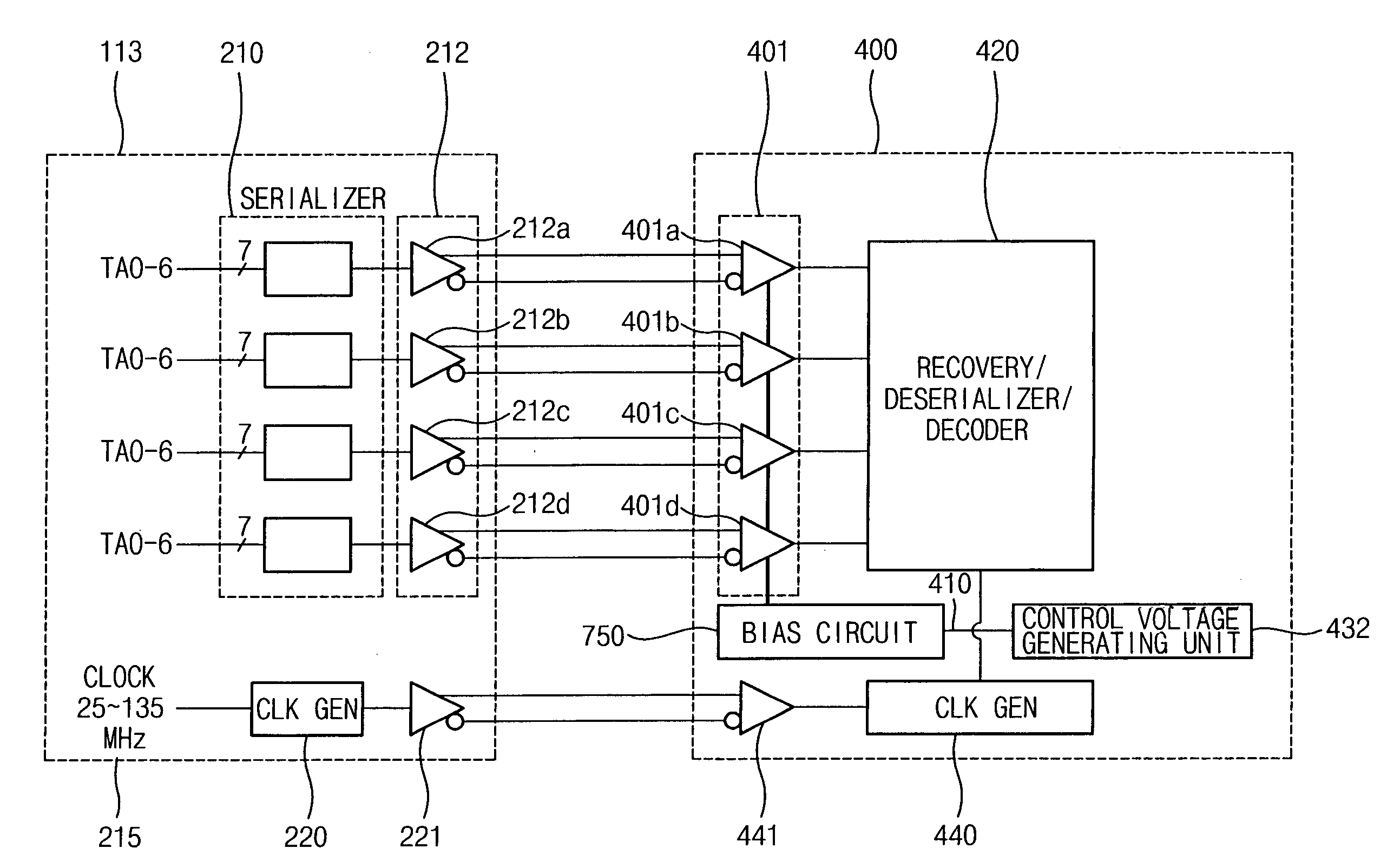
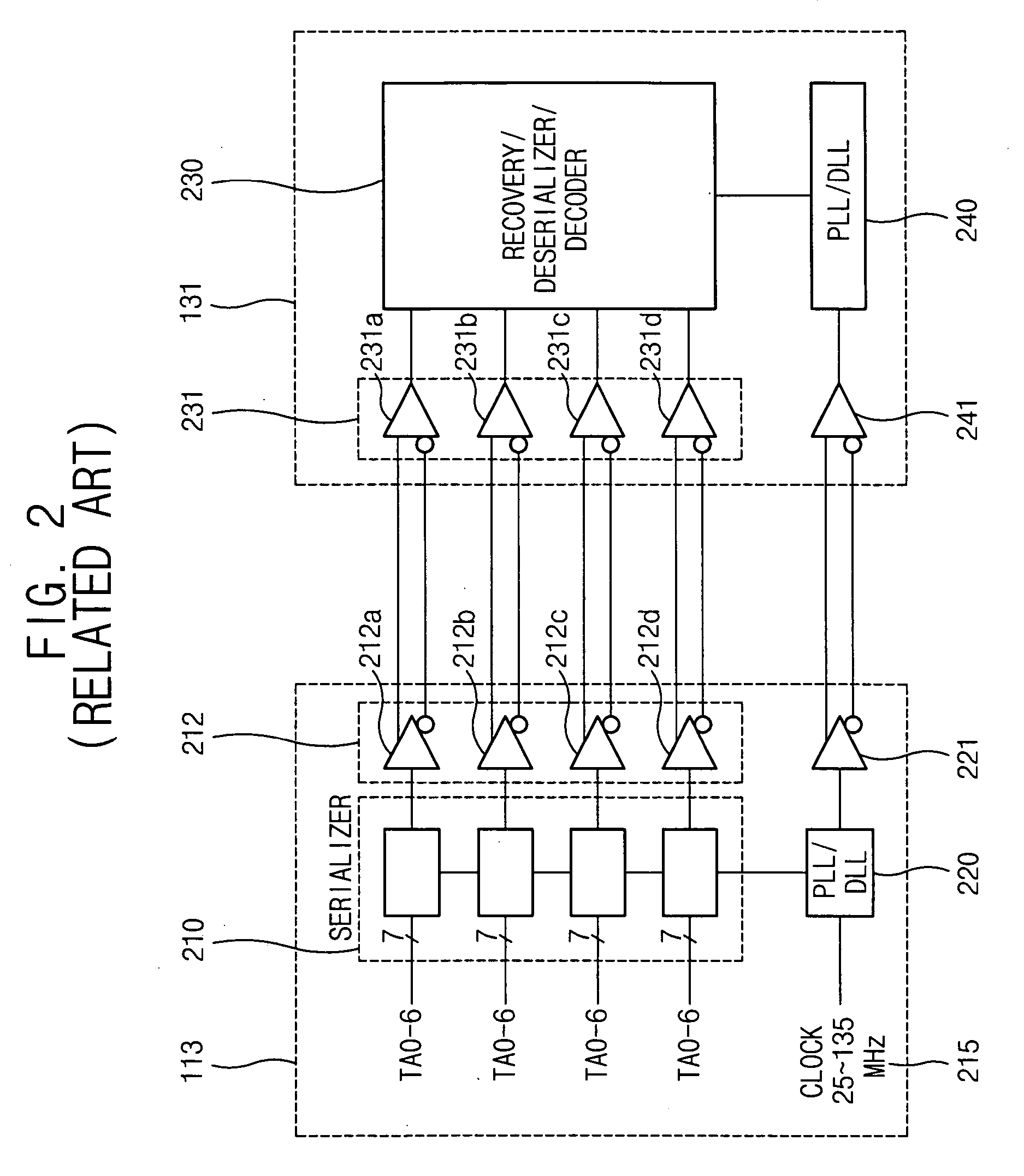
LVDS receiver for controlling current based on frequency and method of operating the LDVS receiver
InactiveUS20060002483A1Save current consumptionSave currentSynchronisation information channelsPulse automatic controlSnubberDifferential amplifier
In an embodiment, an LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling) receiver includes at least one LVDS input buffer, a clock generating unit, and a bias circuit. The clock generating unit includes a voltage controlled oscillator for generating a clock signal tracking a frequency of data received via the at least one LVDS input buffer based on a control voltage. The bias circuit controls current sources that supply current to at least one differential amplifier in the at least one LVDS input buffer based on the control voltage of the clock signal generating unit. Therefore, the LVDS receiver can save current consumed in LVDS input buffers by controlling the amount of current supplied to the at least one differential amplifier included in the at least one LVDS input buffers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Processing device and processing method of high dynamic contrast for liquid crystal display apparatus
ActiveUS20090079688A1Increase contrastQuality improvementAnalogue conversionCathode-ray tube indicatorsCapacitanceDynamic contrast
This invention relates to a processing device and processing method of high dynamic contrast for liquid crystal display apparatus, the processing device comprises a receiver, an inverter, and a source driving IC connected with a central processing module. The processing method includes: performing a histogram statistical process on received low voltage Differential Signaling data; obtaining a backlight source dimming coefficient and a Gamma reference voltage parameter of the same frame of picture according to the result of the histogram statistical process. controlling the brightness of the backlight source according to said backlight source dimming coefficient; controlling the voltage of the pixel capacitor on the liquid crystal panel according to said Gamma reference voltage parameter. This invention respectively adjusts the brightness of the backlight source and the voltage of the pixel capacitor of the liquid crystal panel simultaneously, and hence the dynamic contrast of the picture is increased, the problems of lower contrast and flicker of TFT liquid crystal display apparatus are ameliorated, and the power consumption of the backlight source is saved.
Owner:BEIJING BOE OPTOELECTRONCIS TECH CO LTD
Test method and test system for implementing COMMAND-mode MIPI (mobile industry processor interface) modules
ActiveCN104217667ARealize point screen testImplement configuration parametersStatic indicating devicesRegister allocationCommunications system
The invention discloses a test method and a test system for implementing COMMAND-mode MIPI (mobile industry processor interface) modules and used for configuration testing of the COMMAND-mode MIPI modules before delivery. The test method mainly includes the steps that a PG (program guidance) image generator sets register configuration parameters and image data according to types of the COMMAND-mode MIPI modules, transmits the register configuration parameters to an MCU (microprogrammed control unit), and transmits the image data to an FPGA (field programmable gate array) through an LVDS (low voltage differential signaling) data bus interface; the MCU generates DCS (data communication system) instructions according to the register configuration parameters and transmits the DCS instructions to the FPGA; the FPGA receives image data signals through the LVDS data bus interface and has the DCS instructions and the image data packaged and transmitted to a bridge chip; the bridge chip transmits the DCS instructions for configuration of the MIPI modules and converts the image data to the MIPI signals which are transmitted to the MIPI modules, and the MIPI modules display the image data according to the MIPI signals to complete testing.
Owner:WUHAN JINGCE ELECTRONICS GRP CO LTD
Data transfer apparatus for low voltage differential signaling
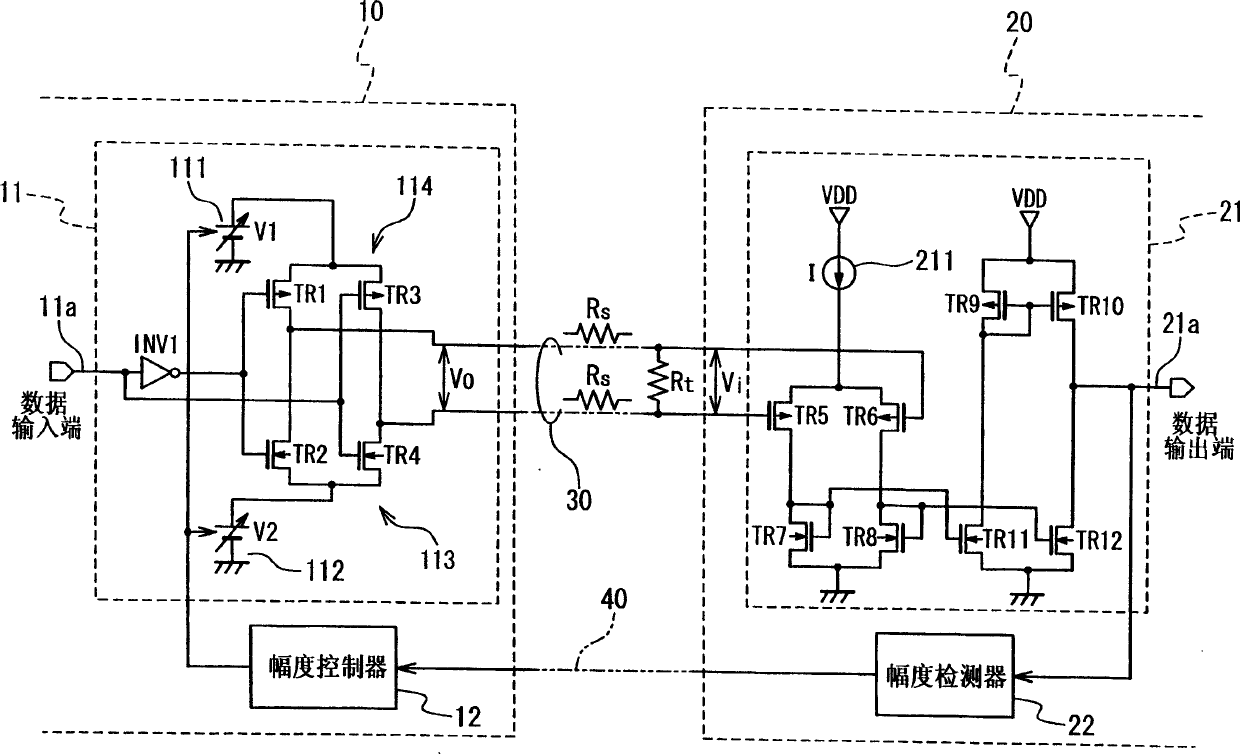
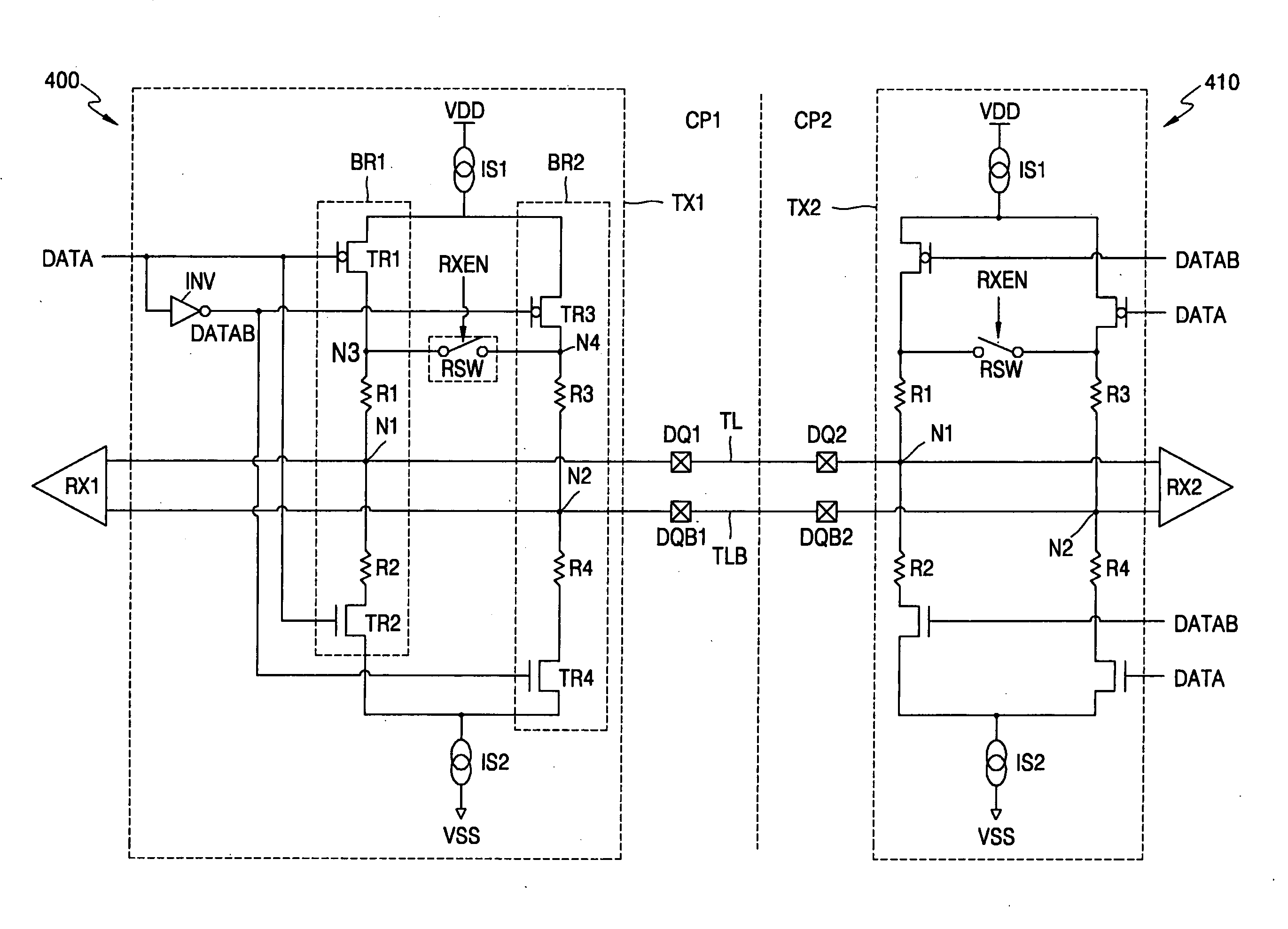
InactiveCN1574672AMultiple input and output pulse circuitsTransmission control/equlisationDifferential signalingAmplitude control
A data transfer apparatus is composed of a transmitter (10) and a receiver (20). The transmitter (10) includes an output buffer developing a differential signal in response to a data signal (11a), and an amplitude controller (12). The receiver (20) includes an input buffer (21) converting the differential signal into a single-end signal (21a), and an amplitude detector (22) developing a feedback signal in response to the single-end signal (21a). The amplitude controller (12) controls an amplitude of the differential signal in response to the feedback signal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Low voltage differential signaling drivers including branches with series resistors
ActiveUS20060132179A1Minimizes signal reflectionReduce in quantityElectric pulse generatorDifferential amplifiersLow voltageResistor
A low voltage differential signal driver includes first and second current sources, a first branch and a second branch. The first branch includes at least two transistors and at least two resistors between them that are all connected in series between the first and second current sources, to define a first node between adjacent resistors that is configured to transmit and receive differential signals. The second branch also includes at least two transistors and at least two resistors between them that also are all connected in series between the first and second current sources, to define a second node between adjacent resistors that is also configured to transmit and receive differential signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
FPGA-based figure signal producing device and method
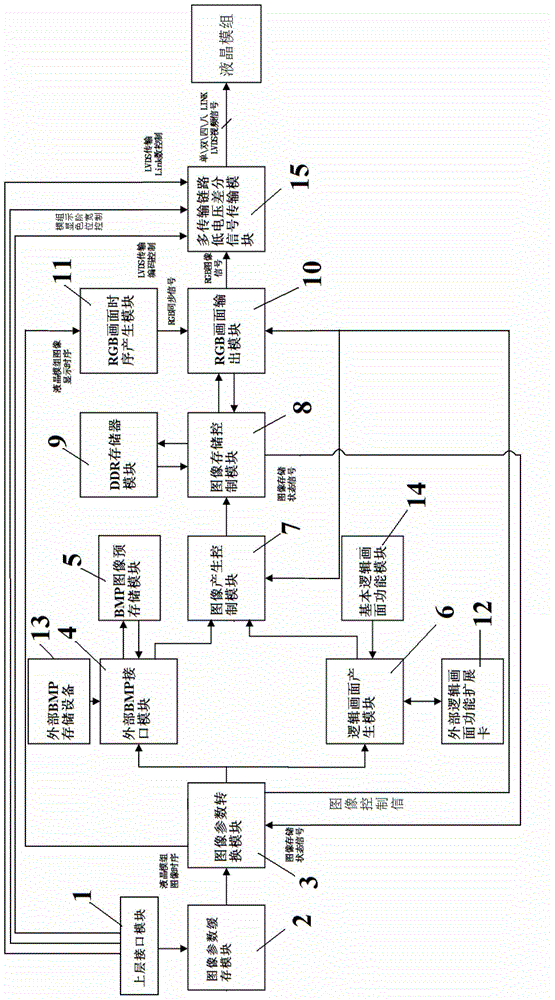
ActiveCN104932124AMeet the test requirementsEasy to implementStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsPattern recognitionGraphics
The invention relates to an FPGA-based figure signal producing device. The FPGA-based figure signal producing device comprises an upper layer interface module, an image parameter caching module, an image parameter conversion module, an external BMP interface module, a logic picture producing module, an image producing control module, an image storage control module, an RGB (red, green and blue) picture output module, an RGB picture timing sequence producing module and a multi-transmission-link low-voltage differential signal transmission module. The FPGA-based figure signal producing device can achieve a function of displaying logic pictures of BMP images and different patterns through an FPGA.
Owner:WUHAN JINGCE ELECTRONICS GRP CO LTD
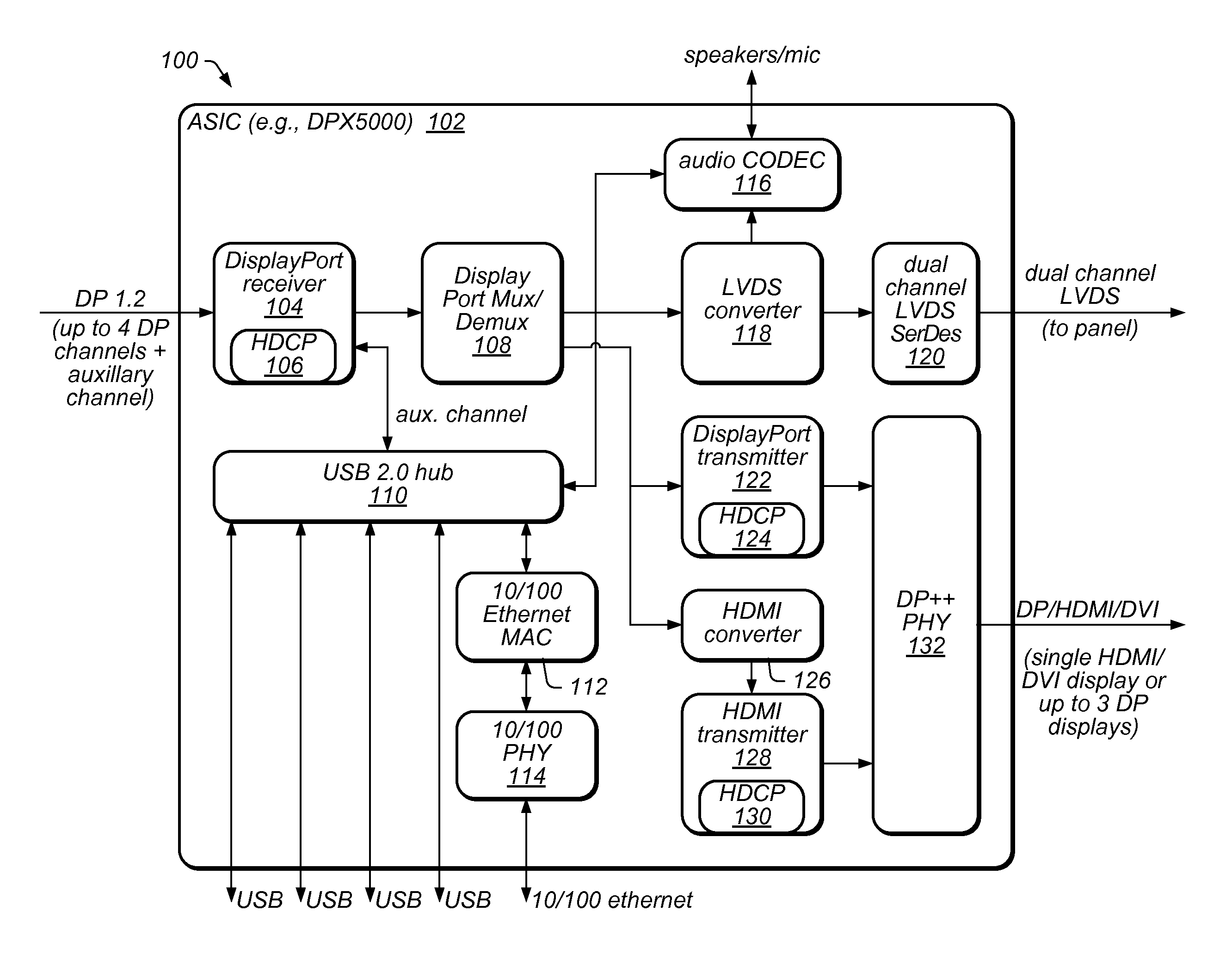
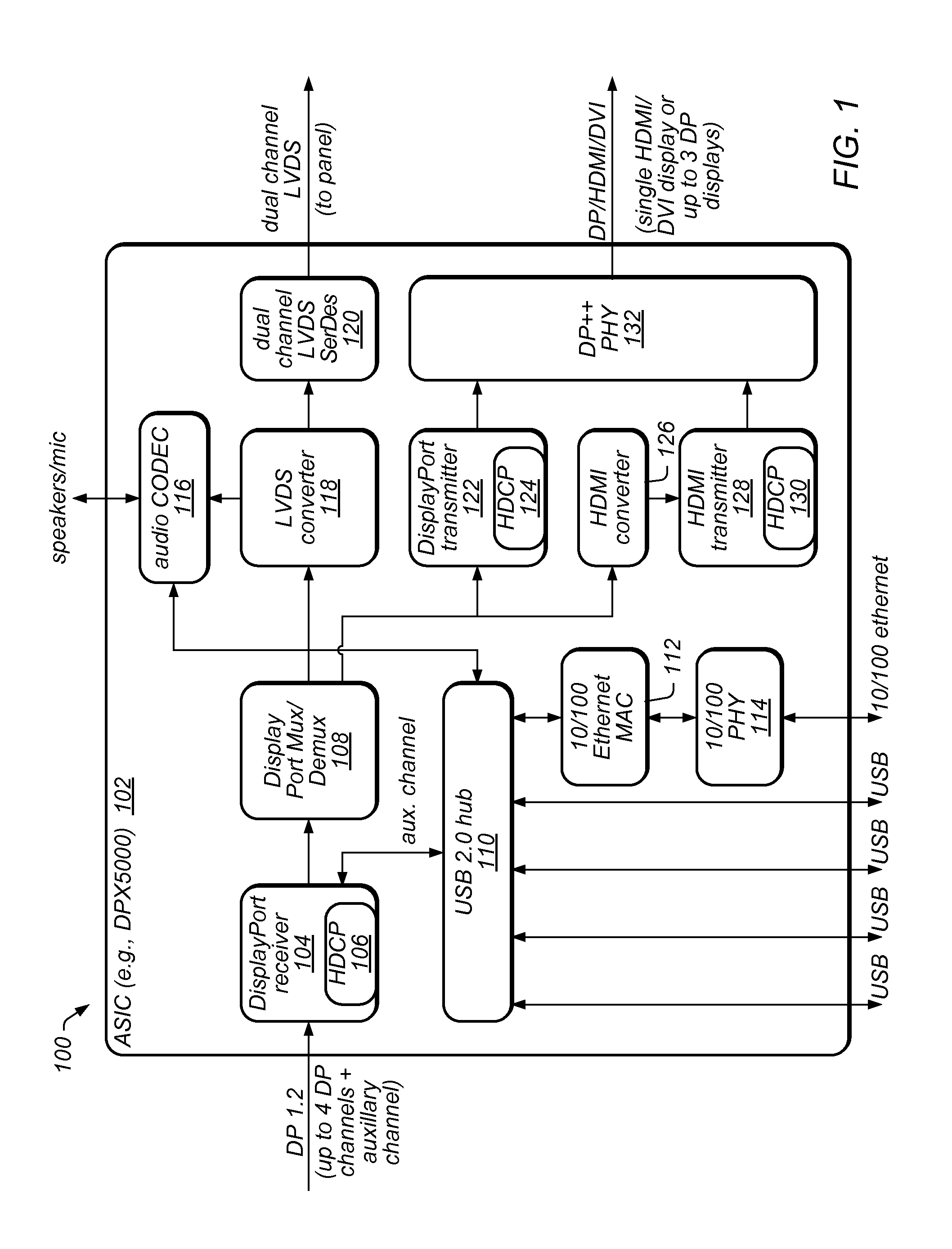
Monitor chaining and docking mechanism
ActiveUS8395605B2Reduce overheadColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceComputer science
A circuit that supports multiple monitors, docking functions, and protected content via one cable. The circuit includes a receiver that receives multiple video streams, each including respective video data, a mux / demux, coupled to the receiver, that determines which video stream to display on a monitor, a low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) converter, coupled to the mux / demux, that generates an LVDS signal based on the video data of the determined video stream, an LVDS serializer / deserializer, coupled to the LVDS converter, that generates a signal based on the LVDS signal and sends the signal to a display panel of the monitor for display, a transmitter coupled to the mux / demux, and a transmit physical interface (TPI) coupled to the transmitter. The mux / demux sends at least a remainder of the video streams to the transmitter, which sends them to the TPI, which transmits them as output, useable as input to further instances of the circuit.
Owner:SMSC HLDG
Multiple signal format output driver with configurable internal load
A multiple signal format output driver is configurable to provide a current-mode logic (CML) output signal in response to a CML value of one or more first values of the control signal. The output driver is configurable to provide a low-power, low-voltage positive emitter-coupled logic (low-power LVPECL) output signal in response to a low-power LVPECL value of the one or more first values of the control signal. The output driver is configurable to provide a low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) output signal in response to an LVDS value of the one or more first values of the control signal. The output driver may be configurable to provide a LVPECL output signal in response to a second value of the control signal. The output driver may be configurable to provide a high-speed current steering logic (HCSL) output in response to a third value of the control signal.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
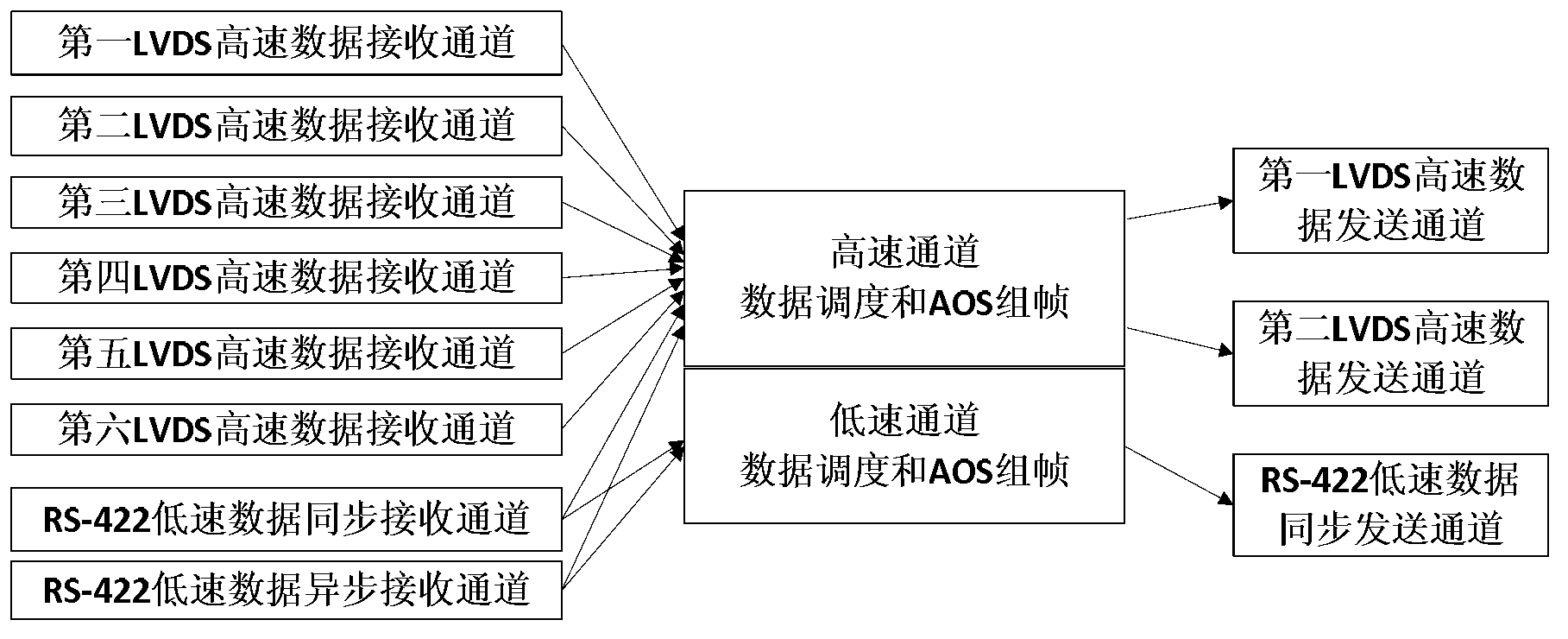
Simulation device of load data processor and implementation method thereof
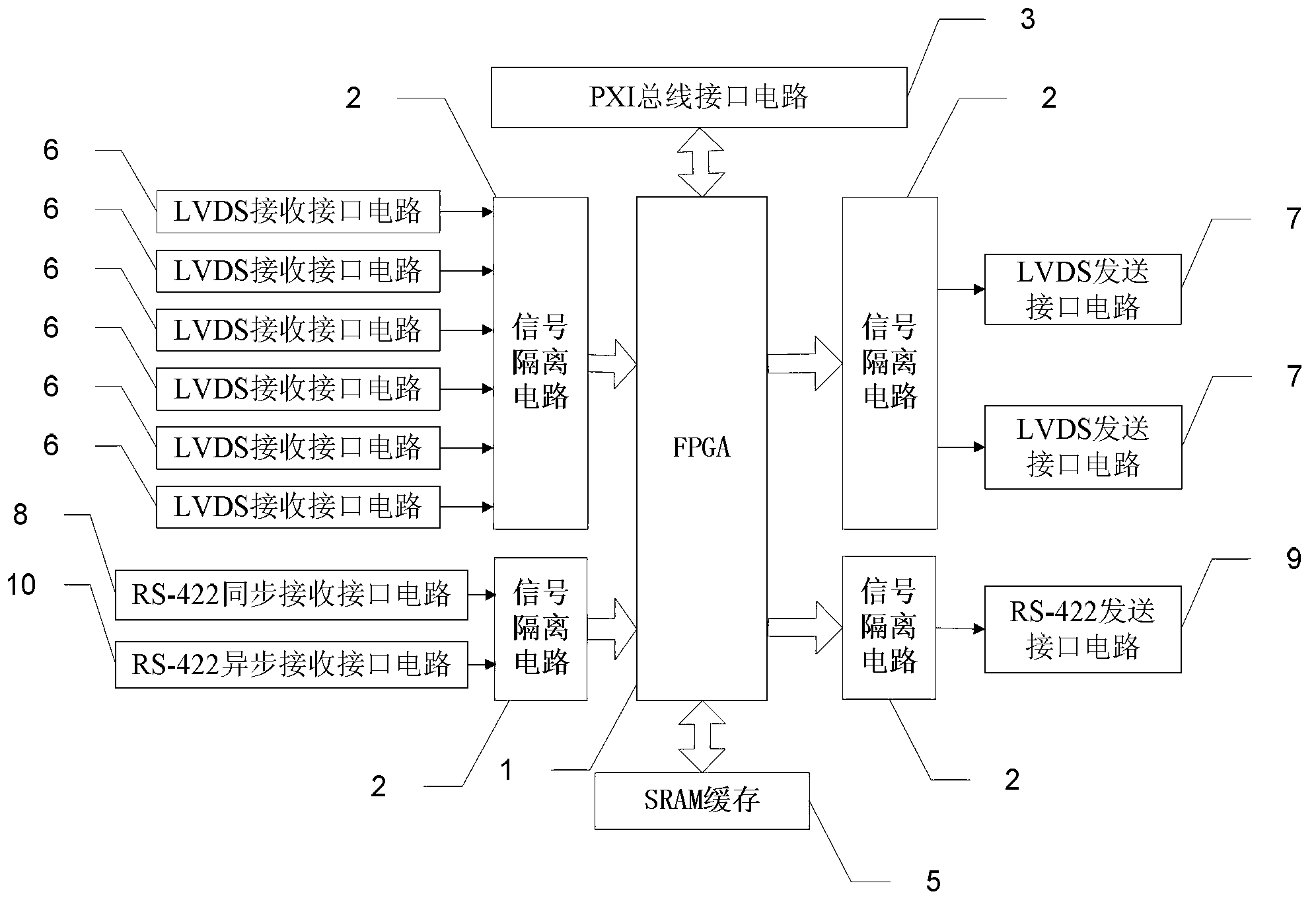
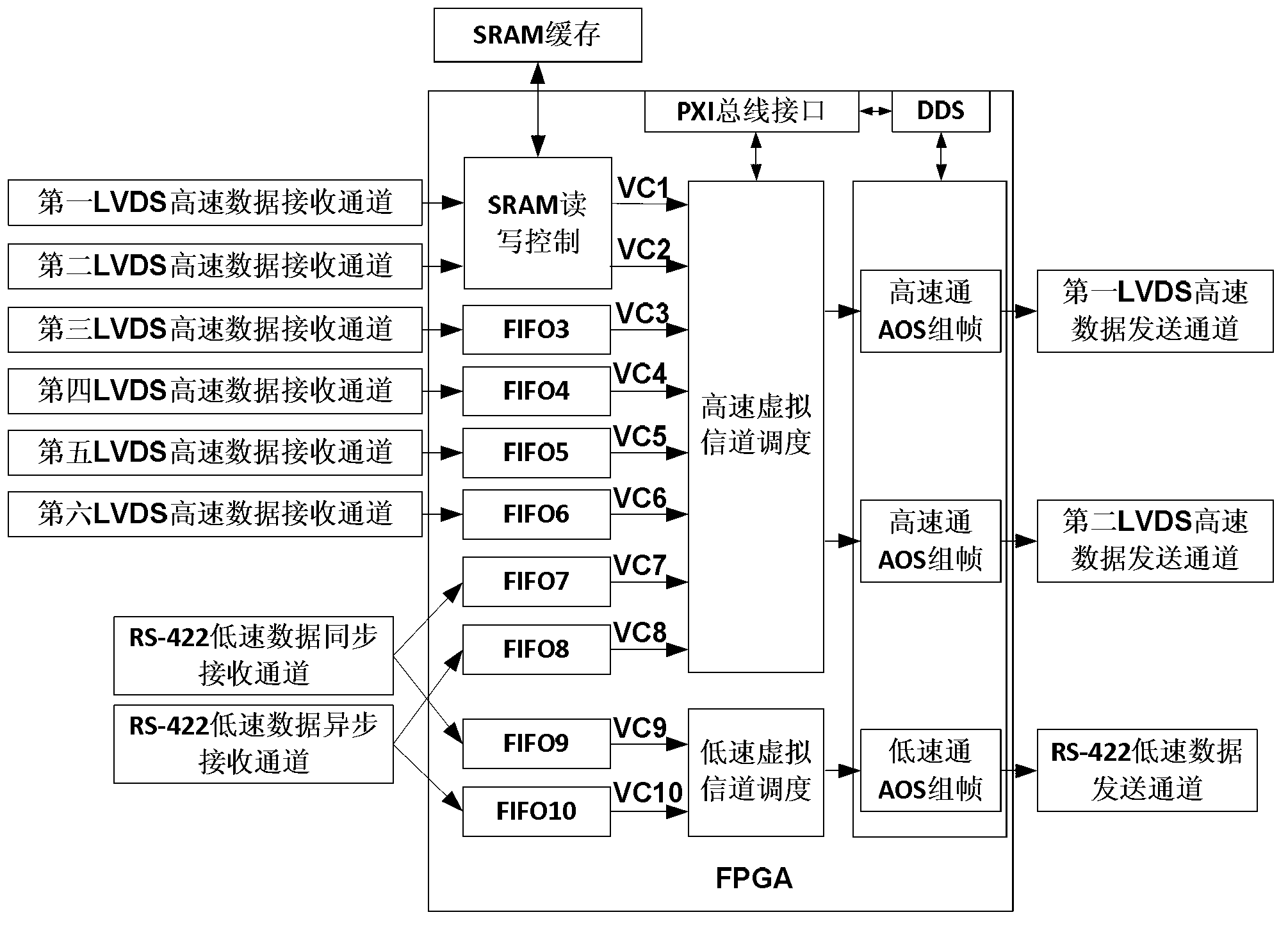
ActiveCN103309780AImplement joint debuggingImplement hierarchical test diagnosticsDetecting faulty computer hardwareSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatic random-access memoryParallel computing
The invention relates to a simulation device of a load data processor and an implementation method thereof, and belongs to the field of satellite test. The invention aims to solve the problems of high cost, low test safety and reliability and low test efficiency caused by that the test process of the existing satellite data transmission subsystem is performed in the sky. The simulation device of the load data processor comprises a field programmable gate array (FPGA), a signal isolation circuit, a PXI bus interface circuit, a low voltage differential signaling (LVDS) receiving and transmitting interface circuit and an RS-422 data receiving and transmitting circuit, wherein the LVDS receiving and transmitting interface circuit comprises an LVDS receiving interface circuit and an LVDS transmitting interface circuit; and the RS-422 data receiving and transmitting circuit comprises an RS-422 synchronous receiving interface circuit, an RS-422 asynchronous receiving interface circuit and an RS-422 transmitting interface circuit. The simulation device of the load data processor also comprises a static random access memory (SRAM) cache. The simulation device of the load data processor is applied to test of a satellite data transmission subsystem.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Low voltage differential signaling [LVDS] driver with pre-emphasis Low voltage differential signaling [LVDS] driver with pre-emphasis](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/74b8f4ad-e594-484b-88fa-38de88ef32f9/US06977534-20051220-D00000.png)
![Low voltage differential signaling [LVDS] driver with pre-emphasis Low voltage differential signaling [LVDS] driver with pre-emphasis](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/74b8f4ad-e594-484b-88fa-38de88ef32f9/US06977534-20051220-D00001.png)
![Low voltage differential signaling [LVDS] driver with pre-emphasis Low voltage differential signaling [LVDS] driver with pre-emphasis](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/74b8f4ad-e594-484b-88fa-38de88ef32f9/US06977534-20051220-D00002.png)