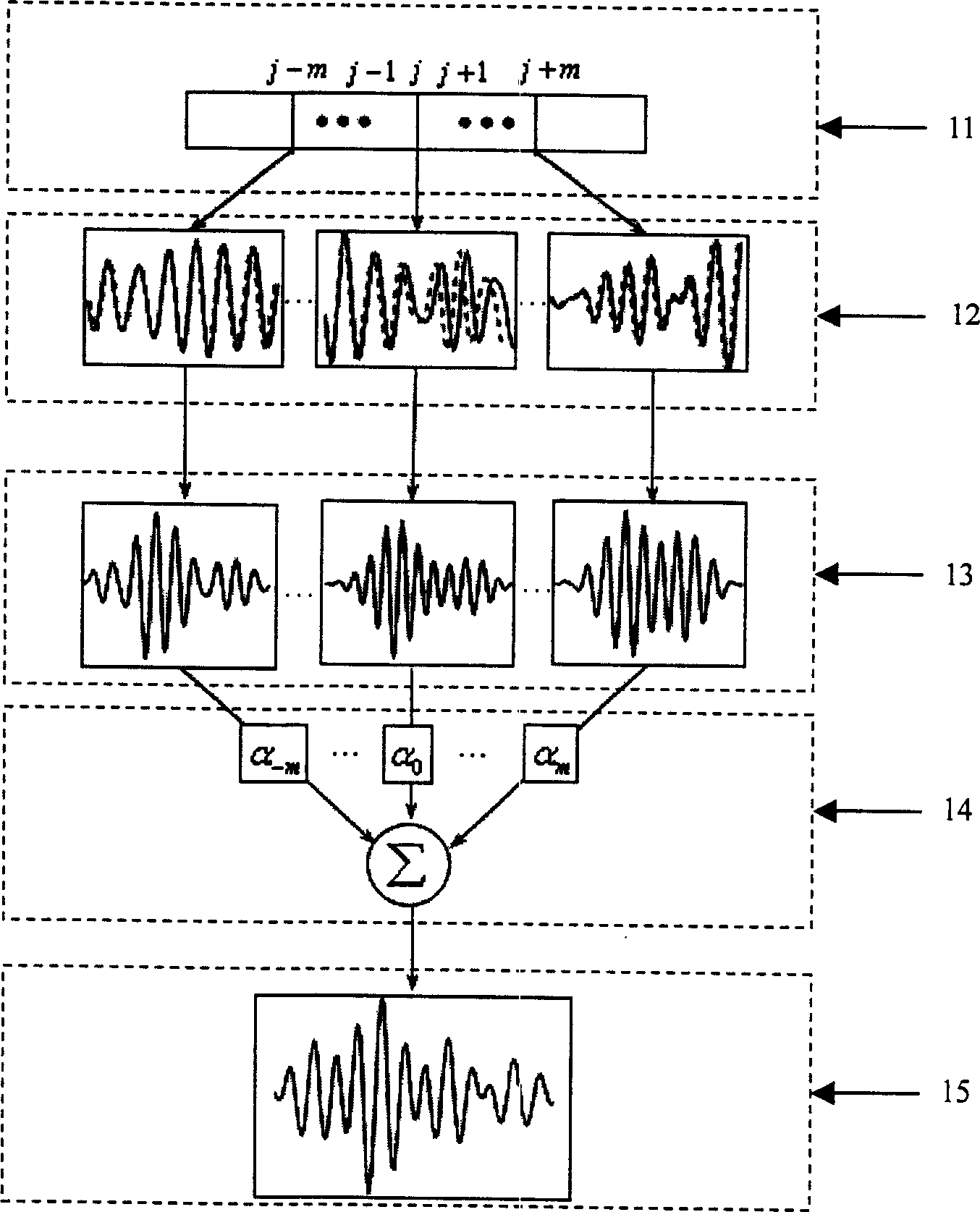
Two dimension complex interrelative biological tissue displacement evaluating method
A technology of cross-correlation and cross-correlation function, applied in ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic Permian technology, ultrasonic/sonic/infrasound image/data processing, organ motion/change detection, etc. , large influence, low signal-to-noise ratio of strain distribution estimation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
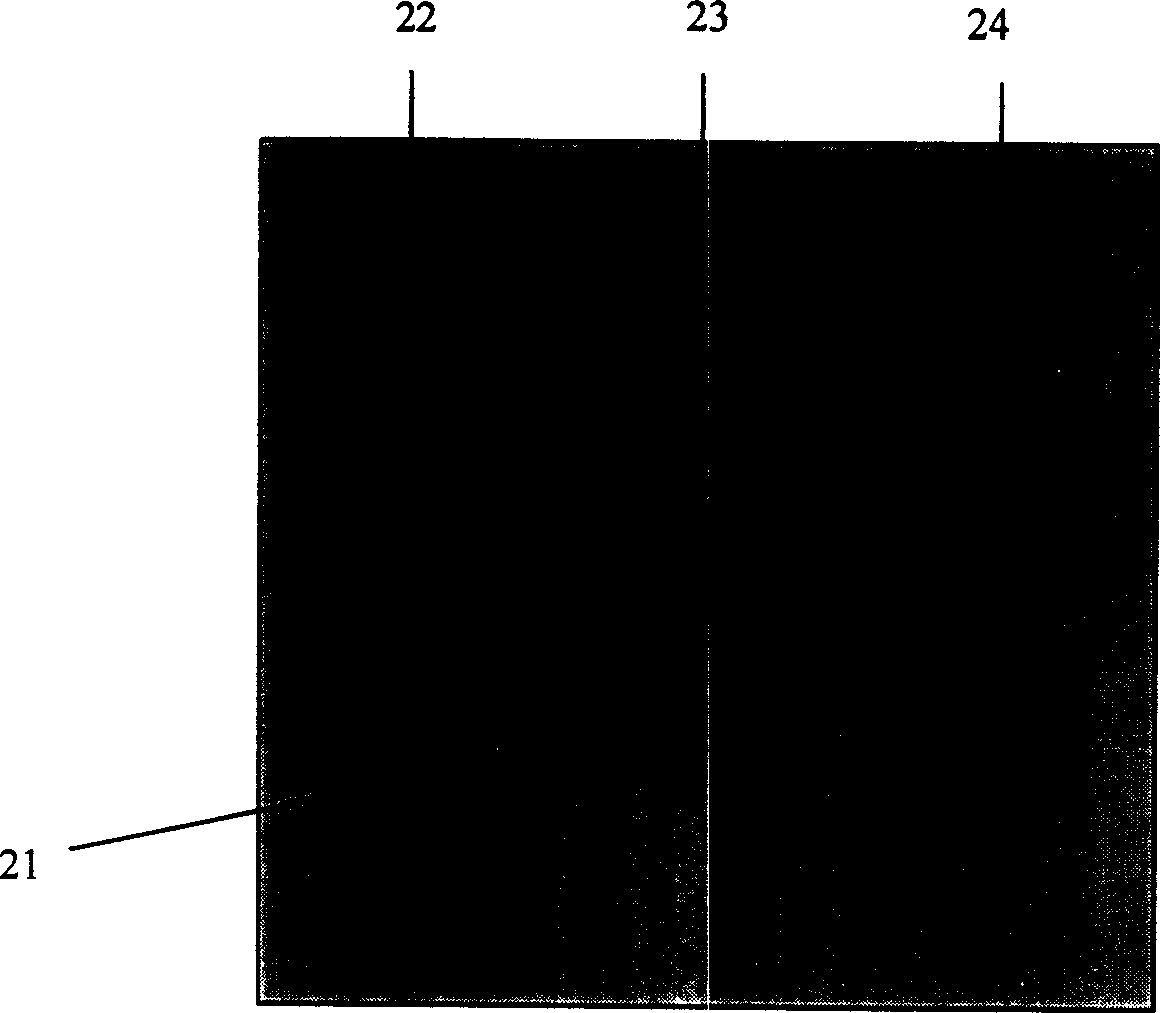
[0062] Embodiment 1 uses a computer program and a general ultrasonic scattering model to simulate and obtain two-dimensional radio frequency signals of a simulated tissue before and after compression. The simulated organizational structure is as figure 2 As shown, tissue 21 size 60×60mm 2 , there are three circular foreign bodies 22, 23, and 24 with large elastic modulus distributed in the tissue, their elastic modulus is twice that of tissue 1, and their diameters are both 5mm; the tissue compression ratio is 1%, that is, the compression The measurement is 0.6mm; the center frequency of the probe is 3.5MHz, the -3dB bandwidth is 2.0MHz, the width and interval of the scanning lines of the probe are 2mm and 0.4mm respectively, and the width of the probe and the width of the tissue are also 60mm, so there are 151 scanning lines in total. That is, M=151, and the central part of the probe and the peripheral part of the probe correspond to the central part of the tissue and the p...
Embodiment 2
[0079] The organizational model and parameter design of Example 2 are the same as those of Example 1, except that the value of m is 2, and the weight α of the cross-correlation function corresponding to each scan line data k (-m≤k≤m) is 1 / 5, and the specific steps are also the same as in Example 1, except that m and α k The value of is different.
[0080] The displacement estimation effect of embodiment 1 and embodiment 2 is compared with general method as follows:
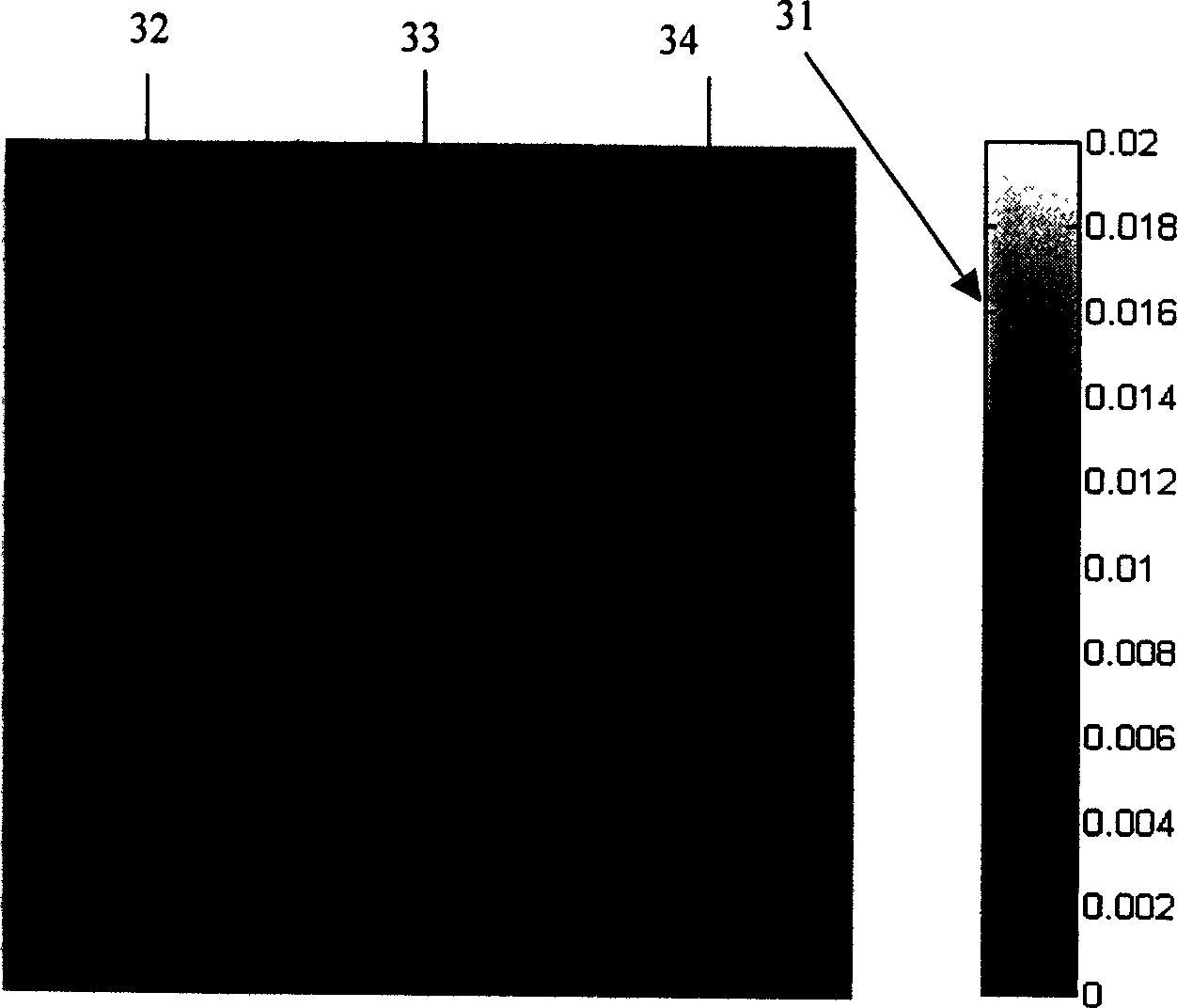
[0081] Figure 4 It is the computer simulation result of the tissue strain distribution obtained by the general tissue displacement estimation method, that is, the result when the comprehensive coefficient m is 0; Figure 5 It is the computer simulation result of the tissue strain distribution obtained in Example 1, that is, the result obtained by using the two-dimensional comprehensive cross-correlation tissue displacement estimation method whose comprehensive coefficient m is 1; Image 6 It is the computer si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com