Method for generating a structure on a substrate
A substrate and nitride layer technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of difficult possibility, impossibility of short gate structure, failure to achieve tolerance, etc., to achieve low tolerance, small gate The effect of extreme length
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
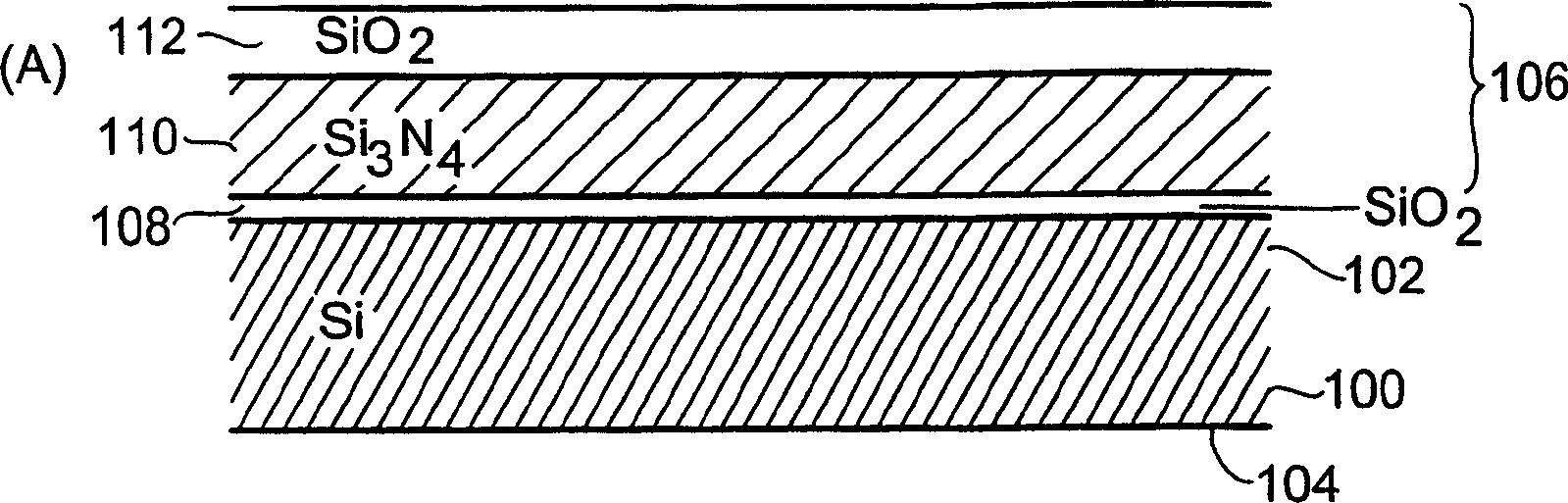
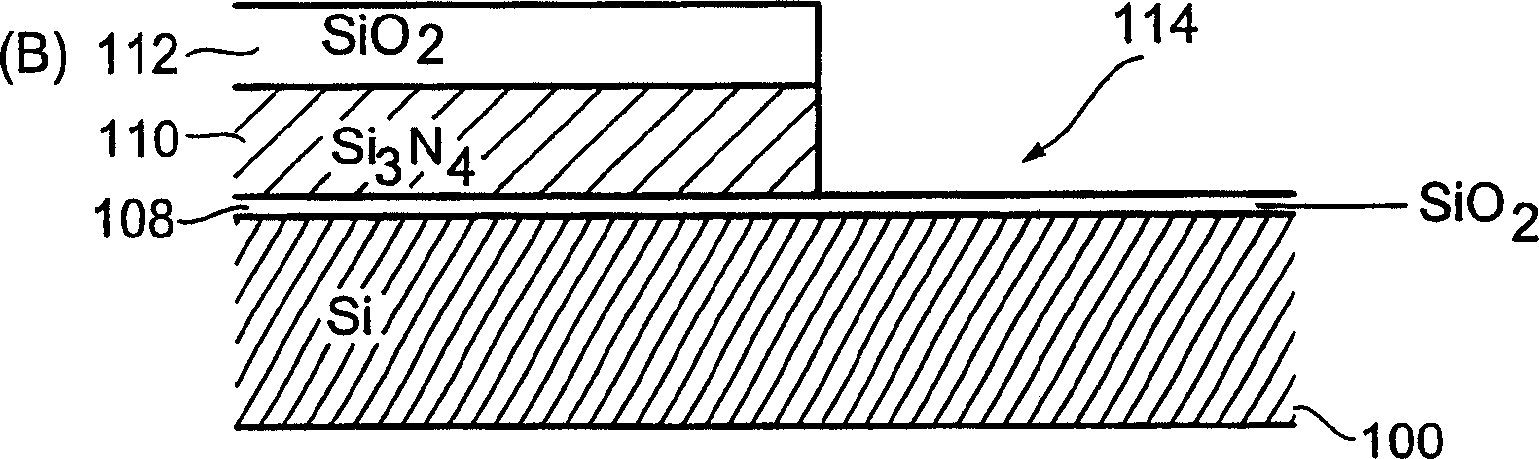
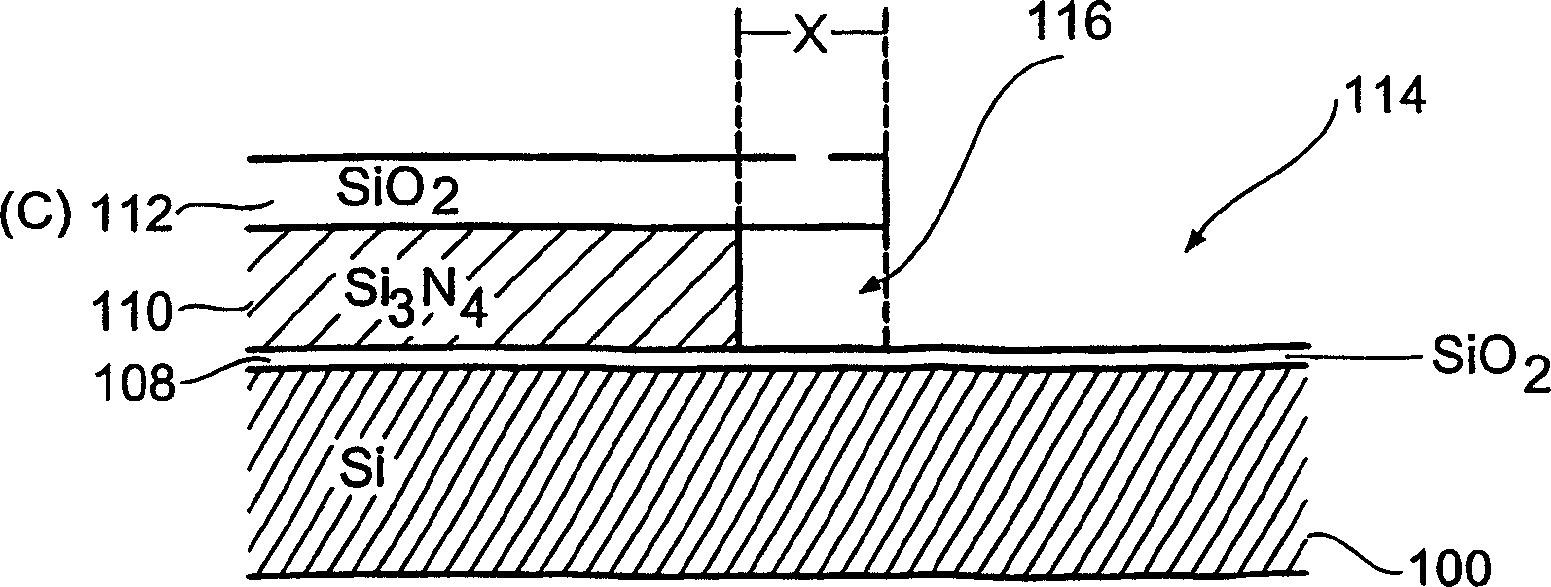
[0017] Now, referring to FIG. 1, a first preferred embodiment of the present invention will be explained in more detail, wherein Figure 1A to Figure 1K According to this preferred embodiment, the different program steps will be explained in more detail.
[0018] in Figure 1A Here, a semiconductor structure is exemplified, which includes a substrate 100, and the substrate has a first main surface 102 and a second main surface 104, and in the embodiment illustrated here is a silicon substrate On the first main surface 102 of the substrate 100, a layer sequence 106 is generated, including a first oxide layer 108 disposed on the substrate 100, and a first oxide layer 108 disposed on the first oxide layer 108 The nitride layer 110, and a second oxide layer 112 disposed on the nitride layer 110. Furthermore, in the illustrated embodiment, the oxide layers 108 and 112 are silicon dioxide layers, and The nitride layer 110 is a silicon nitride layer, and, in Figure 1A The example illust...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| etch rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com