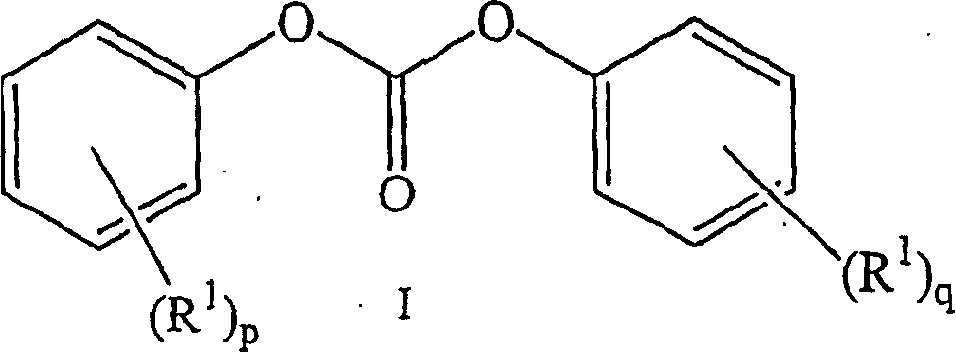
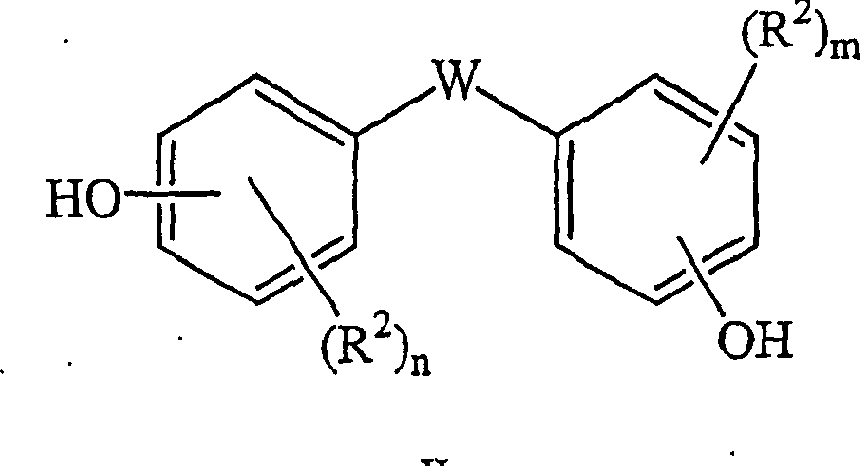
Method for making stable, homogeneous melt solutions
A melt, stable technology used in the preparation of stable, homogeneous melt solutions, which can solve problems such as expensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0073] The following examples are described to provide a detailed description of how one of ordinary skill in the art may evaluate the methods claimed herein, and are not intended to limit the scope of the invention. Unless indicated otherwise, parts are by weight and temperatures are in degrees Celsius (° C.).
[0074] Melt Solution Formation Examples 1-5
[0075] Prepare a stable, homogeneous melt solution in a one-necked, round-bottomed flask fitted with a magnetic stir bar. Diaryl carbonate, high melting point bisphenol, tetrabutylphosphonium acetate were mixed under ambient conditions in the molar ratios shown in Table 1 and in amounts sufficient to generate a stable, homogeneous melt solution with a total weight of about 5 to about 40 grams. The catalyst, and optionally bisphenol A, are charged to the flask. The catalyst was added as a solution in water containing about 40% by weight tetrabutylphosphonium acetate (TBPA). The volume of TBPA catalyst solution added is f...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2 and Comparative Examples 9-11 illustrate the preparation of a stable, homogeneous melt solution from a mixture of bis(methylsalicyl)carbonate (BMSC), 4,4'-diphenol, and transesterification catalyst TBPA. This data shows that a stable, homogeneous melt solution can be obtained in this three-component system, but requires a substantial amount of BMSC (4.55 molar equivalents relative to the high melting point component 4,4'-diphenol). Example 3 shows that this substantial excess of BMSC can be reduced if an additional component, in this case BPA, is added to the mixture. Finally, Examples 4 and 5 illustrate the formation of a stable, homogeneous melt solution of a mixture containing bisphenol as the first dihydroxyaromatic compound respectively at a temperature substantially below the melting point of the high melting point component bisphenol. Phenolic SBI (mp 212-215°C) and BPS (mp 245-247°C).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com