Direct current power supply apparatus and control method for the same, and a compressor drive apparatus
A technology of DC power supply and driving device, which is applied to the conversion device of output power, the conversion of irreversible AC power input to DC power output, electrical components, etc. problems such as high cost and high cost, to achieve the effect of reducing high-order harmonic current, reducing loss and noise, and preventing damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
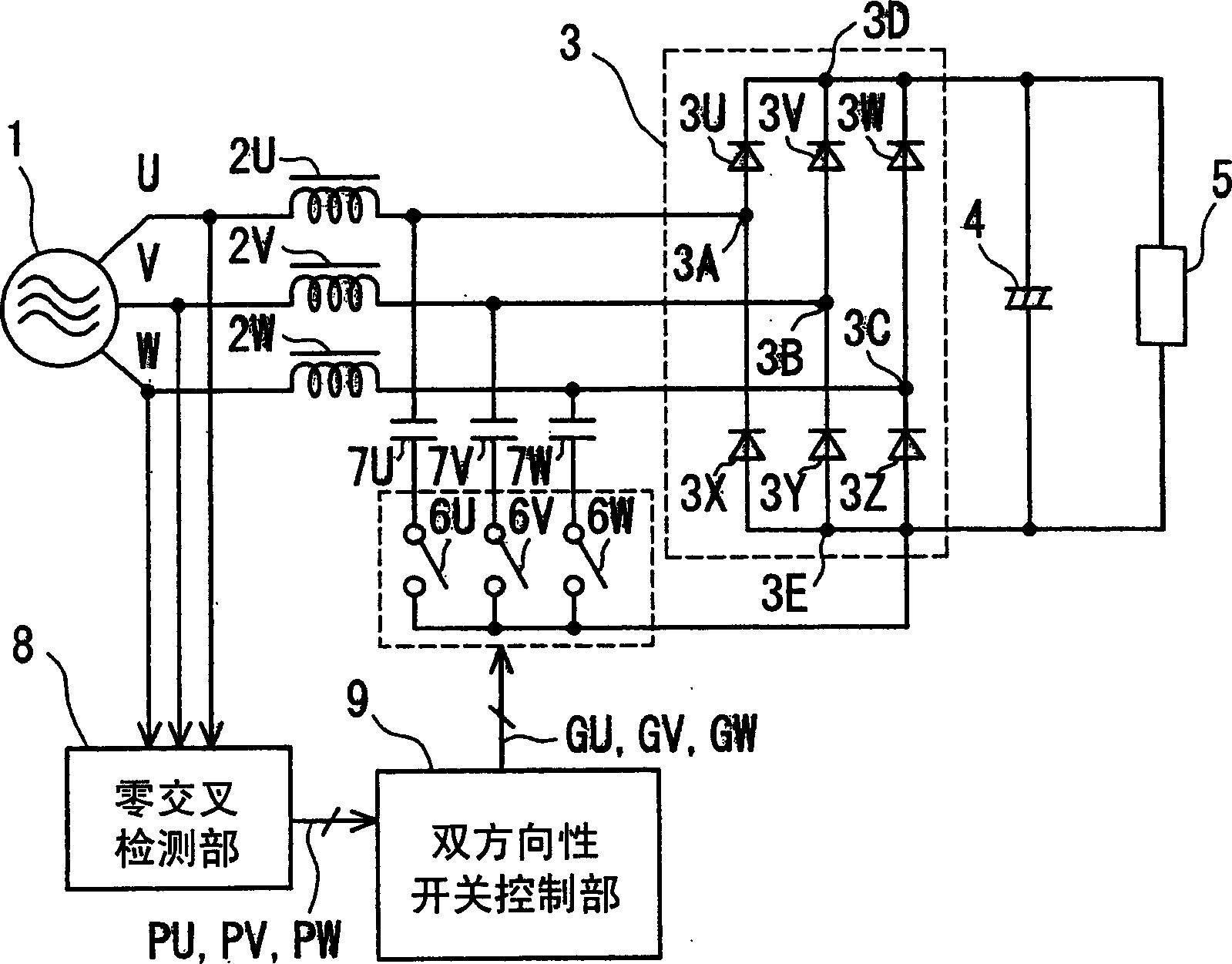
[0057] figure 1 It is a block diagram of the DC power supply device of the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0058] exist figure 1 Among them, each phase of U, V, and W of the three-phase AC power supply 1 is connected to the bridge rectifier circuit 3 composed of diodes 3U, 3V, 3W, 3X, 3Y, and 3Z through each reactor 2U, 2V, and 2W. Each AC input terminal 3A, 3B, 3C. The electrolytic capacitor 4 is connected between the positive DC output terminal 3D and the negative DC output terminal 3E of the bridge rectifier circuit 3 . Load 5 is connected in parallel with electrolytic capacitor 4 . Connect one end of each bidirectional switch 6U, 6V, 6W to the negative DC output end 3E of the bridge rectifier circuit 3, and connect their other ends to 7U, 7V, 7W respectively.
[0059] The other terminals of these capacitors 7U, 7V, and 7W are connected to AC input terminals 3A, 3B, and 3C of the rectifier circuit 3, respectively. In addition, the zero-cross detection un...
no. 2 approach
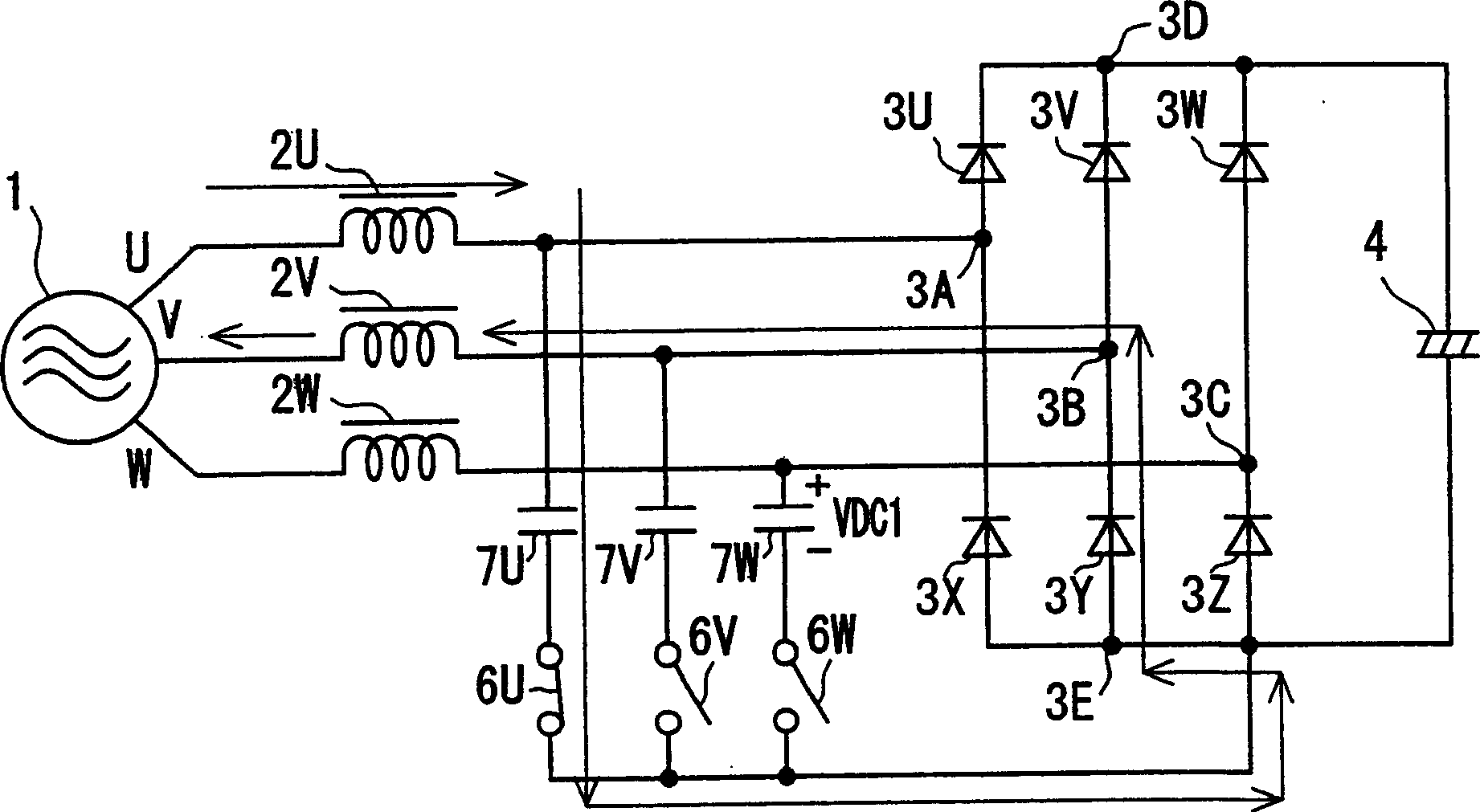
[0091] Figure 12 It is a block diagram of a DC power supply device according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
[0092] Figure 12 With respect to the block diagram of the DC power supply device of the first embodiment, the arrangement of capacitors 7U, 7V, and 7W is replaced by bidirectional switches 6U, 6V, and 6W, respectively, and a single capacitor 28 is integrated.
[0093] In the second embodiment, with respect to the first embodiment, the control and timing of the turn-on operation of each bidirectional switch 6U, 6V, 6W, and the flow through each bidirectional switch 6U, 6V, 6W and the bridge The current of the type DC circuit 3 is the same, and the improvement of the input power factor and the reduction effect of the high-order harmonic are also equivalent. The difference is that all the currents flowing through the capacitors 7U, 7V, and 7W in the first embodiment are configured to flow through the capacitor 28, and the phase in which the charging cu...
no. 3 approach
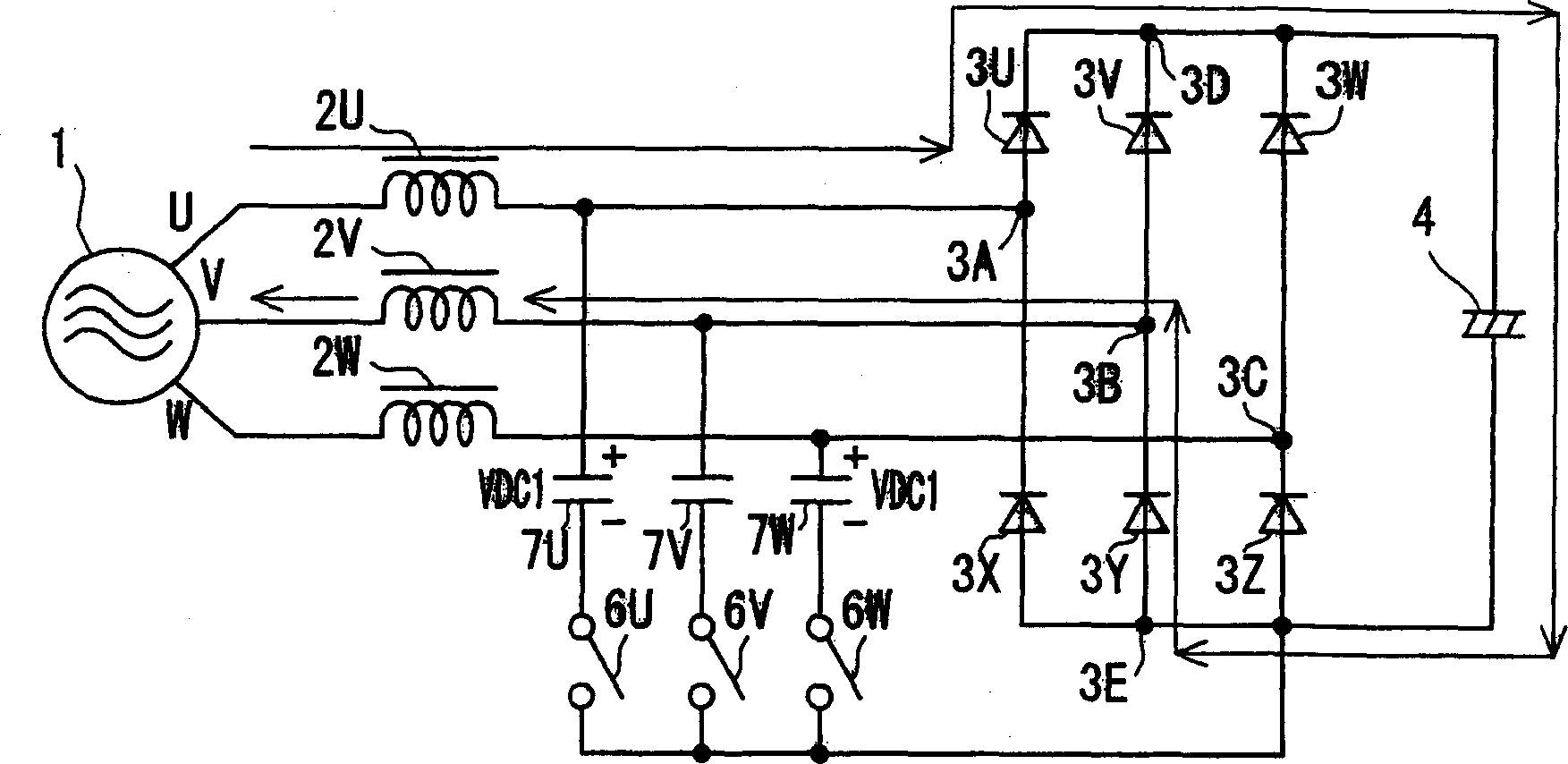
[0099] Figure 14 It is a block diagram of a DC power output device according to a third embodiment of the present invention.
[0100] Figure 14 compared to figure 1 The block diagram of the DC power supply device according to the first embodiment includes a DC voltage detection unit 21 for detecting the DC output voltage across the electrolytic capacitor 4, and a voltage abnormality detection unit 51 for detecting abnormalities in the detected DC voltage value.
[0101] The normal operation of the third embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment. The bidirectional switches 6U, 6V, and 6W are controlled by the bidirectional switch control unit 9, and the input power factor is improved and the harmonic current is reduced. At the same time, DC power is supplied to the load 5 .
[0102] Here, abnormal rise and fall of the DC output voltage may be caused by a sudden change of the load 5 or a malfunction of the bidirectional switch control unit 9 . The difference ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com