Magnetoresistive sensor, comprising a ferromagnetic/antiferromagnetic sensitive element
A technology of magnetoresistance and sensitive element, applied in the field of magnetoresistance magnetic field sensor, which can solve the problems of structure loss and poor barrier.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
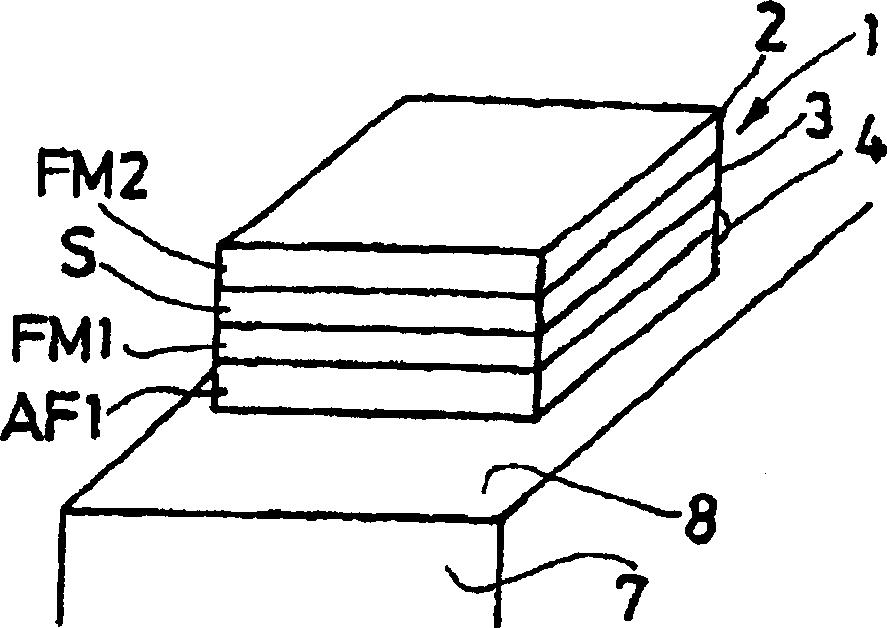
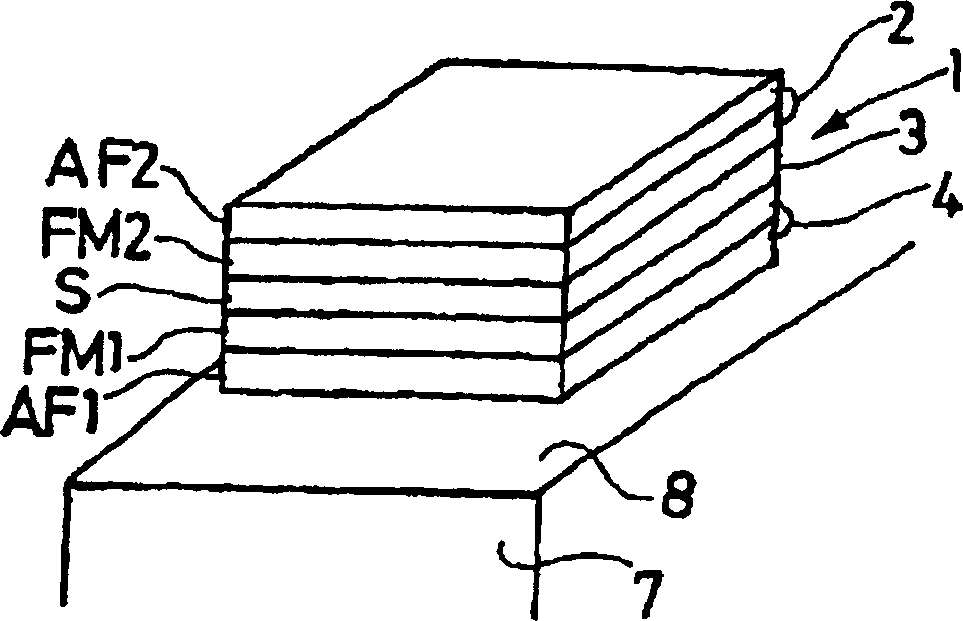
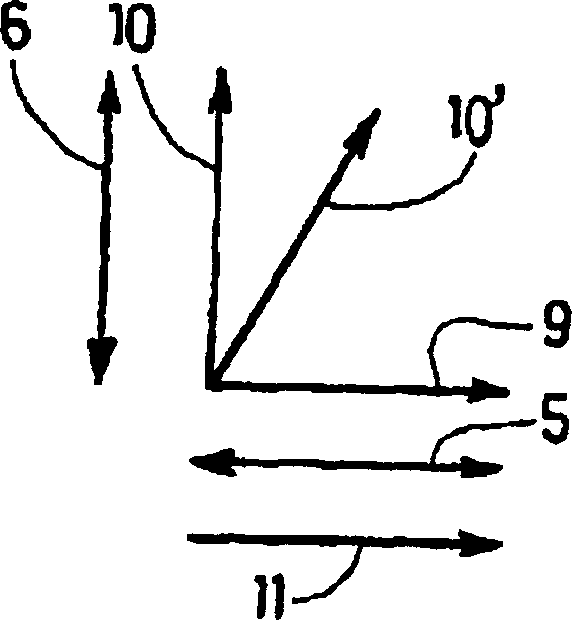
[0024] A property of particular interest here is the response obtained when a field is applied perpendicular to the magnetic axis exhibiting exchange when the ferromagnetic material FM1 and the antiferromagnetic material AF1 have a common interface. In this case, the process of magnetization reversal by nucleation and wall propagation (reversal when the field is applied along the magnetic axis exhibiting exchange) is replaced by a reversible rotation of the magnetization (when the field is perpendicular to the magnetic axis exhibiting exchange inversion when applied). Then the hysteresis characteristic is Figure 4a instead of the reversible properties. Furthermore, the signal is linear over a fairly wide field range.
[0025] Formally, the gradient of the magnetization response to the applied magnetic field is given by:
[0026] ∂ M ∂ H | H ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com