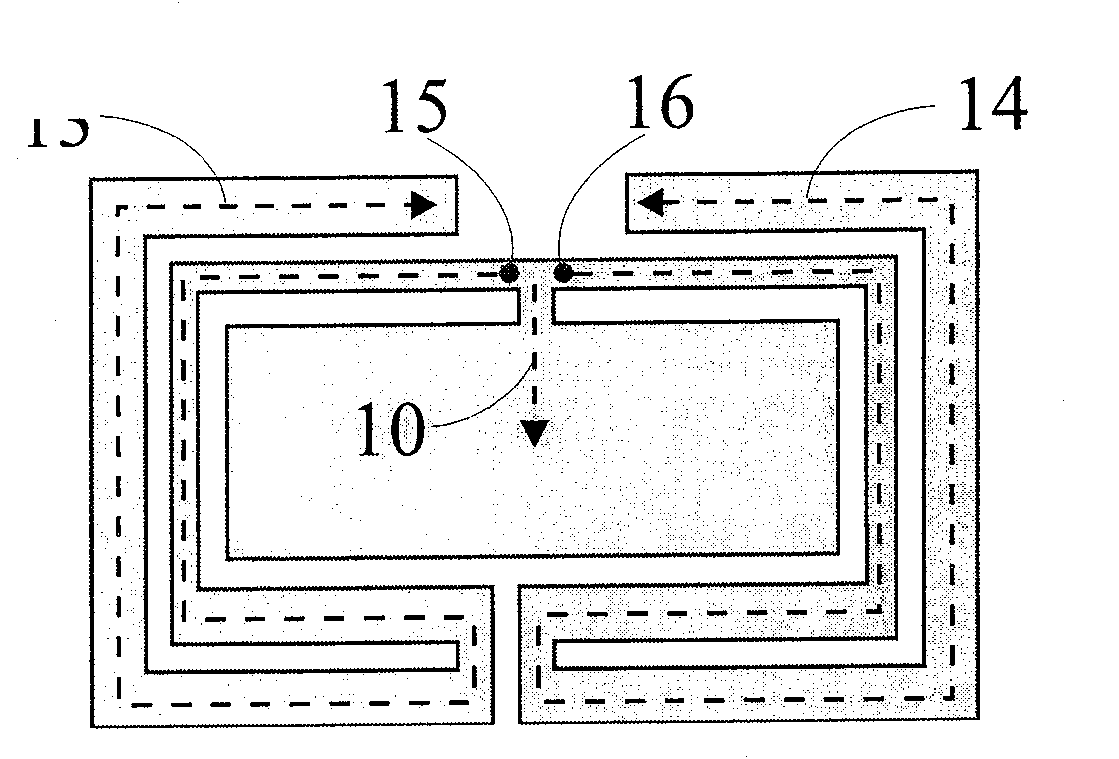
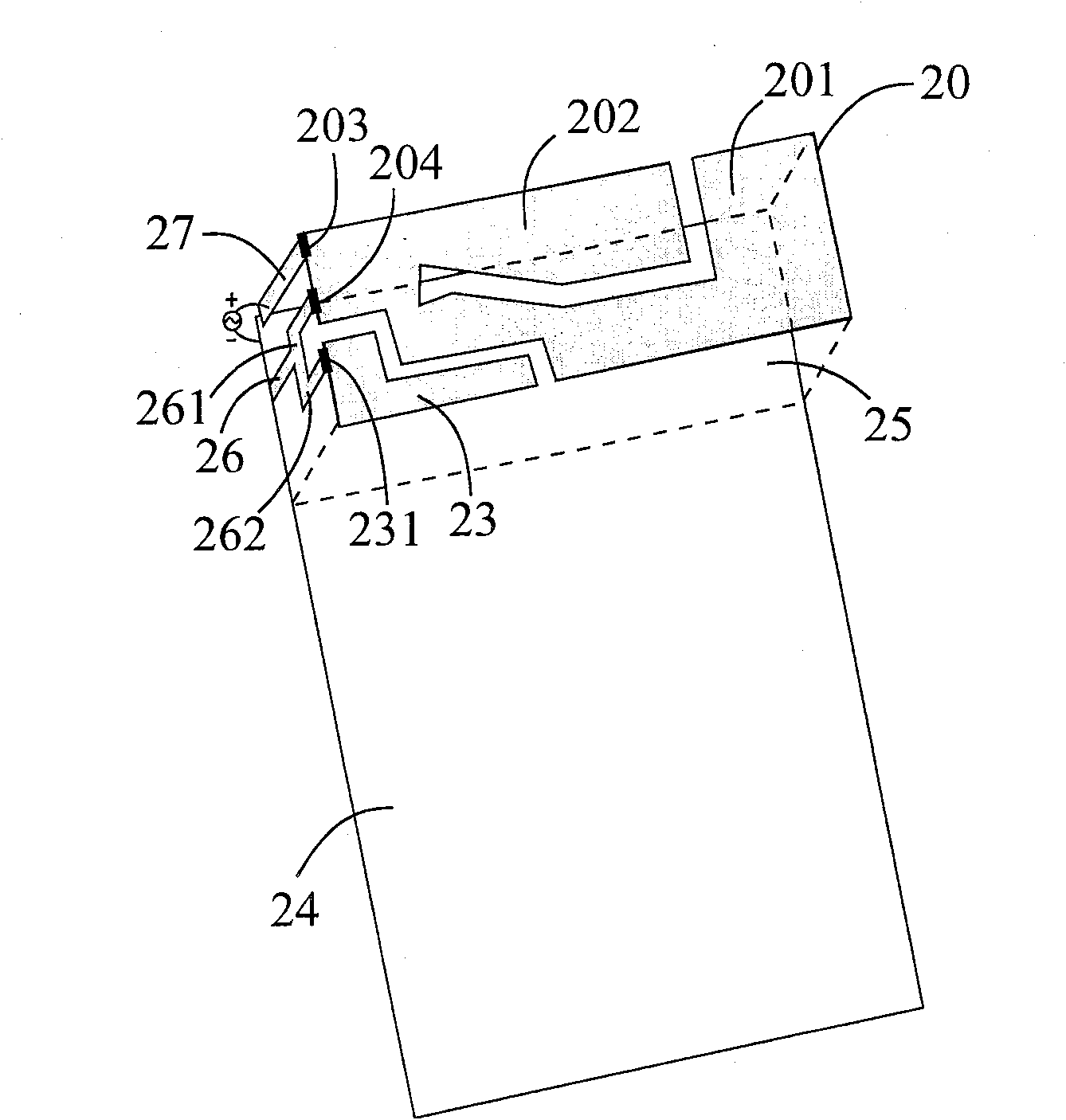
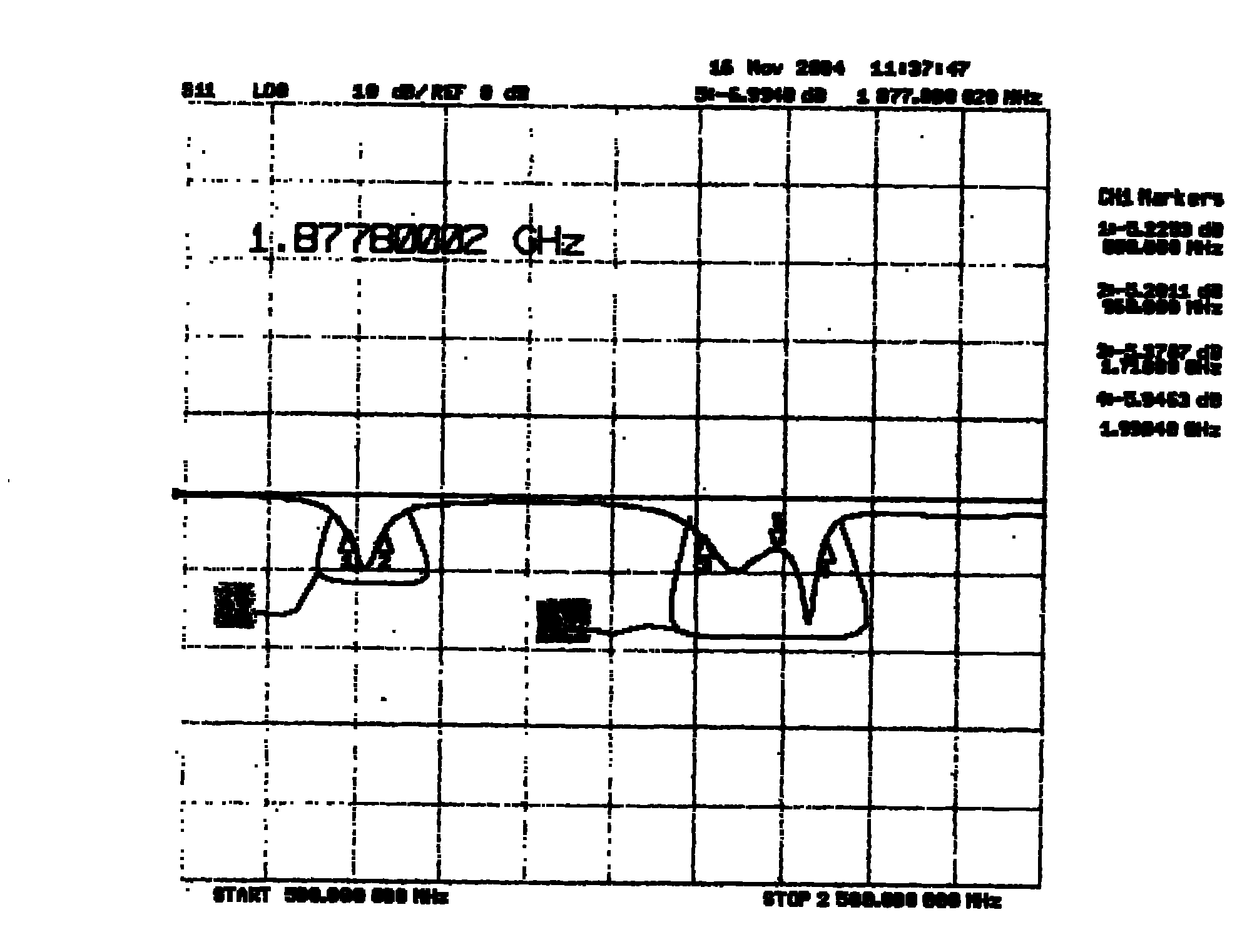
Inverted-F antenna with double-branch, short-circuit structure
A dual-branch, antenna technology, applied in the direction of the antenna, resonant antenna, radiating element structure, etc., can solve the problems of narrow bandwidth, complex structure, and many meandering current paths, etc., to achieve increased bandwidth and good impedance matching. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0011] Such as figure 2 Shown is an embodiment 2 of the inverted-F antenna with a double-branch short-circuit structure of the present invention, which includes: a main radiation metal sheet 20, a secondary radiation metal sheet 23, a ground plane 24, and a dielectric substrate 25 , a double-branch short-circuit metal sheet 26 and a feed-in metal sheet 27; wherein, the main radiation metal sheet 20 includes a first sub-radiation metal sheet 201, a second sub-radiation metal sheet 202, a feed-in point 203 and a The first short-circuit point 204, wherein the feeding point 203 and the first short-circuit point 204 are located on the same edge of the main radiating metal sheet, and the first sub-radiating metal sheet 201 forms a longer current path for The first (low frequency) operation mode of the antenna is generated, and the second sub-radiating metal sheet 202 forms a shorter current path for generating the second (high frequency) operation mode of the antenna; the sub-radia...
Embodiment 4
[0013] Such as Figure 4 Shown is another embodiment 4 of the inverted-F antenna with a double-branch short-circuit structure of the present invention, which includes: a main radiating metal sheet 40, a secondary radiating metal sheet 43, a ground plane 44, and a dielectric substrate 45. A double-branch short-circuit metal sheet 46 and a feed-in metal sheet 47; wherein, the main radiation metal sheet 40 includes a first sub-radiation metal sheet 401, a second sub-radiation metal sheet 402, a feed-in point 403 and A first short-circuit point 404, wherein the feed-in point 403 and the first short-circuit point 404 are located on different edges of the main radiating metal sheet 40, and the first sub-radiating metal sheet 401 forms a longer current path for To generate the first (low frequency) operation mode of the antenna, the second sub-radiating metal sheet 402 forms a shorter current path for generating the second (high frequency) operation mode of the antenna; 43 can gener...
Embodiment 5
[0014] Such as Figure 5Shown is yet another embodiment 5 of the inverted-F antenna with a double-branch short-circuit structure of the present invention, which includes: a main radiation metal sheet 50, a secondary radiation metal sheet 53, a ground plane 54, and a dielectric substrate 55. A double-branch short-circuit metal sheet 56 and a feed-in metal sheet 57; wherein, the main radiation metal sheet 50 includes a first sub-radiation metal sheet 501, a second sub-radiation metal sheet 502, a feed-in point 503 and A first short-circuit point 504, wherein the feeding point 503 is located on an edge of the main radiating metal sheet 50, and the first short-circuit point 504 is located inside the main radiating metal sheet 50, and the first sub-radiating metal sheet The sheet 501 forms a longer current path for generating the first (low frequency) mode of operation of the antenna, and the second sub-radiating metal sheet 502 forms a shorter current path for generating the secon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com