Patents
Literature
230 results about "Inverted-F antenna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
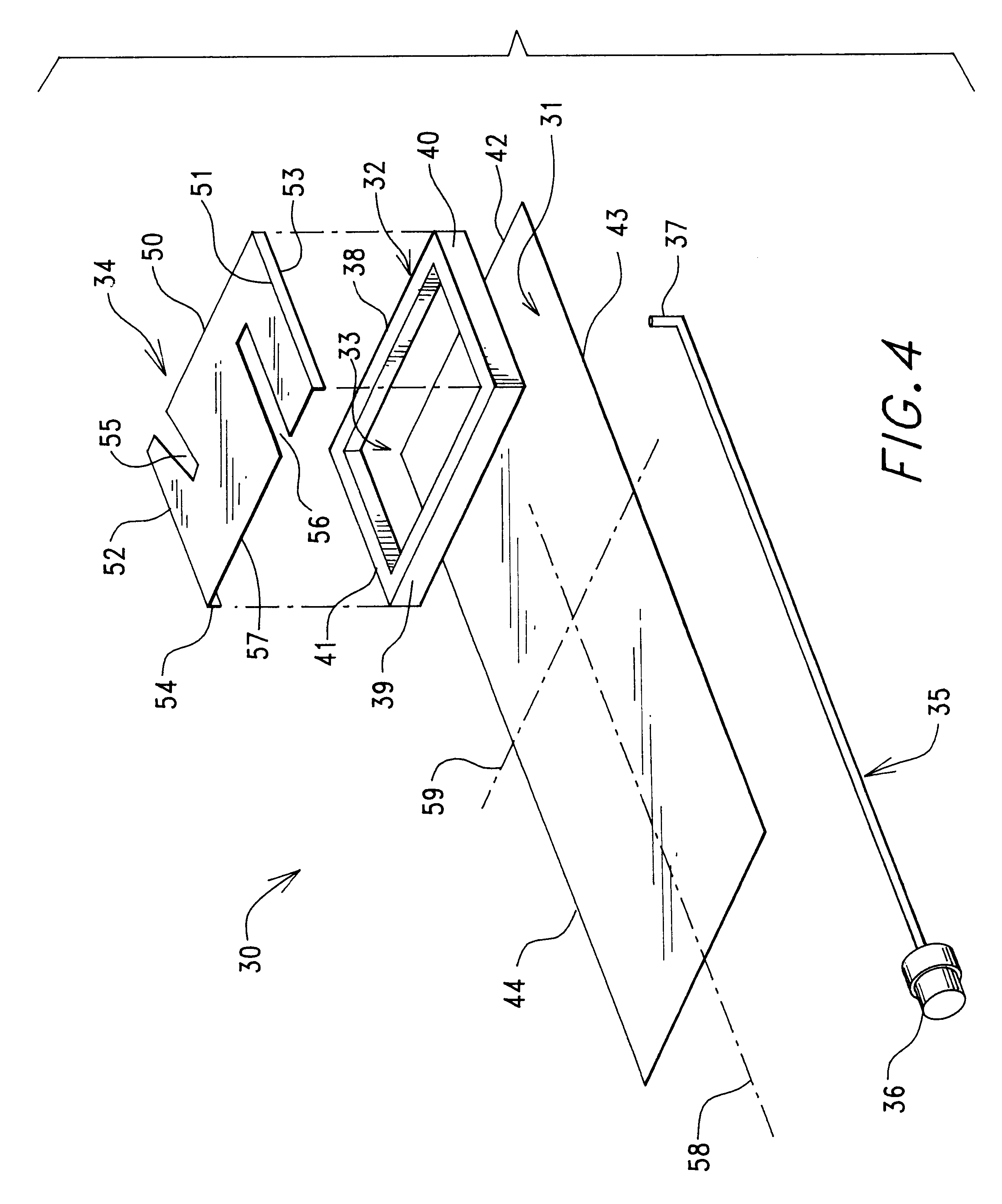
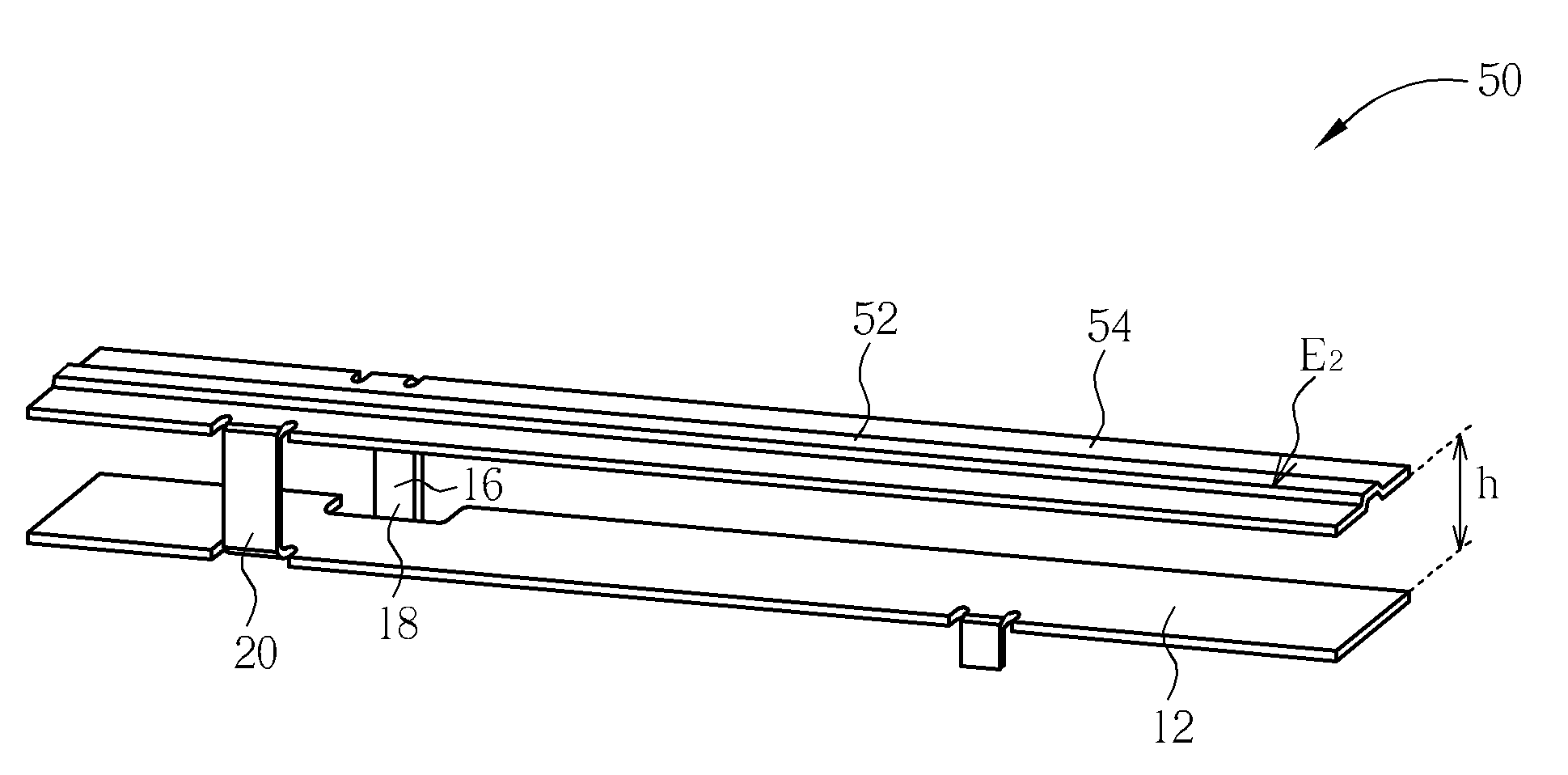
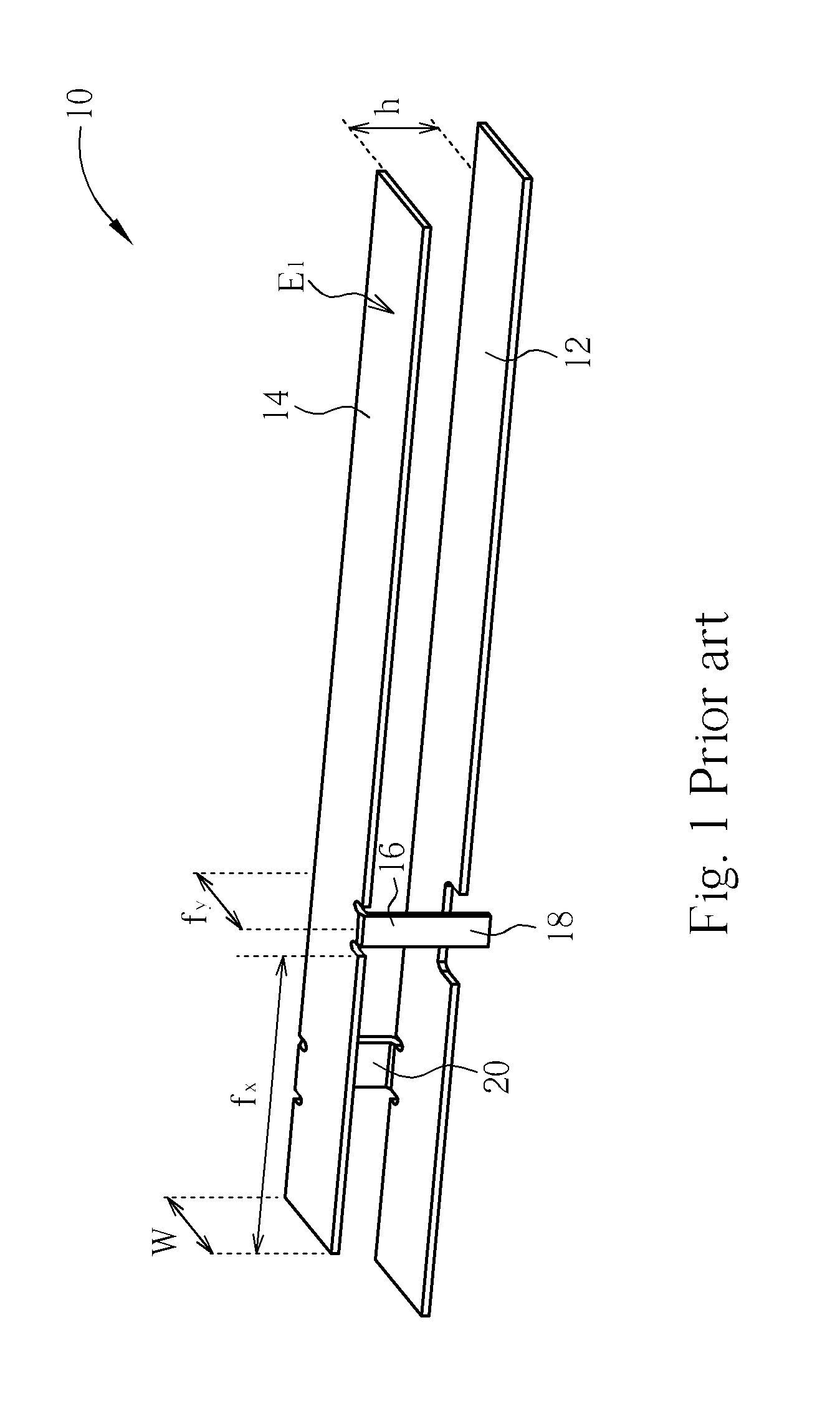
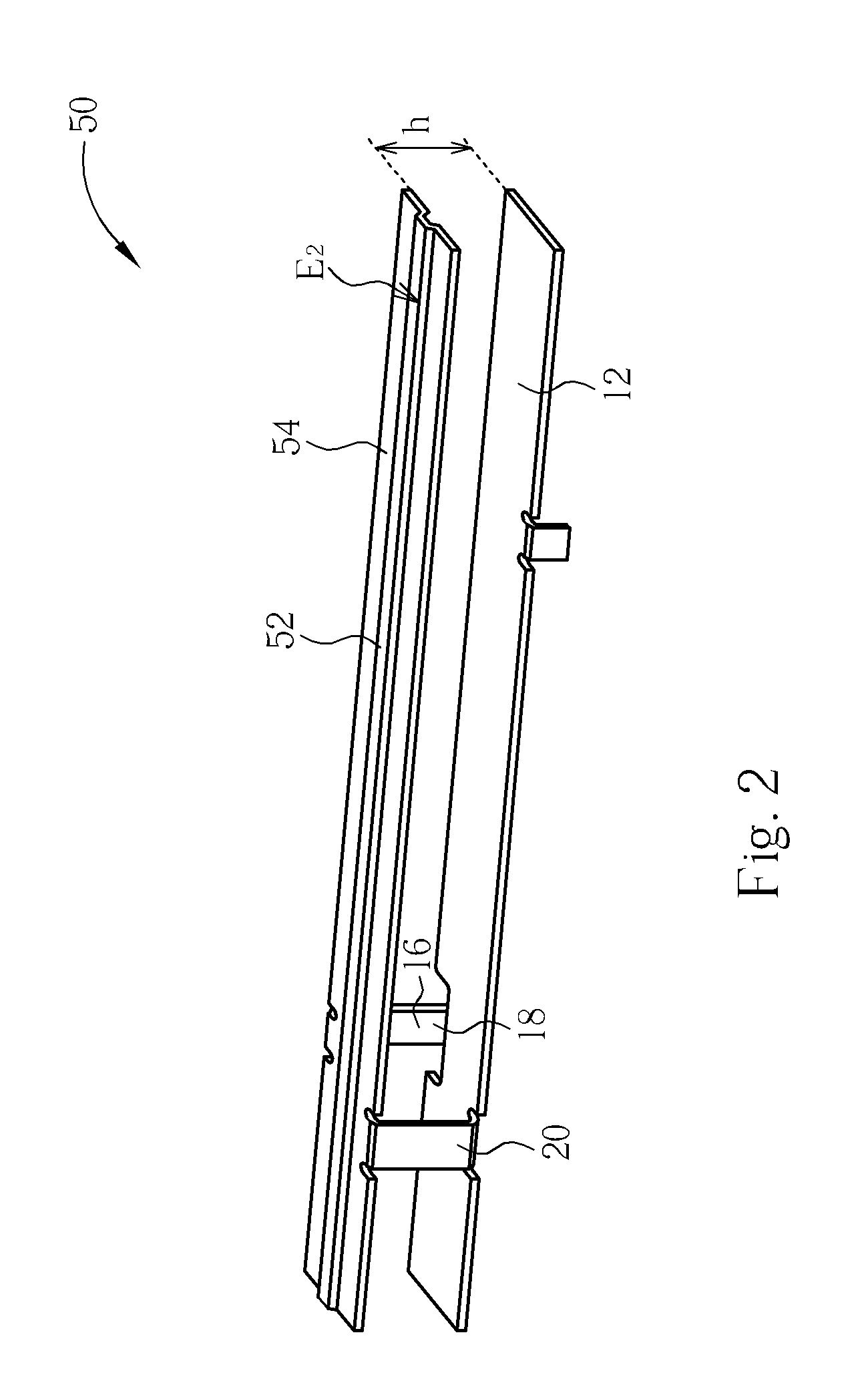
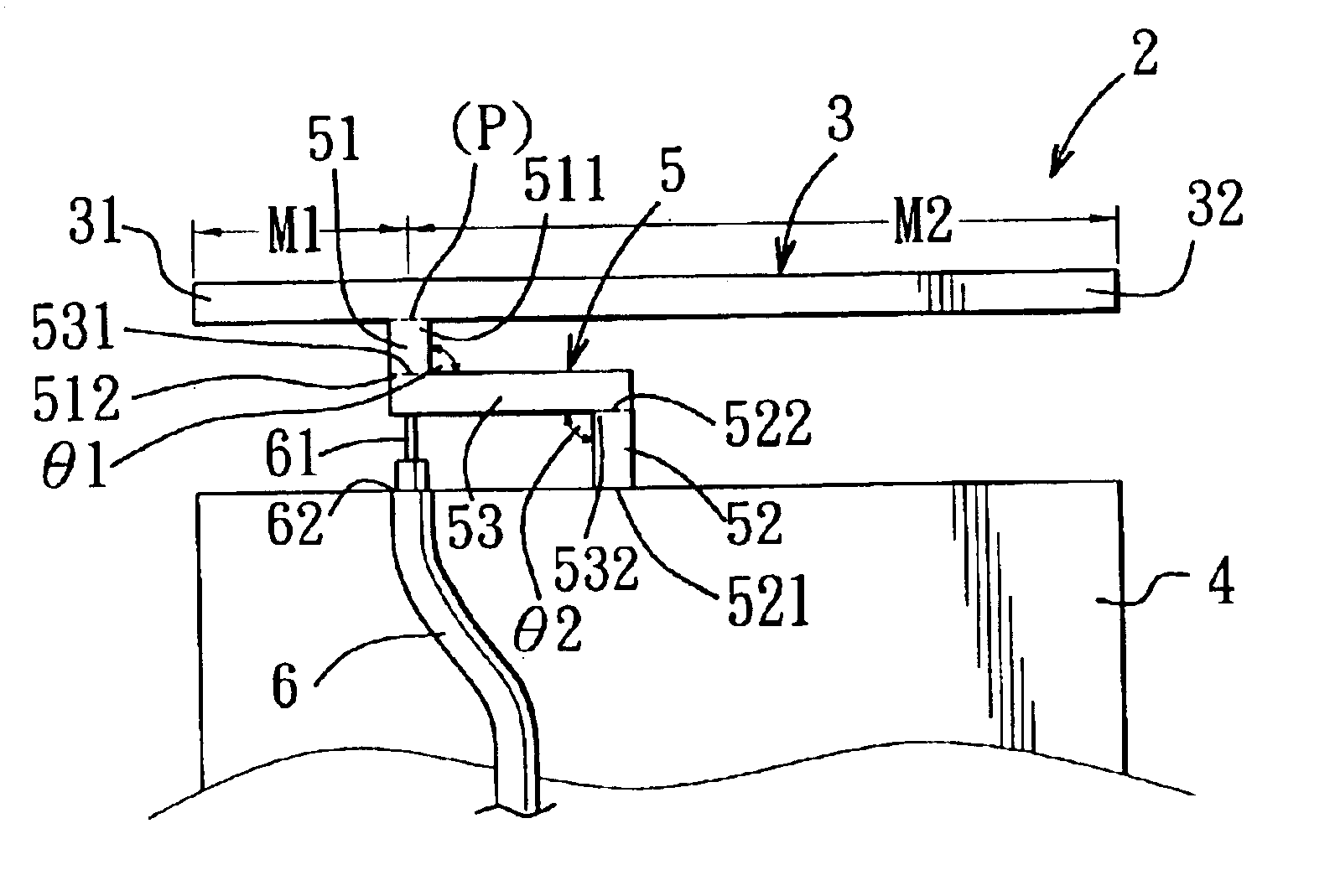
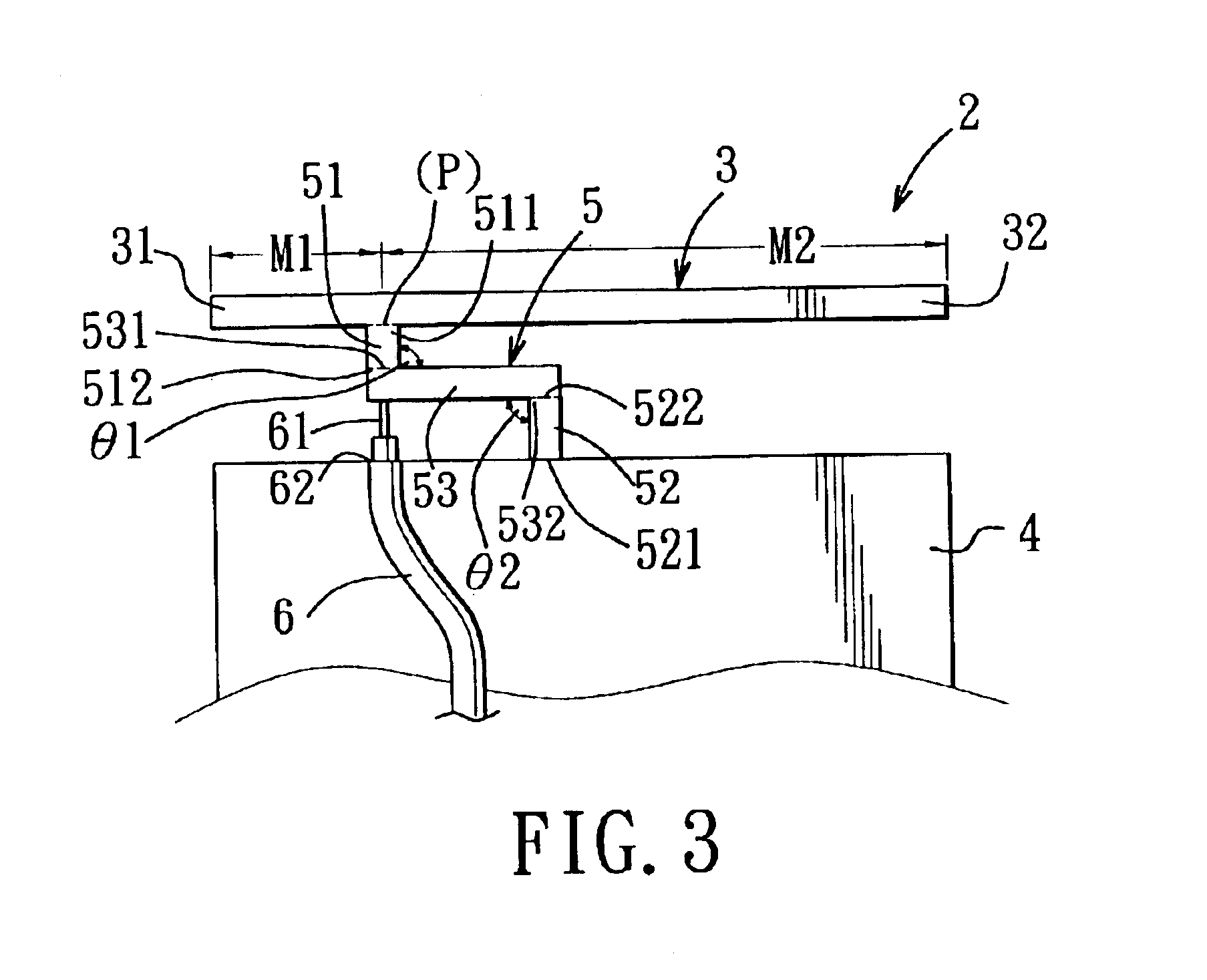
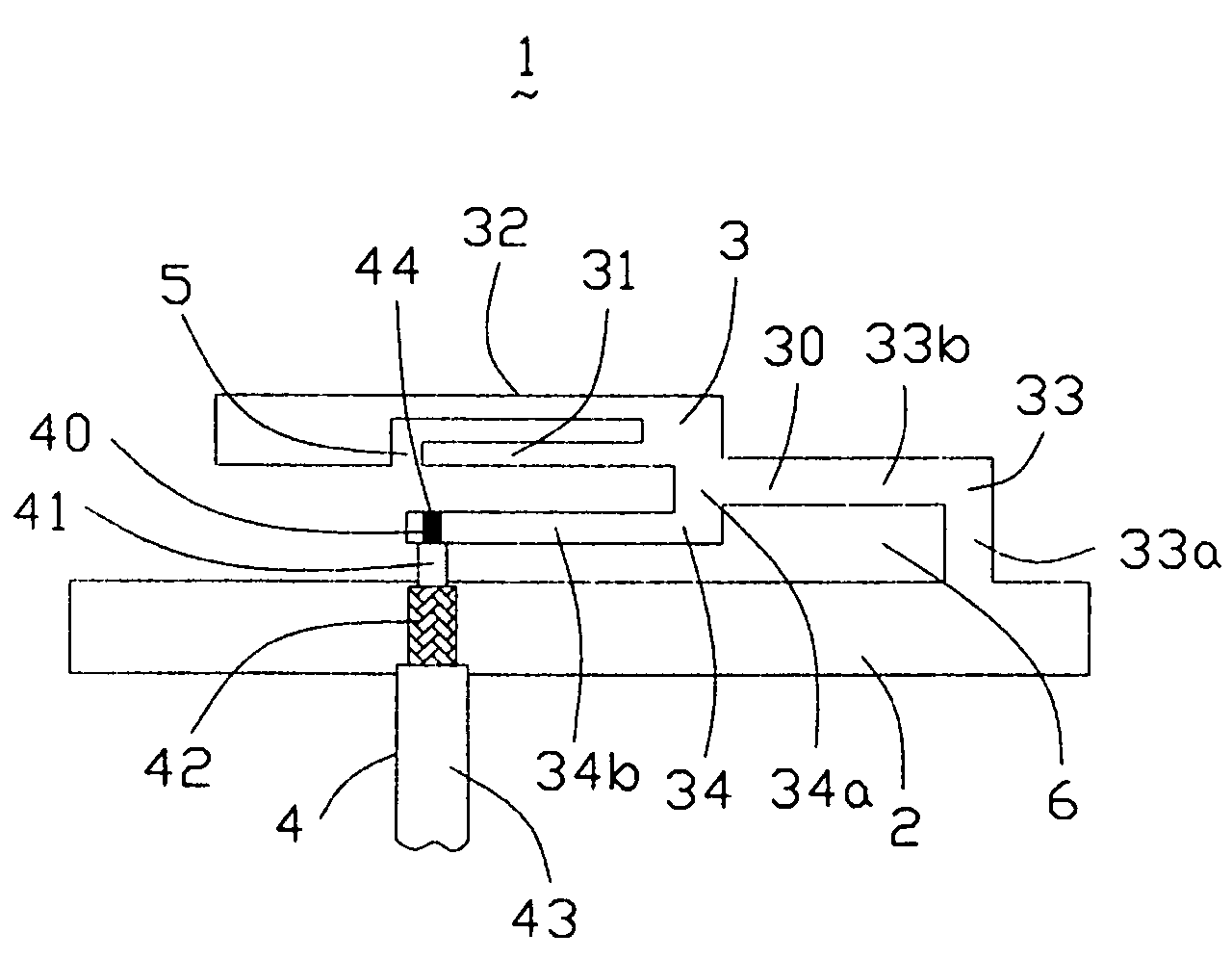
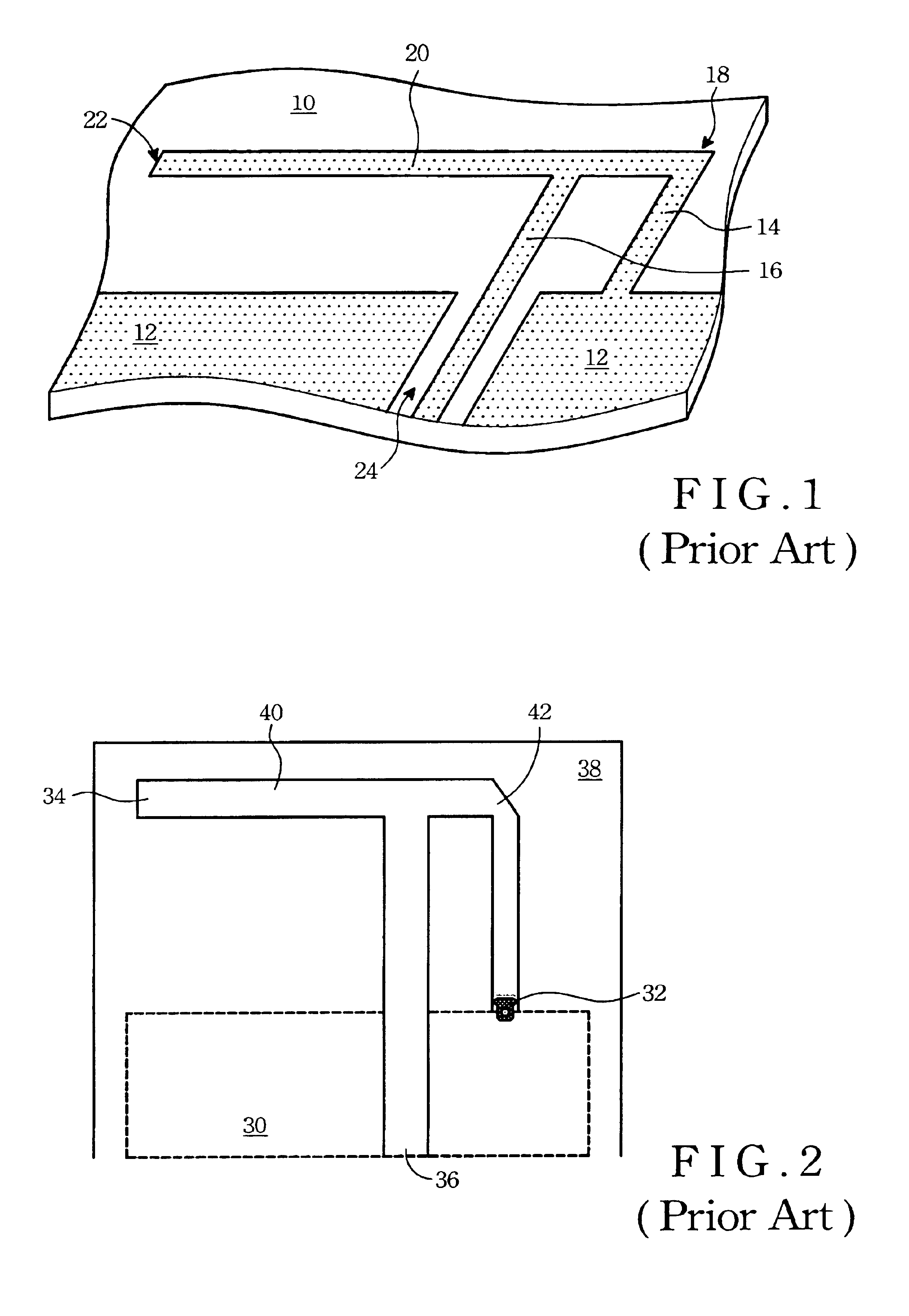
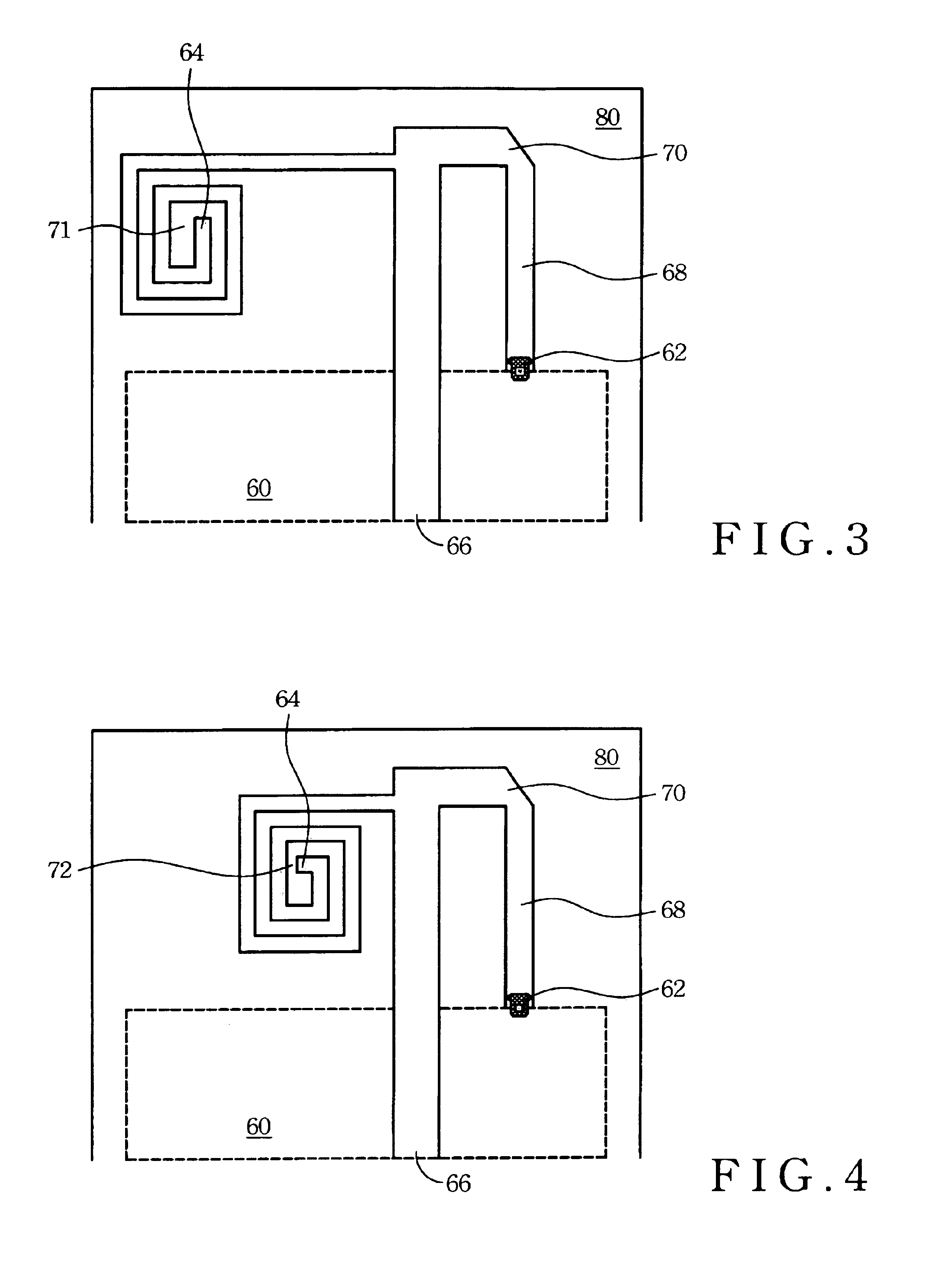
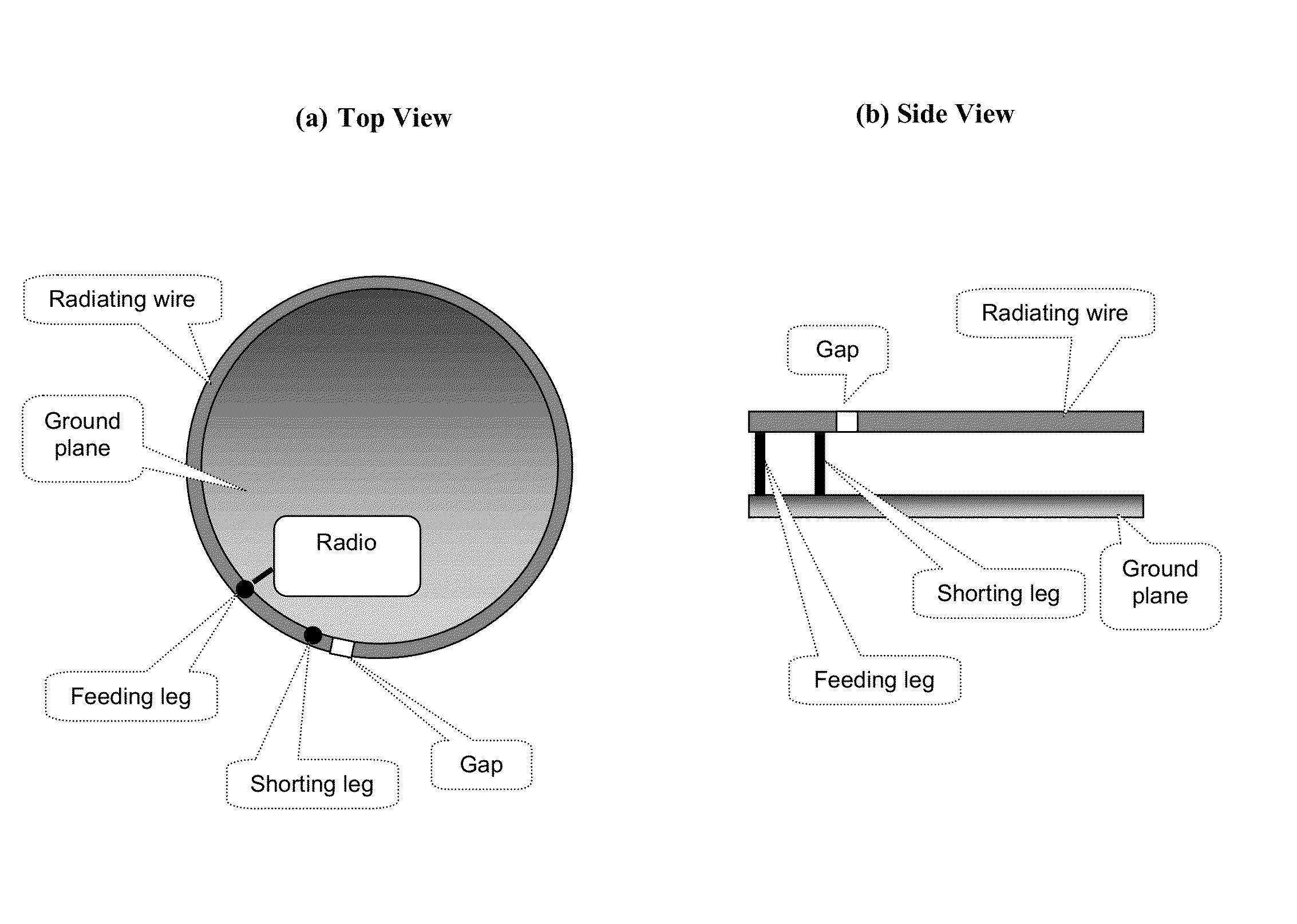
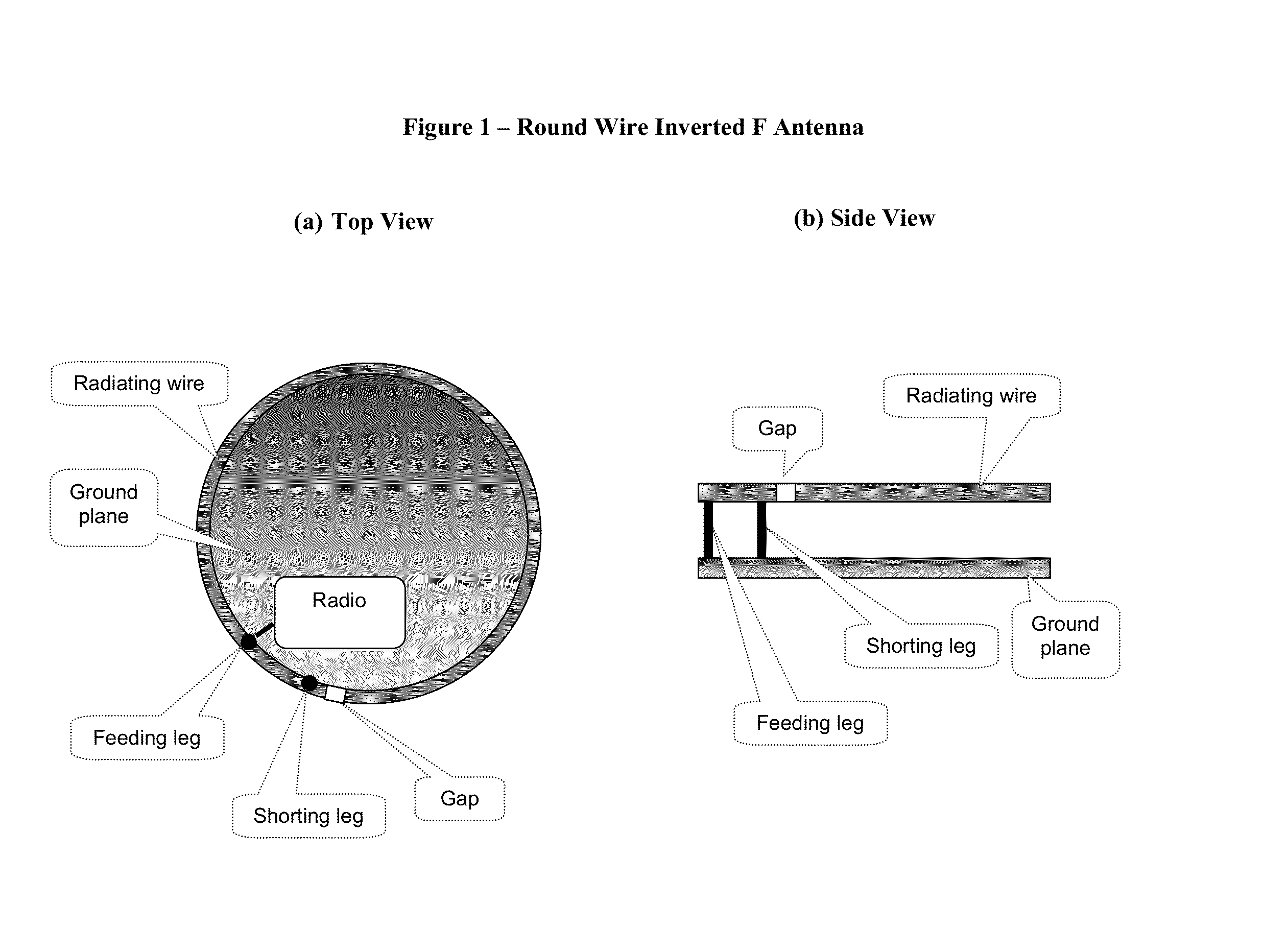
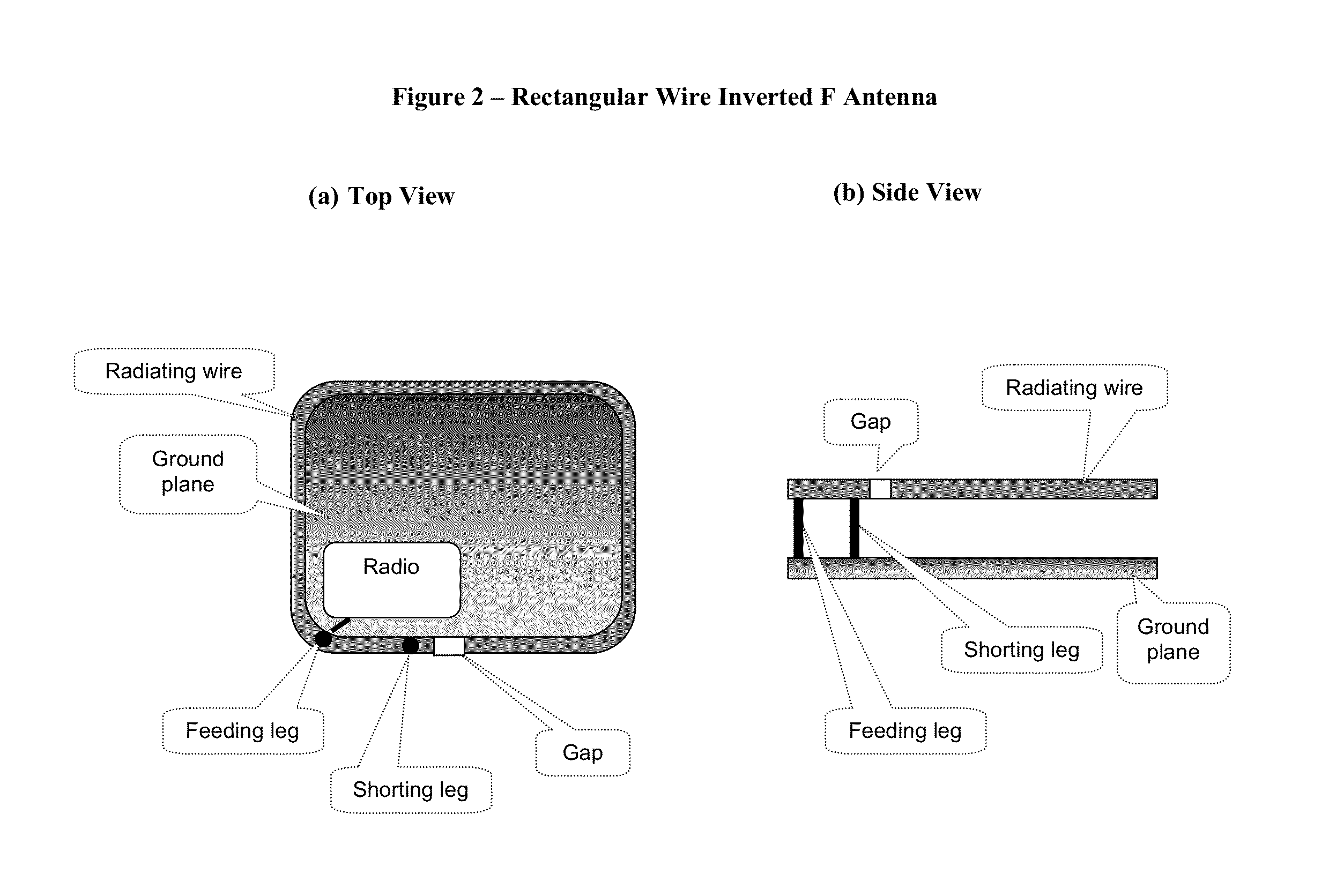
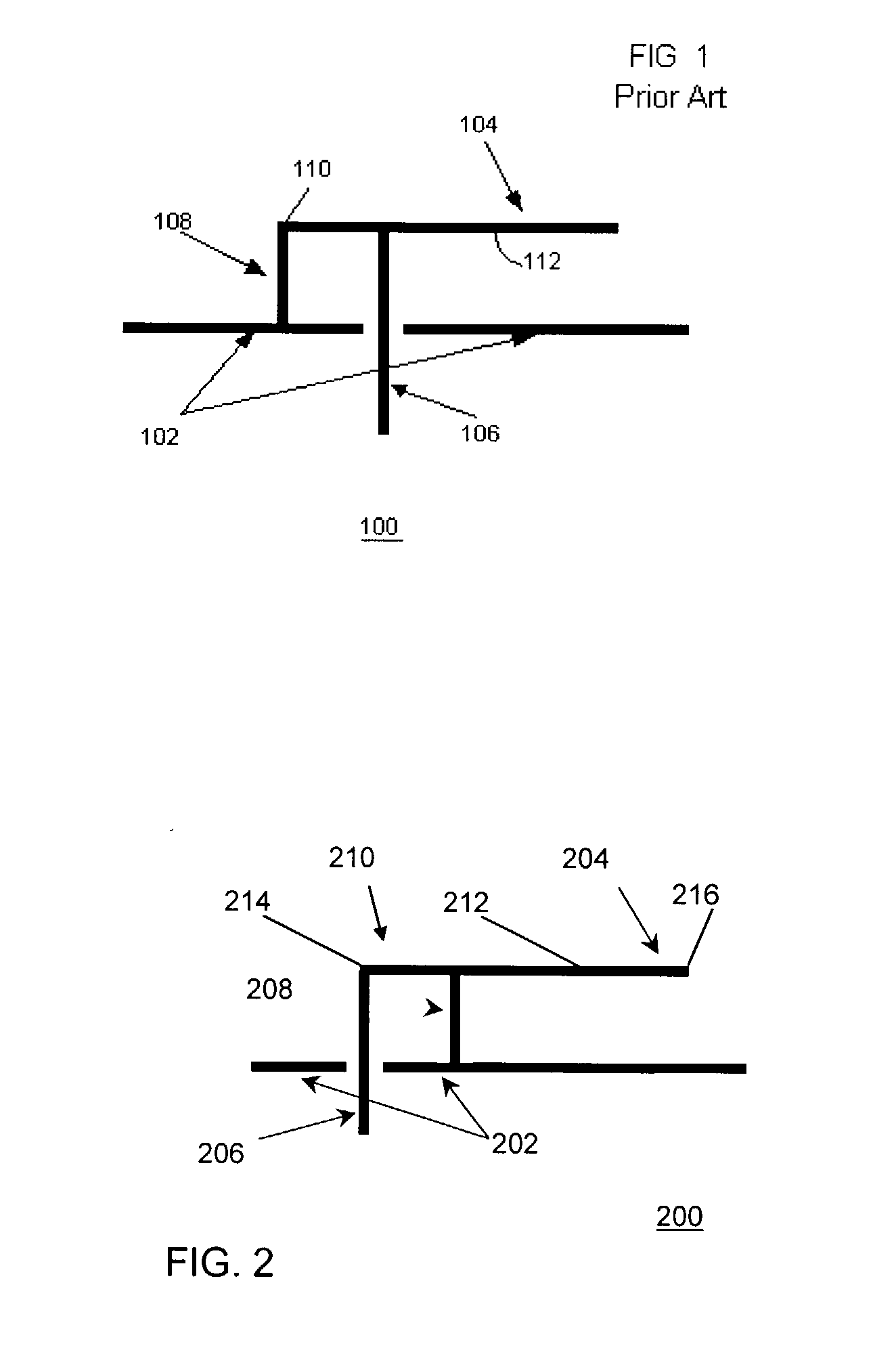
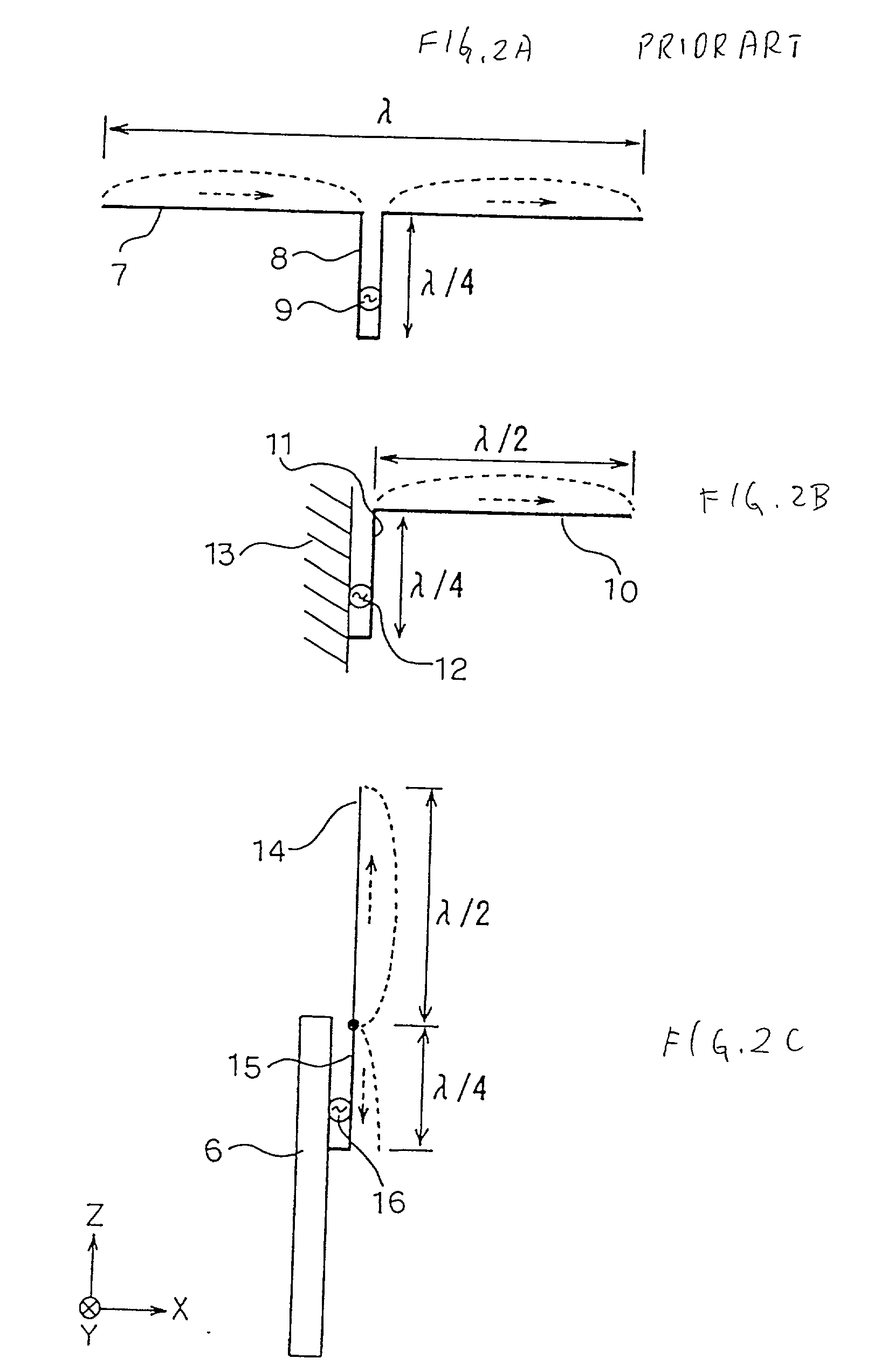
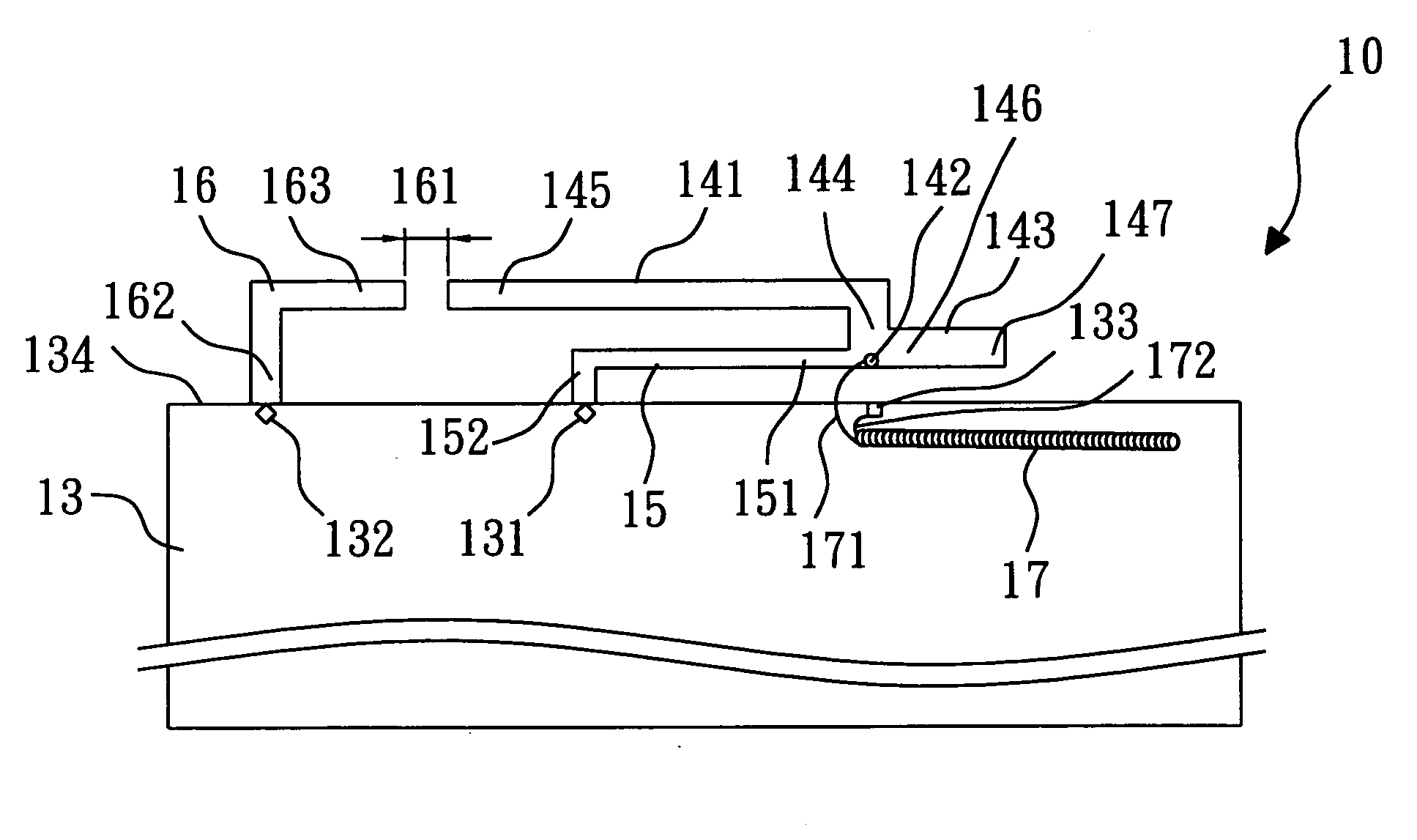
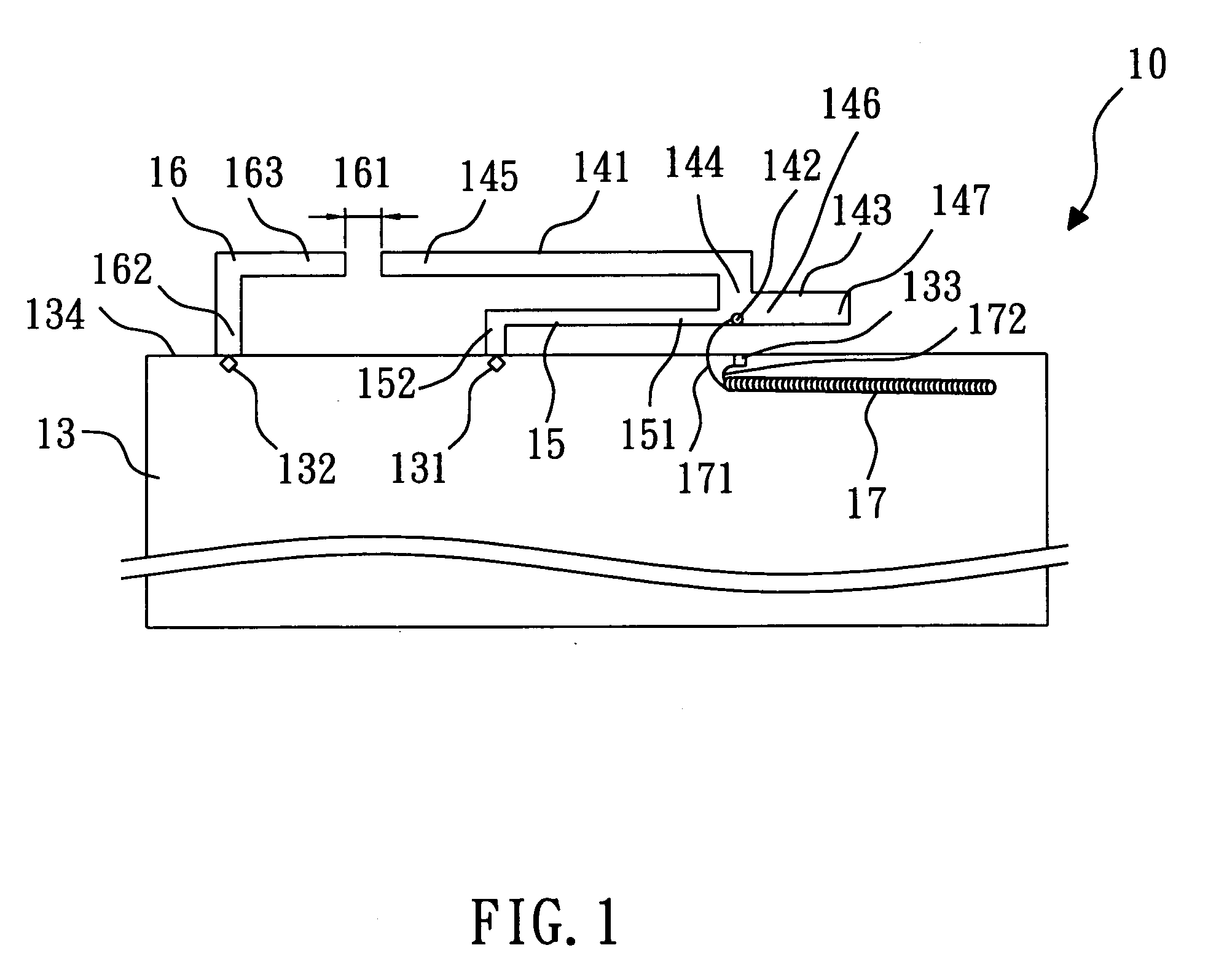
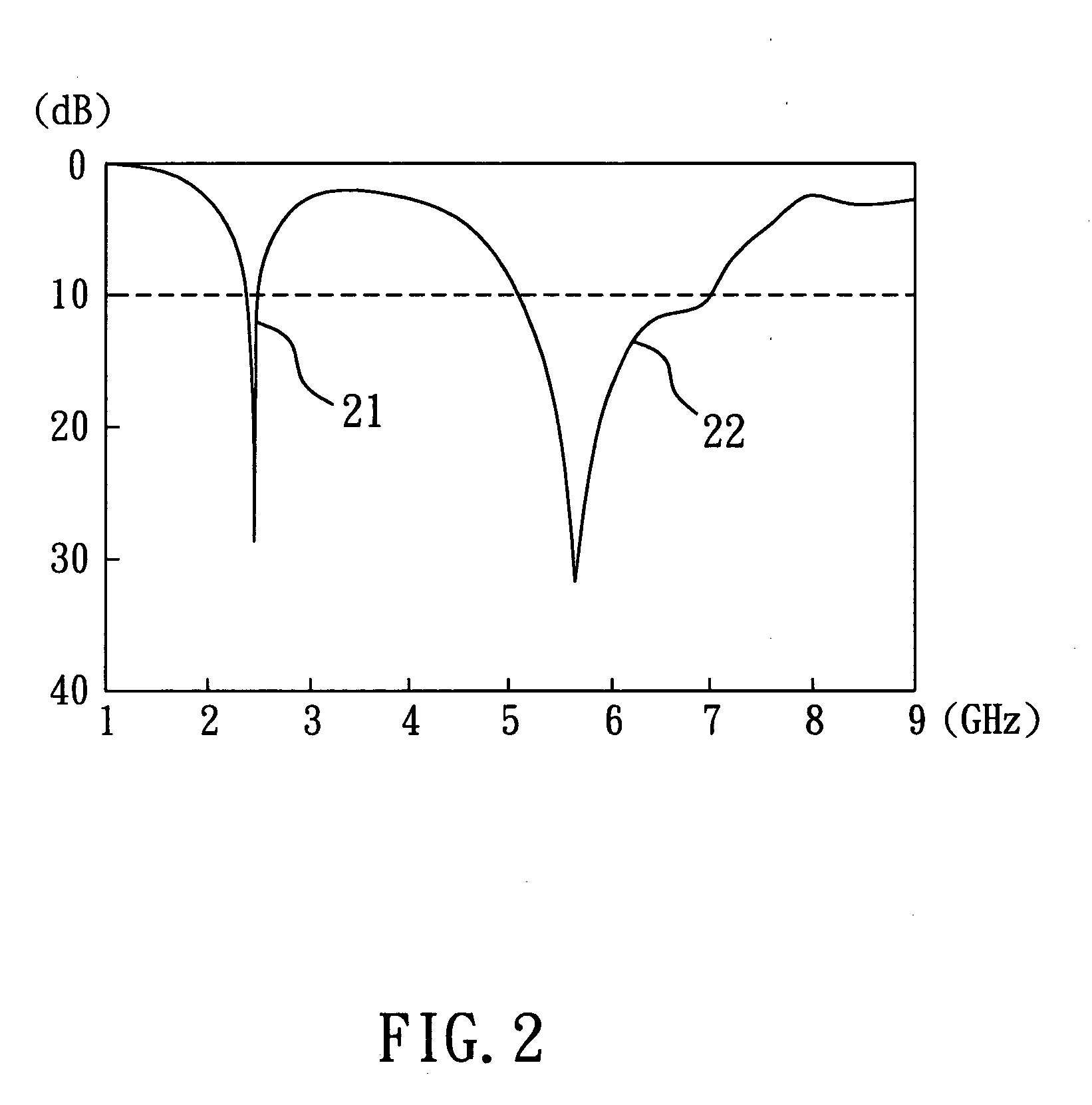
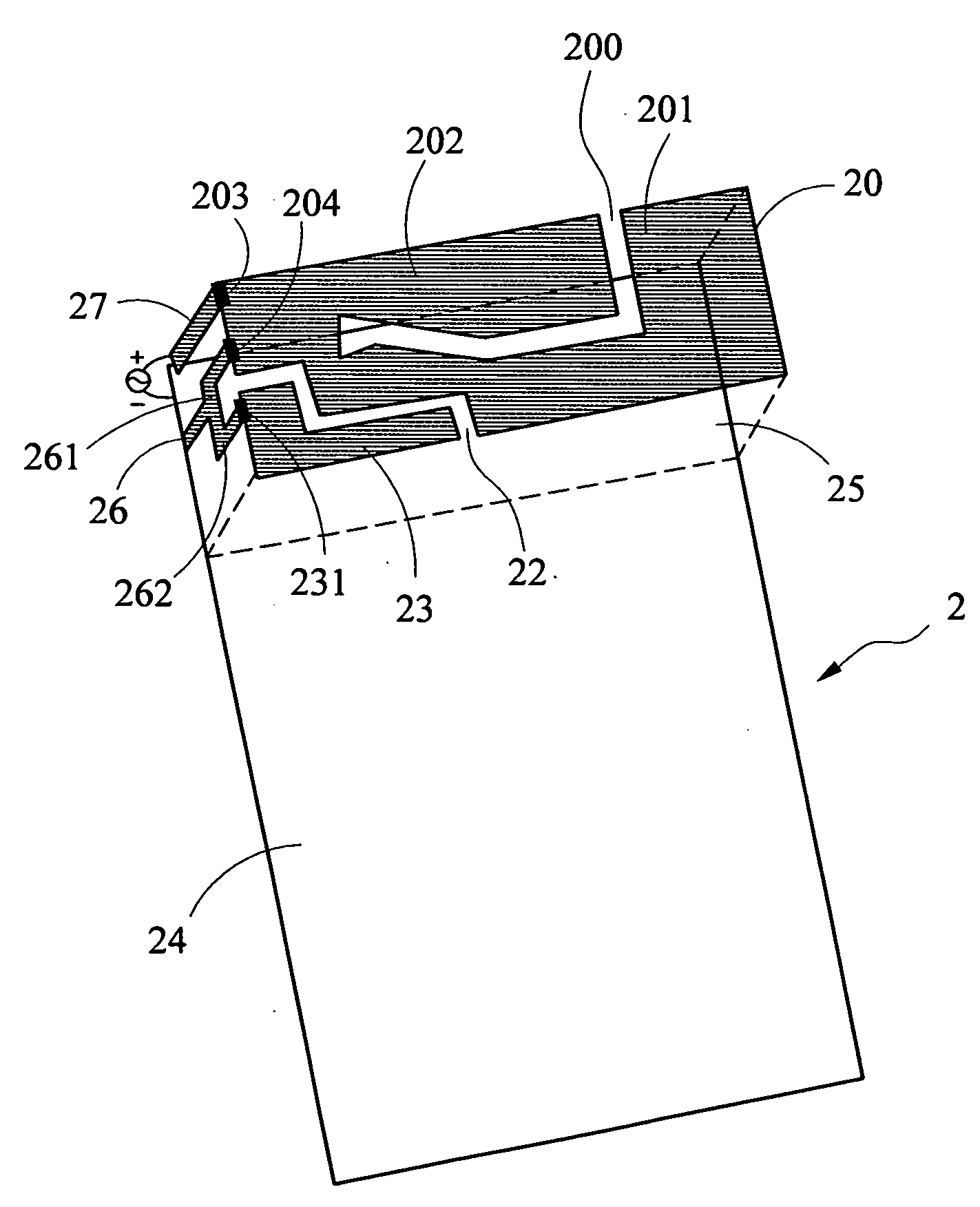
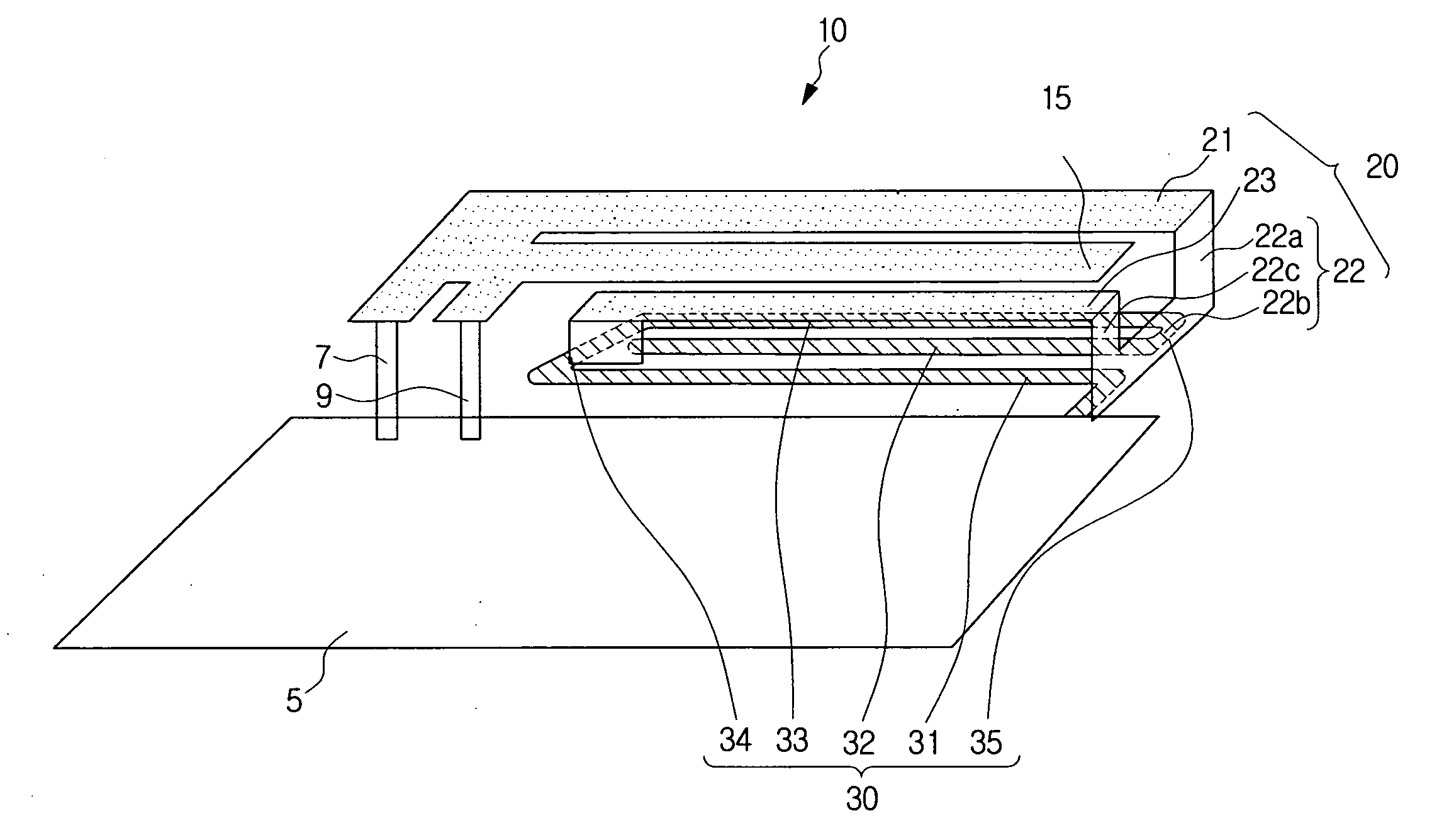
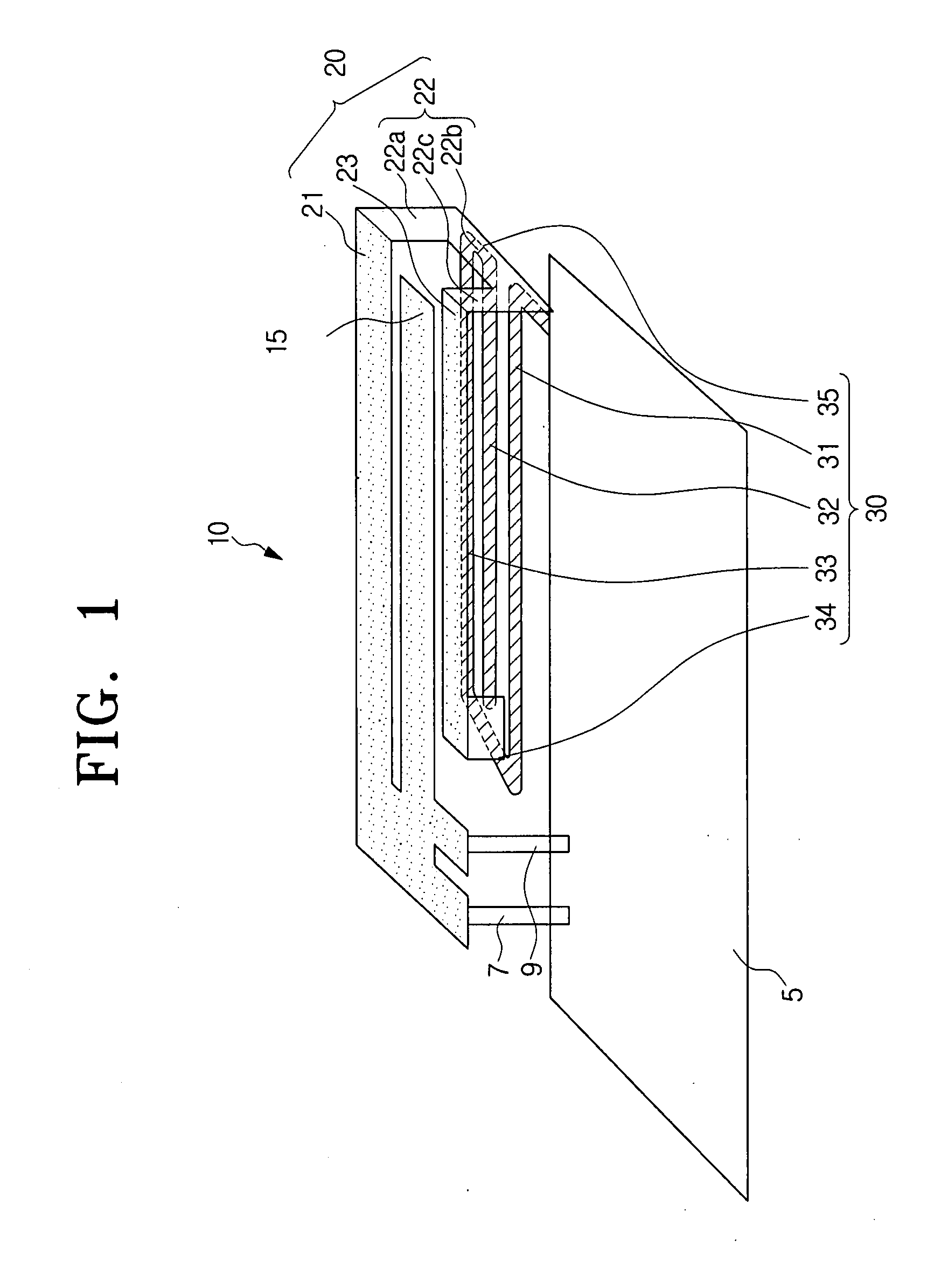
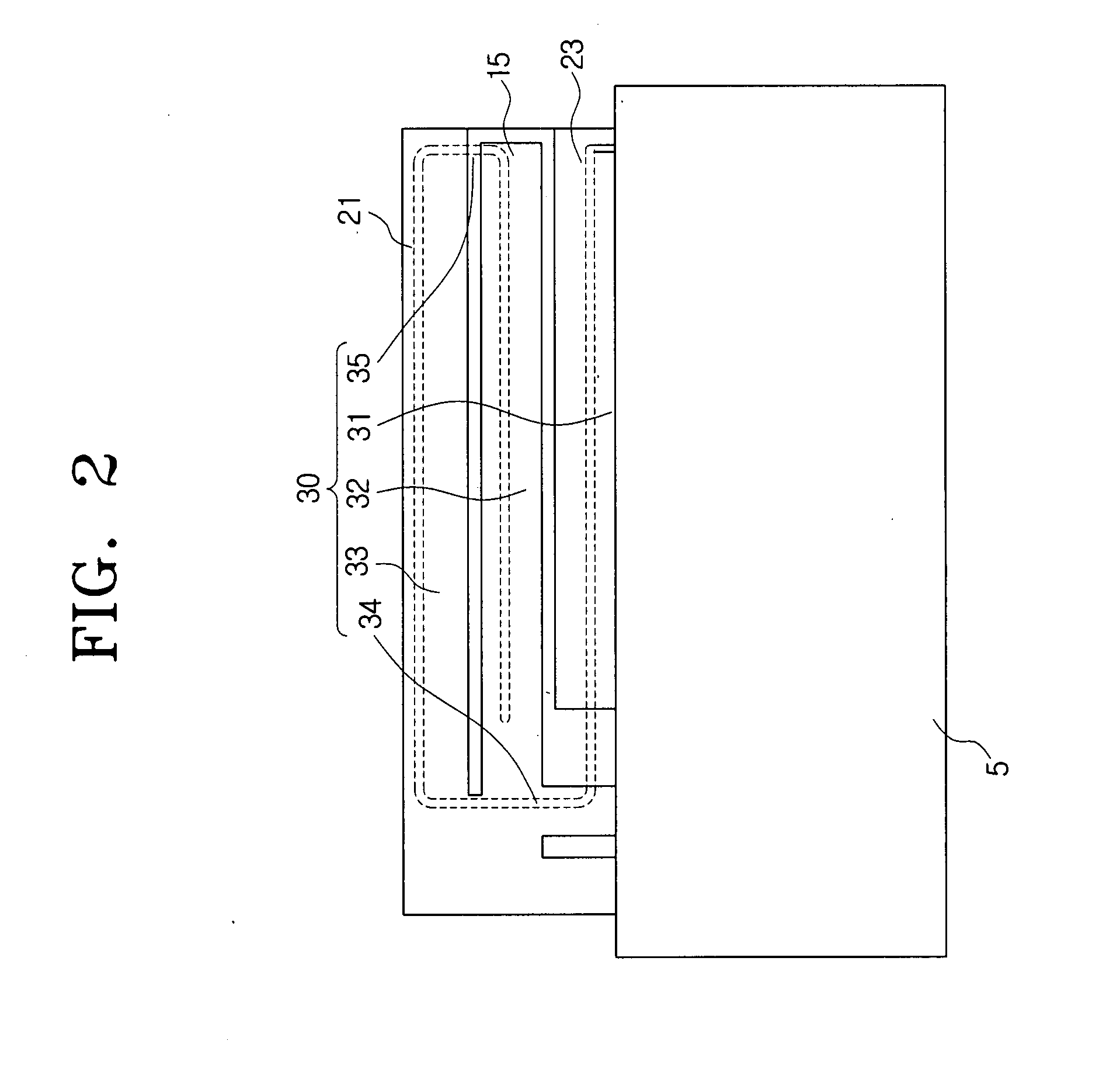
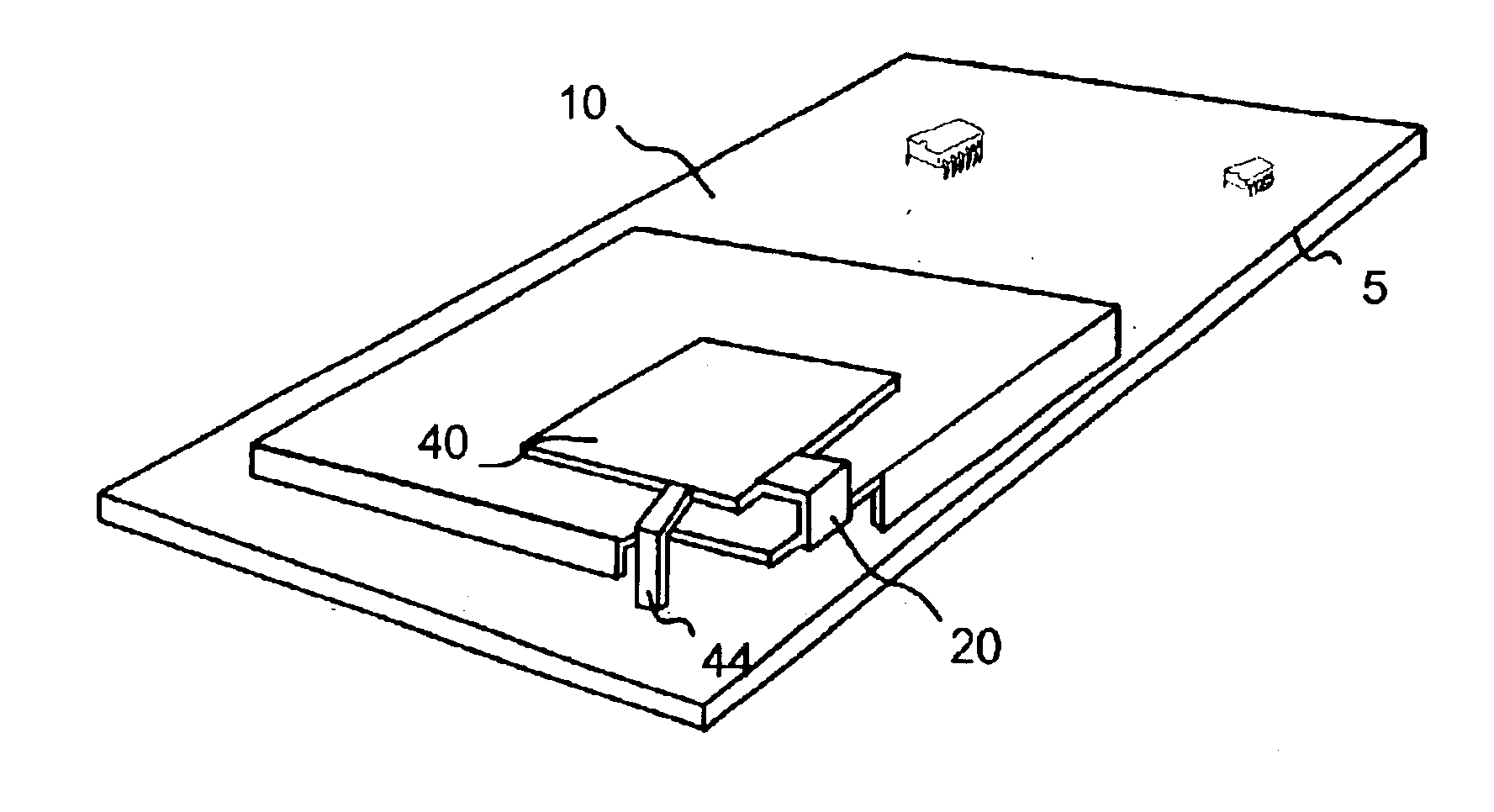
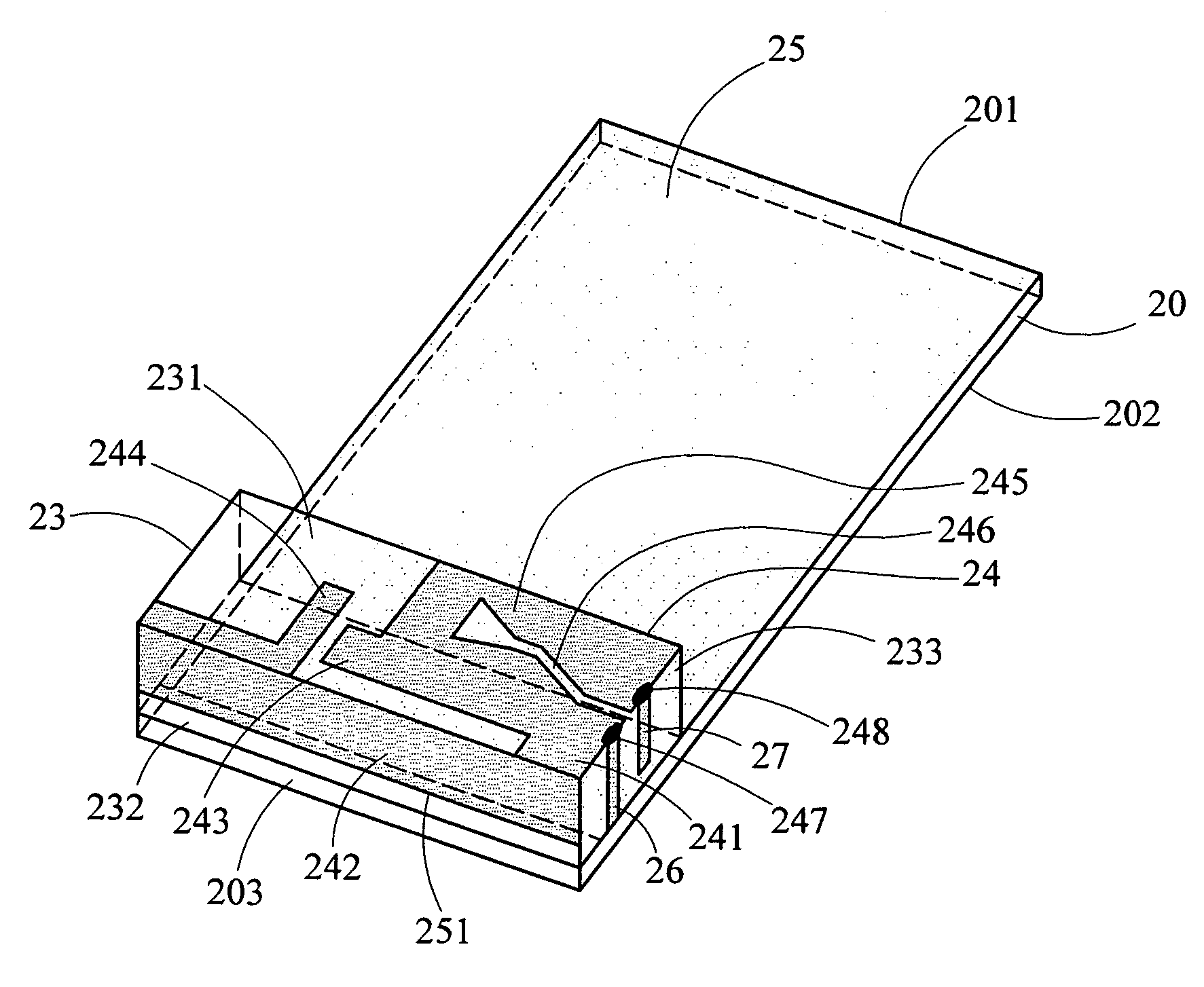
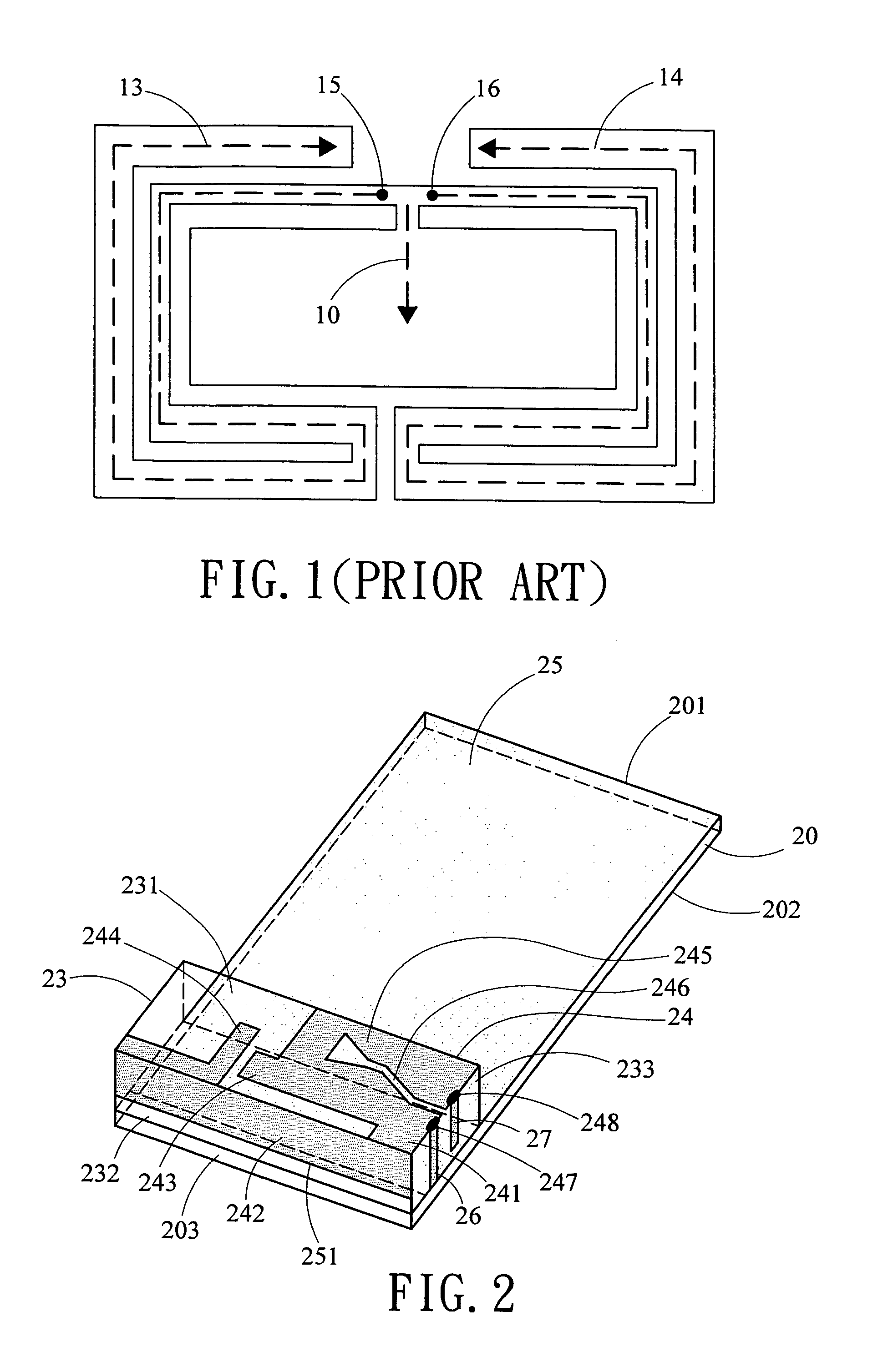
An inverted-F antenna is a type of antenna used in wireless communication. It consists of a monopole antenna running parallel to a ground plane and grounded at one end. The antenna is fed from an intermediate point a distance from the grounded end. The design has two advantages over a simple monopole: the antenna is shorter and more compact, and the impedance matching can be controlled by the designer without the need for extraneous matching components.
Multi-band antenna
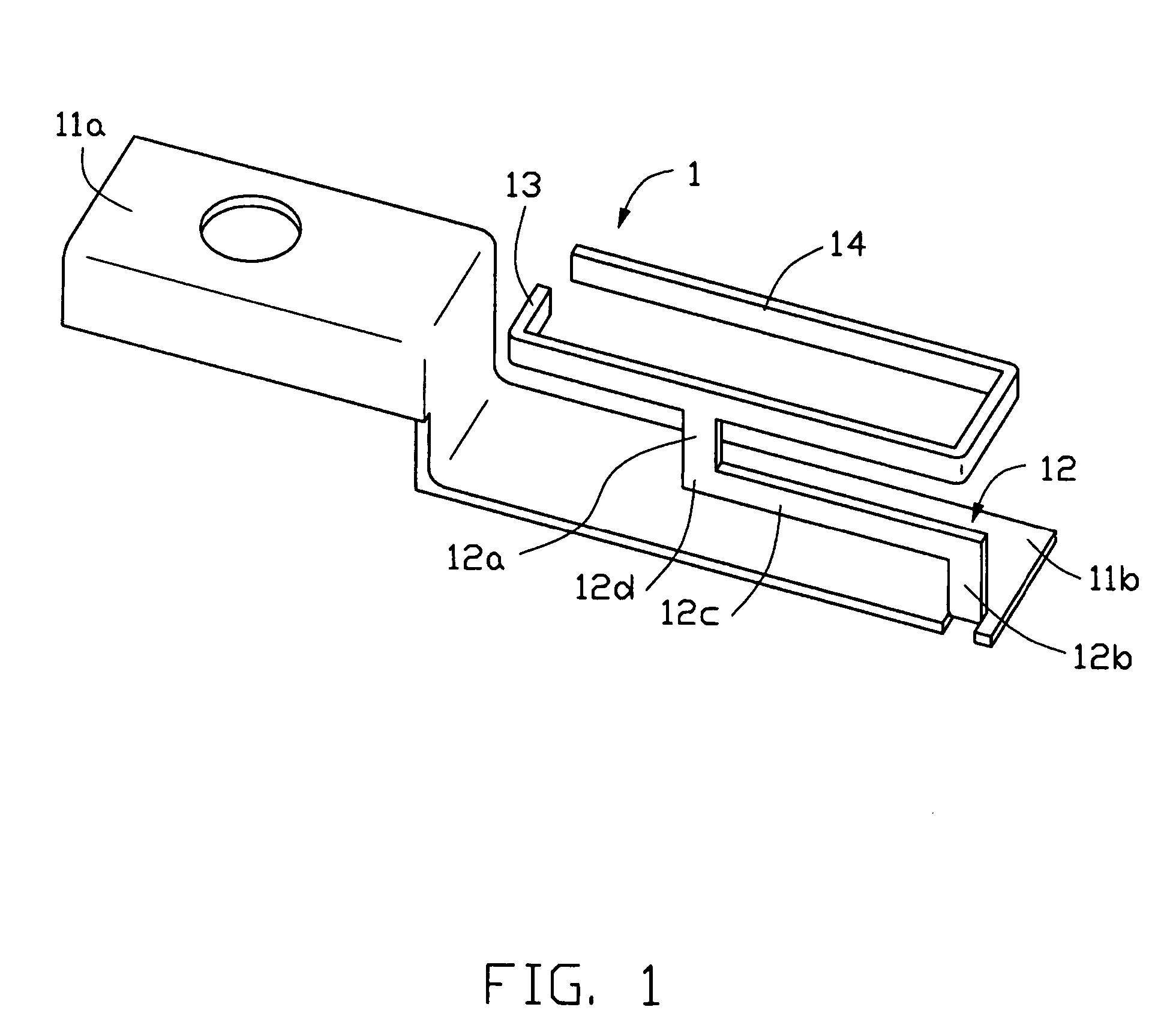
InactiveUS20050190108A1Wide bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandLow frequency band
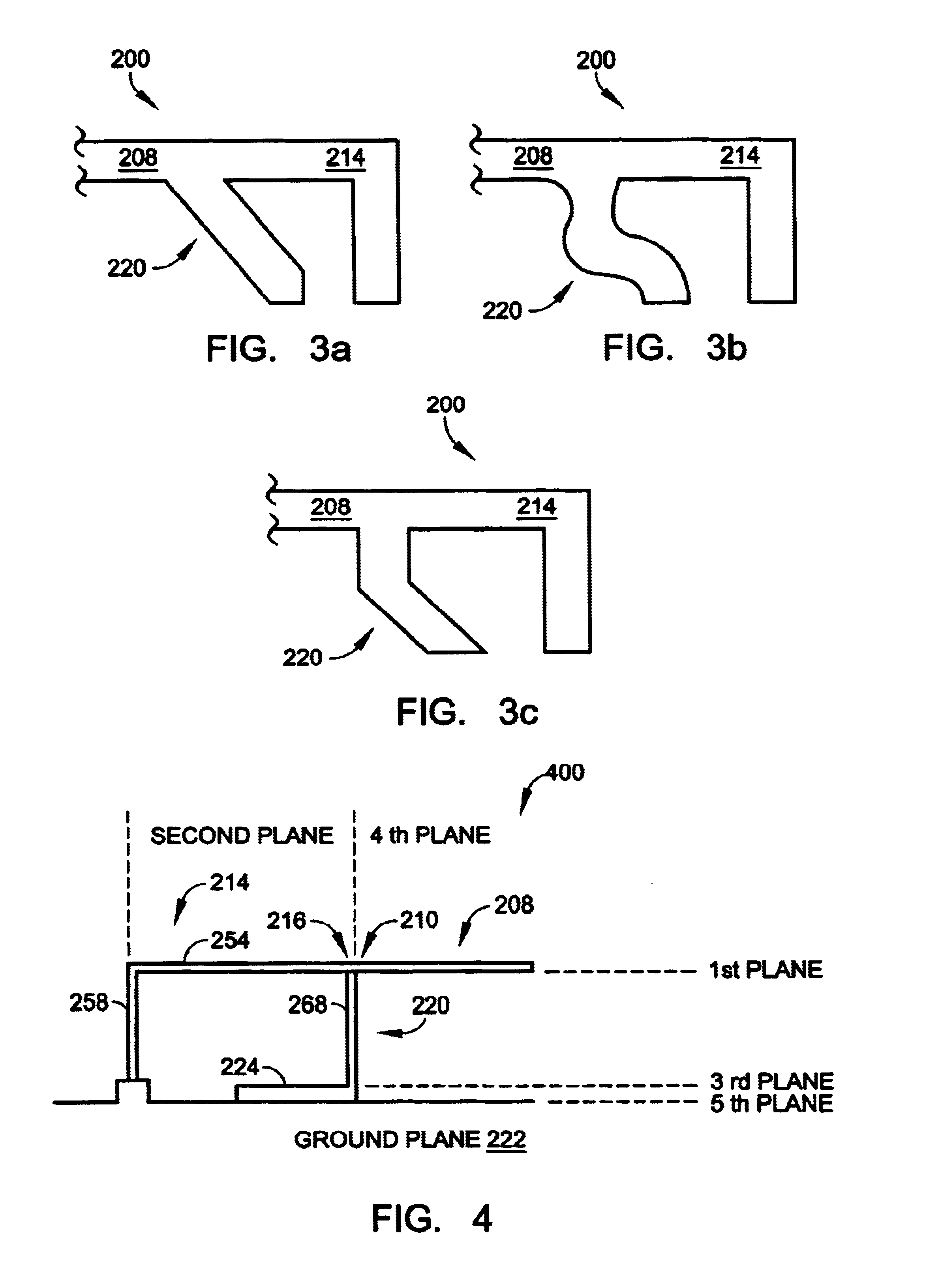
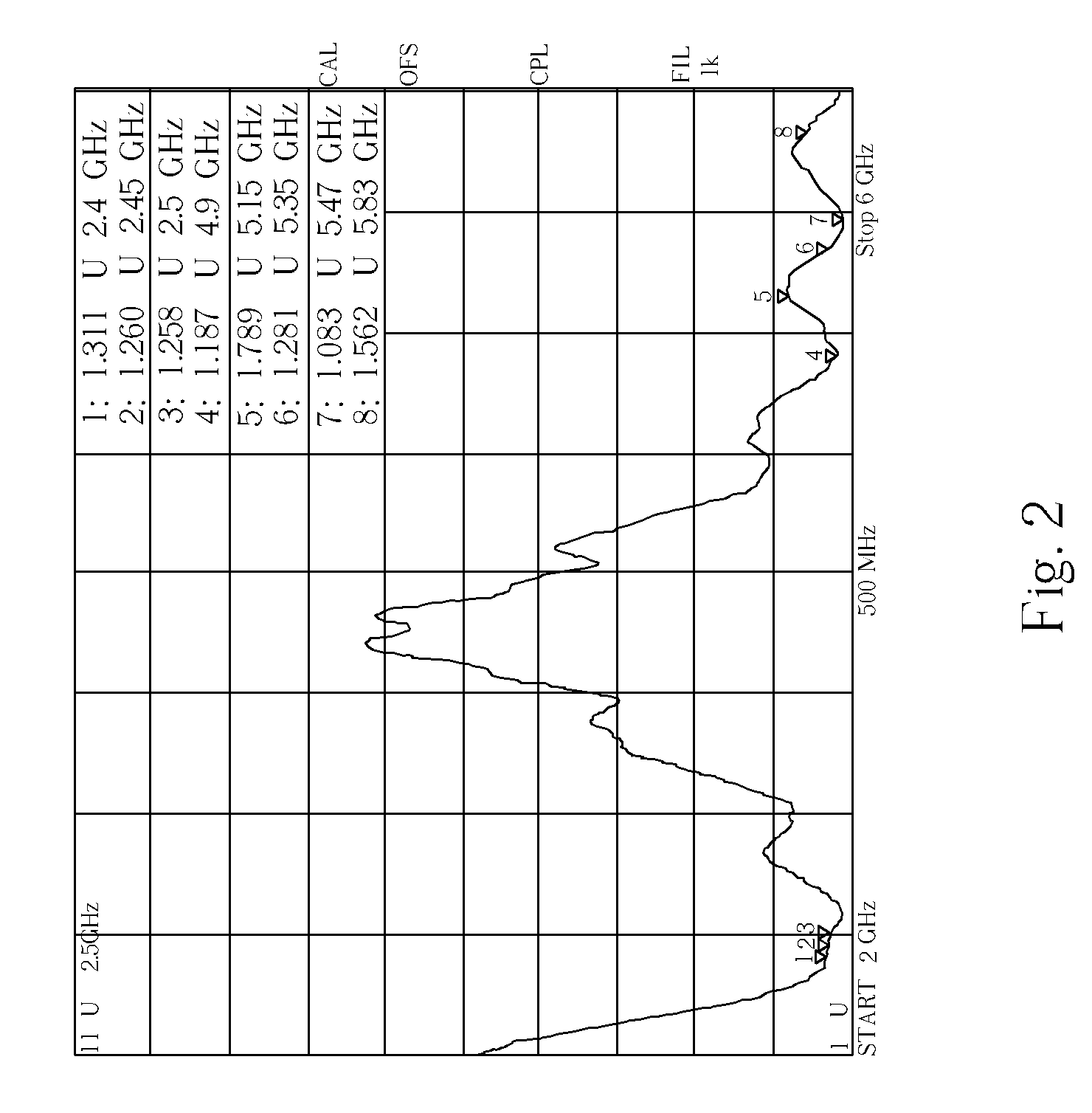
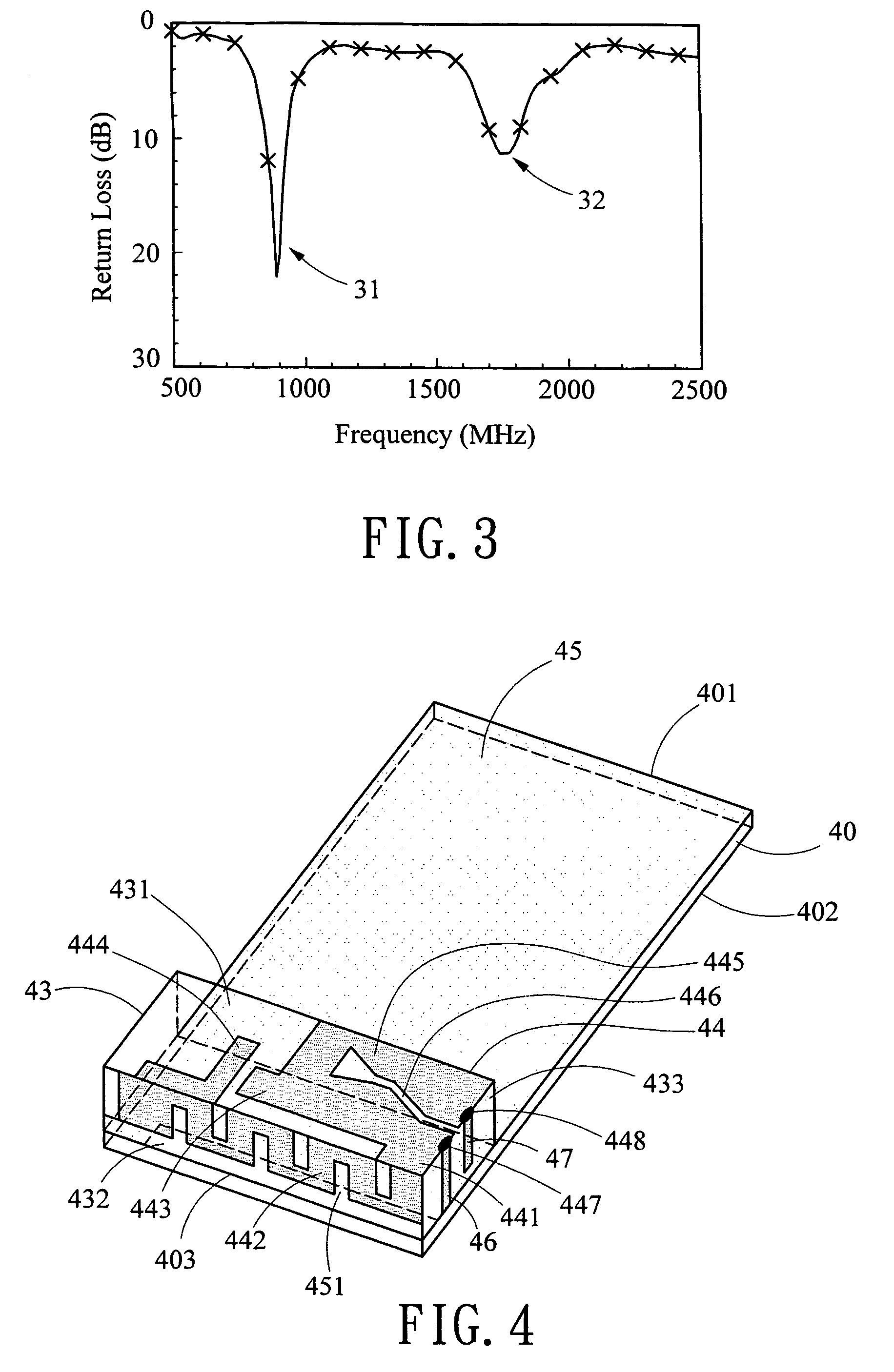
A multi-band antenna (1) used in an electronic device and formed of a metallic sheet by defining holes therein, including a first radiating portion (30), a second radiating portion (31), a third radiating portion (32), a ground portion (2), and a coaxial transmission line (4). The first radiating portion, the ground portion and the coaxial transmission line cooperatively form a loop antenna operated at a higher frequency band of about 5.15-5.875 GHz. The second radiating portion, the ground portion and the coaxial transmission line cooperatively form a first inverted-F antenna operated at another higher frequency band of about 5.725-5.875 GHz. The third radiating portion, the ground portion and the coaxial transmission line cooperatively form a second inverted-F antenna operated at a lower frequency band of about 2.4-2.5 GHz.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
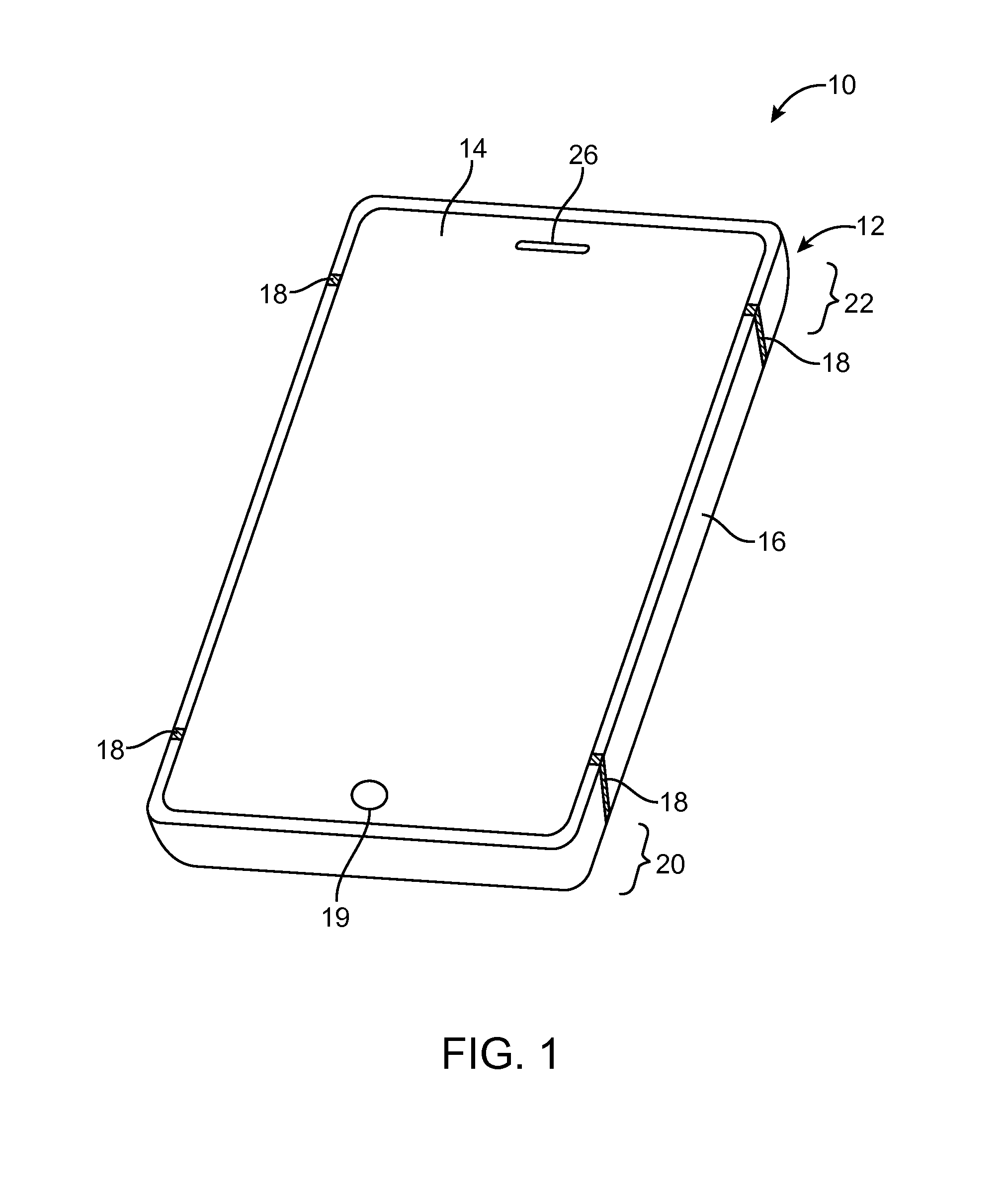
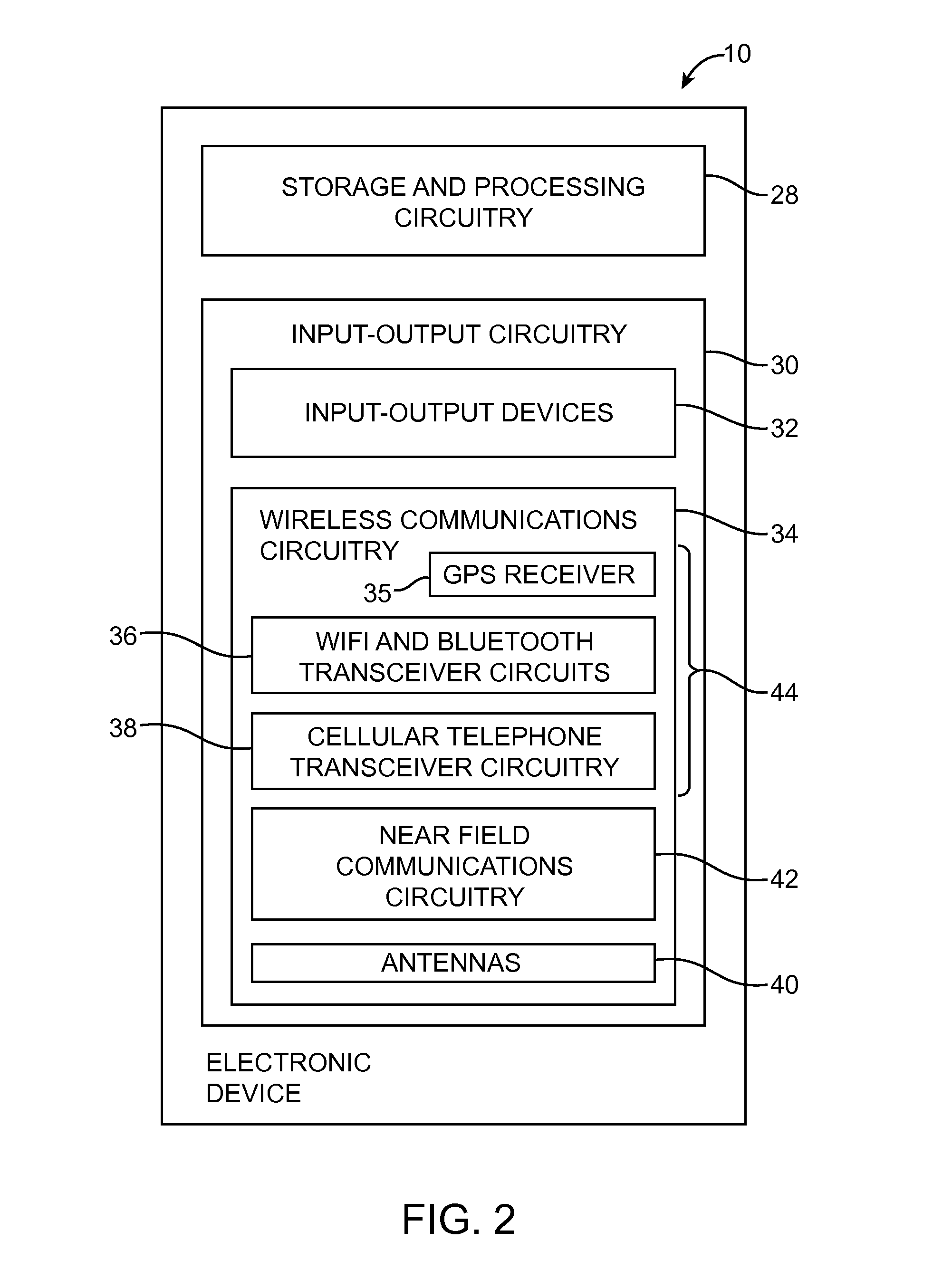
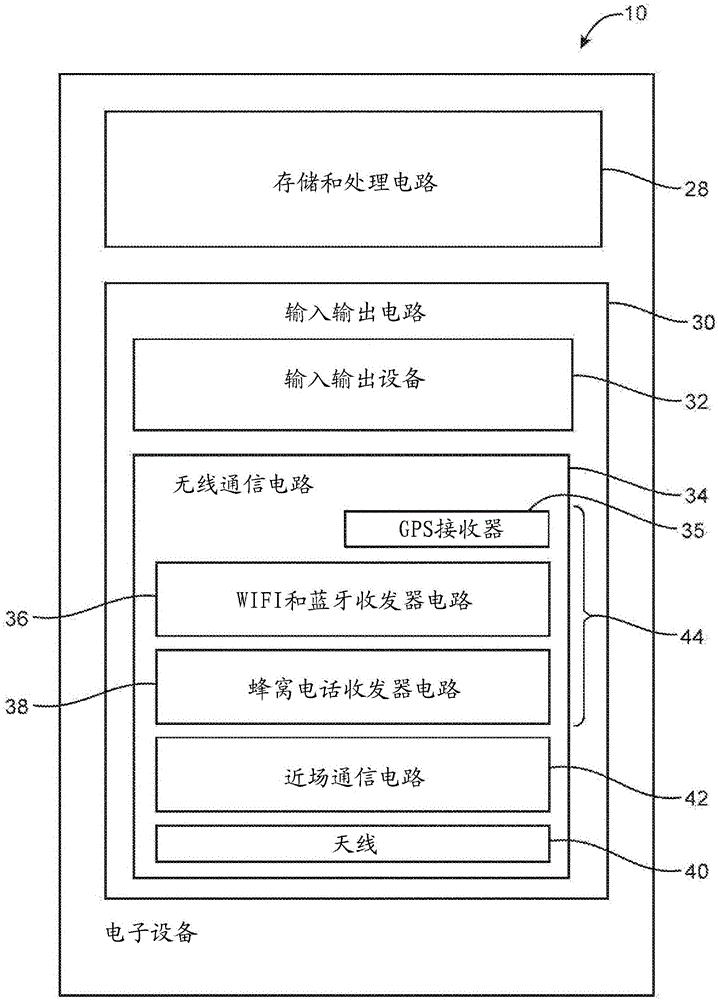
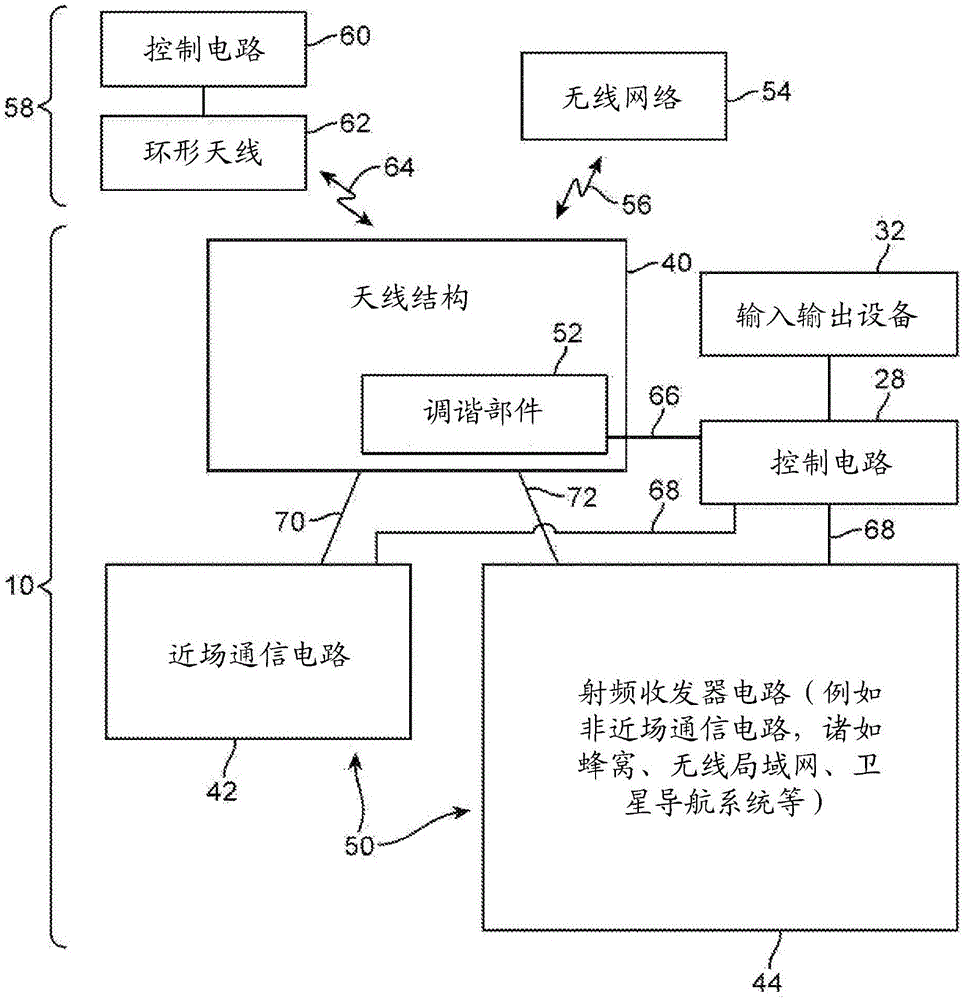
Shared Antenna Structures for Near-Field Communications and Non-Near-Field Communications Circuitry
ActiveUS20140139380A1Minimize size of deviceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsTransceiverEngineering
Electronic devices may be provided that contain wireless communications circuitry. The wireless communications circuitry may include radio-frequency transceiver circuitry and antenna structures. The antenna structures may include conductive housing structures such as a peripheral conductive housing member. The antenna structures may be based on an inverted-F antenna resonating element or other types of antenna resonating element. An electronic device may have near field communications circuitry and non-near-field communications circuitry such as cellular telephone, satellite navigation system, or wireless local area network transceiver circuitry. Antenna structures may be configured to handle signals associated with the non-near-field communications circuitry. The antenna structures may also have portions that form a near field communications loop antenna for handling signals associated with the near field communications circuitry.
Owner:APPLE INC
Dual feel multi-band planar antenna
InactiveUS6670923B1Reduce Design ComplexityCompromise performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandPlanar inverted f antenna
A three-band, two-antenna, assembly includes a planar inverted-F antenna (PIFA) having a radiating / receiving element that is spaced from and extends generally parallel to a ground plane element. The planar radiating / receiving element of an inverted-F antenna (IFA) is located in an open space that exists between the radiating / receiving element of the PIFA and the ground plane element. The radiating / receiving element of the IFA extends either perpendicular to, or parallel to, the radiating / receiving element of the PIFA. The radiating / receiving element of the PIFA includes one or more open slot configurations that operate to provide dual resonant frequencies for the IPFA (AMPS / PCS or GSM / DCS). The radiating / receiving element of the IFA operates in a non-cellular frequency band (ISM or GPS).
Owner:LAIRD CONNECTIVITY LLC
Planner inverted-F antenna having a rib-shaped radiation plate
InactiveUS7061437B2Improve rigidityLow costSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsGround contactGround plane
A planner inverted-F antenna (PIFA) includes a ground plane, a rib-shaped radiation plate installed approximately in parallel with the ground plane, a feeding line installed on the rib-shaped radiation plate, a feeding contact installed on an end of the feeding line, and a ground contact electrically connected to the ground plane.
Owner:SYNCOMM TECH
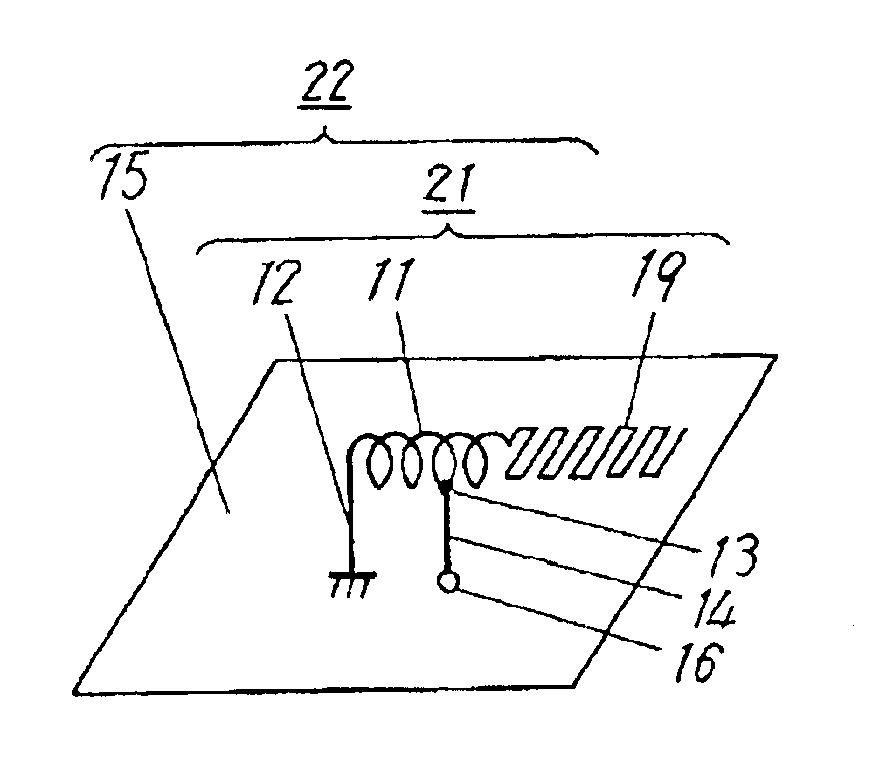
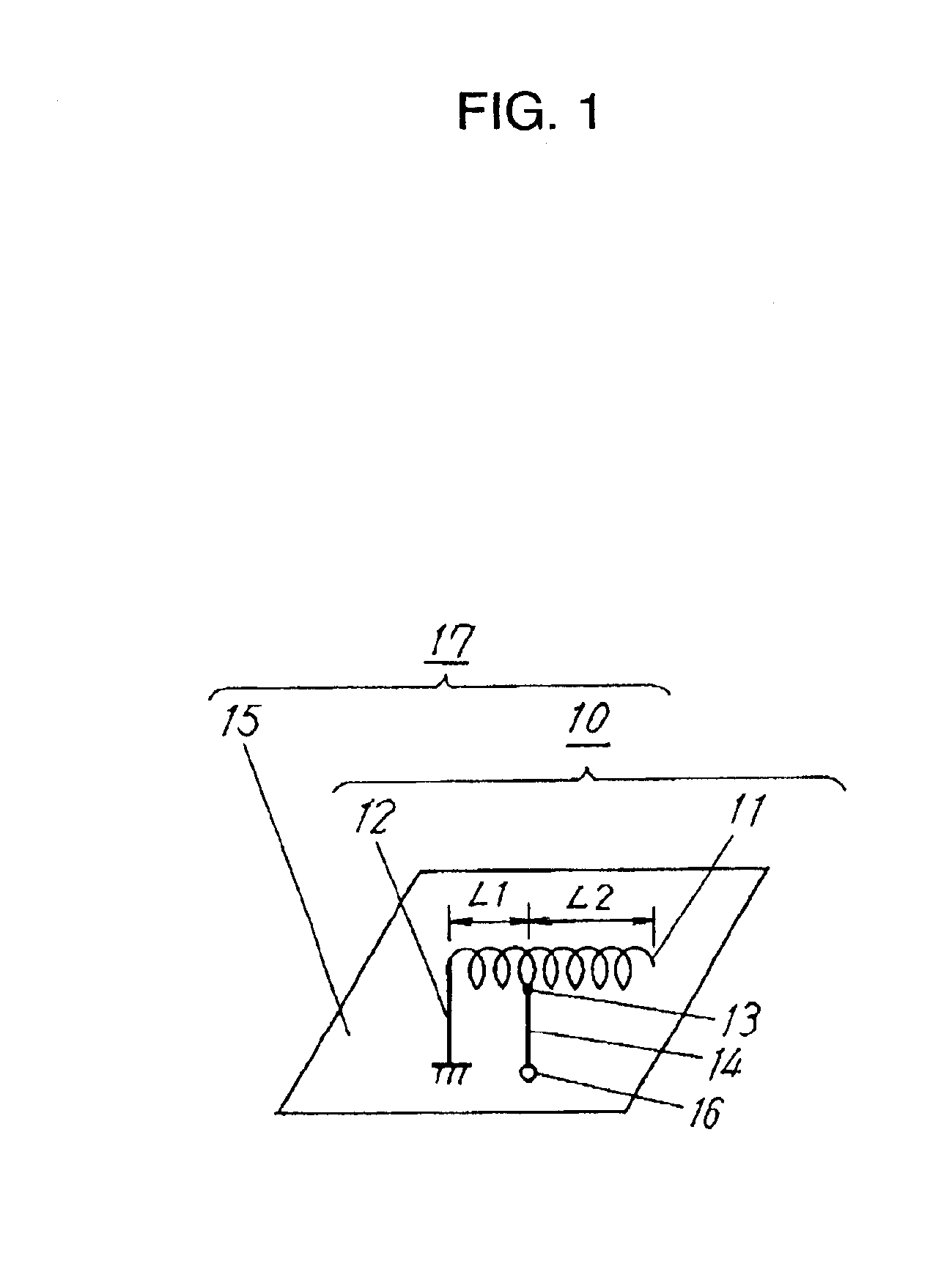
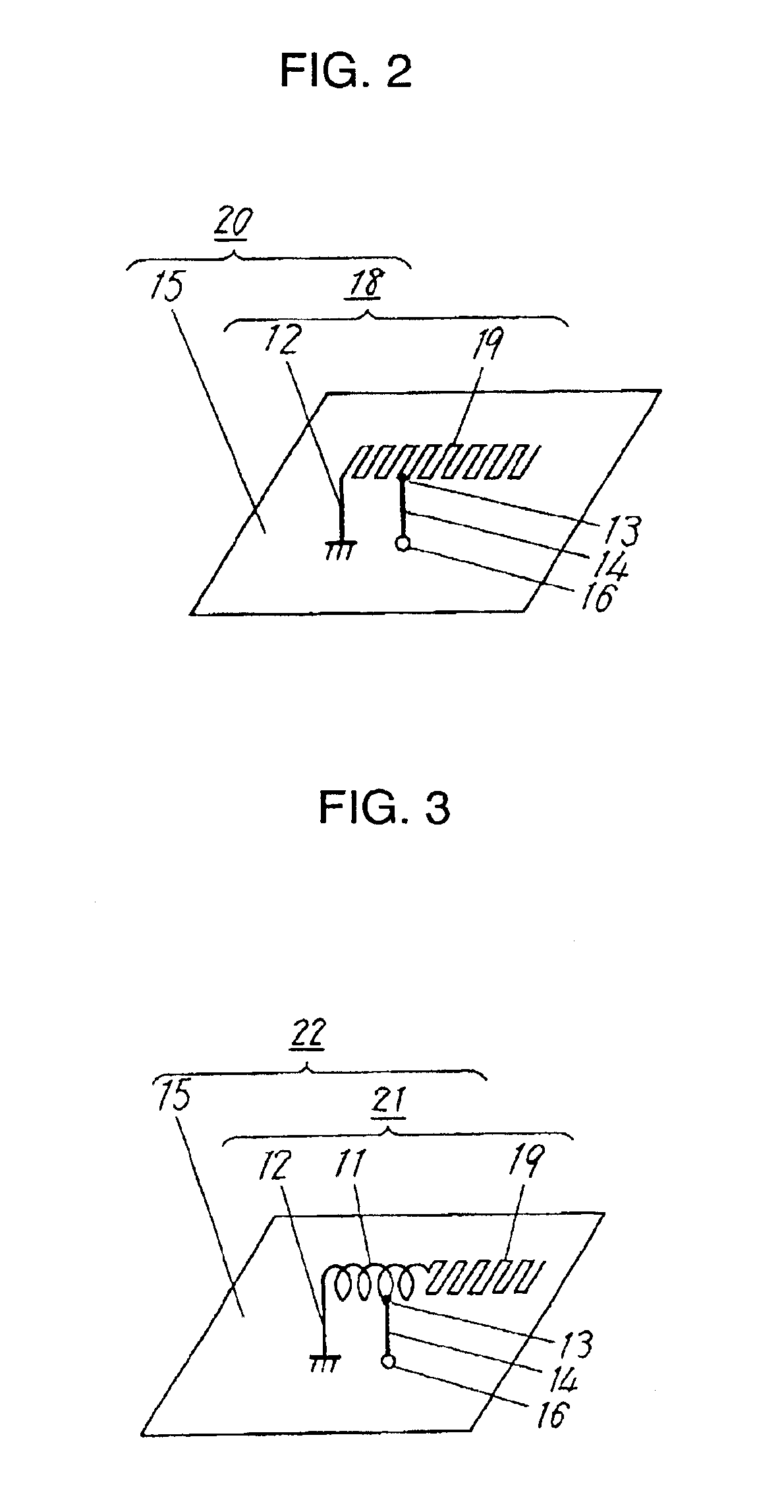
Multifrequency inverted-F antenna
InactiveUS6861986B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsElement spaceRadiating element
A multifrequency inverted-F antenna includes a radiating element having opposite first and second ends, a grounding element spaced apart from the radiating element, and an interconnecting element extending between the radiating and grounding elements and including first, second, and third parts. The first part is connected to the radiating element at a feeding point between the first and second ends. The second part is offset from the first part in a longitudinal direction, and is connected to the grounding element. The third part interconnects the first and second parts. A feeding line is connected to the interconnecting element.
Owner:WISTRON NEWEB
Multi-band antenna
InactiveUS7119747B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandLow frequency band
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Dual frequency band inverted-F antenna
ActiveUS6930640B2Lower resonance frequencySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDual frequencyResonance
A dual frequency band inverted-F antenna used for communicating a low frequency signal and a high frequency signal includes a substrate, a ground metal, a vortical metal structure, a short circuit leg, a feeding leg, and a terminal micro strip. The ground metal and the terminal micro strip are formed on the lower surface of the substrate. The vortical metal structure, formed on the upper surface of the substrate, further has a short circuit end and an open circuit end. The short circuit leg connects electrically the short circuit end of the vortical metal structure with the ground metal. The feeding leg extends along a predetermined direction of the vortical metal structure to couple with a feeding circuit on the substrate. The terminal micro strip connects electrically to the open circuit end through a first conductive aperture. By increasing the encircling number of the vortical metal structure, the coupling effect is generated so that the equivalent wavelength of the high frequency signal can be longer, thus the resonance frequency thereof can be reduced, and so a first frequency can be still kept communicating at a lower frequency band and a second frequency can also be added for communicating at a higher frequency band.
Owner:GEMTEK TECH CO LTD
Wrist Worn Device with Inverted F Antenna
InactiveUS20140354494A1Small widthSmall heightAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesGps receiverDisplay device
The present invention discloses a wrist worn communication device, possibly integrated with a wrist watch, comprising a radio coupled to a low profile antenna. The antenna, obtaining low and medium angle elevation radiation enabling efficient satellite communications, is configured on the perimeter of the device, giving room for a display on top of this compact device. Preferably, the display is configured to indicate the time, but also possibly other parameters such as position, speed, altitude, temperature, air pressure, heart pace, messages, alarms and so on. According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, said device is a Personal Locator Beacon (PLB) configured to broadcast distress signals detectable by satellites. According to another embodiment of the present invention, said radio is a GPS receiver.
Owner:KATZ DANIEL A
Dual-band antenna for a wireless local area network device
ActiveUS7057560B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDual frequencyDual band antenna
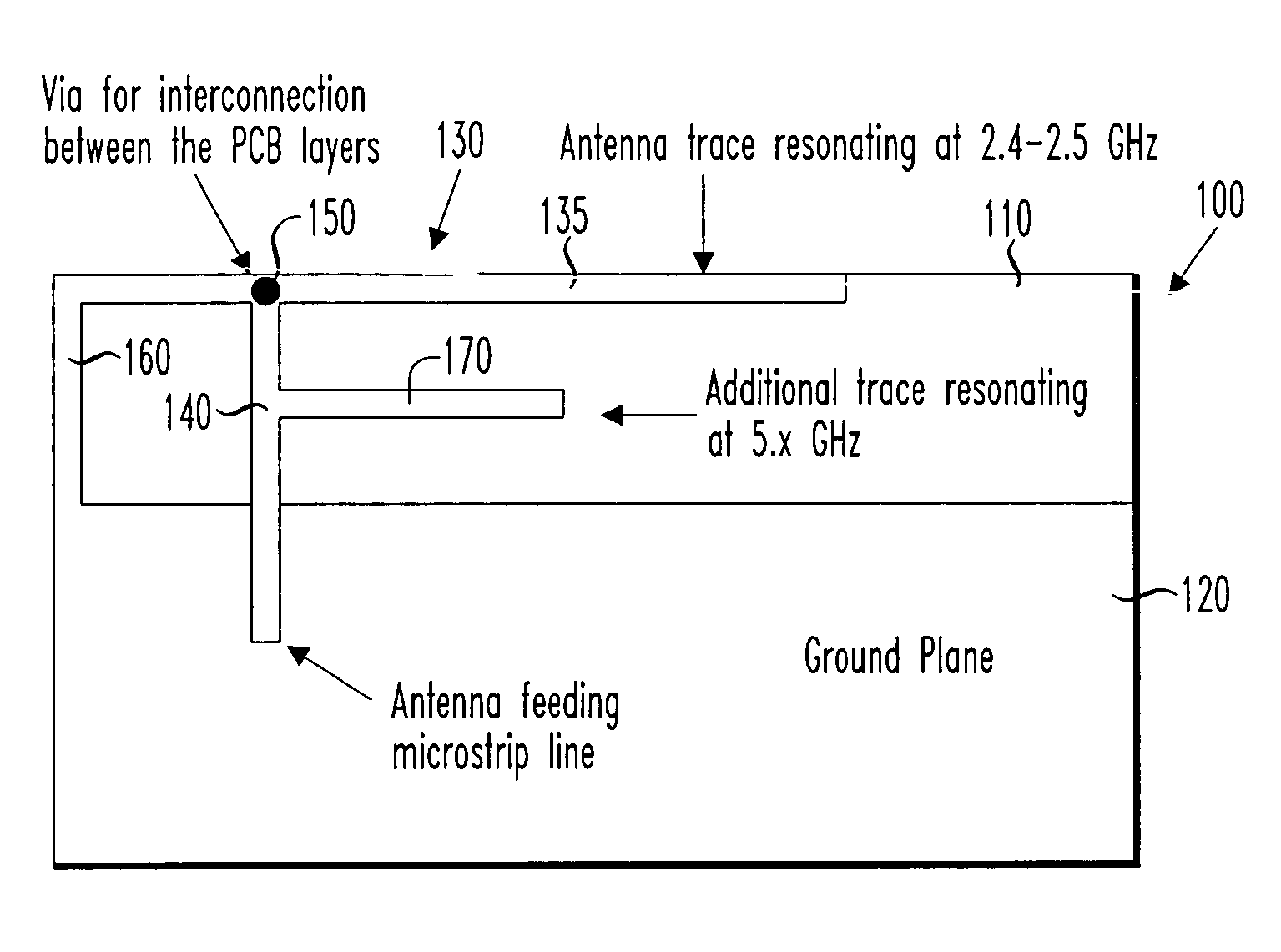
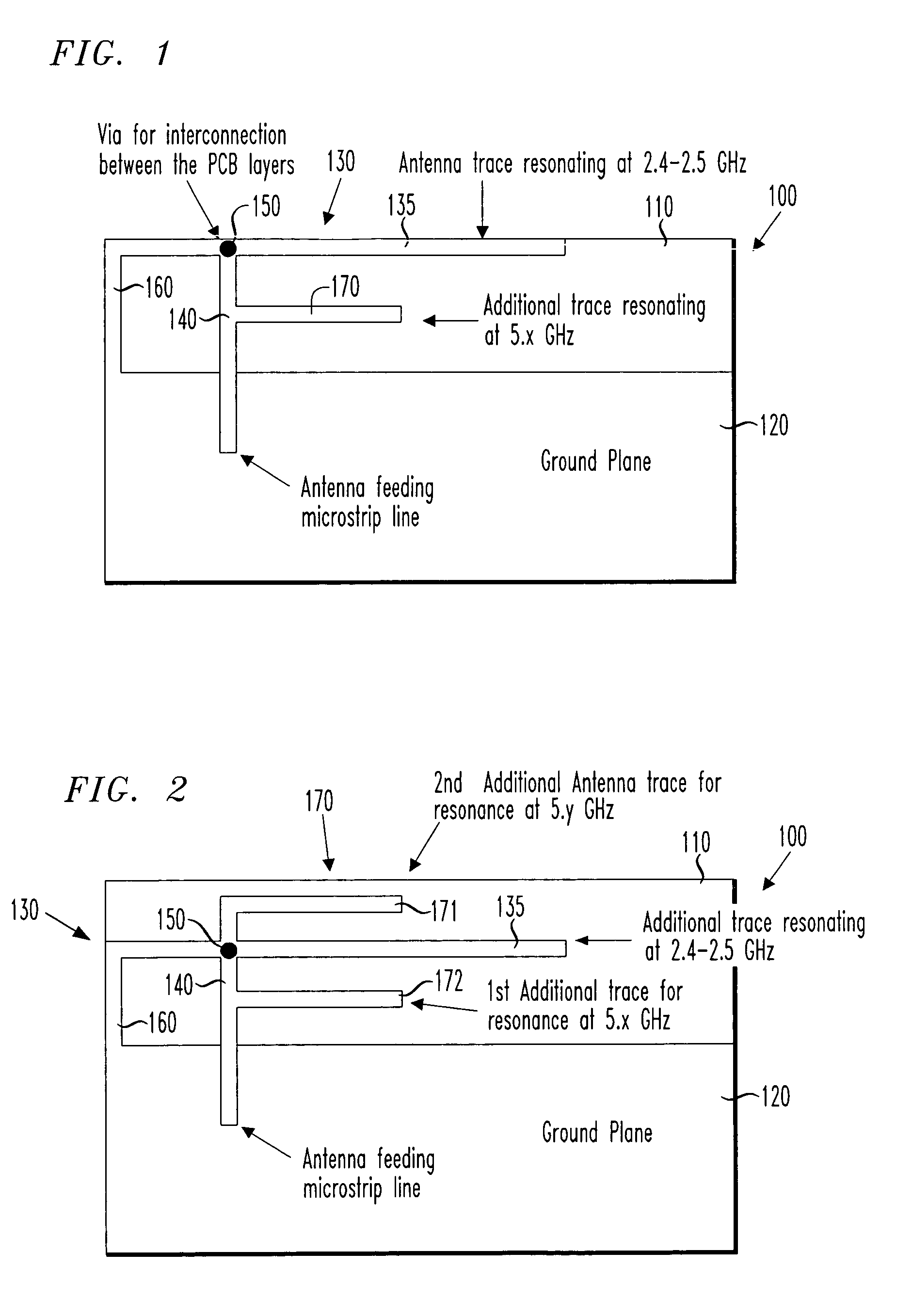
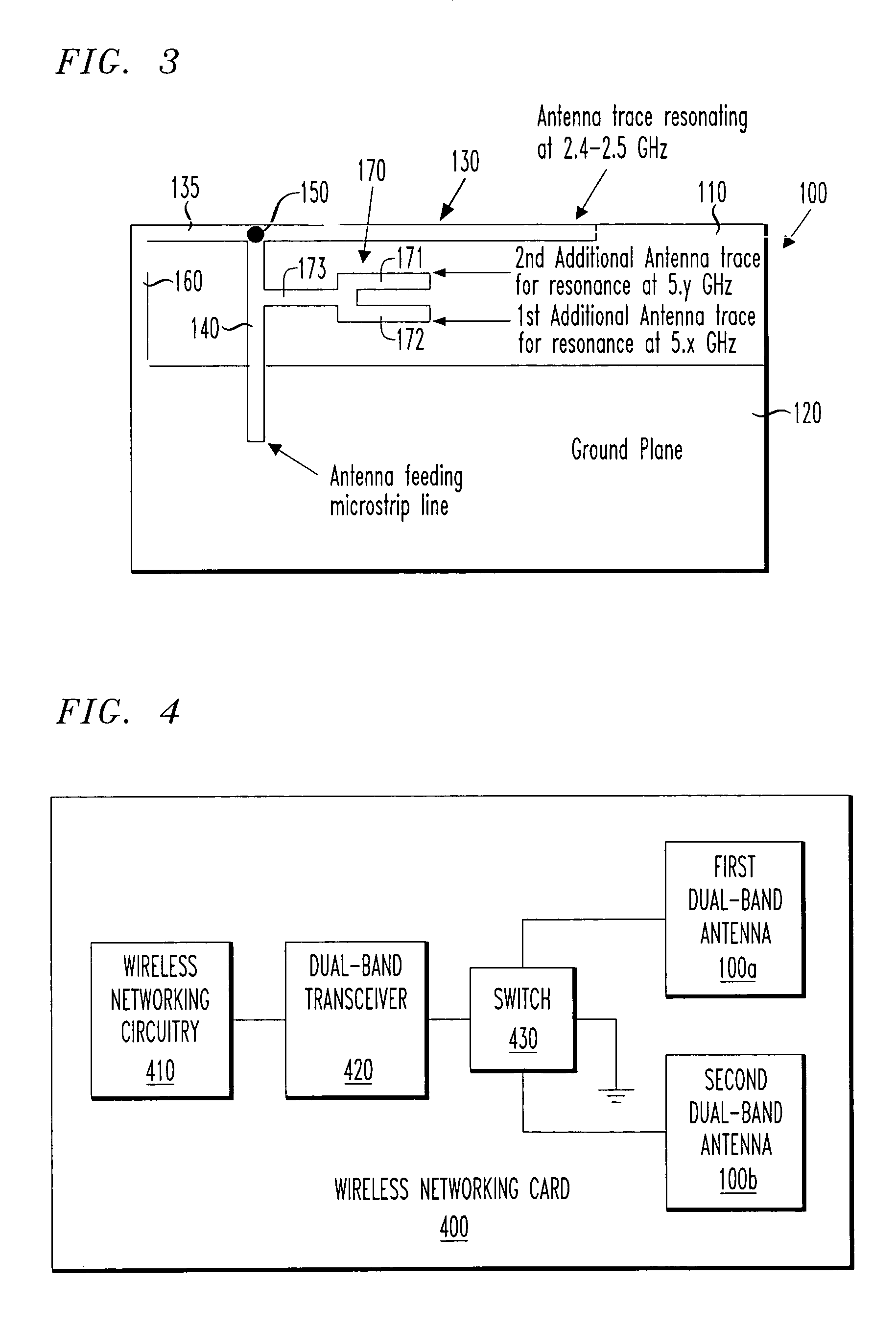
A dual-band antenna, a method of manufacturing the same and a wireless networking card incorporating the antenna. In one embodiment, the antenna includes: (1) a substrate, (2) an inverted F antenna printed circuit supported by the substrate and tuned to resonate in a first frequency band and (3) a monopole antenna printed circuit supported by the substrate, connected to the inverted F antenna printed circuit and tuned to resonate in a second frequency band.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Dual-band inverted-F antenna with shorted parasitic elements
InactiveUS7050010B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsCoaxial cableGround plane
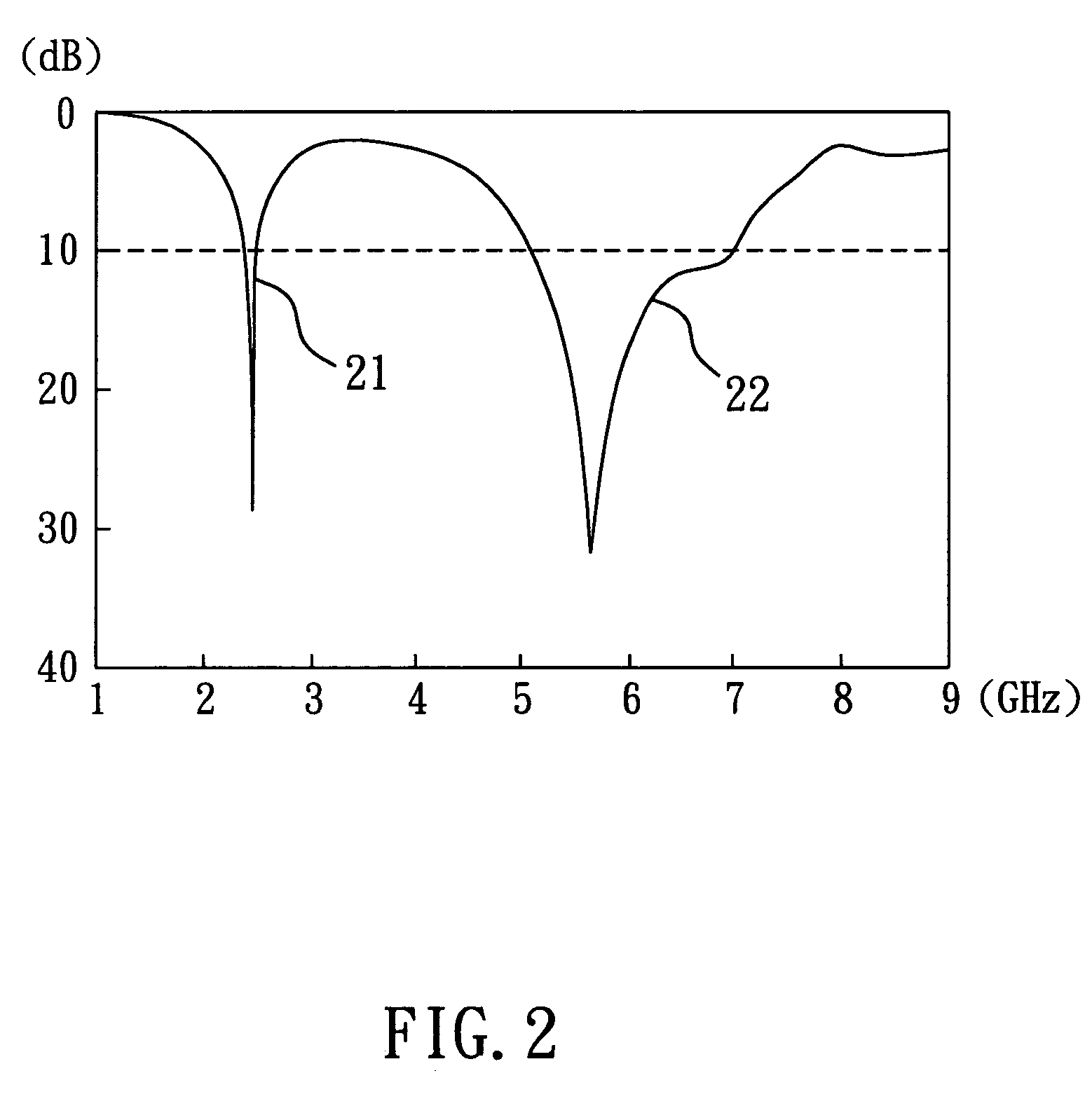
The invention relates to a dual-band inverted-F antenna with shorted parasitic elements. The antenna of the invention comprises a ground plane, a first radiating arm placed above an edge of the ground plane, a second radiating arm placed above the edge of the ground plane, a shorting arm with a substantially inverted-L shape for electrically connecting the first radiating arm and the second radiating arm to the ground plane, a shorted parasitic arm placed above the edge of the ground plane, and a feeding coaxial cable for transmitting signals. There is a distance between the shorted parasitic arm and the first radiating arm so as to induce extra capacitive reactance to compensate the inductive reactance induced by inserting the feeding coaxial cable. The present invention is suitable for the wireless local area network (WLAN) applications in the 2.4 GHz (2.4–2.484 GHz) and 5 GHz (5.15–5.35, 5.725–5.875 GHz) bands.
Owner:YAGEO CORP
Structure of an antenna and method for manufacturing the same
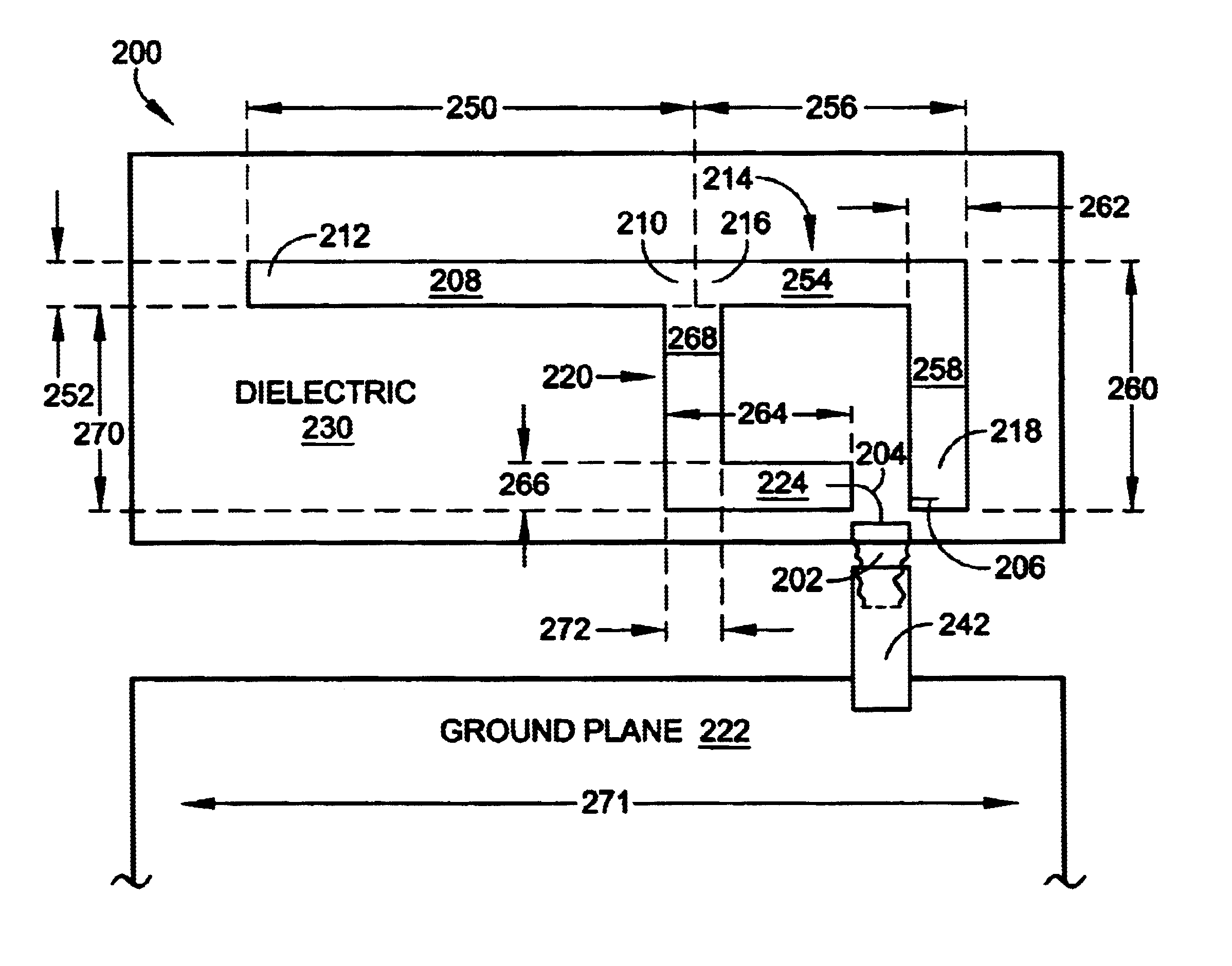
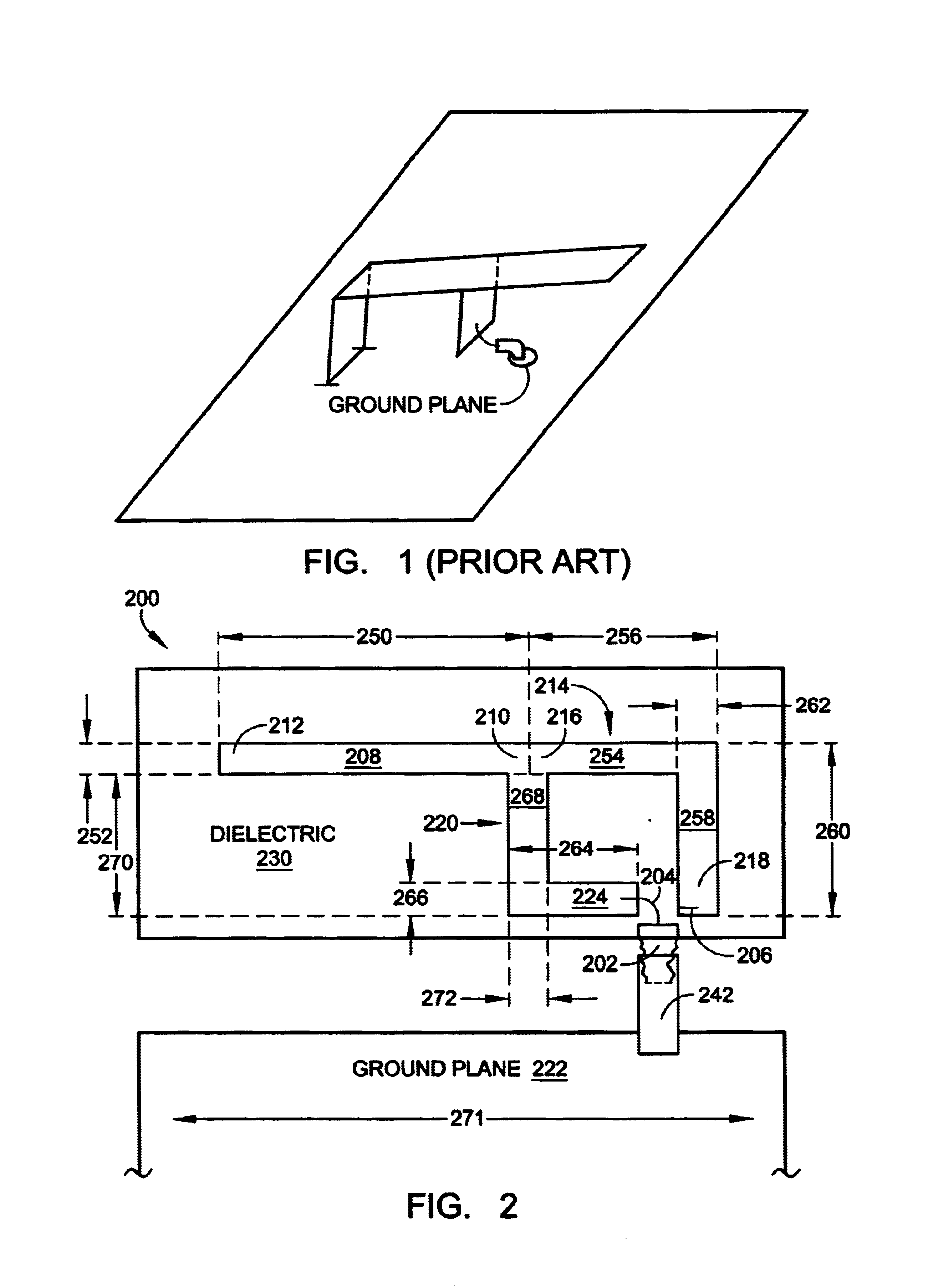
InactiveUS6344823B1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringGround plane
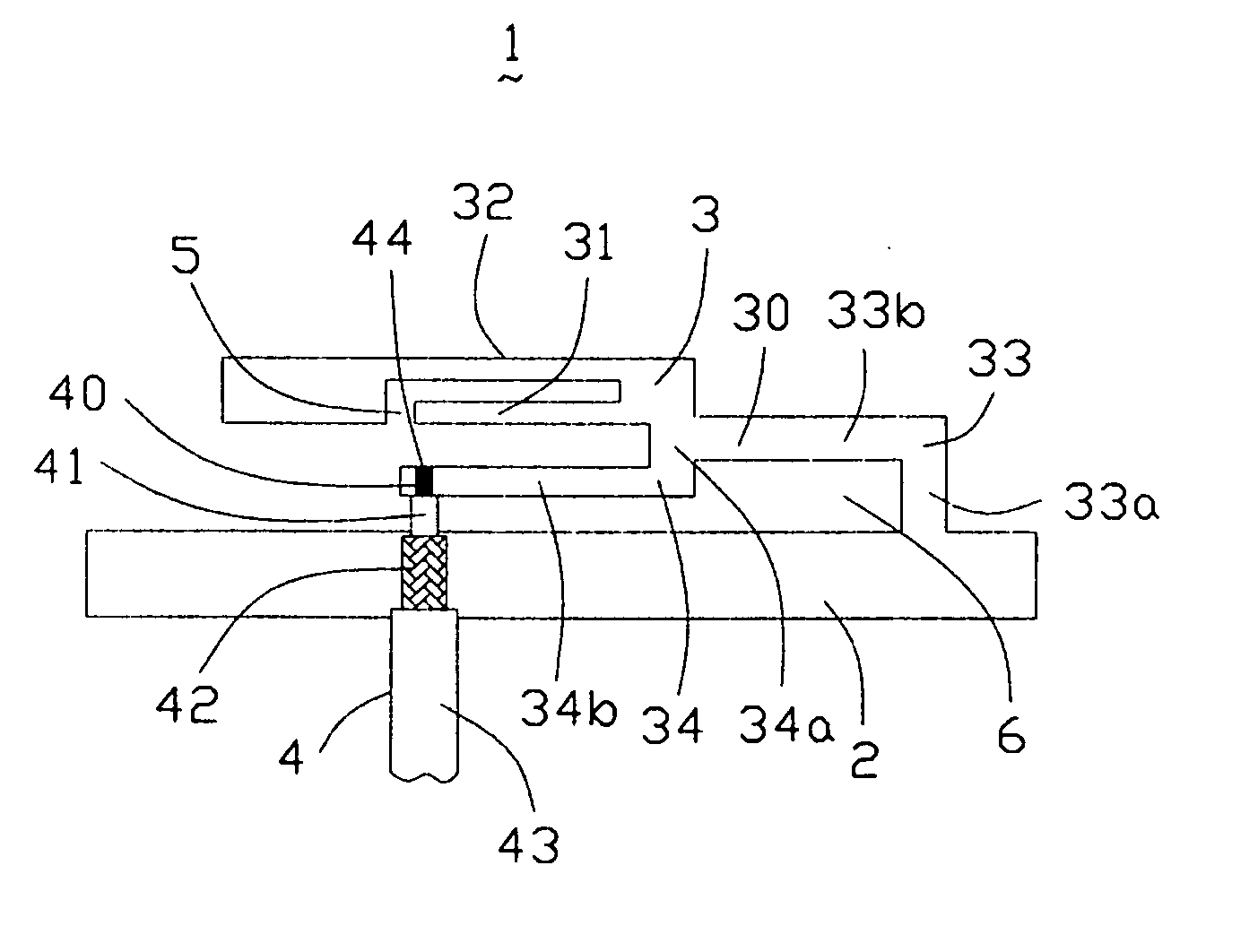
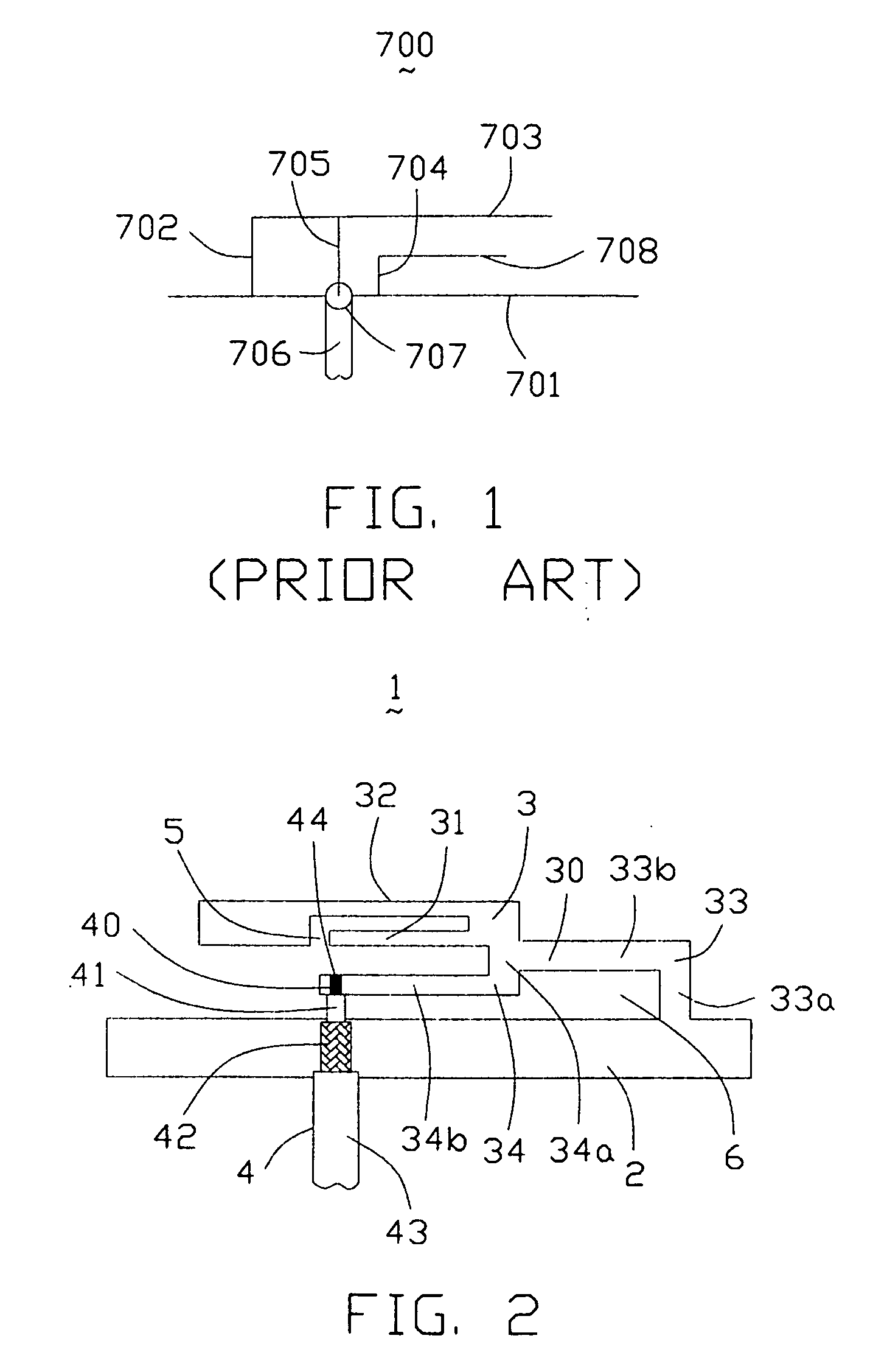
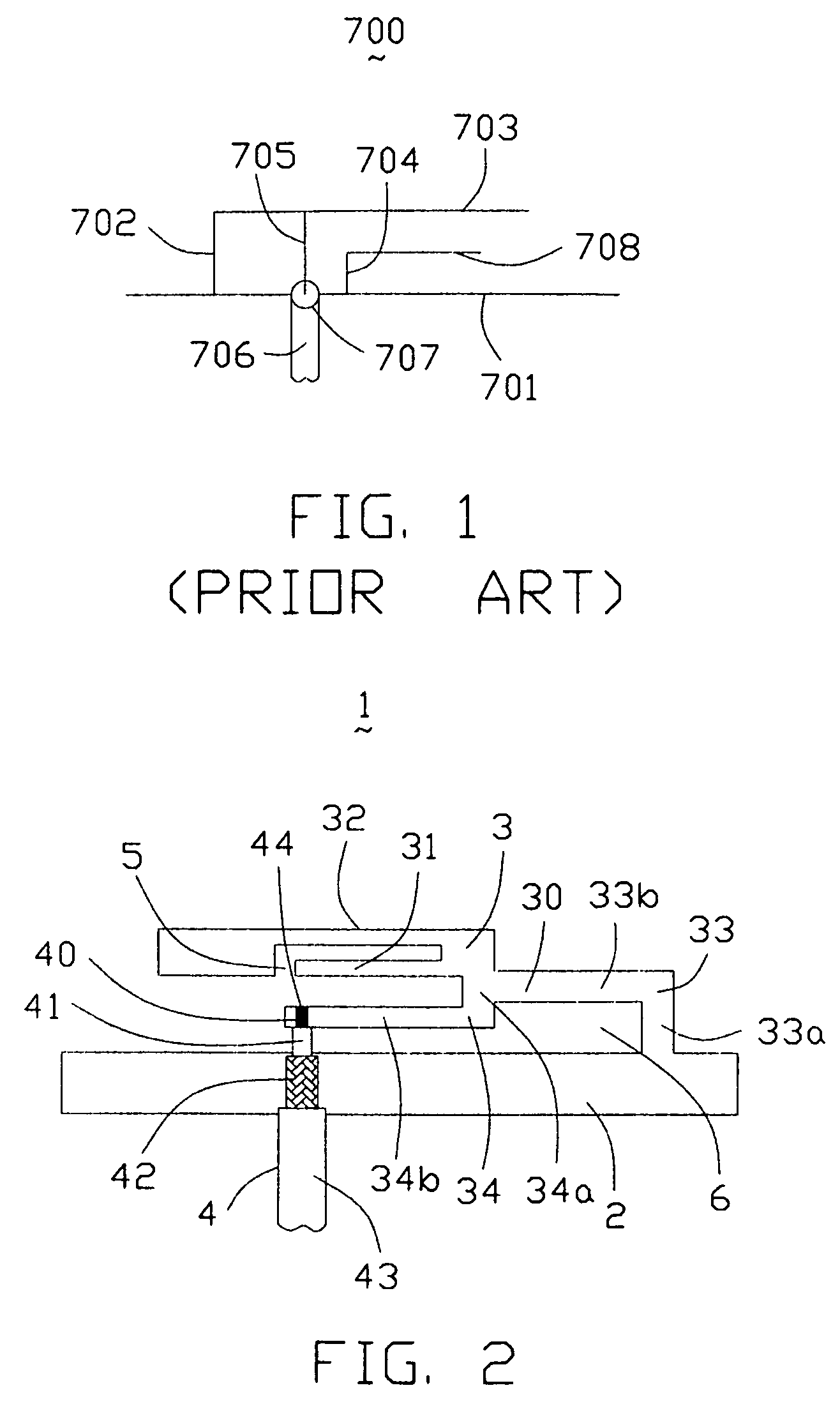
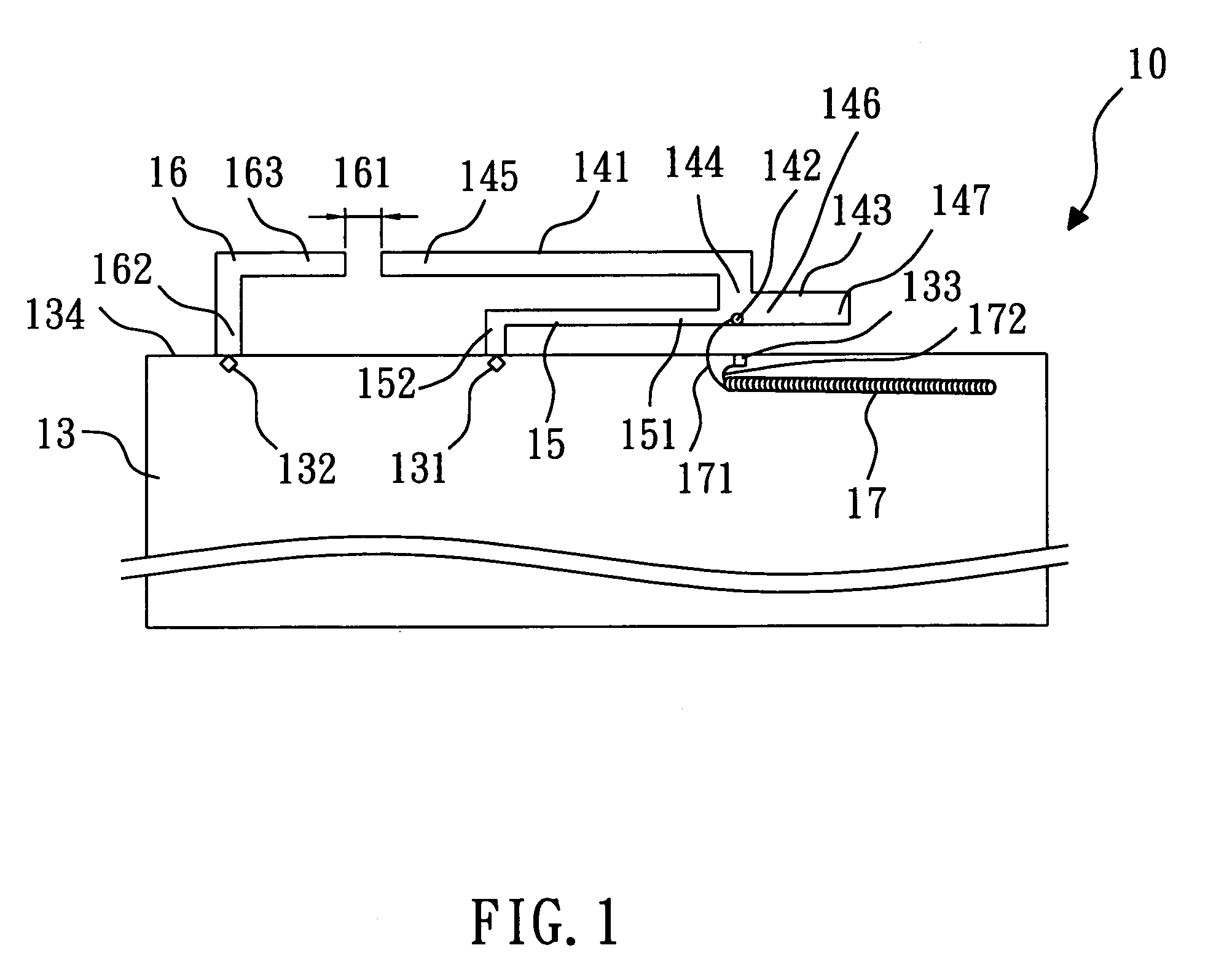
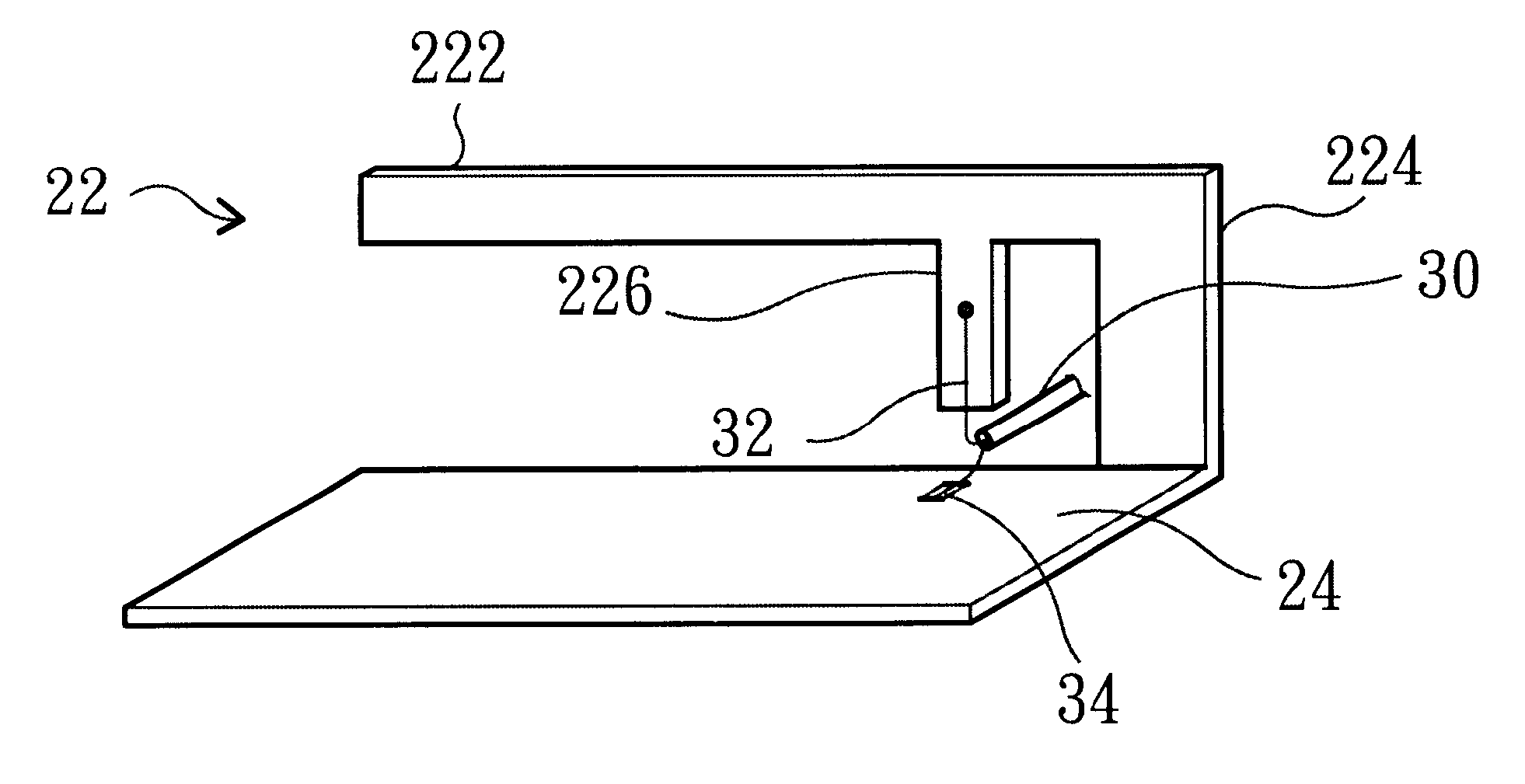
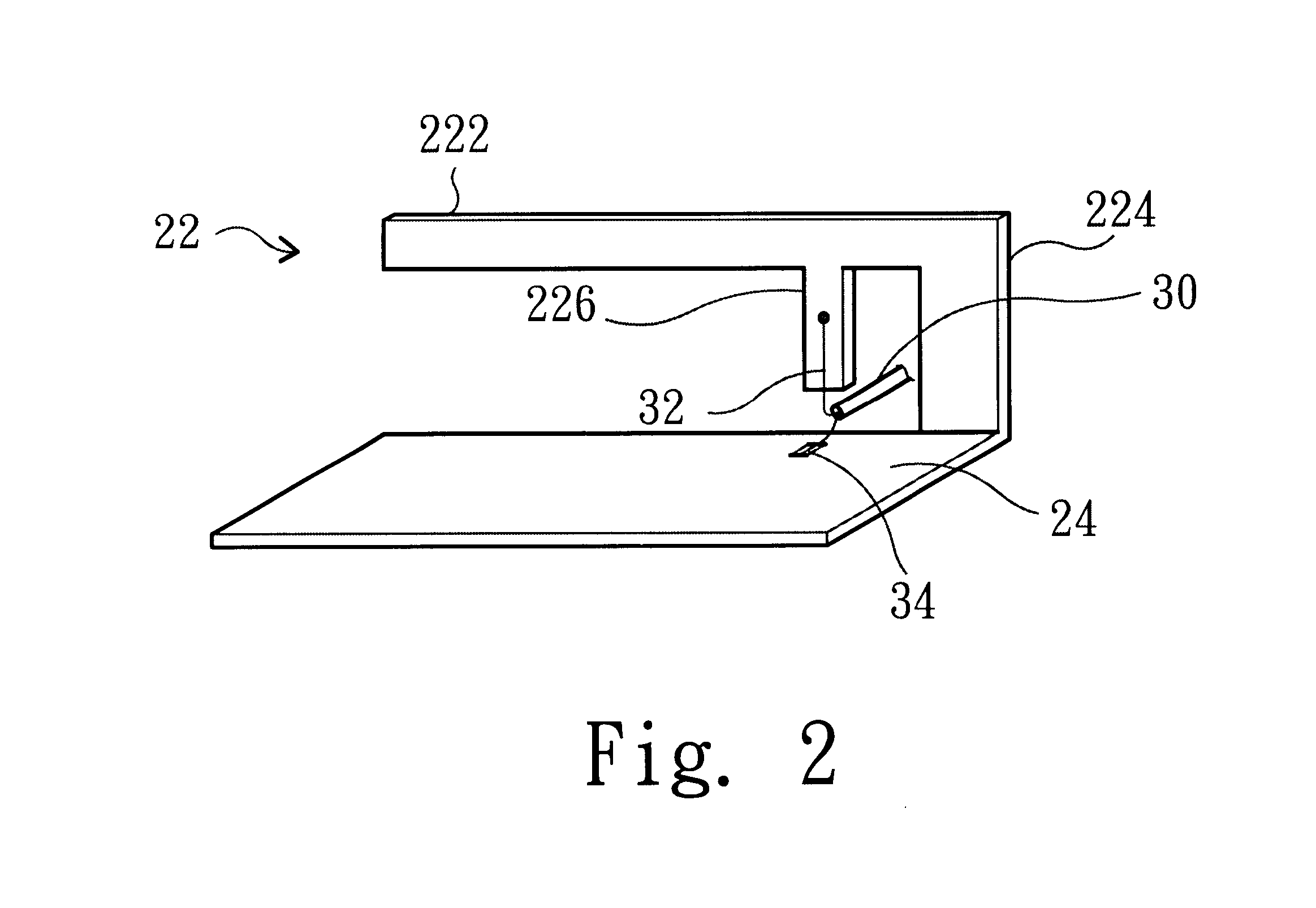
A structure for an Inverted-F antenna includes: a radiating portion forming a longitudinal side of the Inverted-F antenna, a support portion integrally formed with the radiating portion and perpendicularly connected to the radiating portion, a feed-in portion integrally forming a center extending portion of the Inverted-F antenna and a signal transmission line connected to the feed-in portion and the ground plane for signal transmission between the antenna and a connected communication host. The signal transmission line includes a core wire and a ground wire. The core wire is connected to the feed-in portion and the ground wire is connected to the ground plane. The antenna is capable of keeping a stable radio frequency characteristic with its simple and compact structure.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Miniaturized reverse-fed planar inverted F antenna
InactiveUS20030025637A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsPlanar inverted f antennaMiniaturization
In a planar inverted F antenna (PIFA), the feed and RF grounding connections are reversed yielding improved performance. Relative positioning of these connections is selected to tailor the characteristics of the antenna, such as resonant frequency and impedance bandwidth.
Owner:E TENNA CORP
Multiband antenna device and communication terminal device
InactiveUS20090231213A1Reduce thicknessReduce the amount requiredSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandTerminal equipment
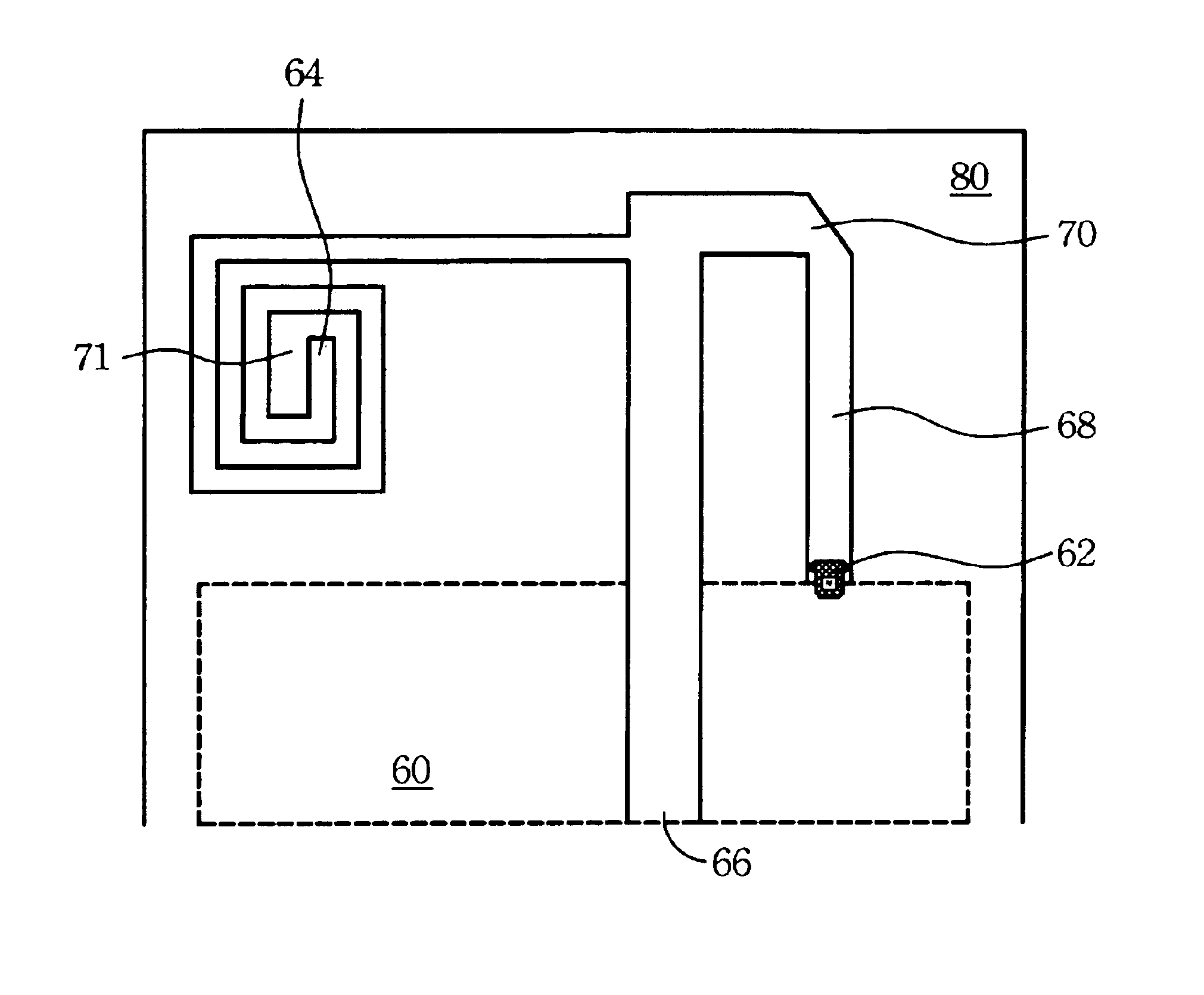
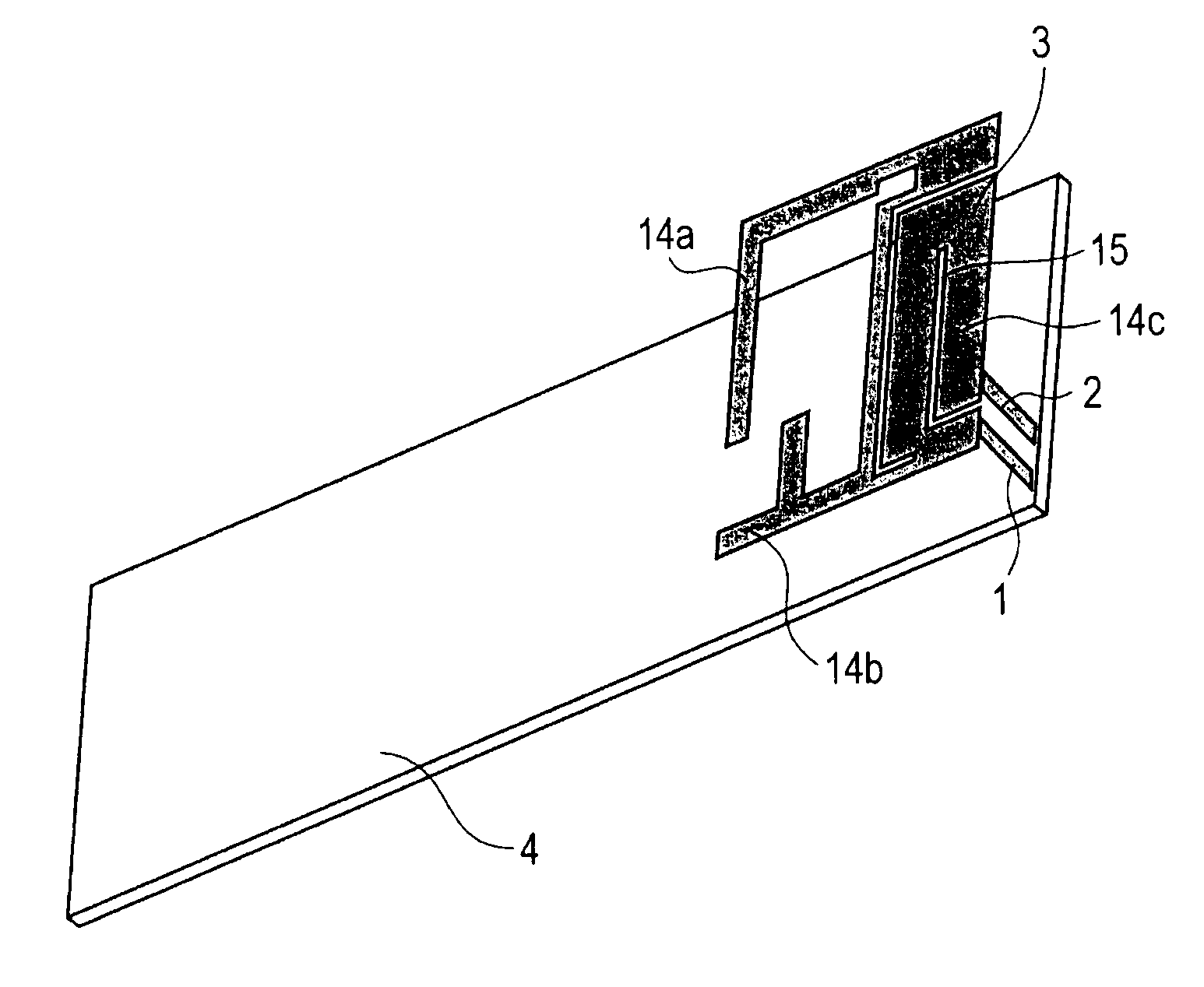
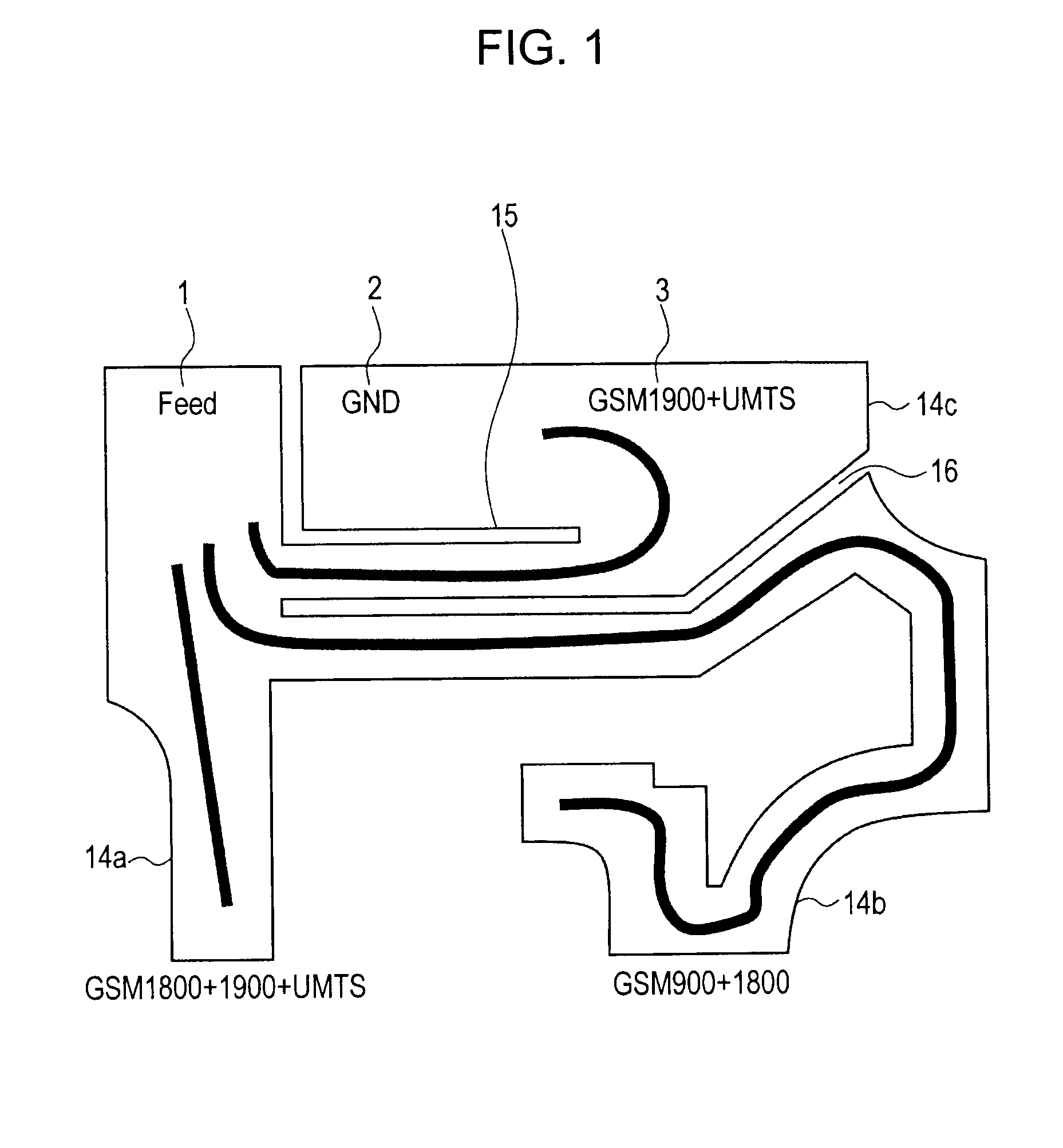
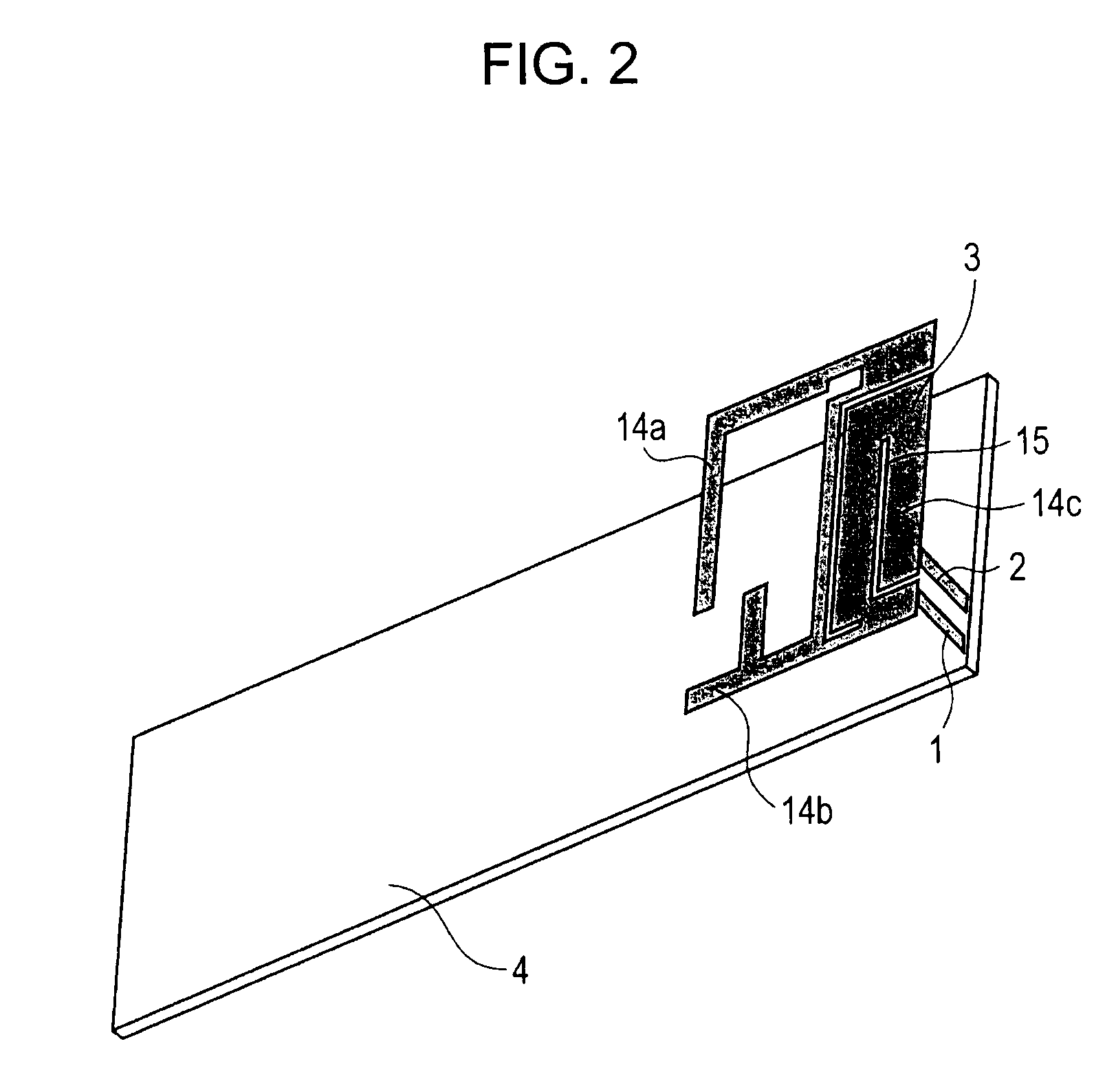
A slit (15) is formed between a feed point and GND point of an inverted-F antenna to make the points electrically distant from each other, and at least three antenna elements (14a, 14b, and 14c) are formed. The at least three antenna elements (14a, 14b, and 14c) generate at least three resonance points. An antenna radiating plate (3) projects outwardly so that at least a major part thereof does not face a ground plate (4). Therefore, a multi-band antenna device capable of achieving a wider bandwidth without using a parasitic element, and a communication terminal apparatus are provided.
Owner:SONY MOBILE COMM INC
Dual-band inverted-F antenna with a branch line shorting strip
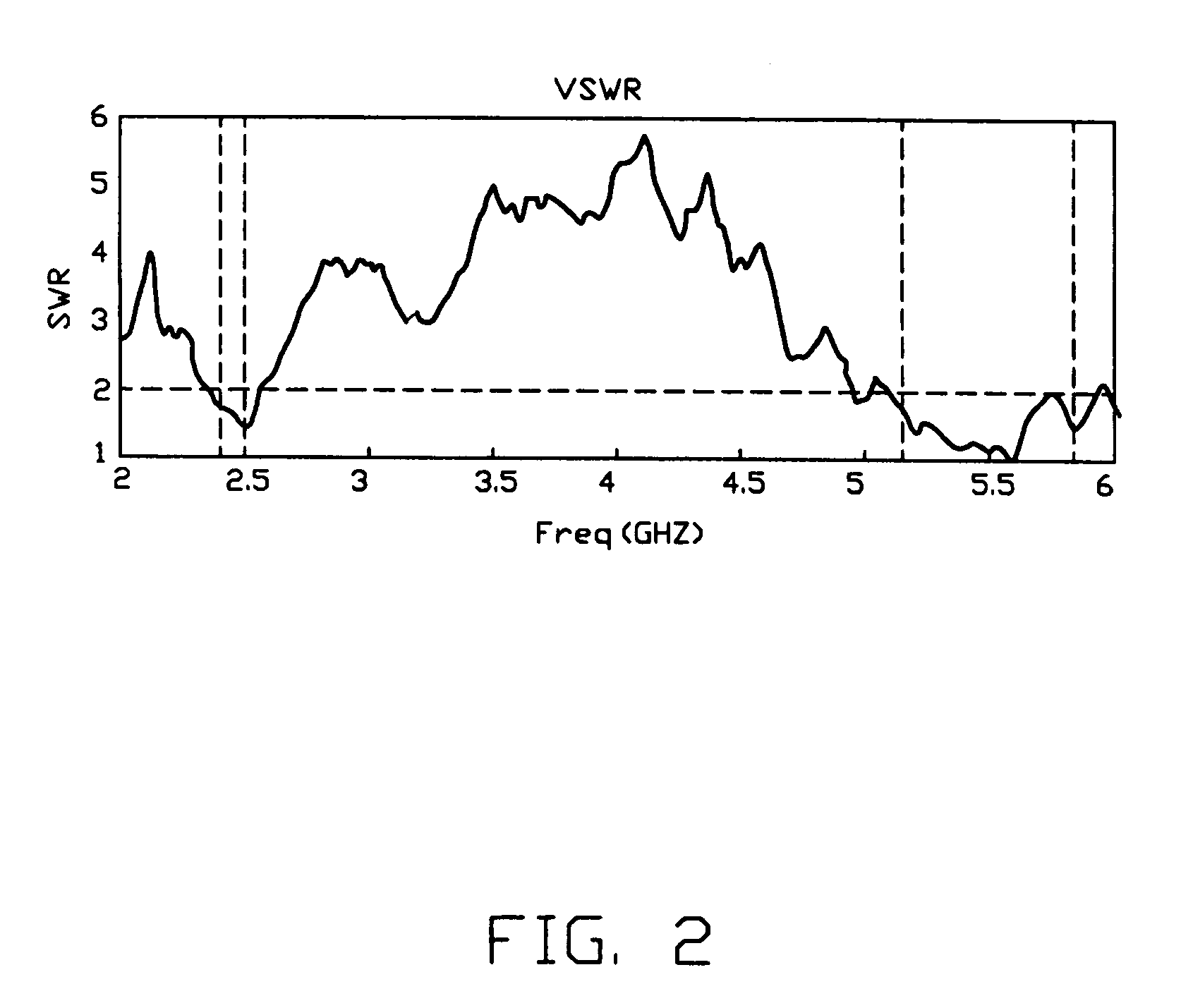
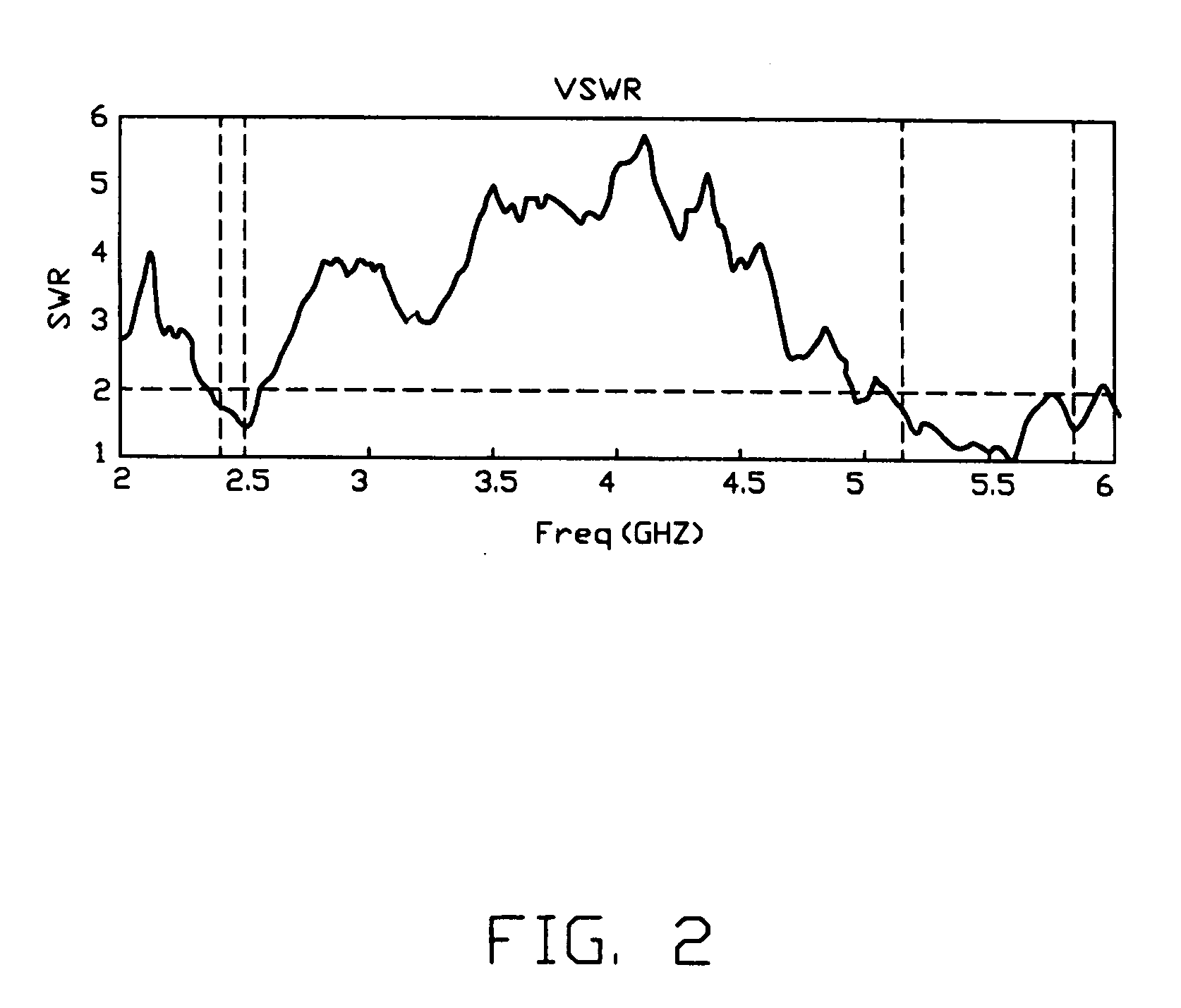
Provided is dual-band inverted-F antenna for GSM, DCS, and PCS bands comprising a primary radiating member including integral first and second metallic strips, a feeding point, and a first shorting point wherein a long current path is created in the first strip such that the antenna can operate in a first low frequency operating mode, and a shorting current path is created in the second strip such that the antenna can operate in a second high frequency operating mode; a secondary radiating member comprising a second shorting point; a branch line shorting strip having one grounded end and a bifurcation including a first branch connected to the first shorting point and a second branch connected to the second shorting point; and a feeding member interconnected the feeding point and a signal source. Operating frequencies of the antenna are 90 MHz and 300 MHz respectively when it operates in 3.5:1 VSWR impedance bandwidth.
Owner:ADVANCED CONNECTEK INC
Antenna apparatus and a portable wireless communication apparatus
InactiveUS20020041256A1Antenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsPrinted circuit boardCommunication device
A microstrip antenna (MSA) above a ground plane, having a size corresponding to an operation frequency, at a junction point thereof, electrically connected to one end of a monopole antenna having a size corresponding to the operation frequency to operate as a complex antenna. A distance between the feed point of MSA and the junction point determines the input impedance for matching. A microstrip line or an (planer) inverted-F antenna may provide the MSA. The monopole element may be a monopole antenna or helical antenna. A portable wireless communication apparatus includes the antenna apparatus having a housing. The monopole antenna is connected to the MSA when the monopole antenna is extended from the housing. A switch may be provided between the monopole antenna and the MSA for diversity operation. The antenna apparatus may be formed on a Printed circuit board and folded.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Antenna device and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20150116168A1Reduce antenna sizeSmall sizeSimultaneous aerial operationsElongated active element feedElectrical conductorElectric devices
A square bracket-shaped radiation element is in a non-ground region of a board. A first reactance element that equivalently enters a short-circuited state in a second frequency band is connected between a second end of the radiation element and a ground conductor. A second reactance element that equivalently enters a short-circuited state in a first frequency band s connected between a first end of the radiation element and the ground conductor. In the UHF band, the radiation element and the ground conductor function as an inverted F antenna that contributes to field emission. In the HF band, a loop including the radiation element and the ground conductor functions as a loop antenna that contributes to magnetic field emission.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Dual-band inverted-F antenna with shorted parasitic elements
InactiveUS20050168384A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsCoaxial cableGround plane
The invention relates to a dual-band inverted-F antenna with shorted parasitic elements. The antenna of the invention comprises a ground plane, a first radiating arm placed above an edge of the ground plane, a second radiating arm placed above the edge of the ground plane, a shorting arm with a substantially inverted-L shape for electrically connecting the first radiating arm and the second radiating arm to the ground plane, a shorted parasitic arm placed above the edge of the ground plane, and a feeding coaxial cable for transmitting signals. There is a distance between the shorted parasitic arm and the first radiating arm so as to induce extra capacitive reactance to compensate the inductive reactance induced by inserting the feeding coaxial cable. The present invention is suitable for the wireless local area network (WLAN) applications in the 2.4 GHz (2.4-2.484 GHz) and 5 GHz (5.15-5.35, 5.725-5.875 GHz) bands.
Owner:YAGEO CORP
Dual-band inverted-f antenna with a branch line shorting strip
InactiveUS20060145924A1Increase working frequencySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsGSMOperating frequency
Provided is dual-band inverted-F antenna for GSM, DCS, and PCS bands comprising a primary radiating member including integral first and second metallic strips, a feeding point, and a first shorting point wherein a long current path is created in the first strip such that the antenna can operate in a first low frequency operating mode, and a shorting current path is created in the second strip such that the antenna can operate in a second high frequency operating mode; a secondary radiating member comprising a second shorting point; a branch line shorting strip having one grounded end and a bifurcation including a first branch connected to the first shorting point and a second branch connected to the second shorting point; and a feeding member interconnected the feeding point and a signal source. Operating frequencies of the antenna are 90 MHz and 300 MHz respectively when it operates in 3.5:1 VSWR impedance bandwidth.
Owner:ADVANCED CONNECTEK INC
Planar inverted-F antenna with parasitic conductor loop and device using same
ActiveUS7265720B1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsPlanar inverted f antennaElectrical conductor
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
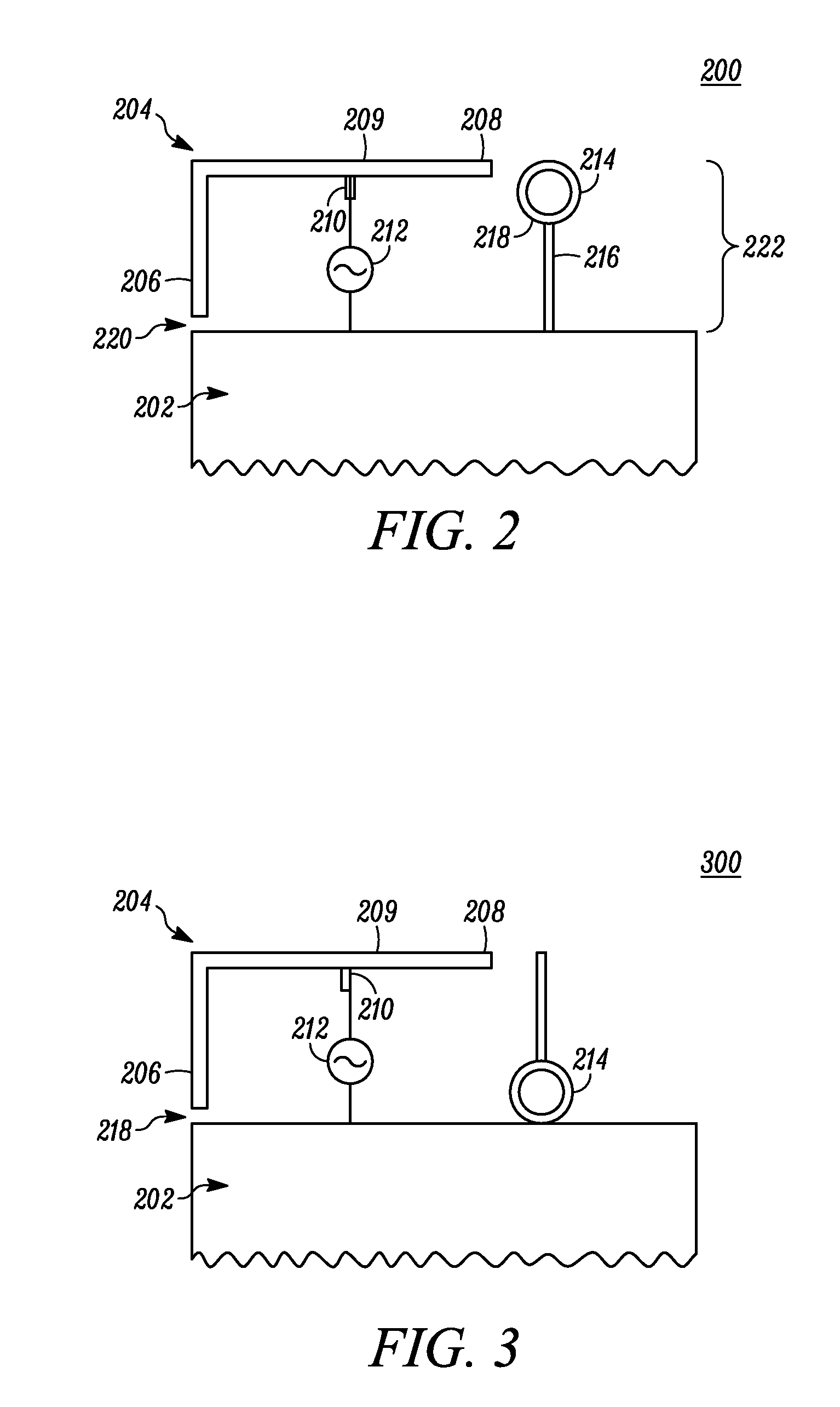
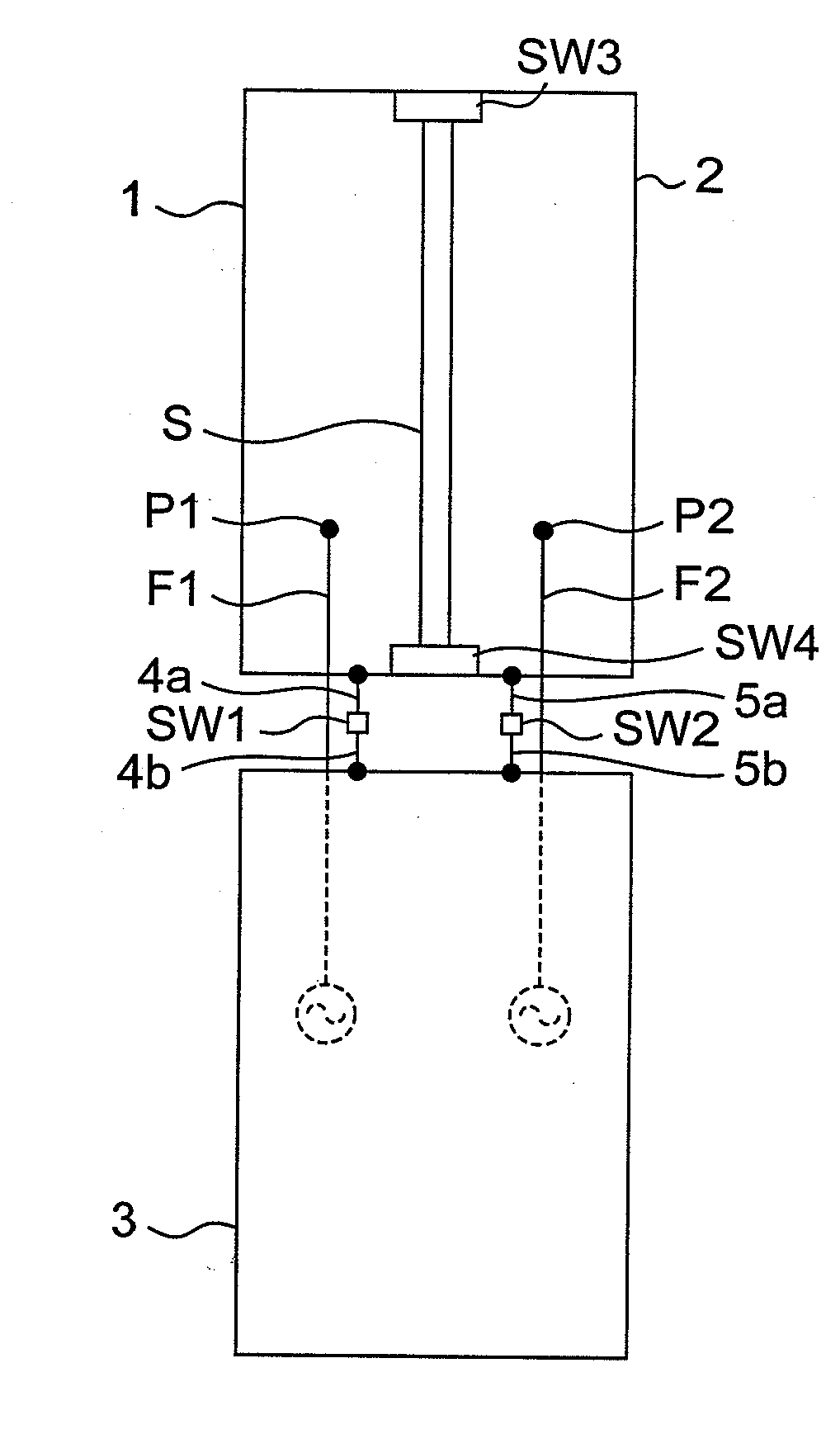
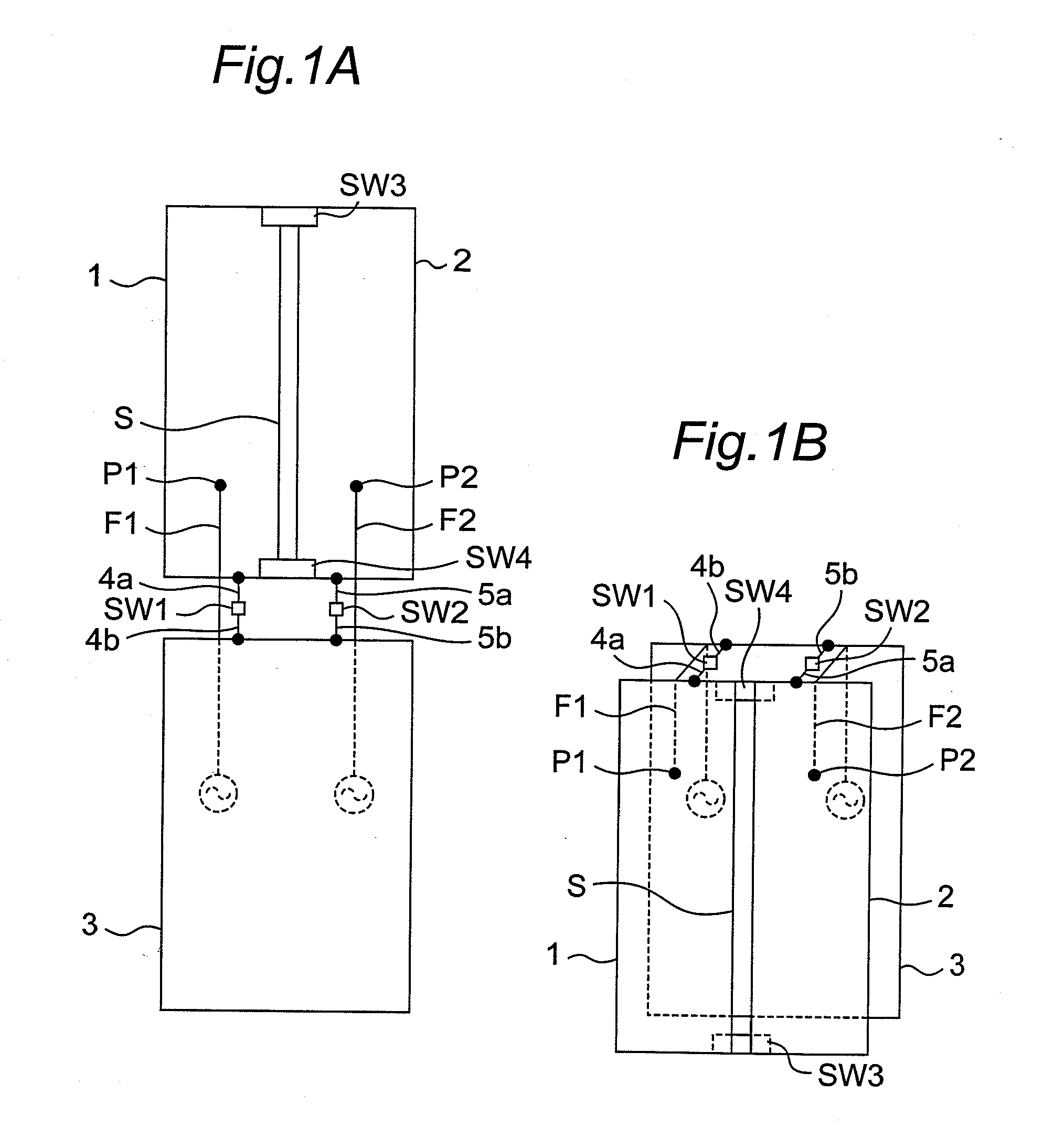
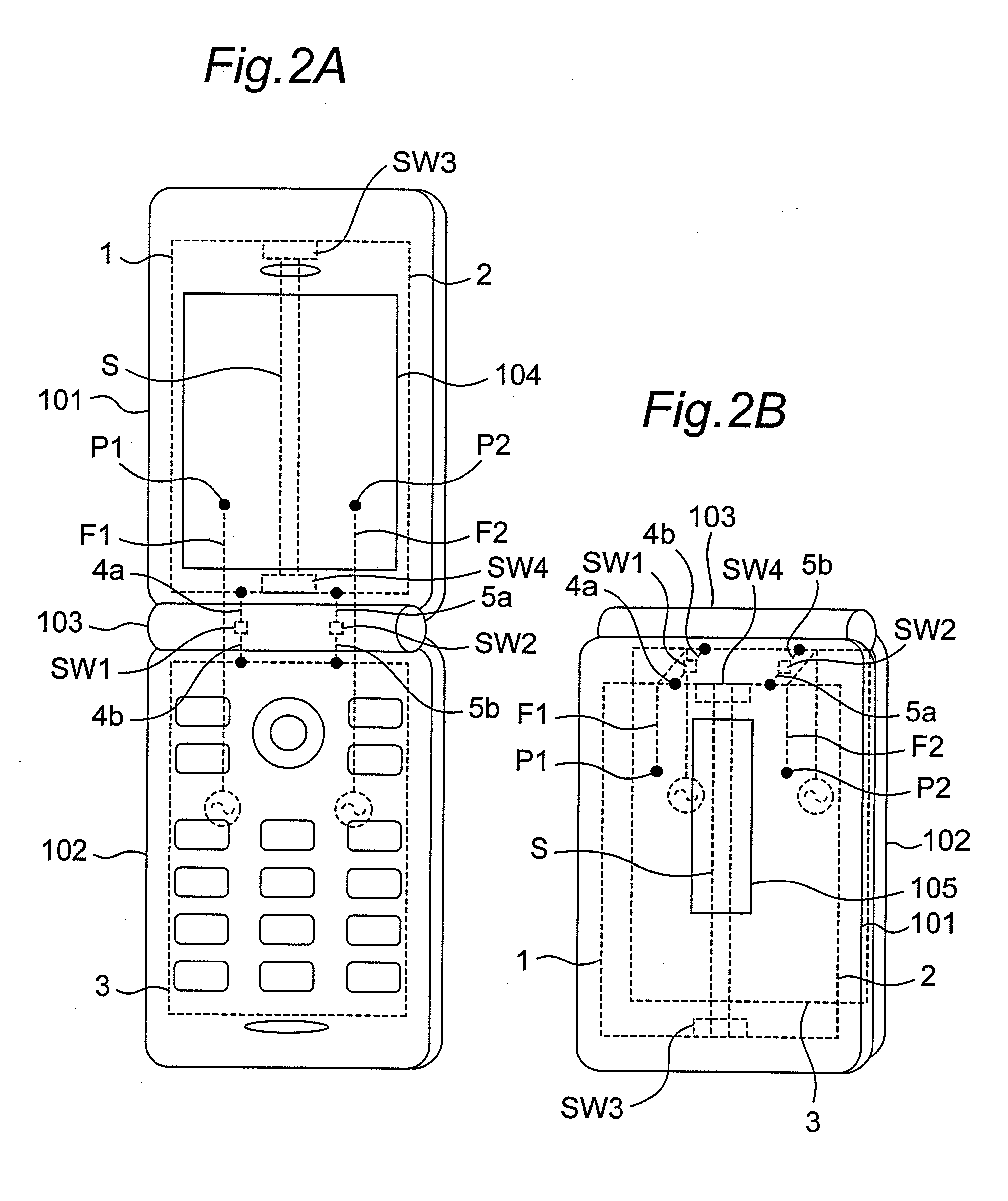
Wireless communication apparatus with housing changing between open and closed states
ActiveUS20100013720A1Reduce correlationMinimize reflection coefficientSpatial transmit diversityCollapsable antennas meansElectrical conductorEngineering
When first and second housings are in an open state, first and second switches are electrically opened, and thus, a first antenna element and a ground conductor operate as a first dipole antenna, and a second antenna element and the ground conductor operate as a second dipole antenna with isolation from the first dipole antenna by the slit. When the first and second housings are in the closed state, the first and second switches are electrically closed, and thus, the first antenna element operates as a first inverted F antenna on the ground conductor, and the second antenna element operates as a second inverted F antenna on the ground conductor with isolation from the first inverted F antenna by the slit.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Tunable dual-band antenna using lc resonator
InactiveUS20100053007A1Easily incorporated into cell phoneEasily other wireless deviceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsCapacitanceLc resonator
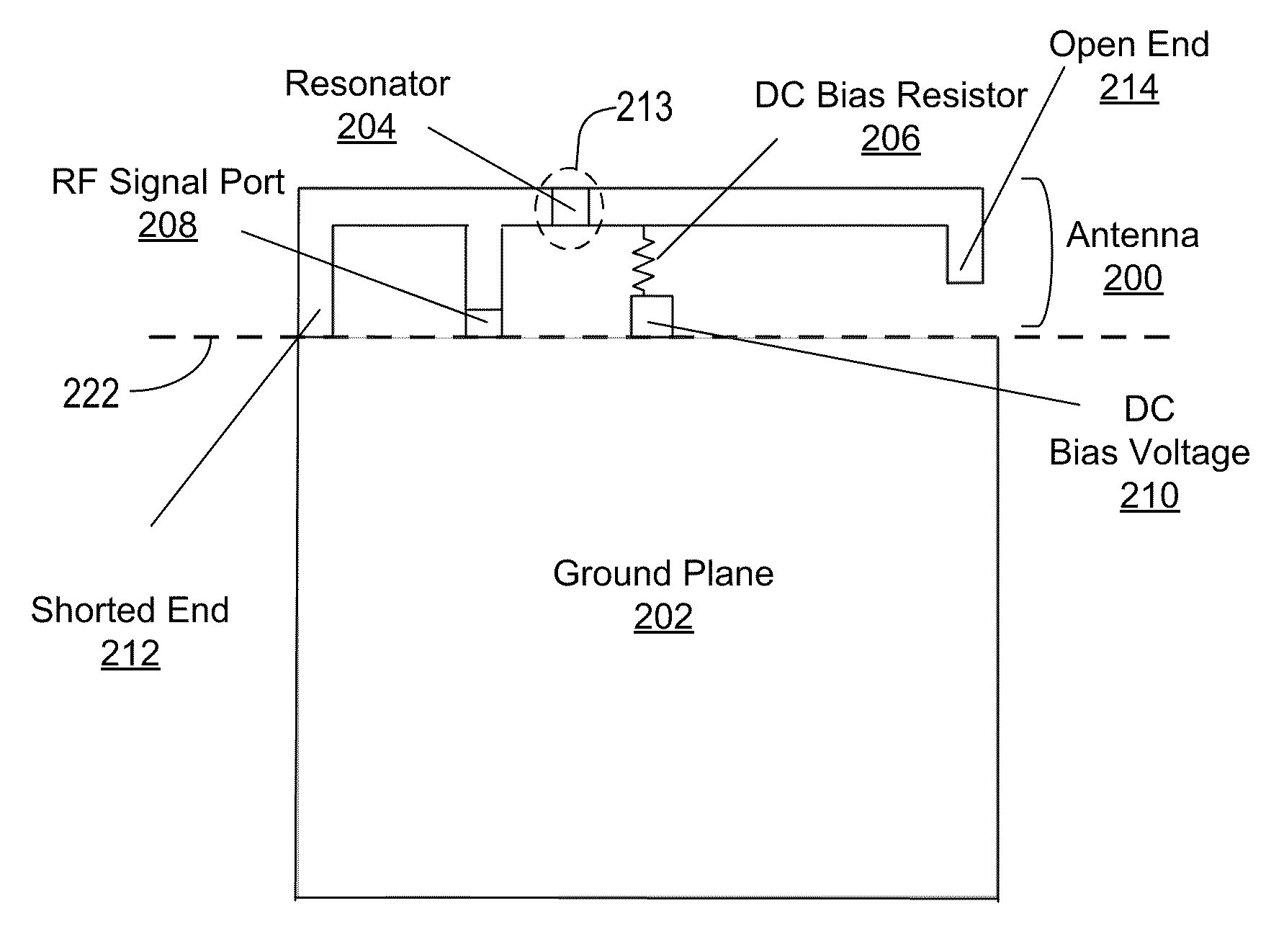
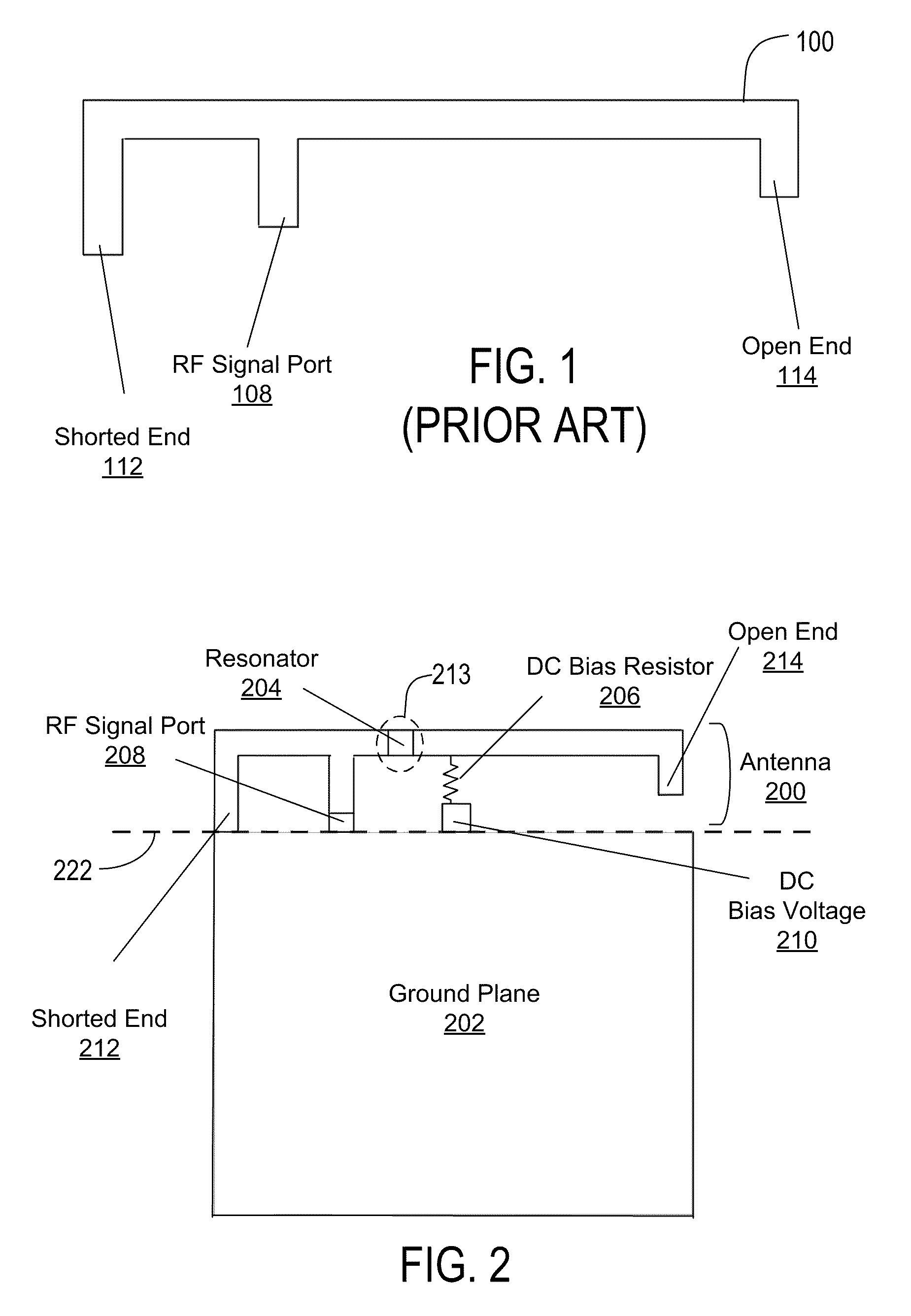
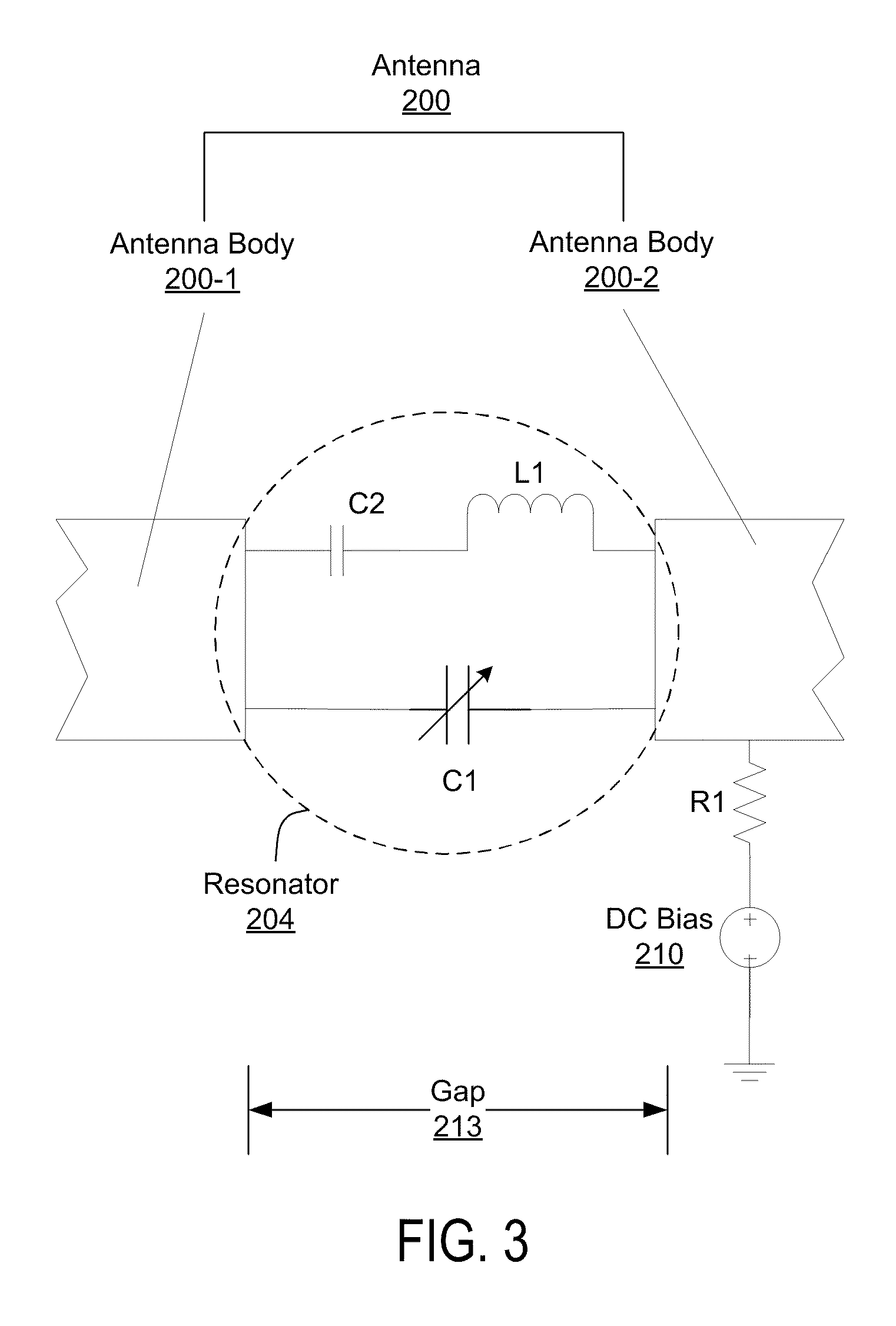
An Inverted-F antenna (IFA) includes a tunable parallel LC resonator physically inserted between two antenna bodies of the IFA structure. The LC resonator is comprised of a tunable capacitor C1 connected in parallel with a combination of a DC blocking capacitor C2 and an inductor L1 connected in series to each other. A DC bias voltage is applied to the tunable capacitor C1 through a DC bias resistor R1, in order to adjust the capacitance of the tunable capacitor C1. The IFA exhibits dual band characteristics, and its resonant frequencies and bandwidths may be turned by adjusting the capacitance of the tunable capacitor C1. The tunable capacitor C1 may be a BST capacitor.
Owner:AGILE RF
Multi-band antenna
InactiveUS7034754B2Improving Impedance MatchingEasy to testSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandEngineering
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Inverted-F antenna
InactiveUS6894647B2Reduce overall form factorMinimize mutual interferenceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsInverted-F antennaTransmission line
A coupled-feed inverted-F antenna is provided comprising a transmission line port, an open radiator with an unterminated end, a shorted “L” shaped radiator connected to the open radiator with a terminated end, a coupled-feed connected between the transmission line port signal interface and the open and shorted radiators, and a groundplane. The coupled-feed is oriented parallel to the open radiator. A coplanar inverted-F antenna is provided comprising a transmission line port, an open radiator oriented in a first plane, a shorted “L” shaped radiator oriented in the first plane connected to the open radiator and having an terminated end, a feed oriented in the first plane and connected between the transmission line port signal interface and the radiators, and a groundplane oriented in the first plane. The shorted radiator is terminated in the transmission line port ground interface. The antenna may also employ both coplanar and coupled-feed features.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Multi-band antenna
InactiveUS20050068234A1Improving Impedance MatchingEasy to testSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandElectron
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Dual-band inverted F antenna reducing SAR
ActiveUS20080055160A1Reduce SARSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMiniaturizationDouble frequency
An inverted F antenna (IFA) which reduces specific absorption rate (SAR) includes a ground; an auxiliary radiator which is attached to one end of the ground and disposed along a plane direction of the ground; a radiator which lies at an interval from the auxiliary radiator in parallel and radiates electromagnetic waves; a feed which supplies current to the radiator; and a short which interconnects the radiator with the ground and discharges the current to the ground. Accordingly, the SAR can be decreased and the antenna size can be miniaturized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Integrated inverted F antenna and shield can
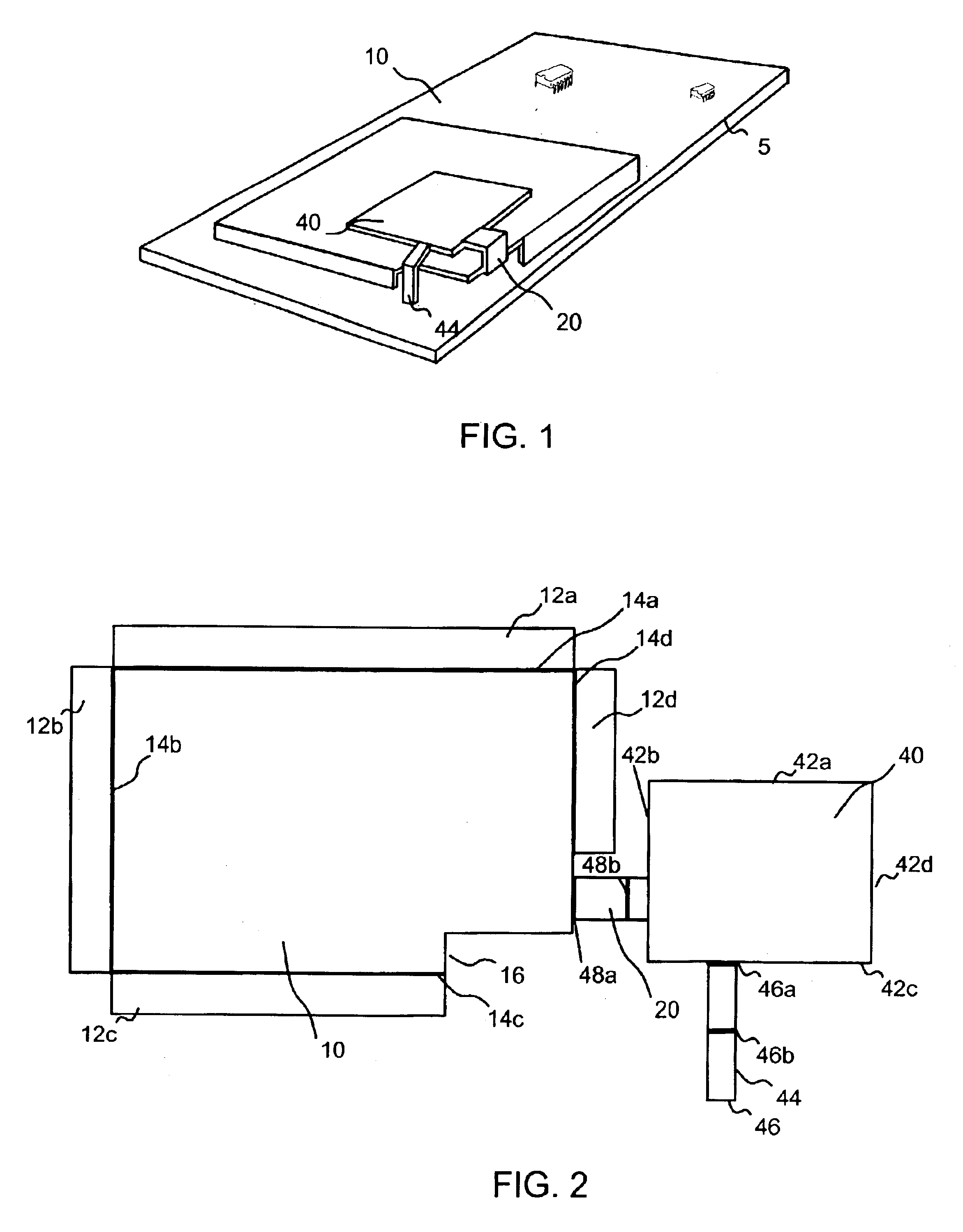
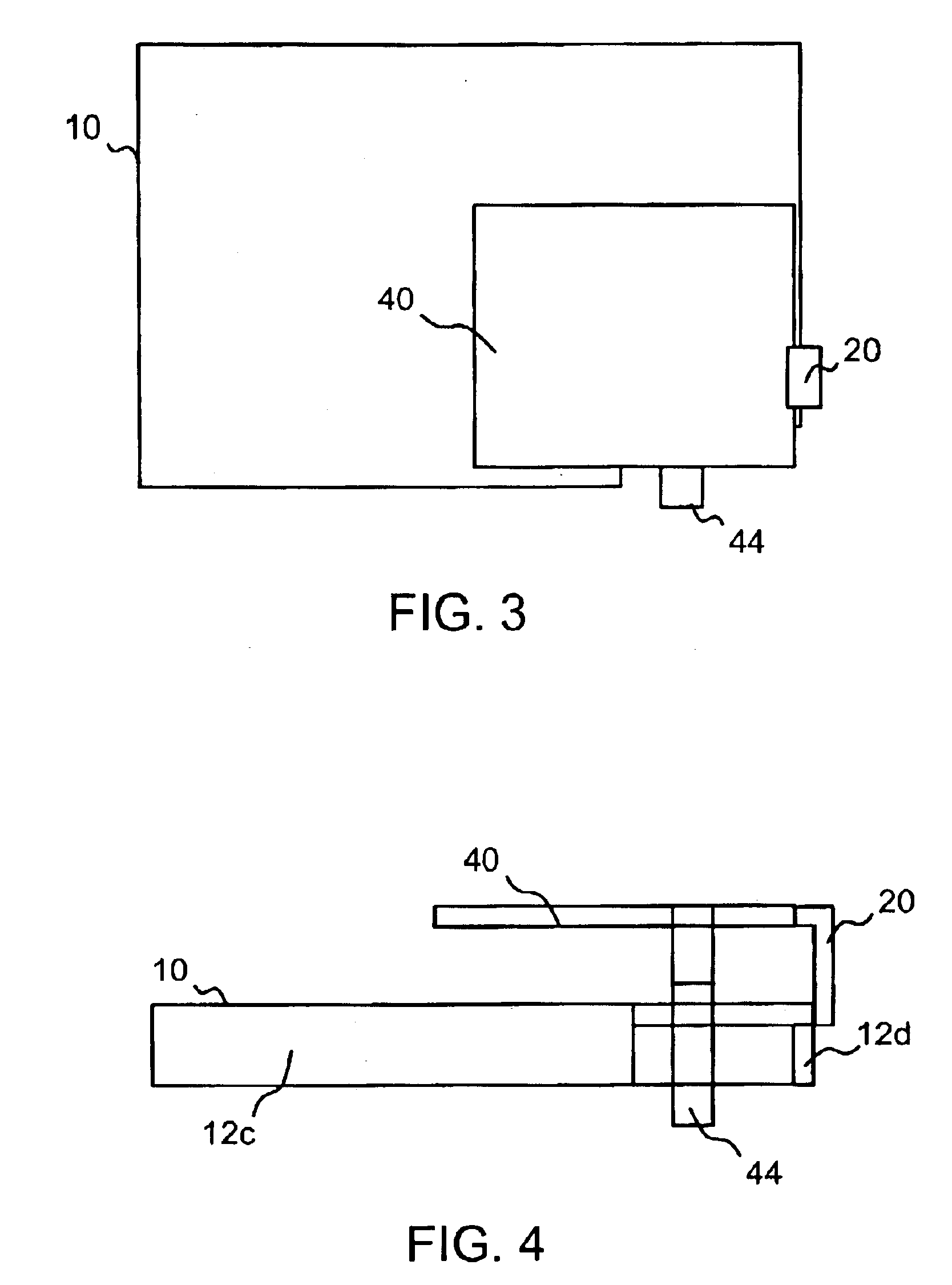
InactiveUS6850196B2Small sizeEasy to assembleLocalised screeningAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringGround plane
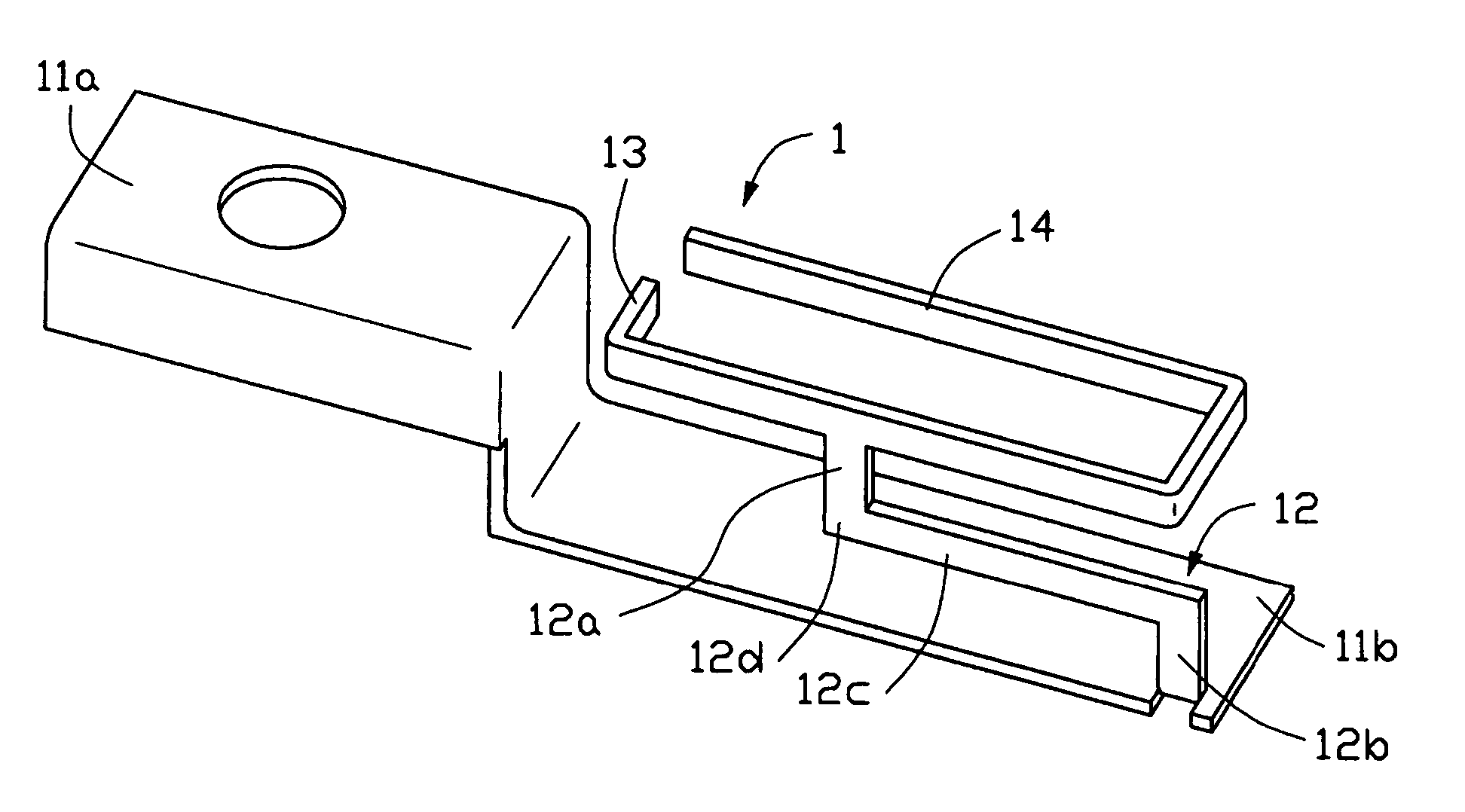
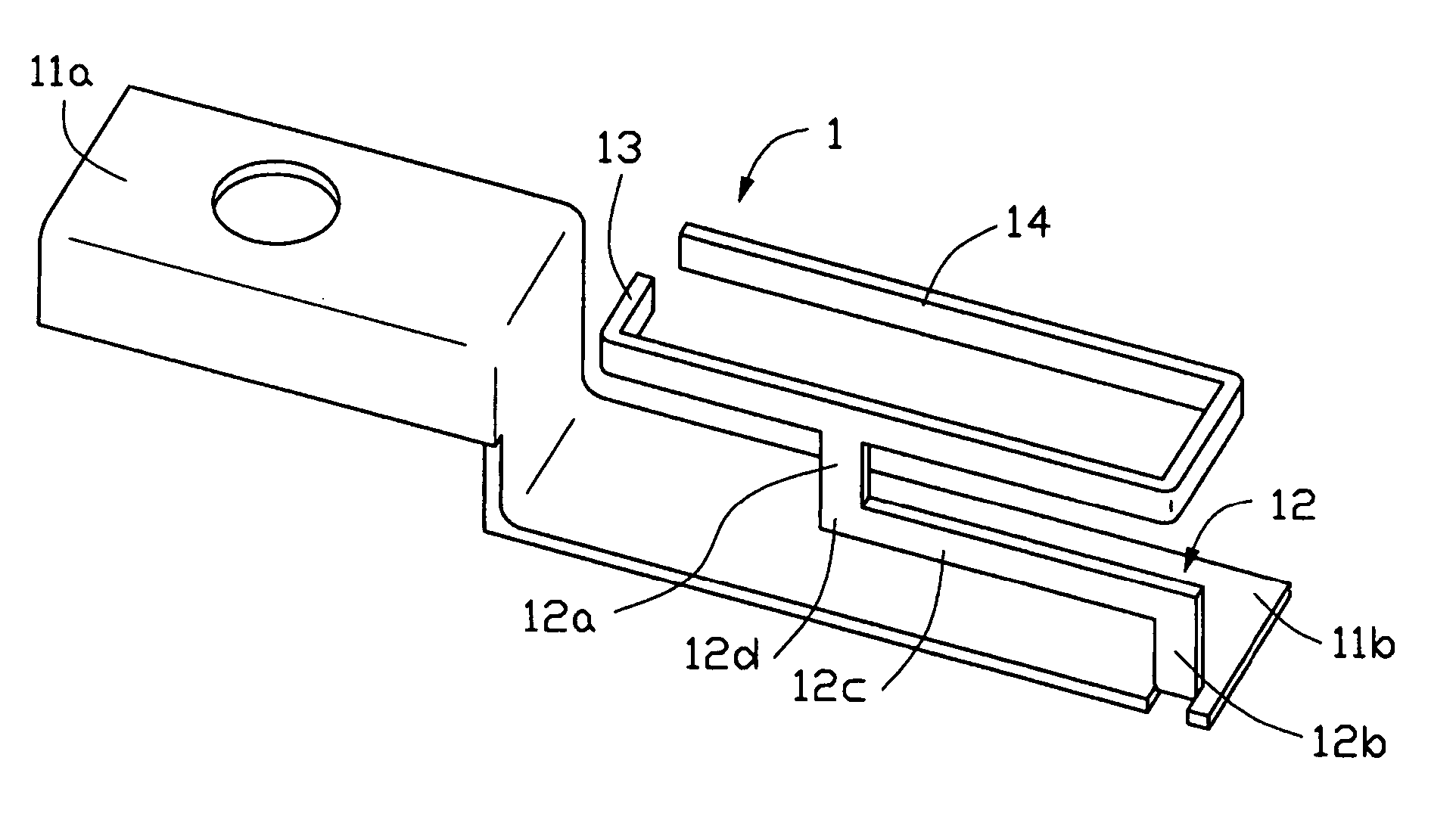
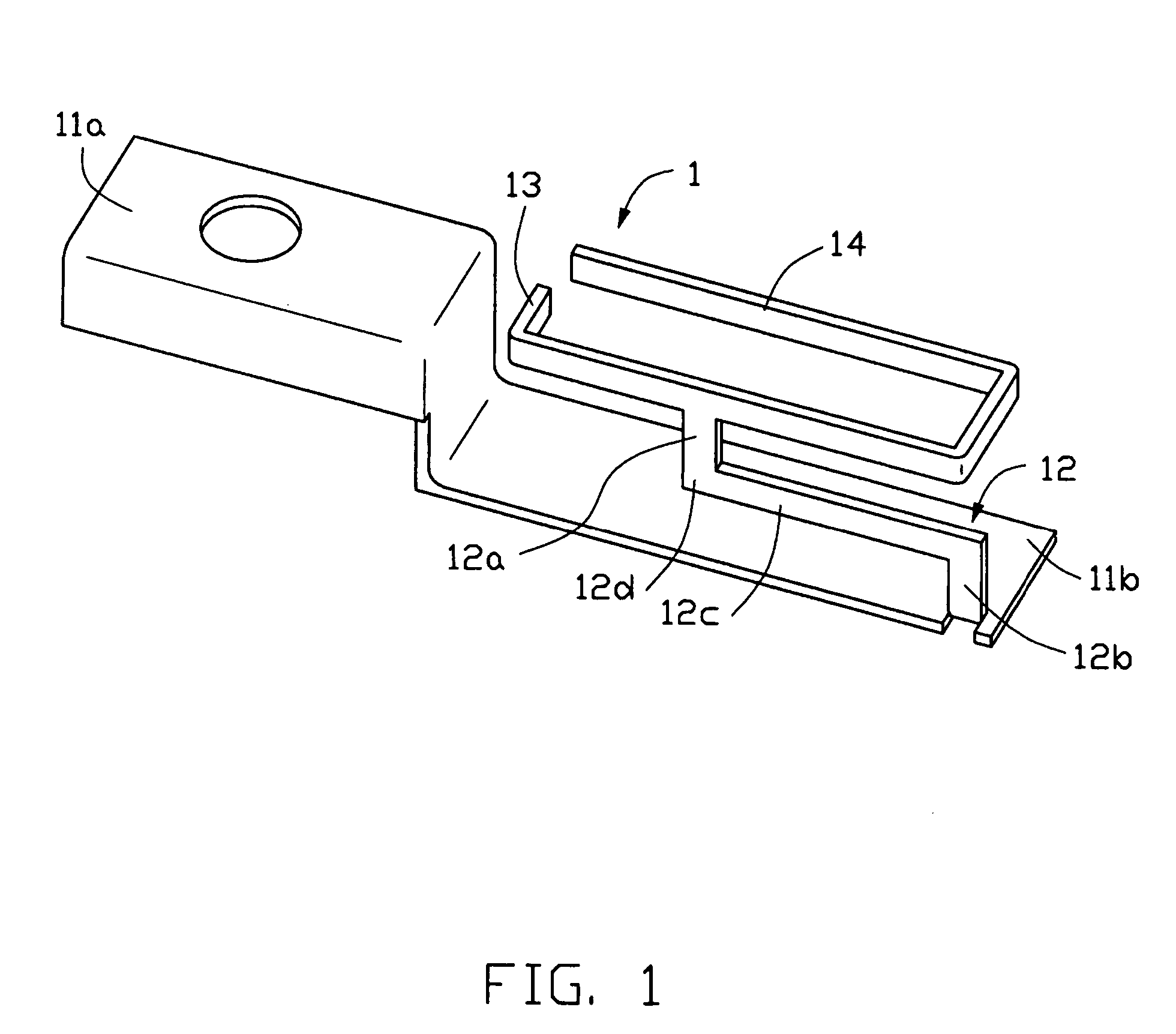
An inverted F antenna with integrated shield is constructed from an electrically conducting sheet that is folded into a shape that provides both a shield can covers an RF module of circuit and an inverted F antenna such that shield can functions also as a ground plane for the antenna. In a pre-folded state the sheet has a shield can portion and a radiating element portion that are connected to each other by a ground feed line that bridges the shield can portion and radiating element portion. The shield can portion preferably includes a plurality of walls that are foldable along respective folds. The radiating element portion preferably includes a plurality of edges and a signal feed line extending from a first one of the plurality of edges. The ground feed line extends from a second one of said plurality of edges. When the sheet is folded, the radiating element portion is suspended over the shield can portion and is substantially fixed with respect to the shield can portion by the ground feed line and the signal feed line.
Owner:VTECH TELECOMM
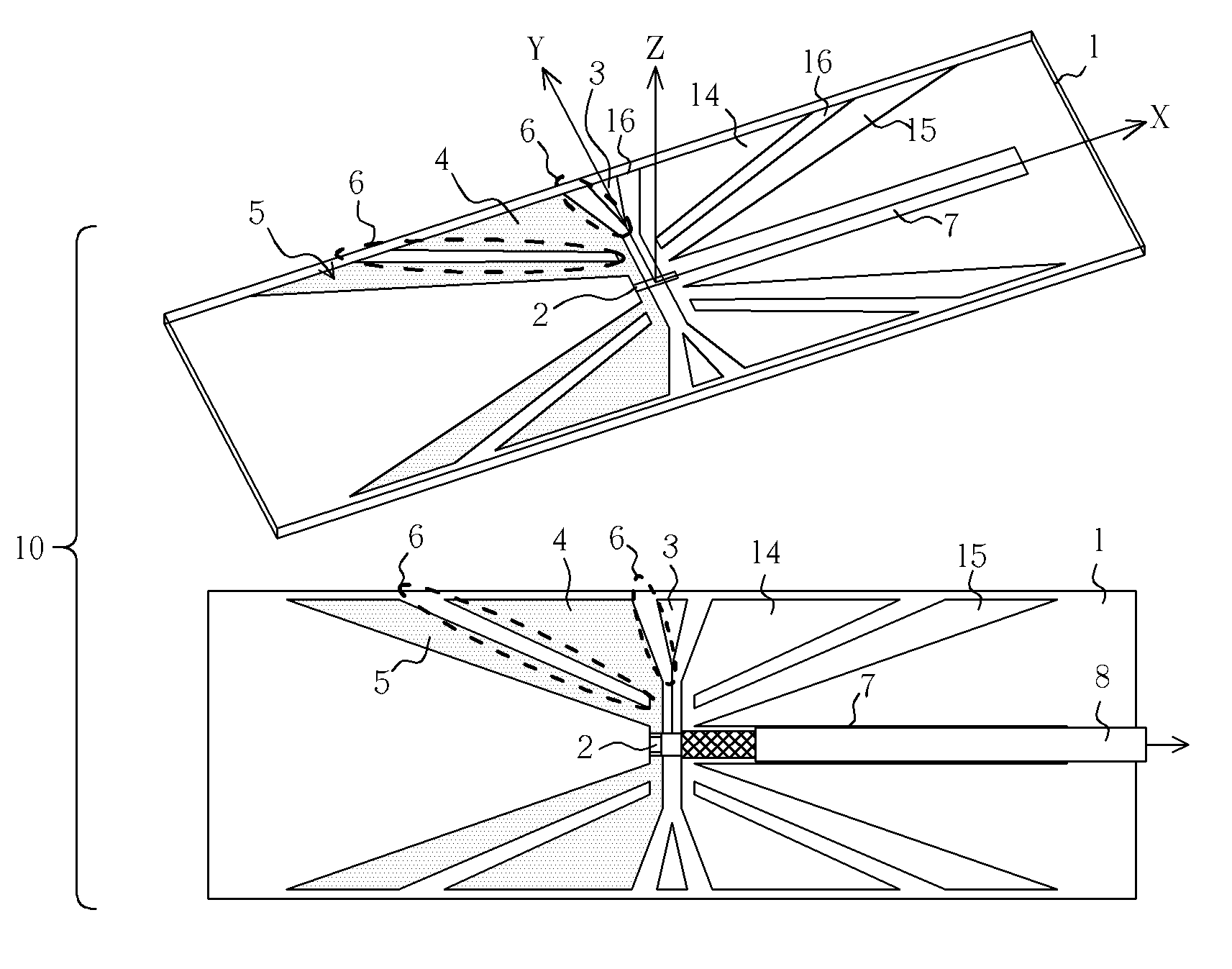
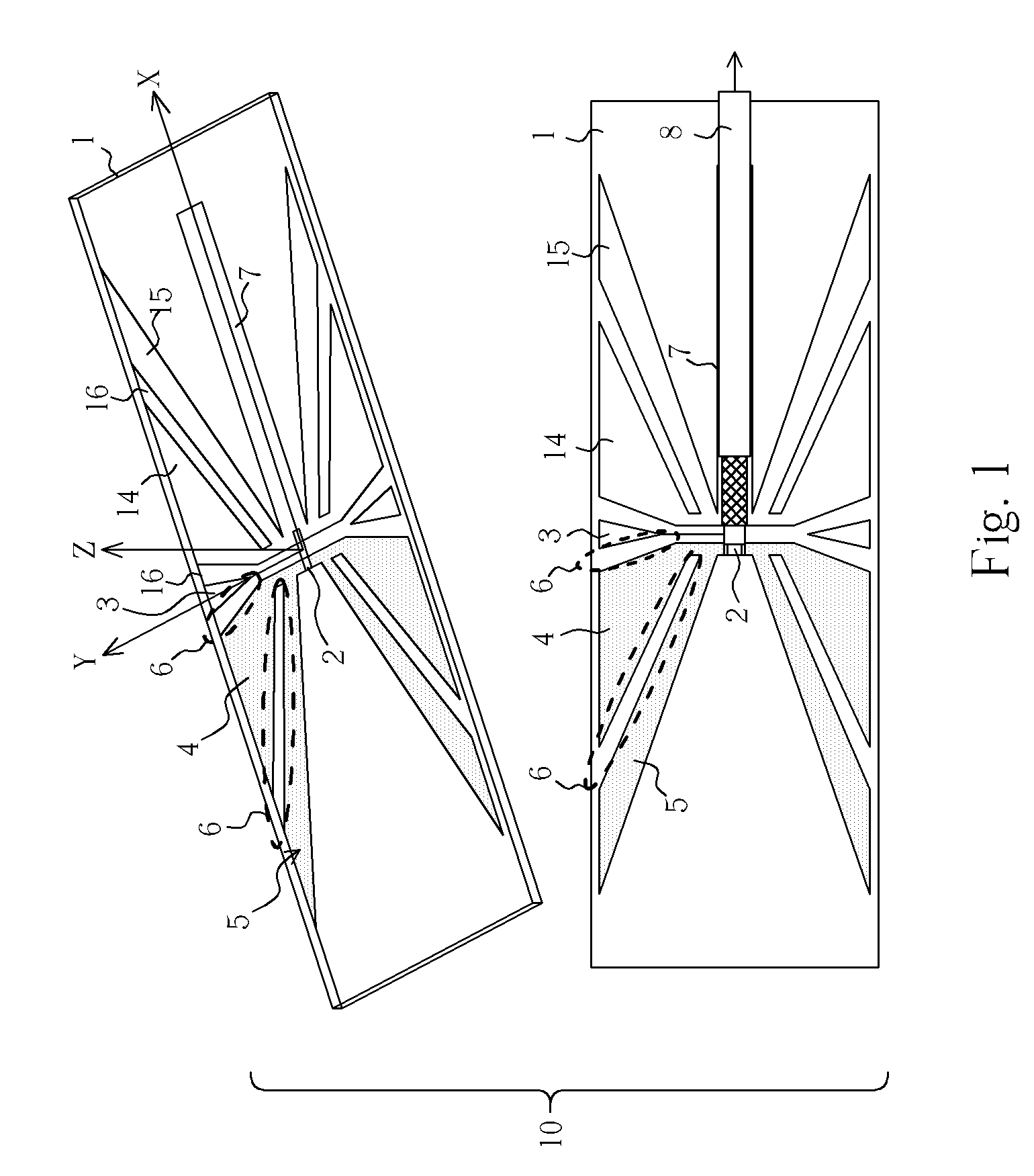
Compact multiple-frequency Z-type inverted-F antenna
ActiveUS7265718B2Small sizeHigh gainParticular array feeding systemsSimultaneous aerial operationsDielectric substrateHorizontal axis
A compact multiple-frequency Z-type Inverted-F antenna includes a dielectric substrate having a horizontal axis and a vertical axis perpendicular to the horizontal axis. A feed point is disposed along the horizontal axis on a first side of the vertical axis and a ground strip is disposed along the horizontal axis on a second side of the vertical axis opposite the feed point. A plurality of wedge-shaped radiating traces is arranged symmetrically with respect to the horizontal axis and disposed on the first side of the vertical axis. A plurality of wedge-shaped ground traces symmetrical to the plurality of radiating traces with respect to the vertical axis are disposed on the second side of the vertical axis.
Owner:WISTRON NEWEB
Inverted-F antenna
InactiveUS7183980B2Increase bandwidth and efficiencyLow capacitance rateSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMetal stripsMicrowave
An inverted-F antenna comprises a microwave plate, a dielectric substrate, a radiating metal sheet, a ground surface, a shorting metal strip, and a feeding metal strip. The radiating metal sheet comprises a connecting metal sheet, first, second, and third child radiating metal sheets, a matching metal sheet, a slot, a shorting point, and a feeding point. The first child radiating metal sheet is for forming a low frequency operating mode. The second child radiating metal sheet is for forming a high frequency operating mode. The third child radiating metal sheet is for adjusting operating frequency and bandwidth of the second operating mode. The slot, the shorting point, and the feeding point are for adjusting impedance matching. The grounding surface is for increasing the operating bandwidth of the low frequency operating mode. The shorting metal sheet and the feeding metal sheet are for grounding the antenna and signal transmission.
Owner:ADVANCED CONNECTEK INC
Antenna and radio device using the same
InactiveUS6930641B2Wide bandwidthHigh sensitivitySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsRadio equipmentElectrical conductor
An inverted-F type antenna and a wireless device using the same. The antenna element comprises a grounding conductor plate and a conductor at least a part of which is generally spiral in shape and is disposed above the grounding conductor plate apart from the grounding conductor plate. A stub connects one end of the antenna element with the grounding conductor plate. A feeding point locates on the antenna element at a predetermined distance from one end of the antenna element and a feeder line electrically connects the feeding point with an external circuit. The antenna element is secured on the grounding conductor plate with a support member made of a dielectric material.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Electronic device with shared antenna structures and balun
ActiveCN105940550ANear-field transmissionSimultaneous aerial operationsTransceiverDifferential signaling
An electronic device may be provided with shared antenna structures that can be used to form both a near-field-communications antenna such as a loop antenna and a non-near-field communications antenna such as an inverted-F antenna. The antenna structures may include conductive structures such as metal traces on printed circuits or other dielectric substrates, internal metal housing structures, or other conductive electronic device housing structures. A main resonating element arm may be separated from an antenna ground by an opening. A non-near-field communications antenna return path and antenna feed path may span the opening. A balun may have first and second electromagnetically coupled inductors. The second inductor may have terminals coupled across differential signal terminals in a near-field communications transceiver. The first inductor may form part of the near-field communications loop antenna.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com