Method for modifying artificial implanter by covalent cross-linking gel
A technology of covalent cross-linking and implants, which is applied in the field of biomedical materials, can solve the problems of the influence of the material body structure, complex operation process, and expensive equipment, so as to improve anticoagulant performance, simple process, and reduce viscosity. echo the effect of aggregation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0018] Specific embodiment one: this embodiment is achieved in this way: a, the artificial implant body is soaked in the organic solvent ultrasonic cleaning, dry; b, the concentration is the polyanion of 0.01-100 mg / ml ml of polycations are alternately deposited on the surface of the artificial implant by electrostatic attraction, or directly deposit a cationic surfactant with a concentration of 0.01-100 mg / ml on the surface of the artificial implant instead of polyanions and polycations, The adsorption time is 0.1-300 minutes; c. Prepare a polymer solution containing carboxylic acid groups at a concentration of 0.01-100mg / ml or a mixed solution with biologically active substances, and apply it to the artificial implant On the surface, add polyamine with a concentration of 0.01-100M and [1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)]-carbodiimide (EDC) with a concentration of 0.01-100M for crosslinking, and let stand for 0.1 to 300 hours; d. Use CaCl 2 (or BaCl 2 ) and other inorganic ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0030] Specific implementation mode two: this implementation mode is realized in this way:
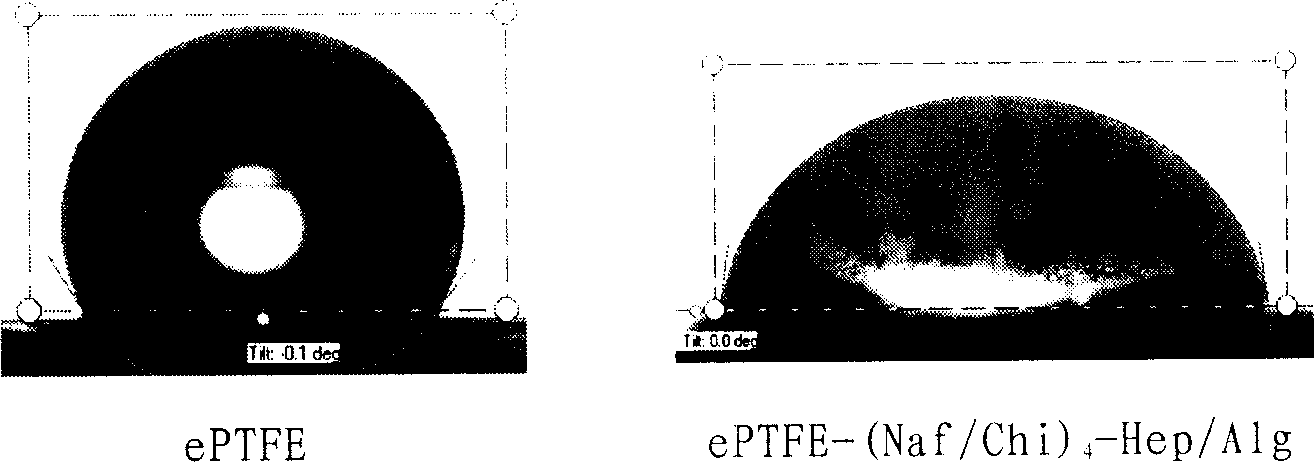
[0031] (1) Artificial blood vessel pretreatment: ultrasonically clean the artificial blood vessel in absolute ethanol for 1-300 minutes, and dry at 10-150°C for 0.1-24 hours.
[0032] (2) The artificial blood vessel is perfused with 0.01-30 wt% perfluorosulfonic acid solution, soaked for 1-300 minutes, and dried.
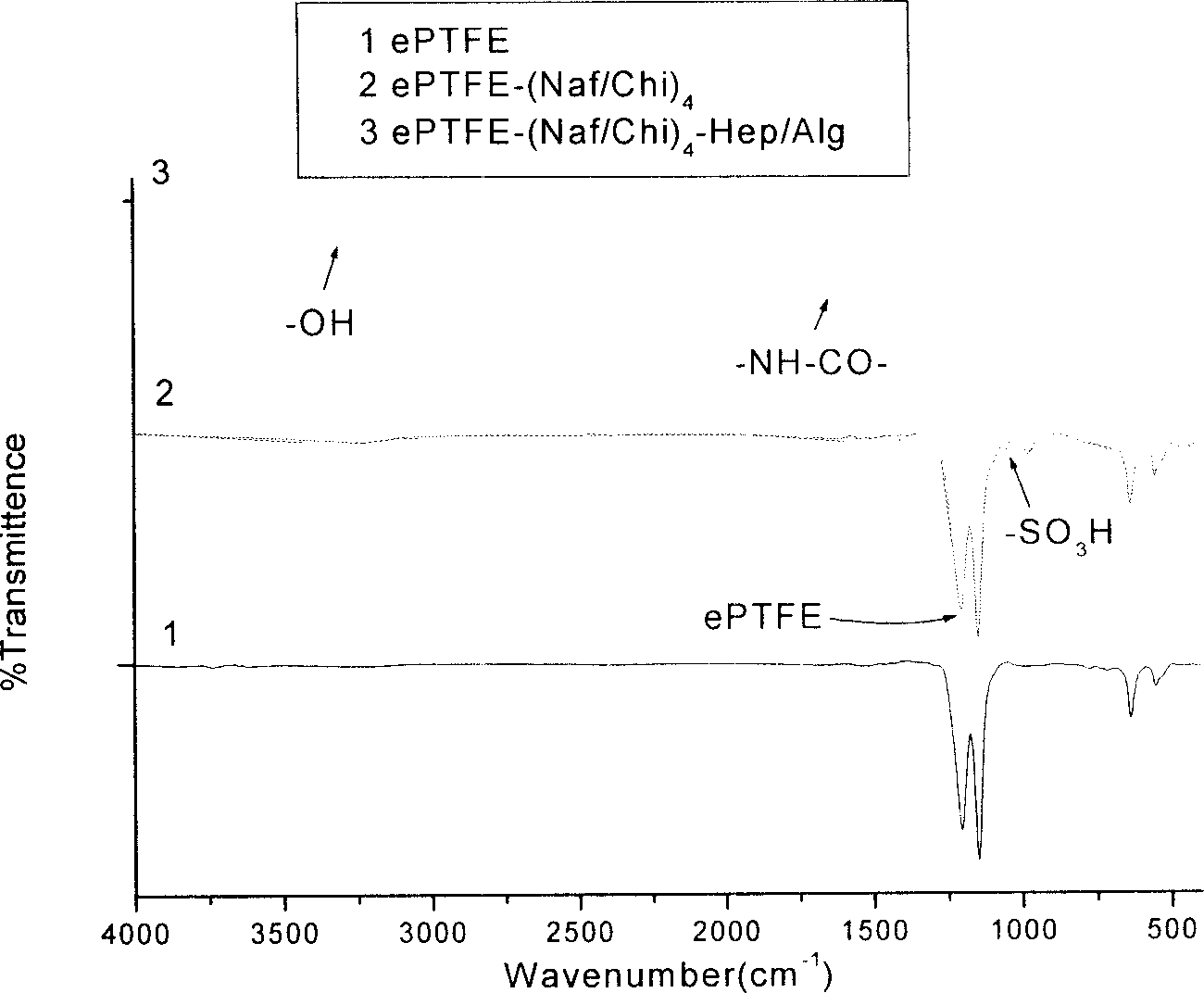
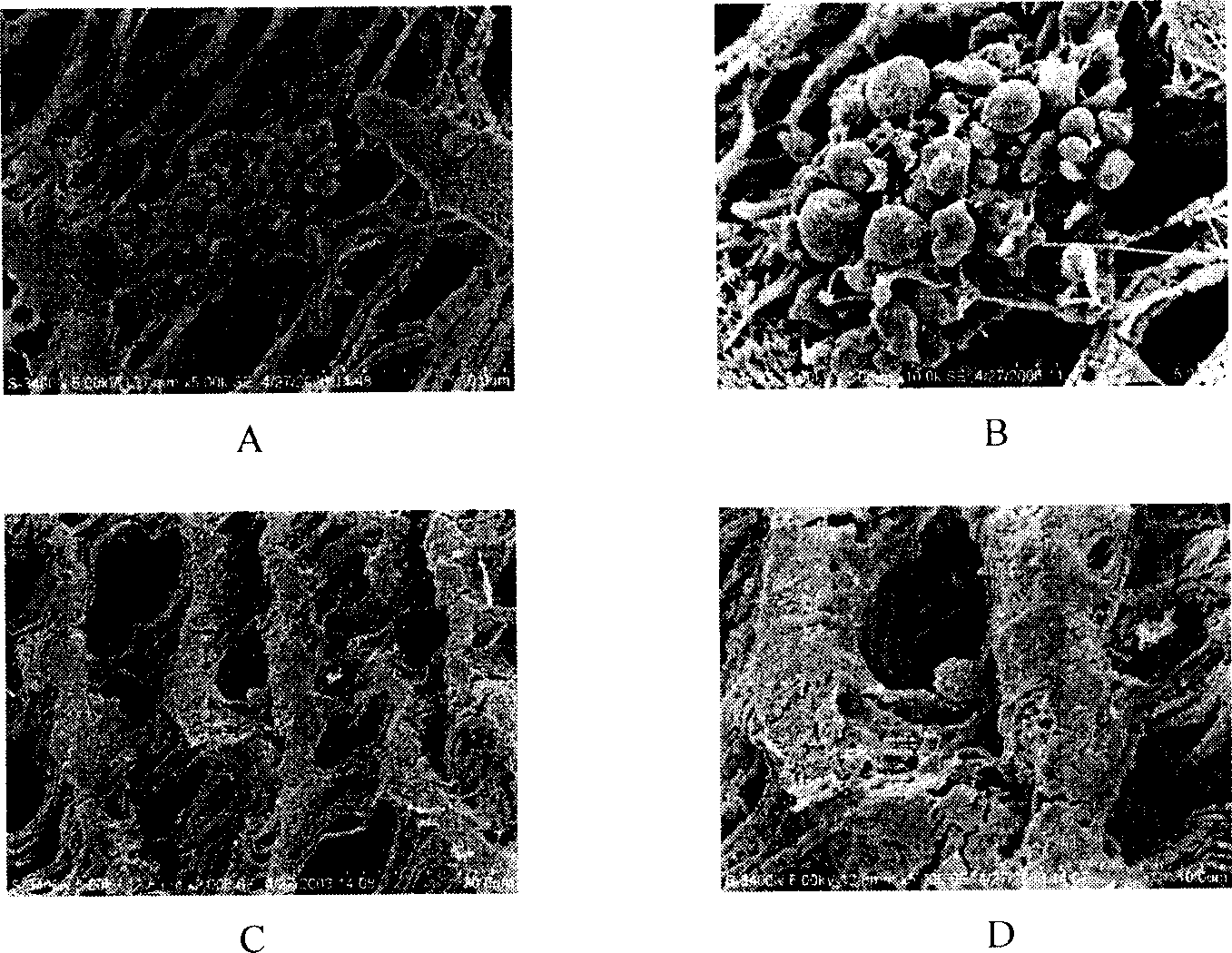
[0033] (3) Perfuse the dried artificial blood vessel with 0.01-100 mg / ml chitosan solution, soak for 1-300 minutes, and wash with water.
[0034] (4) Repeat steps (2) and (3) until the desired number of (perfluorosulfonic acid / chitosan) bilayers is reached.
[0035] (5) Prepare a mixed solution of heparin and sodium alginate, add an appropriate amount of ethylenediamine and [1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)]-carbodiimide (EDC), mix well, and infuse the modified perfluorosulfonic acid / chitosan artificial blood vessel, let stand for 0.1 to 300 hours.
[0036] (6) Use Ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com