Lens driver, imaging device, lens barrel used in the imaging device, and camera body
A technology of lens driving device and lens barrel, which is applied in the directions of installation, optics, and instruments, and can solve the problems of inability to realize the miniaturization of the camera device, errors, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
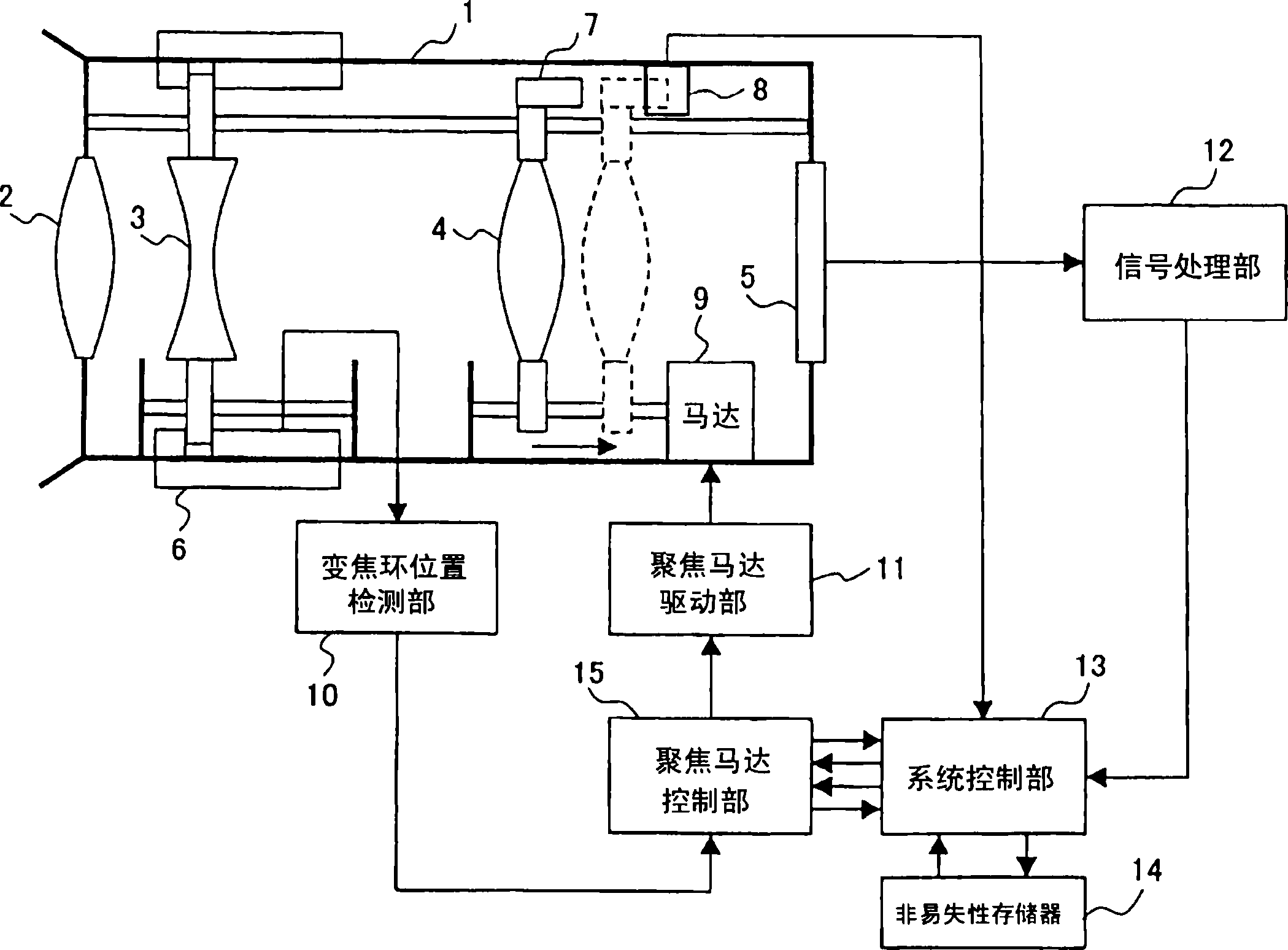
[0179] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram and a block diagram of a lens driving device according to a first embodiment of the present invention. figure 1 Among them, 1 is a lens barrel, 2 is a fixed lens fixed on the lens barrel 1, and 3 is a zoom lens, and the zoom lens 3 rotates the zoom ring 6 along the outer circumference of the lens barrel 1, and the optical axis direction A lens that moves the zoom lens to adjust the zoom magnification. The focus lens 4 is a lens for adjusting focus by moving in the direction of the optical axis along a threaded lead screw by rotation of a motor 9 as a driving mechanism.
[0180] Motor 9 is a stepping motor, in figure 1 In an example, the rotation is performed according to the phase of the motor coil drive signal (excitation signal) output from the focus motor drive unit 11 . Reference numeral 5 denotes an imaging element as an imaging device, which converts an image of an object captured after passing through the fixed lens 2, the...
no. 2 approach
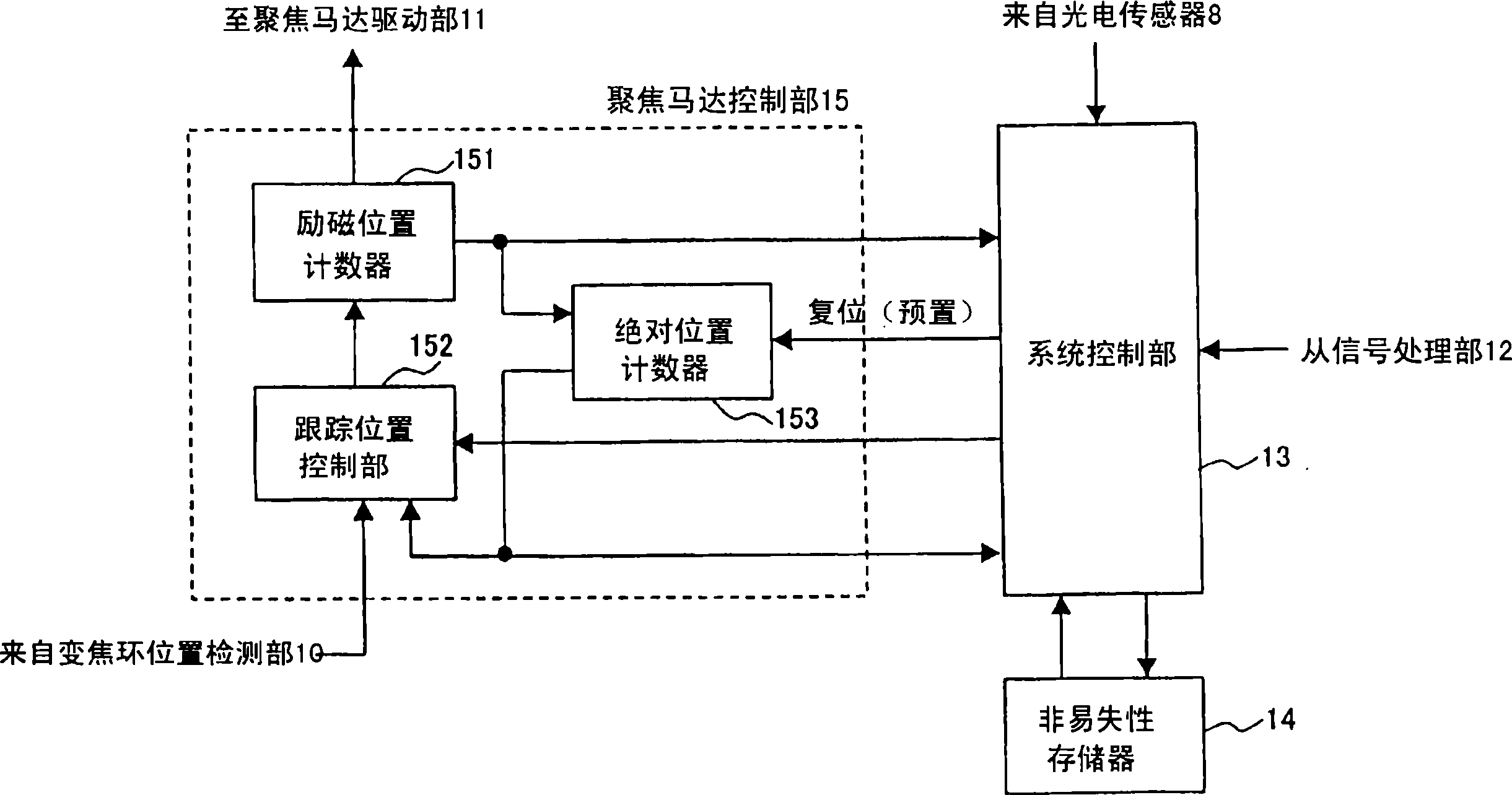
[0223] Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described. described in the first embodiment figure 1 , figure 2 The structure shown, and the image 3 , 4 The origin detection operation at the time of the described process adjustment is also the same in the second embodiment.
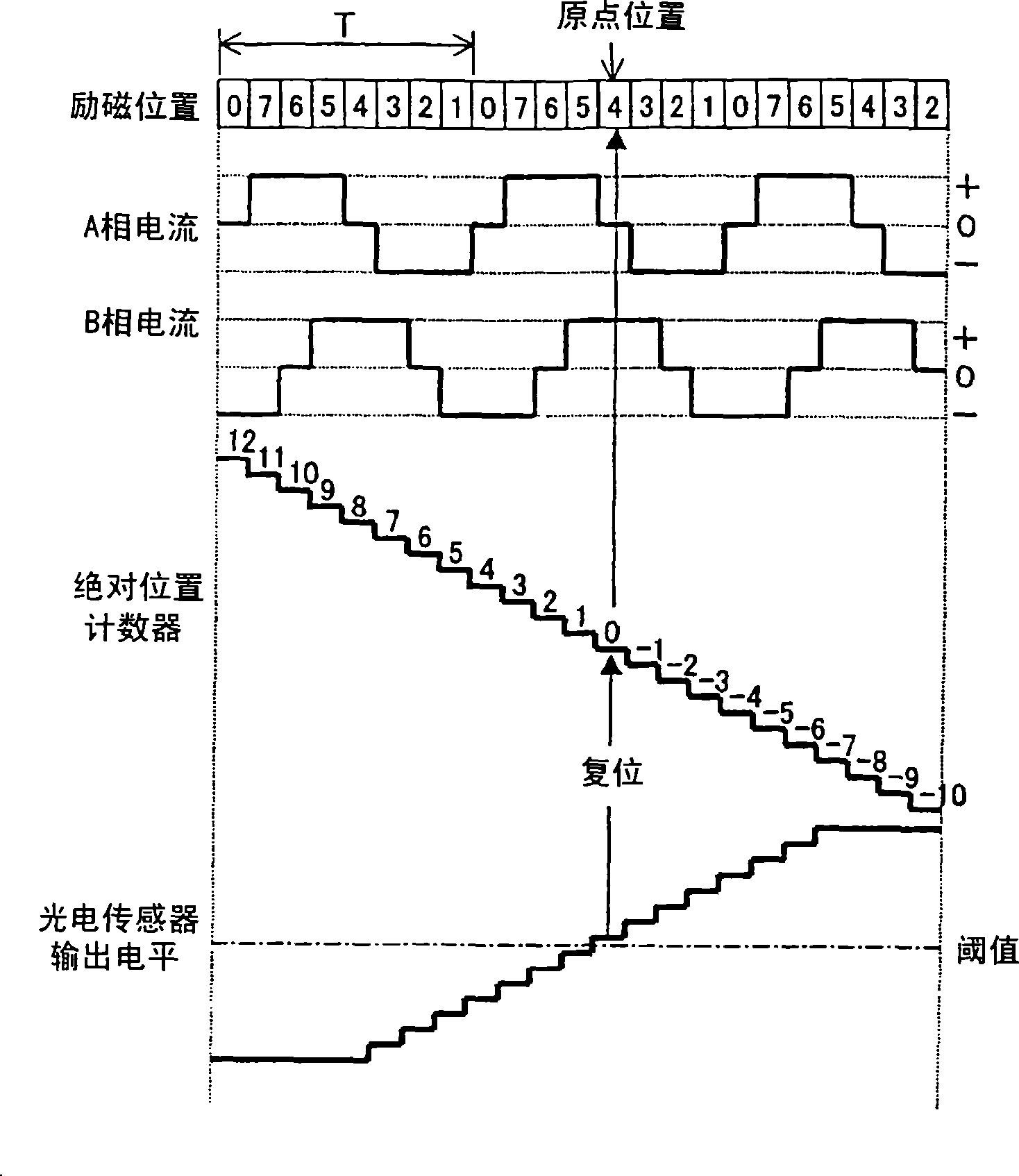
[0224] refer to Figure 8 , 9 , the origin detection operation of the focus lens 4 in normal use in the second embodiment will be described. Figure 8 It is an explanatory diagram of the origin detection operation in normal use according to the second embodiment. also, Figure 8 The excitation position, A-phase current, B-phase current, absolute position counter and photoelectric sensor output level indicated by image 3 The description is the same as in , so the description of the overlapping part is omitted.
[0225] In the second embodiment, unlike the first embodiment, the excitation position is decremented by two as the focus lens 4 moves toward the imaging element 5 si...
no. 3 approach
[0236] Next, a third embodiment of the present invention will be described. For the same as described in the first embodiment figure 1 , figure 2The structure shown is repeated, and the explanation is omitted. In the third embodiment, an example in which the focus motor drive unit 11 rotationally drives the drive motor 9 by approximately sinusoidal drive (also referred to as micro-step drive) will be described. also, figure 2 The excitation position counter 151 in is a 5-bit counter that expresses one cycle (360 degrees) of the driving electrical angle of the motor 9 with a count value of 32, and the absolute position counter 153 operates synchronously with the count value of the excitation position counter 151, as specified later. Conditions are preset or reset.
[0237] Below, refer to Figure 10 Explain its action. Figure 10 It is an explanatory diagram of the origin detection operation at the time of process adjustment in the third embodiment. Figure 10 The ind...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com