Blade assembly with damping elements
a technology of damping elements and blades, which is applied in the direction of marine propulsion, vessel construction, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of inability to convert vibration energy in low oscillation modes into frictional energy to a sufficient degree, and insufficient effectiveness of above damping elements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
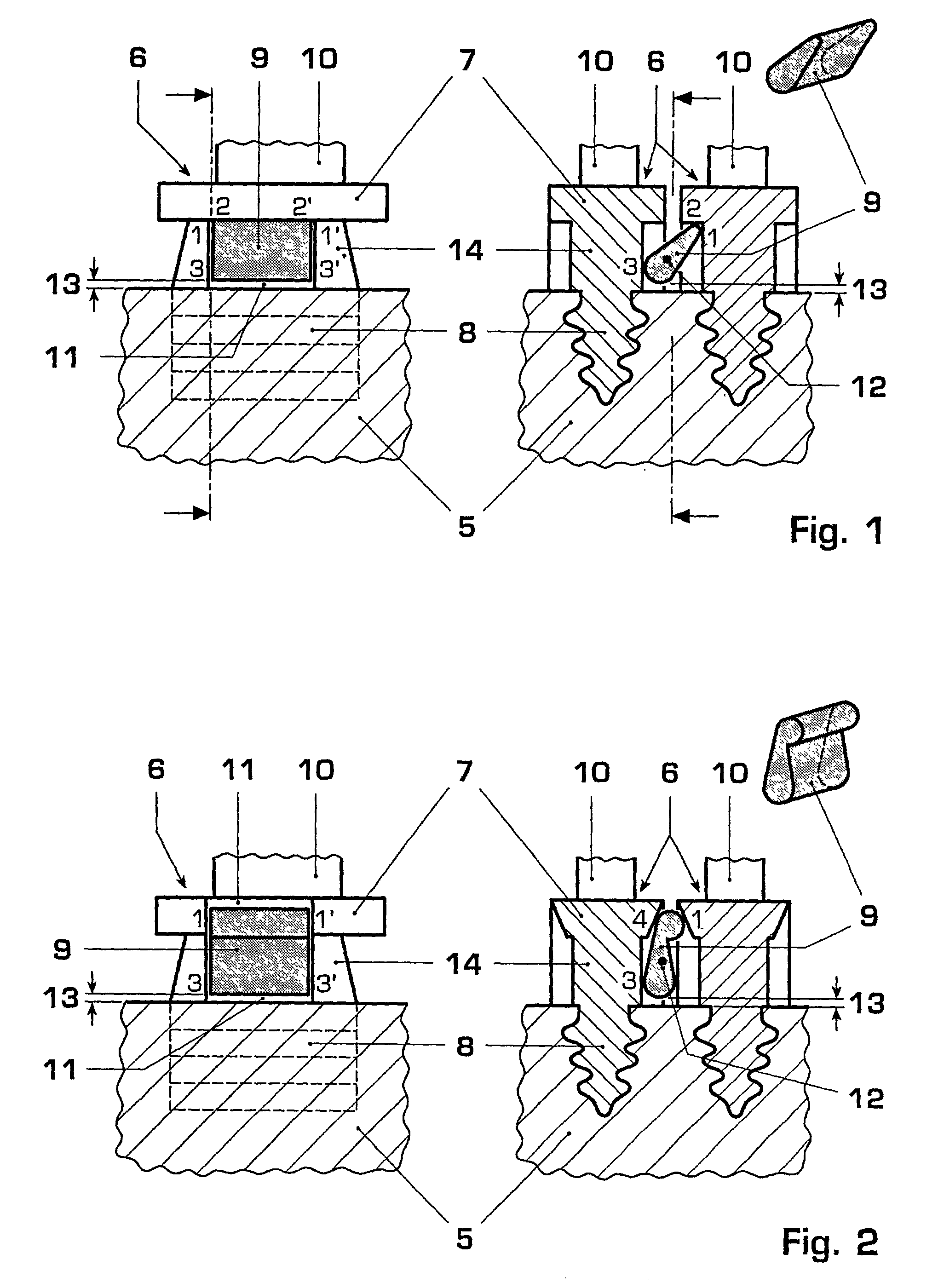
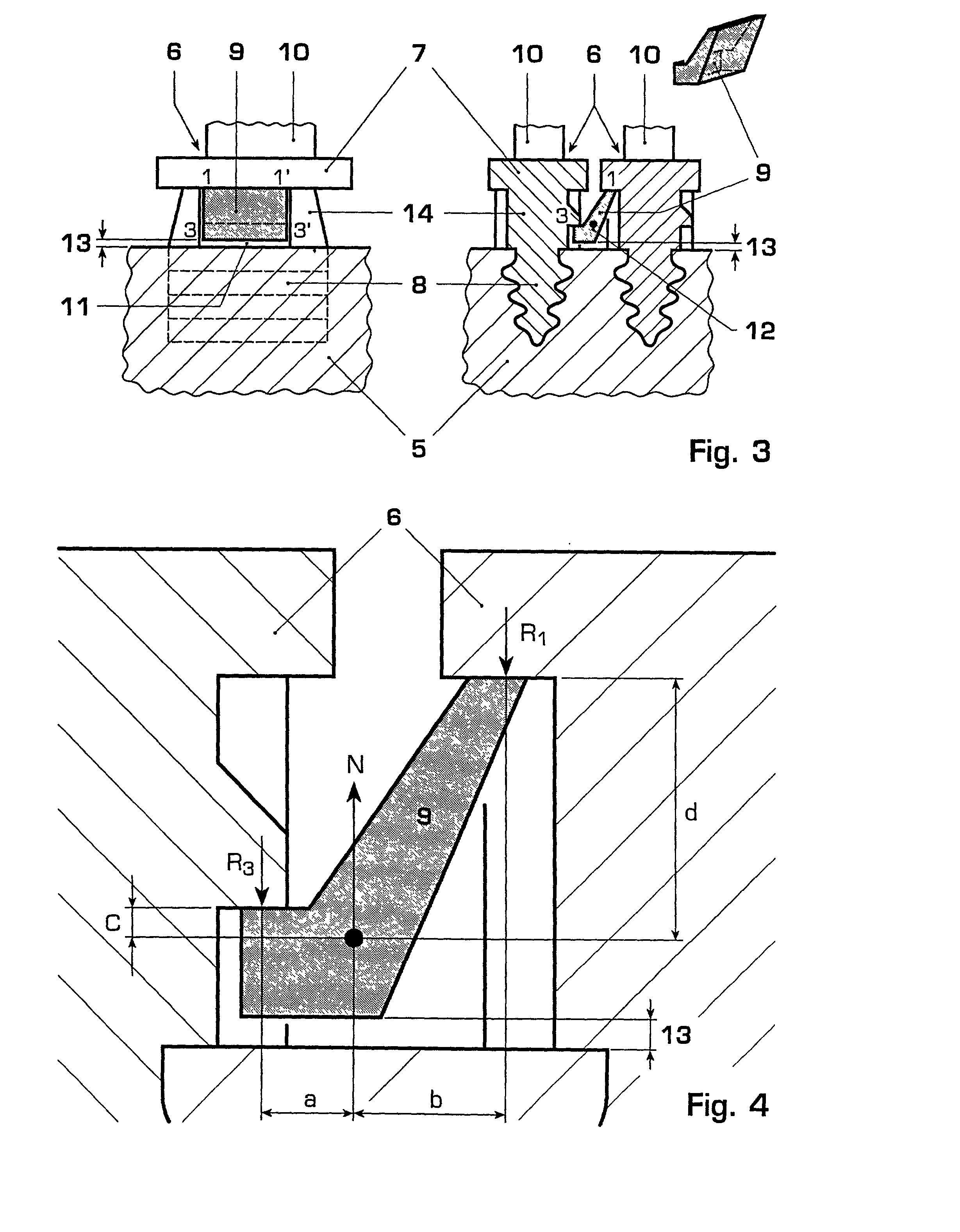
[0022] FIG. 1 shows a detail of a first example of an embodiment of the blade assembly according to the invention. A section through the blade assembly parallel to the axis of rotation is shown here in the left-hand part of the figure. The sectional plane includes the axis of rotation. In this partial view, it is possible to see the rotor 5 into which the root 8 of a blade in which the root 8 of a blade 6 s installed in a manner known per se. The shank 14 and the blade platform 7 extend between the blade element 10 (illustrated only schematically) and the rotor 5. The same arrangement is illustrated in the right-hand part of the figure in a section perpendicular to the axis of rotation, that is to say in a radial plane. A detail from the rotor 5 with two inserted blades 6 (blade i; adjacent blade i+1) with the blade platforms 7 and the shanks 14 protruding out of the rotor can also be seen here.
[0023] In this example, a damping element 9 is arranged between the adjacent blades and i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com