Plastic profile for sealing air gaps between body parts of motor vehicles
a technology for air gaps and motor vehicles, applied in the field of foam strips, can solve the problems of difficult and complicated fixing or inserting of foam strips into gaps to be sealed, deformation of enamel spots, etc., and achieves the effects of safe and durable support of foam profiles, convenient removal from car body parts, and efficient adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
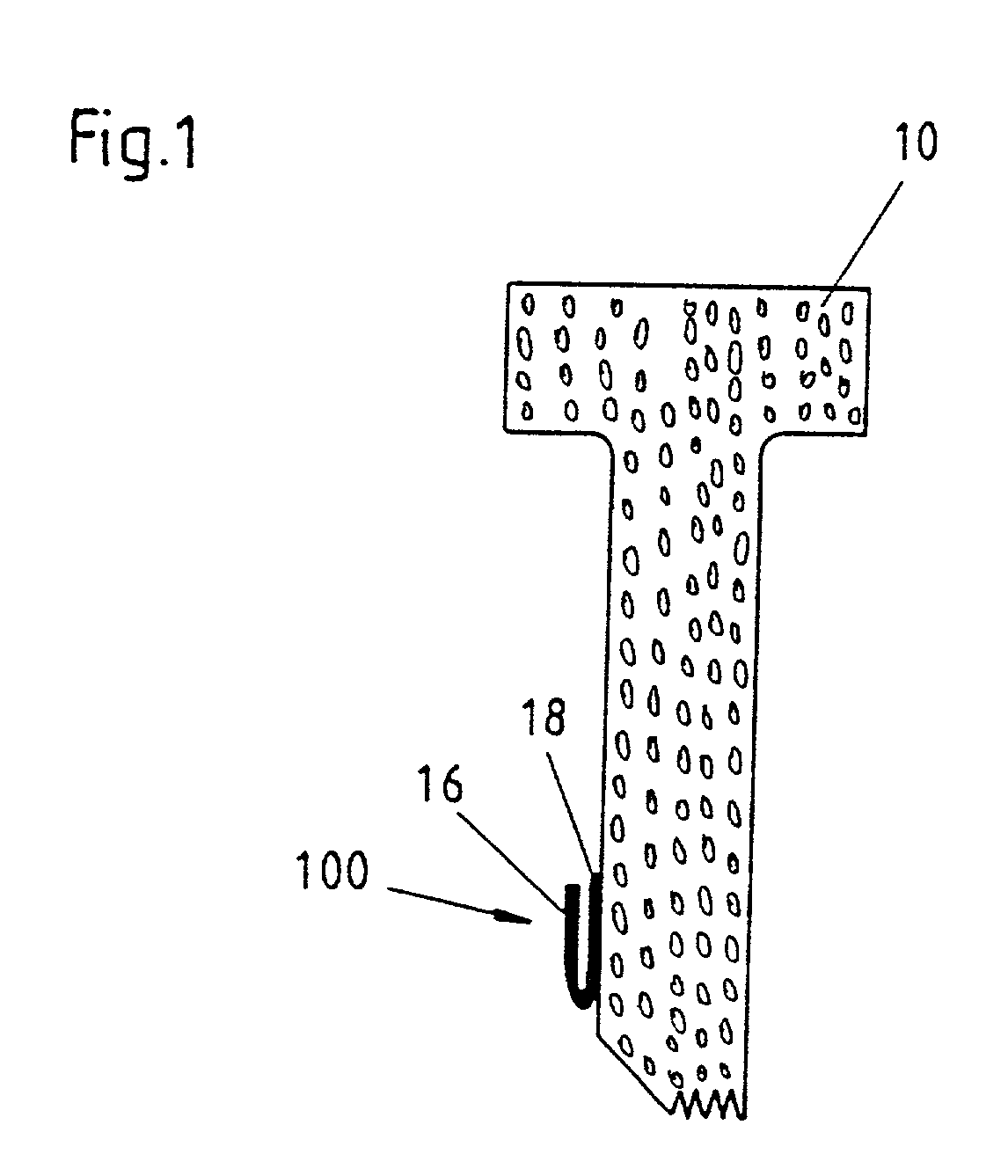
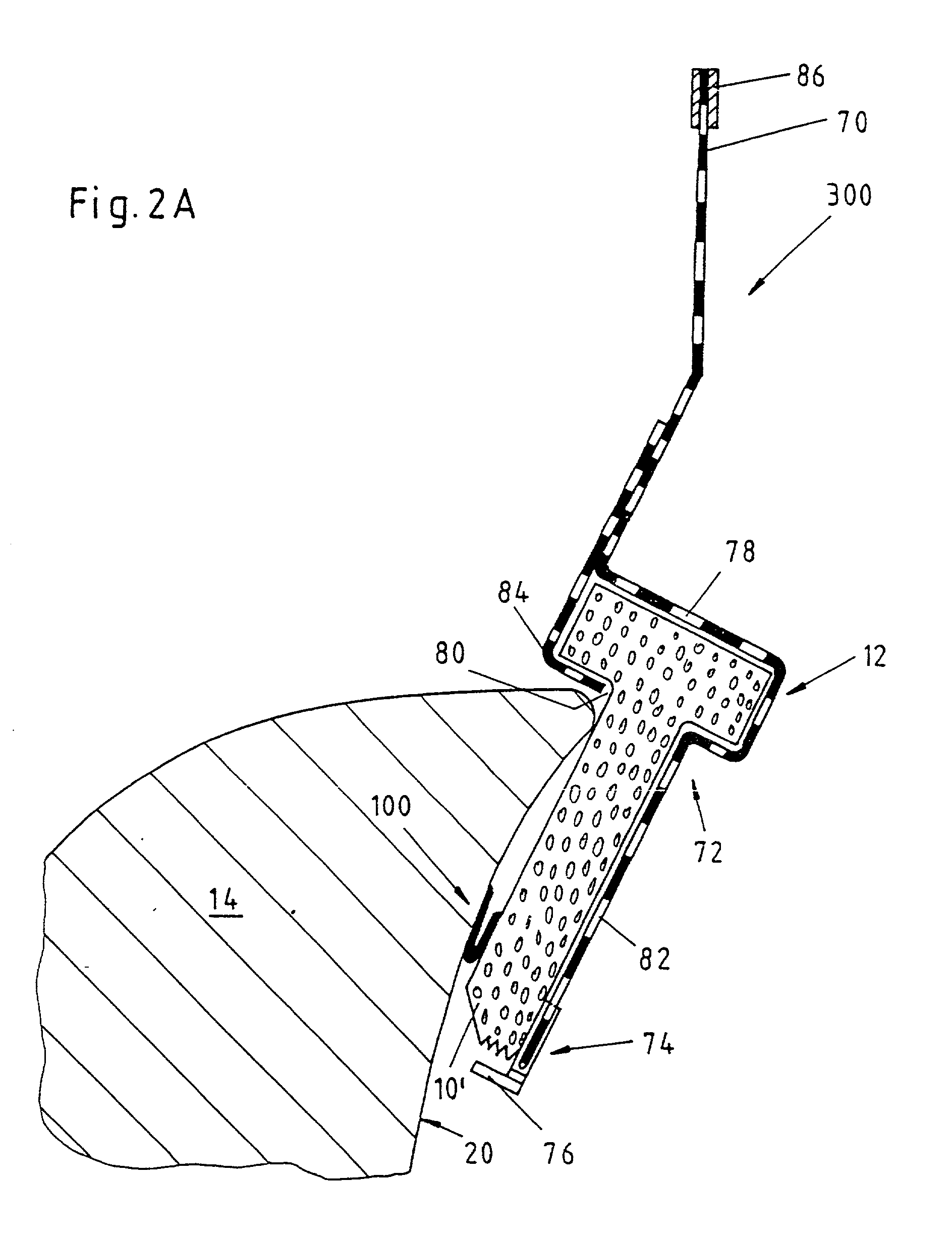
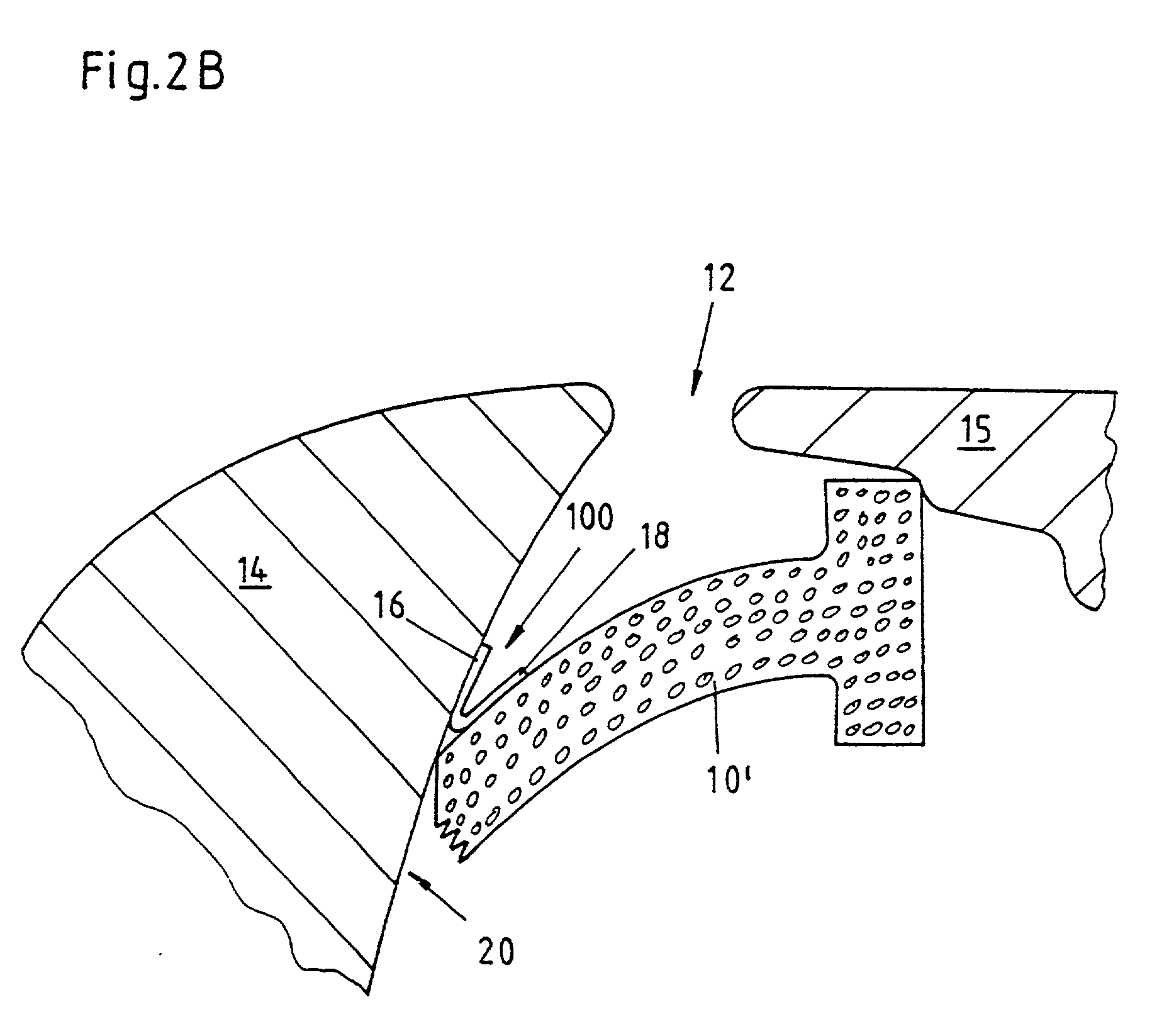
[0188] FIGS. 3A and 3B illustrate the same process as FIGS. 2a and 2B, however with another embodiment of the foam strip 10. For this embodiment, the foam strip 10' is approximately rectangular. A represented second embodiment of the applicator 400 is appropriately adapted with its rail 78 of the receptacle 72. As may be seen in FIG. 3B, the hinge type swinging open of the fixing means again assures that the adhesive joint between the leg 16 and the car body part 14 is, as far as possible, free from the lateral power on the foam strip 10'.
[0189] Moreover, the applicator 400 has a second stopper 84, adjustable over a screw 88, and an elastic rubber profile 76 at the lower end in FIG. 3A of the first stopper 82. This rubber profile 76 secures the foam strip 10' in the applicator 400, since a corresponding design of the rail 78 and of the foam strip 10, like in FIG. 2A, is missing. Moreover, the rubber profile 76 supports the realization of the adhesive joint between the leg 16 and the...
embodiment 200
[0191] FIGS. 6 and 7 show a further preferred embodiment 200 of the fixing means according to the invention. This fixing means is carried out in two layers, namely with a first layer 50 and a second layer 52. The first layer 50 is a solid nondetachable glue 56 between the second layer 52 and the foam strip 10 or 10'. The first layer 50 constitutes an adhesive joint between the foam strip 10 or 10' and the second layer 52 which is greater than the respective inherent strength of these layers and assures in this way a solid bonding between the fixing means 200 and the foam strip 10 or 10'.
[0192] The second layer 52 is preferably a paper or a plastic strip and is sufficiently big dimensioned for a desired adhesive force.
[0193] The FIGS. 6 and 7 or 4 and 5 only differ from each other by different embodiments of the profile of the plastic strip 10 or 10'. Once a rectangular profile is represented, once a T-shaped profile; however, any other profile, adequate for sealing the gap 12, is al...
embodiment 1200
[0209] The embodiment 1200 according to FIG. 15 is particularly preferred, since here the fixing means additionaly has a protective function against enamel and its solvents through the sunk joint 220. This is due to the fact that, after the fixing means has adhered to a surface, the lateral borders 222 additionally seal the area of the surface around the adhesive side outwards and thus avoid the penetration of distributed enamel or its solvents. This is represented in FIGS. 31 and 32 for a better illustration.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com