Compositions for isolating a cDNA encoding a membrane-bound protein
a membrane-bound protein and cdna technology, applied in the field of selective and efficient isolating genes encoding membrane-bound proteins, can solve the problems of not being able to know whether it is a secretory protein or a membrane-bound protein, and not being able to achieve the effect of superior selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
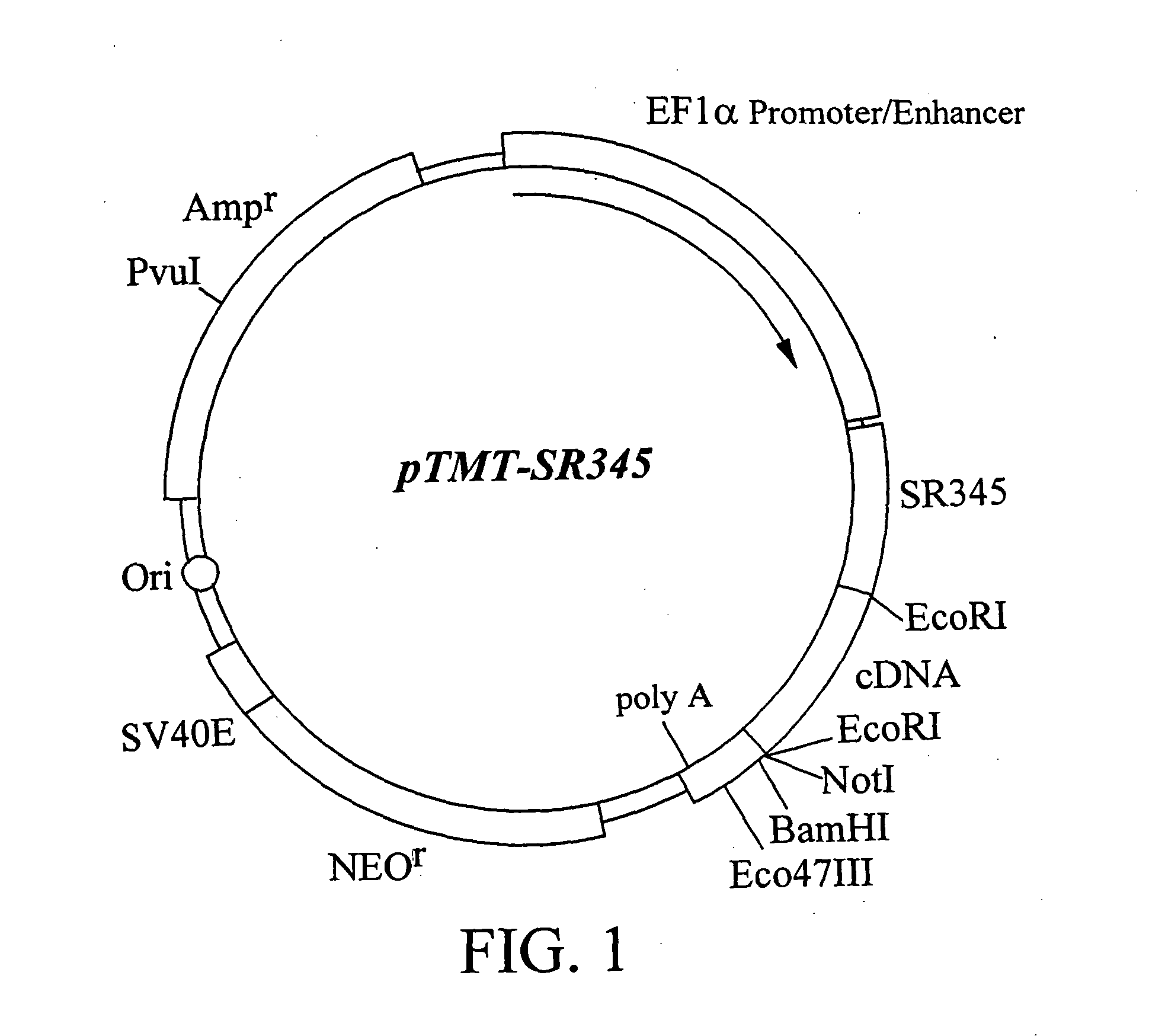
Construction of Expression Cloning Vector pTMT-SR345
[0069] Expression cloning vector pTMT-SR345 was constructed. SR345, encoded by the DNA contained in expression cloning vector pTMT-SR345, is the extracellular region portion of human IL-6 receptor, and consists of 345 amino acid residues from the N terminus. In the expression cloning vector pTMT-SR345, the protein encoded by cDNA inserted downstream of the DNA encoding SR345 is expressed as a fusion protein with SR345. The nucleotide sequence of SR345 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 together with the amino acid sequence.
[0070] First, in order to amplify the app. 1.1 kb fragment containing the cDNA encoding SR345 from the cDNA of IL-6 receptor (Yamasaki, K. et al, Science (1988) 241, 825-828), PCR primers IL6R1 (SEQ ID NO: 3) and IL6R2 (SEQ ID NO: 4) were designed. A PCR reaction mixture (100 ml) containing 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH8.3), 50 mM KCl, 0.1 mM dNTPs, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 100 pmol each of the above-mentioned primers, 100 ng of template DNA ...
example 2
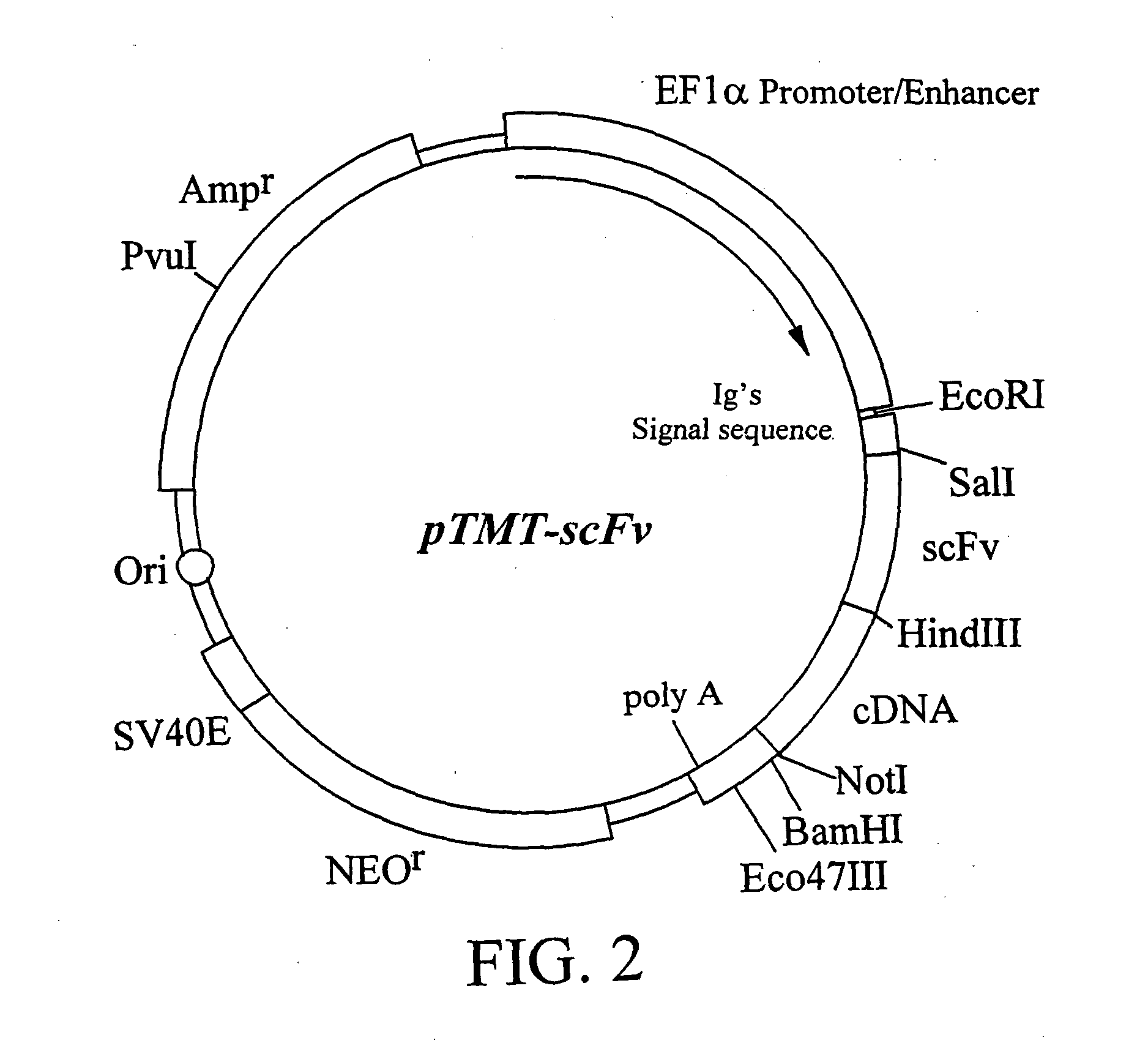
Construction of Expression Vector pTMT-scFv
[0072] Expression vector pTMT-scFv was constructed. The single-chain antibody (scFv) encoded by the DNA contained in the expression vector pTMT-scFv was designed using the variable region of the humanized monoclonal antibody PM-1, which recognizes human IL-6 receptor, and a linker region. In the expression vector pTMT-scFv, the protein encoded by the cDNA inserted downstream of the DNA encoding scFv, is expressed as a fusion protein with scFv. The nucleotide sequence of scFv gene is shown in SEQ ID NO: 5 together with the amino acid sequence.
[0073] 1) Amplification of the DNA Fragment Encoding Antibody V Region
[0074] The genes of humanized PM1 antibody H chain and L chain V region (Sato, K et al, Cancer Res. (1993) 53, 851-856) were amplified by PCR. Backward primer TMT1 (SEQ ID NO: 6) for H chain V region was designed in such a manner that it should hybridize to DNA encoding the N terminus of H chain V region and comprise a SalI restric...
example 3
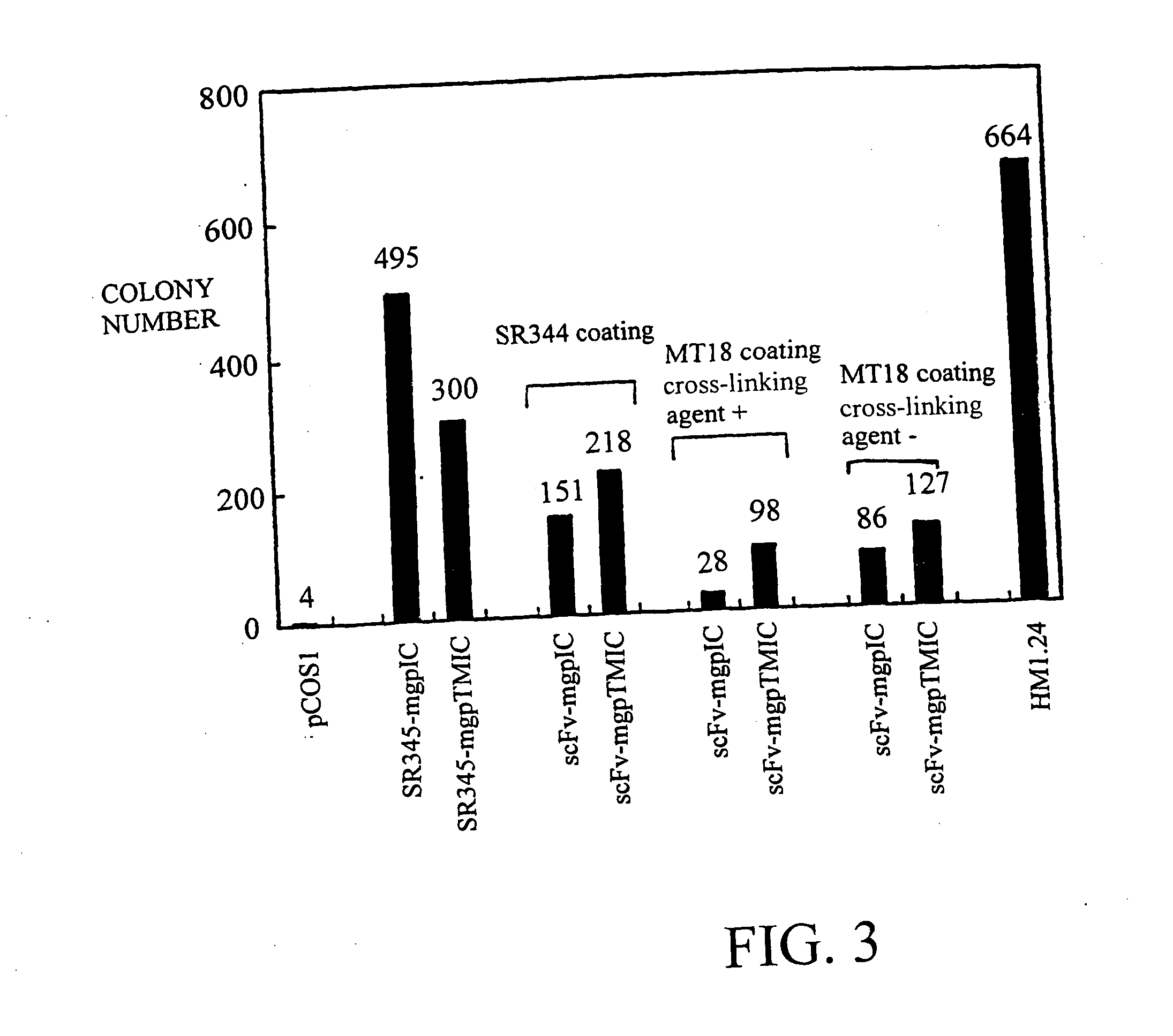
Construction of SR345-gp130 and scFV-gp130 Fusion Protein Expression Systems
[0081] (A) SR345-gp130
[0082] The cytokine signal transduction molecule gp130 is a type I membrane-bound protein (Taga, T. et al., Cell (1989) 58, 573-581 Saito, M., et al., J. Immunol. (1992) 148, 4066-4071). A portion of mouse gp130 cDNA was ligated downstream of a cDNA encoding soluble-type IL-6 receptor (SR345) of the expression vector pTMT-SR345, to express a fusion protein comprising SR345 and a partial sequence of mouse gp130, in COS cells. Two types of fusion proteins were constructed according to their differences in the gp130 partial regions. One of them is a membrane-bound fusion protein (SR345-mgpTMIC) in which the transmembrane region of gp130 and the subsequent intracellular region are ligated, and the other is a secretory fusion protein (SR345-mgpIC) in which only the intracellular region of gp130 is ligated. SEQ ID NO: 17 shows the amino acid sequence and the nucleotide sequence of full-leng...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap