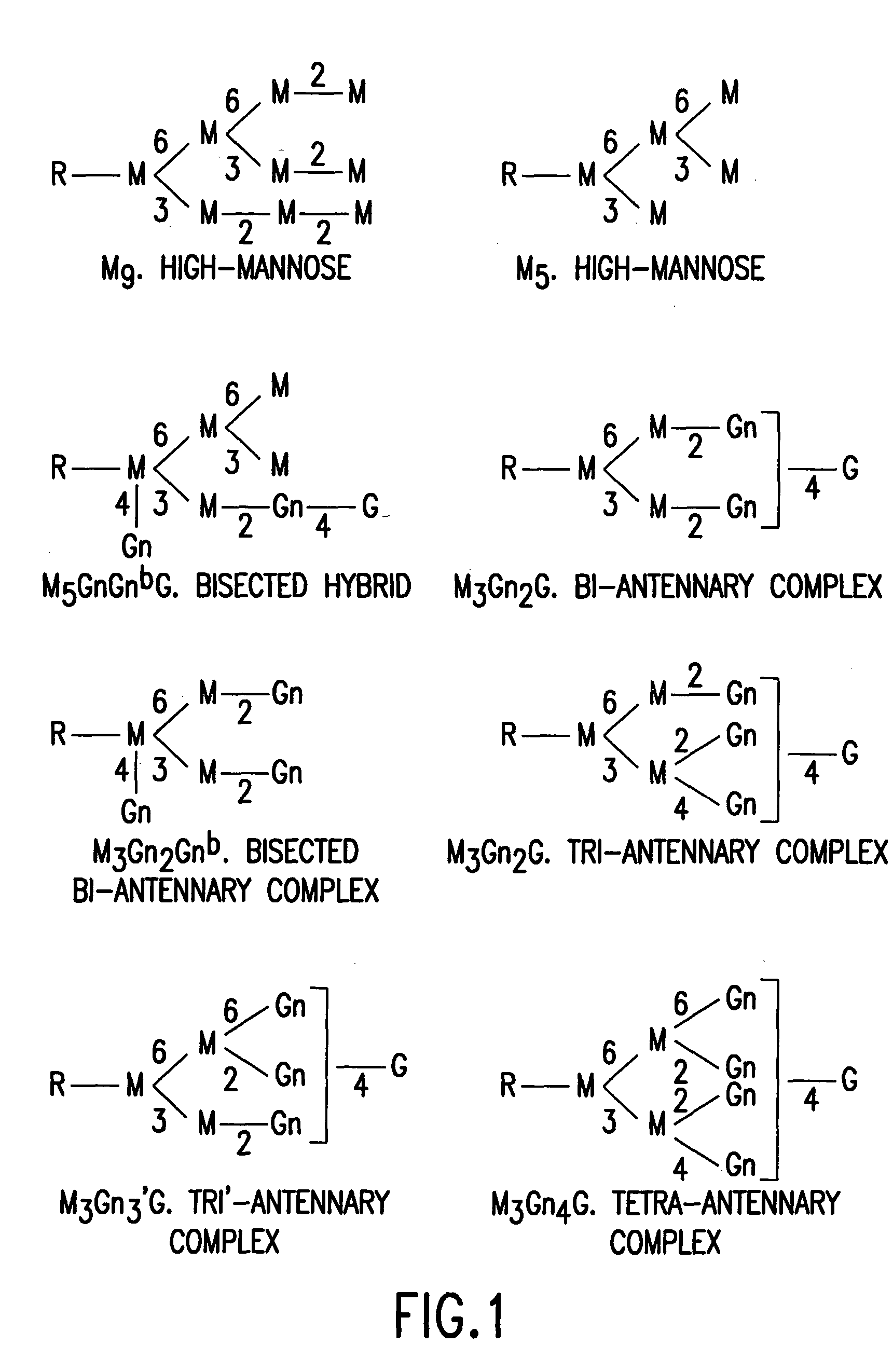
Glycosylation engineering of antibodies for improving antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
a technology of glycosylation engineering and antibodies, which is applied in the direction of peptides, drug compositions, and fused cells, can solve the problems of little attention to expression levels and reduce biological activity, and achieve the effect of improving therapeutic values and enhancing fc-mediated cellular cytotoxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
A. Example 1
Tetracycline-Regulated Overexpression of Glycosyl Transferases in Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells
[0085] To establish a cell line in which the expression of GnT III could be extemally-controlled, a tetracycline-regulated expression system was used. Gossen, M. and Bujard, H., 1992, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 89: 5547-5551. The amount of GnT III in these cells could be controlled simply by manipulating the concentration of tetracycline in the culture medium. Using this system, it was found that overexpression of GnT III to high levels led to growth inhibition and was toxic to the cells. Another CHO cell line with tetracycline-regulated overexpression of GnT V, a distinct glycoprotein-modifying glycosyl transferase, showed the same inhibitory effect, indicating that this may be a general feature of glycoprotein-modifying glycosyl transferase overexpression. This phenomenon has not been reported previously, probably due to the fact that inventigators generally have used constitu...
example 2
B. Example 2
Inhibition of Cell Growth Effected by Glycosyl Transferase Overexpresseion
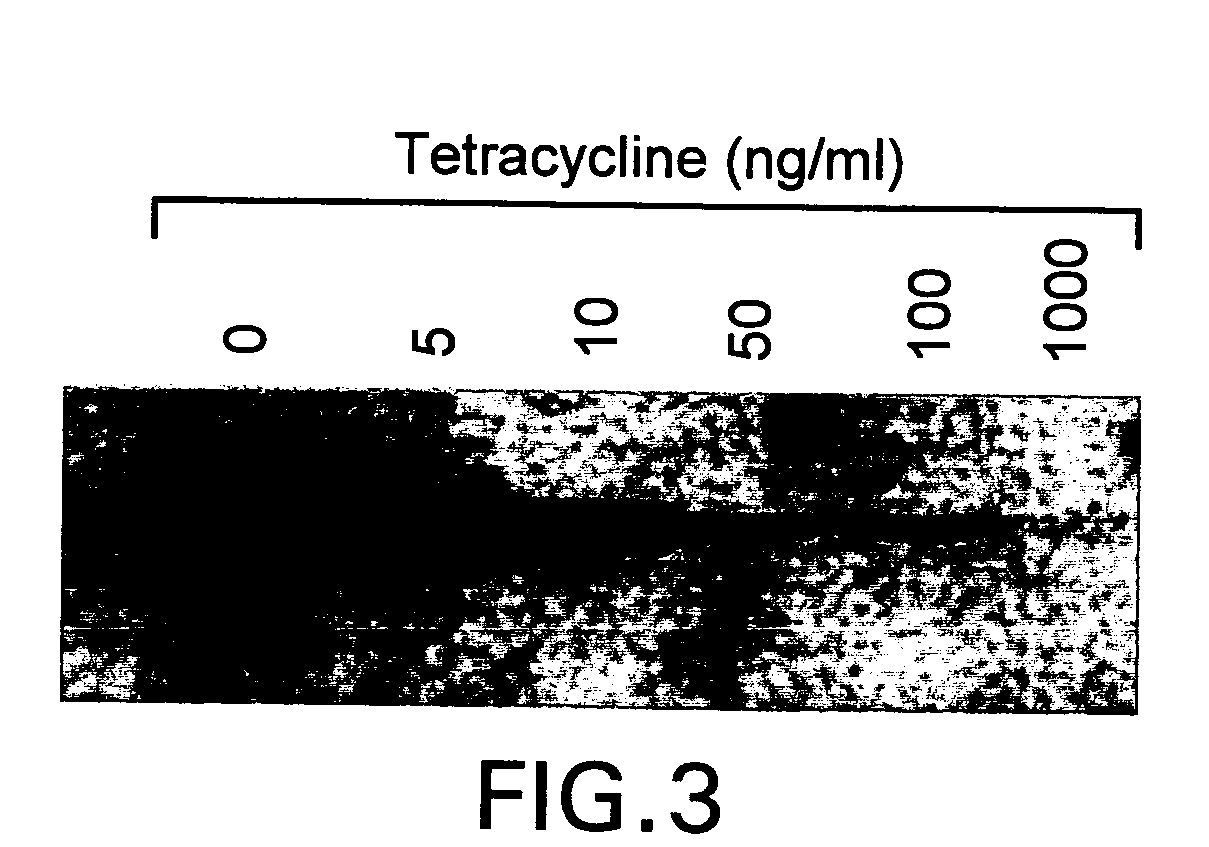
[0096] During screening of GnT III- and GnT V-expressing clones in the absence of tetracycline, see, Example 1, supra, approximately half of each set of clones showed a strong inhibition of growth. The extent of growth-inhibition varied among clones, and comparison with expression levels estimated from western blot analysis (FIG. 4) suggested a correlation between the degree of growth-inhibition and glycosyl transferase overexpression. This correlation was firmly established by growing the final clones, CHO-tet-GnT IIIm and CHO-tet-GnT V, in different concentrations of tetracycline. A strong inhibition of growth was evident after two days of culture at low levels of tetracycline (FIG. 6). Growth-inhibited cells displayed a small, rounded morphology instead of the typical extended shape of adherent CHO cells. After a few days, significant cell death was apparent from the morphology of the growth-in...
example 3
C. Example 3
Engineering the Glycosylation of an Anti-Human Neuroblastoma Antibody in Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells
[0101] In order to validatelthe concept of engineering a therapeutic antibody by modifying its glycosylation pattern, a chimeric anti-human neuroblastoma IgG1 (chCE7) was chosen which has insignificant ADCC activity when produced by SP2 / 0 recombinant mouse myeloma cells. ChCE7 recognizes a tumor-associated 190-kDa membrane glycoprotein and reacts strongly with all neuroblastoma tumors tested to date. It has a high affinity for its antigen (Kd of 1010M−1) and, because of its high tumor-specificity, it is routinely used as a diagnostic tool in clinical pathology. Amstutz et al., 1993, Int. J. Cancer 53:147-152. In recent studies, radiolabelled chCE7 has shown good tumor localization in human patients. Durr, 1993, Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 20:858. The glycosylation pattern of chCE7, an anti-neuroblastoma therapeutic monoclonal antibody (mAb) was engineered in CHO cells with tetracy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com