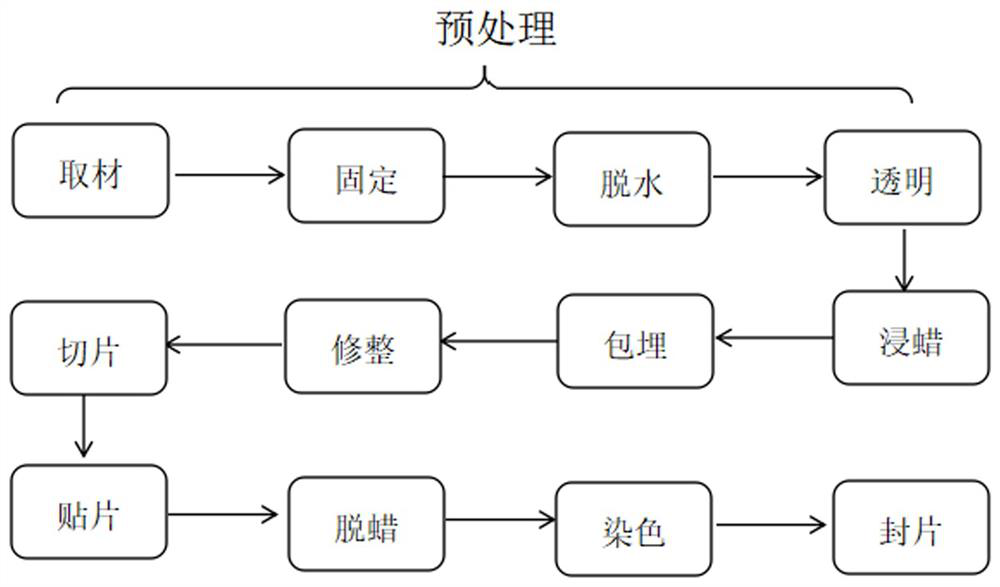
Patents
Literature
54 results about "Clinical pathology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Clinical pathology (US, UK, Ireland, Commonwealth, Portugal, Brazil, Italy, Japan, Peru), Laboratory Medicine (Austria, Germany, Romania, Poland, Eastern Europe), Clinical analysis (Spain) or Clinical/Medical Biology (France, Belgium, Netherlands, North and West Africa...), is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the laboratory analysis of bodily fluids, such as blood, urine, and tissue homogenates or extracts using the tools of chemistry, microbiology, hematology and molecular pathology. This specialty requires a medical residency.
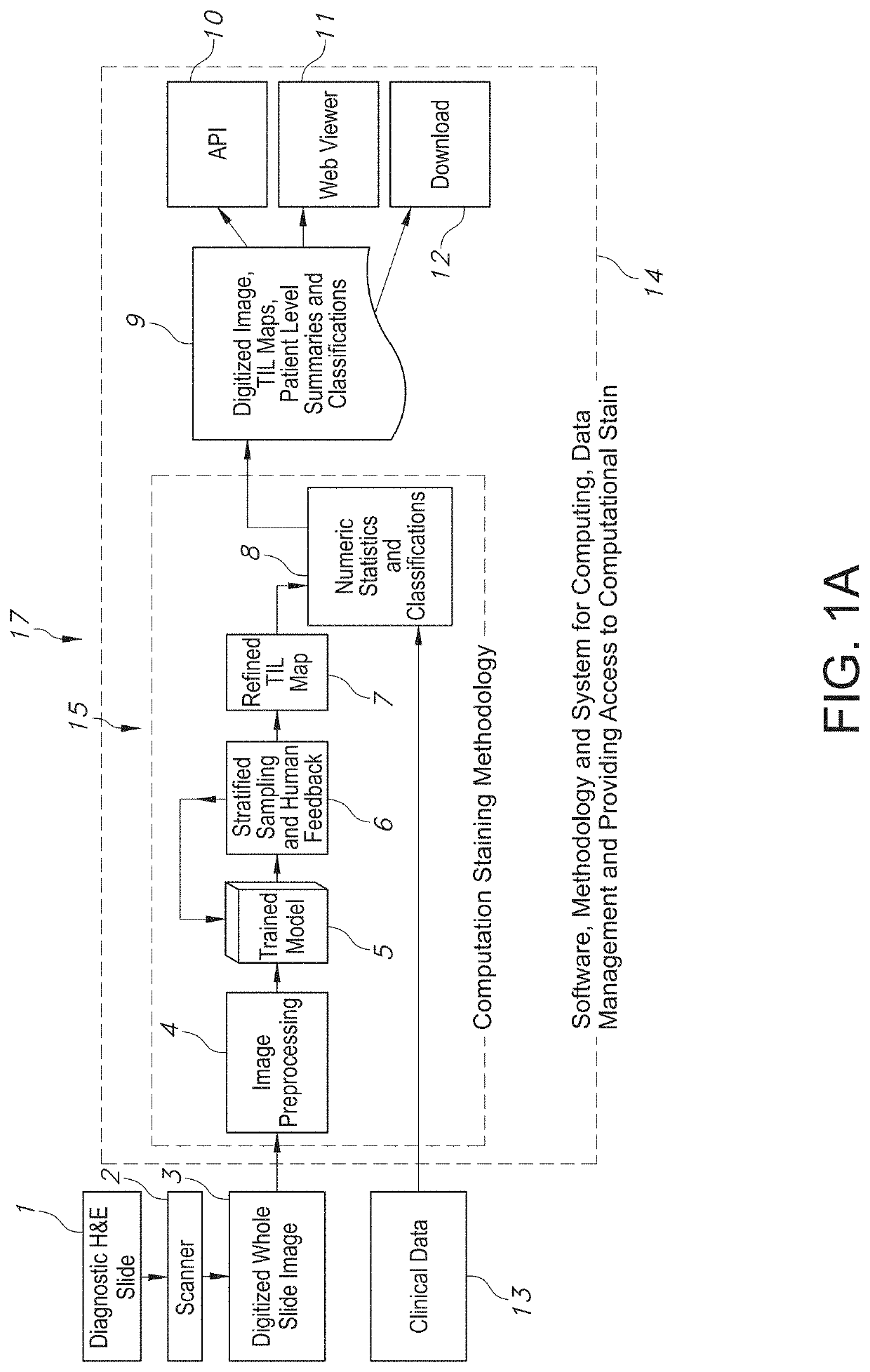
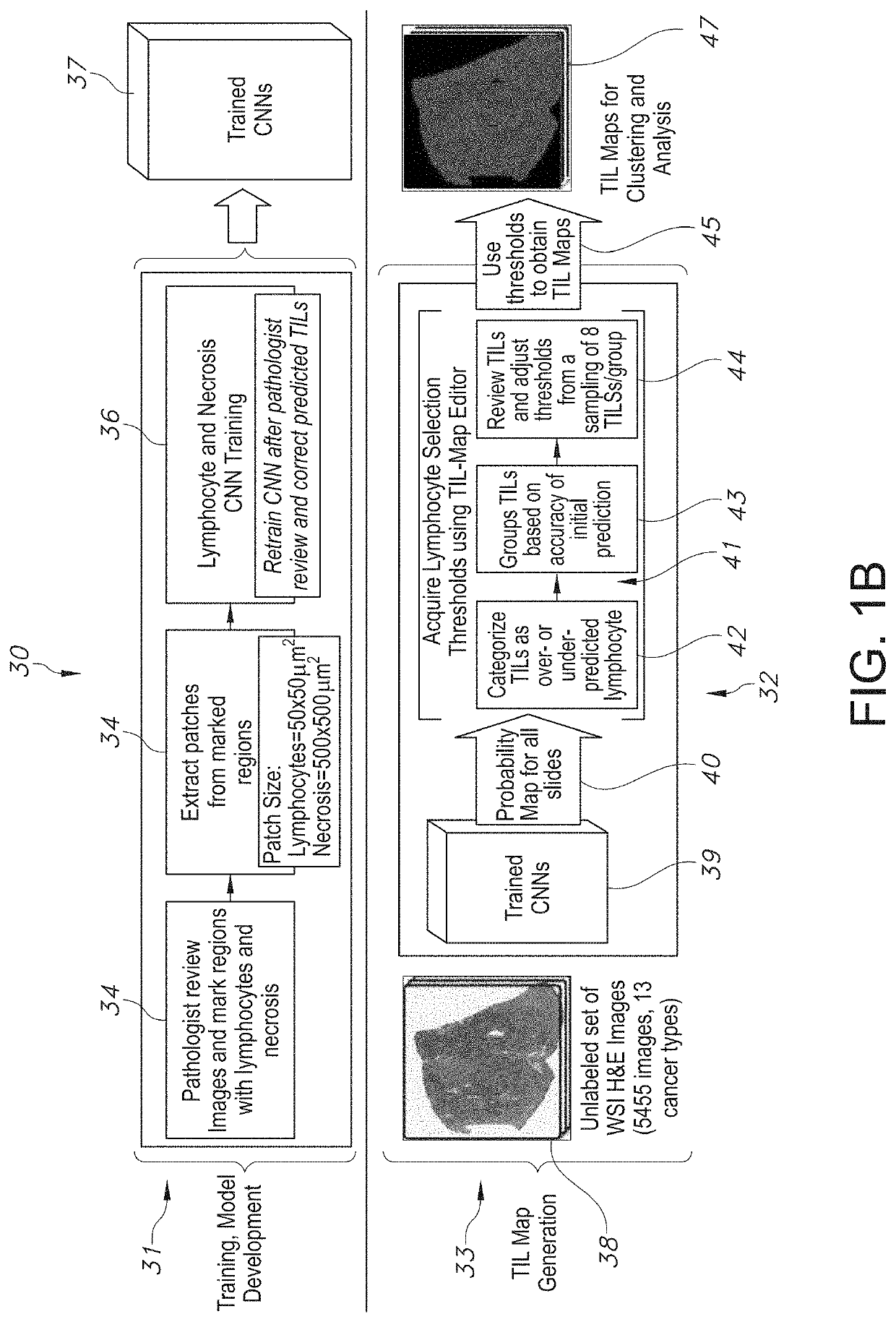
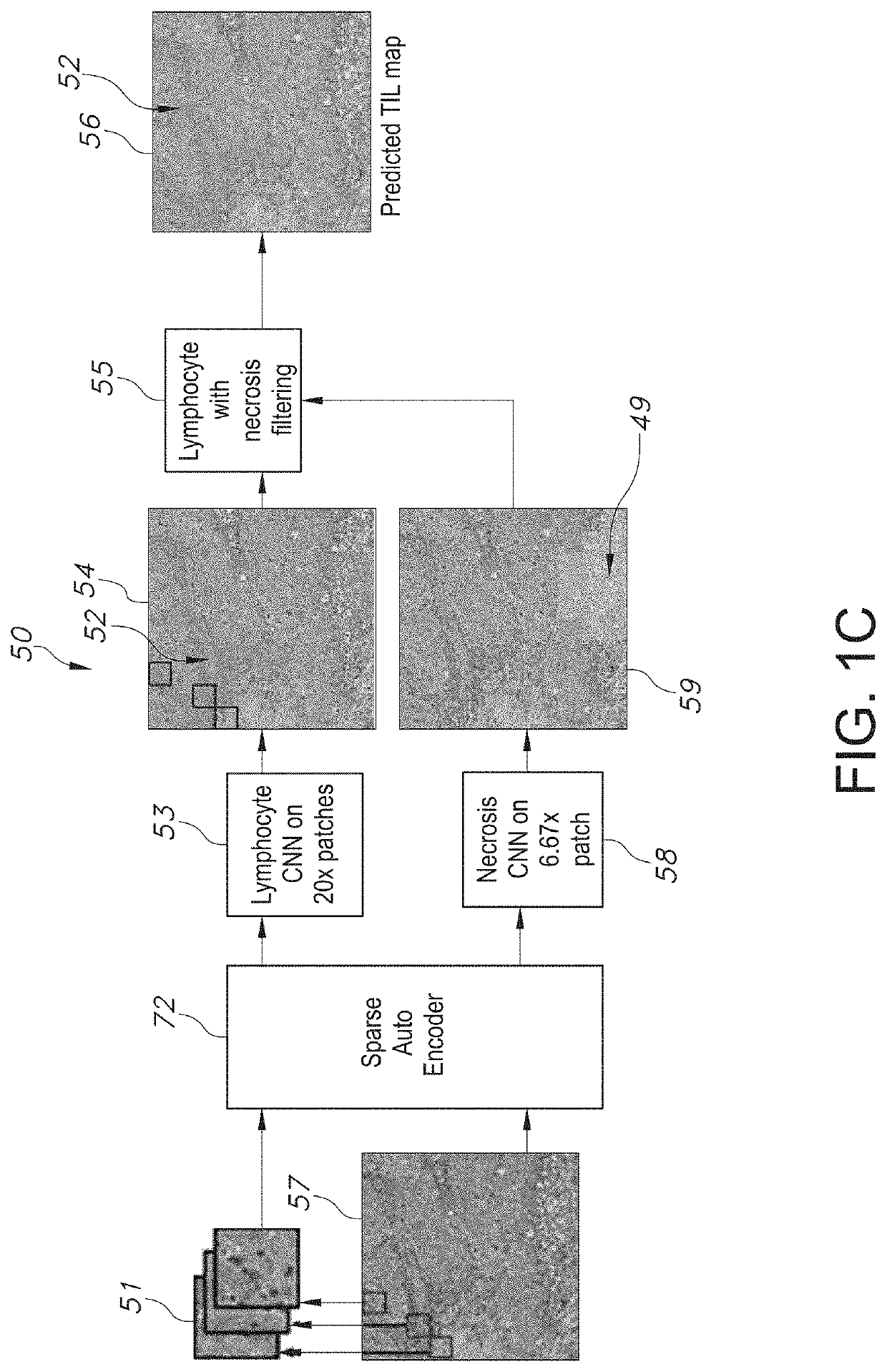
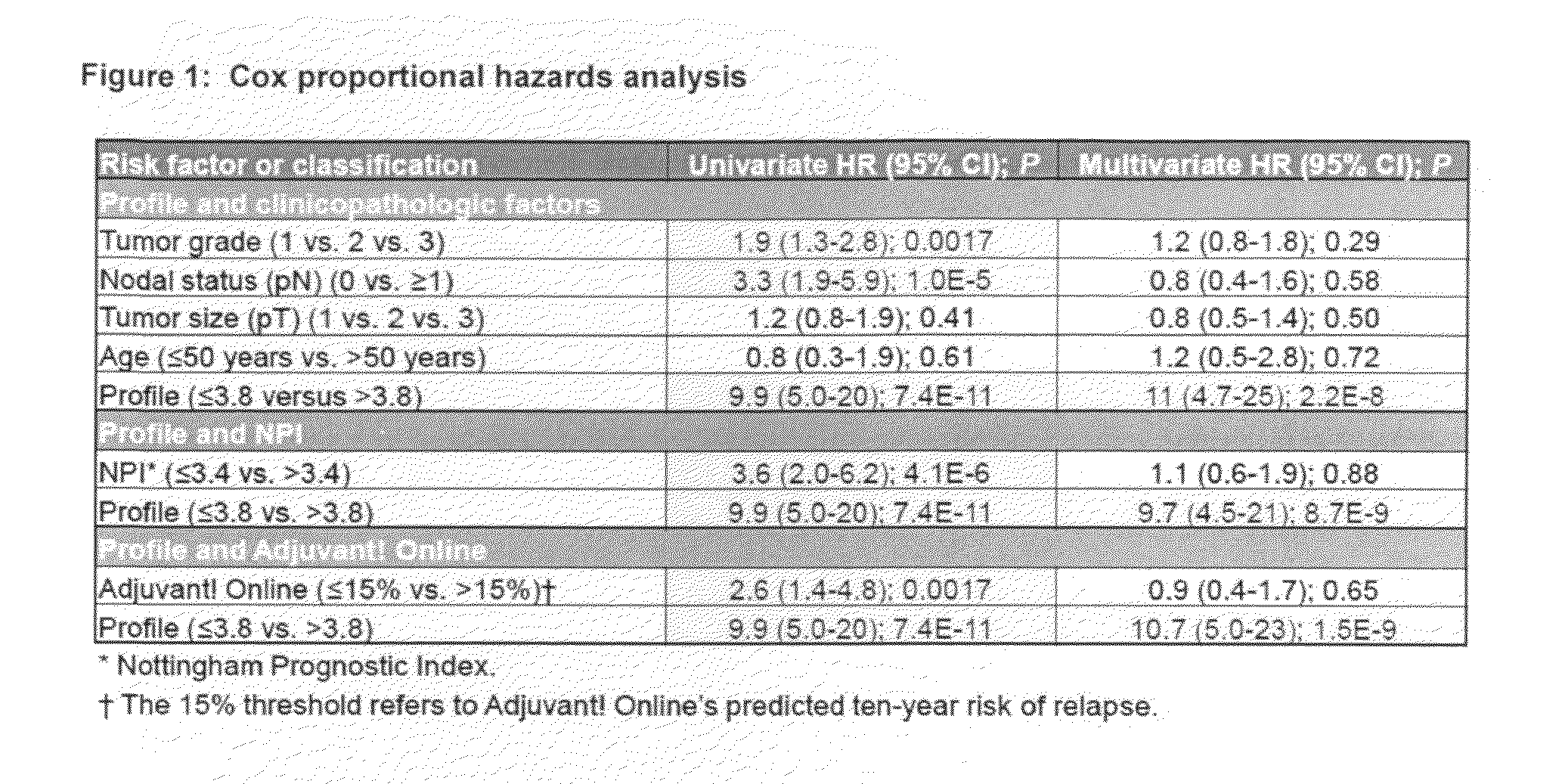
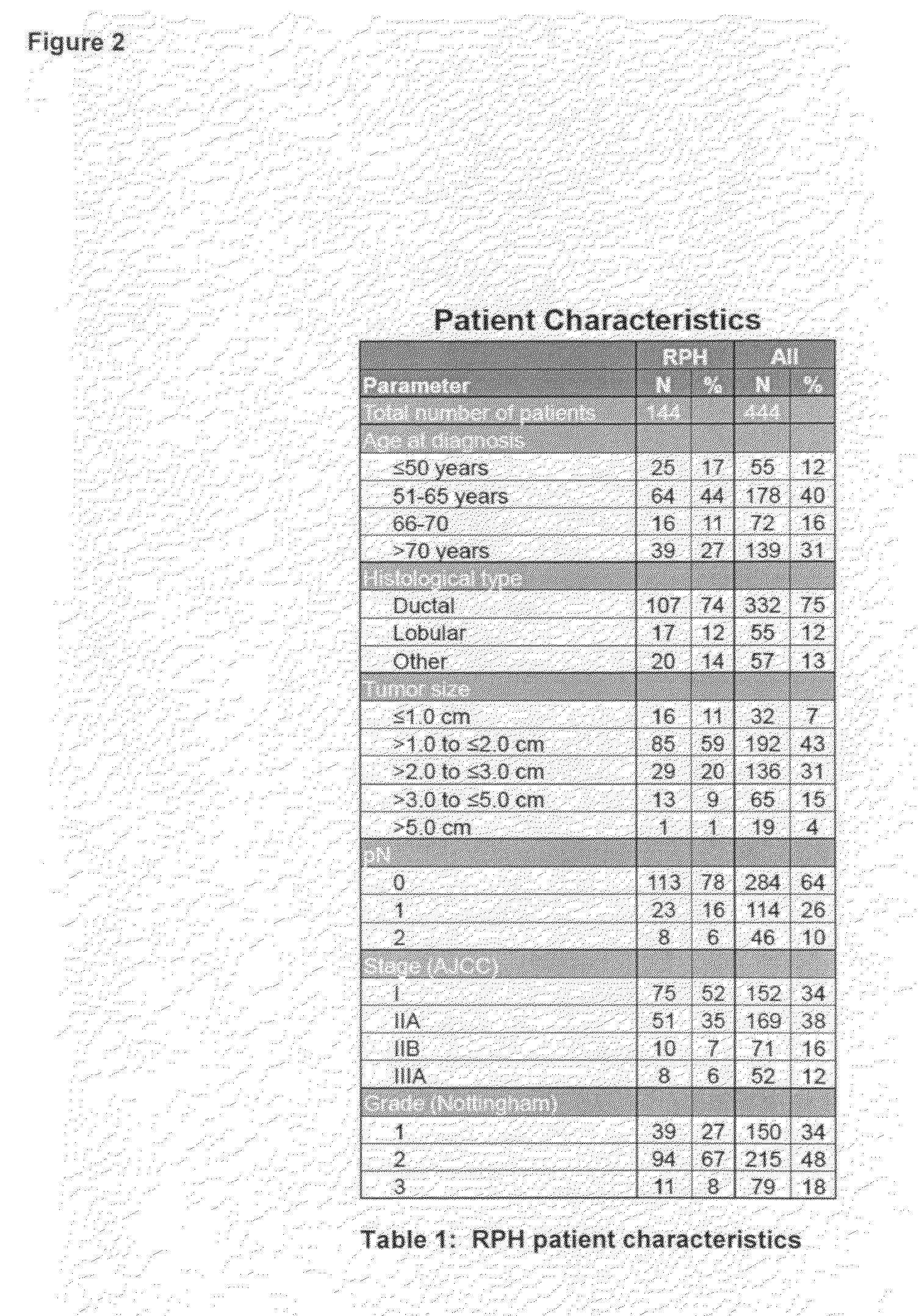
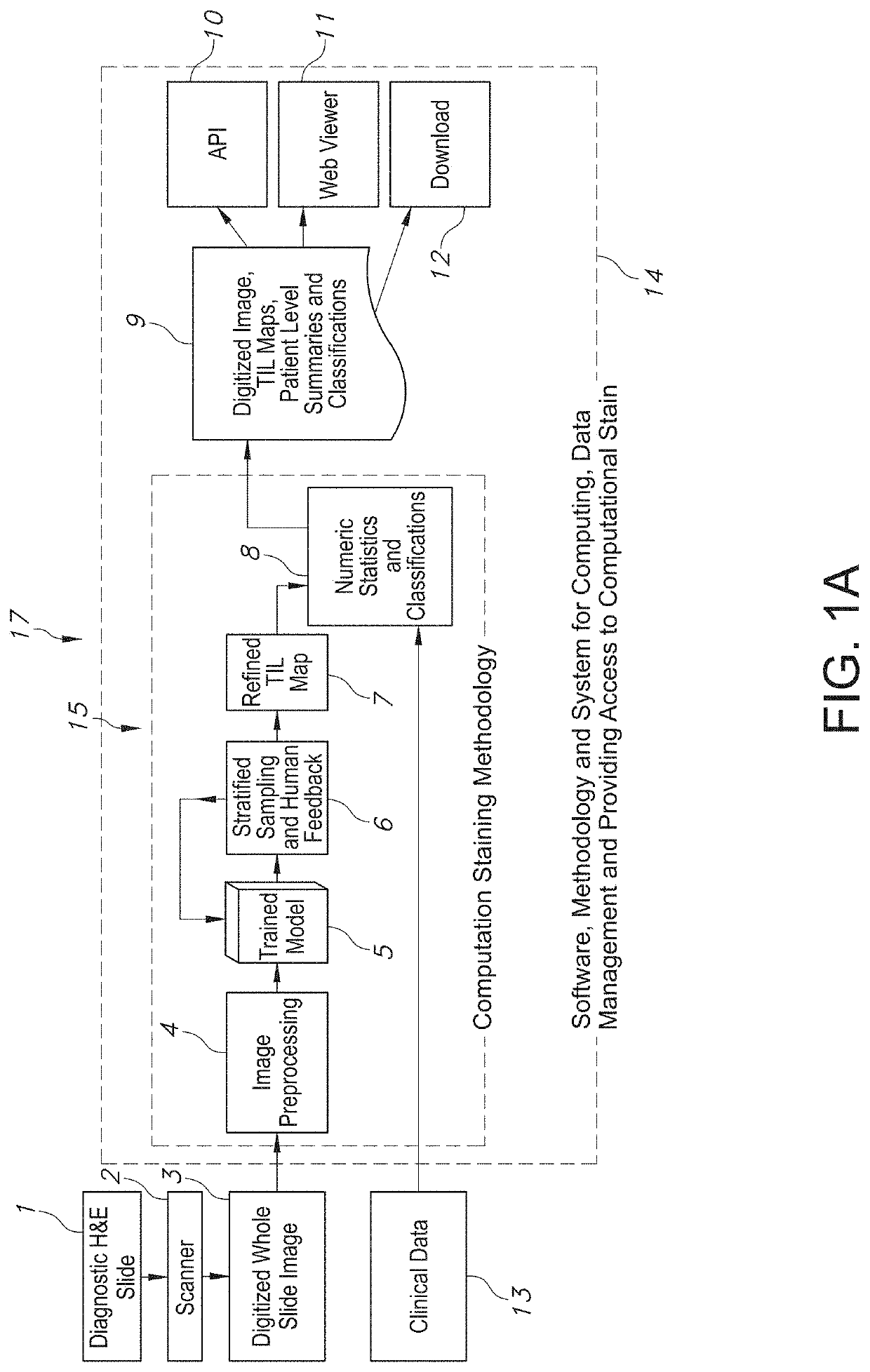
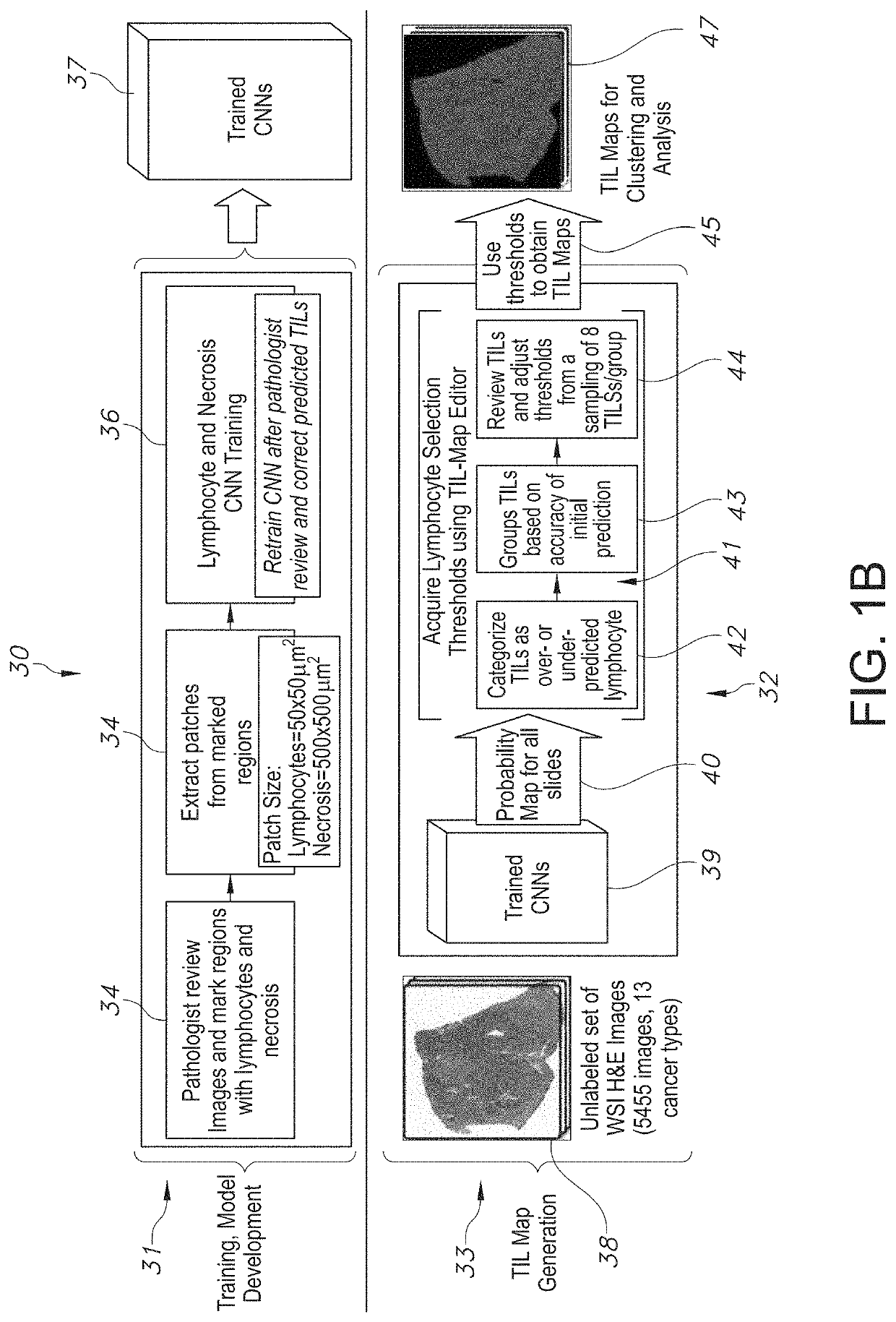
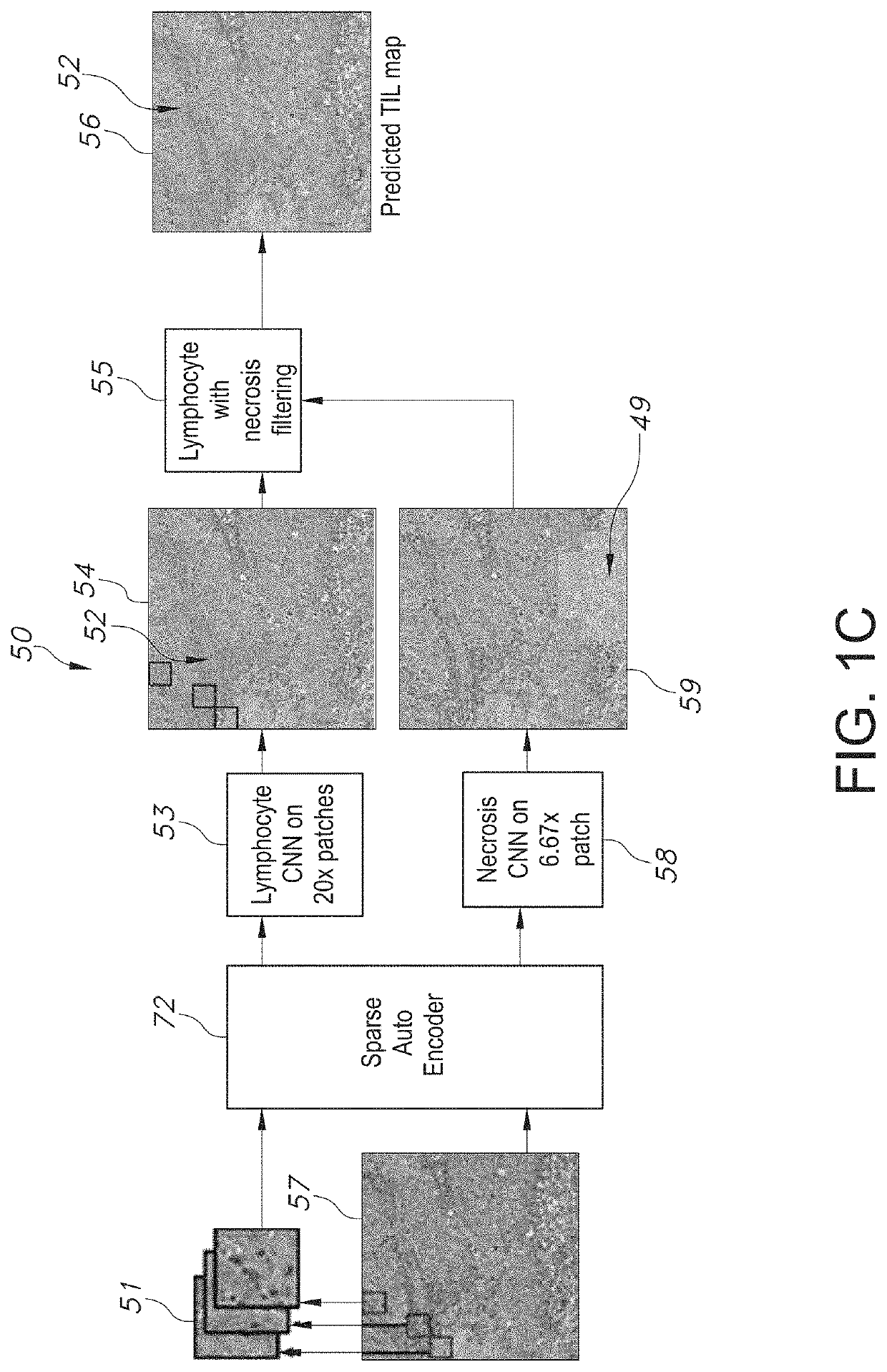
System and Method to Quantify Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) for Clinical Pathology Analysis Based on Prediction, Spatial Analysis, Molecular Correlation, and Reconstruction of TIL Information Identified in Digitized Tissue Images
A system associated with quantifying a density level of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, based on prediction of reconstructed TIL information associated with tumoral tissue image data during pathology analysis of the tissue image data is disclosed. The system receives digitized diagnostic and stained whole-slide image data related to tissue of a particular type of tumoral data. Defined are regions of interest that represents a portion of, or a full image of the whole-slide image data. The image data is encoded into segmented data portions based on convolutional autoencoding of objects associated with the collection of image data. The density of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is determined of bounded segmented data portions for respective classification of the regions of interest. A classification label is assigned to the regions of interest. It is determined whether an assigned classification label is above a pre-determined threshold probability value of lymphocyte infiltrated. The threshold probability value is adjusted in order to re-assign the classification label to the regions of interest based on a varied sensitivity level of density of lymphocyte infiltrated. A trained classification model is generated based on the re-assigned classification labels to the regions of interest associated with segmented data portions using the adjusted threshold probability value. An unlabeled image data set is received to iteratively classify the segmented data portions based on a lymphocyte density level associated with portions of the unlabeled image data set, using the trained classification model. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte representations are generated based on prediction of TIL information associated with classified segmented data portions. A refined TIL representation based on prediction of the TIL representations is generated using the adjusted threshold probability value associated with the classified segmented data portions. A corresponding method and computer-readable device are also disclosed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND TOR THE STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +2
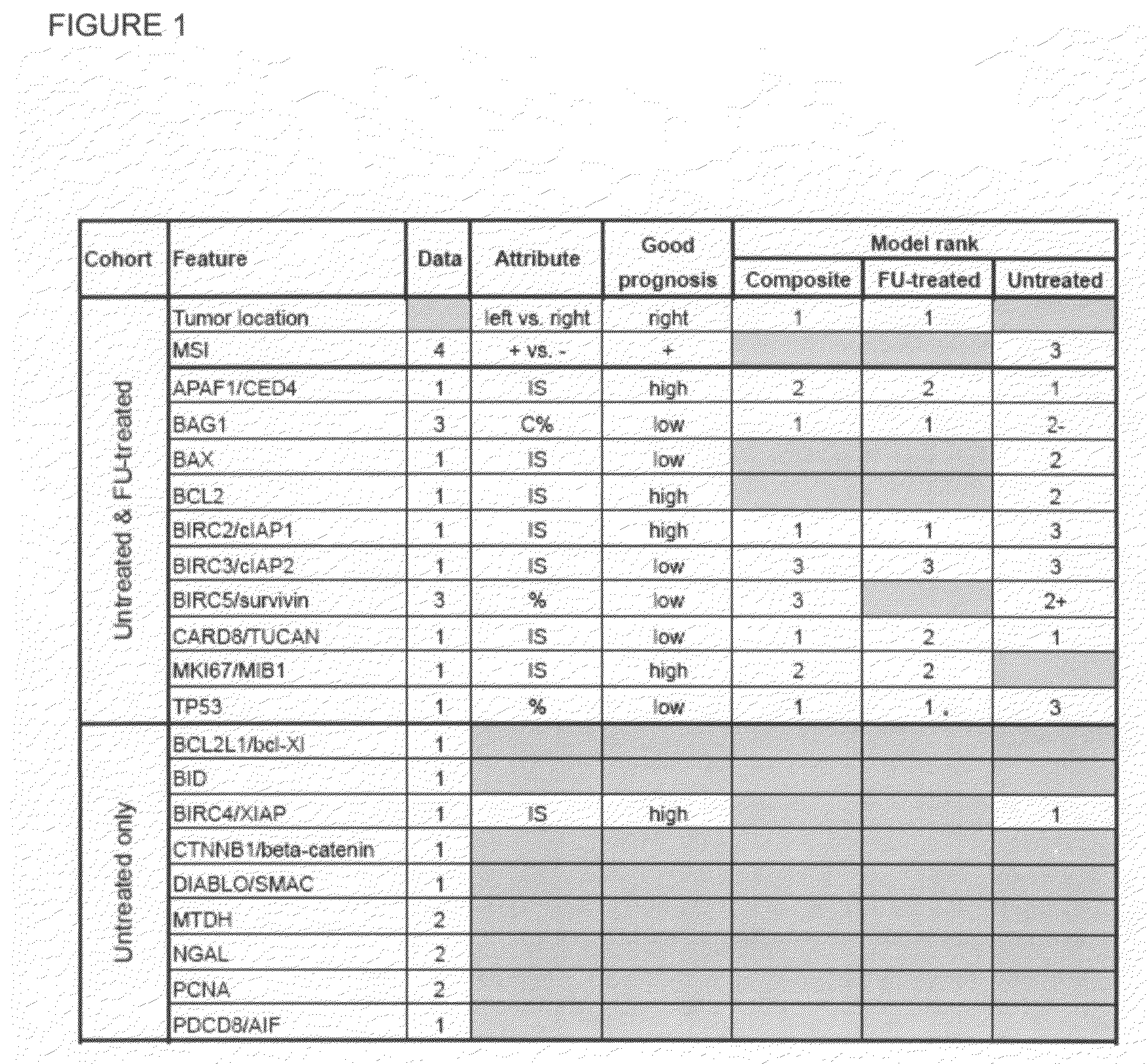
Diagnostic markers predictive of outcomes in colorectal cancer treatment and progression and methods of use thereof
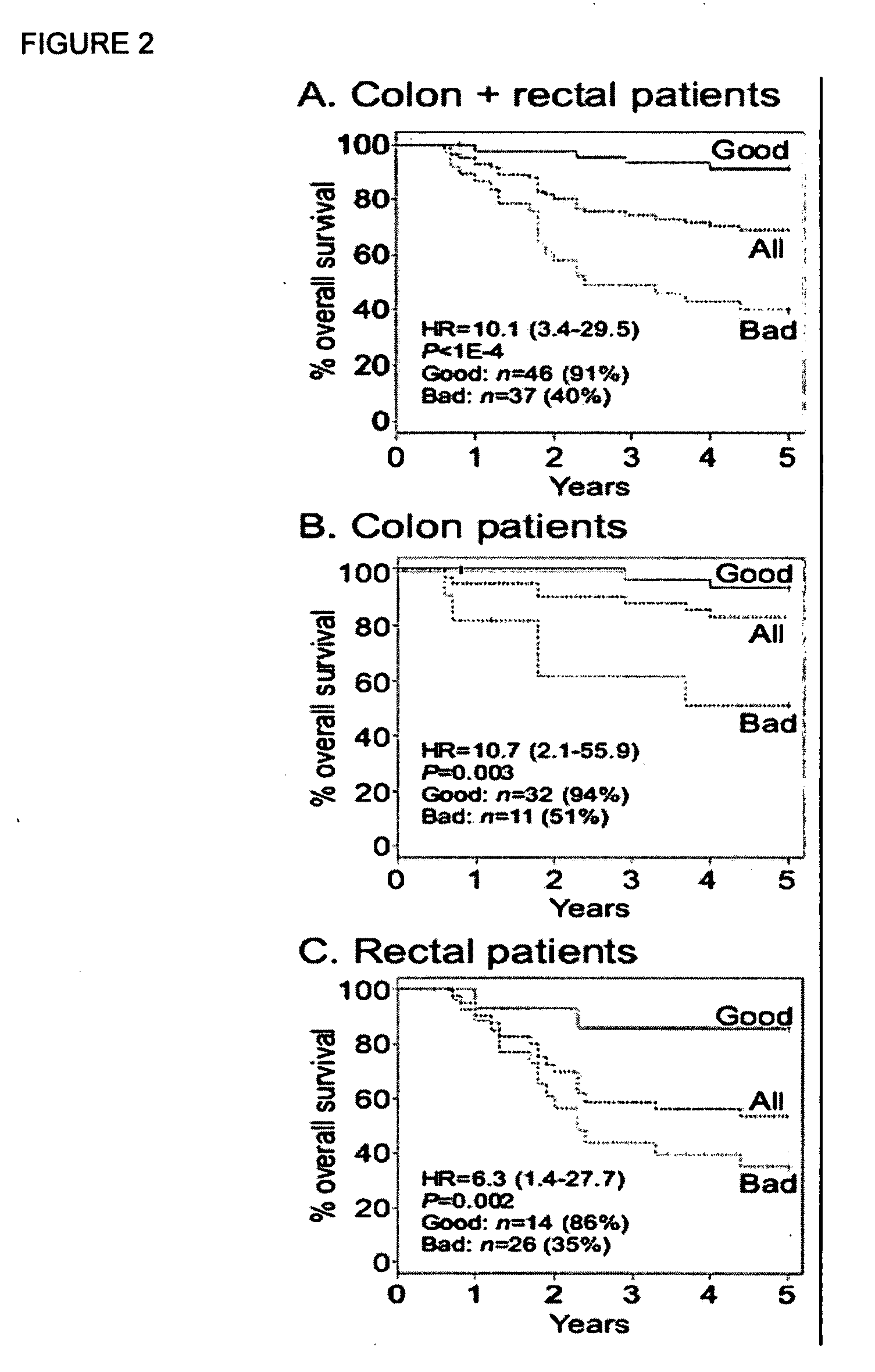
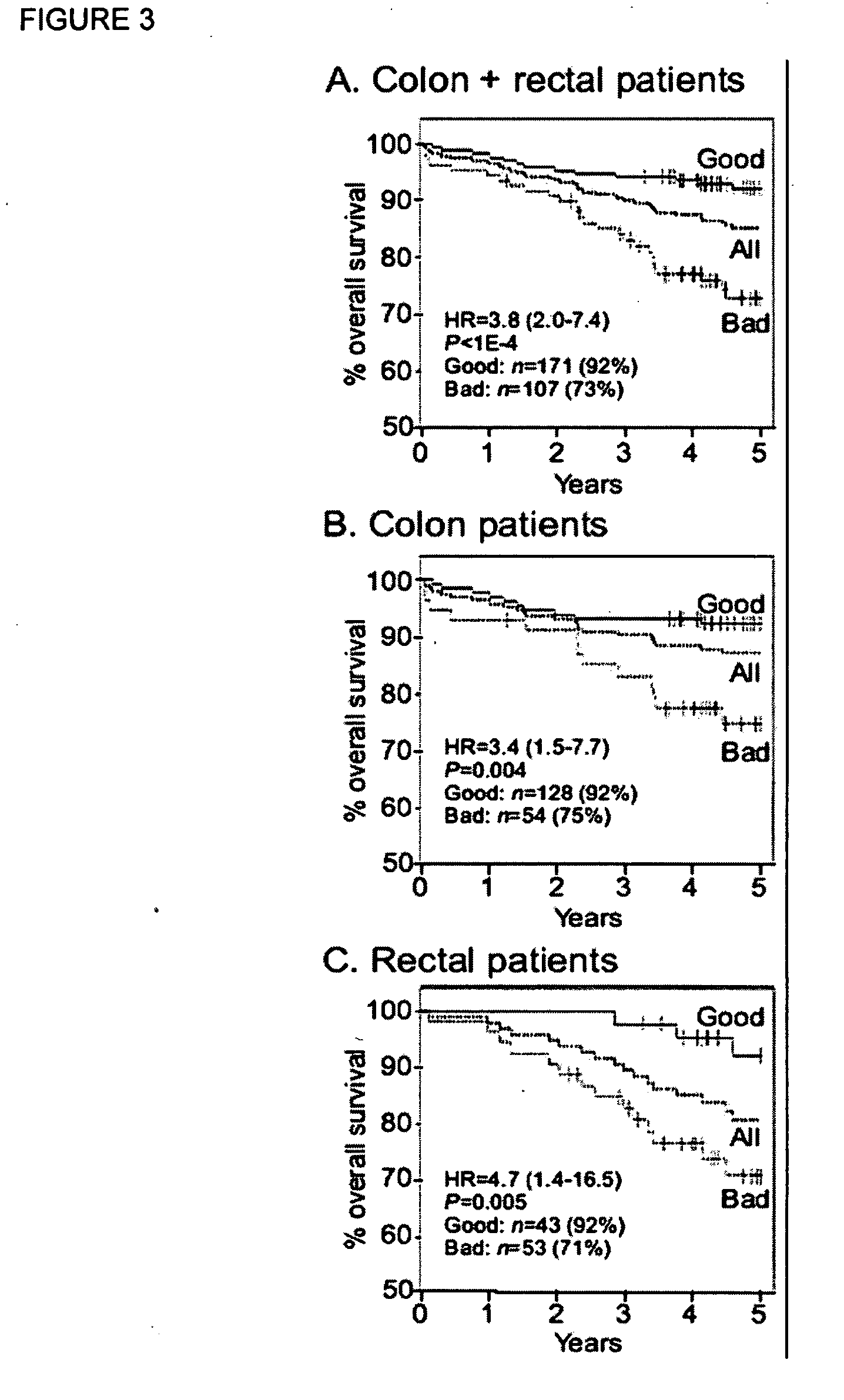
Colorectal cancer patients with operable tumors must decide whether to receive adjuvant therapy after surgical resection in order to reduce their chances of recurrence. Current clinical guidelines are crudely based on the stage of the disease, as well as a few other clinicopathologic features. The instant invention integrates data from these clinicopathologic features with data on multiple biomarkers using advanced informatic methods to provide a far more accurate prediction of recurrence than the current guidelines. The instant invention consists of a panel of biomarker assays plus an algorithm into which the scored biomarker data, as well as standard clinicopathologic data, is entered. A tumor sample from an individual patient is submitted for test, and an individualized report is produced with a prognostic score that accurately reflects the patient's risk of recurrence. This helps guide the patient and his / her oncologist in their choice of whether to receive adjuvant treatment. Low-risk patients are spared the unnecessary toxicities associated with cytotoxic treatments, and high-risk patients are given the best chance for a cure, maximizing both life expectancy and quality of life.
Owner:LINKE STEVEN P +2
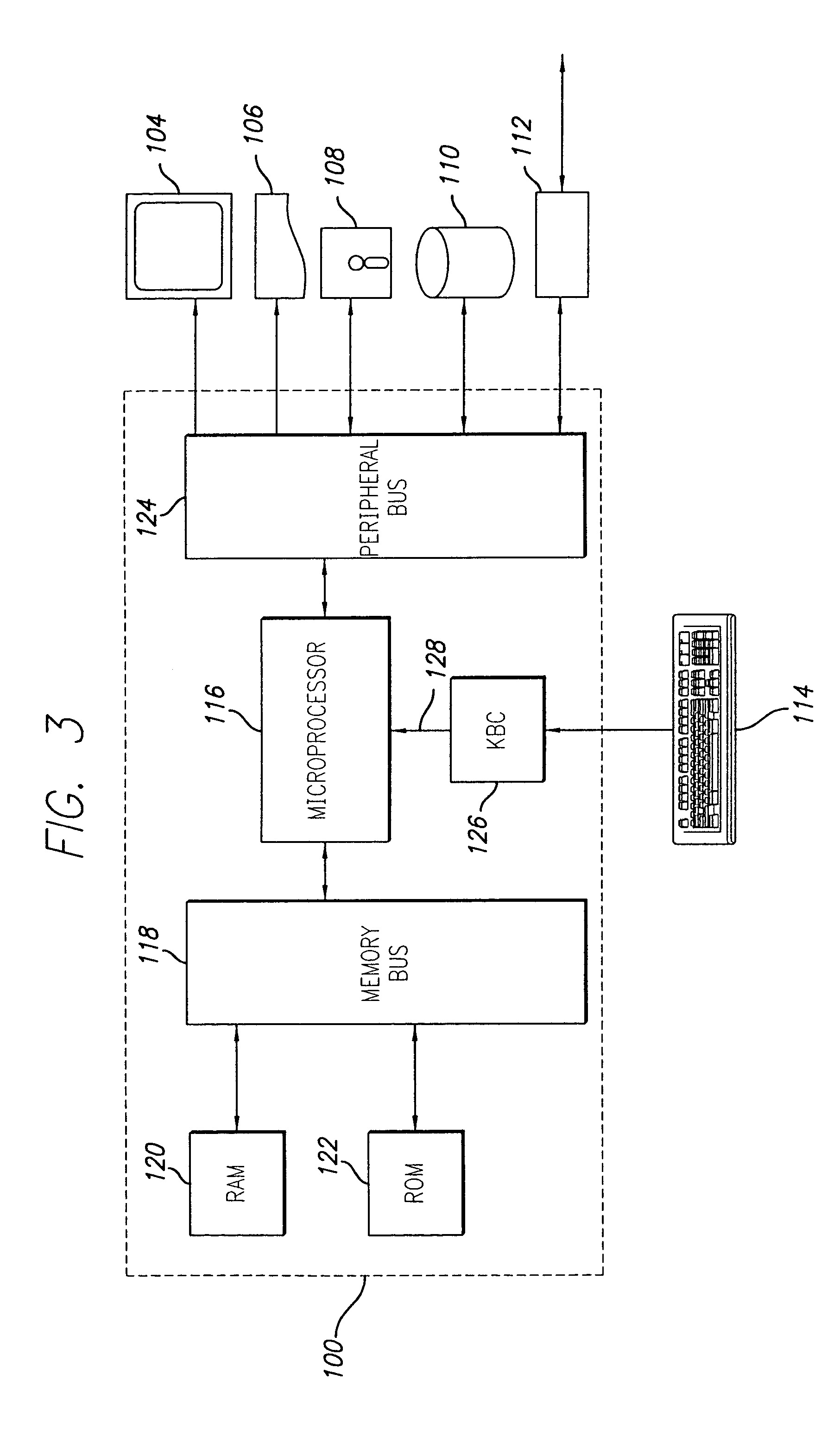
System for animal health diagnosis
InactiveUS7548839B2Efficient developmentSurgeryComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionInternet networkAnimal health
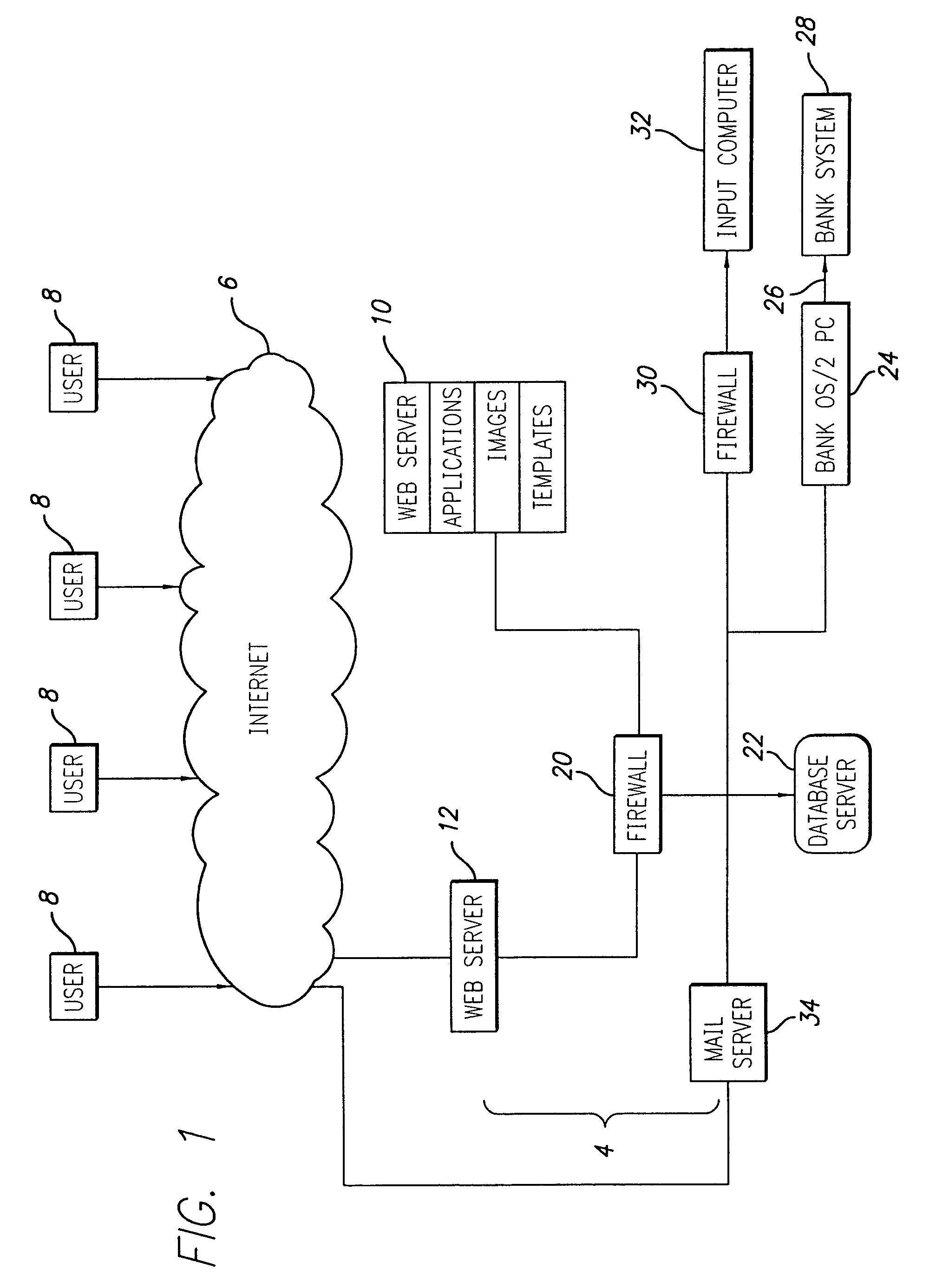
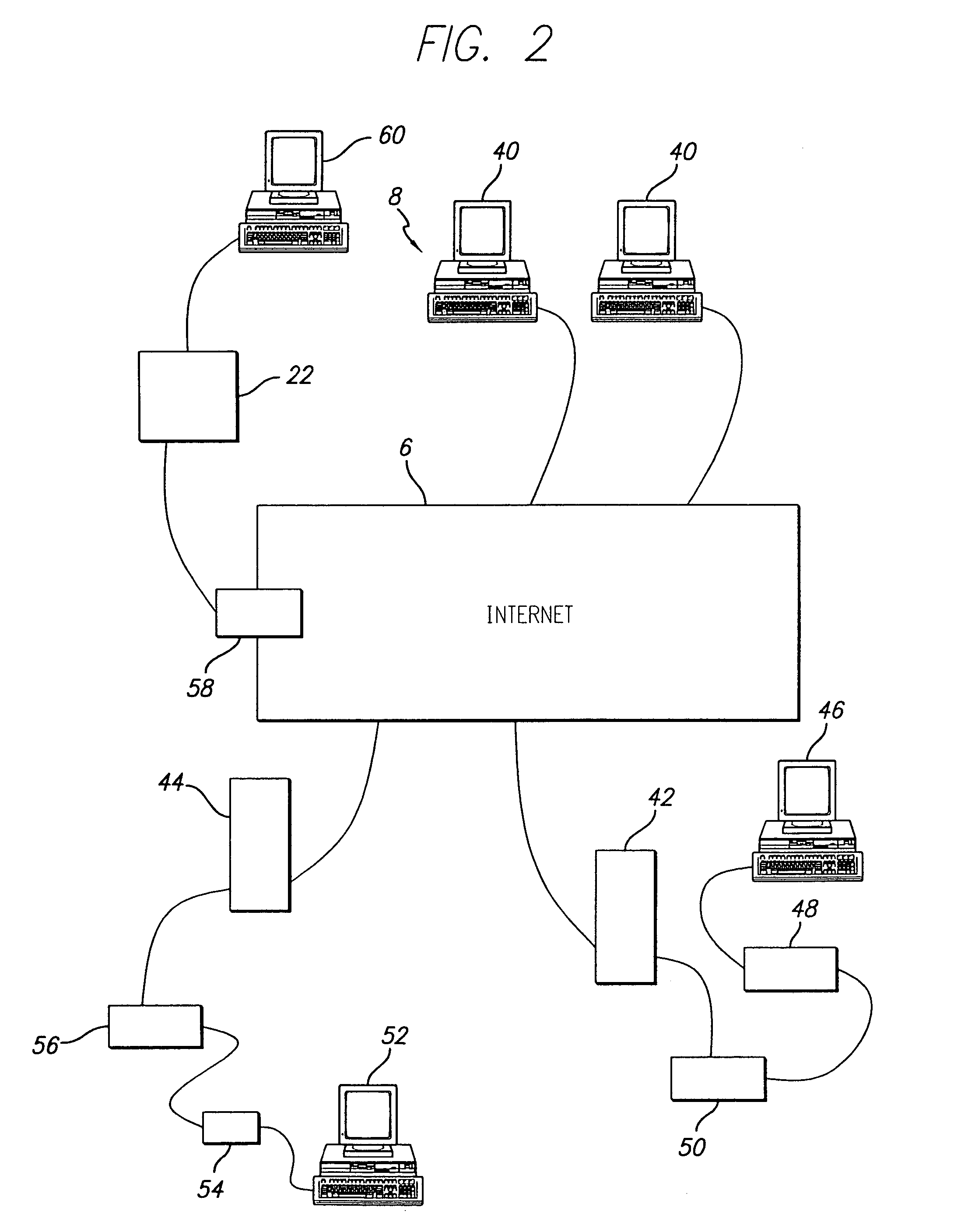
A diagnosis of the health of an animal is obtained through a combination of computerized data and human interpretation. Data relates to the physical characteristics of the animal, and includes data obtained from a physical inspection of the animal. A blood or other fluid sample is used to obtain a computer generated laboratory analysis. This is reported through an internet network to the clinical pathologist. The clinical pathologist has the data relating to the physical characteristics, and thereby makes a diagnosis of the animal health. A drop-down menu on a computer screen provides supplemental reports to support the diagnosis. This can be enhanced by further input from the pathologist through keyboard entry into the computer to obtain an integrated computer report having the laboratory analysis, supplemental report, and selectively an enhanced report. The integrated report is electronically communicated to a client.
Owner:HEMOPET
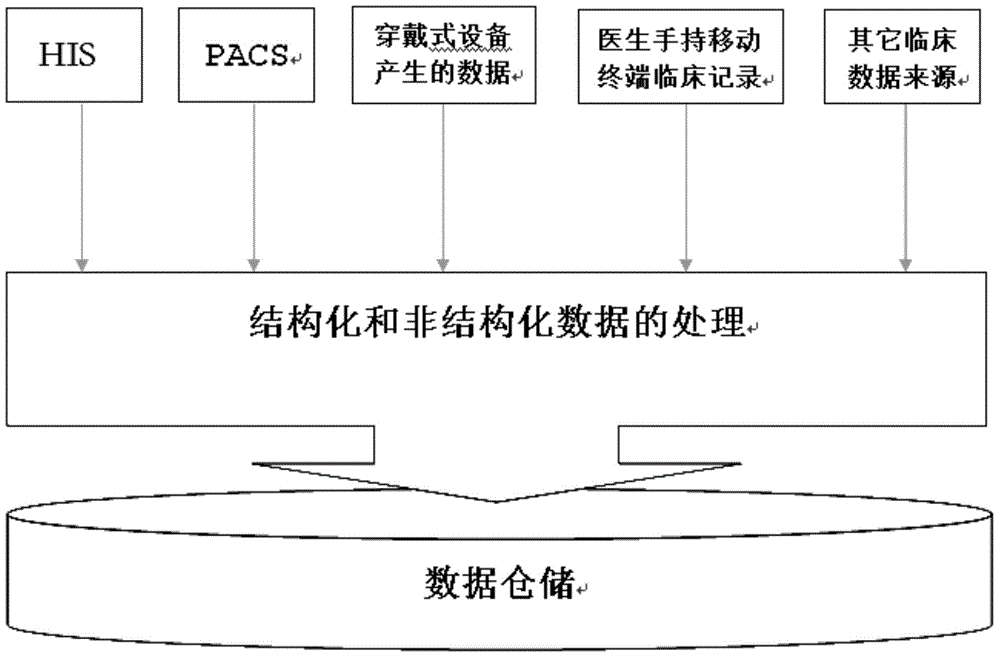
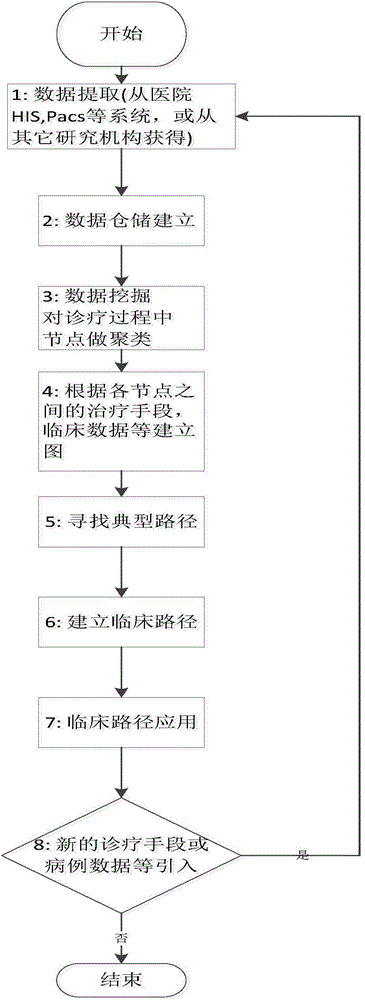
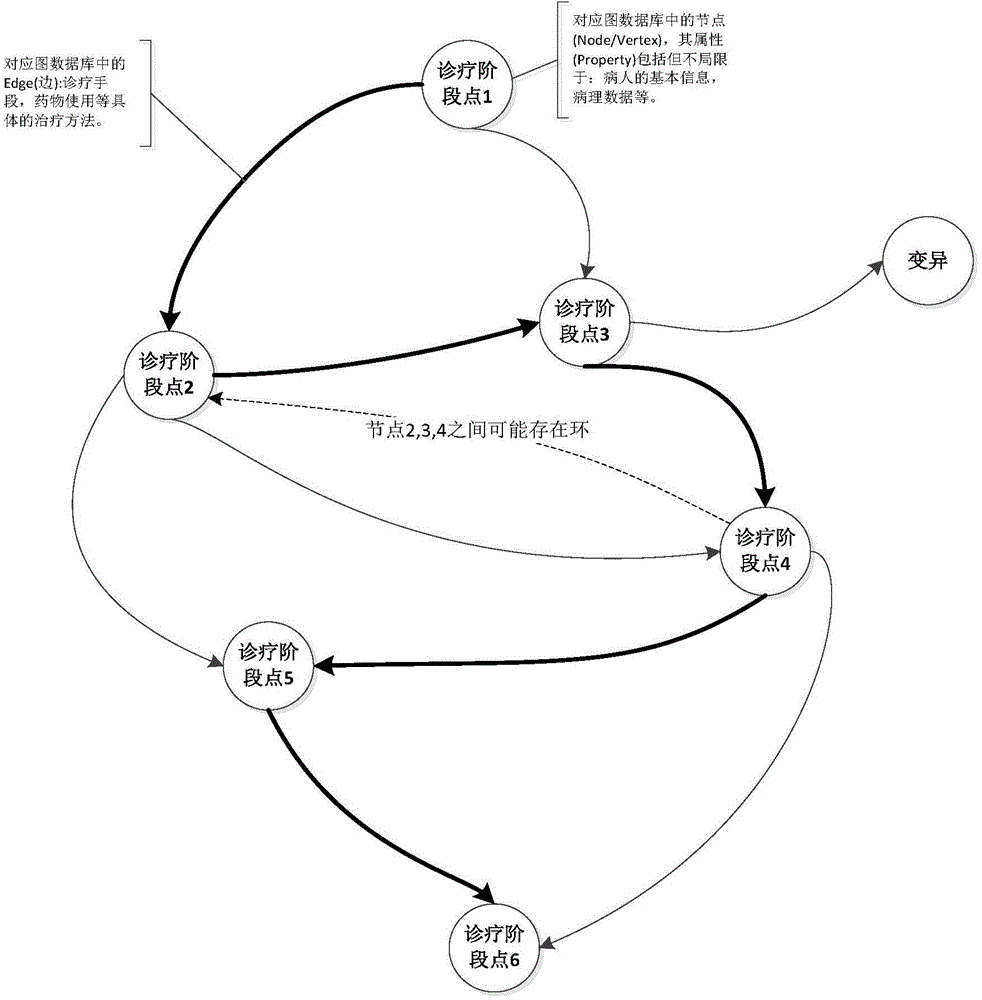
Clinical path establishing and optimizing method and system based on data mining and graph theory technology
ActiveCN104834826ABig amount of dataFast growthSpecial data processing applicationsDiseasePhases of clinical research
The invention discloses a clinical path establishing and optimizing method and system based on data mining and a graph theory technology. The method includes the steps that S1, data are extracted for different diseases; S2, data in a distributed database are analyzed, and all diagnosis and treatment stage points of a complete treatment course are set for different diseases respectively; S3, based on the graph theory technology, the diagnosis and treatment stage points are stored and at least include diagnosis and treatment stages, information of treatment needing to be performed between the diagnosis and treatment stages and clinical pathology data included in each diagnosis and treatment stage; S4, by the utilization of the related algorithm of the graph theory, a typical path for the disease is searched for; S5, according to each diagnosis and treatment stage pint and the diagnosis and treatment activity of each diagnosis and treatment stage point, a clinical path is established and stored in a clinical path database; S6, the result and variation of applying the clinical path are recorded, and if variation exists, the clinical path is optimized again.
Owner:NANJING PLASO NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Molecular markers predicting response to adjuvant therapy, or disease progression, in breast cancer
Predicting response to adjuvant therapy or predicting disease progression in breast cancer is realized by (1) first obtaining a breast cancer test sample from a subject; (2) second obtaining clinicopathological data from said breast cancer test sample; (3) analyzing the obtained breast cancer test sample for presence or amount of (a) one or more molecular markers of hormone receptor status, one or more growth factor receptor markers, (b) one or more tumor suppression / apoptosis molecular markers; and (c) one or more additional molecular markers both proteomic and non-proteomic that are indicative of breast cancer disease processes; and then (4) correlating (a) the presence or amount of said molecular markers and, with (b) clinicopathological data from said tissue sample other than the molecular markers of breast cancer disease processes. A kit of (1) a panel of antibodies; (2) one or more gene amplification assays; (3) first reagents to assist said antibodies with binding to tumor samples; (4) second reagents to assist in determining gene amplification; permits, when applied to a breast cancer patient's tumor tissue sample, (A) permits observation, and determination, of a numerical level of expression of each individual antibody, and gene amplification; whereupon (B) a computer algorithm, residing on a computer can calculate a prediction of treatment outcome for a specific treatment for breast cancer, or future risk of breast cancer progression.
Owner:LINKE STEVEN +2
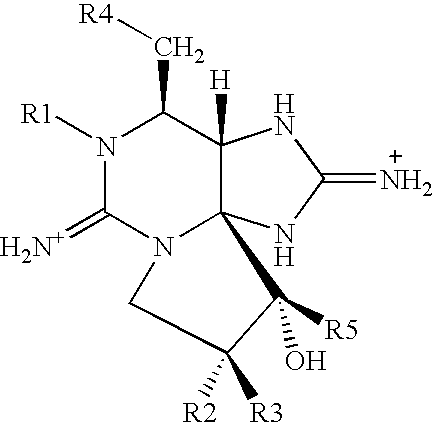
Use and application of a pharmaceutical composition containing a mixture of natural- origin heterocyclical guanidine, for cosmetology, wound healing, focal dystonia and muscular spasm- related clinical pathologies
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising tricyclic 3,4-propinoperhydropurines and uses thereof for blocking neuronal transmission are provided.
Owner:PHYTOTOX LTD
Kit and detection method for detecting pathogenic microorganisms of infectious eye disease
ActiveCN103045761AEfficient amplificationReduce lossesMicrobiological testing/measurementConserved sequencePositive control
The invention relates to a kit and a detection method for detecting pathogenic microorganisms of the infectious eye disease. The kit consists of a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) amplification reagent, a universal primer combination, positive control nucleic acid and sterilized distilled water, wherein the DNA amplification reagent is formed by a premixed reagent which directly carries out amplification without extracting DNA of a sample and corresponding DNA polymerase mixed solution; and the universal primer combination is mixed solution of equal quantities of universal forward and reverse primers, which is designed and synthesized for respective conserved sequences of a plurality of types of common pathogenic microorganism bacteria, fungi, I-type herpes simplex virus and acanthamoeba protozoa of the infectious eye disease. The primers adopted by the invention are universal in various pathogenic agent types, but are specific for other pathogenies; a direct PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) reaction system and a program also have high efficiency; a step of extracting DNA of a template is omitted and the highest utilization degree of limited clinical samples is ensured; and meanwhile, detection time is also greatly shortened and the kit and the detection method can take a good auxiliary effect on early diagnosis of clinical pathology.
Owner:SHANDONG EYE INST
System and method to quantify tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) for clinical pathology analysis based on prediction, spatial analysis, molecular correlation, and reconstruction of TIL information identified in digitized tissue images
Owner:THE RES FOUND TOR THE STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +2
Analytical method for beta-amyloid protein pathology by using thioflavine T staining
InactiveCN103278626AClear etiologyStrong impetusFluorescence/phosphorescencePharmacological interventionsDisease patient
The invention relates to an analytical method for beta-amyloid protein pathology by using thioflavine T staining. The method comprises the following processes: A, a patient pathological specimen source, B, an experimental animal pathological specimen source, C, treatment of patient and experimental animal brain tissue specimens, D, immumohistochemical staining of specimen beta-amyloid protein 1-42, E, thioflavine T staining of the specimen, and F, optical / fluorescence microscope pathological examination. The method has the advantages of introducing and widely using the thioflavine T to mark an amyloid protein disease patient brain tissue pathological specimen and assess the pharmacological intervention effect of alzheimer disease (AD) transgenic animals; compared with the traditional silver staining method and A beta immunohistochemical method, the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of being simple and feasible, and sensitive and reliable, is beneficial for clearing the nosetiology of cerebral hemorrhage, and has great guide value on formulation of patient secondary intervening measures. The wide application of the technology has a powerful promoting effect on clinical pathological research and translational medicine research of the A beta related diseases (alzheimer disease and amyloid angiopathy).
Owner:徐俊
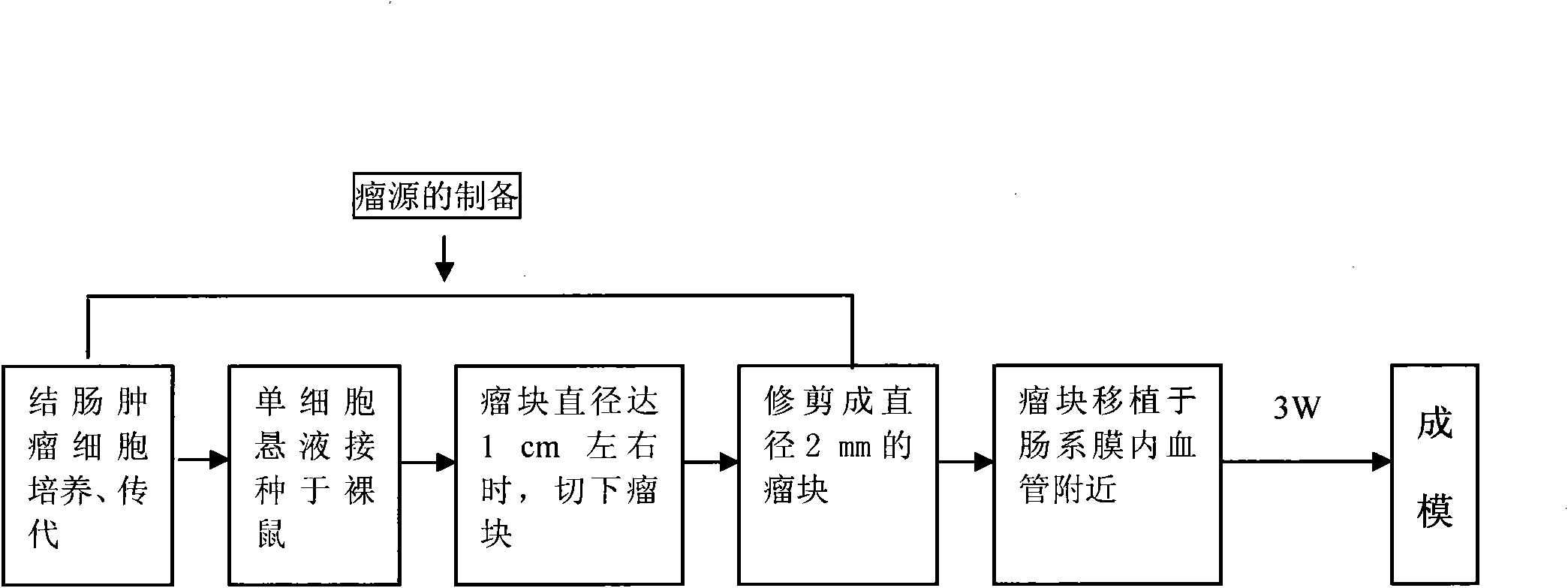
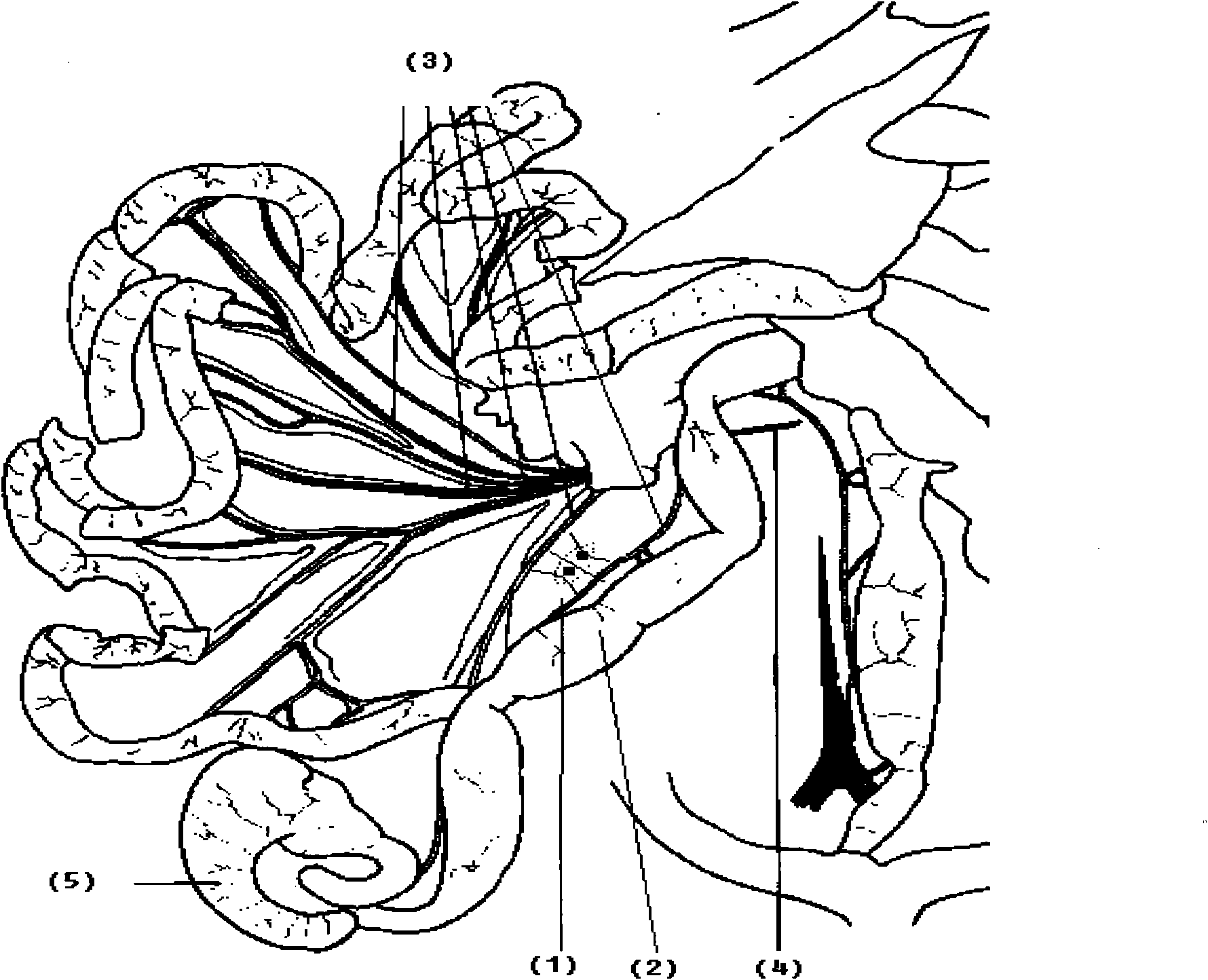
Method for building improved orthotopic transplantation tumor model of colorectal tumor in nude mice
InactiveCN101919747AProlong survival timeReduce mortalityVeterinary instrumentsAbnormal tissue growthSingle cell suspension
The invention discloses a transplantation tumor model of colorectal tumor for medical scientific research, which is produced by improving the orthotopic transplantation tumor model of colorectal tumor in nude mice. The invention aims to overcome the defect that the orthotopic transplantation tumor model of colorectal tumor has high intestinal obstruction incidence rate and short model animal survival time and is not suitable for long-time experiments. In the invention, the prepared tumor is transplanted close to the blood vessel in mesocolon. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparation of tumor: injecting single cell suspension of the tumor cell to subcutis of nude mice and preparing the source of the transplantation tumor; (2) transplanting the prepared tumor close to the blood vessel in mesenterium of nude mice but not the serosa of the intestinal tube; and (3) raising the nude mice in an aseptic laminar flow room, controlling the room temperature to be (25+ / -1) DEG C and relative humidity to be 40-50% and continuously observing the nude mice. The animal model built by the invention can reproduce the natural clinical pathology process of human colorectal tumor, can not suffer from obstruction of the lumen in the digestive tract in the short term and has transfer mode similar to that of the patients.
Owner:LONGHUA HOSPITAL SHANGHAI UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Prostate cancer markers and application thereof
ActiveCN107904311AMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsProstate cancer cellOncology
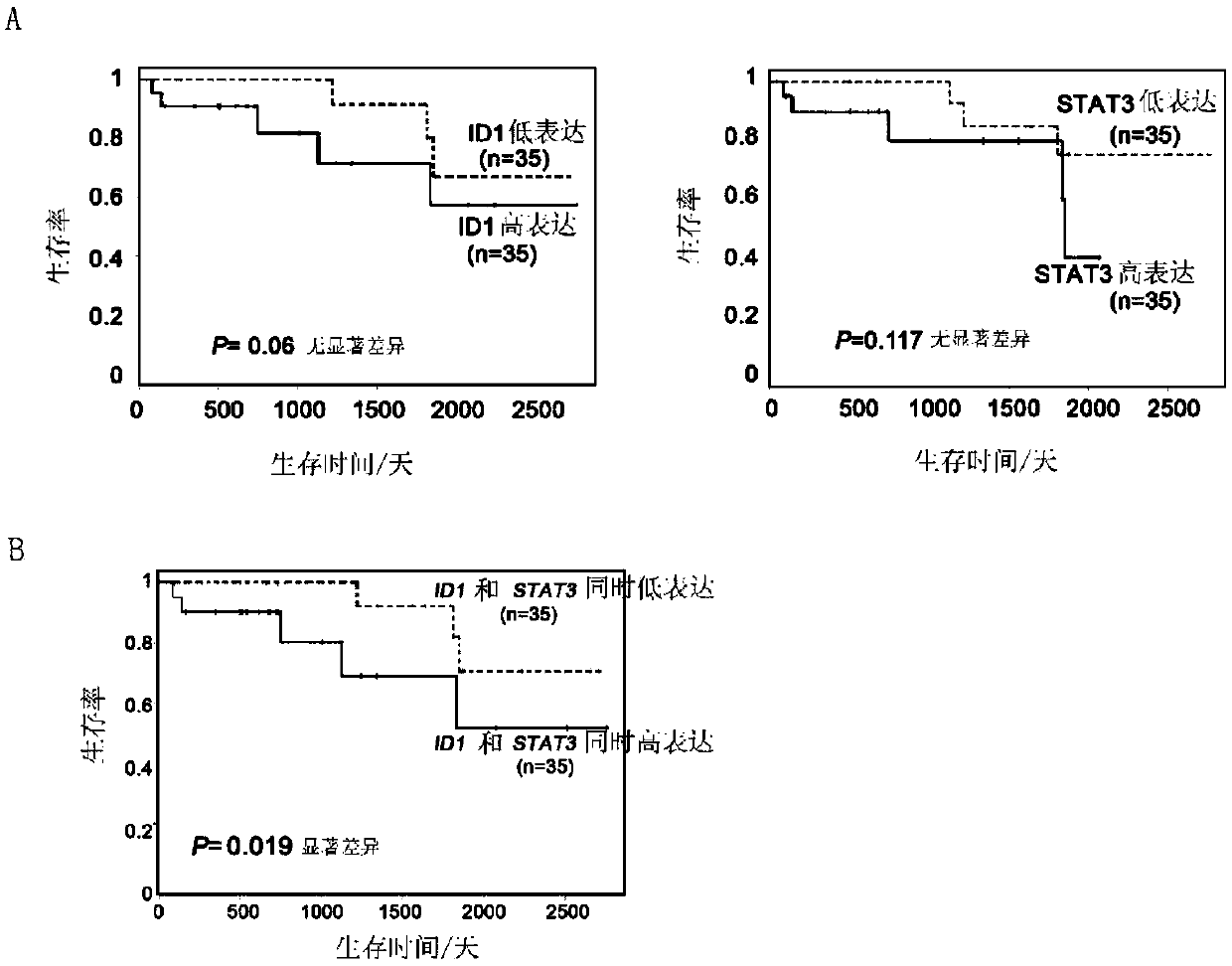
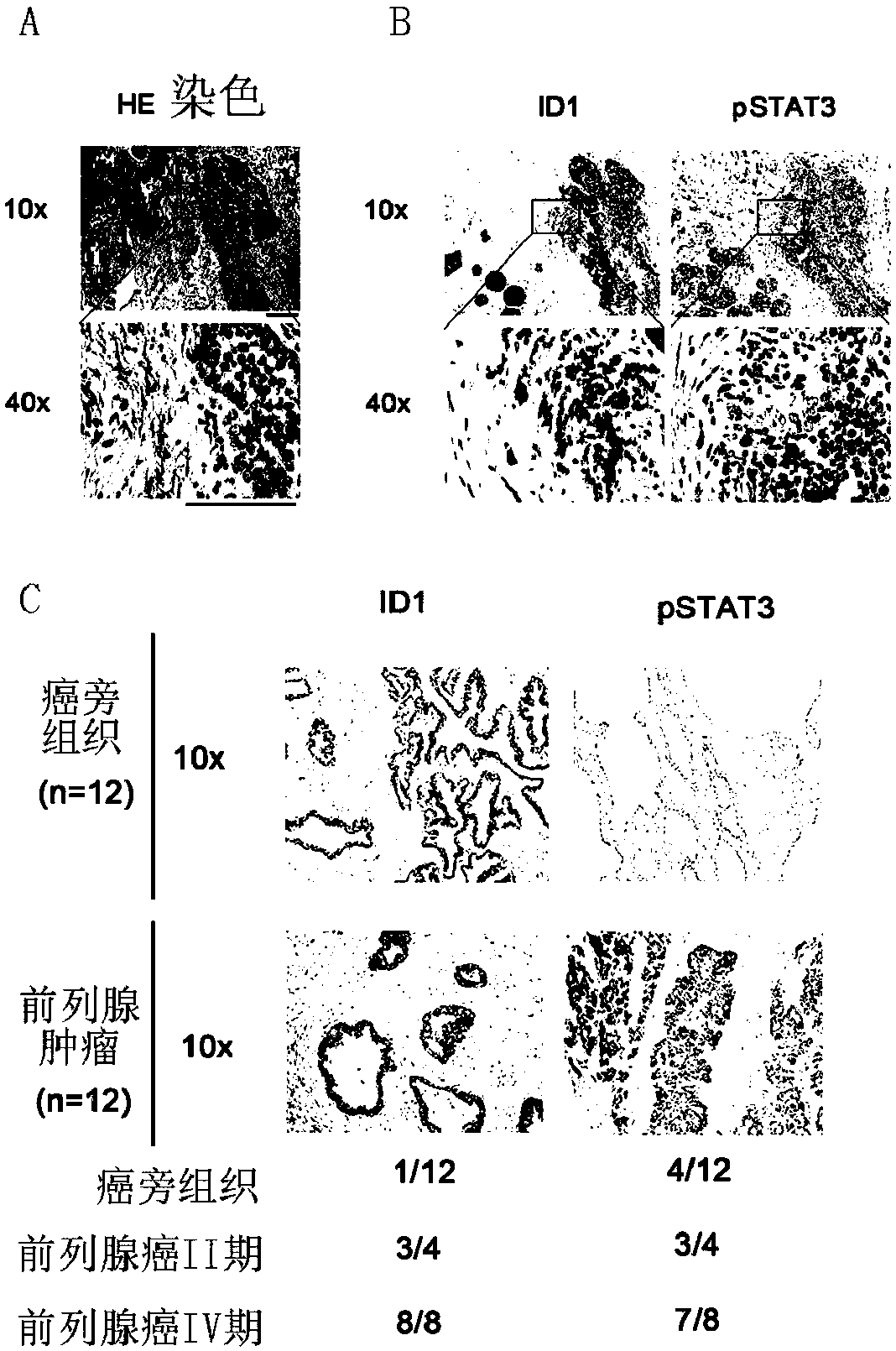
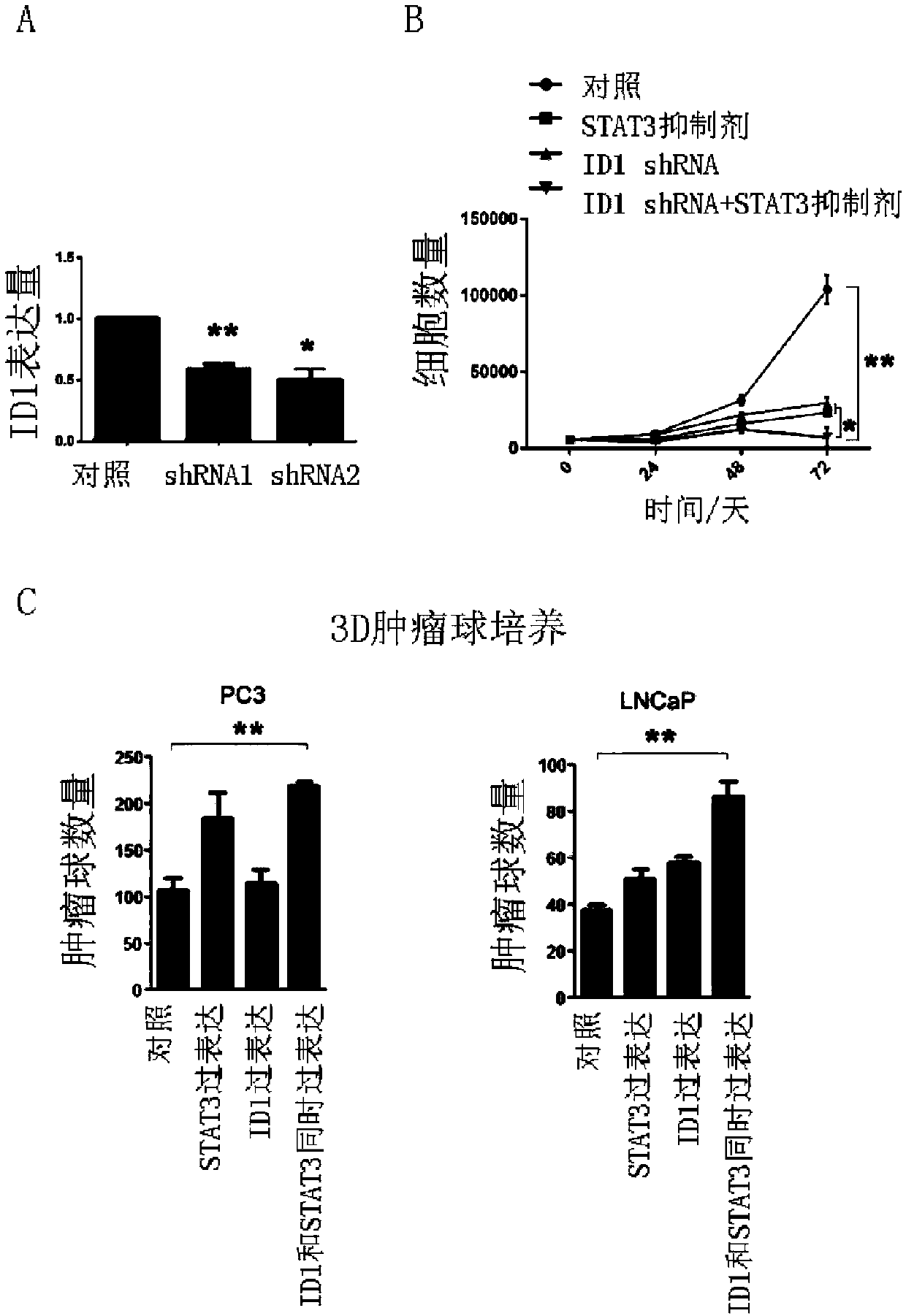
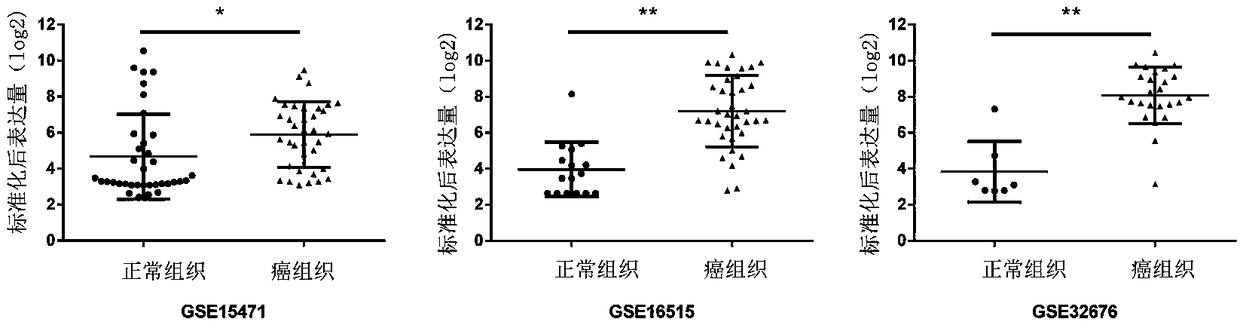
The invention relates to prostate cancer markers STAT3 and ID1 and application of a kit which is used for detecting STAT3 and ID1 protein expression levels in prostate cancer detection and diagnosis or prognostic evaluation of patients. As STAT3 and ID1 gene sequences in prostate cancer cells have remarkably high expression, whether the expression of the two genes is high or not has remarkable correlation with clinical pathology parameters; thus, the STAT3 and the ID1 can serve as specific tumor markers or treating targets in early detection of prostate cancer and have important clinical application values.
Owner:徐州维康生物科技有限公司
Method for investigating relationship between lung cancer clinical pathology and gene expression
PendingCN110564853AOptimize treatment planPrevent proliferationMicrobiological testing/measurementLymphatic SpreadCancer cell
The invention belongs to the field of medical exploration methods, and provides a method for investigating the relationship between lung cancer clinical pathology and gene expression; the method is used for guiding personalized and accurate lung cancer treatment and prognosis in the aspect of gene mutation. The method comprises the steps: confirmation of candidate genes; selection of a target gene; establishment of database; verification of lung cancer candidate genes; relevance of the target gene with lung cancer prognosis and clinical pathology characteristics; verification of expression ofthe target gene in lung adenocarcinoma; screening of a target gene low-expression lung cancer cell strain; influence of target gene overexpression / interference on lung cancer cell in-vitro invasion and metastasis; hypothesis of regulation and control of the target gene on the aspects of cell cycle apoptosis and invasion; regulation and control experiments of the target gene on the aspects of cellcycle apoptosis and invasion; and influence of target gene overexpression on a downstream signal path. In combination with various databases, various hypotheses are provided, the correctness of the hypotheses is verified through the experiments, and the next diffusion condition of lung cancer cells and the information interaction condition between cancer cells are predicted.
Owner:XIN HUA HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma marker and application thereof
InactiveCN108456733AOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementClinical valueAdenocarcinoma
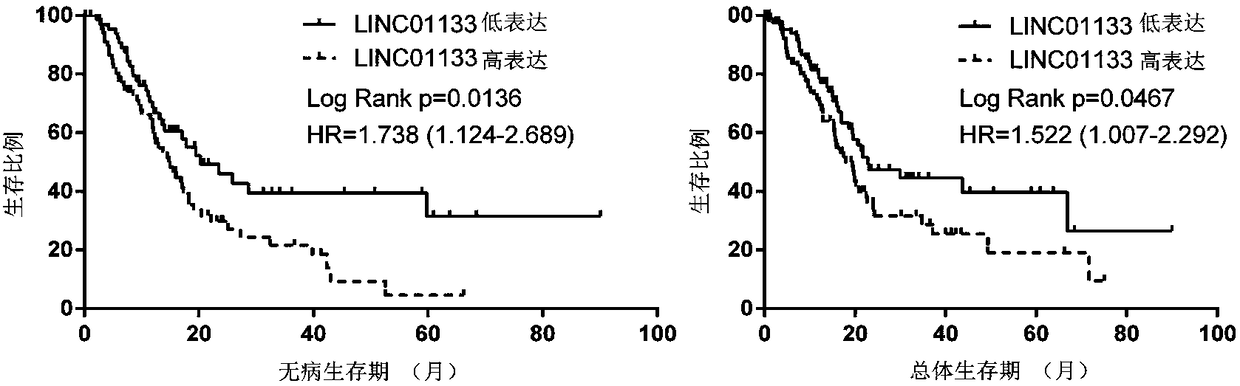
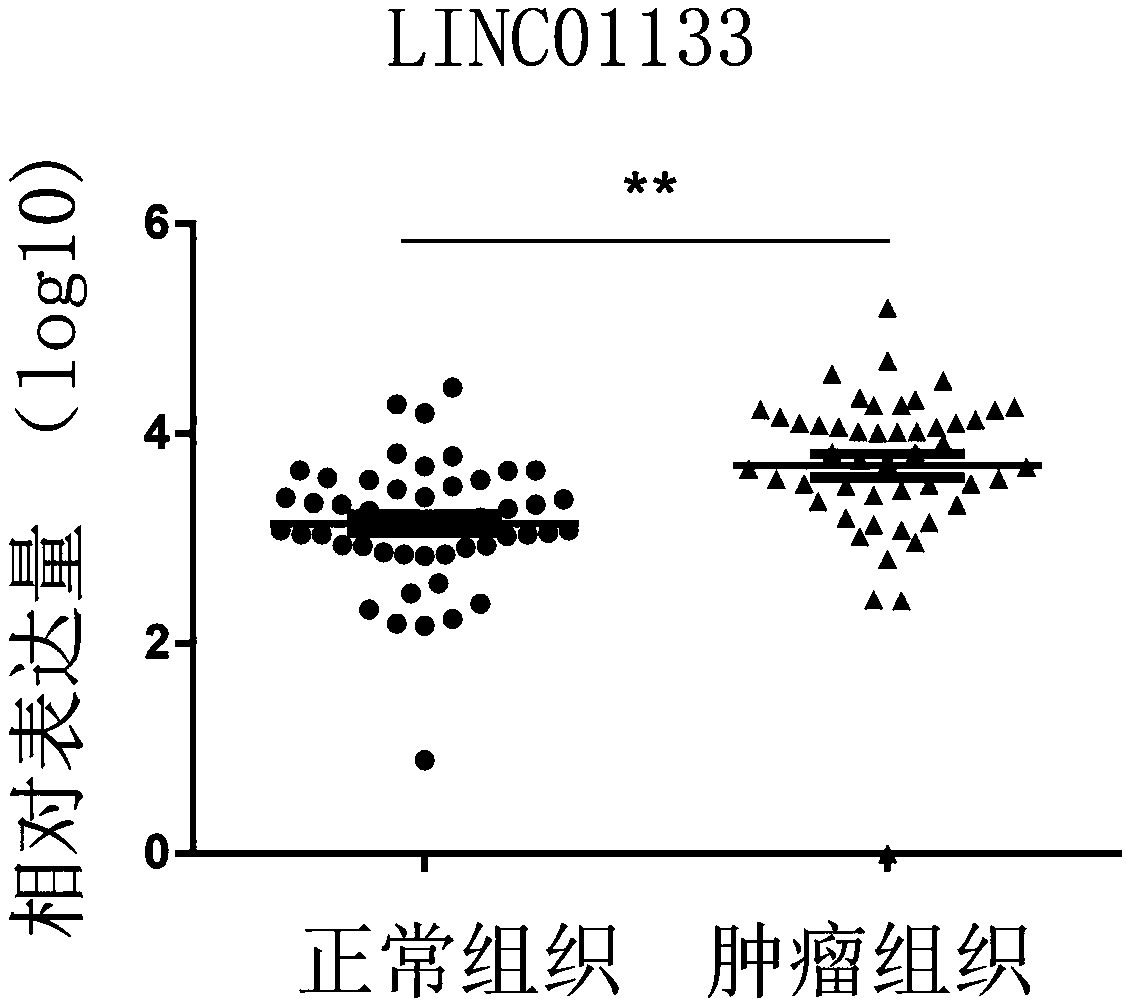
The invention discloses a pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma related tumor marker LINC01133, and application of a kit for detecting expression level of LINC01133 in the detection and diagnosis of pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma or patient prognostic evaluation. The expression level of LINC01133 is closely related to the clinical pathological parameters of pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma and the patientprognosis, and can be adopted as a specific tumor marker in pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma detection and a prognostic indicator, and thus is of an important clinical value.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
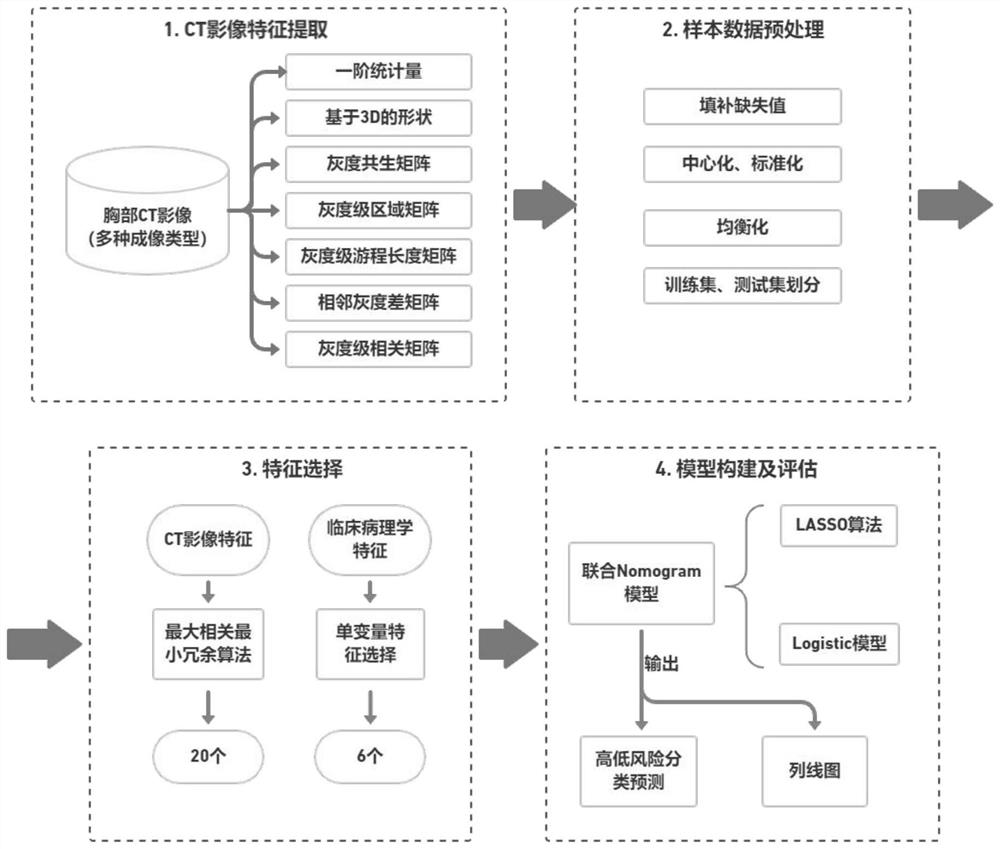
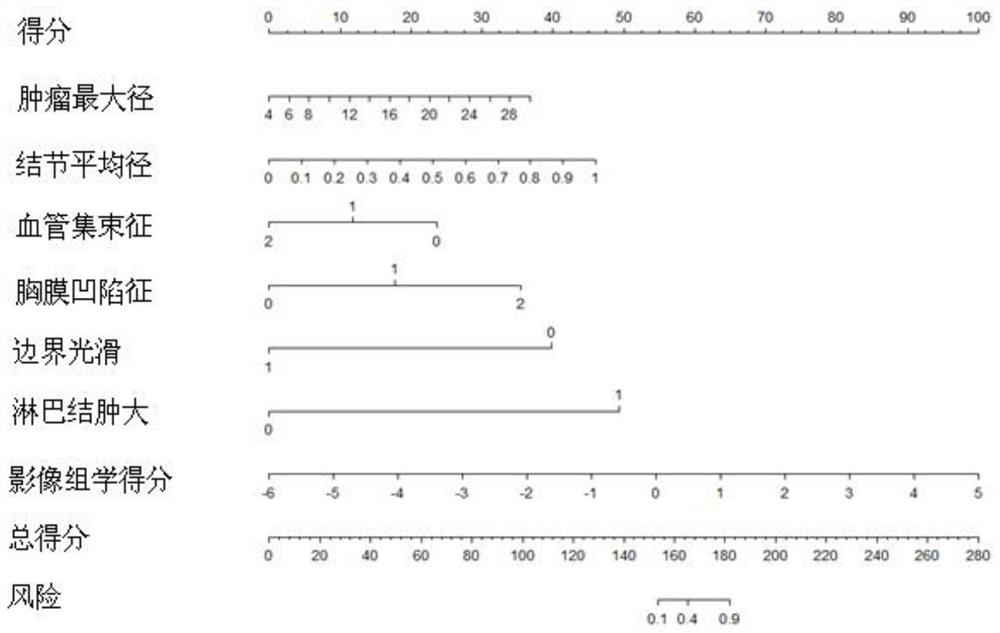
Non-small cell lung cancer risk prediction method based on machine learning
PendingCN112530592AArrange in timePrediction is accurateImage enhancementImage analysisTreatment effectData set
The invention provides a non-small cell lung cancer risk prediction method based on machine learning, and the method comprises the steps of carrying out the typical feature extraction of a chest CT image of a patient, and recording the typical feature as a CT image feature; obtaining CT image features of all patients in the sampling sample, forming a sample data set by combining clinical pathologyfeatures of all patients in the sampling sample, and preprocessing the CT image features in the sample data set; dividing the preprocessed sample data set into a test set and a training set; and performing feature screening on CT image features and clinical pathology features of patients in the divided test set and training set, and based on the training set subjected to feature screening, performing prediction training on high and low risks of non-small cell lung cancer by adopting a joint Nomogram model to obtain a non-small cell lung cancer risk prediction result. The invention can accumulate the experience of excellent doctors and experts, so as to copy the experience to other small cities and hospitals for popularization and application, improve the risk prediction accuracy, and improve the treatment effect of patients.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
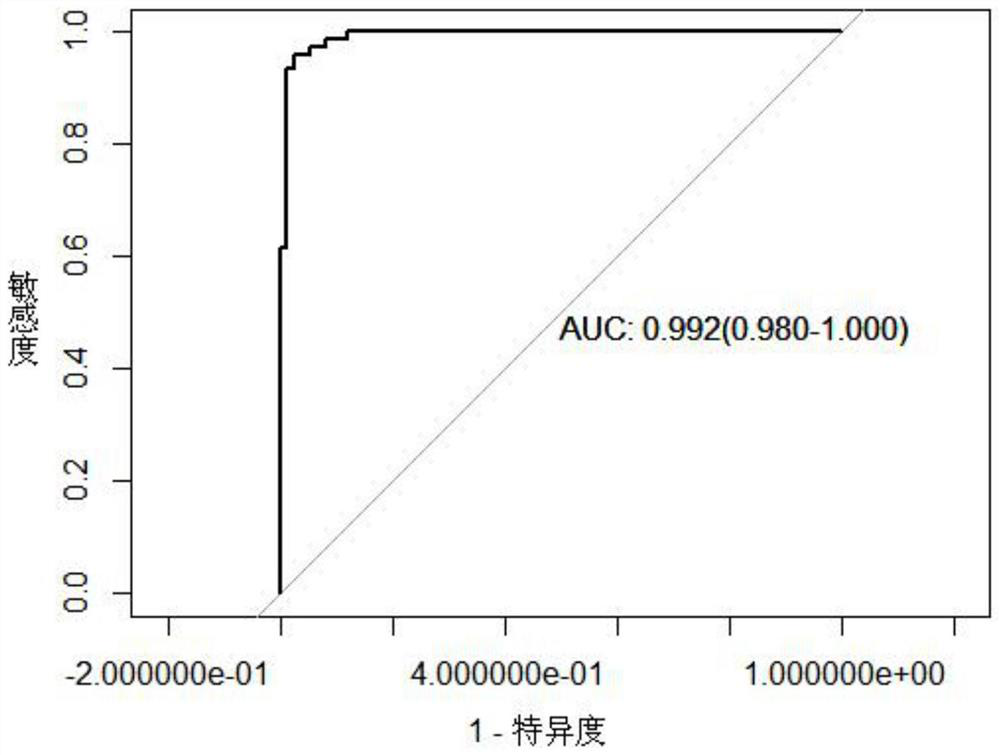
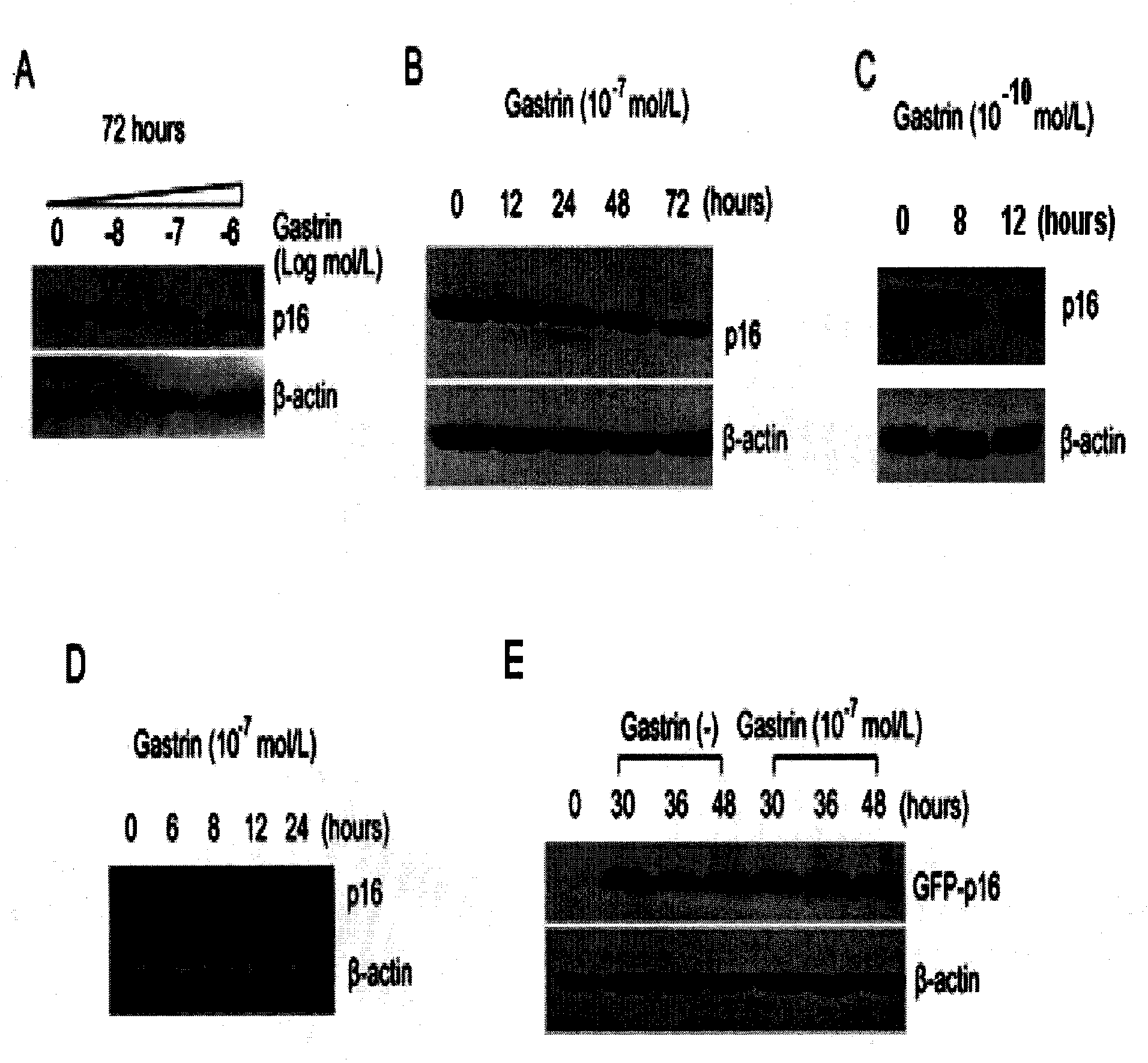
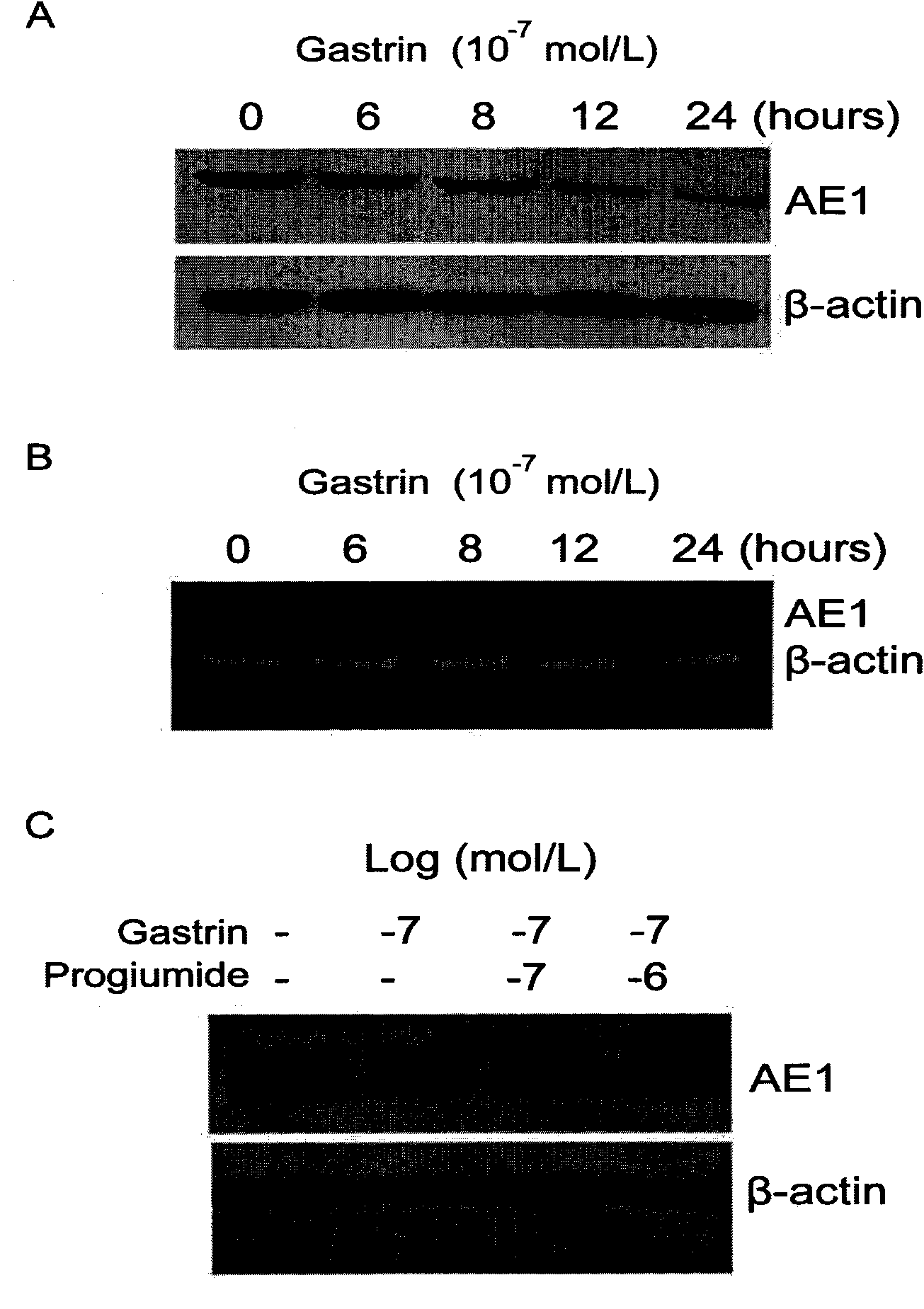
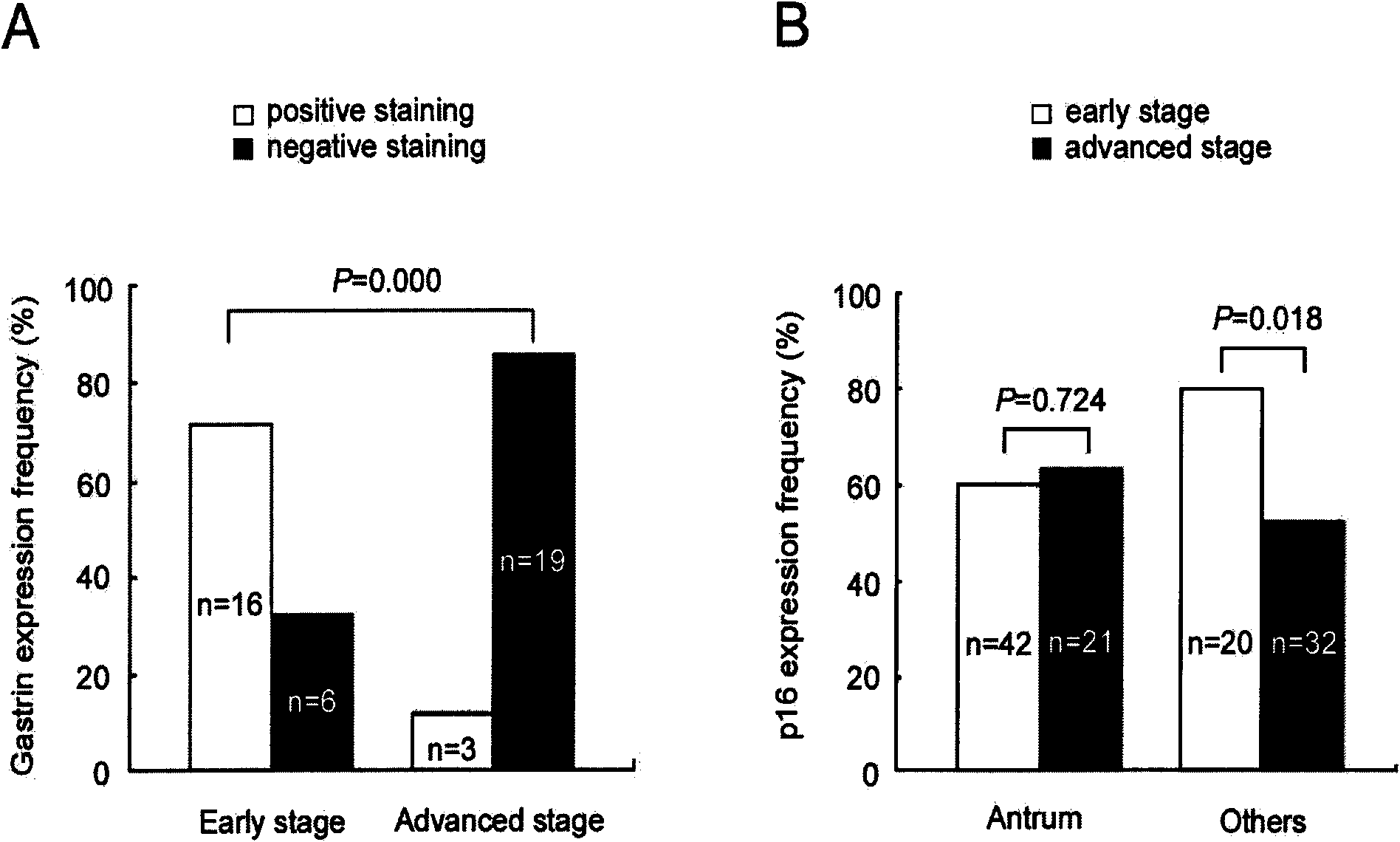
Application of gastrin in inhibiting gastrointestinal tumor tumors
ActiveCN101890157AHas therapeutic effectSignificant negative correlationPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemMultiple Tumor Suppressor-1Stomach cancer
The invention discloses a novel application of gastrin in inhibiting gastrointestinal tumor tumors. Gastric cancer target gene anion exchange protein 1 is interacted with tumor suppressor protein p16 so as to induce gastric cancer, however, 17 peptide gastrin (H-pGlu-Gly-Pro-Trp-Leu-Glu-Glu-Glu-Glu-Glu-Ala-Tyr-Gly-Trp-Met-Asp-Phe-NH2) can effectively inhibit expression of gastric cancer target gene AE1 and p16 and breaks through the traditional view that gastrin induces tumors, and clinical pathologies show that the gastrin has obvious negative correlation with AE1 and p16. The invention alsodiscloses that the gastrin with the concentration of 10-10mol / L-10-70mol / L has obvious inhibition effect on gastric cancer cell activity after a certain time, thus prompting that the gastrin has curing effect on gastric antrum cancer and providing a new direction for curing gastric cancer based on the test results.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Breast cancer marker and application thereof
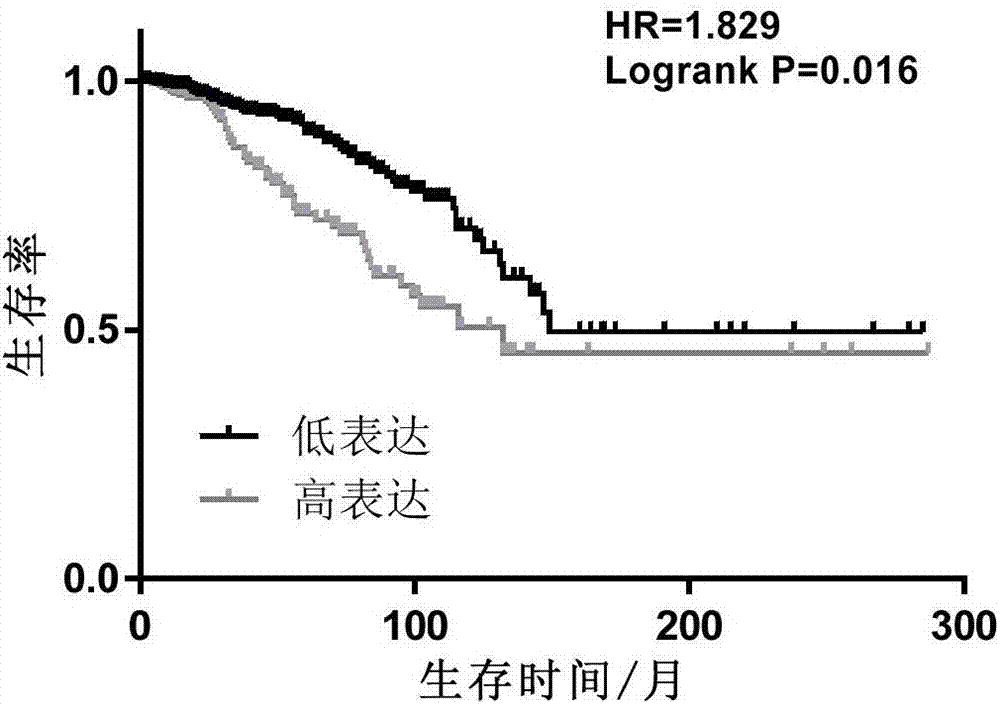
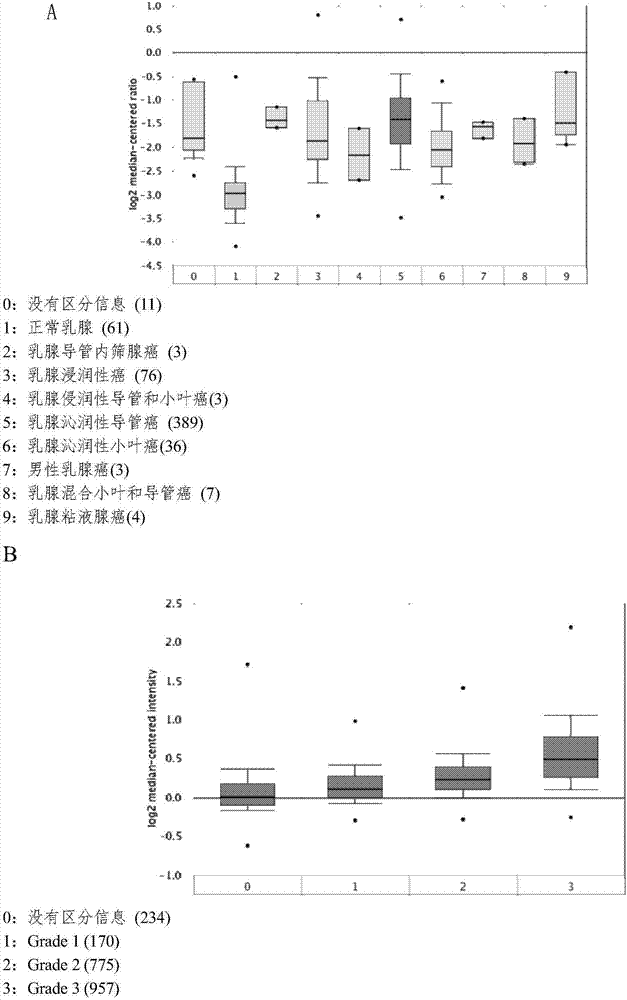
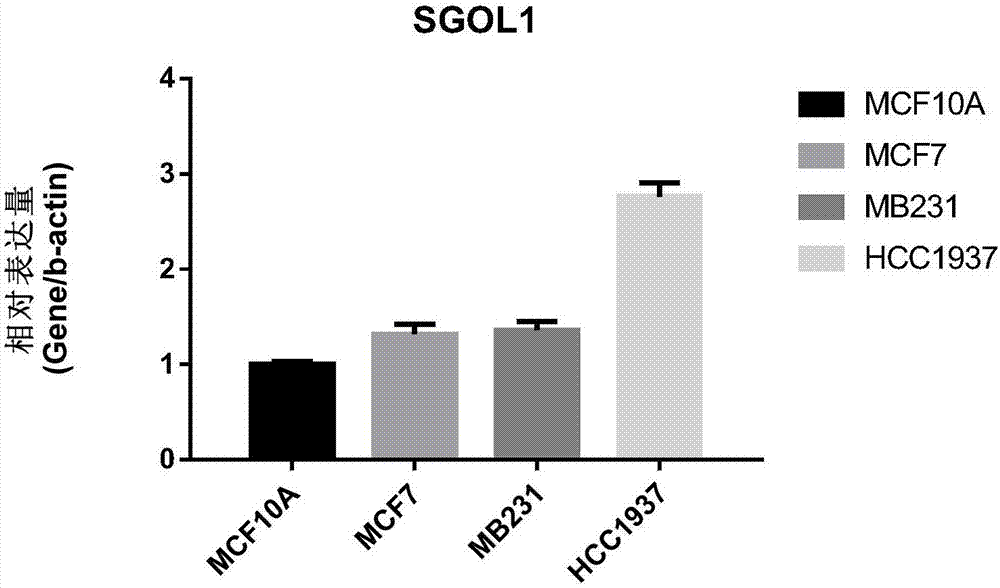
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering and oncology, and relates to a breast cancer marker SGOL1. The inventor researches different comparative cell systems, results show that an SGOL1 coded sequence is completely lowly expressed in normal cells and tissue of mammary gland and is remarkably highly expressed in tumor cells, and in addition expression of the gene is remarkably related to clinical pathology parameters. The SGOL1 provided by the invention can be used as a specific tumor marker for early-stage detection on breast cancer or a treatment target, and has significant clinical application values.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Pap staining solution and application method
InactiveCN108535077AFast coloringRinsing floating color is convenient and simplePreparing sample for investigationClear cellNuclear staining
The invention discloses a Pap staining solution and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. Specifically, the Pap staining solution contains a cell nuclear staining solution and a cytosolic staining solution. The Pap staining solution provided by the invention is simple to operate, and ensures uniform staining, clear cell structure after staining and bright cell colors, soas to facilitate diagnostic observation and judgment of clinical pathology.
Owner:南京福怡科技发展股份有限公司
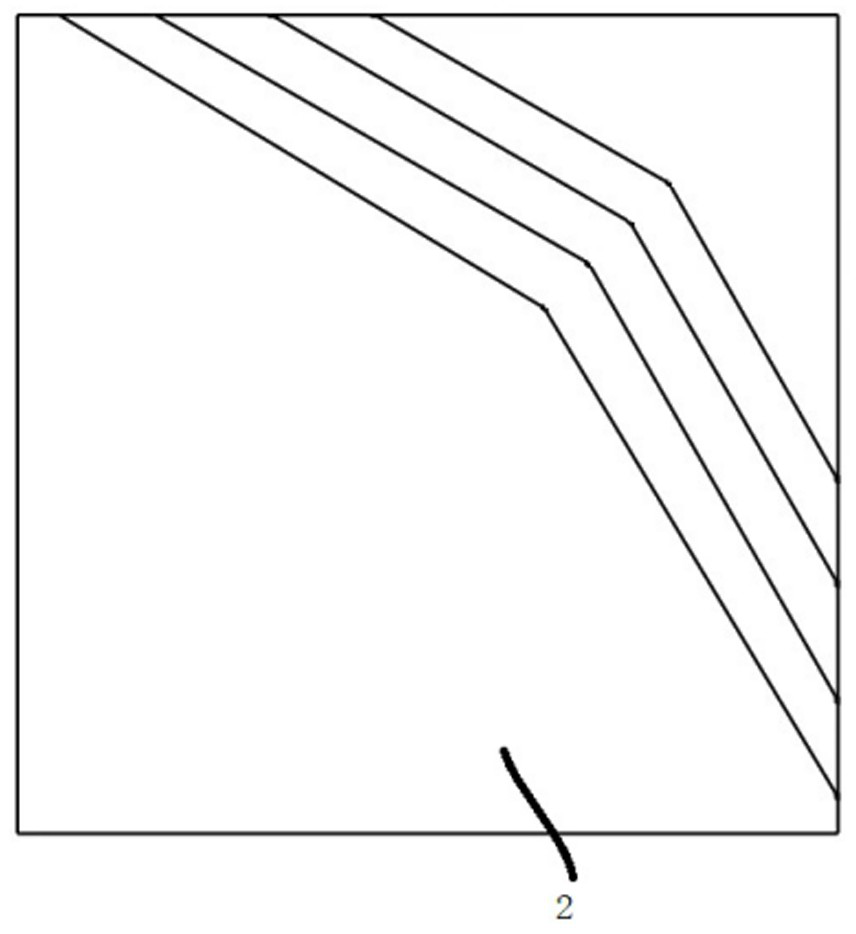
Multi-view tumor tissue pathological section and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112798381AObserve growth characteristicsReduce difficultyPreparing sample for investigationAnatomyTumor tissue
The invention discloses a multi-view tumor tissue pathological section. The pathological section comprises a tumor tissue, a glass slide, a supporting cover glass and an overlying cover glass, wherein the supporting cover glass and the overlying cover glass are oppositely distributed; the tumor tissue is pasted among the glass slide, the supporting cover glass and the overlying cover glass; the tumor tissue is of a cylinder structure, and the cross section is V-shaped with different included angles; the thickness of each part of the tumor tissue is 4-6 microns, and the flatness of each part is kept consistent; the supporting cover glass and the overlying cover glass are matched with different models according to the V-shaped included angles of the sections of the tumor tissues, and the tumor tissues with different included angles can be packaged. According to the pathological section, the form of a tumor tissue can be observed from X, Y and Z visual angles, and the three-dimensional whole tissue state of the tumor tissue is observed, so the growth characteristics of forward tissue textures and reverse tissue textures of the tumor tissue are effectively observed, difficulty of clinical pathology judgment is reduced, and accuracy of clinical pathology judgment is improved.
Owner:THE PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHAANXI PROV
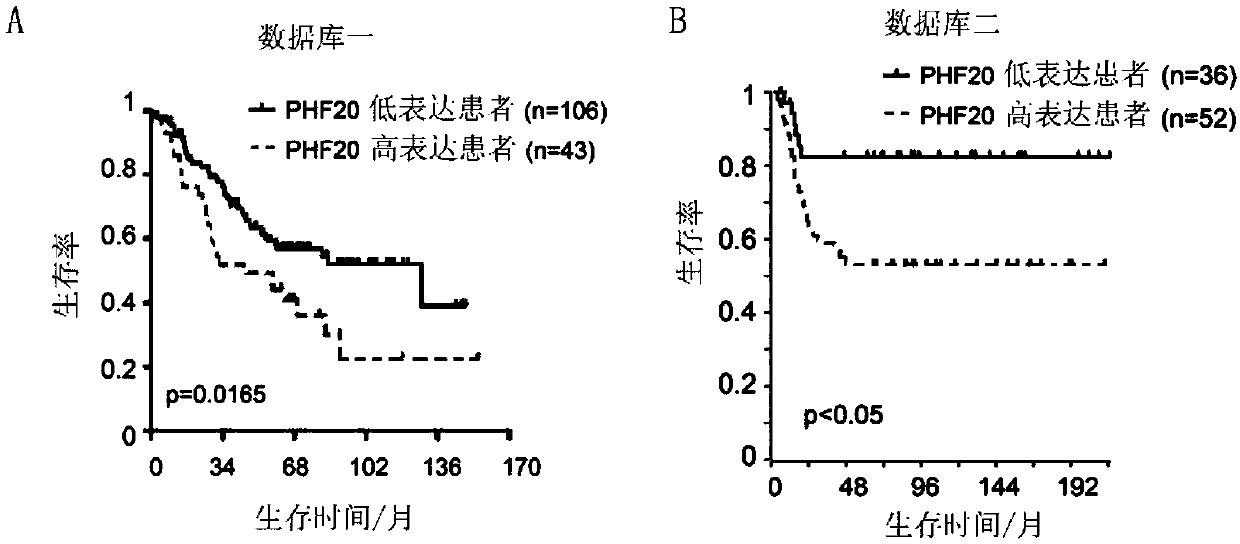
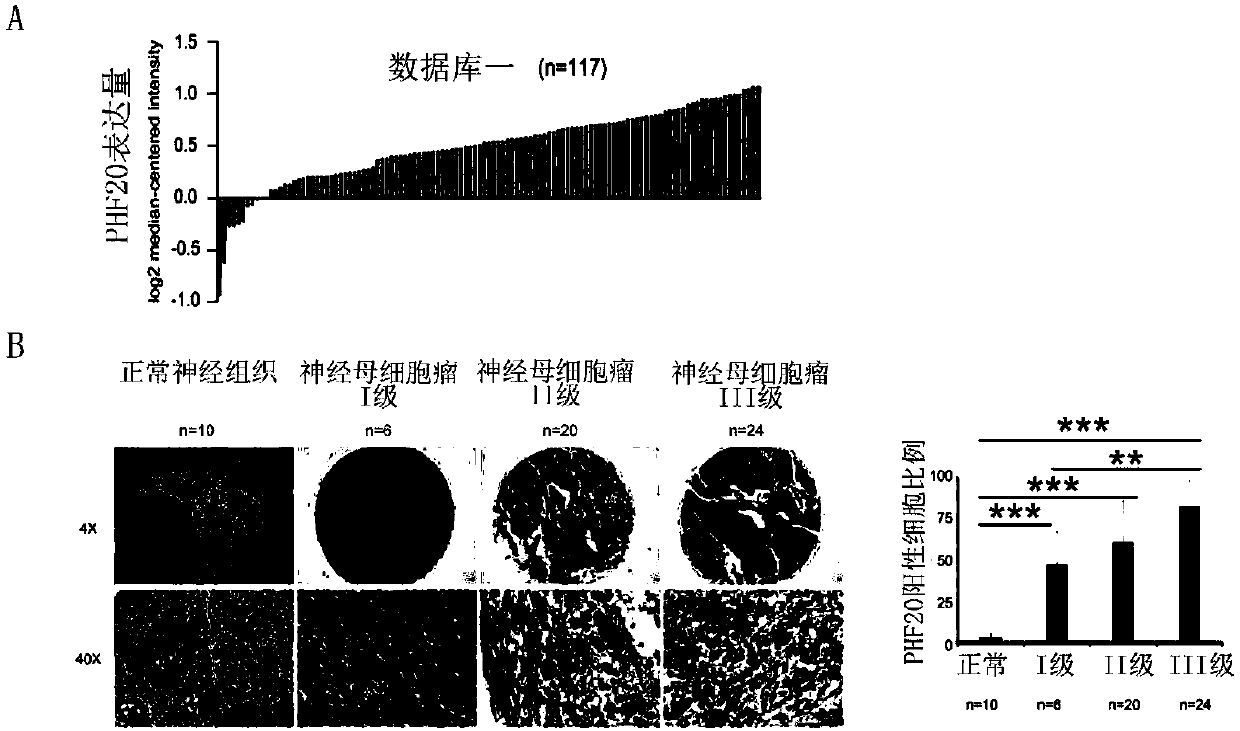
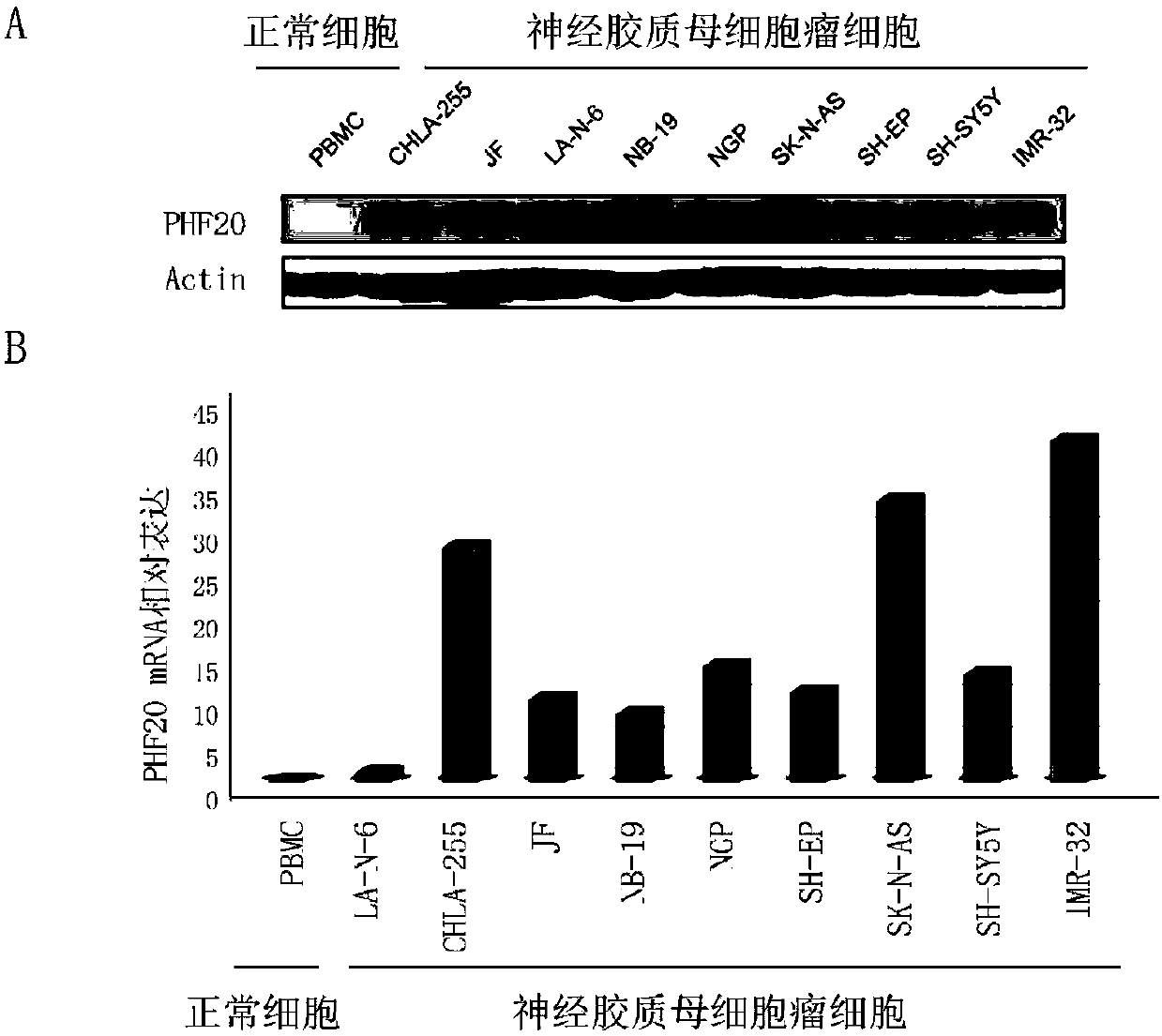
Neuroblastoma-related tumor marker and application thereof
ActiveCN107937526AOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNeoplasm diagnosisPatient evaluation
The invention discloses a neuroblastoma-related tumor marker PHF20 and application of a kit for detecting the expression level of PHF20 to neuroblastoma detection and diagnosis or prognostic patient evaluation, and belongs to the field of tumor diagnosis and molecular targeted therapy. The expression level of the PHF20 is closely related to clinicopathological parameters and patient prognosis, sothat the PHF20 can be used as a specific tumor marker for early detection of neuroblastoma or a prognostic index.
Owner:徐州维康生物科技有限公司
Method for transiting cells through electrostatic adherence
InactiveCN101556227APrevent insufficient transferWill not deformMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationAlcoholThin layer
The invention relates to a method for transiting cells through electrostatic adherence. The method is used when a cell, in particular a liquid-based thin-layer cell, is collected and made into a slide during the clinical pathology examination. The method is characterized in that the liquid-based thin-layer cell has an alcohol ion (CHO) and a hydrogen ion (H), and the slide has ferric trichloride (Fe(OH)3). During cell transition, because the cell has the alcohol ion (CHO) and the hydrogen ion (H), the cell is easily adhered by the (Fe(OH)3) on the slide so that the process of transiting a great number of cells from a filtering membrane to a slide can be smoothly realized. The invention prevents the insufficient cell transition, and the cell is not deformed, therefore, the aims of high quality slide making and accurate judgment can be achieved.
Owner:孝感宏翔生物医械技术有限公司
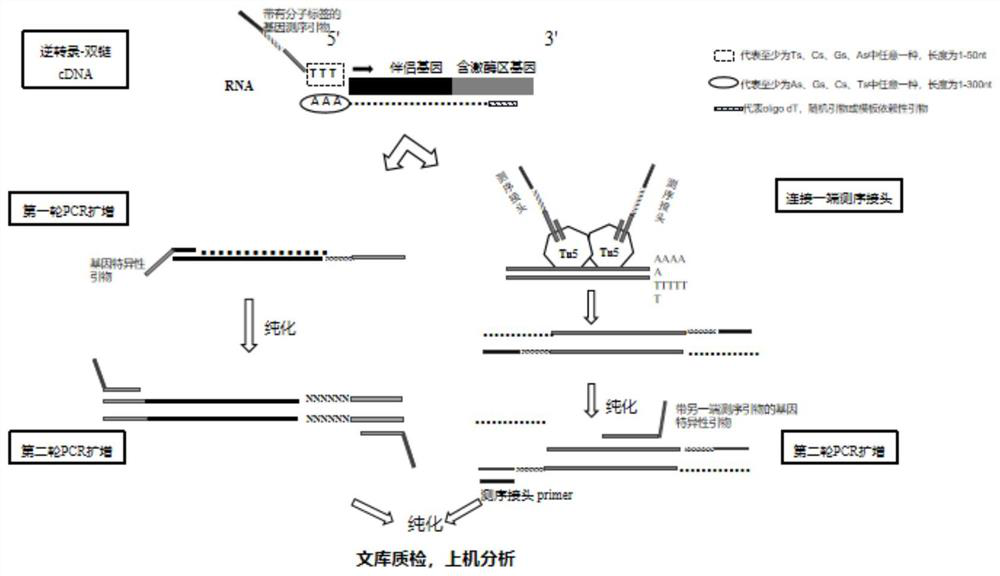
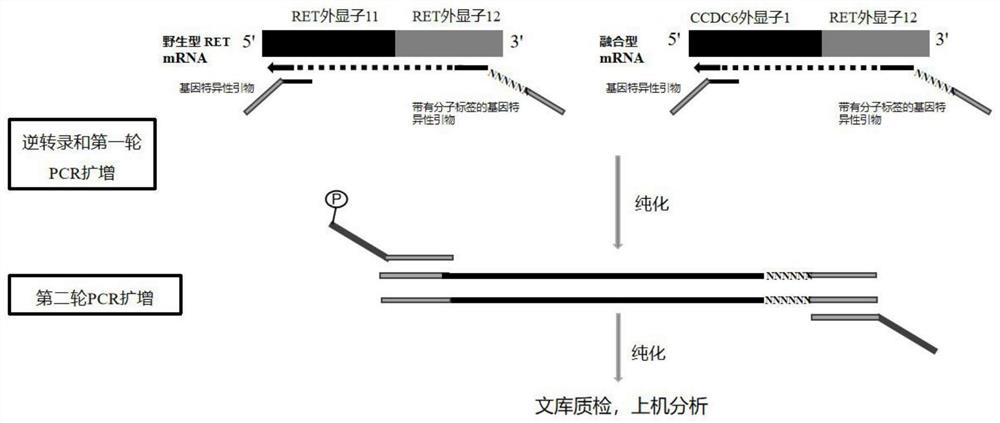
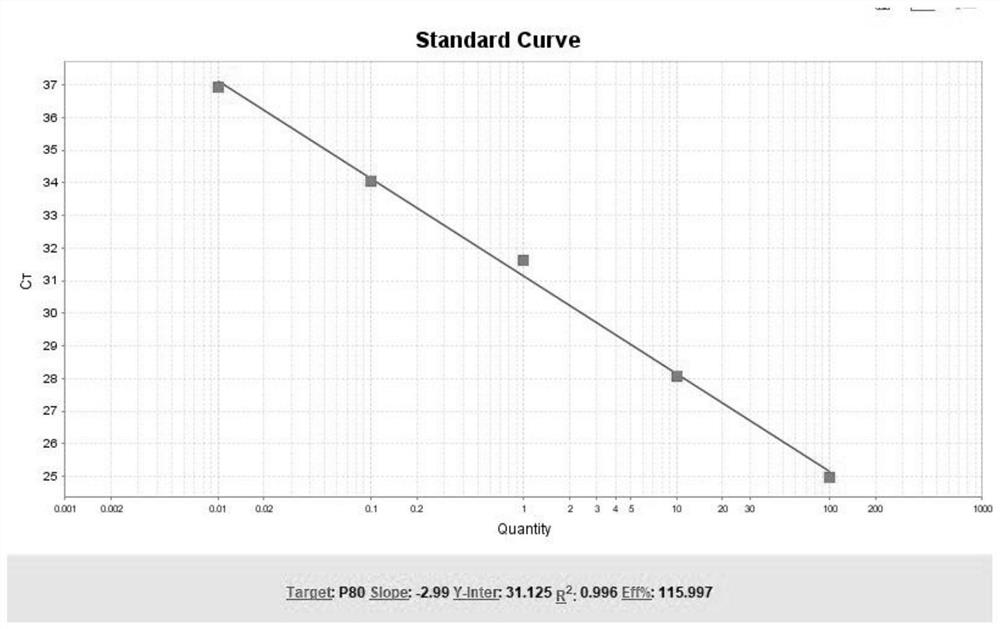
Method and kit for organism fusion gene detection and fusion abundance quantification
InactiveCN112795654ASolving fusion detection challengesImprove detection accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplexBiological body
The invention discloses a method and a kit for organism fusion gene detection and fusion abundance quantification in the technical field of molecular biology. The kit is used for quantitatively detecting the abundance of various variation forms of a fusion gene in an organism by combining a multiplex PCR capture technology with a molecular tag deduplication technology; based on the detection result and a clinical pathology analysis result, the kit can provide help for scientific research, new drug development or auxiliary diagnosis and treatment of tumors.
Owner:上海睿璟生物科技有限公司
Application of VEGF-C in screening of medicine for diagnosing or treating implantation metastasis cancer
InactiveCN106421788APromote hyperplasiaPromote differentiationAntineoplastic agentsPharmaceutical active ingredientsOvarian epithelial cancerLymphatic Spread
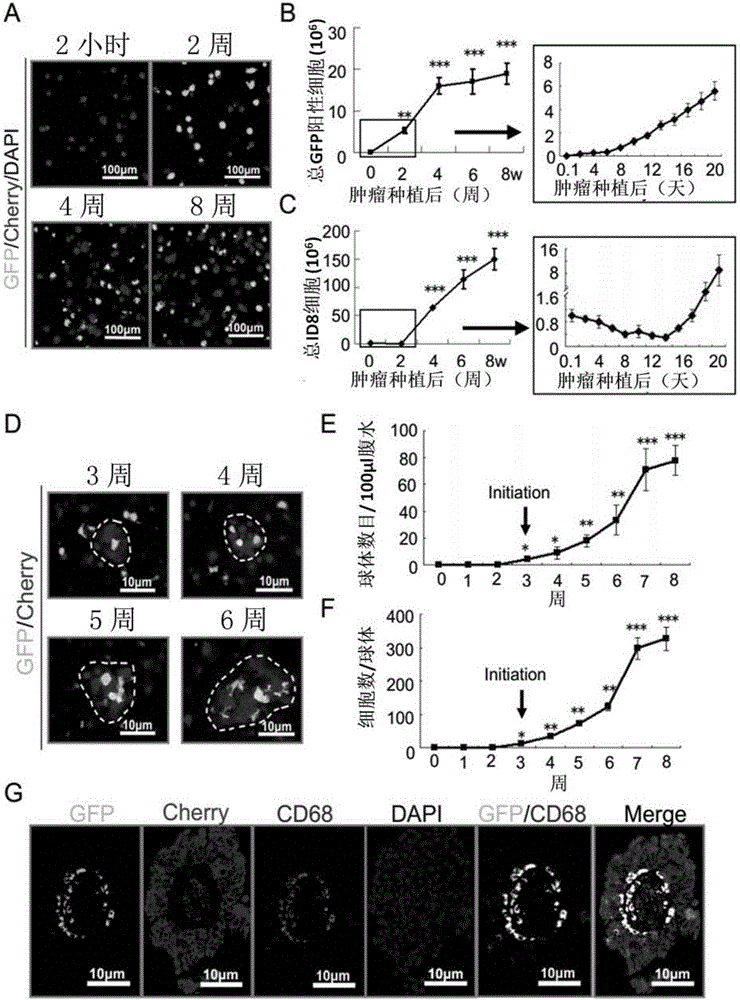
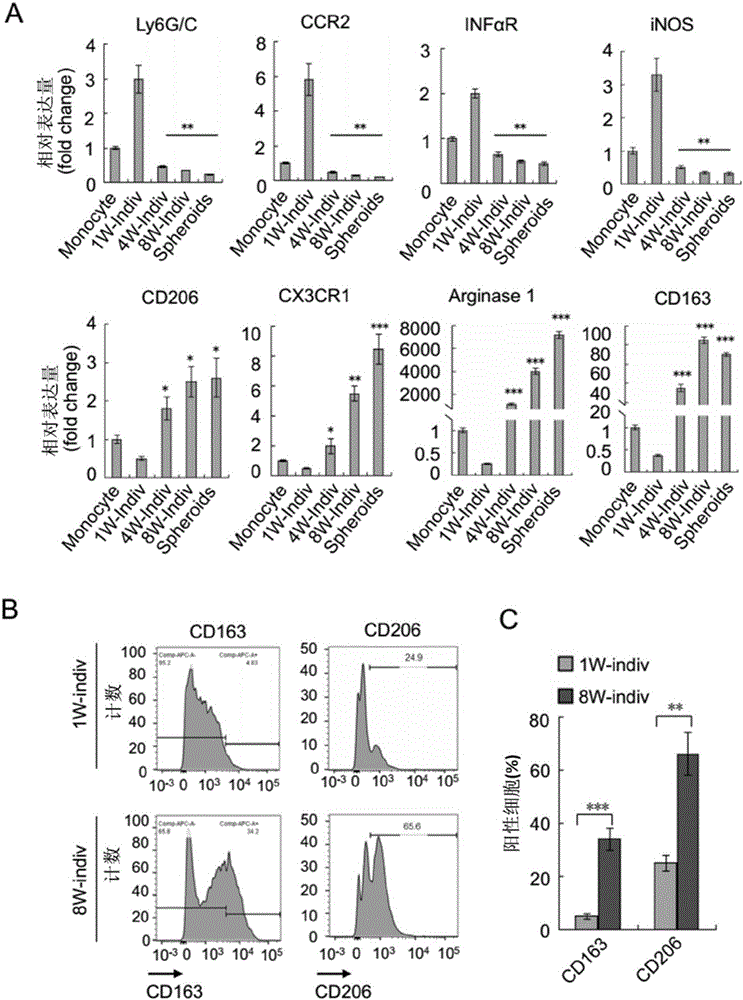
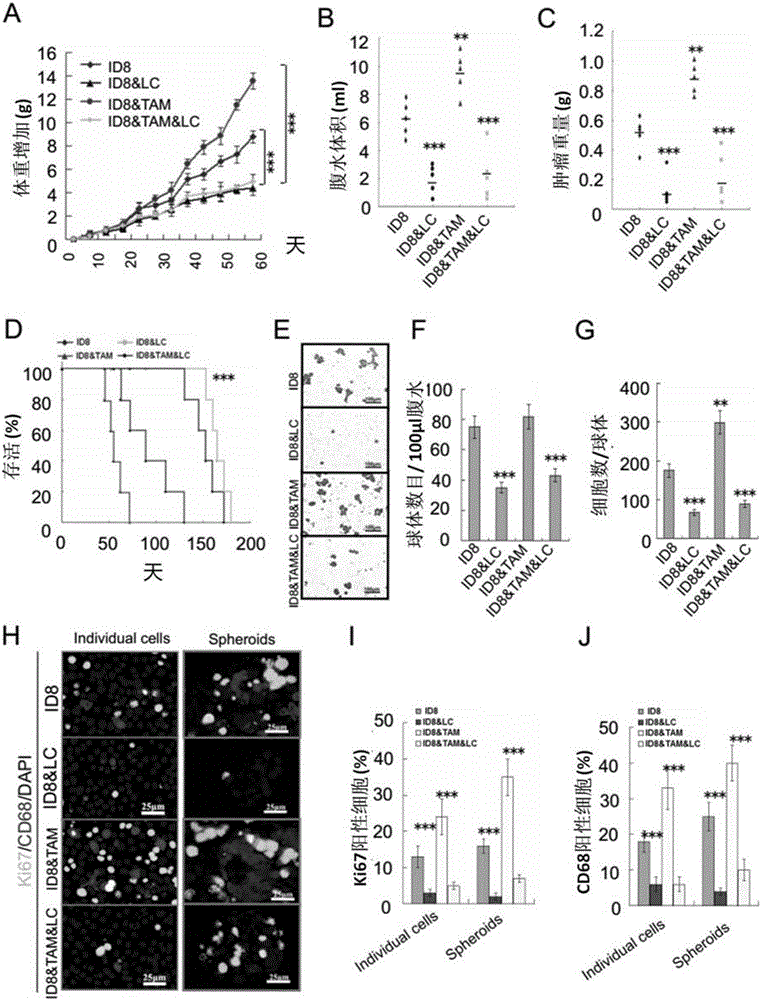
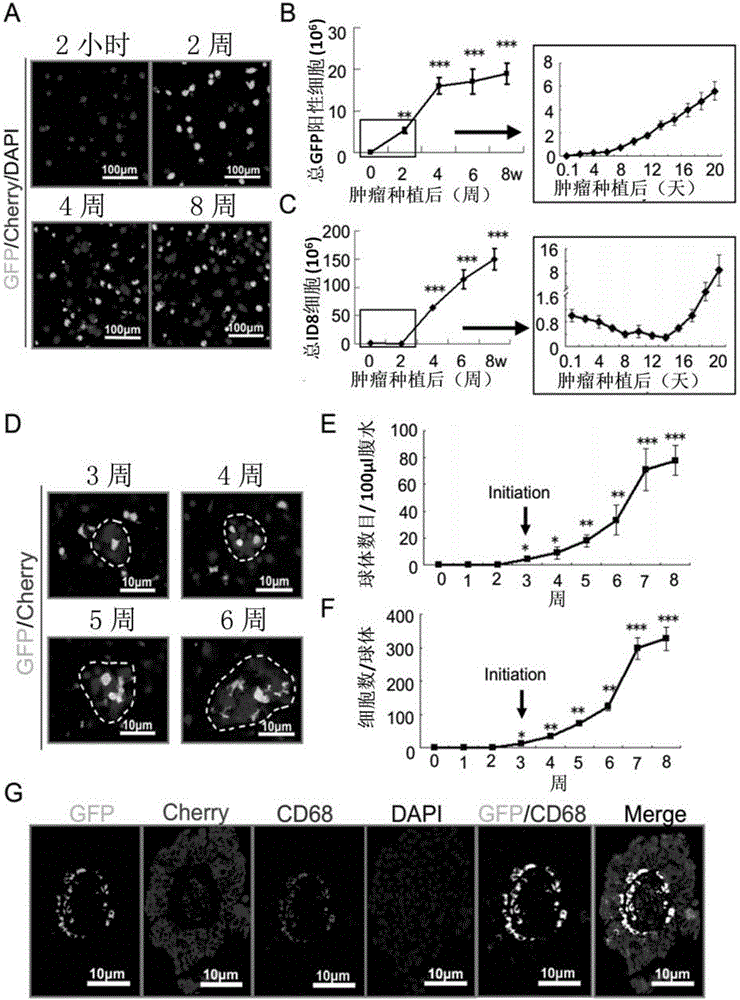
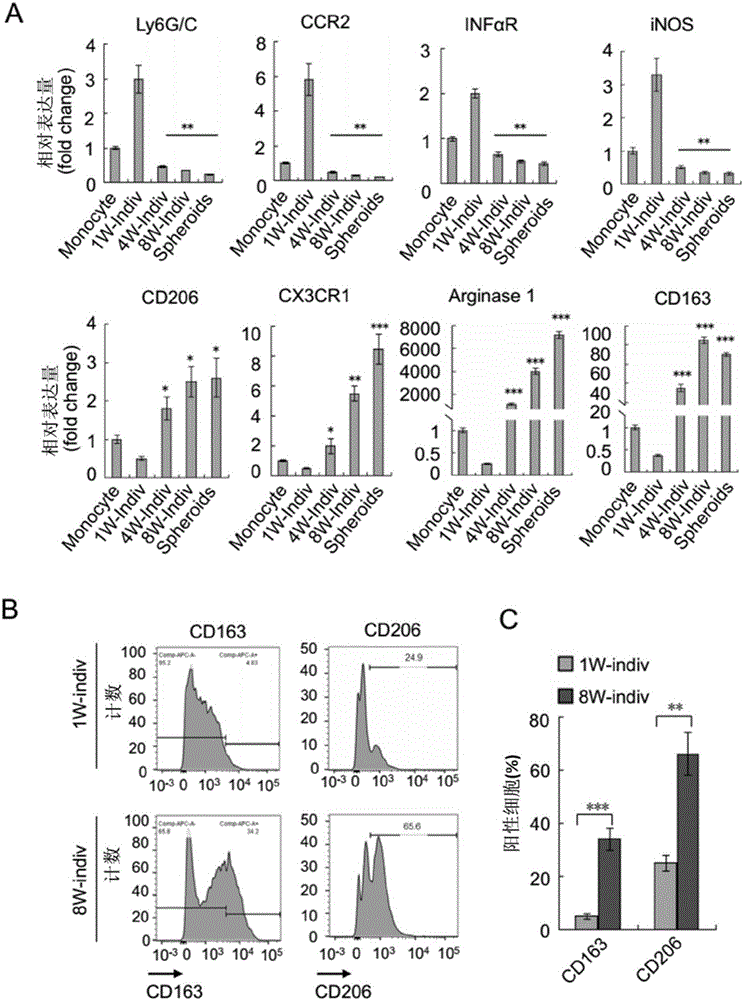
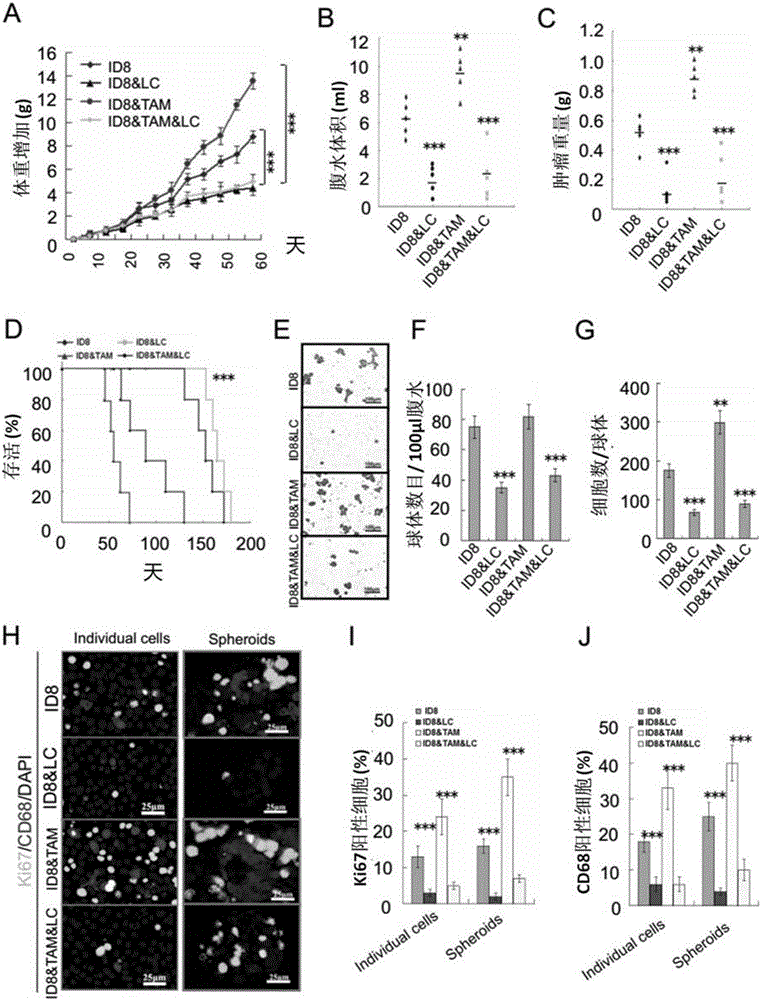
The invention discloses application of VEGF-C in screening of medicine for diagnosing or treating implantation metastasis cancer, and belongs to the field of medicine. It is proved that TAM relevant spheroids and the ovarian cancer clinical pathology are closely connected, an ovarian epithelial cancer model established in a mouse indicates that TAM promotes spheroid forming and tumor growing in the ovarian cancer implantation metastasis early stage, after EGF excreted by TAM activates EGFR on tumor cells, the EGF up-regulates tumor cells VEGFs-VEGFRs pathway signal transduction in return and then promotes tumor cell proliferation and differentiation, the EGF can up-regulate expression of alphaMbeta2 integral protein on TAM and expression of ICAM-1 on the tumor cells, and the tumor cell-TAM association is promoted. After TAM or medicine retardant VEGF or ICAM-1 in antibodies are removed from the rat, spheroid forming and ovarian cancer progression are hindered. A new mechanism of TAM mediated spheroids is disclosed, and new targeted therapy is provided for ovarian cancer and other distant metastatic cancer.
Owner:广州道瑞医药科技有限公司
Method for analyzing influence of discovered protein marker on liver cancer
The invention discloses a method for analyzing influence of a discovered protein marker on liver cancer. The method comprises the following steps: through real-time fluorescence quantitative RT-PCR and a Western blot technology, detecting a novel liver cancer marker in liver tissues of a liver cancer patient, a benign liver tumor patient and a normal person respectively, determining the expressionamount thereof in gene and protein levels and location thereof, and analyzing a relationship between the novel liver cancer marker and the clinical pathology of the liver cancer patient; constructingan eukaryotic expression vector of a novel liver cancer protein marker encoding gene with a fluorescent label, and transfecting expression of a liver cancer cell line; measuring cell characteristicsbefore and after transfection by using laser confocal microscopy and the like. The invention finds an effective tumor marker, which is of a great significance in research of a canceration mechanism, early diagnosis of a disease and prognostic judgment.
Owner:南宁科城汇信息科技有限公司
Applications of EGF in screening drugs used for diagnosing or treating implantation metastatic cancer
InactiveCN106498031APromote hyperplasiaPromote differentiationOrganic active ingredientsCompound screeningOvarian epithelial cancerLymphatic Spread
The invention discloses applications of EGF in screening drugs used for diagnosing or treating implantation metastatic cancer, and belongs to the field of medicine. Close connection between tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) related globoid with ovarian cancer clinical pathology is confirmed; it is shown by an ovarian epithelial cancer mouse model that TAM is capable of promoting forming of the globoids and the growth of tumour in the early phase of ovarian cancer implantation metastasis; EGF secreted by TAM is capable of activating EGFR on tumor cells, and then the EGFR is capable of realizing up regulation of surrounding tumor cell VEGFs-VEGFRs channel signal transduction and promoting tumor cell proliferation and differentiation; EGF is capable of realizing up regulation of expression of alpha M beta2 integral protein on TAM and ICAM-1 on tumor cells, and promoting association of tumor cells-TAM. In mouse, removing of TAM and drug blocking EGFR or neutralizing of ICAM-1 with an antibody is capable of inhibiting forming of the globoid and ovarian cancer development. The invention discloses a new mechanism of TAM-mediated globoid forming, and providing a novel targeted therapy method for ovarian cancer and other remote metastatic cancers.
Owner:广州道瑞医药科技有限公司
Ultrasonic image processing method and device and electronic equipment
PendingCN113469919AEnhance image detail featuresImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingTransformation algorithm
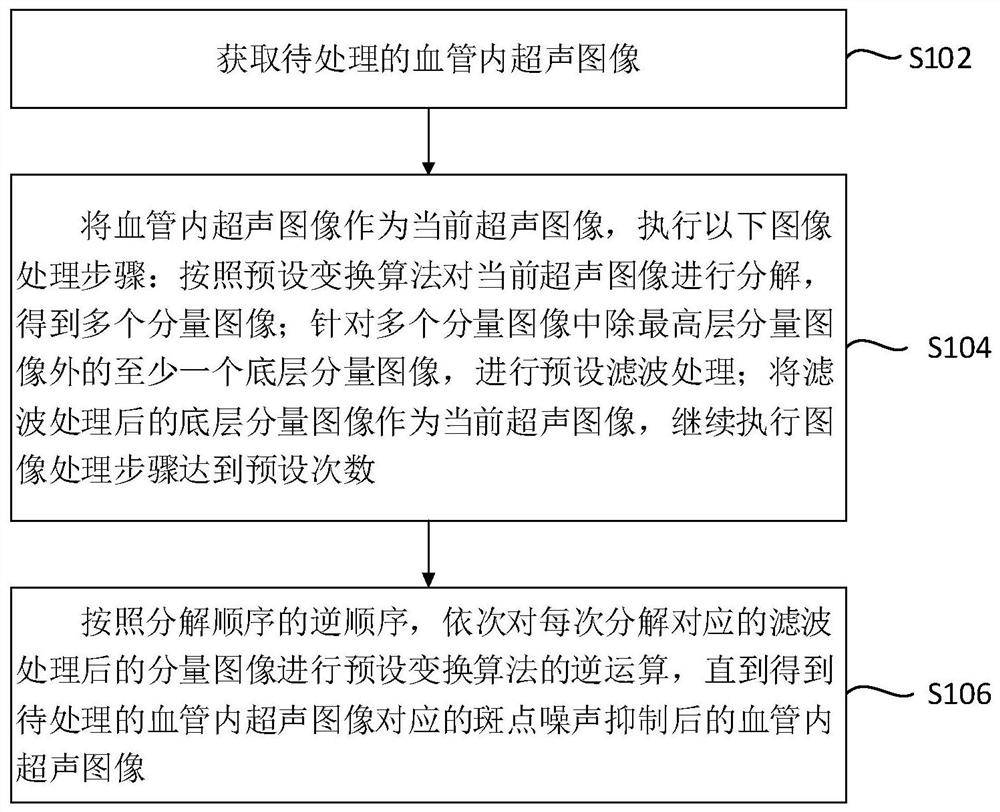
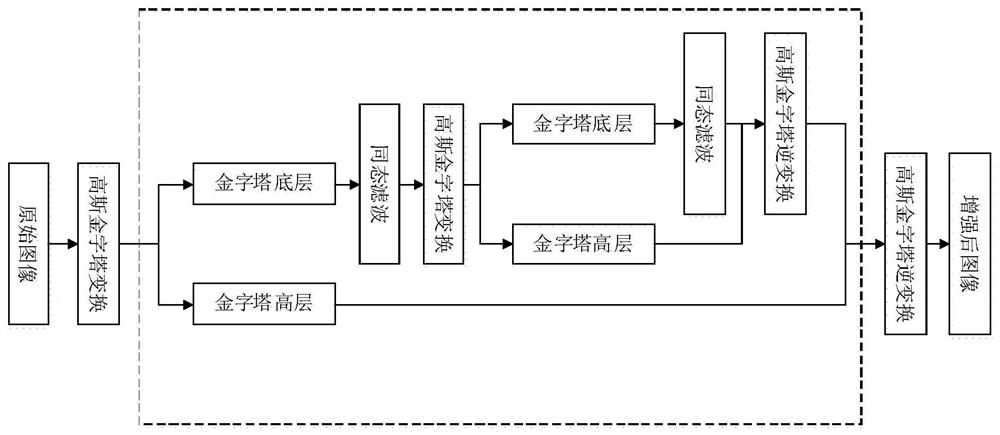
The invention provides an ultrasonic image processing method and device and electronic equipment. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a to-be-processed intravascular ultrasonic image, taking the intravascular ultrasonic image as a current ultrasonic image, and executing the following image processing steps of decomposing the current ultrasonic image according to a preset transformation algorithm to obtain a plurality of component images, performing preset filtering processing on at least one bottom-layer component image except the highest-layer component image in the plurality of component images, taking the filtered bottom-layer component image as a current ultrasonic image, and continuing to execute the image processing step to reach a preset number of times, and according to an inverse sequence of the decomposition sequence, sequentially carrying out inverse operation of a preset transformation algorithm on the filtered component image corresponding to each decomposition until the intravascular ultrasonic image after speckle noise suppression is obtained. According to the method, image detail features can be reserved and enhanced while speckle noise is suppressed, and the method is of great significance to diagnosis of clinical pathology.
Owner:SONOSEMI MEDICAL CO LTD
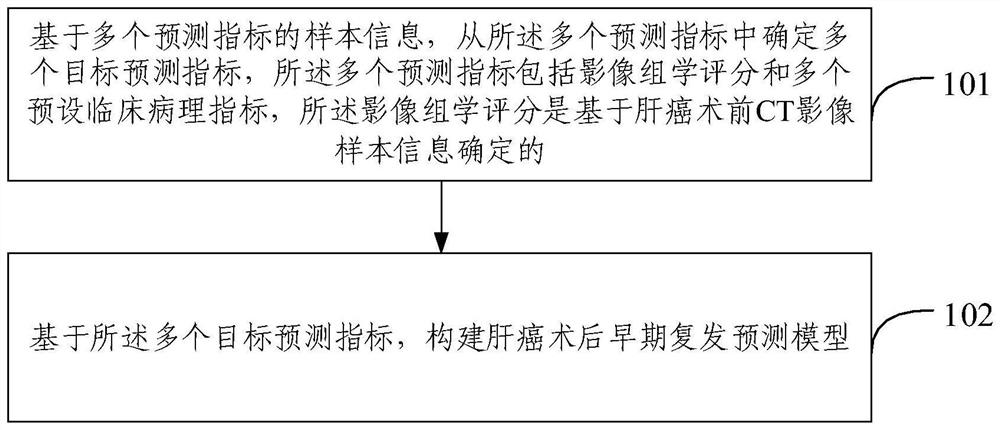
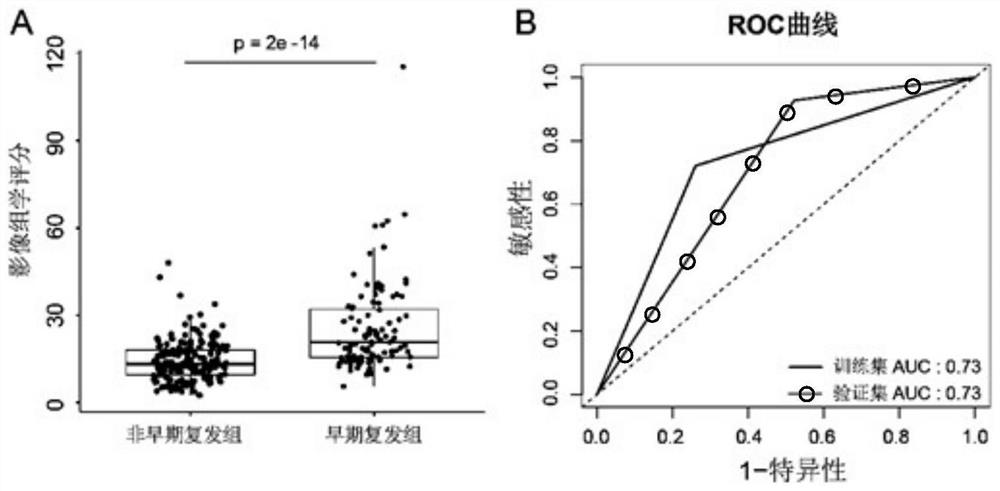
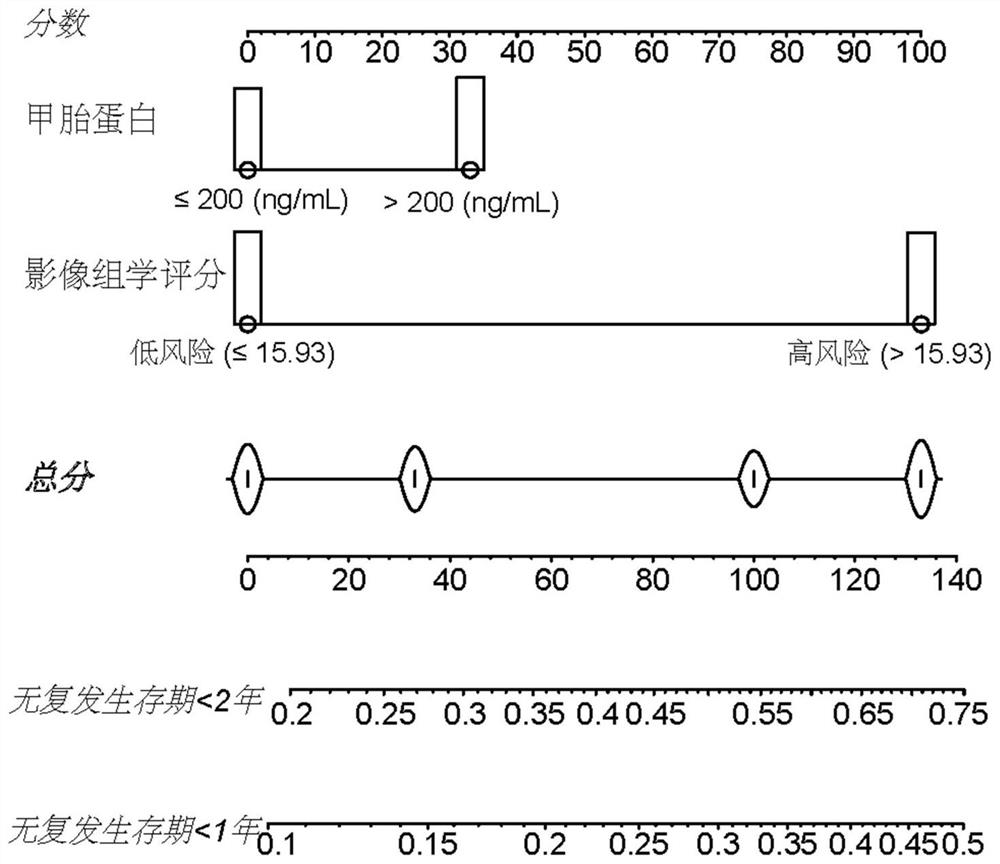
Method and device for constructing postoperative early recurrence prediction model of liver cancer
PendingCN114300135AEarly Relapse AccurateEarly recurrence prediction is accurateHealth-index calculationMedical practises/guidelinesEarly RecurrenceRecurrence prediction
The invention provides a liver cancer postoperative early recurrence prediction model construction method and device, and the method comprises the steps: determining a plurality of target prediction indexes from a plurality of prediction indexes based on the sample information of the plurality of prediction indexes, the plurality of prediction indexes comprise radiomics scores and a plurality of preset clinical pathology indexes, and the preset clinical pathology indexes comprise the radiomics scores and the preset clinical pathology indexes; the radiomics score is determined based on liver cancer preoperative CT image sample information; and constructing a liver cancer postoperative early recurrence prediction model based on the plurality of target prediction indexes. The prediction model provided by the invention can efficiently and accurately predict the early recurrence of the liver cancer patient, and greatly improves the prognosis of the liver cancer postoperative patient.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUILIN MEDICAL UNIV
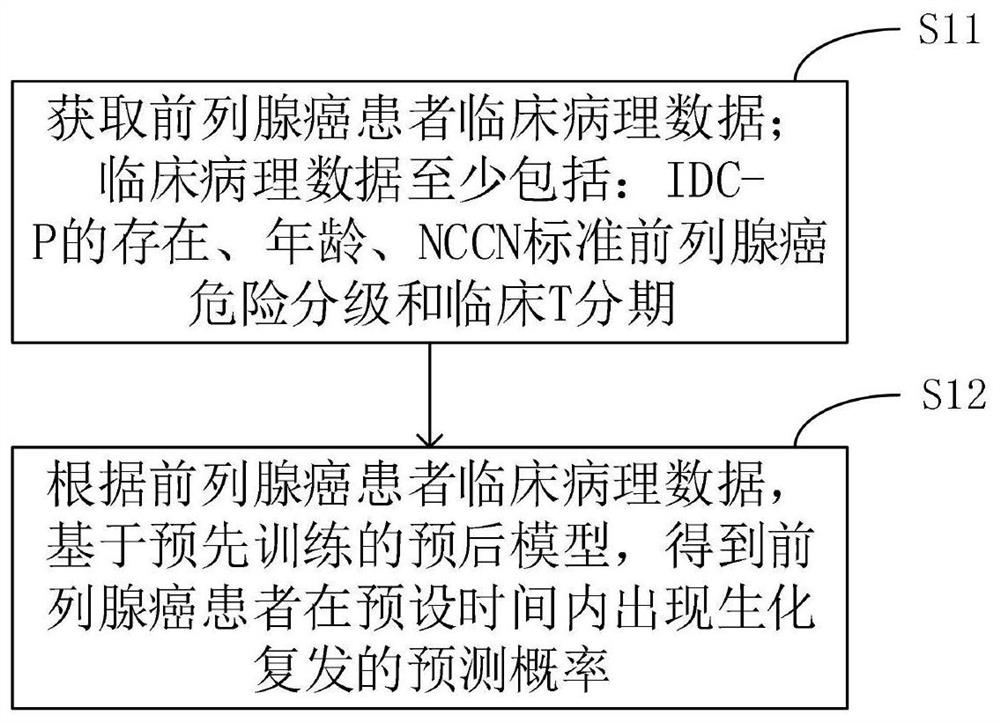
Method and equipment for predicting postoperative biochemical relapse of prostate cancer patient
PendingCN113284619AImprove forecast accuracyImprove forecasting efficiencyHealth-index calculationForecastingClinico pathologicalPrediction probability
The invention relates to a method and equipment for predicting postoperative biochemical relapse of a prostate cancer patient. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring clinical pathological data of the prostate cancer patient, wherein the clinical pathology data at least comprise existence of IDC-P, age, NCCN standard prostate cancer risk classification and clinical T stage, and the clinical pathology data has certain correlation with the probability of biochemical recurrence of the prostate cancer patient. According to the clinical pathology data of the prostate cancer patient, based on a pre-trained prognosis model, a prediction probability of biochemical recurrence of the prostate cancer patient within a preset time is obtained. Prediction is performed through the prognosis model, compared with physicians, the prediction efficiency is higher, the prediction accuracy of the prognosis model can be continuously improved along with increase of sample data, and the prediction accuracy is higher compared with the physicians.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Method for establishing acute high altitude anoxia and anxiety stress response animal model
ActiveCN106035210AContinuous exposureStable temperatureAnimal husbandryHigh elevationHigh altitude hypoxia
The invention provides a method for establishing an acute high altitude anoxia and anxiety stress response animal model. The method comprises the following steps of (1) raising mice at conventional elevation environment, and performing cold water forced swimming adaptability training; (2) and then enabling the mice obtained in the step (1) to be exposed to high-elevation environmental conditions for raising, and performing high-elevation environment composite cold water forced swimming so as to obtain the acute high altitude anoxia and anxiety stress response animal model. The acute high altitude anoxia and anxiety stress response animal model obtained by the method disclosed by the invention has cerebral anoxia pathology characteristics that an aerobic metabolism way of sugar in brain tissues is blocked, so that the supply of ATP energy sources is obviously reduced, and lactic acid is accumulated, and behavioral expression of anorexia and enhanced anxiety behavior, and the induced stimulating factors and clinical pathology behavioral expression of the model both approach the actual situations of acute altitude stress response.
Owner:NAVY MEDICINE RES INST OF PLA
Non-alcoholic fatty liver animal model and establishment method
The invention relates to the technical field of animal model establishment, in particular to a non-alcoholic fatty liver animal model and an establishment method. The animal model is established by adopting an NR4A1- / -gene knockout mouse. The NR4A1- / -gene knockout mouse is adopted to establish the non-alcoholic fatty liver animal model, the relationship between the NR4A1- / -gene and glycometabolism and fat metabolism of the liver is fully utilized, the glycolipid metabolism of the NR4A1- / -gene knockout mouse is disturbed, and fat can be deposited on the liver after high-fat feeding, so that the non-alcoholic fatty liver is formed; the method is simple to operate and obvious in effect. The animal model has the characteristics of obesity, dyslipidemia and the like, and has high similarity with NAFLD clinical pathology.
Owner:北京基谱生物科技有限公司
Primer set for detecting I-type herpes simplex virus and kit
InactiveCN103045760AEfficient specificityHigh amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationConserved sequencePositive control
The invention relates to a primer set for detecting I-type herpes simplex virus and a kit. Primer sequences of the primer set respectively are SEQ ID NO:1 to 2. The kit disclosed by the invention consists of a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) amplification reagent, a forward and reverse primer combination, positive control nucleic acid and sterilized distilled water. According to the invention, viruses are detected by a method of designing and synthesizing forward and reverse primers capable of amplifying I-type herpes simplex virus specific DNA according to a conserved sequence of I-type herpes simplex virus genome DNA and utilizing a special PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification reagent to direct perform PCR reaction without carrying out extraction on DNA of a sample. According to the invention, the step of extracting DNA of a template is omitted, one important link of losing the sample size is reduced and the highest utilization degree of limited clinical samples is ensured; and meanwhile, detection time is greatly shortened, a detection result can be obtained in 2 hours, and the primer set and the kit can take a good auxiliary effect on early diagnosis of clinical pathology.
Owner:SHANDONG EYE INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com