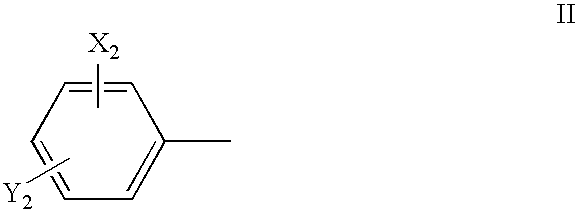Patents
Literature
421 results about "Lymph Cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lym·pho·cyte. A white blood cell formed in bone marrow and distributed throughout the body in lymphatic tissue (for example, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, Peyer patches), where it undergoes proliferation. In normal adults, lymphocytes make up 22-28% of the total number of leukocytes in the circulating blood.
Novel receptor TREM (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) and uses thereof
InactiveUS20030165875A1Strong upregulationAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsReceptor for activated C kinase 1Monocyte
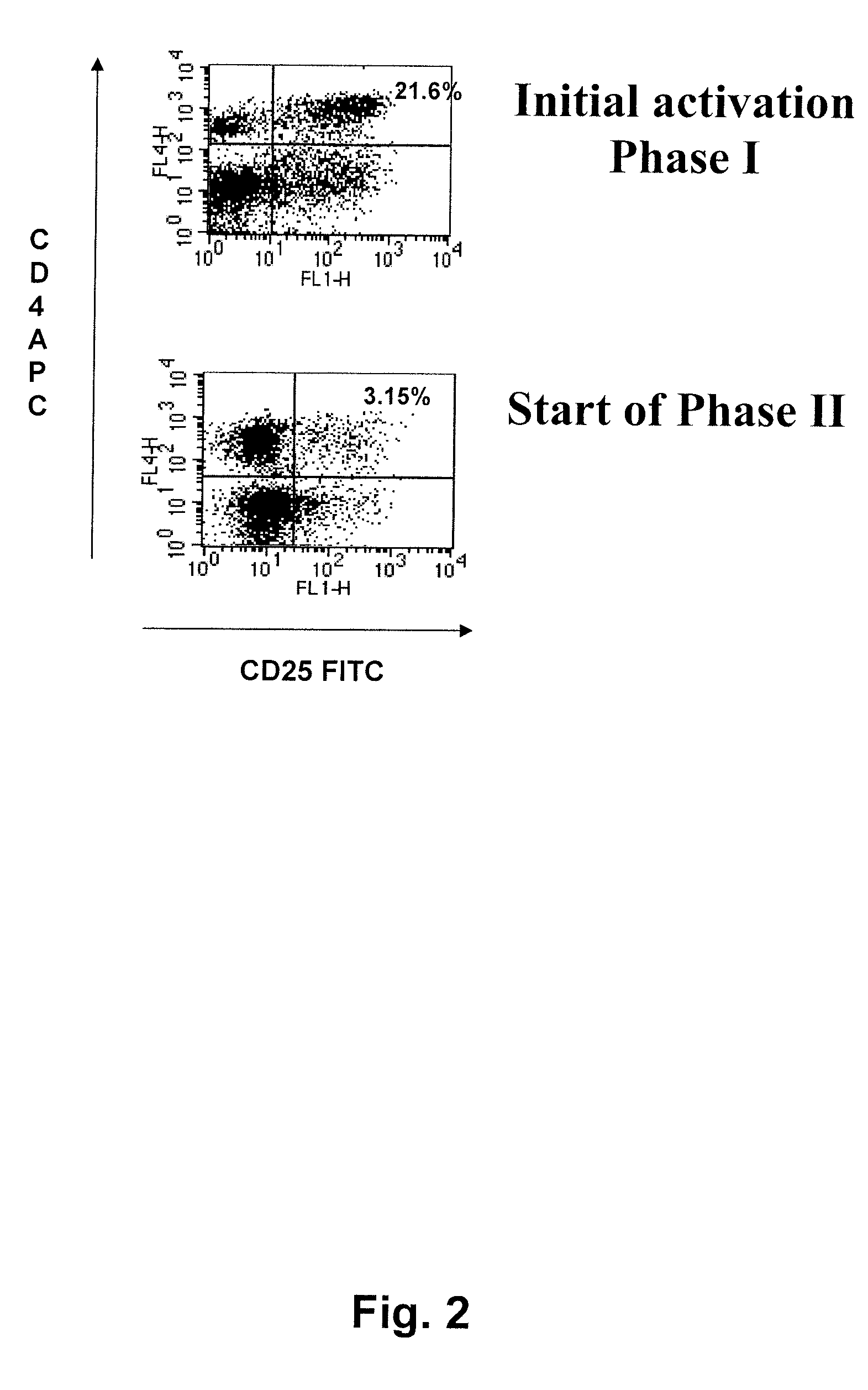
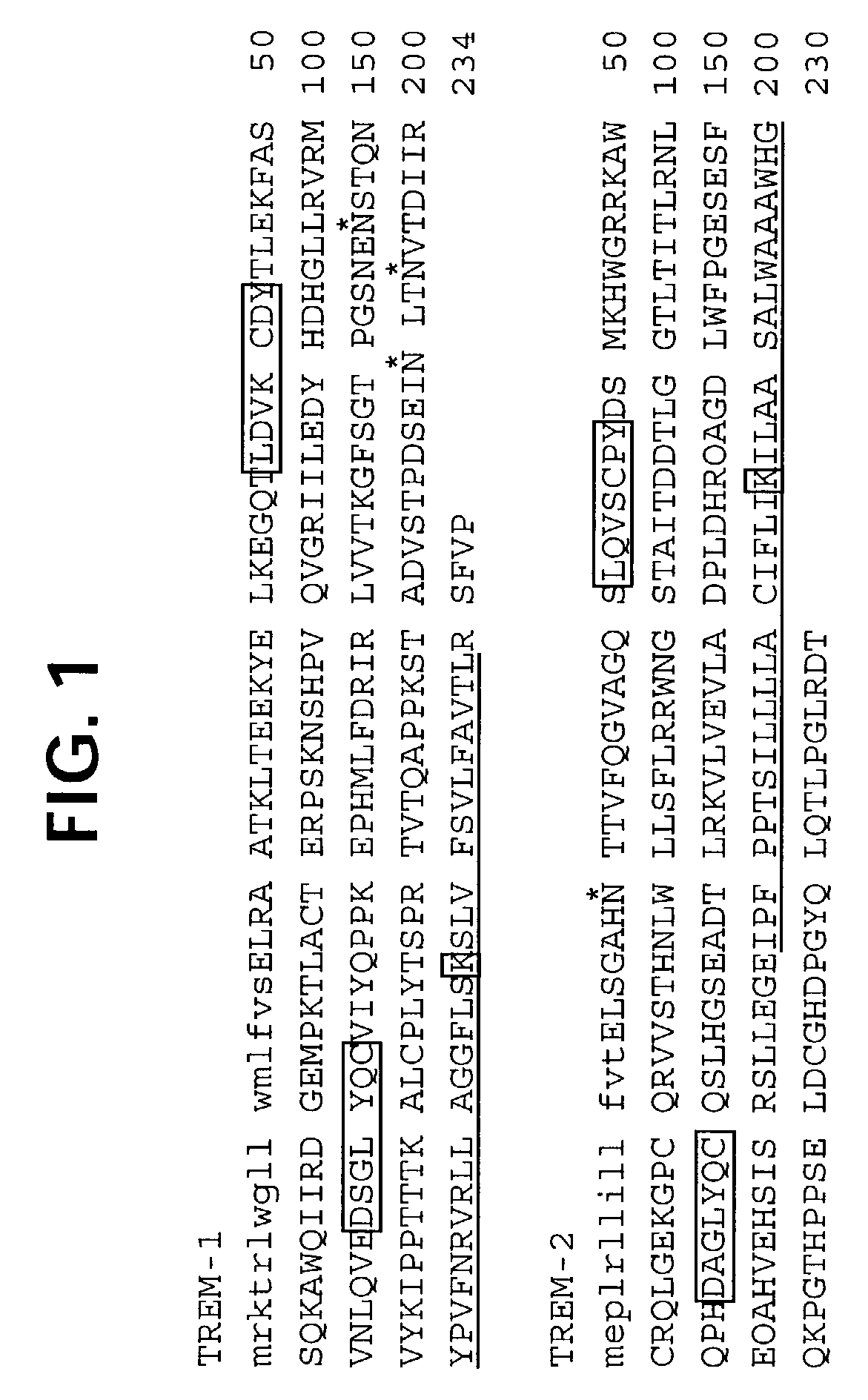
Novel activating receptors of the Ig super-family expressed on human myeloid cells, called TREM(s) (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) are provided. Specifically, two (2) members of TREMs, TREM-1 and TREM-2 are disclosed. TREM-1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on blood neutrophils and a subset of monocytes but not on lymphocytes and other cell types and is upregulated by bacterial and fungal products. Use of TREM-1 in treatment and diagnosis of various inflammatory diseases is also provided. TREM-2 is also a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on mast cells and peripheral dendritic cells (DCs) but not on granulocytes or monocytes. DC stimulation via TREM-2 leads to DC maturation and resistance to apoptosis, and induces strong upregulation of CCR7 and subsequent chemotaxis toward macrophage inflammatory protein 3-beta. TREM-2 has utility in modulating host immune responses in various immune disorders, including autoimmune diseases and allergic disorders.
Owner:BIOXELL
Method for automatically analyzing nucleated bone marrow cells
InactiveUS20030219850A1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationStainingLipid particle
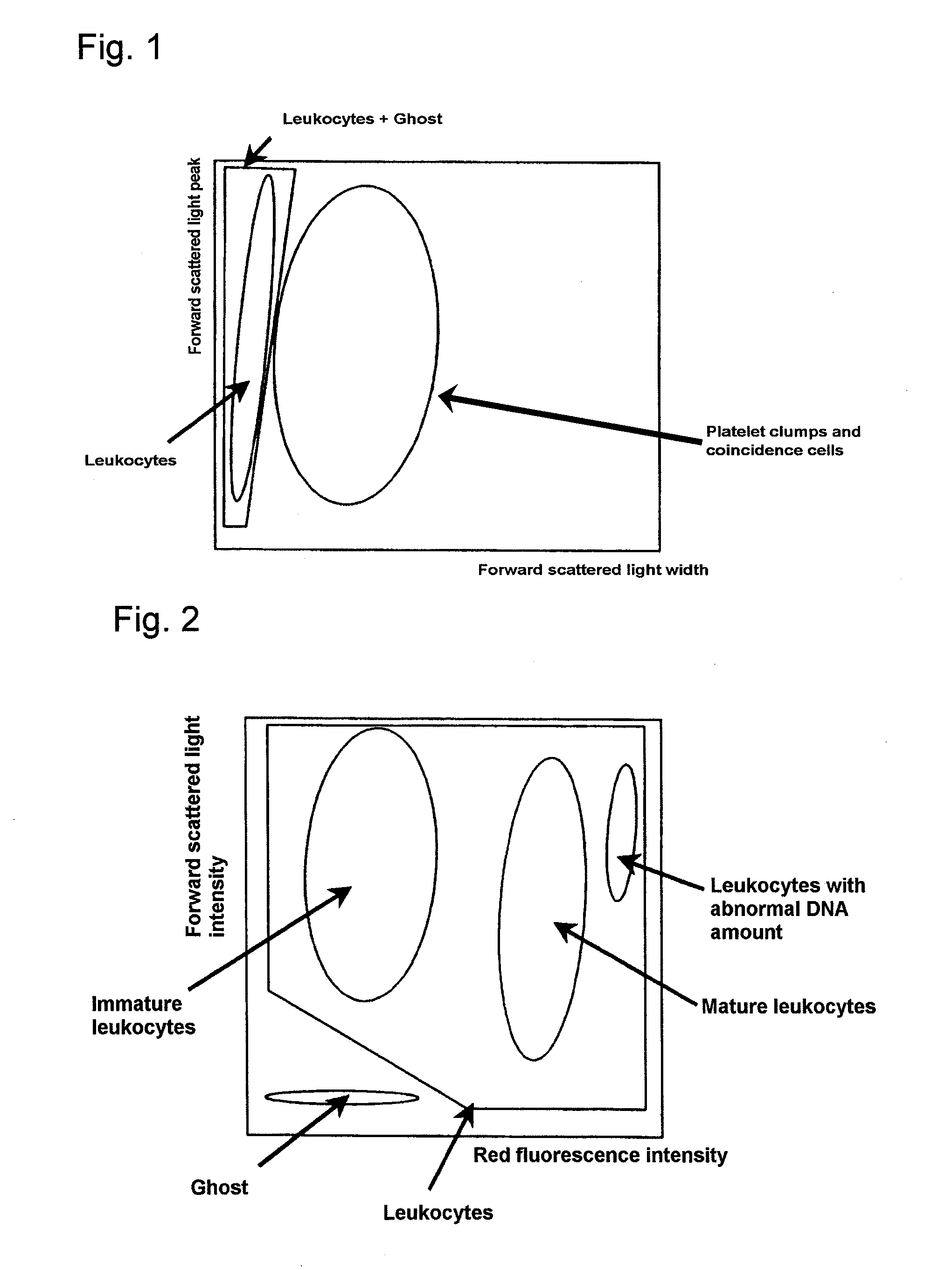
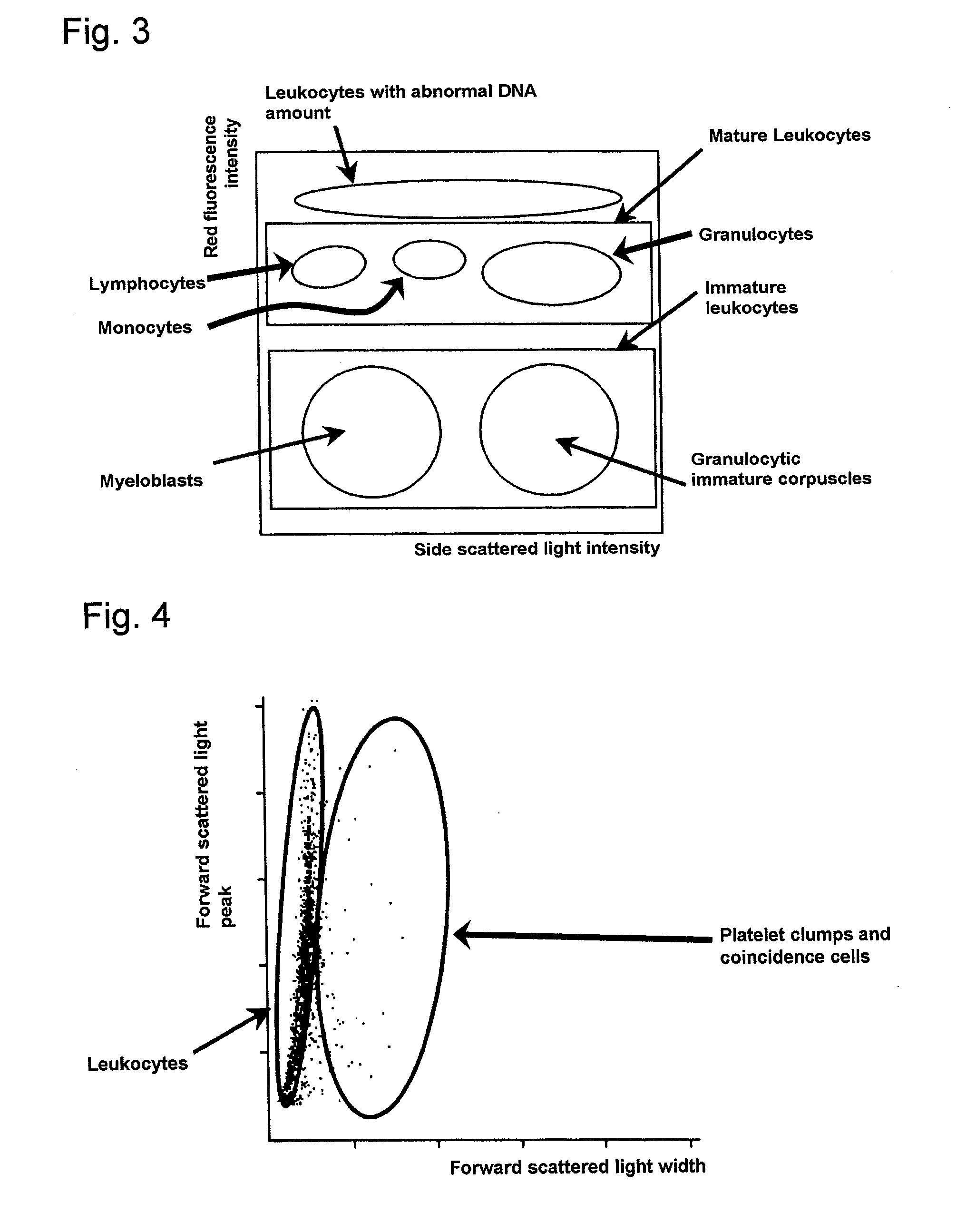
An automatic method for analyzing nucleated bone marrow cells comprising partitioning one sample of bone marrow fluid with two samples, one sample being treated with a first lysing agent and a first staining solution and the other sample being treated with a second lysing agent and a second staining solution; and measuring each samples in a flow cytometer using a scattered light and fluoresence which enables to classify and count leukocytes, erythroid cells and lipid particles, as well as mature myeloid cells, lymphoid cells and immature myeloid cells, and to calculate the number of myeloid cells as well as the ratio of myeloid cells and erythroid cells.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
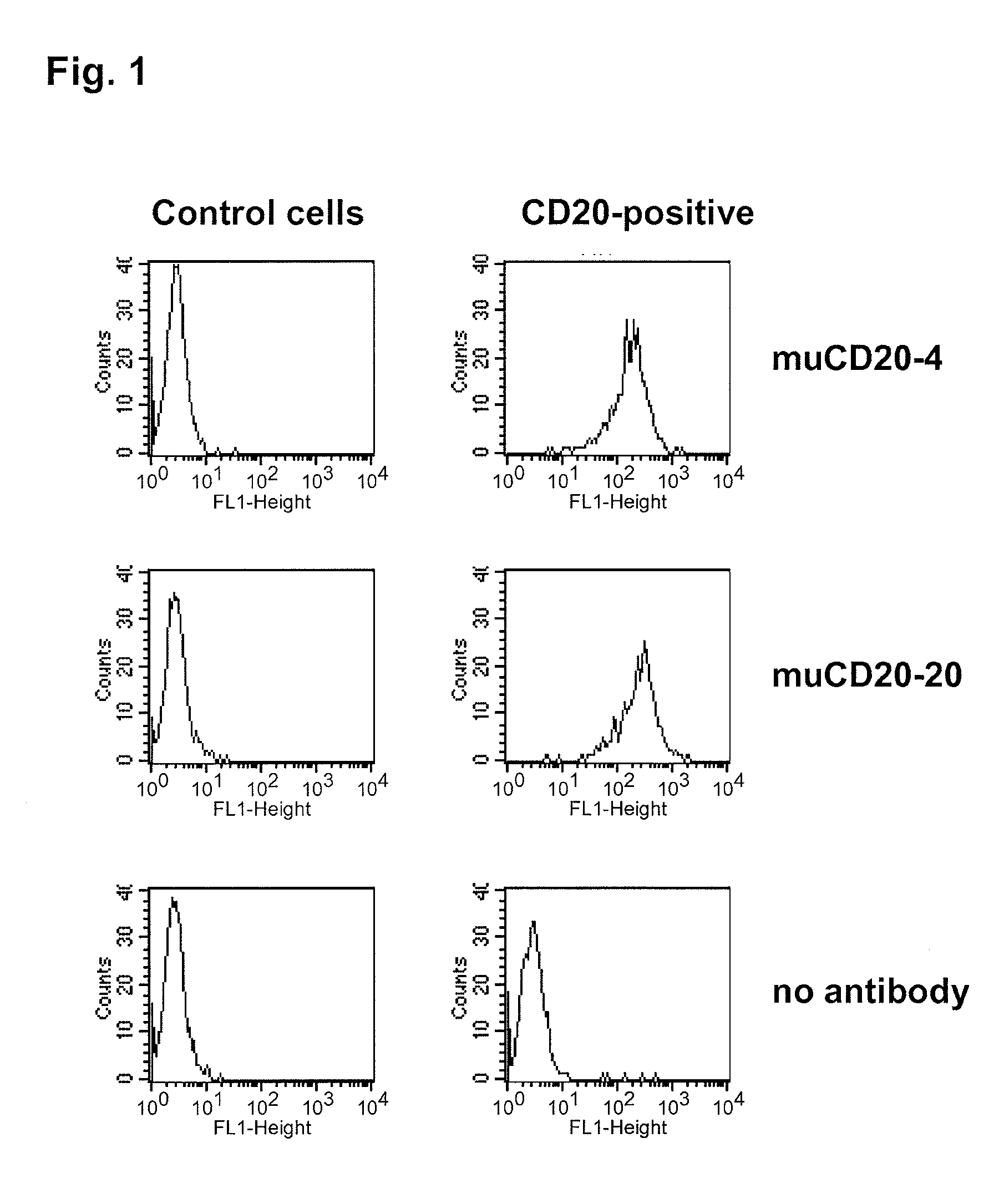
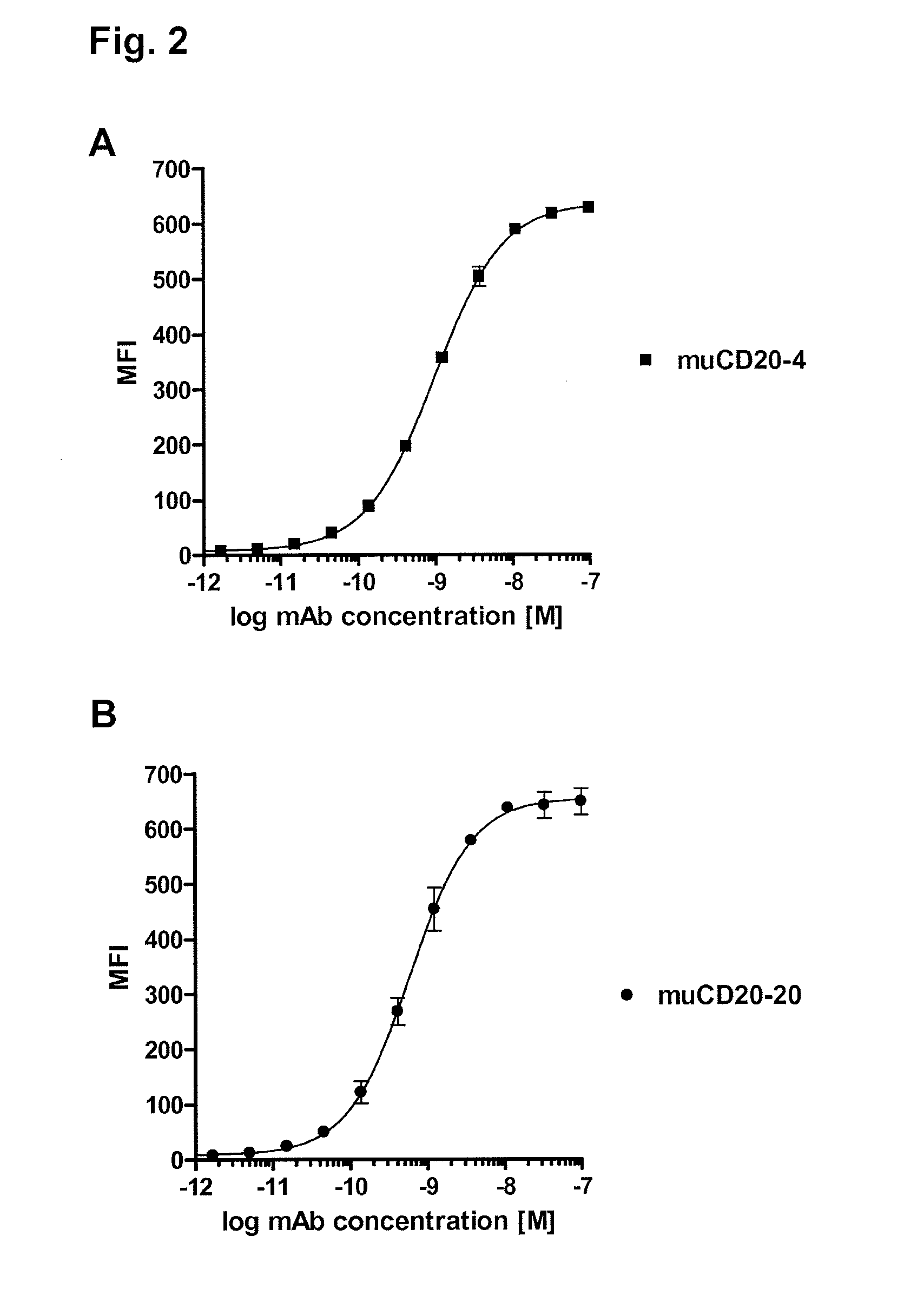
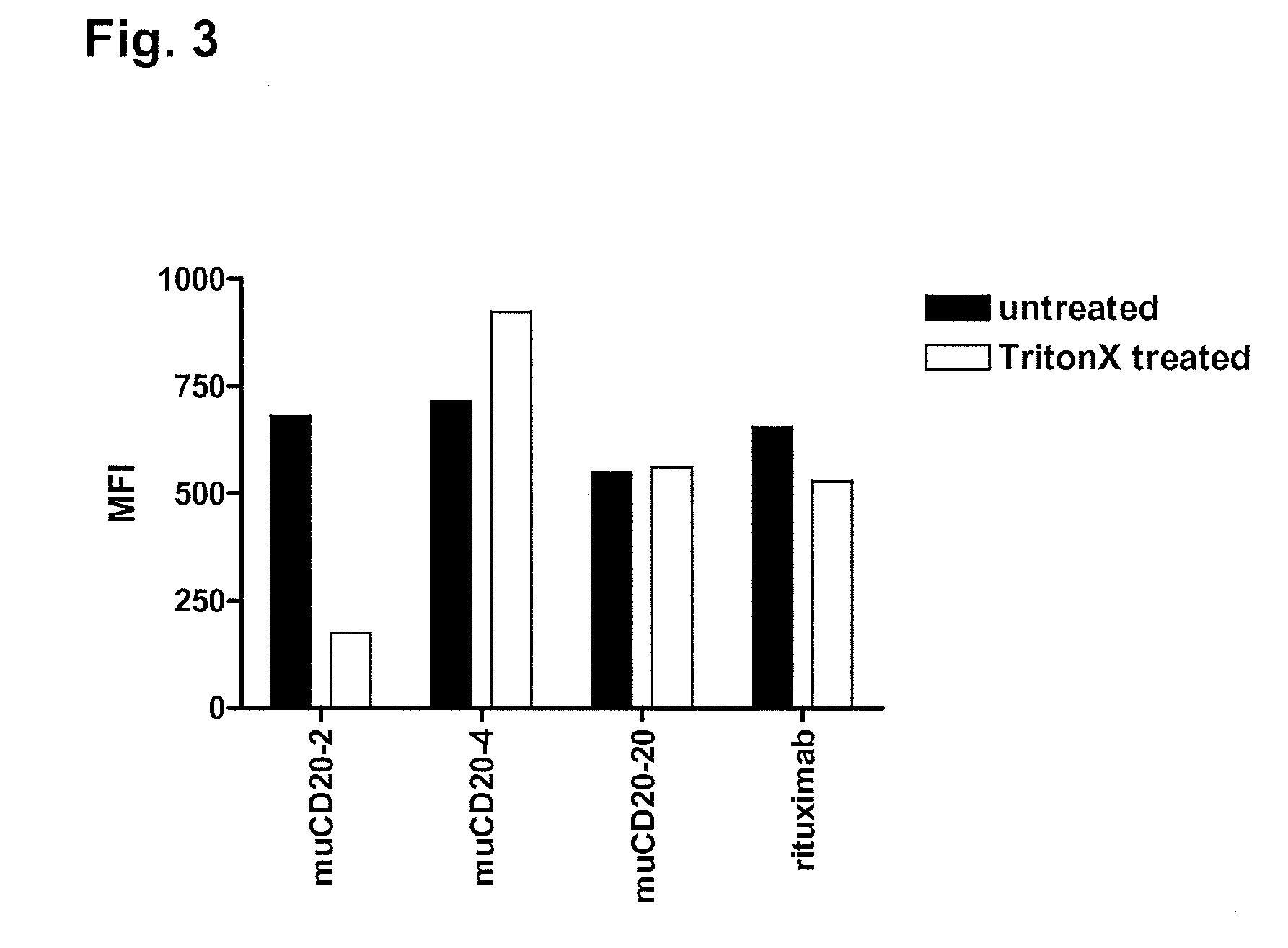
Cd20 antibodies and uses thereof
CD20 is a transmembrane protein of the tetra-spanin family expressed on the surface of B-cells and has been found on B-cells from peripheral blood as well as lymphoid tissues. CD20 expression persists from the early pre-B cell stage until the plasma cell differentiation stage. Conversely, it is not found on hematopoietic stem cells, pro-B cells, differentiated plasma cells or non-lymphoid tissues. In addition to expression in normal B-cells, CD20 is expressed in B-cell derived malignancies such as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) and B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). CD20 expressing cells are known to play a role in other diseases and disorders, including inflammation. The present invention includes anti-CD20 antibodies, forms and fragments, having superior physical and functional properties; immunoconjugates, compositions, diagnostic reagents, methods for inhibiting growth, therapeutic methods, improved antibodies and cell lines; and polynucleotides, vectors and genetic constructs encoding same.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC
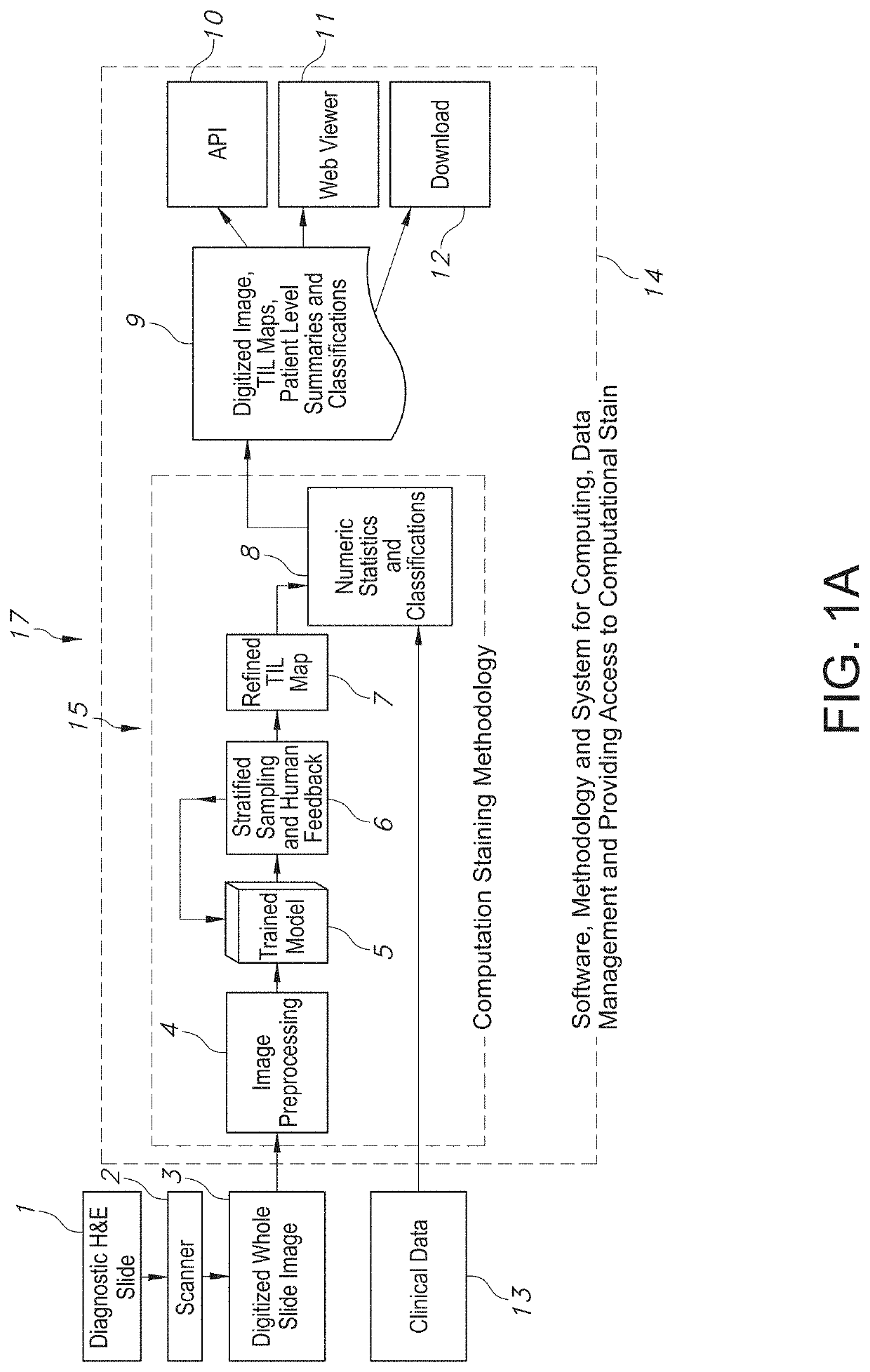
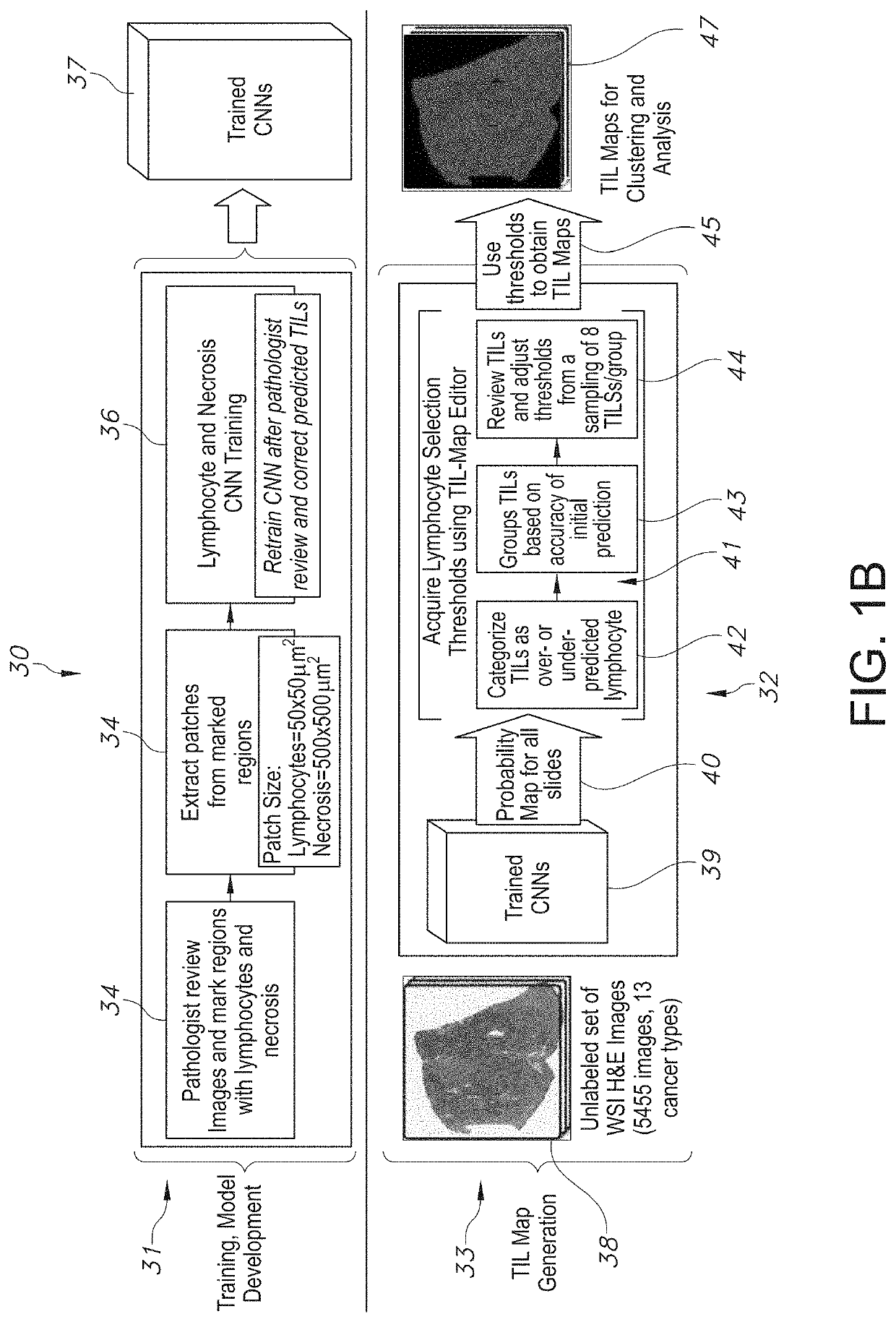
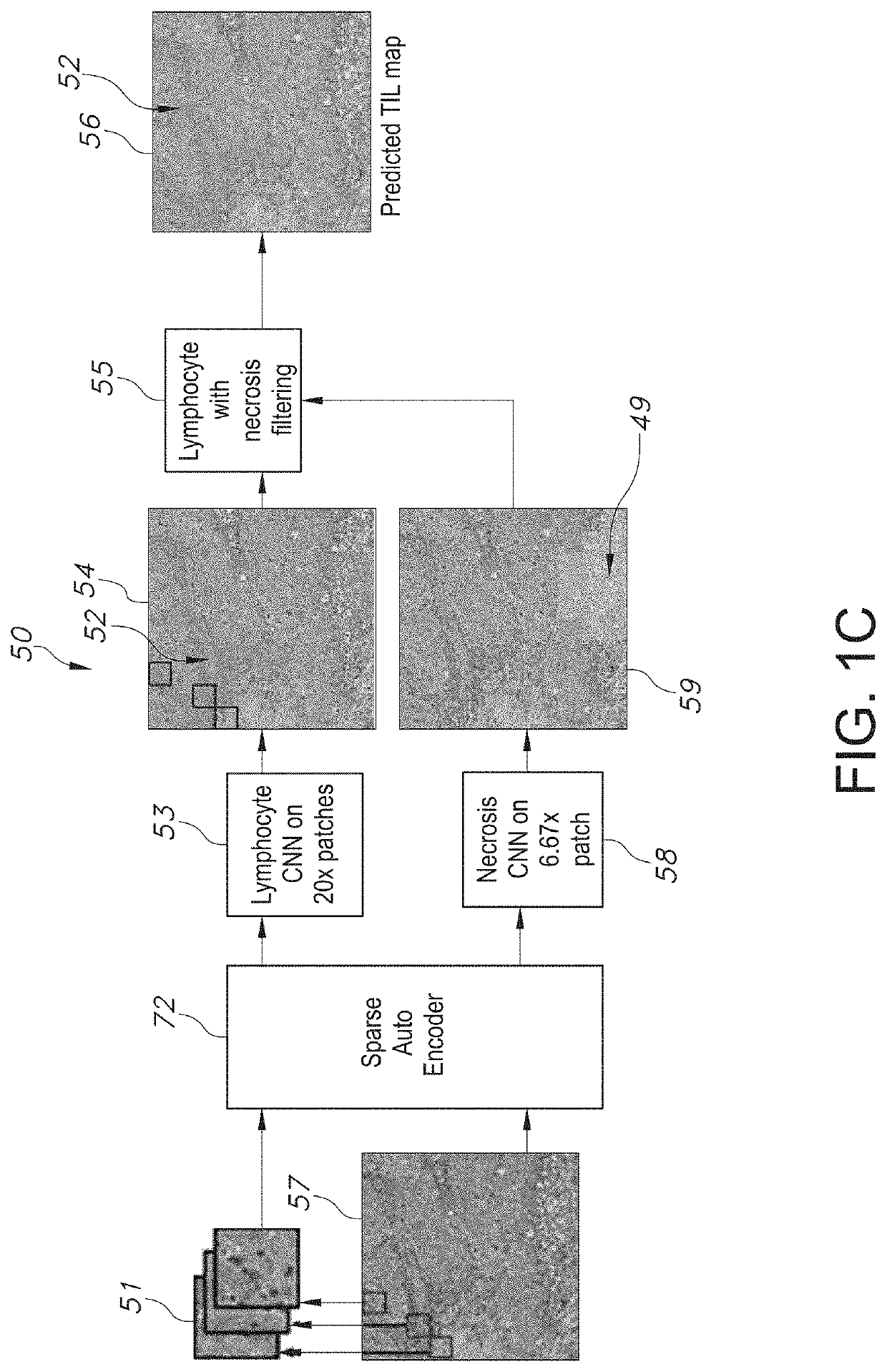
System and Method to Quantify Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) for Clinical Pathology Analysis Based on Prediction, Spatial Analysis, Molecular Correlation, and Reconstruction of TIL Information Identified in Digitized Tissue Images
A system associated with quantifying a density level of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, based on prediction of reconstructed TIL information associated with tumoral tissue image data during pathology analysis of the tissue image data is disclosed. The system receives digitized diagnostic and stained whole-slide image data related to tissue of a particular type of tumoral data. Defined are regions of interest that represents a portion of, or a full image of the whole-slide image data. The image data is encoded into segmented data portions based on convolutional autoencoding of objects associated with the collection of image data. The density of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is determined of bounded segmented data portions for respective classification of the regions of interest. A classification label is assigned to the regions of interest. It is determined whether an assigned classification label is above a pre-determined threshold probability value of lymphocyte infiltrated. The threshold probability value is adjusted in order to re-assign the classification label to the regions of interest based on a varied sensitivity level of density of lymphocyte infiltrated. A trained classification model is generated based on the re-assigned classification labels to the regions of interest associated with segmented data portions using the adjusted threshold probability value. An unlabeled image data set is received to iteratively classify the segmented data portions based on a lymphocyte density level associated with portions of the unlabeled image data set, using the trained classification model. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte representations are generated based on prediction of TIL information associated with classified segmented data portions. A refined TIL representation based on prediction of the TIL representations is generated using the adjusted threshold probability value associated with the classified segmented data portions. A corresponding method and computer-readable device are also disclosed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND TOR THE STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +2
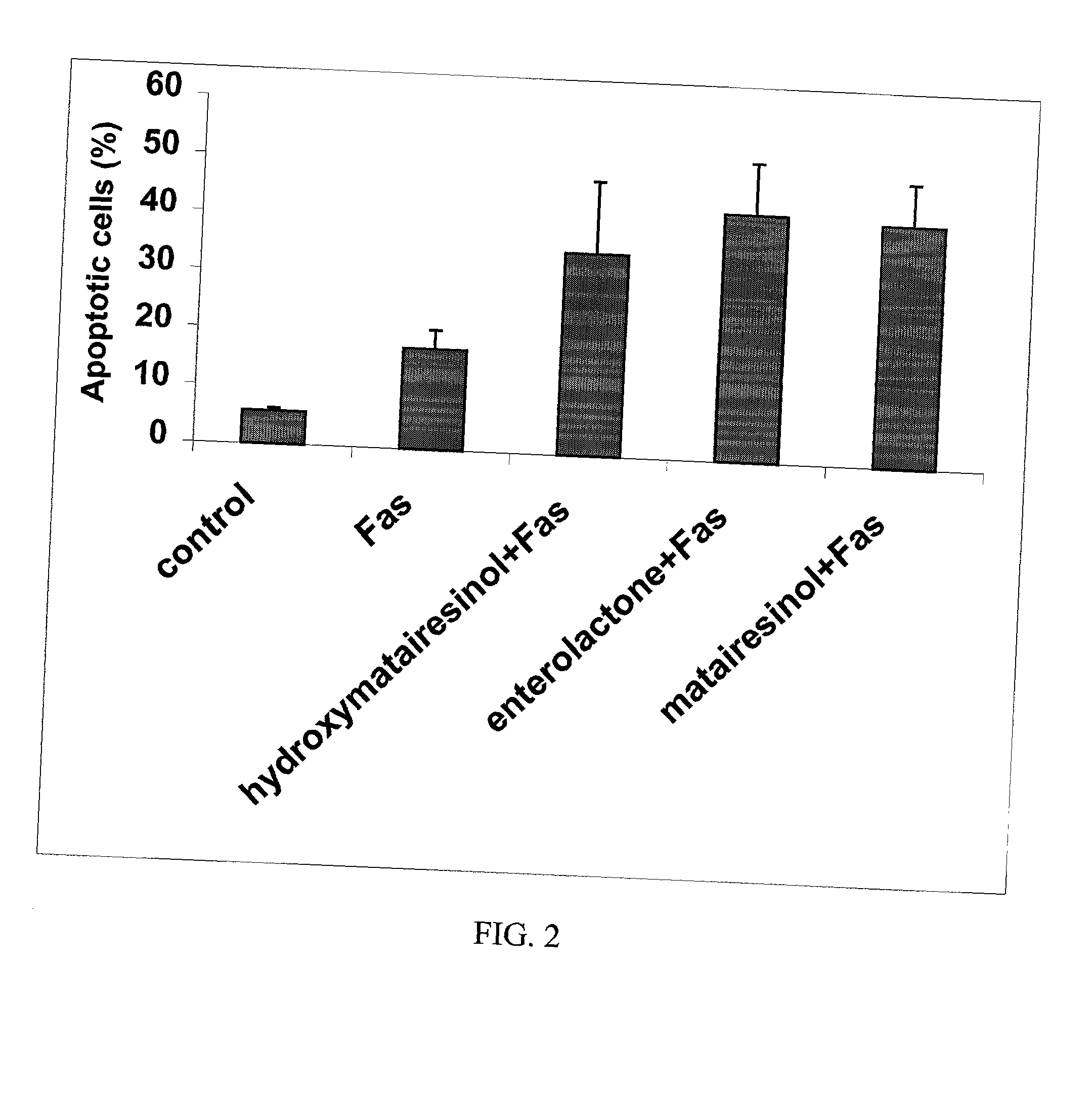
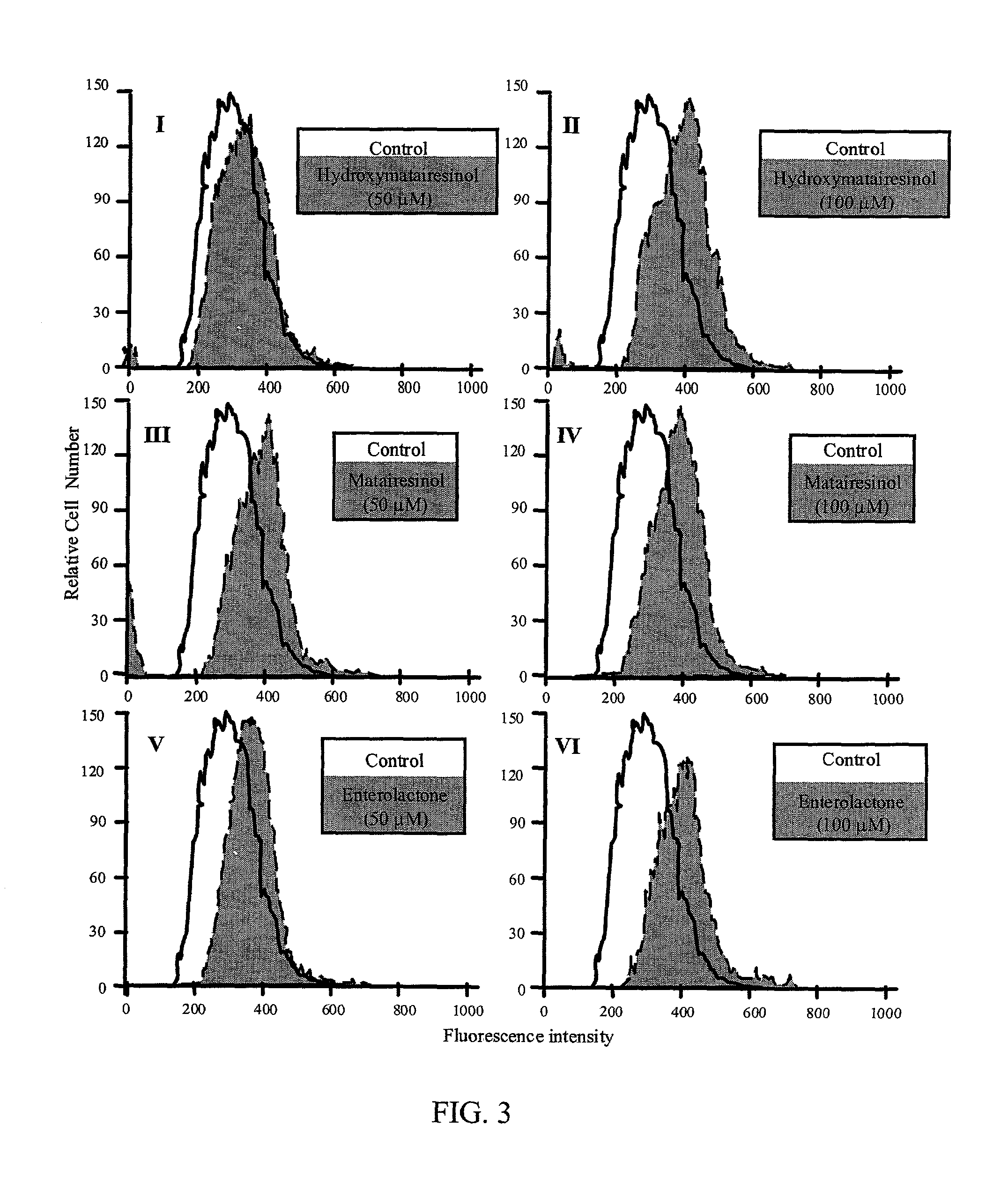
Method of inhibiting overactivity of phagocytes or lymphocytes in an individual
InactiveUS20030100514A1Reduce formationReduce riskBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsPhagocyteEnterolactone
This invention relates to a method of inhibiting the overactivity of phagocytes or lymphocytes in an individual by administering to said individual an effective amount of a lignan, wherein i) the phagocytes are neutrophils and the lignan is hydroxymatairesinol or matairesinol or mixtures thereof, or ii) the phagocytes are cells of myeloid origin and the lignan is enterolactone or hydroxymatairesinol or mixtures thereof, or iii) the lymphocytes are T-lymphocytes and the lignan is hydroxymatairesinol, matairesinol or enterolactone or mixtures thereof. Furthermore, this invention concerns a method of treating or preventing an acute ischemia-reperfusion injury or a chronic condition, caused by overactivity of phagocytes or lymphocytes in an individual, said method comprising decreasing the activity of phagocytes in an individual by administering to said individual an effective amount of a lignan.
Owner:HORMOS NUTRACEUTICAL
Method of classifying and counting leucocytes
ActiveUS20080176274A1Low costAccurate classificationMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividual particle analysisStainingWhite blood cell
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Health food for improving immunity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102415568AEnhance immune functionEnhance humoral immune functionFood preparationBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses a health food for improving immunity and a preparation method thereof. The health food is prepared from the following raw materials in part by weight: 1 to 3 parts of dendrobium officinale, 2 to 6 parts of American ginseng and 6 to 18 parts of Chinese wolfberry. Pharmacological experiments prove that: the health food has an obvious effect of promoting an immune system, canobviously improve a phagocytic index of macrophage of immunosuppressed mice and increase coefficients of immune organs in nonspecifc immune experiments, can improve the conversion rate of lymphocytes, improve the level of immunoglobulin IgG, IgA and IgM in serum of the immunosuppressed mice and assist in conditioning immunodeficiency disease, and diseases such as weakened immune system, low resistance and the like.
Owner:常熟雷允上制药有限公司
Blood analyzer, blood analysis method, and computer program product
ActiveCN102768179AScattering properties measurementsIndividual particle analysisBlood specimenHemolytic Agents
A blood analyzer, a blood analysis method, and a computer program product that can distinguishably detect abnormal lymphocytes, blasts, and atypical lymphocytes are provided. A blood analyzer prepares a first measurement sample from a first reagent containing a hemolyzing agent, a second reagent containing a fluorescence staining dye, and the blood specimen, and prepares a second measurement sample from a third reagent containing a hemolyzing agent, a fourth reagent containing a fluorescence staining dye, and the blood specimen. The blood analyzer measures each of the measurement samples, and distinguishably detects abnormal lymphocytes, blasts, and atypical lymphocytes in a blood specimen based on the measurement data.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Compositions and methods for protecting organs, tissue and cells from immune system-mediated damage
InactiveUS20080241194A1Organic active ingredientsFungiVascular endotheliumNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
This invention concerns novel compositions and methods for for the protection of organs and cells from damage caused by activated lymphocytes, NK-cells and NK-like cells, more particularly compositions and methods for the protection of vascular endothelial cells from immune system-mediated damage.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
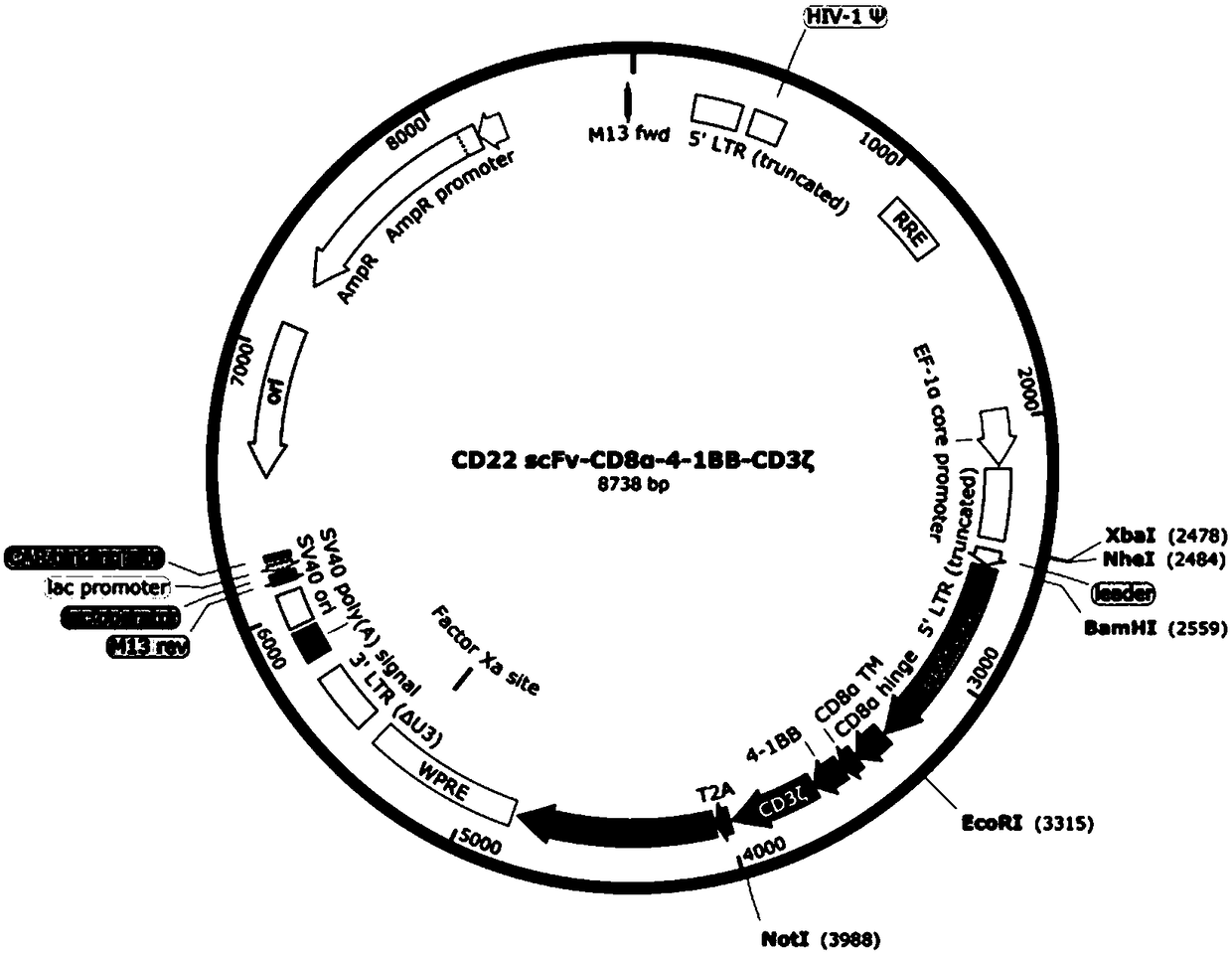
Chimeric antigen receptor targeting CD22 and application of chimeric antigen receptor
ActiveCN108715859AGood killing effectNo lethal effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigenOn cells
The invention provides a nucleic acid molecule for encoding a chimeric antigen receptor targeting CD22. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises an extracellular region, a transmembrane region and a intracellular signal transduction region, the extracellular region encoded by the nucleic acid molecule comprises a CD22 binding domain, and the CD22 binding domain is amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 3. By using flow cytometry, a degranulation analysis experiment and ELISA to detect cell factors secreted by a T cell, a fact that the CAR-T cell has a high lethal effect on B cell lymphoma cells and acute B cell lymphoma cell leukemia cells expressing CD22 and hardly has a lethal effect on cells which do not express CD22, and an off-target effect is prevented effectively is proved. The chimeric antigen receptor CD22scFv-CD8alpha-4-1BB-CD3zeta can be used for treating CD22<+>B cell hematologic neoplasms and is applicable to combined treatment with a CD19 CAR-T cell.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Expansion method of various lymphocyte subpopulations and application of expansion method
ActiveCN105624107ASuppress deathImprove developmentGenetic material ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsWhite blood cellNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
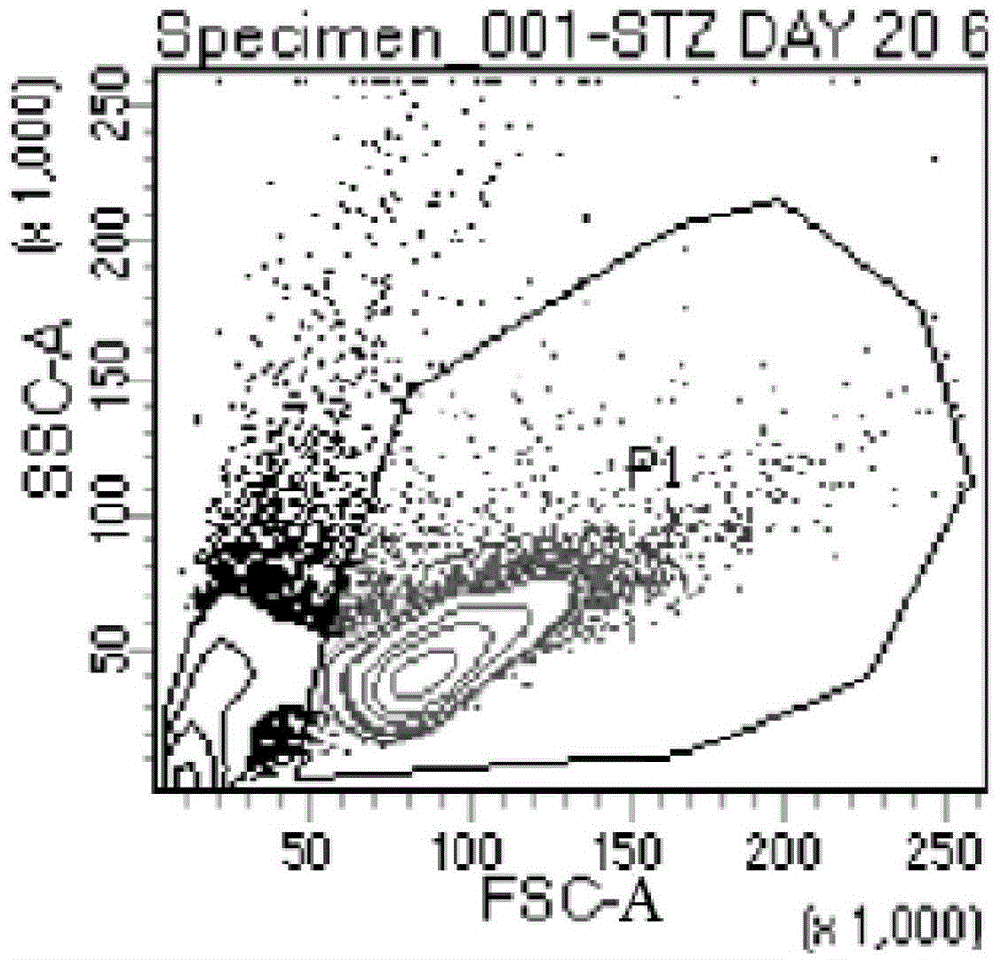
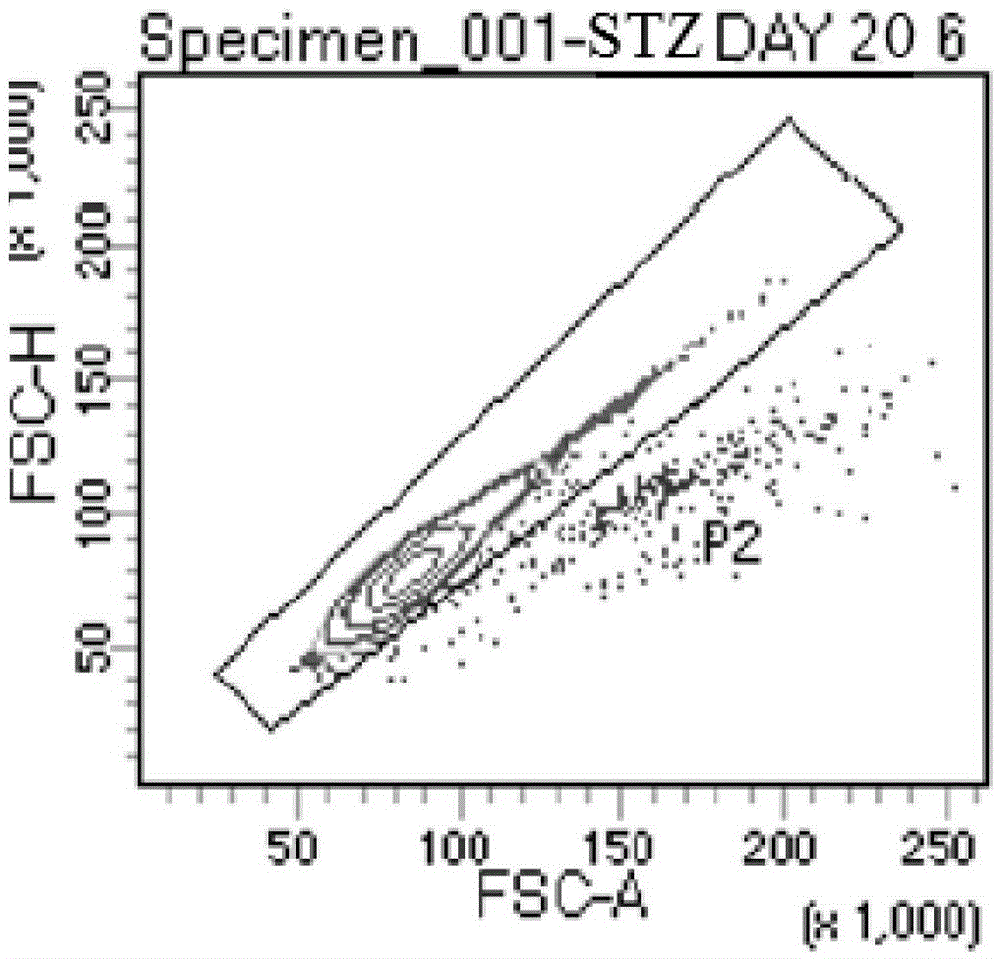
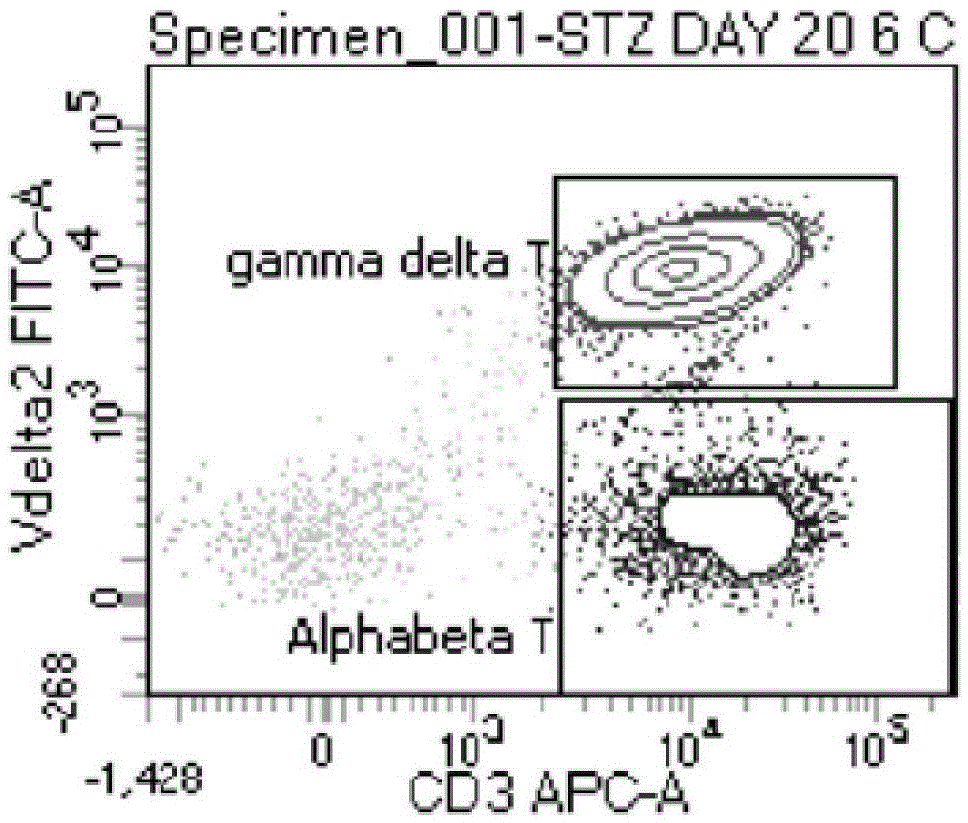
The invention discloses an expansion method of various lymphocyte subpopulations and application of the expansion method to preparation of an adoptive immunotherapy medicine for cancers. The expansion method comprises the following steps: S1, adding IFN gamma and zoledronic acid into a culture medium of PBMC collected in the blood of a tumor patient, and re-adding an OKT3 antibody and recombinant human interleukin-2 after culture to stimulate PBMC so as to finish preliminary expansion; S2, after finish of preliminary expansion, mixing immune lymphocytes with feeder layer cells, and after adding zoledronic acid, an OKT3 antibody and recombinant human interleukin-2, continually performing expansion. By adoption of the expansion method, after twice expansion, the sum of the immune cells can be 10,000 to 80,000 times by expansion, the expanded immune cells include alpha beta T cells, gamma delta T cells, NKT cells and NK cells, and tumor cells can be directly killed, or a cellular immunotherapy drug is prepared to kill the tumor cells.
Owner:杭州朔溪生物医药有限公司
(3,4-disubstituted)propanoic carboxylates as SLP (EDG) receptor agonists
InactiveCN1894225AAdjustable transportImprove integrityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderPropanoic acidWhite blood cell
The present invention encompasses compounds of Formula A: A as well as the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The compounds are S1P1 / Edg1 receptor agonists and thus have immunosuppressive, anti-inflammatory and hemostatic activities by modulating leukocyte trafficking, sequestering lymphocytes in secondary lymphoid tissues, and enhancing vascular integrity. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds and methods of treatment or prevention.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Bioactive polypeptide SKHSSLDCVL, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107226860AGood antioxidant activityGood for regulating the body's immune systemCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsNeutral red stainPathogen
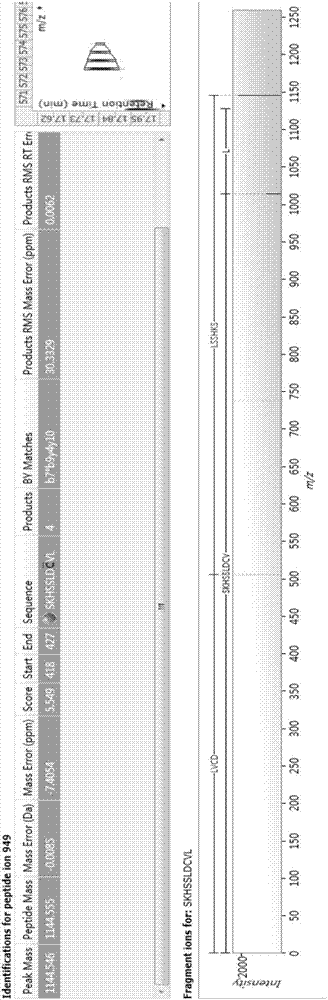
The invention relates to the field of protein, and in particular to a bioactive polypeptide SKHSSLDCVL, and a preparation method and application thereof. An amino acid sequence of the bioactive polypeptide SKHSSLDCVL is Ser-Lys-His-Ser-Ser-Leu-Asp-Cys-Val-Leu. An in-vitro antioxidant experiment and an in-vitro immunological function promoting experiment verify that the bioactive polypeptide SKHSSLDCVL has better antioxidant biological activity and a better immune modulating function; on one hand, the bioactive polypeptide SKHSSLDCVL has better antioxidant activity and is capable of removing free radicals in a body and increasing the quality of life; on the other hand, the bioactive polypeptide SKHSSLDCVL is capable of enhancing in-vitro proliferation ability of lymphocytes and macrophages, promoting the ability of swallowing neutral red by the macrophages, increasing the ability of defending external pathogen infection by the body and reducing the morbidity of the body, and has a very important significance in developing food, healthcare products and drugs having an immune modulating function and an antioxidant function.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUITAI LIFE HEALTH TECH CO LTD
Methods For Detecting Th1 Cells
InactiveUS20080248502A1Suppress immune responseDisease controlMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisActivated LymphocyteCell biology
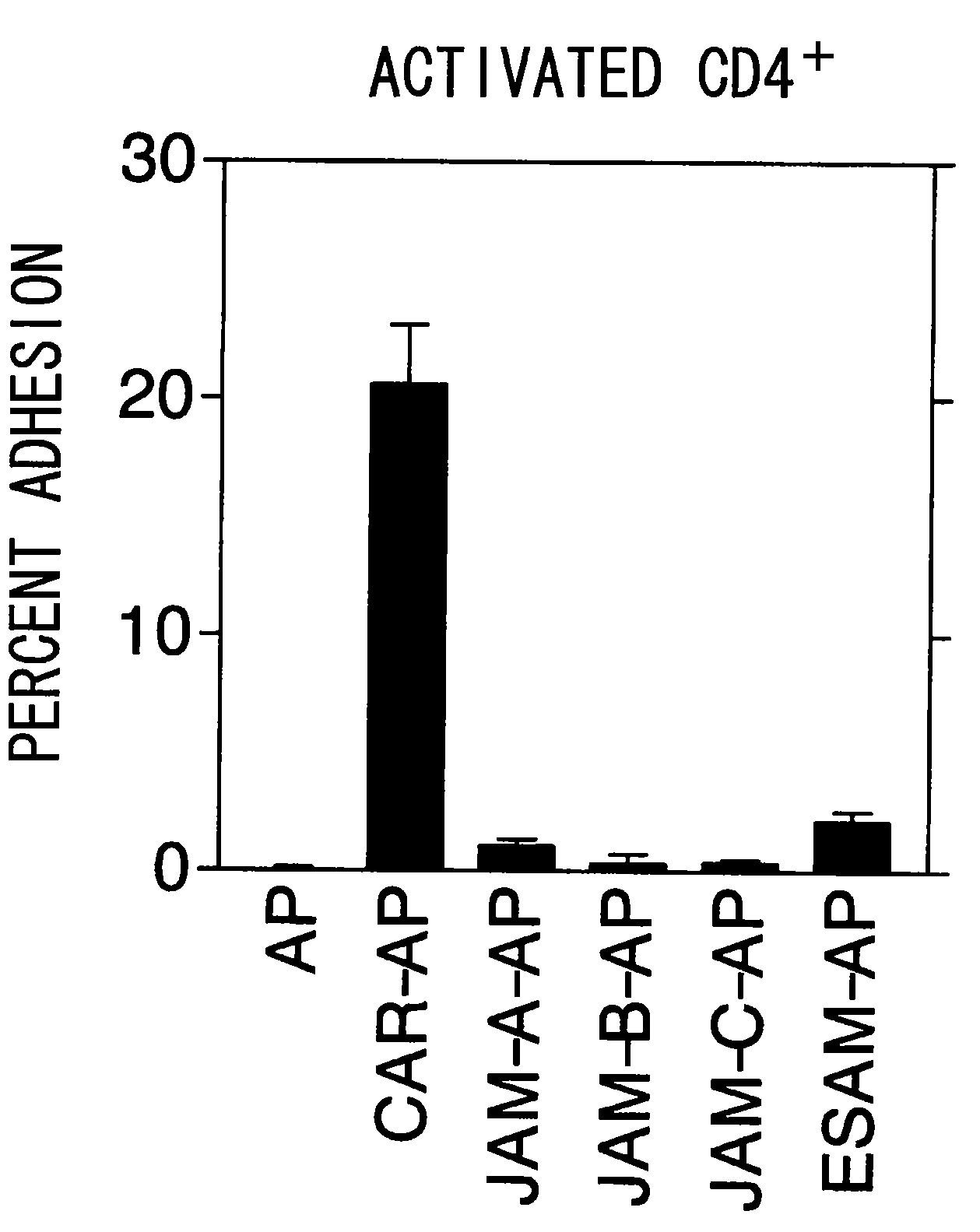
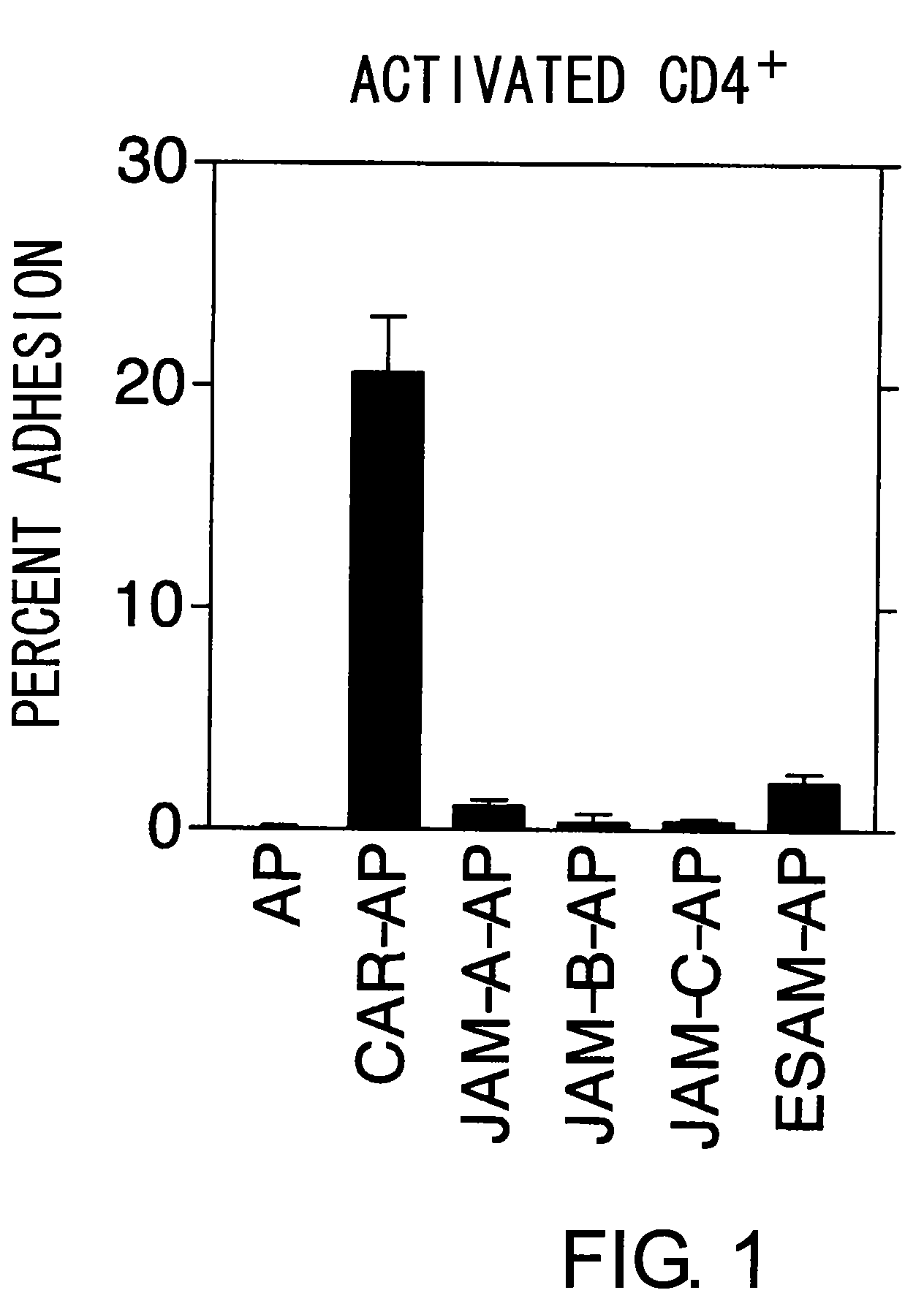
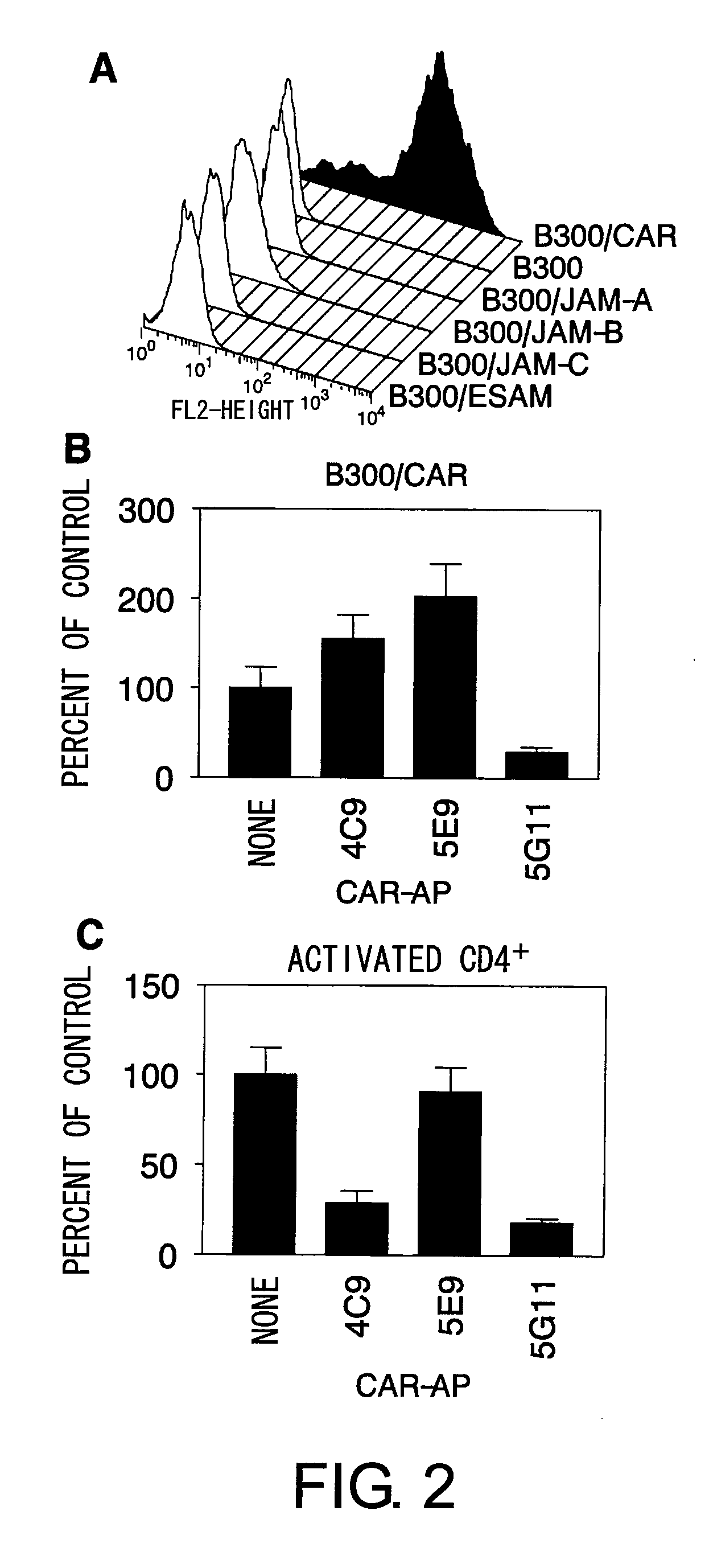
The inventors discovered that the adhesion molecule CAR, known to be localized in intracellular adhesion sites, functioned as an adhesion molecule for activated lymphocytes. Further, the inventors identified CARL, a novel CAR ligand expressed in lymphocytes, and clarified that the ligand was expressed selectively in Th1 cells. In addition, they found that anti-CAR antibodies could inhibit the adhesion of activated lymphocytes to CAR molecules. Thus, the present invention provides methods for detecting Th1 cells using CAR or anti-CARL antibodies, and methods of screening for inhibitors suppressing the adhesion of Th1 cells using the binding between CAR and CARL as an index. Furthermore, the present invention relates to methods of screening for inhibitors of the binding between CAR and CARL, antibodies that inhibit the binding between CAR and CARL, and therapeutic compositions comprising these antibodies. These are expected to be useful in diagnosing diseases, such as inflammation, in which infiltration of Th1 cells is involved, and in providing pharmaceutical agents for alleviating such diseases.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Bioactive polypeptide QEPVL, and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN102964427AImproves antioxidant activityBoosts immune activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganism based processesLymphocyteDrug biological activity
The invention relates to the field of a protein and particularly relates to a milk-derived bioactive polypeptide QEPVL with in-vitro antioxidant activity and body immunity promoting activity, wherein an amino acid sequence of the bioactive polypeptide QEPVL is Gln-Glu-Pro-Val-Leu. Through an in-vitro antioxidant test and an in-vitro immunity promoting test, the polypeptide QEPVL is proved to have relatively good antioxidant biological activity and immunity improving function; on one hand, free radicals in the body can be removed to reduce the harm on the human body caused by the free radicals; on the other hand, according to the bioactive polypeptide QEPVL, the immunity of the body can be further enhanced and the multiplication capacity of lymphocytes in vitro can be promoted, thereby improving the ability of the body to resist infections of external pathogens and reducing the incidence rate of the body without causing immunological rejections. The bioactive polypeptide QEPVL has great significance for the development of milk products, healthcare products and medicines with the antioxidant function and the immunity enhancement.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUITAI LIFE HEALTH TECH CO LTD
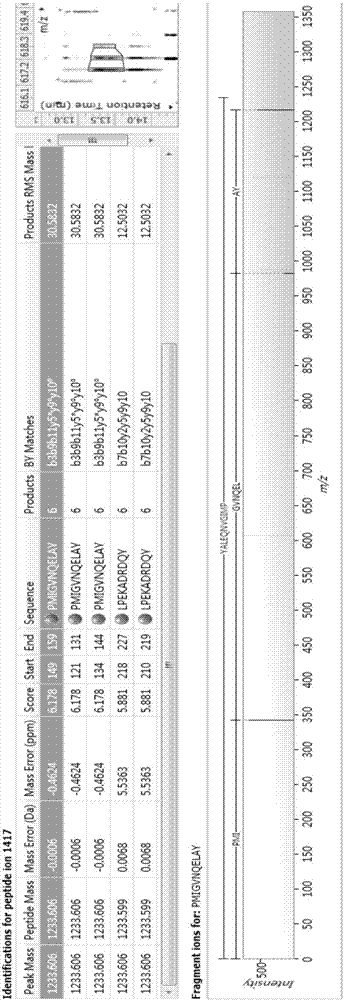
Bioactive polypeptide PMIGVNQELAY, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107236031AGood antioxidant activityGood for regulating the body's immune systemCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsDrugChemistry
The invention relates to the field of protein, in particular to a bioactive polypeptide PMIGVNQELAY, and a preparation method and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the bioactive polypeptide PMIGVNQELAY is Pro-Met-Ile-Gly-Val-Asn-Gln-Glu-Leu-Ala-Tyr. In vitro antioxidant experiments and in vitro immune function promoting experiments prove that the polypeptide PMIGVNQELAY has better antioxidant biological activity and immune modulating functions; on one hand, good antioxidant activity is realized; free radicals in the body can be cleared away; the life quality is improved; on the other hand, the bioactive polypeptide PMIGVNQELAY can enhance the in vitro multiplication capacity of lymphocytes and macrophages; the capability of the macrophages for devouring toluylene red is promoted; the capability of the body for resisting the external pathogen infection is improved; the body morbidity is reduced; very important significance is realized for developing food, health care products and medicines with the immune modulating function and the antioxidant function.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUITAI LIFE HEALTH TECH CO LTD
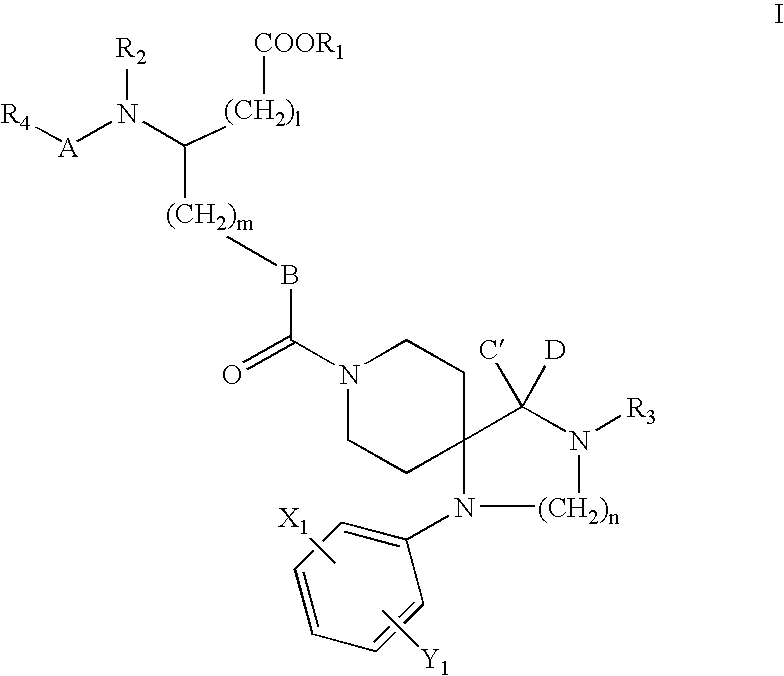
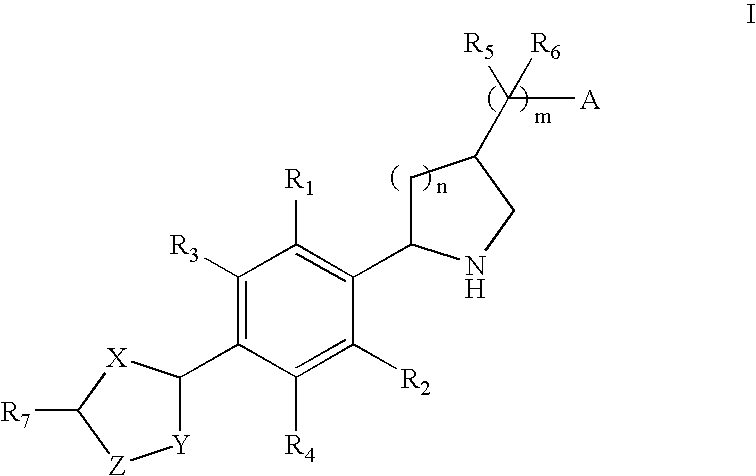
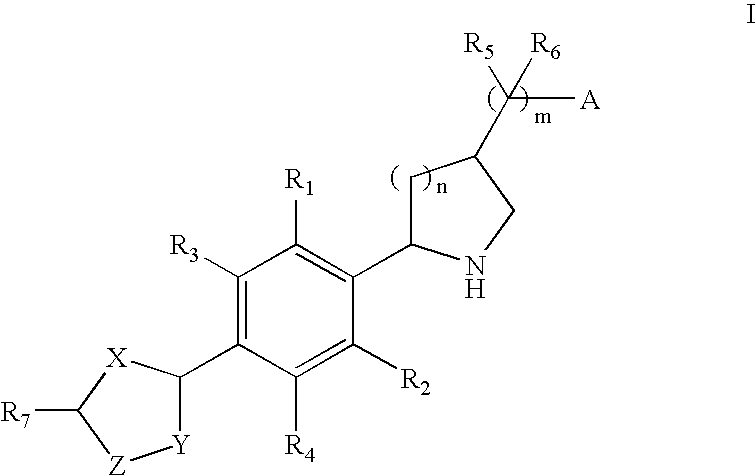
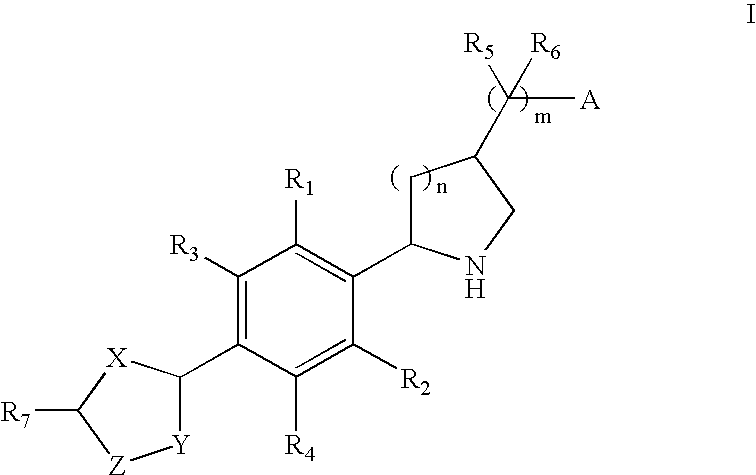
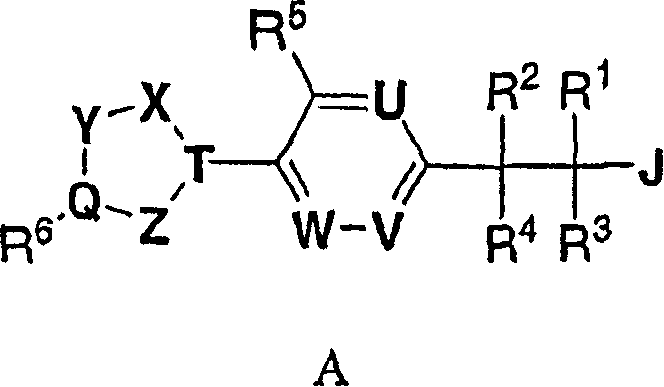
Substituted pyrido [3′, 2′: 4, 5] thieno [3, 2-D] pyrimidines and pyrido [3′, 2′: 4, 5] furo [3, 2-D] pyrimidines used as inhibitors of the PDE-4 and/or the release of TNF-ALPHA
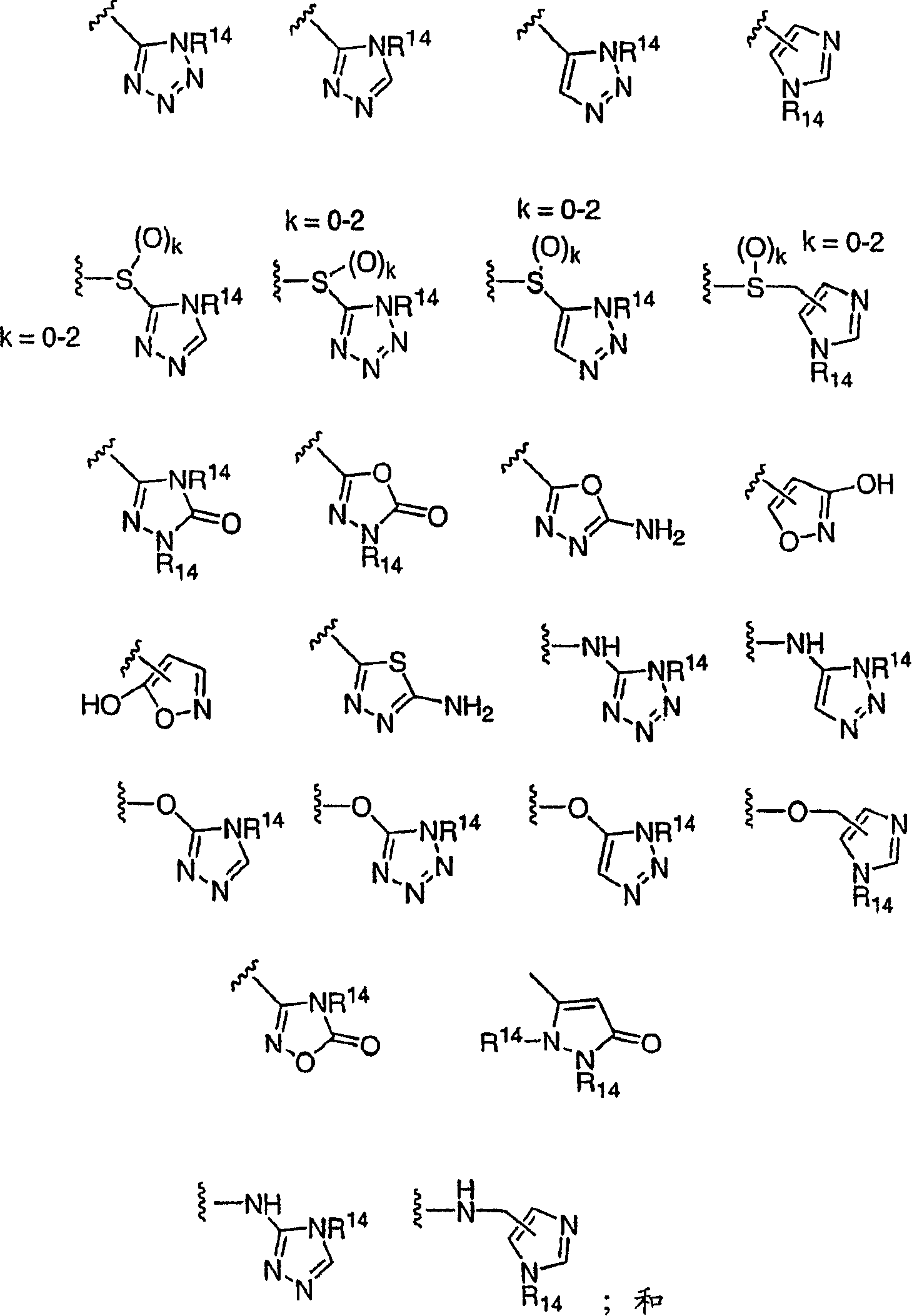
The invention relates to compounds of general formula (I); 1a, 1 b, 1 c and 1 d. The invention also relates to a method for the production thereof, pharmaceutical preparations containing said compounds and / or physiologically compatible salts thereof which can be produced therefrom and / or solvates thereof, and to the pharmaceutical use of said compounds, salts or solvates thereof as inhibitors of phosphodiesterase 4. The compounds comprise active ingredients for the treatment of diseases which can have a positive influence by inhibiting the activity of phosphodiesterase 4 and / or TNFα-release, for example, in lymphocytes, eosinophile and basophile granulocytes, macrophages and mastocytes.
Owner:THE MEDICINES CO (LEIPZIG) GMBH
Materials and methods for immune system stimulation
InactiveUS20060009501A1Enhance phagocytosisAdditional componentBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAdjuvantChemical compound
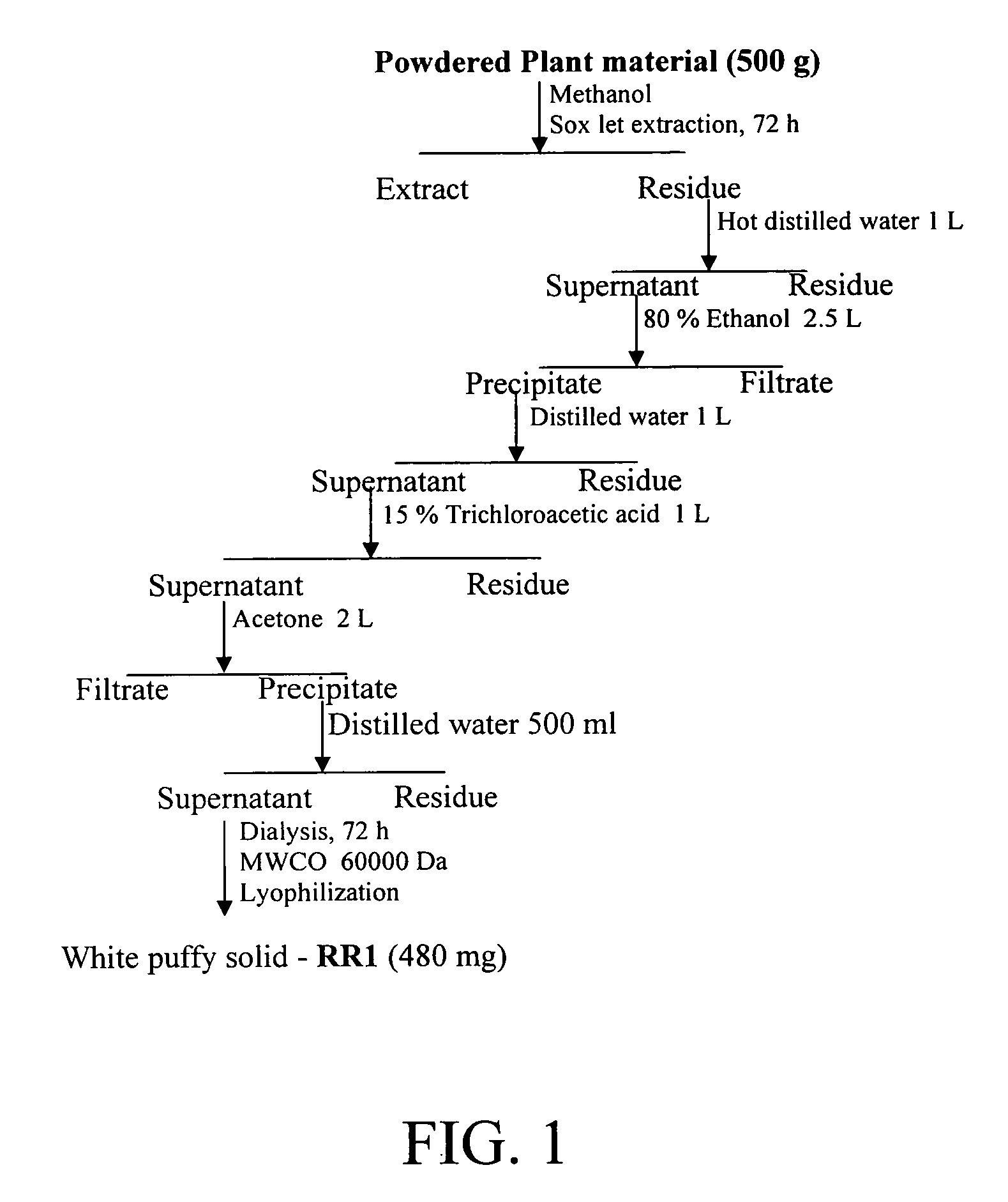
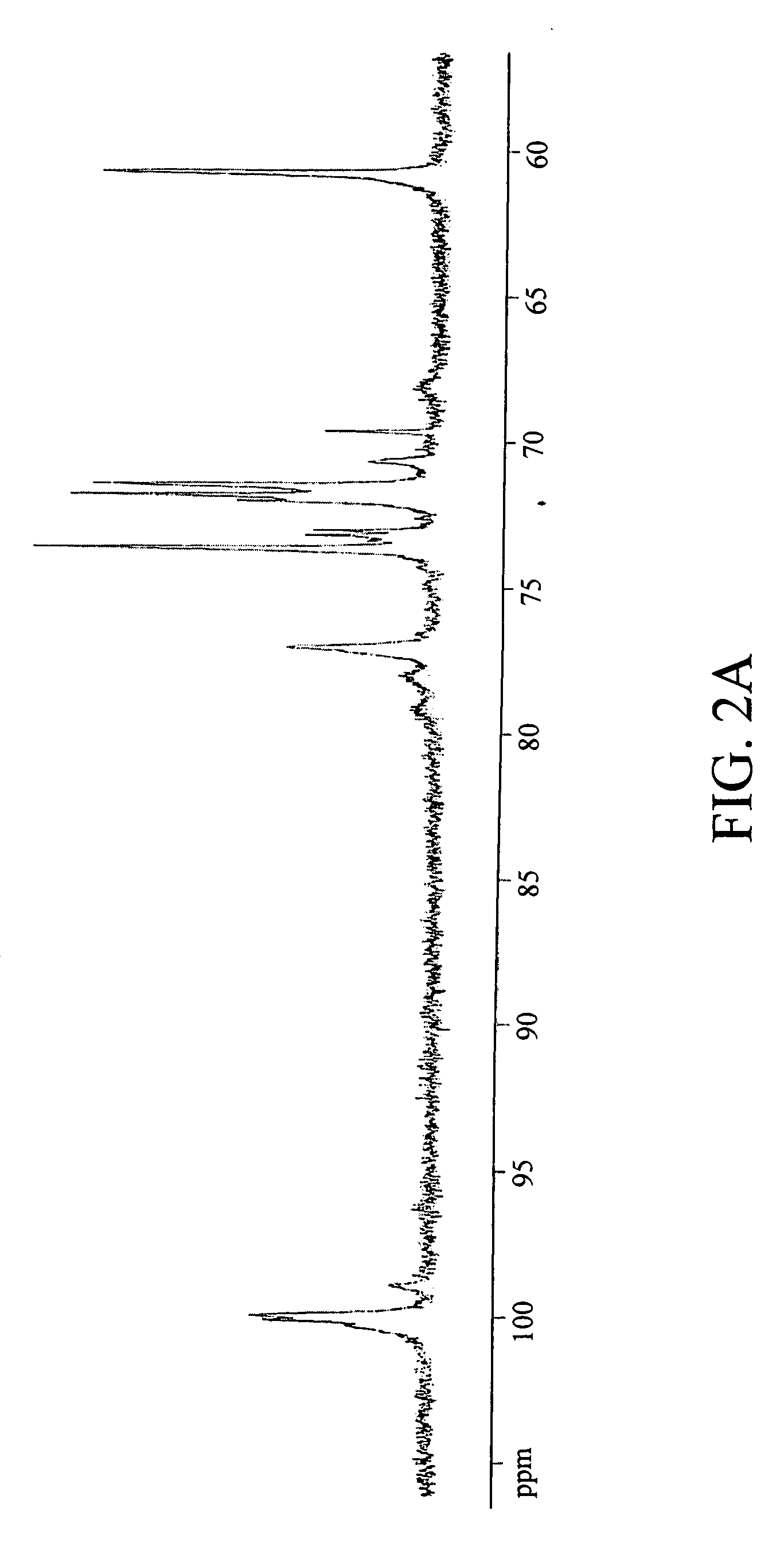
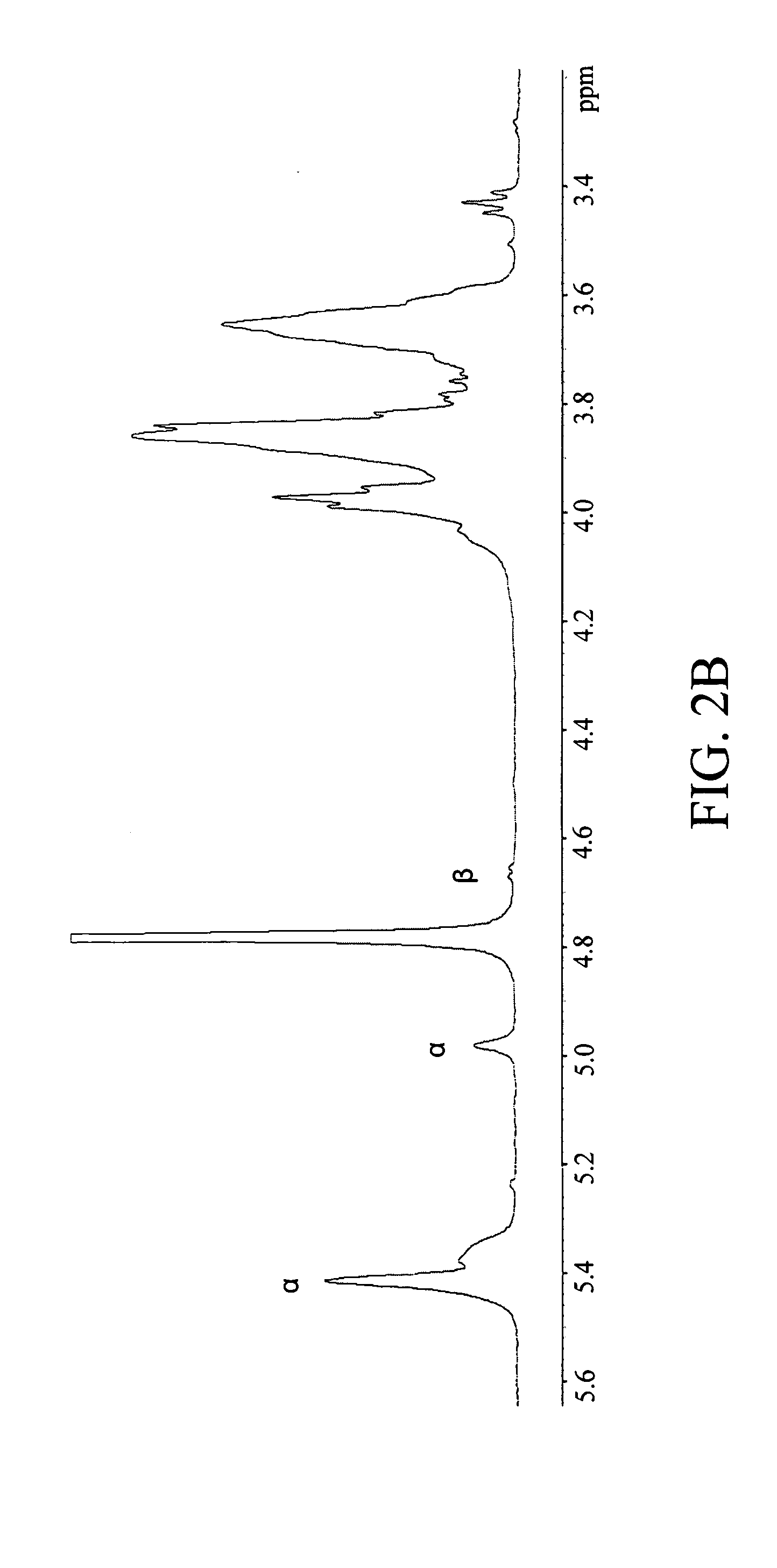
The subject invention concerns a novel polysaccharide. RR1 is an α-D-glucan polysaccharide composed of a (1→4) linked back bone and (1→6) linked branches, which has been isolated from a medicinal herb, Tinospora cordifolia. RR1 exhibits unique immune-stimulating properties, is non-cytotoxic, and non-proliferating to normal lymphocytes, as well as tumor cell lines. The subject invention also concerns compositions containing an RR1 compound and methods for modulating an immune response in a subject using RR1 compounds. The present invention also provides methods for the use of an RR1 compound in conjunction with an antigen to stimulate an immune response, the RR1 compound providing an adjuvant-like activity in the generation of a Th1-type immune response to the antigen.
Owner:VARIETY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Modified pig propagation and respiratory syndrome virus ORF5 gene and use thereof
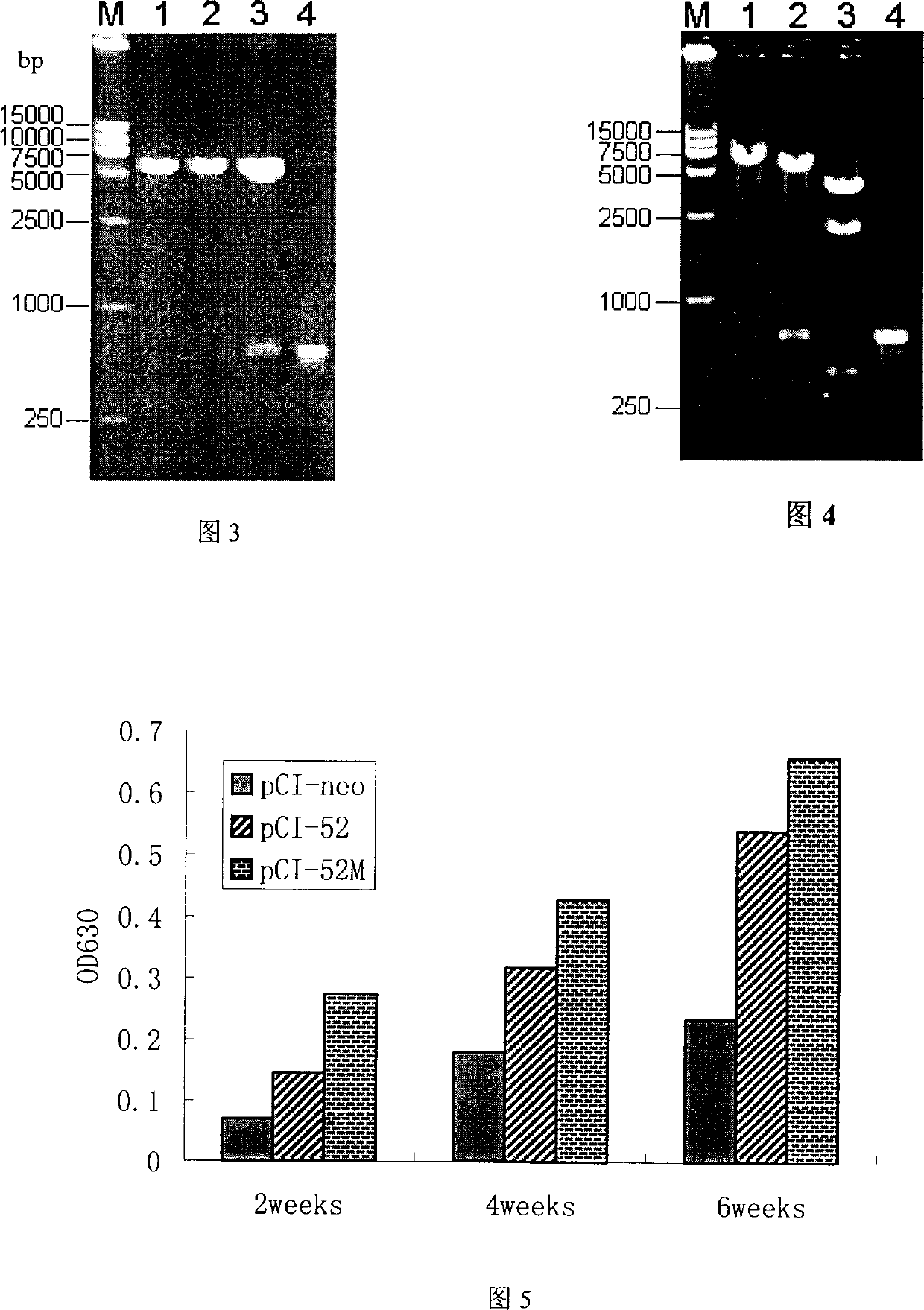
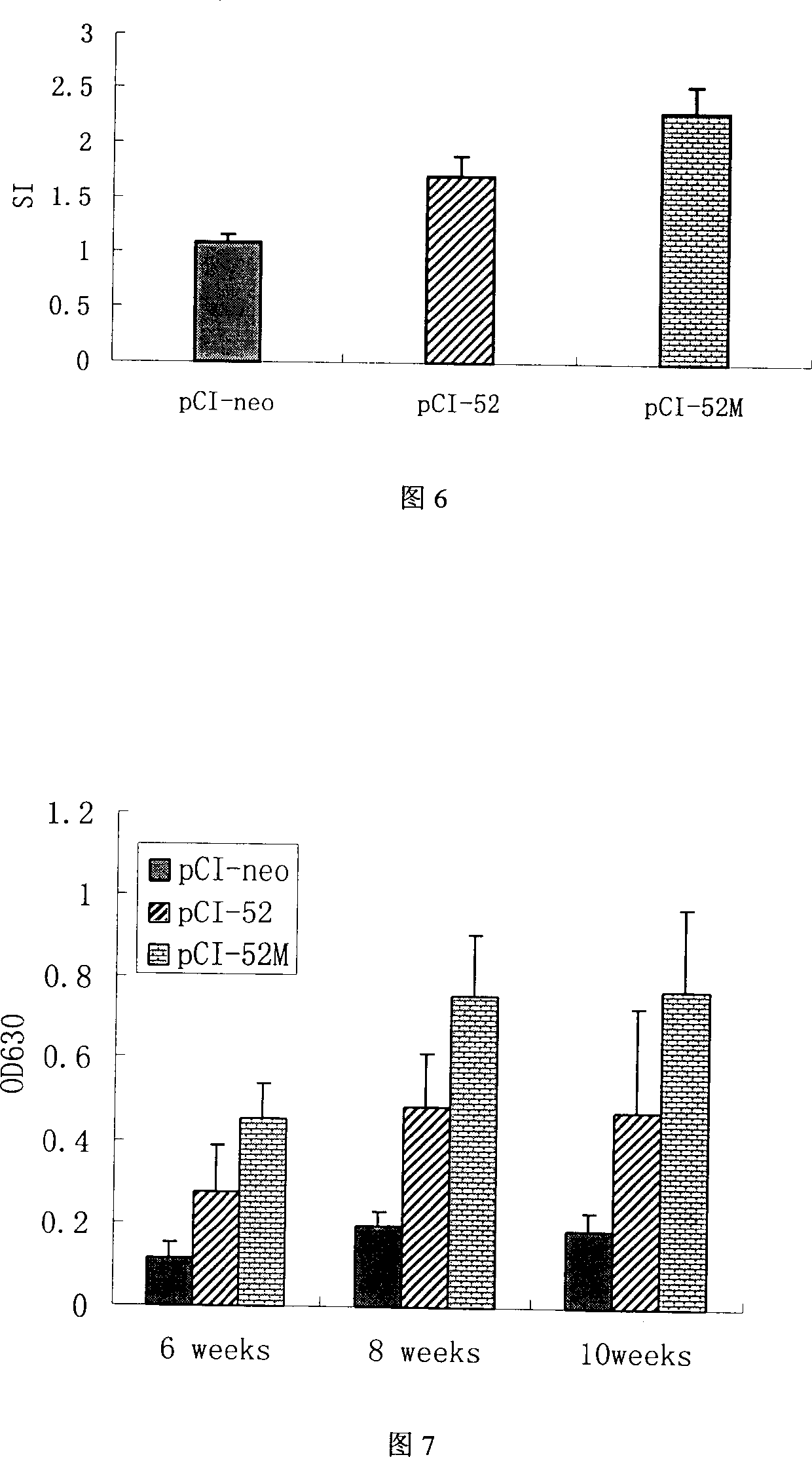
The invention belongs to the animal gene engineering technology field. It is about a gene and its application, the gene is modificatory porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus ORF5. Its attribute is to insert nucleotide sequence between the neutralization and cover list of GP5, the nucleotide sequence is artificial synthesis coding accessorial T-lymph cell list. The sequence of this nucleotide is just as the sequence list of SEQ ID NO:1 and attached figure 1. This modificatory gene is included in eukaryotic expression plasmid, and the Escherichia coliDH5 / pCI-52M, which includes the plasmid, is conserved in CCTCC, and the number is CCTCC NO: M204080. This invention also presents the use of this gene in the preparation of pig bread and respiratory syndrome DNA vaccineíú
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Spiro derivatives and adhesion molecule inhibitors comprising the same as active ingredient
InactiveUS20060241132A1Inhibition of activationNot inhibit progressBiocideNervous disorderCell adhesionWhite blood cell
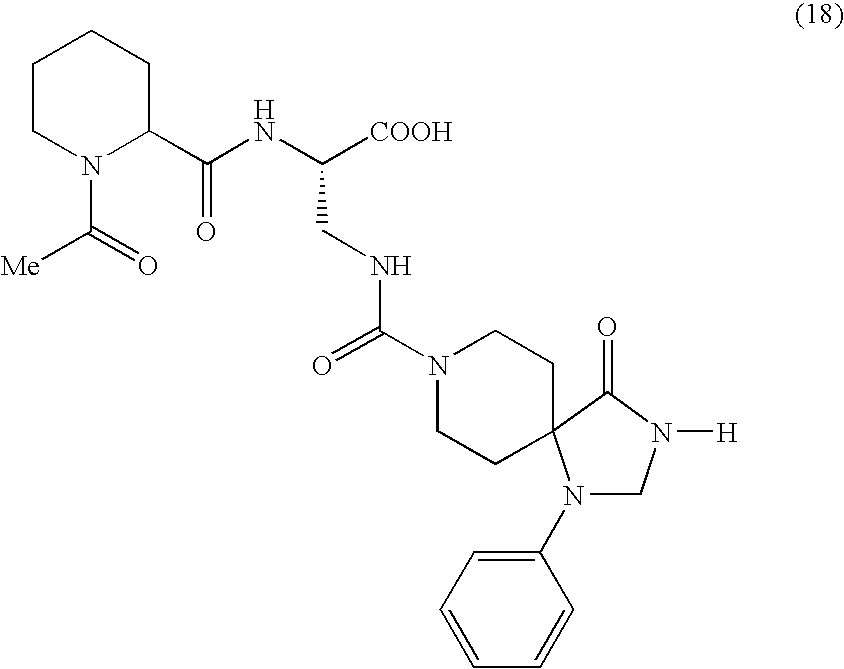
Disclosed is the use of an adhesion molecule inhibitor that is effective in the prevention and treatment of inflammatory diseases caused by infiltration of leukocytes such as monocytes, lymphocytes and eosindphils, by inhibiting cell infiltration which mediates adhesion molecules, especially adhesion molecule VLA-4. Since the spiro acid derivatives according to the present invention are excellent in the effect of inhibiting cell adhesion via adhesion molecules, especially adhesion molecule VLA-4, they are useful as therapeutic drugs against various inflammatory diseases. For example, provided are the spiro derivative and the adhesion molecule inhibitor which includes as an active ingredient the spiro derivative as shown by the below formula (18).
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Novel efficient method for separating human T-Lymphocytes by immunomagnetic beads
InactiveCN102719398AProlong survival timeEasy to operateBlood/immune system cellsHuman lymphocyteLymphocyte culture
The invention establishes an operation method in T-Lymphocytes culture in vitro by immunomagnetic bead separation technique to maximize the separation of human T-Lymphocytes from the same volume of human peripheral blood to obtain a lot of purified T-Lymphocytes and cover the shortage that lymphocytes can be only primary cultured but not be subcultured to the greatest extent. The method is simple and practicable.
Owner:赵品楠
Method for constructing hybridoma cell line of heterogeneity of seereting human monoclonal antibody for anti hepatitis B
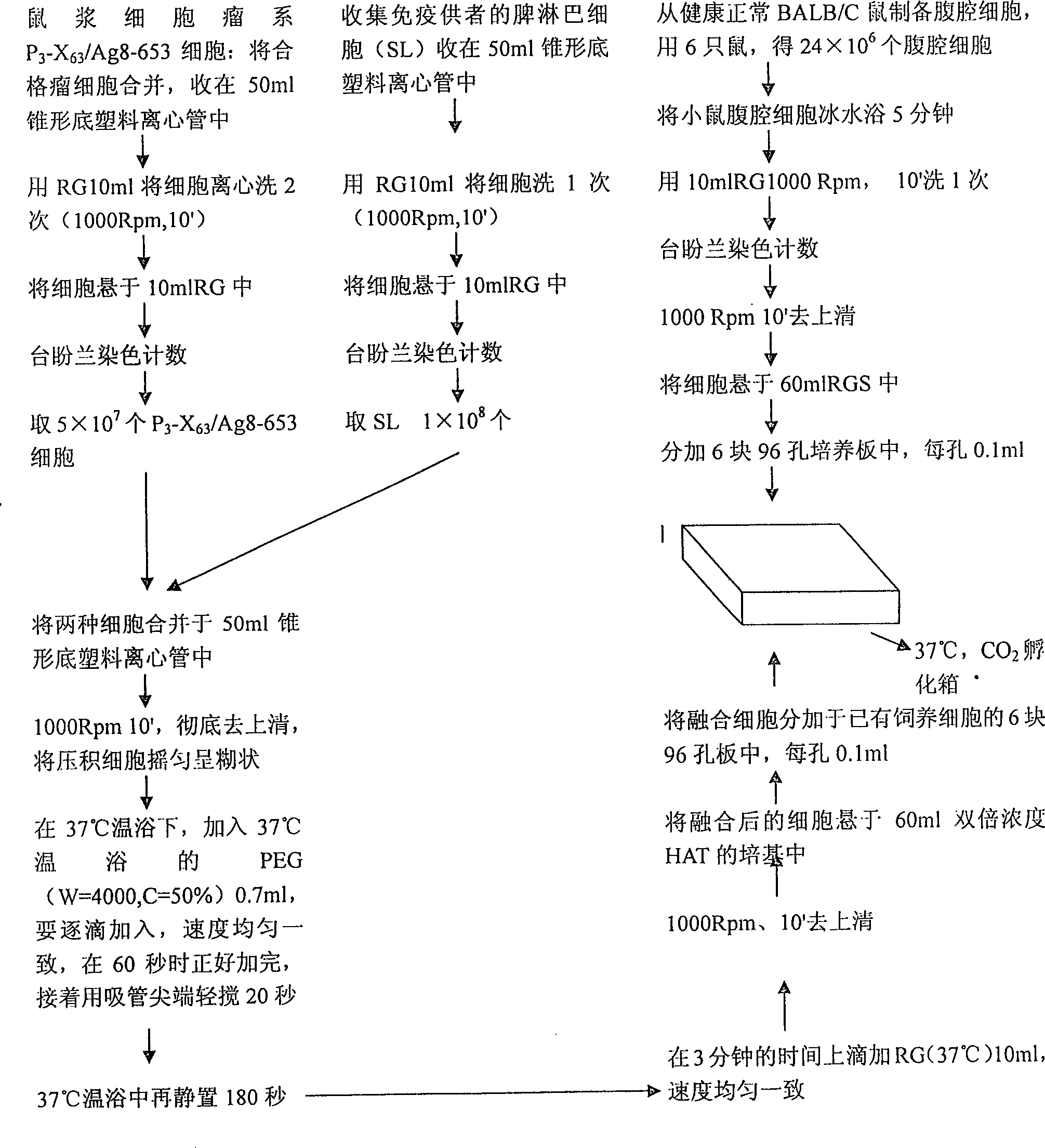
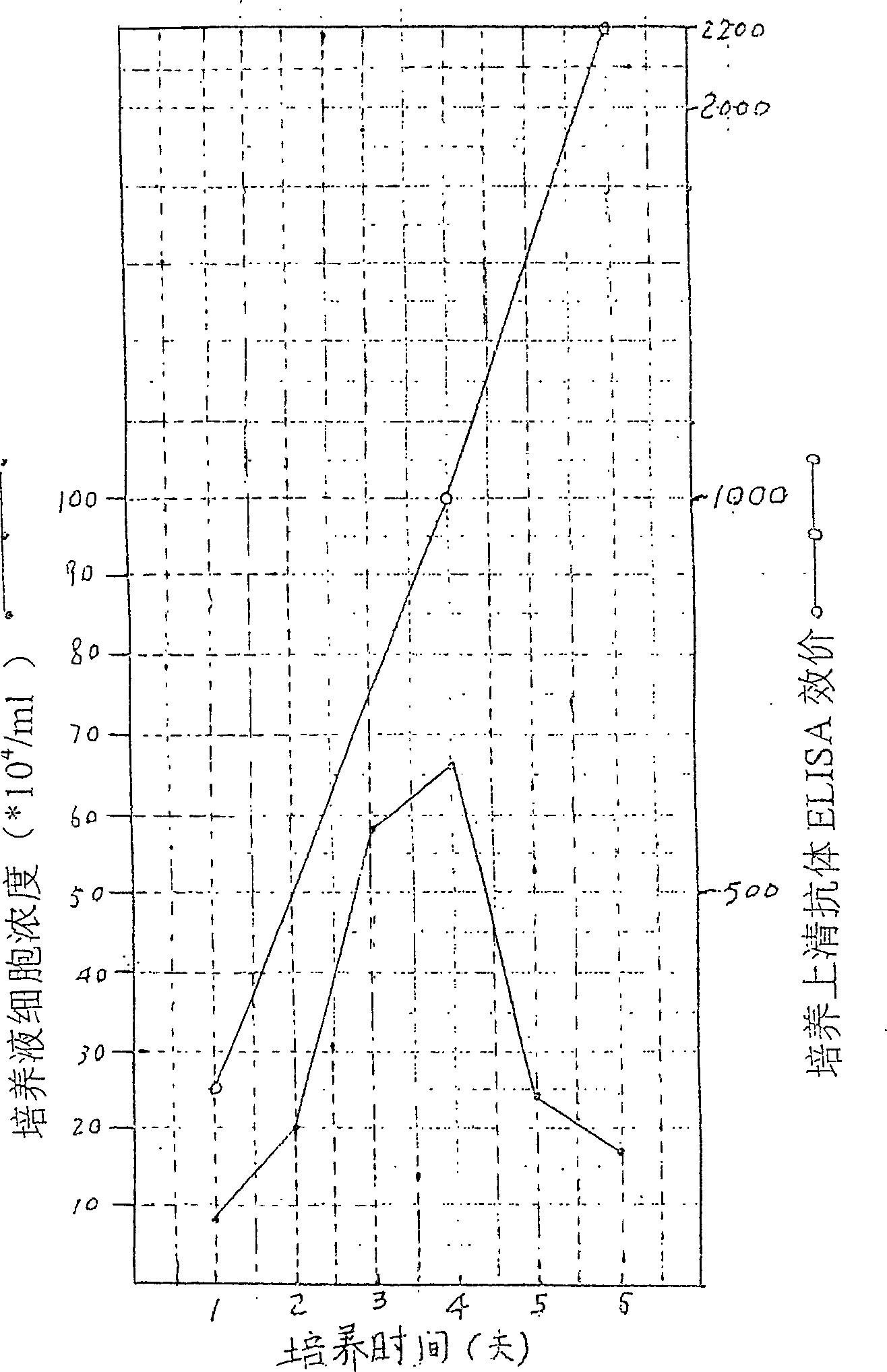
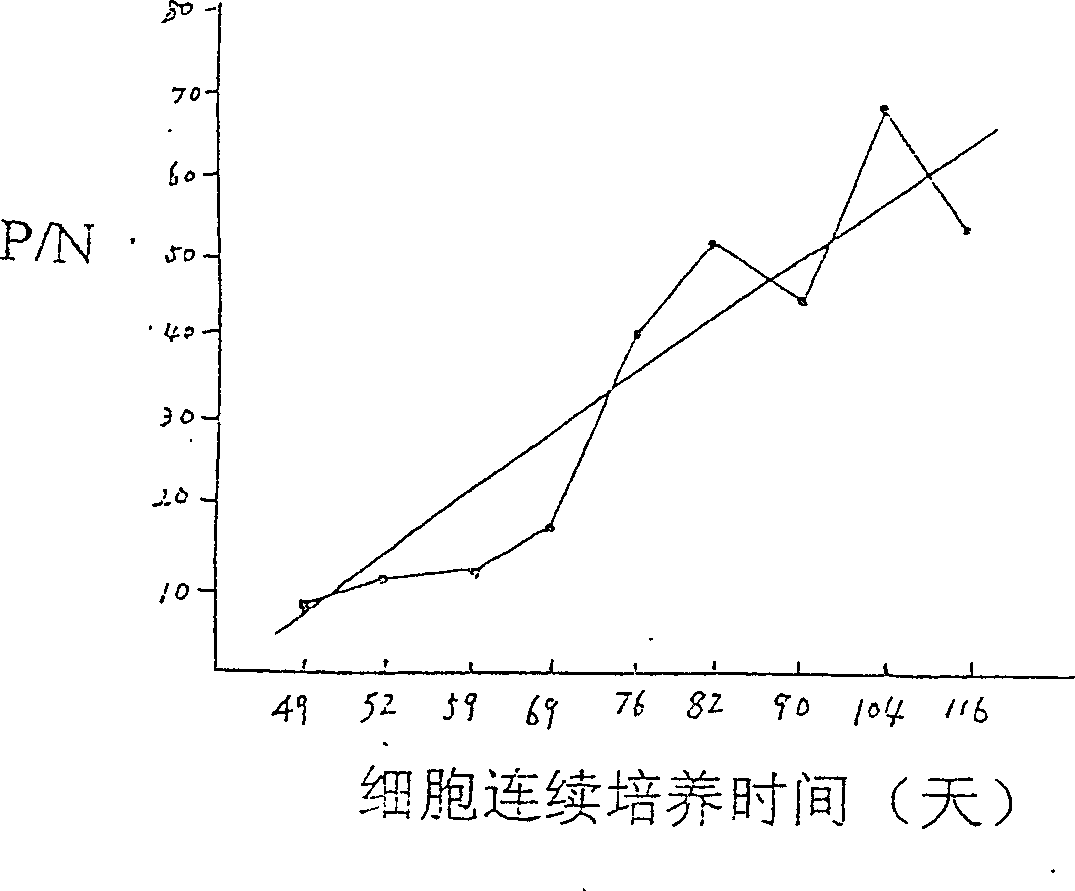
This invention provides a method for establishing hetero-hybrid tumor engineering cell sequence for producing human monoclonal antibody for anti-hepatitis B virus. The anti-HBs positive human splenic lymph cell (SL) is fused with mouse plasmacytoma sequence P3-X63 / Ag8-653 cell. Limiting dilution method is used for cloning the positive antibody poro-hybrid-tumor cell to obtain hetero hybrid tumor engineering cell sequence which produces human monoclonal antibody for anti-hepatitis B virus, with stable and high product, rate. Said monoclonal antibody is proceeded with purification and cross-linkage with interferon to produce target prepn. of anti-hepatitis B virus human monoclonal antibody crosslinking with itnerferon, and passive immune prepn. for hepatitis B, and testing agent for hepatitis B.
Owner:SHAANXI JIUZHOU BIOTECH
SARS-CoV-2 lymphocyte antigen epitope peptides and application thereof
InactiveCN112961223ASsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsAntigen epitopeLymphocyte antigen
The invention discloses lymphocyte antigen epitope peptides and application thereof, belongs to the fields of medical immunology and infectious diseases, and particularly relates to 164 thymus dependent lymphocyte antigen epitope peptides of five proteins of SARS-CoV-2 and application thereof. The antigen epitope peptides can be presented by HLA-A molecules to stimulate activation, proliferation and differentiation of SARS-CoV-2 specific thymus dependent lymphocytes, so that the immune effect of resisting SARS-CoV-2 infection is exerted. The antigen peptides can be used for preparing mixed polypeptide vaccines of SARS-CoV-2, recombinant protein vaccines connected with a plurality of epitope peptides in series and DNA and RNA vaccines, can be used for preparing a detection kit for detecting SARS-CoV-2 specific thymus dependent lymphocytes, can also be used for preparing effector thymus dependent lymphocytes or drugs for treating SARS-CoV-2 infection, and have a potential application value in the prevention, treatment and diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +2
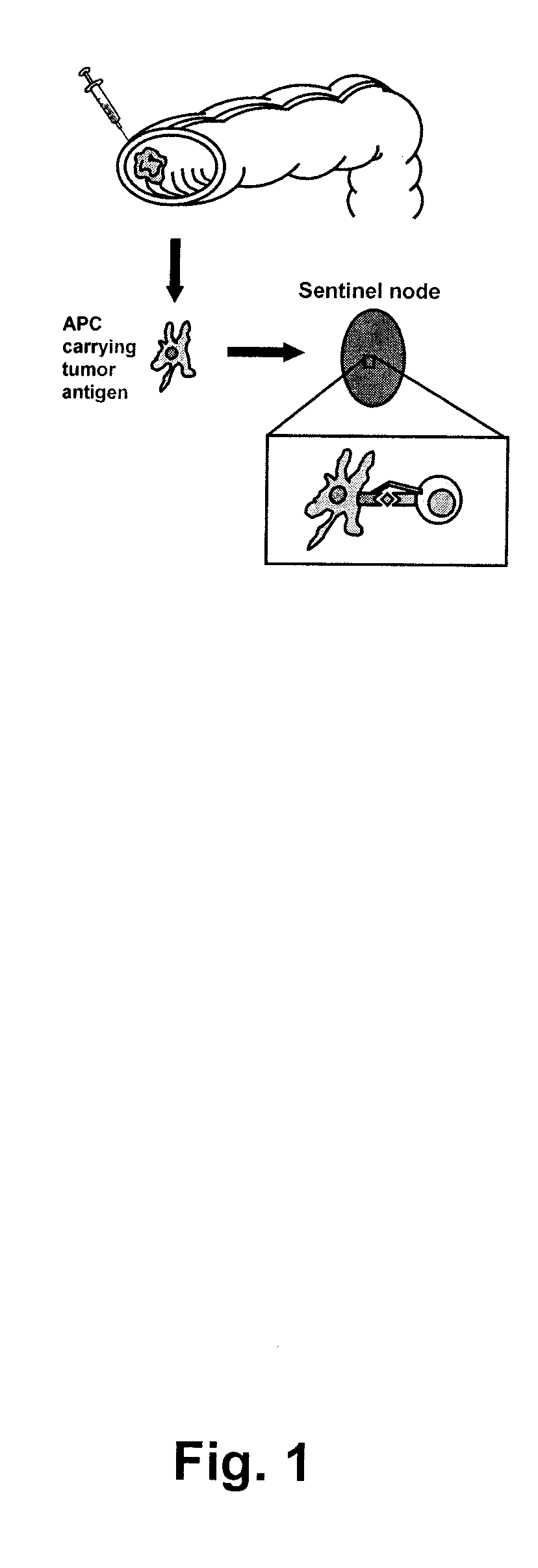
Method for expansion of tumour-reactive T-lymphocytes for immunotherapy of patients with specific cancer types
ActiveUS7951365B2Conducive to survivalRaise the ratioBiocideInanimate material medical ingredientsDiseasePresent method
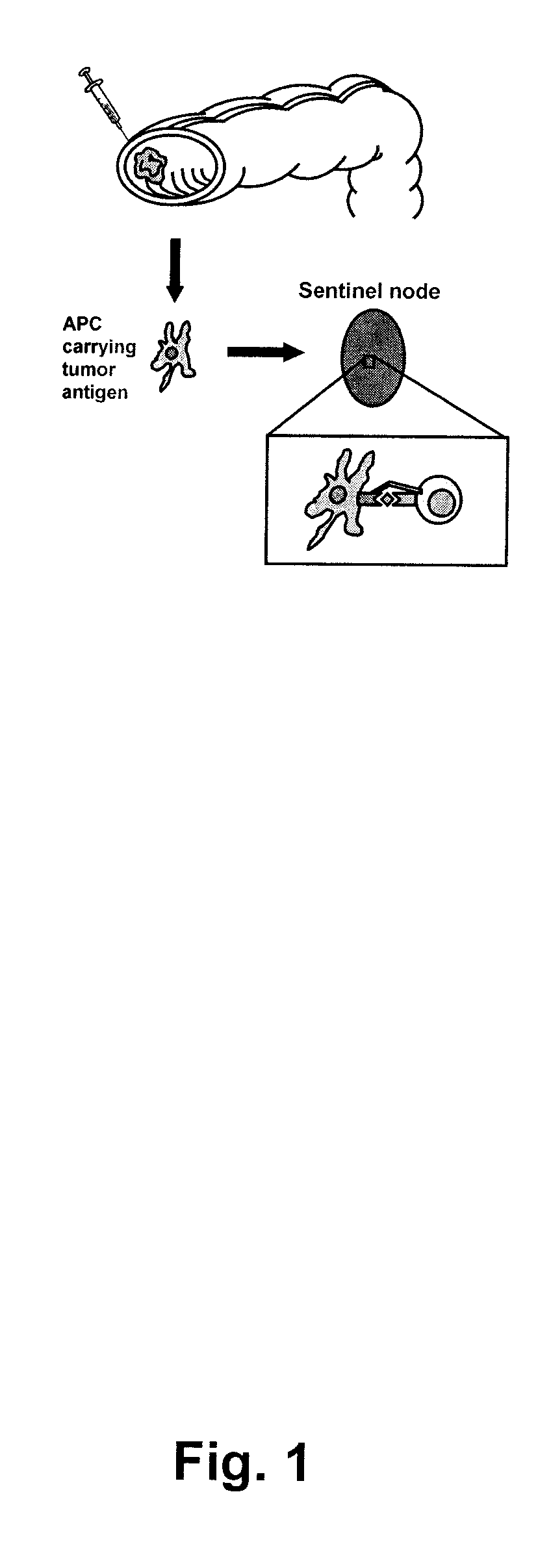
Methods for treating a patient suffering from a neoplastic disease are disclosed and described. A number of diseases can be treated under the present methods, including without limitation gall bladder cancer, hepato cellular cancer, ovarian cancer, small intestine cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, breast cancer, kidney cancer, pancreas cancer, prostate cancer, carcinoid cancer, leiomyosarcoma, or metastasis thereof. A general method for providing such treatment may include: 1) identifying in a patient one or more sentinel and / or metinel lymph nodes draining the neoplasm; 2) resecting the one or more nodes and, optionally all or part of the tumour or metastasis; 3) isolating tumour-reactive T-lymphocytes from said lymph nodes; 4) in vitro expanding said tumour-reactive T-lymphocytes; and 5) administering the thus obtained tumour-reactive T-lymphocytes to the patient.
Owner:SENTOCLONE INT AB
Human monoclonal antibody of human endophloeodal growth factor receptor 2 protein and its preparing process
InactiveCN1396182ASolve the HAMA problemGood treatment effectImmunoglobulins against growth factorsFermentationTreatment effectAnti her2
A humanized monoclonal antibody of human endophloeodal growth factor receptor 2 protein is prepared from enternal segment of HER2 / neucell through such steps as culturing the B cells of the person sensitive to HER2; fusing the said B cells with human osteoma cells (karpas 707 H); screening the external segment monoclonal anti body against HER2 cell; and amplification of the said monoclonal antibody. It features that antigen epitope is the external segment polypeptide of HER2 / neu cell for specifically binding the external segment of HER2 / neu cell, and the all gene sequences for syntehsis come from human B lymph cells and human osteoma cells.
Owner:陕西超英生物医学研究开发有限公司
2-(Aryl)Azacyclylmethyl Carboxylates, Sulfonates, Phosphonates, Phosphinates and Heterocycles as S1p Receptor Antagonists
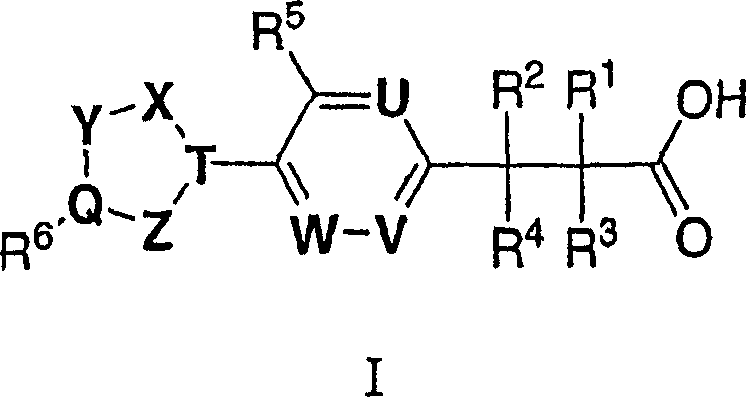
The present invention encompasses compounds of Formula I:as well as the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The compounds are S1P1 / Edg1 receptor agonists and thus have immunosuppressive, anti-inflammatory and hemostatic activities by modulating leukocyte trafficking, sequestering lymphocytes in secondary lymphoid tissues, and enhancing vascular integrity. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds and methods of treatment or prevention.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
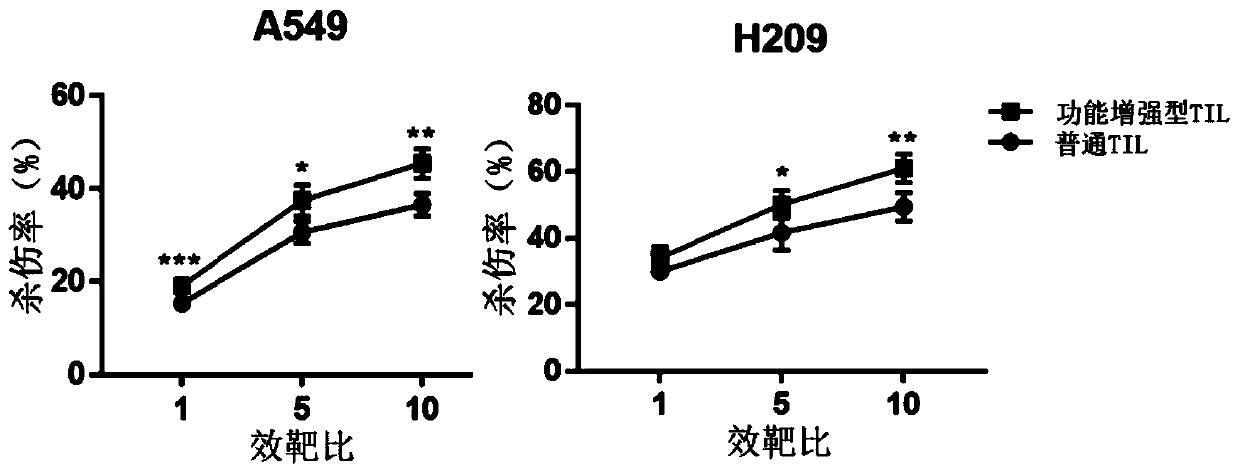
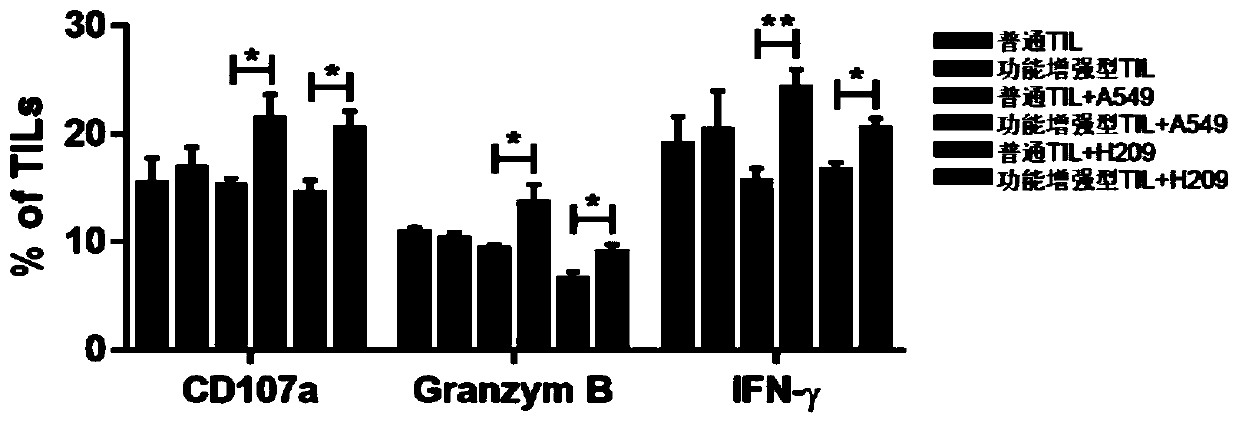
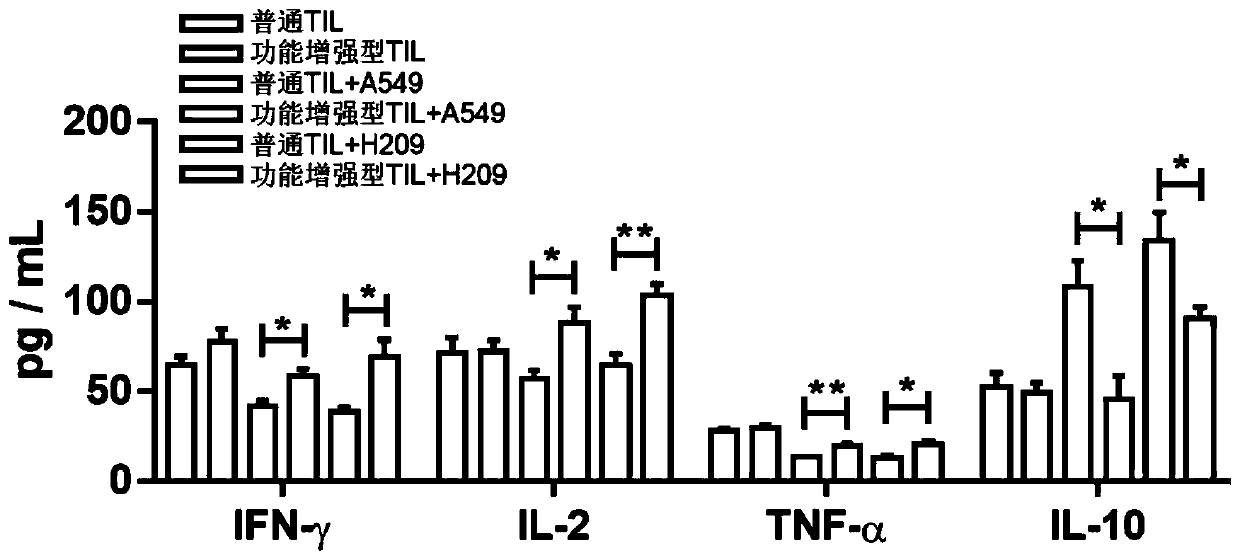
Culture method for functionally enhanced TILs
PendingCN110938594AHigh activityPromote secretionBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsLymphocyte cultureTumor cells
The invention discloses a culture method for functionally enhanced tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). The method includes the following steps: separating lymphocytes from tumor tissue, adding a start culture medium, performing inoculation in a 12-well culture plate (4 ml / well), performing start lymphocyte culture for 10 days or 14 days to obtain start TILs, and performing cryopreservation on the obtained start TILs for standby application; suspending the lymphocytes in a 25 cm<2> culture flask (20 ml / flask) by using an induction culture medium, placing the culture flask in an incubator having 5% CO2 at 37 DEG C, and performing TIL induction culture for 1 day; performing half quantity change by using an expansion culture medium, and performing expansion flask culture and expansion bag culture for 13 days or 14 days; on the 14th or 15th day of culture, collecting TILs, performing washing by using normal saline, and resuspending the TILs by using a function enhancement culture medium,and performing incubation for 30 min; and collecting TILs, and performing functional test to obtain the functionally enhanced TILs. The culture method described in the invention can obtain the functionally enhanced TILs with stronger tumor cell killing activity and higher-level anti-tumor cytokine secretion ability.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT
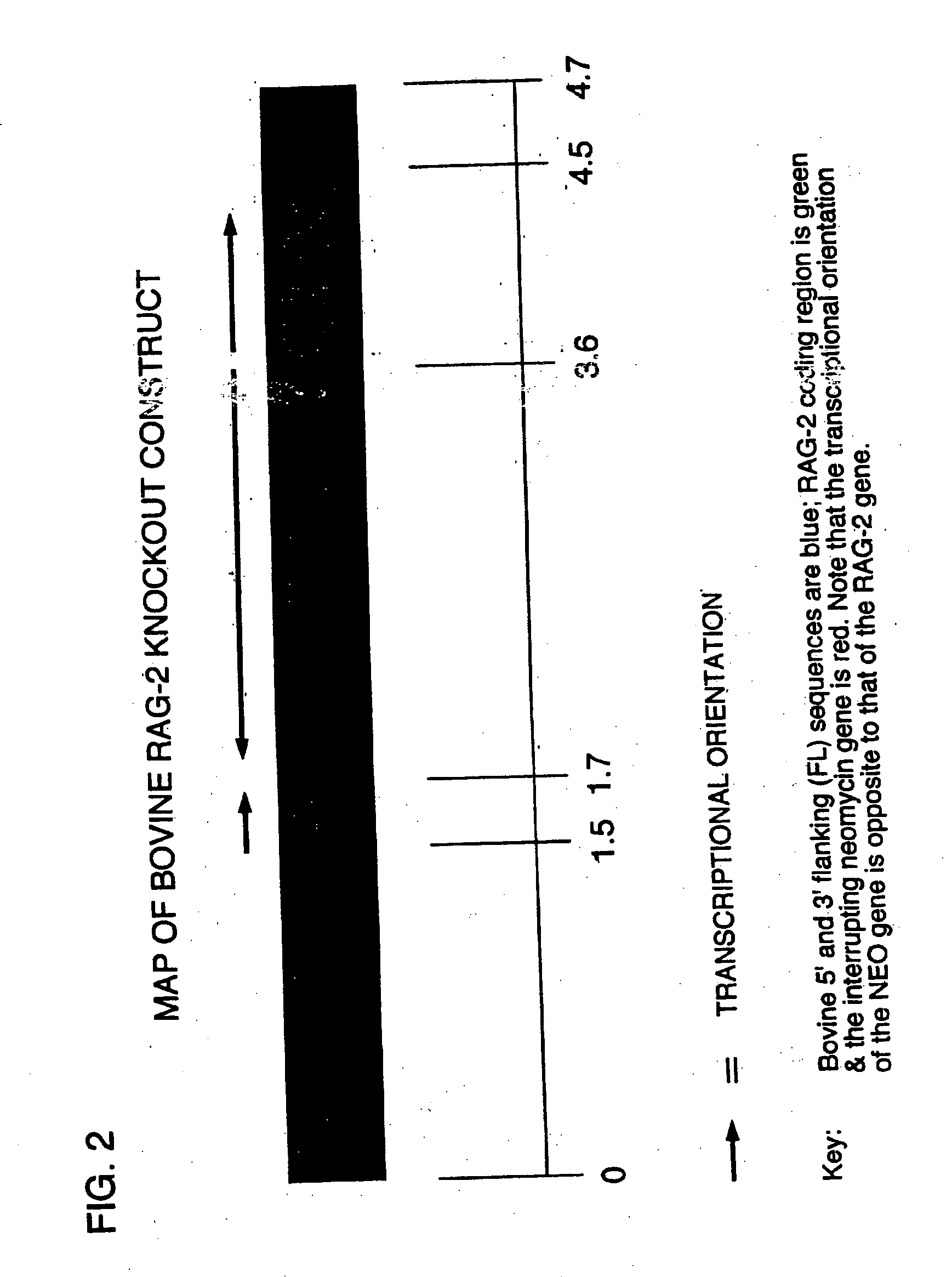
Production of ungulates, preferably bovines that produce human immunoglobulins
The present invention relates to a method of producing an ungulate having both copies of the IgM heavy chain (mu) rag-1 and / or rag-2 gene eliminated from its genome. Animals which have IgM, rag-1 and / or rag-2 eliminated from their genome are unable to conduct the gene rearrangements that are necessary to generate the antigen receptors of B or T lymphocytes, and therefore will not develop native B or T cells. Because they are unable to produce B and T lymphocytes, these IgM, rag-1 or rag-2 ungulates cannot reject human hematopoietic stem cell preparations, and B and T lymphocytes which develop therefrom. Therefore, the present invention also involves injecting into IgM, rag-1 and / or rag-2 deficient ungulates, in utero or shortly after birth, human B and T lymphocytes whose immune systems produce human immunoglobulin that can be processed for therapeutic uses in humans.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Method for expansion of tumour-reactive t-lymphocytes for immunotherapy of patients with specific cancer types
ActiveUS20090022695A1Conducive to survivalRaise the ratioBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseCancer type
Methods for treating a patient suffering from a neoplastic disease are disclosed and described. A number of diseases can be treated under the present methods, including without limitation gall bladder cancer, hepato cellular cancer, ovarian cancer, small intestine cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, breast cancer, kidney cancer, pancreas cancer, prostate cancer, carcinoid cancer, leiomyosarcoma, or metastasis thereof. A general method for providing such treatment may include: 1) identifying in a patient one or more sentinel and / or metinel lymph nodes draining the neoplasm; 2) resecting the one or more nodes and, optionally all or part of the tumour or metastasis; 3) isolating tumour-reactive T-lymphocytes from said lymph nodes; 4) in vitro expanding said tumour-reactive T-lymphocytes; and 5) administering the thus obtained tumour-reactive T-lymphocytes to the patient.
Owner:SENTOCLONE INT AB
MLL translocations specify a distinct gene expression profile, distinguishing a unique leukemia
InactiveUS20060024734A1Easy diagnosisConvenient treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAcute lymphocytic leukemiaProtein translocation
The present invention relates to the diagnosis of mixed lineage leukemia (MLL), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), and acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) according to the gene expression profile of a sample from an individual, as well as to methods of therapy and screening that utilize the genes identified herein as targets.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




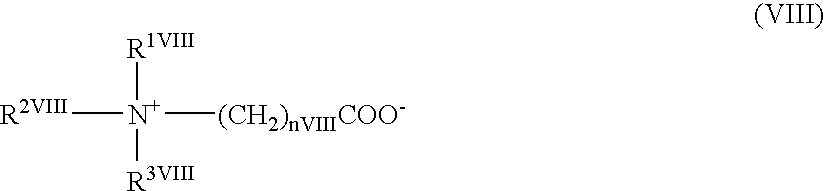



![Substituted pyrido [3′, 2′: 4, 5] thieno [3, 2-D] pyrimidines and pyrido [3′, 2′: 4, 5] furo [3, 2-D] pyrimidines used as inhibitors of the PDE-4 and/or the release of TNF-ALPHA Substituted pyrido [3′, 2′: 4, 5] thieno [3, 2-D] pyrimidines and pyrido [3′, 2′: 4, 5] furo [3, 2-D] pyrimidines used as inhibitors of the PDE-4 and/or the release of TNF-ALPHA](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/354b4038-6bc4-4dda-9bb1-fc6c796178da/US08058285-20111115-D00001.png)
![Substituted pyrido [3′, 2′: 4, 5] thieno [3, 2-D] pyrimidines and pyrido [3′, 2′: 4, 5] furo [3, 2-D] pyrimidines used as inhibitors of the PDE-4 and/or the release of TNF-ALPHA Substituted pyrido [3′, 2′: 4, 5] thieno [3, 2-D] pyrimidines and pyrido [3′, 2′: 4, 5] furo [3, 2-D] pyrimidines used as inhibitors of the PDE-4 and/or the release of TNF-ALPHA](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/354b4038-6bc4-4dda-9bb1-fc6c796178da/US08058285-20111115-C00001.png)
![Substituted pyrido [3′, 2′: 4, 5] thieno [3, 2-D] pyrimidines and pyrido [3′, 2′: 4, 5] furo [3, 2-D] pyrimidines used as inhibitors of the PDE-4 and/or the release of TNF-ALPHA Substituted pyrido [3′, 2′: 4, 5] thieno [3, 2-D] pyrimidines and pyrido [3′, 2′: 4, 5] furo [3, 2-D] pyrimidines used as inhibitors of the PDE-4 and/or the release of TNF-ALPHA](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/354b4038-6bc4-4dda-9bb1-fc6c796178da/US08058285-20111115-C00002.png)