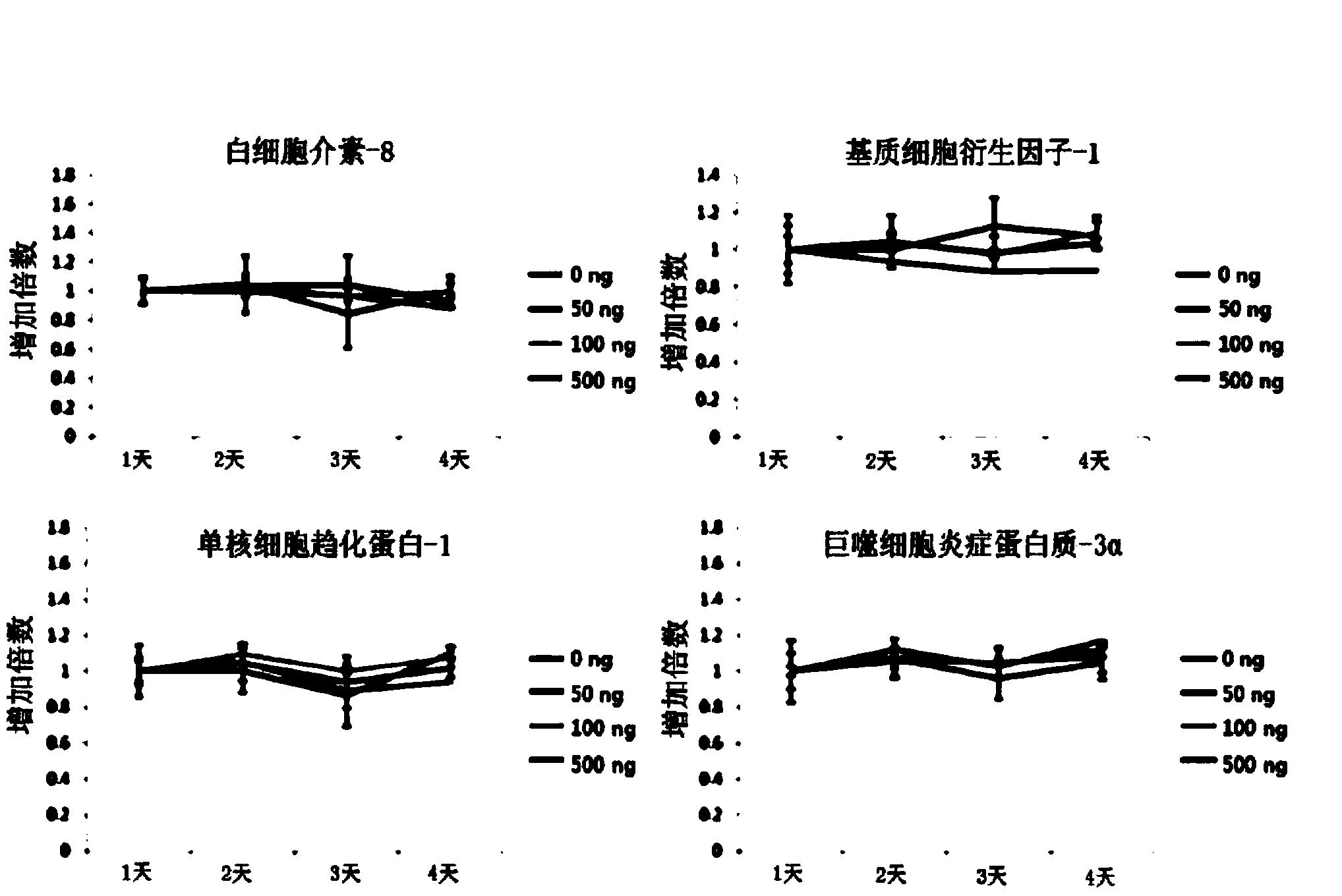
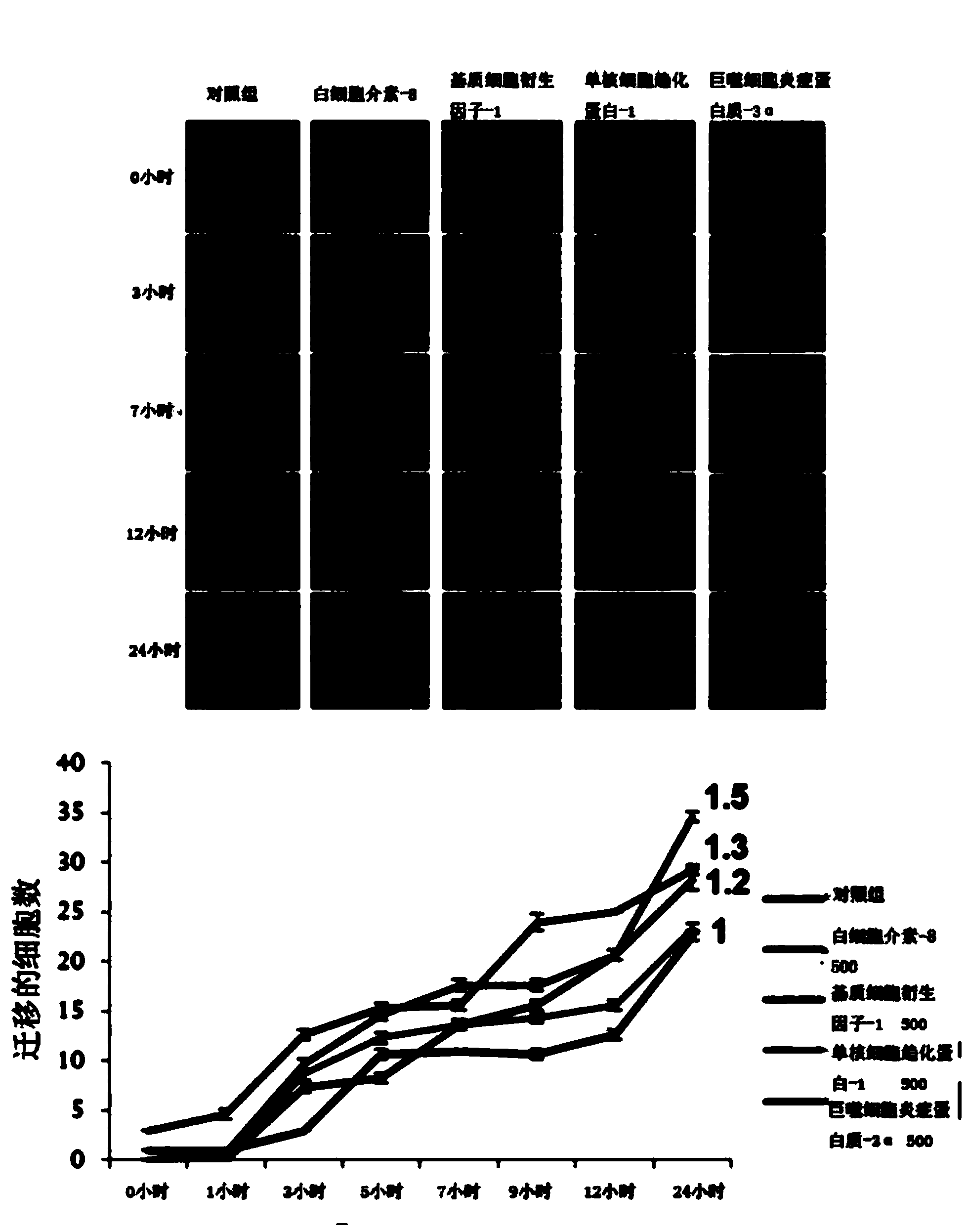
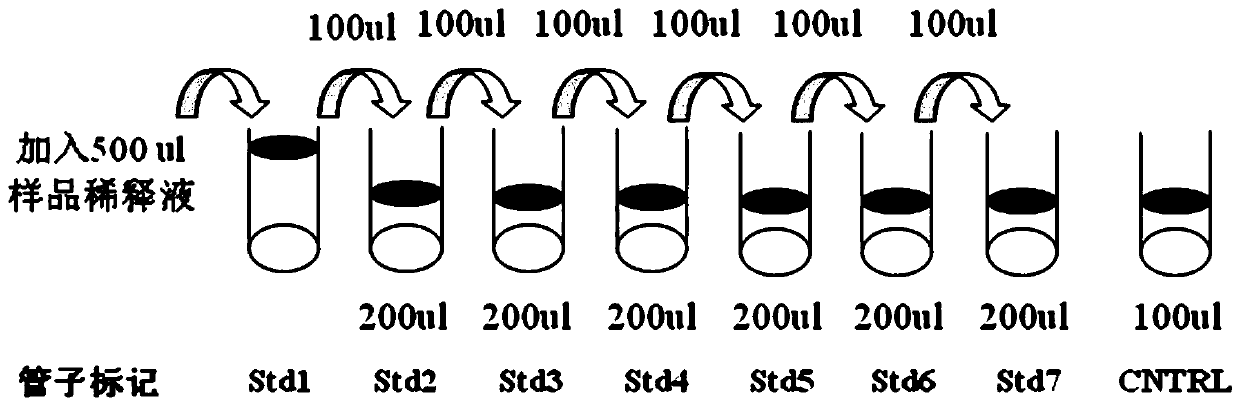
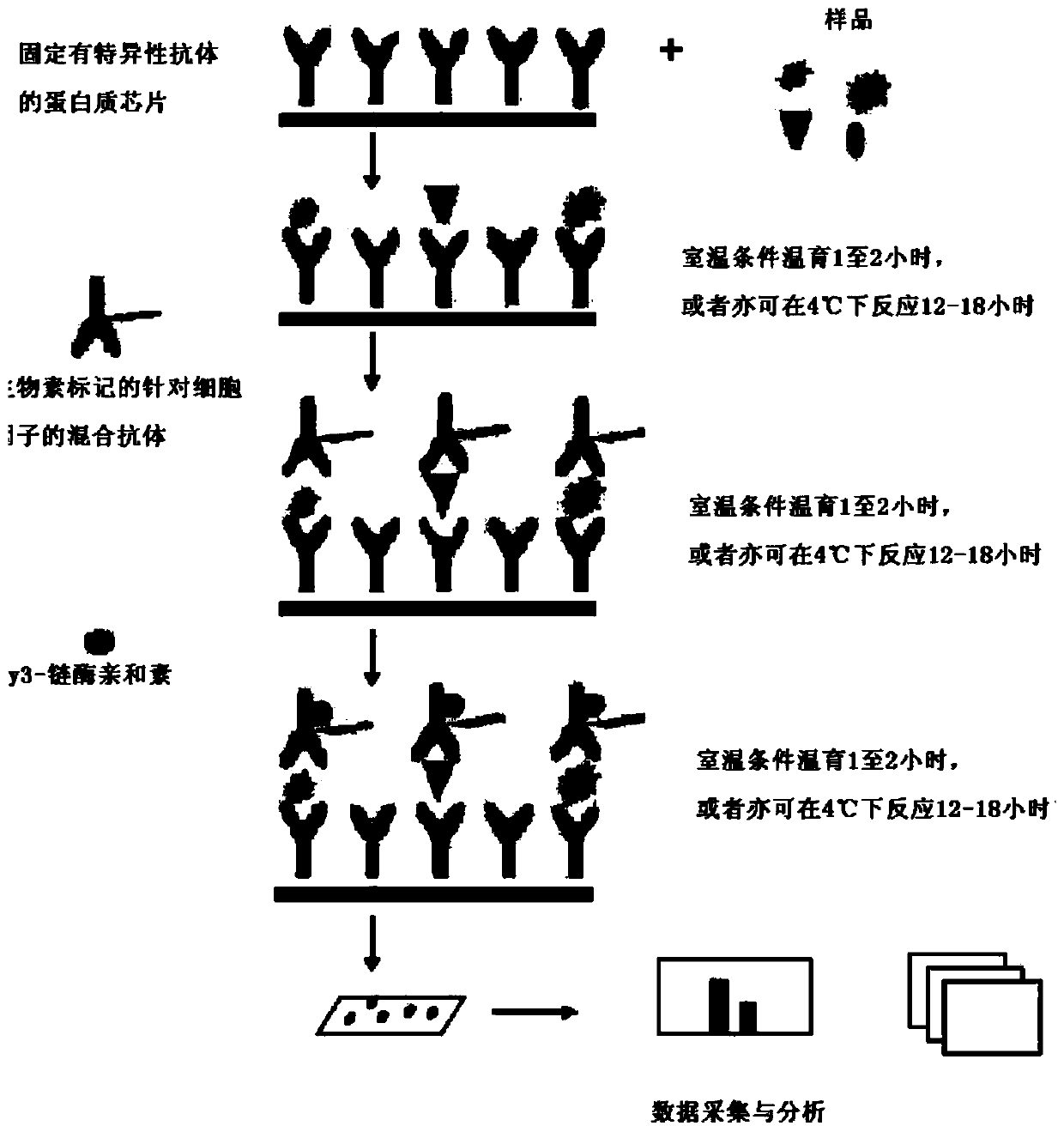
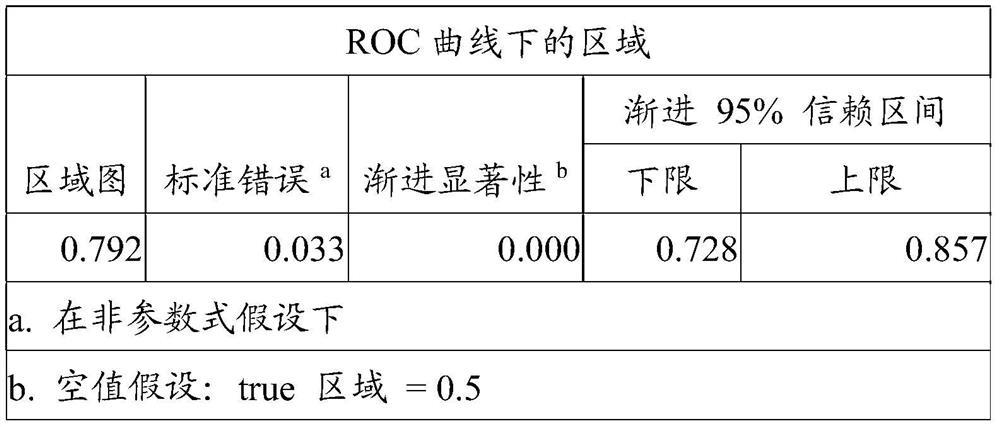
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Macrophage inflammatory protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Macrophage Inflammatory Proteins (MIP) belong to the family of chemotactic cytokines known as chemokines. In humans, there are two major forms, MIP-1α and MIP-1β that are now officially named CCL3 and CCL4, respectively. Both are major factors produced by macrophages after they are stimulated with bacterial endotoxin. They are crucial for immune responses towards infection and inflammation. They activate human granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils) which can lead to acute neutrophilic inflammation. They also induce the synthesis and release of other pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin 1 (IL-1), IL-6 and TNF-α from fibroblasts and macrophages. The genes for CCL3 and CCL4 are both located on human chromosome 17.
Novel receptor trem (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) and uses thereof
InactiveUS20130150559A1Strong upregulationImmunoglobulin superfamilyImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAutoimmune conditionDc maturation
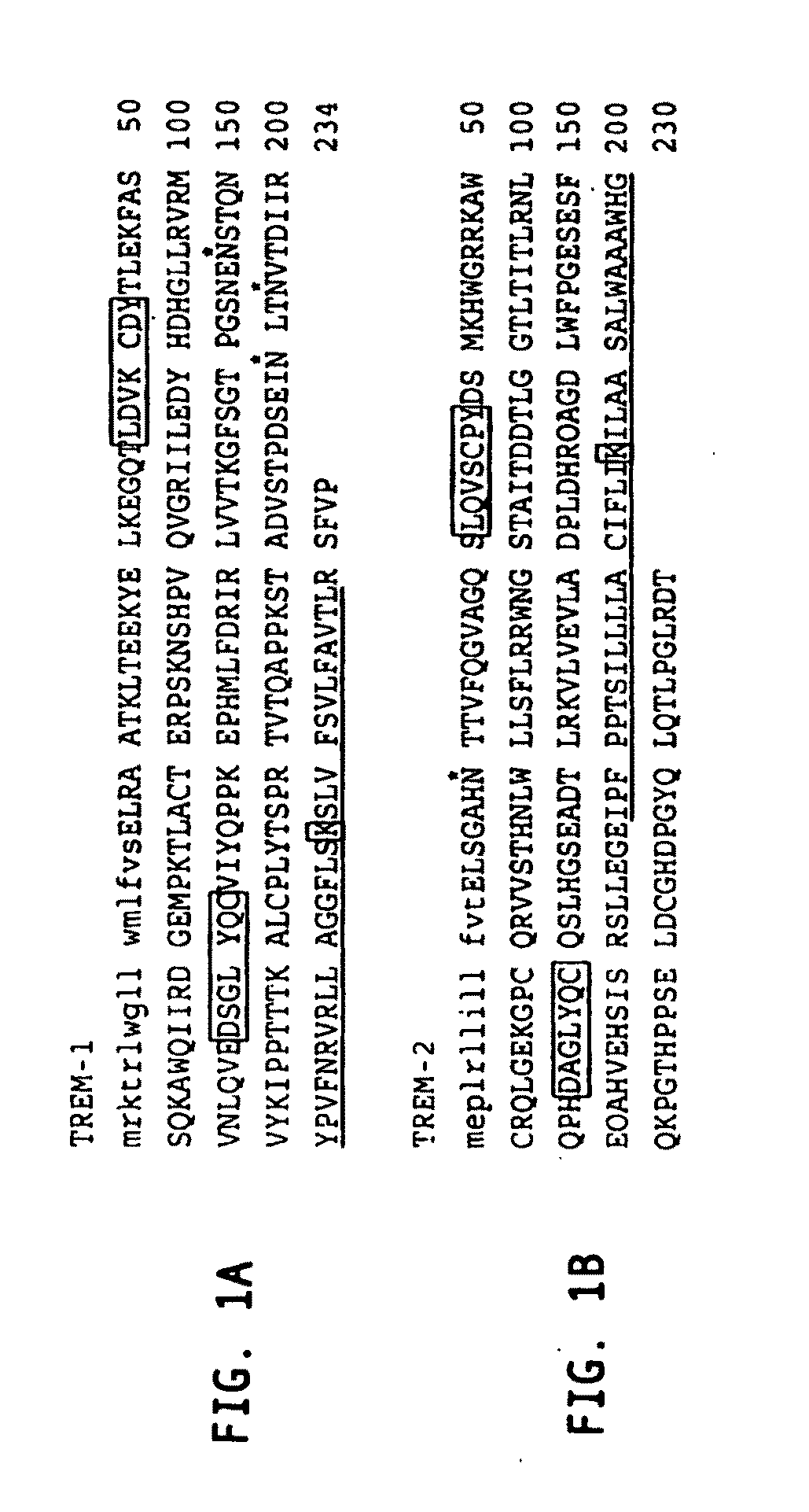
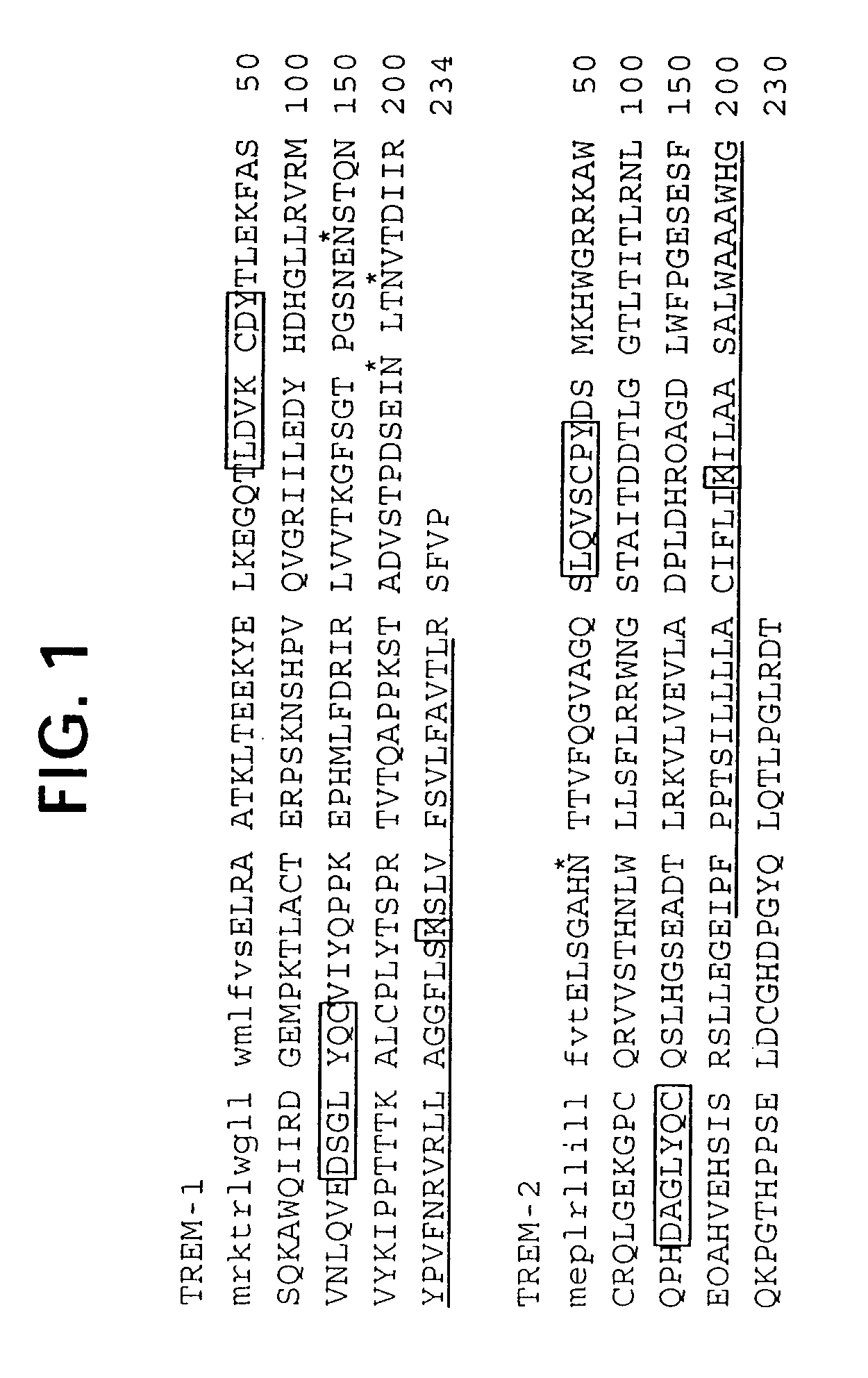
Novel activating receptors of the lg super-family expressed on human myeloid cells, called TREM(s) (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) are provided. Specifically, two (2) members of TREMs, TREM-1 and TREM-2 are disclosed. TREM-1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on blood neutrophils and a subset of monocytes but not on lymphocytes and other cell types and is upregulated by bacterial and fungal products. Use of TREM-1 in treatment and diagnosis of various inflammatory diseases is also provided. TREM-2 is also a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on mast cells and peripheral dendritic cells (DCs) but not on granulocytes or monocytes. DC stimulation via TREM-2 leads to DC maturation and resistance to apoptosis, and induces strong upregulation of CCR7 and subsequent chemotaxis toward macrophage inflammatory protein 3-β. TREM-2 has utility in modulating host immune responses in various immune disorders, including autoimmune diseases and allergic disorders.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Receptor trem (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) and uses thereof
InactiveUS8231878B2Strong upregulationImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsDc maturationAutoimmune disease
Novel activating receptors of the Ig super-family expressed on human myeloid cells, called TREM(s) (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) are provided. Specifically, two (2) members of TREMs, TREM-1 and TREM-2 are disclosed. TREM-1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on blood neutrophils and a subset of monocytes but not on lymphocytes and other cell types and is upregulated by bacterial and fungal products. Use of TREM-1 in treatment and diagnosis of various inflammatory diseases is also provided. TREM-2 is also a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on mast cells and peripheral dendritic cells (DCs) but not on granulocytes or monocytes. DC stimulation via TREM-2 leads to DC maturation and resistance to apoptosis, and induces strong upregulation of CCR7 and subsequent chemotaxis toward macrophage inflammatory protein 3-β. TREM-2 has utility in modulating host immune responses in various immune disorders, including autoimmune diseases and allergic disorders.
Owner:COSMO TECH LTD
Novel receptor trem (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100310560A1Strong upregulationOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulin superfamilyAutoimmune responsesDc maturation
Novel activating receptors of the Ig super-family expressed on human myeloid cells, called TREM(s) (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) are provided. Specifically, two (2) members of TREMs, TREM-1 and TREM-2 are disclosed. TREM-1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on blood neutrophils and a subset of monocytes but not on lymphocytes and other cell types and is upregulated by bacterial and fungal products. Use of TREM-1 in treatment and diagnosis of various inflammatory diseases is also provided. TREM-2 is also a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on mast cells and peripheral dendritic cells (DCs) but not on granulocytes or monocytes. DC stimulation via TREM-2 leads to DC maturation and resistance to apoptosis, and induces strong upregulation of CCR7 and subsequent chemotaxis toward macrophage inflammatory protein 3-β. TREM-2 has utility in modulating host immune responses in various immune disorders, including autoimmune diseases and allergic disorders.
Owner:COSMO TECH LTD
Receptor TREM (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) and uses thereof
InactiveUS8981061B2Strong upregulationImmunoglobulin superfamilyImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDc maturationApoptosis
Novel activating receptors of the lg super-family expressed on human myeloid cells, called TREM(s) (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) are provided. Specifically, two (2) members of TREMs, TREM-1 and TREM-2 are disclosed. TREM-1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on blood neutrophils and a subset of monocytes but not on lymphocytes and other cell types and is upregulated by bacterial and fungal products. Use of TREM-1 in treatment and diagnosis of various inflammatory diseases is also provided. TREM-2 is also a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on mast cells and peripheral dendritic cells (DCs) but not on granulocytes or monocytes. DC stimulation via TREM-2 leads to DC maturation and resistance to apoptosis, and induces strong upregulation of CCR7 and subsequent chemotaxis toward macrophage inflammatory protein 3-β. TREM-2 has utility in modulating host immune responses in various immune disorders, including autoimmune diseases and allergic disorders.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Novel receptor trem (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090081199A1Strong upregulationOrganic active ingredientsCompound screeningApoptosisAutoimmune disease
Novel activating receptors of the Ig super-family expressed on human myeloid cells, called TREM(s) (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) are provided. Specifically, two (2) members of TREMs, TREM-1 and TREM-2 are disclosed. TREM-1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on blood neutrophils and a subset of monocytes but not on lymphocytes and other cell types and is upregulated by bacterial and fungal products. Use of TREM-1 in treatment and diagnosis of various inflammatory diseases is also provided. TREM-2 is also a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on mast cells and peripheral dendritic cells (DCs) but not on granulocytes or monocytes. DC stimulation via TREM-2 leads to DC maturation and resistance to apoptosis, and induces strong upregulation of CCR7 and subsequent chemotaxis toward macrophage inflammatory protein 3-β. TREM-2 has utility in modulating host immune responses in various immune disorders, including autoimmune diseases and allergic disorders.
Owner:BIOXELL
Novel receptor trem (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050260670A1Strong upregulationAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsAutoimmune diseaseApoptosis
Novel activating receptors of the Ig super-family expressed on human myeloid cells, called TREM(s) (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) are provided. Specifically, two (2) members of TREMs, TREM-1 and TREM-2 are disclosed. TREM-1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on blood neutrophils and a subset of monocytes but not on lymphocytes and other cell types and is upregulated by bacterial and fungal products. Use of TREM-1 in treatment and diagnosis of various inflammatory diseases is also provided. TREM-2 is also a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on mast cells and peripheral dendritic cells (DCs) but not on granulocytes or monocytes. DC stimulation via TREM-2 leads to DC maturation and resistance to apoptosis, and induces strong upregulation of CCR7 and subsequent chemotaxis toward macrophage inflammatory protein 3-beta. TREM-2 has utility in modulating host immune responses in various immune disorders, including autoimmune diseases and allergic disorders.
Owner:COLONNA MARCO +1
Novel receptor trem (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) and uses thereof
InactiveUS20160251434A1Strong upregulationImmunoglobulin superfamilyImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDc maturationApoptosis
Novel activating receptors of the lg super-family expressed on human myeloid cells, called TREM(s) (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells) are provided. Specifically, two (2) members of TREMs, TREM-1 and TREM-2 are disclosed. TREM-1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on blood neutrophils and a subset of monocytes but not on lymphocytes and other cell types and is upregulated by bacterial and fungal products. Use of TREM-1 in treatment and diagnosis of various inflammatory diseases is also provided. TREM-2 is also a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed selectively on mast cells and peripheral dendritic cells (DCs) but not on granulocytes or monocytes. DC stimulation via TREM-2 leads to DC maturation and resistance to apoptosis, and induces strong upregulation of CCR7 and subsequent chemotaxis toward macrophage inflammatory protein 3-β. TREM-2 has utility in modulating host immune responses in various immune disorders, including autoimmune diseases and allergic disorders.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
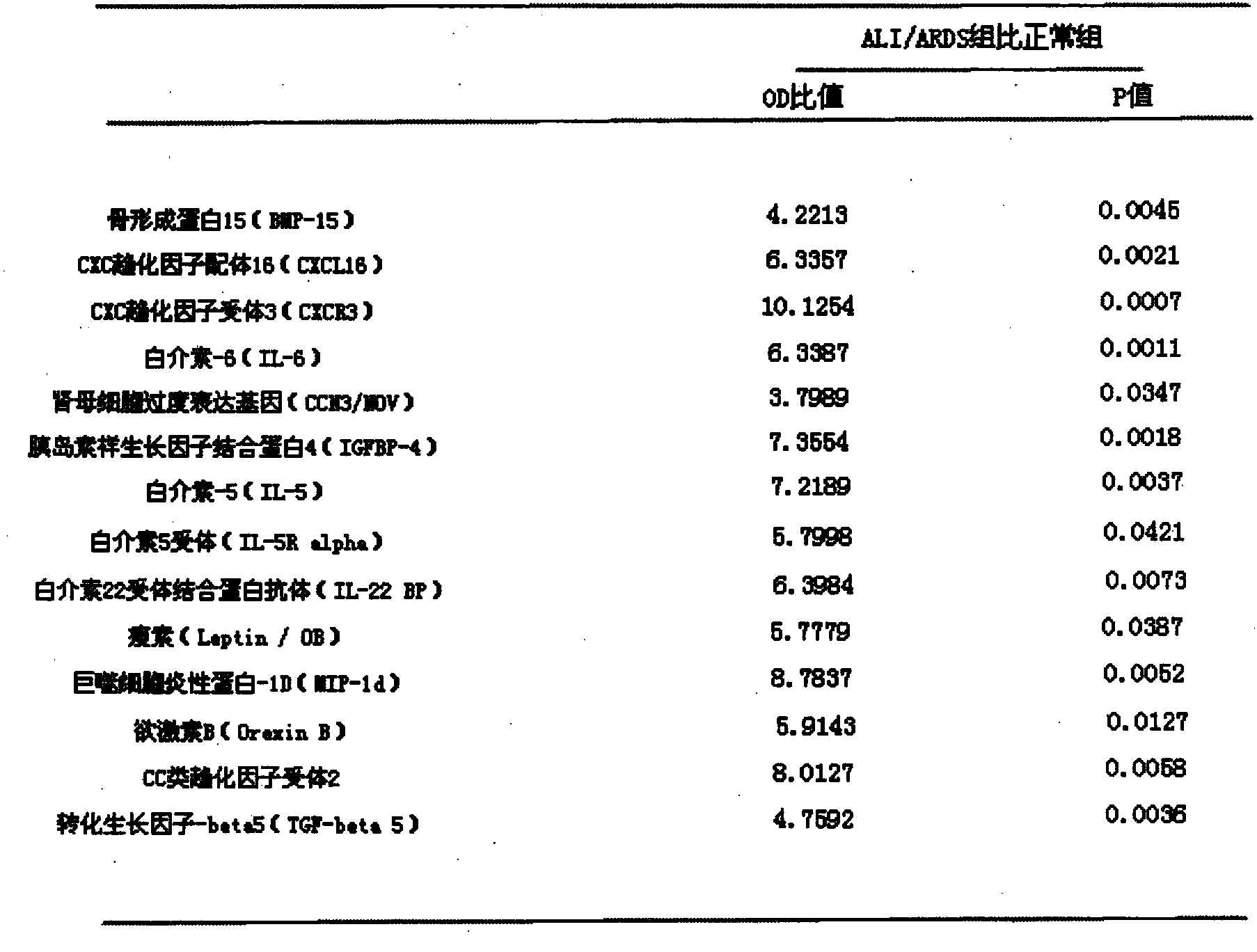
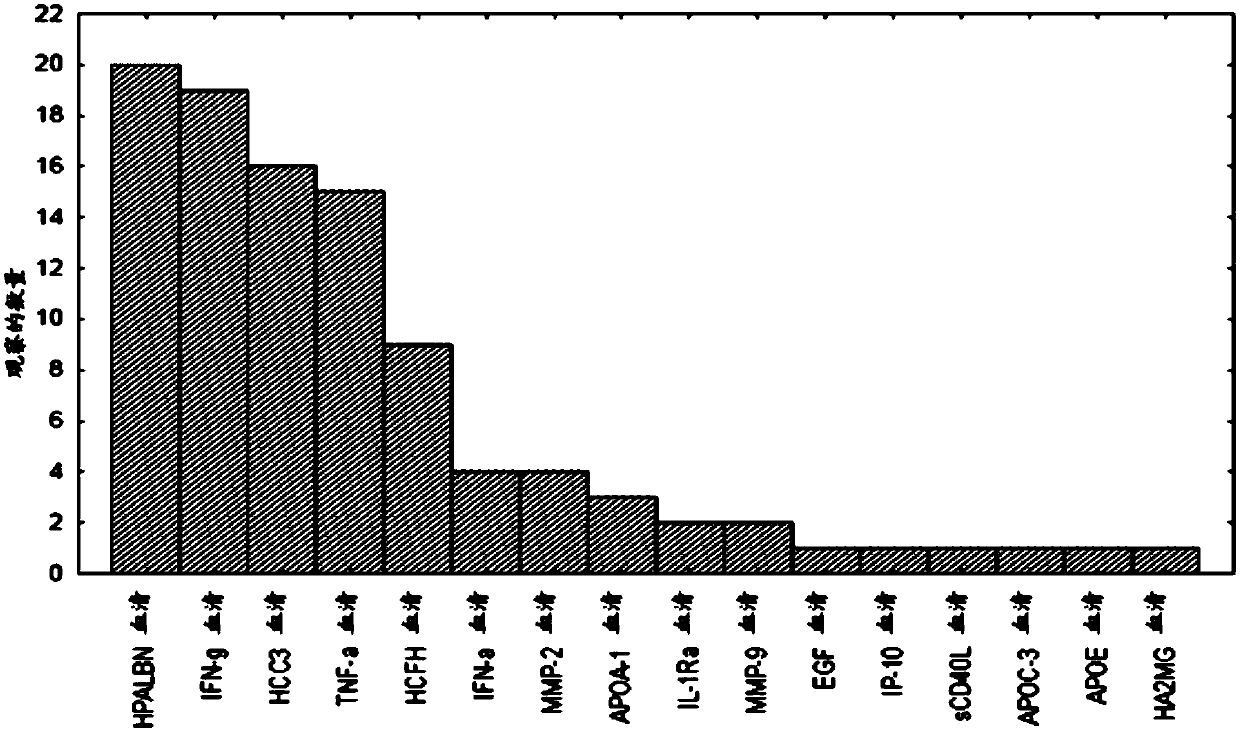
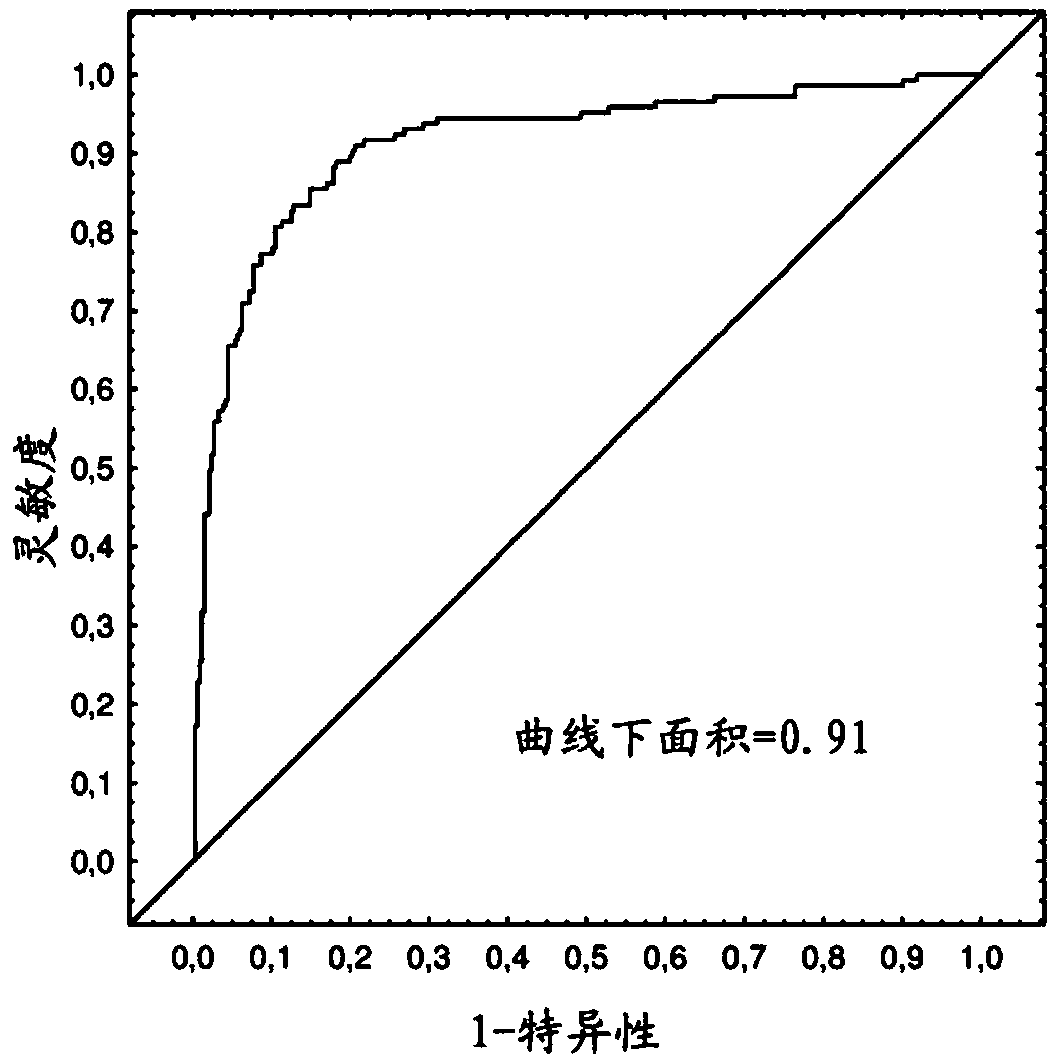
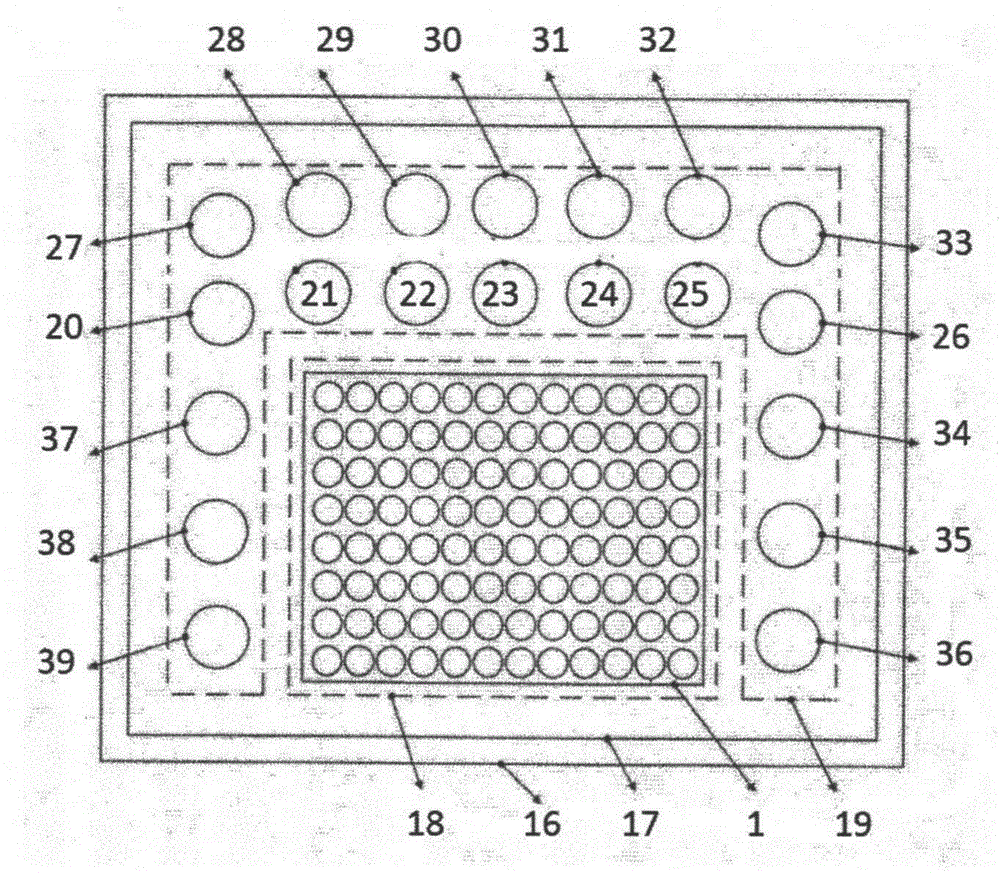
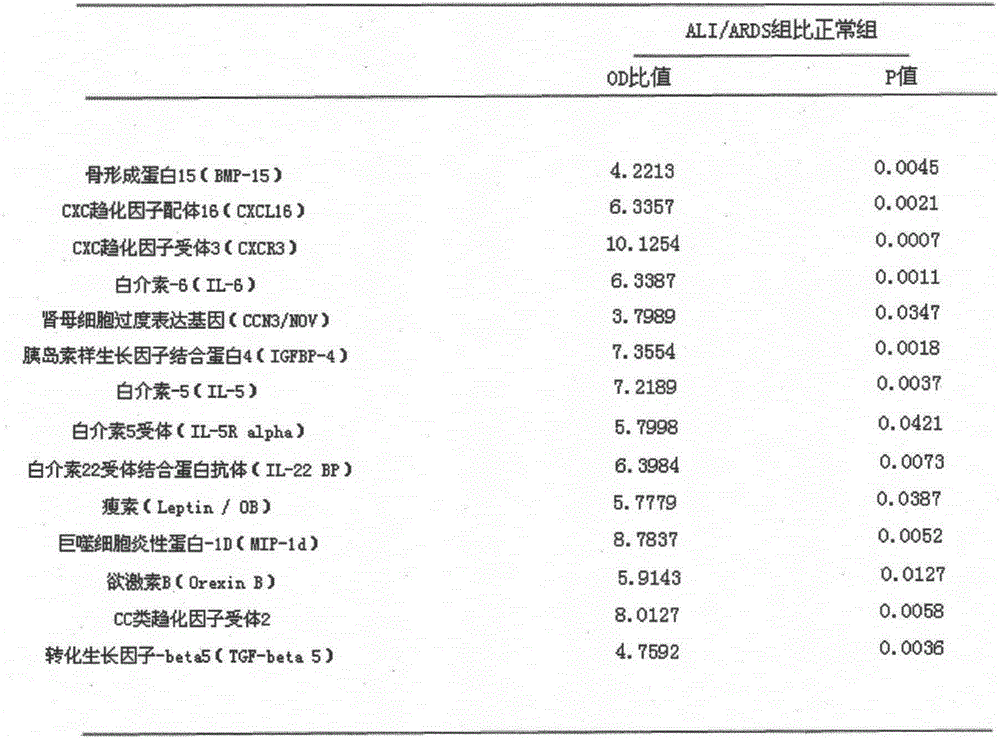
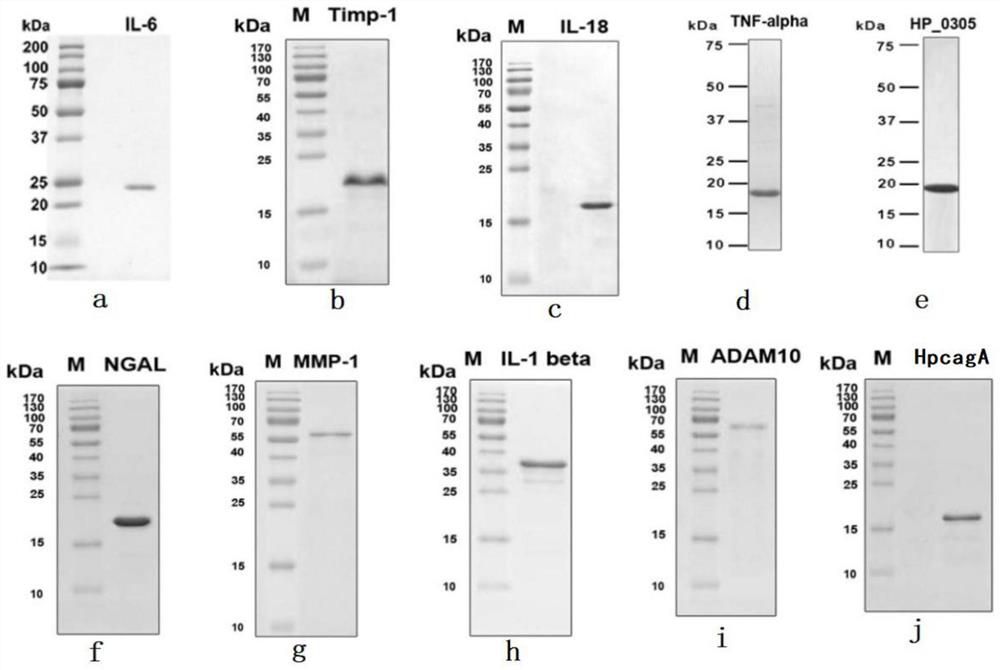
ELISA (Enzyme-linked Immunoassay Assay) plate and kit for predicting ALI (Acute Lung Injury)/ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) and assessing prognosis of ALI/ARDS
ActiveCN103969439AThe result is accurateEasy to operateDisease diagnosisInterleukin 6Insulin-like growth factor binding
The invention provides an ELISA (Enzyme-linked Immunoassay Assay) plate and kit for predicting ALI (Acute Lung Injury) / ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) and assessing prognosis of the ALI / ARDS. The ELISA plate comprises a solid phase carrier which is provided with a monoclonal antibody of bone morphogenetic protein 15, a monoclonal antibody of CXC chemokine ligand 16, a monoclonal antibody of CXC chemokine receptor 3, a monoclonal antibody of interleukin-6, a monoclonal antibody of nephroblastoma overexpression genes, a monoclonal antibody of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 4, a monoclonal antibody of interleukin-5, a monoclonal antibody of interleukin 5 receptor, a monoclonal antibody of interleukin 22 receptor binding protein, a monoclonal antibody of leptin, a monoclonal antibody of macrophage inflammatory protein-1D, a monoclonal antibody of orexin B, a monoclonal antibody of CC type chemokine receptor 2, a monoclonal antibody of transforming growth factor-beta5 and blank control holes. The ELISA plate and kit can achieve accurate results and are simple to operate.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
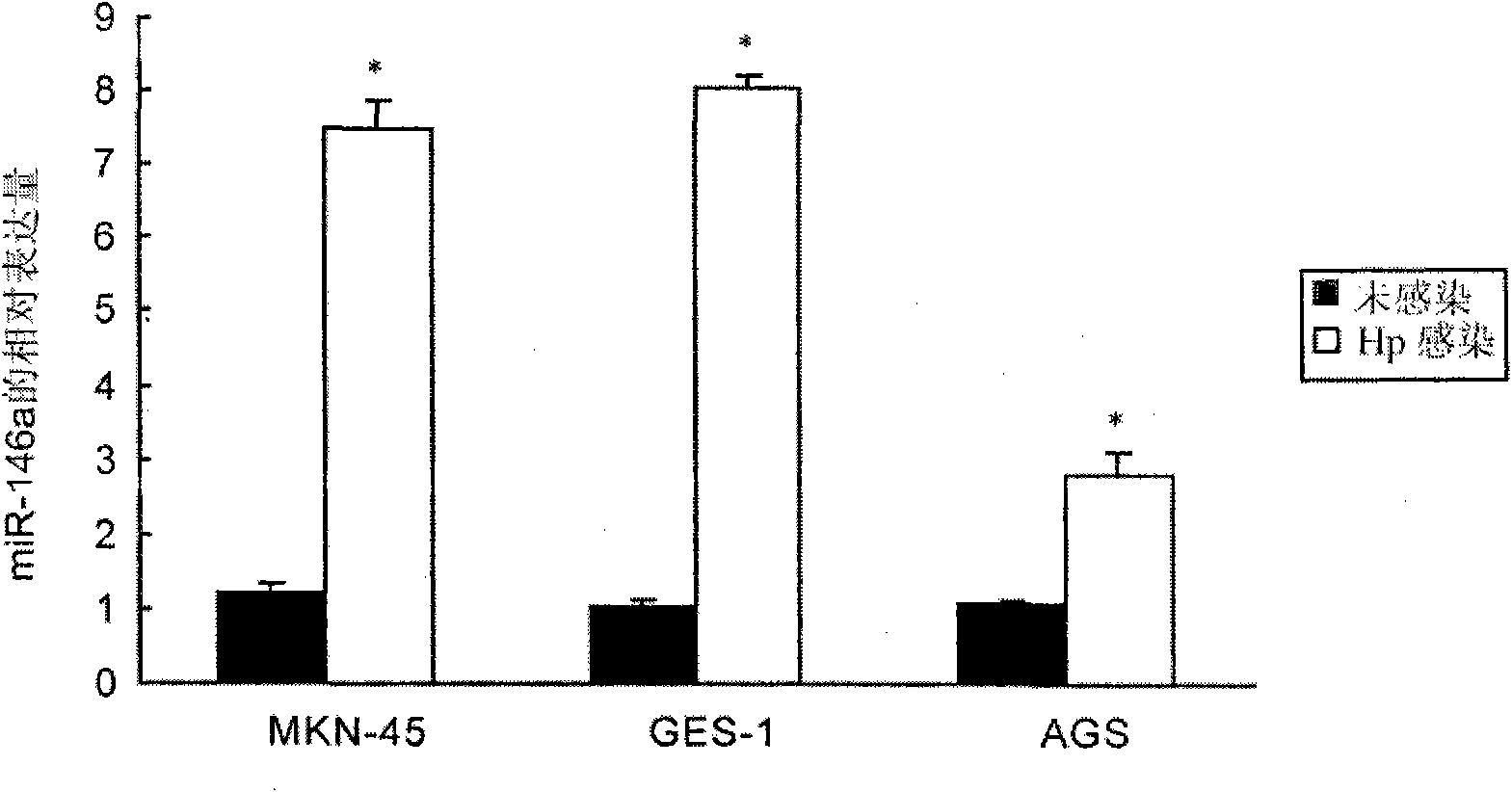
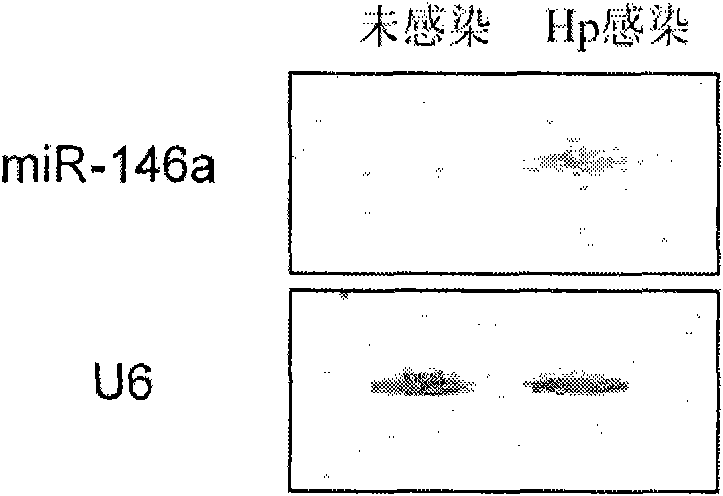
Application of miR-146a in preparing medicine for curing gastricism
InactiveCN101670117AInhibit the inflammatory responseGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemInflammatory factorsFhit gene
The invention relates to an application of a non-coding small RNA gene miR-146a in preparing a medicine for curing gastricism. The gastricism can be caused by helicobacter pylori infection. The miR-146a is highly expressed in helicobacter pylori infected gastric epithelial cells and human gastric mucosa tissues; furthermore, after the gastric epithelial cells GES-1 are transfected by a miR-146a simulator or a miR-146a inhibitor respectively, the miR-146a simulator can obviously reduce the protein secretion level of inflammatory factor lnterleukin 8, macrophage inflammatory protein 3Alpha and growth-related oncogene Alpha and the protein secretion level of the macrophage inflammatory protein 3Alpha, thus indicating that the miR-146a can effectively inhibit inflammatory response related to the helicobacter pylori infection.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
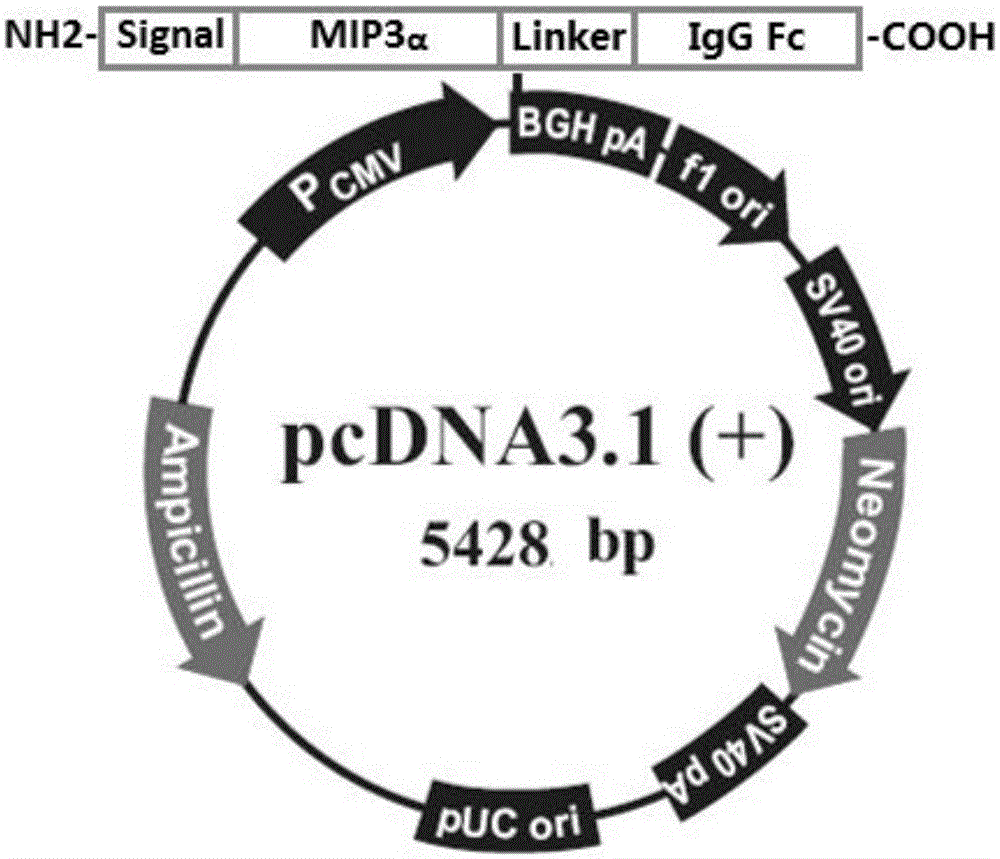
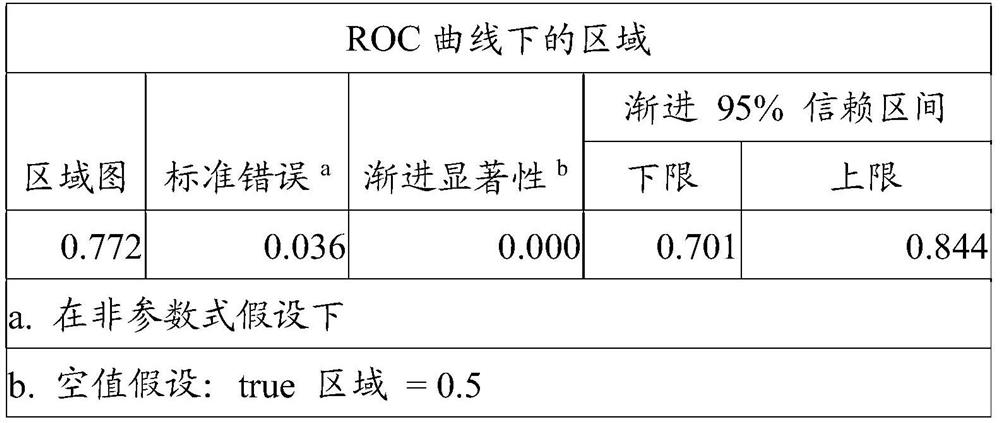
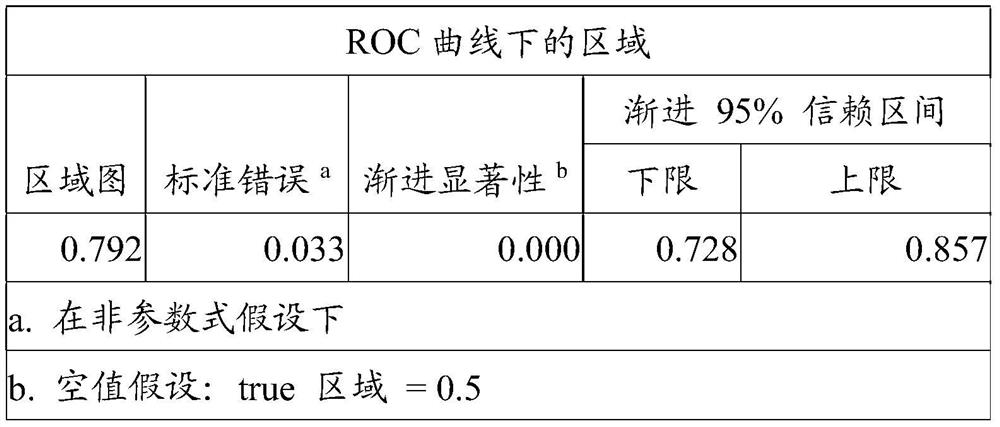
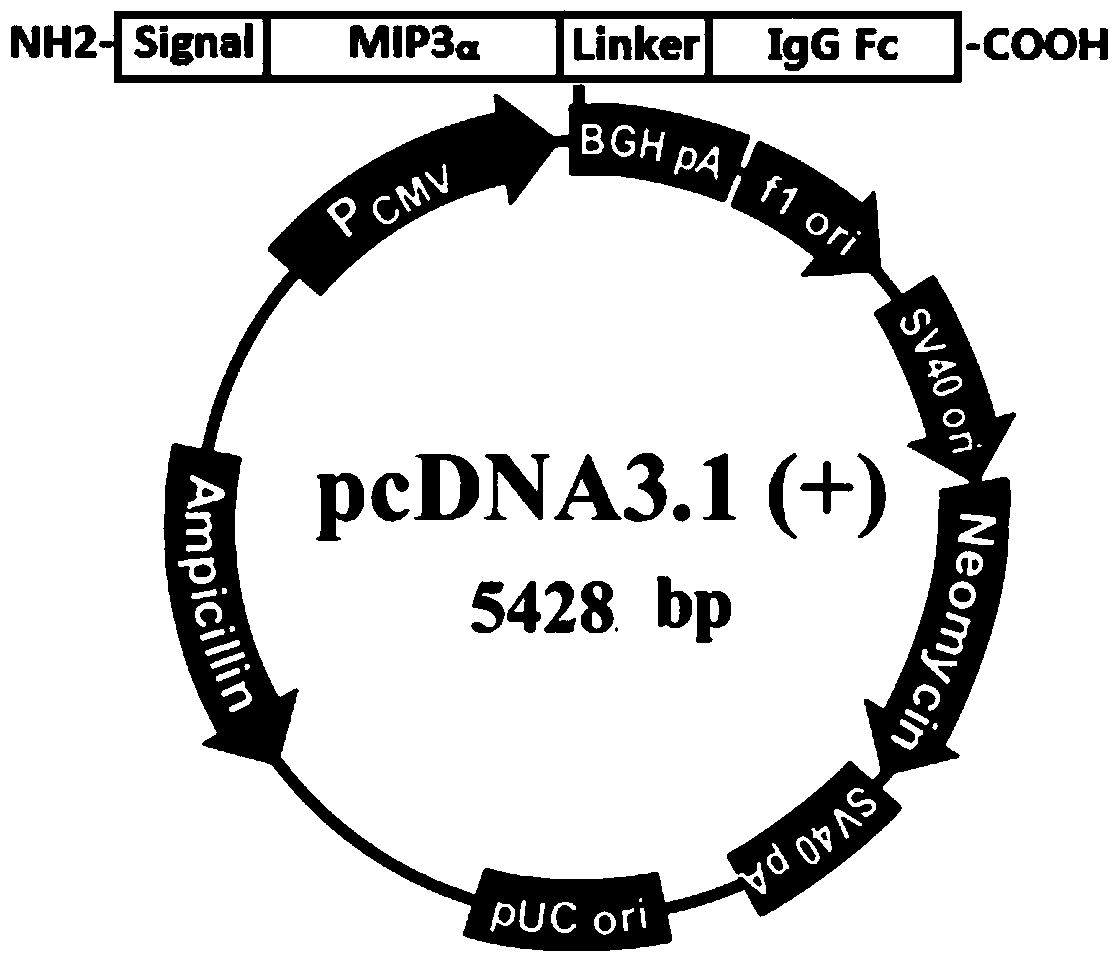
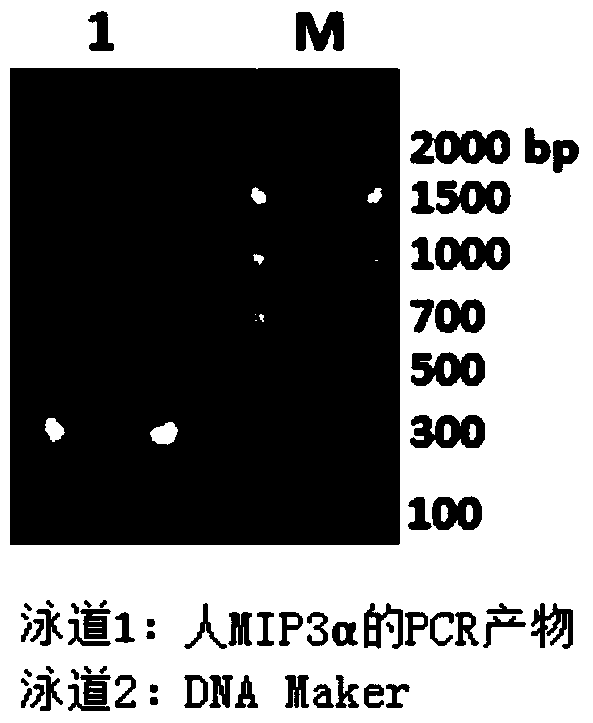
MIP (macrophage inflammatory protein) 3alpha-Fc fusion protein and application thereof
ActiveCN105111315AImprove biological activityGood biological stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsHybrid peptidesDimerIntravenous gammaglobulin
The invention provides MIP (macrophage inflammatory protein) 3alpha-Fc fusion protein. The fusion protein is macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP3alpha) and dimer fusion protein of Fc; and the MIP3alpha is connected with the Fc through a hinge region or a flexible peptide of immunoglobulin. The invention provides the long-acting MIP3alpha-Fc fusion protein. The fusion protein has good bioactivity and stability in vitro and vivo, and has a chemotaxis effect on immature dendritic cells; after the MIP3alpha-Fc fusion protein is injected into a tumor, growth of the tumor can be inhibited, and the MIP3alpha-Fc fusion protein has long plasma half-life.
Owner:HAINAN MEDICAL COLLEGE
Method for inducing in vivo migration of stem cell
The present invention relates to an implantable composition for treating a damaged tissue and a method for inducing an in vivo migration of a cell for treatment to a damaged tissue region. The present invention treats the damaged tissue by inducing / promoting homing of a cell for tissue generation by implanting a biodegradable scaffold reacted with chemotactic factors (for example, IL-8 or MIP-3±) to a damaged location (for example, joint cartilage or skin). Thus, the composition of the present invention can not only be applied to the treatment of a damaged bone tissue, a joint cartilage, or a skin tissue more conveniently and efficiently compared to the conventional technology, but can also be used as a useful treatment supplement agent in cell treatment using allogeneic cell by enabling efficient utilization of cell resources for treatment, the cell resources which are high in scarcity.
Owner:TEGO SCI
Ophthalmic neuromyelitis spectrum disease biomarker group, application thereof, protein chip and kit
ActiveCN111521812AOvercome operabilityOvercoming detectionDisease diagnosisBiological testingHerpesvirus entry mediatorPancreatic hormone
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological medicines and particularly relates to a biological marker group for optic neuromyelitis spectrum diseases, application of the biological marker group, a protein chip and a kit. The invention provides an optic neuromyelitis spectrum disease biomarker group which is characterized by comprising monocyte chemotactic protein-3, LIGHT, macrophage inflammatory protein-1 delta, insulin-like growth factor-2, a glucocorticoid induced tumor necrosis factor receptor, thrombopoietin and a herpes virus entry medium, wherein the LIGHT is a lymphotoxin analogue which can be induced and expressed on a T cell and competes with glycoprotein D of HSV to be combined with HVEM. The application fills the blank that no reliable and accurate product and method for diagnosing and identifying optic neuromyelitis lineage diseases exist clinically at present.
Owner:RAYBIOTECH INC GUANGZHOU
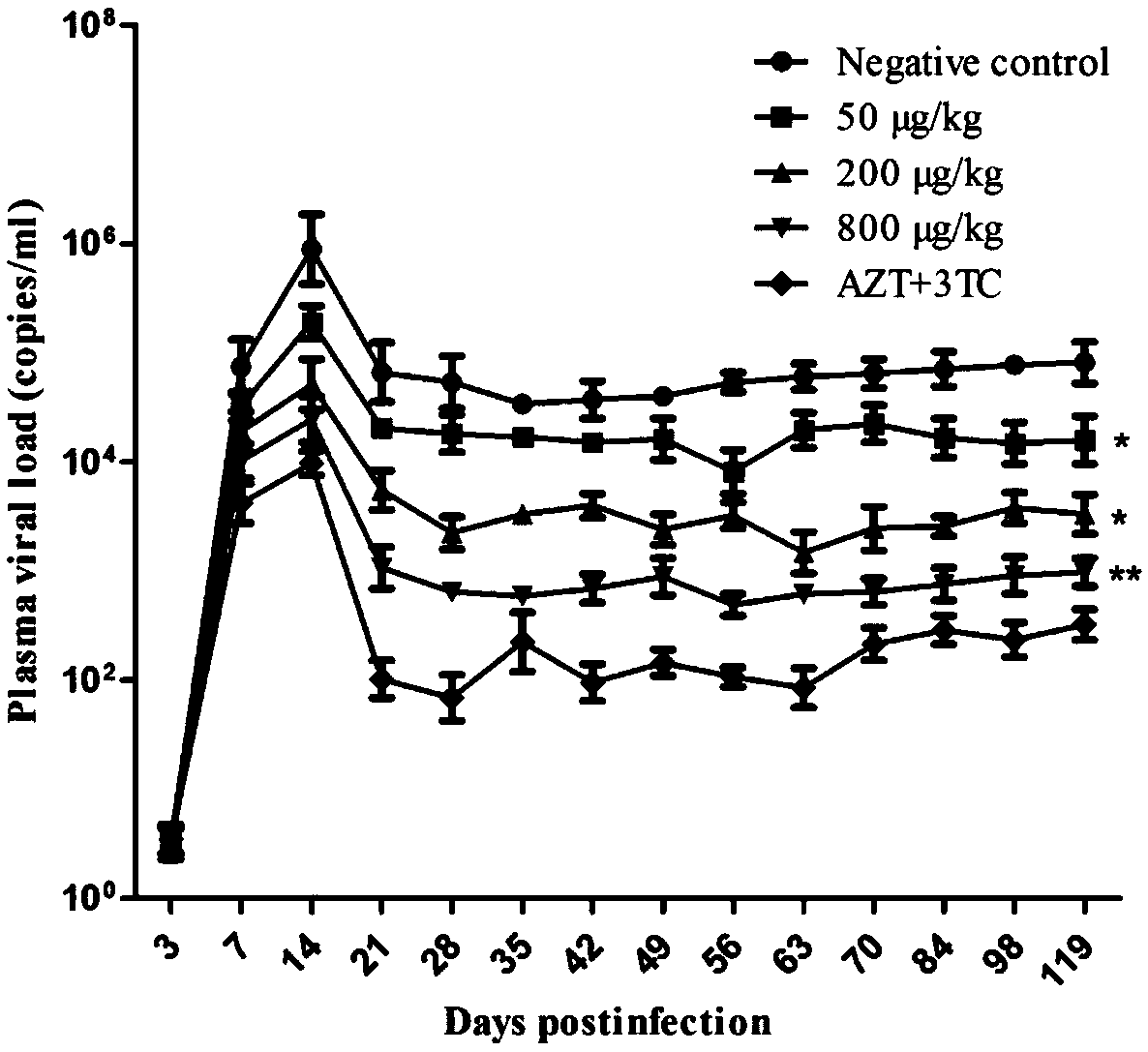
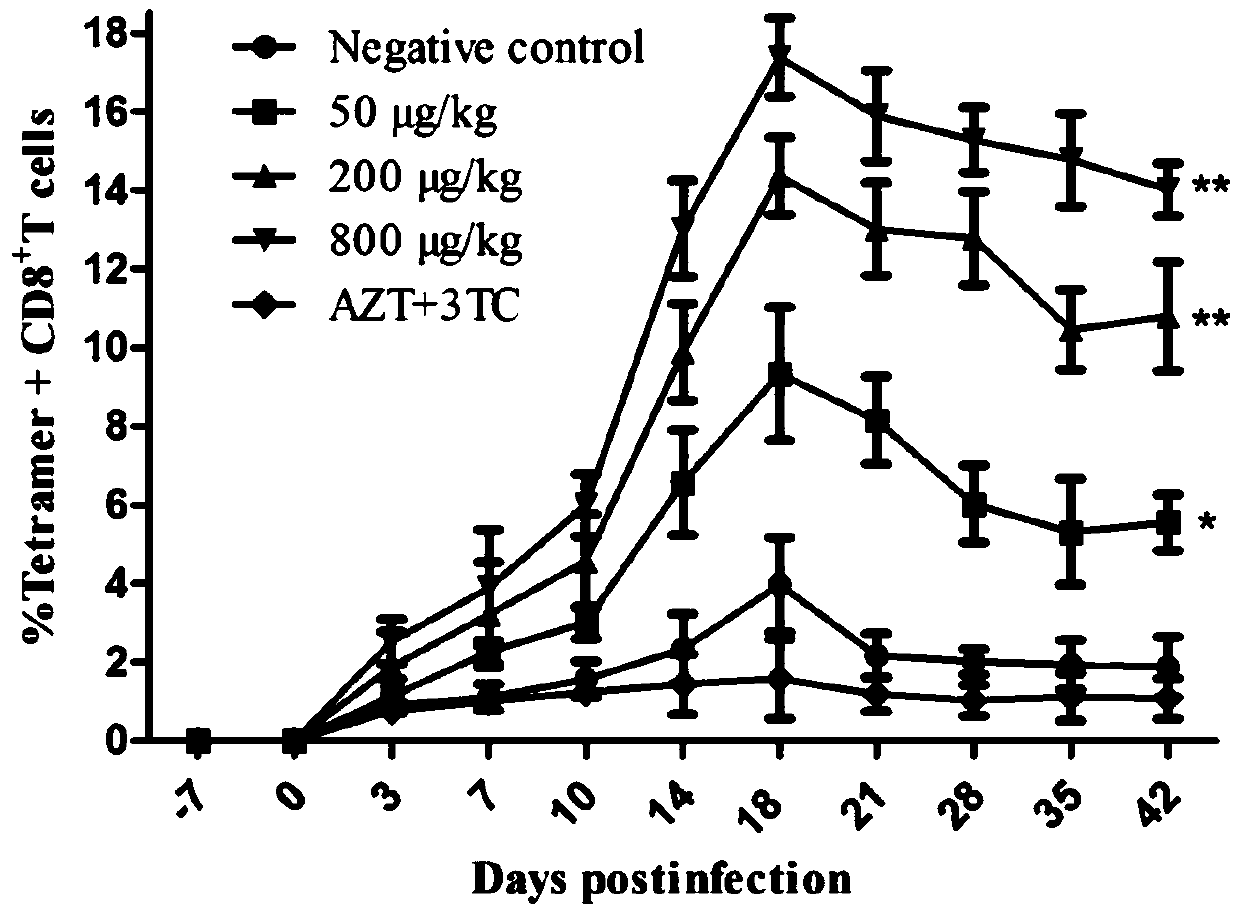
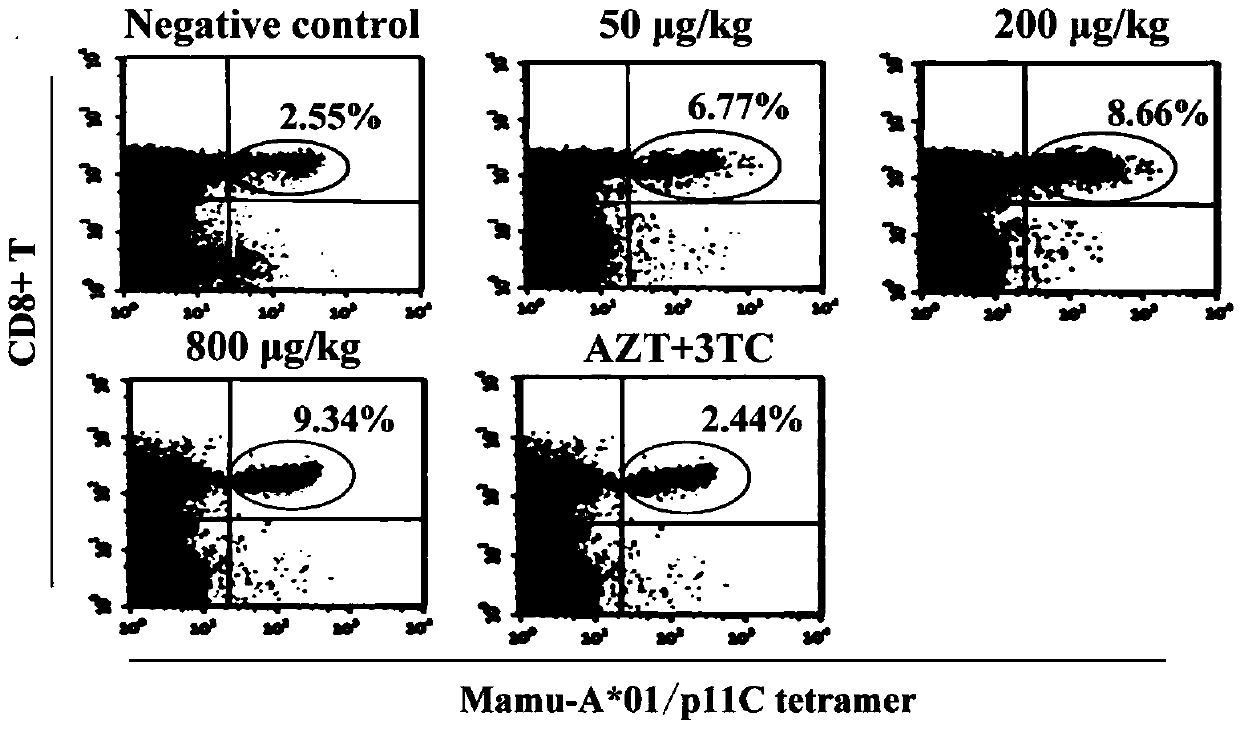
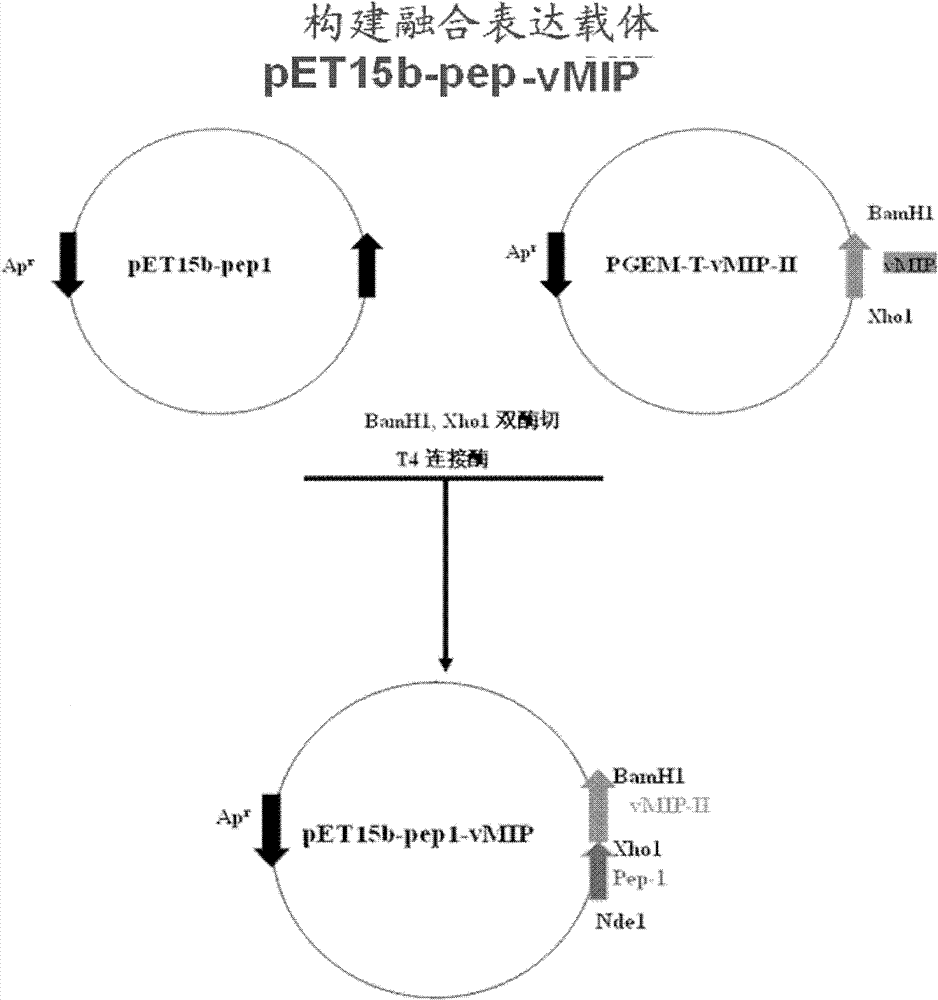
VMIP-II for inducing dephosphorylation of CD8<+> T cells to form Tcm and application of vMIP-II in medicines
The invention discloses application of virus macrophage inflammatory protein vMIP-II for inducing dephosphorylation of CD8<+> T cells to form Tcm. The vMIP-II for inducing dephosphorylation of the CD8<+> T cells to form the Tcm is developed in a laboratory and is verified by the National Institute for Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products. According to the invention, the CD8<+> T cellsare researched through a rhesus SIV infection model. The research finds that: the vMIP-II can enable Tcm to be proliferated depending on the dosage of the vMIP-II, and the differential gene of the proliferative cell is mainly enriched in a chemokine receptor and a phosphorylation pathway. The research further finds that: the proliferation is as follows: the vMIP-II closes a CD8<+> T chemokine receptor, promotes low expression of G protein, reduces the concentration of intracellular Ca<2+> and mitochondrial membrane potential, inhibits phosphorylation related genes, and promotes low expressionof phosphorylated proteins ERK1 / 2 and Akt, so that a CD8<+> T phosphorylation signal is weakened, metabolic reprogramming is carried out, and the CD8<+> T is converted into the Tcm. Therefore, the discovery of the vMIP-II action mechanism provides a brand-new strategy for drug research and development of HIV / SIV infected AIDS, provides a new means for adoptive immunotherapy of virus resistance and tumor resistance, and has important clinical application value.
Owner:广州溯原生物科技股份有限公司
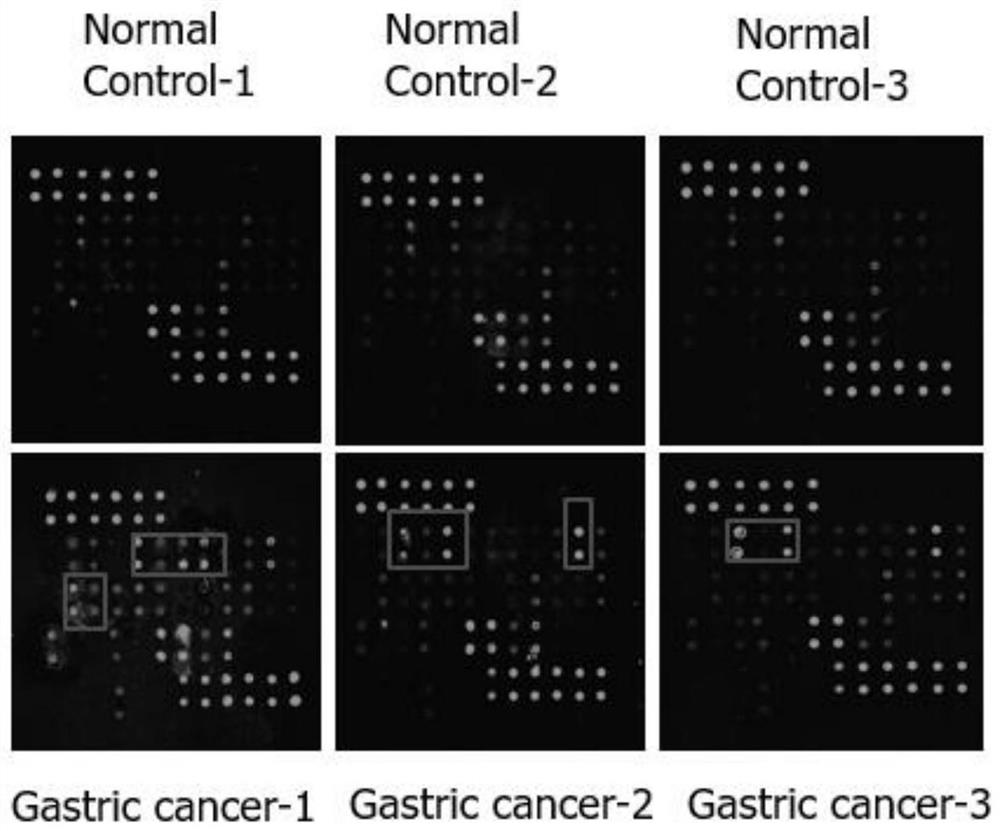
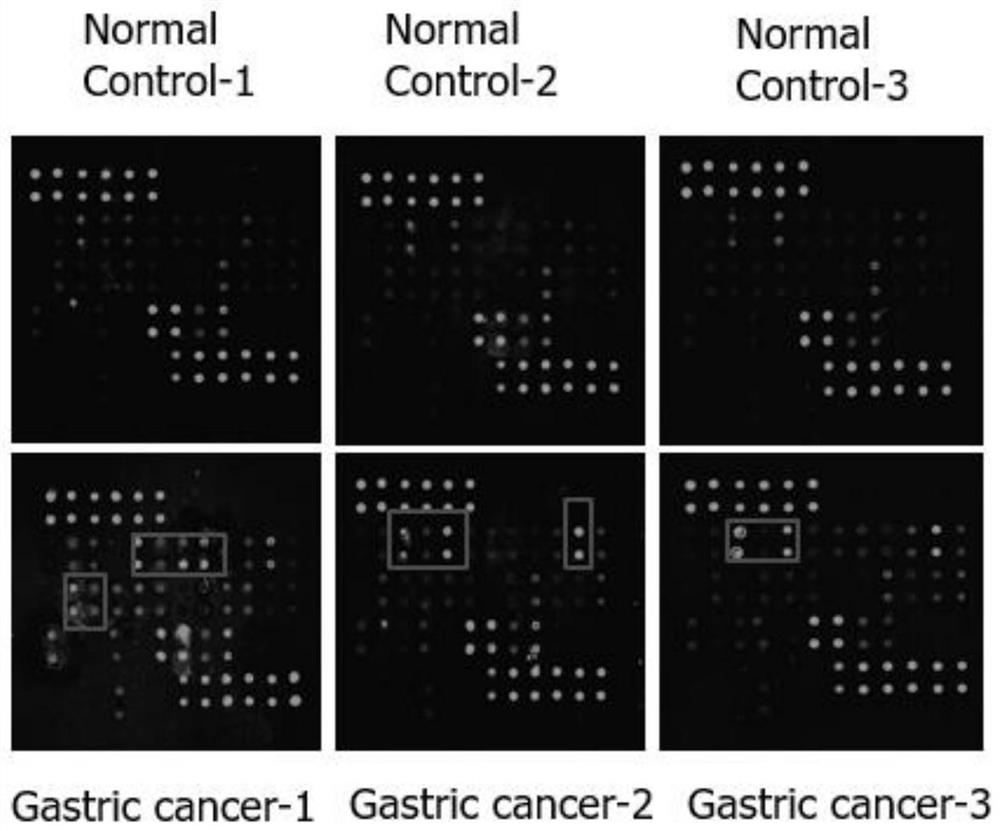
Biomarker composition for detecting gastric cancer autoantibody in gastritis patient and application
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and particularly relates to a biomarker composition for detecting a gastric cancer autoantibody in a gastritis patient and application of the biomarker composition, which can be used for detecting the autoantibody in serum of the gastric cancer patient in the gastritis patient. The invention provides a biomarker combination for detecting a gastric cancer autoantibody in a gastritis patient. The biomarker combination comprises depolymerized metalloproteinase 17, macrophage inflammatory protein-1beta and matrix metalloproteinase-7. The invention provides a biomarker composition for detecting a gastric cancer autoantibody in a gastritis patient. The biomarker composition can effectively overcome the technical defects that an existing marker is not high in specificity, sensitivity and accuracy when used for detecting the gastric cancer autoantibody.
Owner:RAYBIOTECH INC GUANGZHOU
mip3α-fc fusion protein and use thereof
ActiveCN105111315BImprove biological activityGood biological stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsHybrid peptidesDendritic cellHalf-life
The present invention provides a MIP3α-Fc fusion protein, the fusion protein is a dimeric fusion protein of macrophage inflammatory protein MIP3α and Fc, and the hinge region of immunoglobulin or Flexible peptide linkage. The present invention provides a long-acting MIP3α-Fc fusion protein. This new type of fusion protein exhibits good biological activity and stability both in vivo and in vitro, and can chemoattract immature dendritic cells. Intratumoral injection of MIP3α‑Fc fusion protein can effectively inhibit tumor growth and has long-term Plasma half-life.
Owner:HAINAN MEDICAL COLLEGE
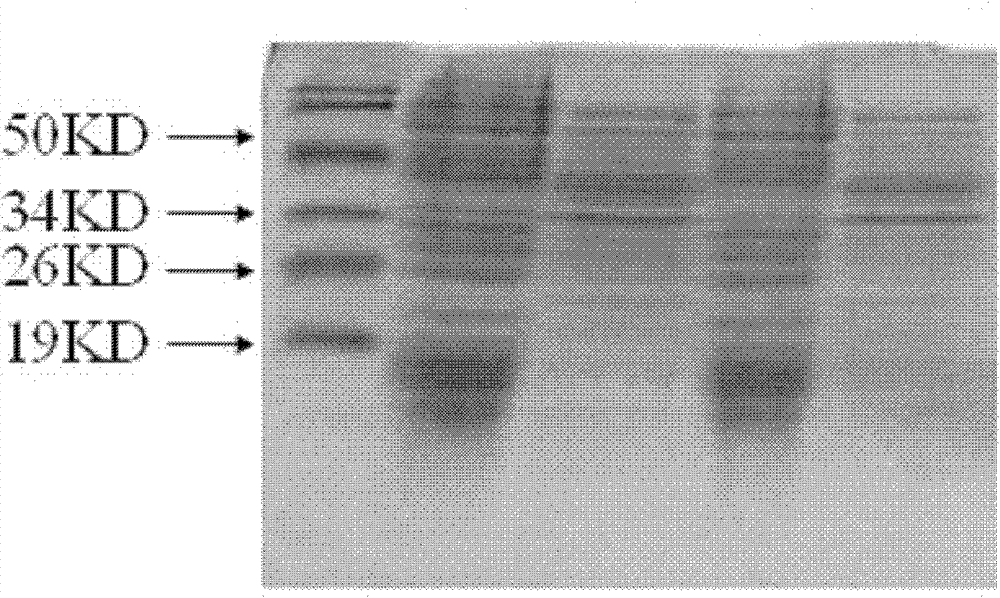
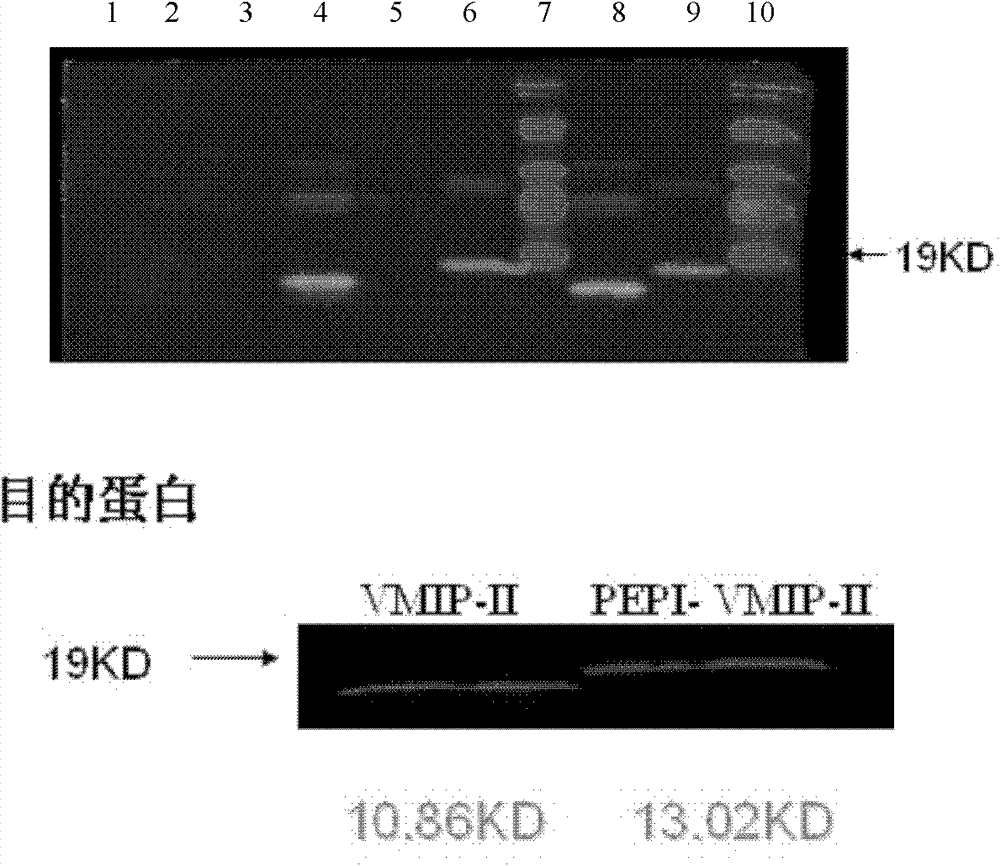
Solid-phase synthesis method of vMIP-II (viral macrophage inflammatory protein-II) protein
InactiveCN102241749AHigh purityHigh synthesis efficiencyVirus peptidesPeptide preparation methodsMedicineNinhydrin
The invention discloses a solid-phase synthesis method of vMIP-II (viral macrophage inflammatory protein-II) protein, comprising the following steps of: adding dimethyldichlorosilane into a reaction flask, ventilating and staying overnight to silanize the reaction flask, coarsely washing with ethanol and cooling at the temperature of minus 80 DEG C, washing and drying again, weighing resin and placing the resin into the reaction flask, adding three times volume of the resin of DCM (dichloromethane) solution, swelling for 30min and evacuating liquid, and then carrying out amino acid coupling, ninhydrin reaction detection and alpha-amino group deprotection circularly from a terminal C to a terminal N on a polypeptide synthesizer until all the amino acid residues are coupled; after the coupling is completed, taking down the reaction flask and cleaning with the DCM, draining the resin and then cutting with precooled cutting fluid, and purifying the cut polypeptide by adopting HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography), wherein the polypeptide is purified on a Waters600E high pressure liquid phase chromatograph; and carrying out high pressure reversed phase chromatography by adopting a Kromasil100-5C18 pillar, and collecting target peak polypeptide, namely the vMIP-II protein.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
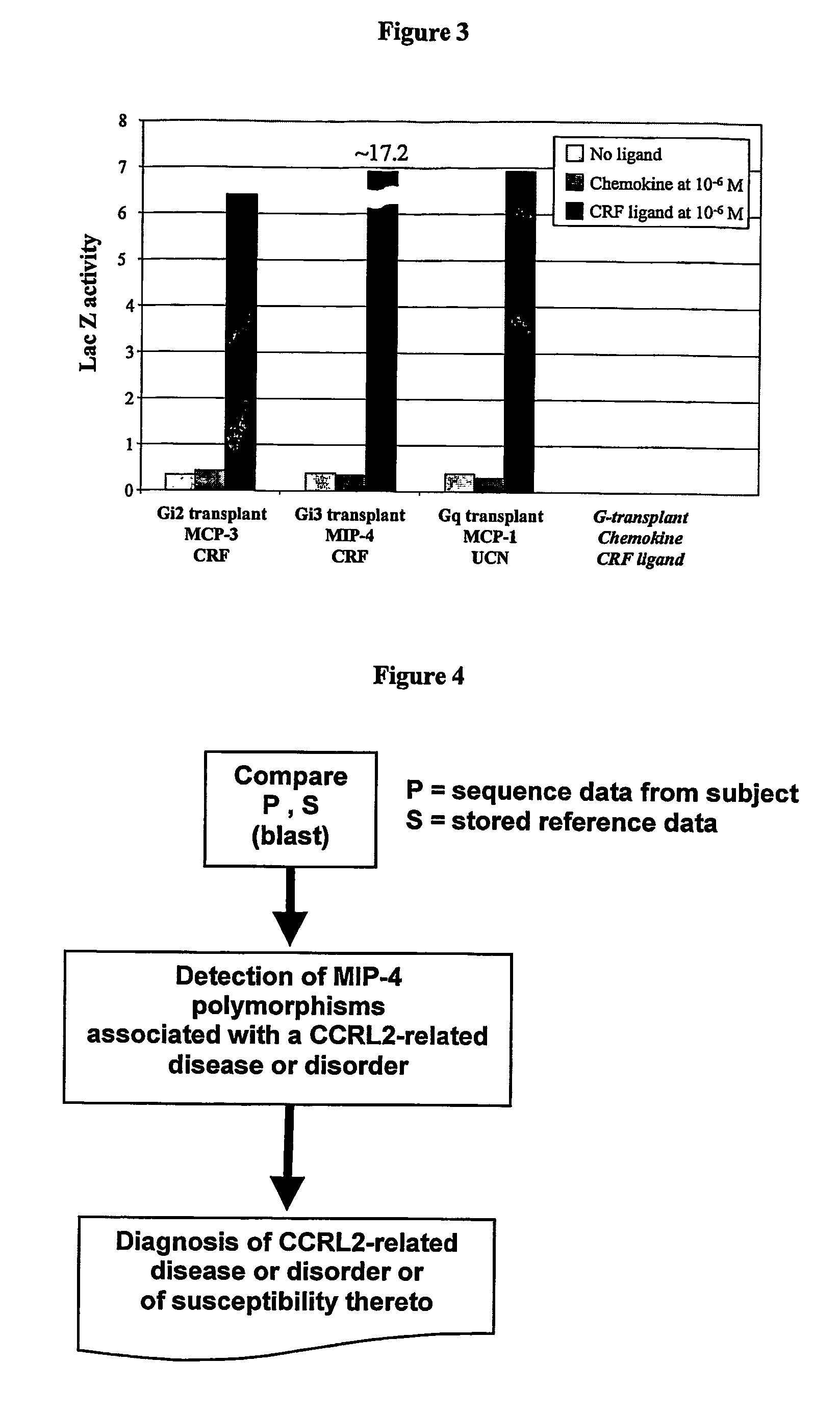
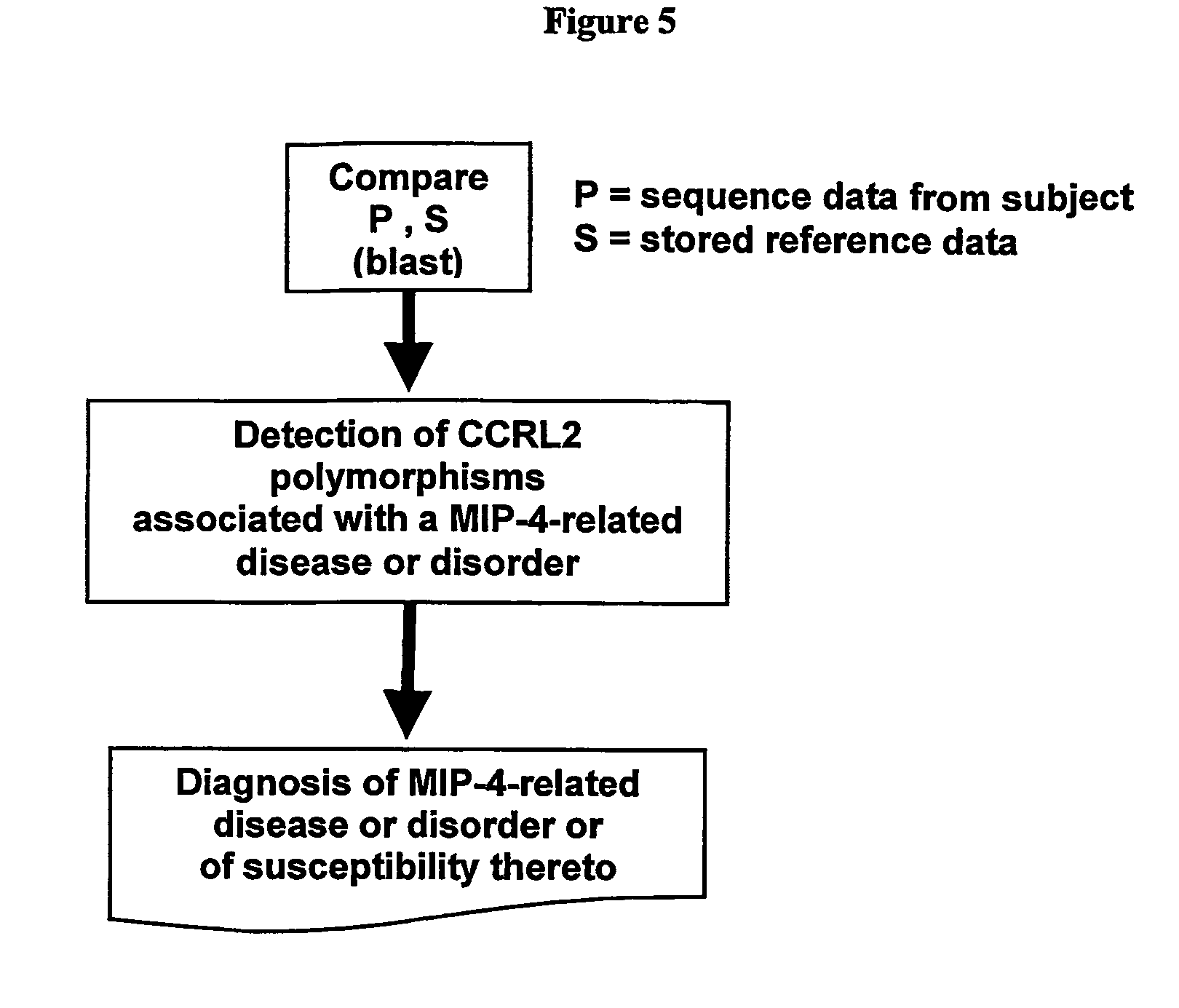
Method for detection of MIP-4 and CCRL2 binding and activity modulating agents
A method of detecting an agent that modulates the activity of CCRL2, the method comprising: (a) contacting a CCRL2 polypeptide with a macrophage inflammatory protein-4 (MIP-4) polypeptide in the presence of a candidate agent under conditions, which in the absence of the test agent, permit the binding of the MIP-4 polypeptide to the CCRL2 polypeptide; and (b) determining whether the candidate agent is capable of modulating the interaction between said CCRL2 polypeptide and said MIP-4 polypeptide.
Owner:OXAGEN
Biomarker composition for detecting gastric cancer autoantibody and application of biomarker composition
ActiveCN112630433AEasy to identifyHigh sensitivityBiological material analysisBiological testingAutoantibodyGastric carcinoma
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and relates to a biomarker composition for detecting a gastric cancer autoantibody and application of the biomarker composition. The biomarker composition can be used for detecting the autoantibody in serum of a patient with gastric cancer. The biomarker combination for detecting the gastric cancer autoantibody comprises macrophage inflammatory protein -3alpha, macrophage inflammatory protein -1beta, a monocyte chemotactic factor -1 and matrix metalloproteinase -9. With the biomarker composition for detecting the gastric cancer autoantibody, the technical defects of low specificity, sensitivity and accuracy of an existing marker for detecting the gastric cancer autoantibody can be eliminated.
Owner:RAYBIOTECH INC GUANGZHOU
Biomarker group, application thereof, protein chip, protein chip kit and ELISA kit
ActiveCN110850096AOvercome operabilityOvercoming detectionDisease diagnosisBiological testingElisa kitWhite blood cell
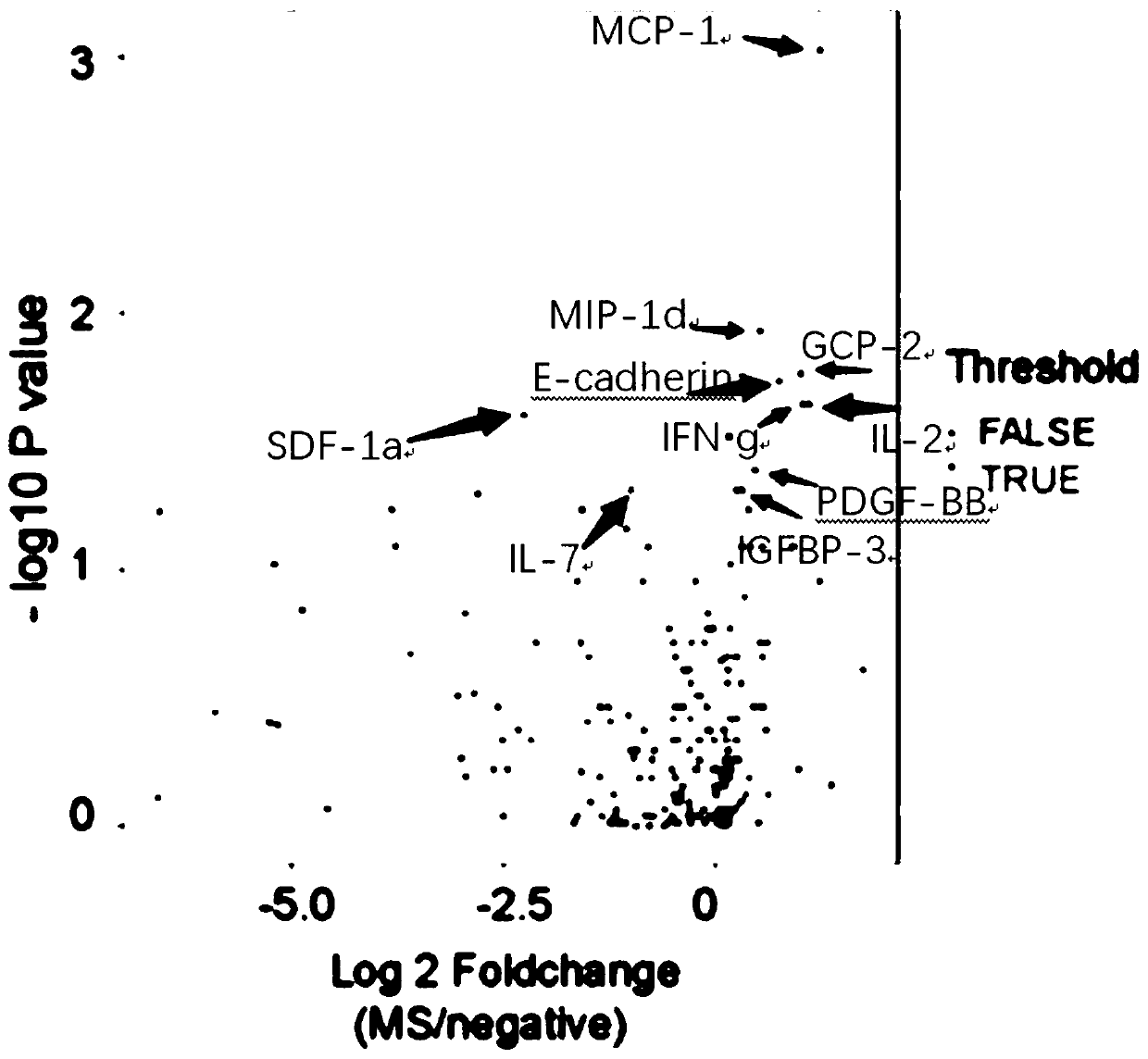
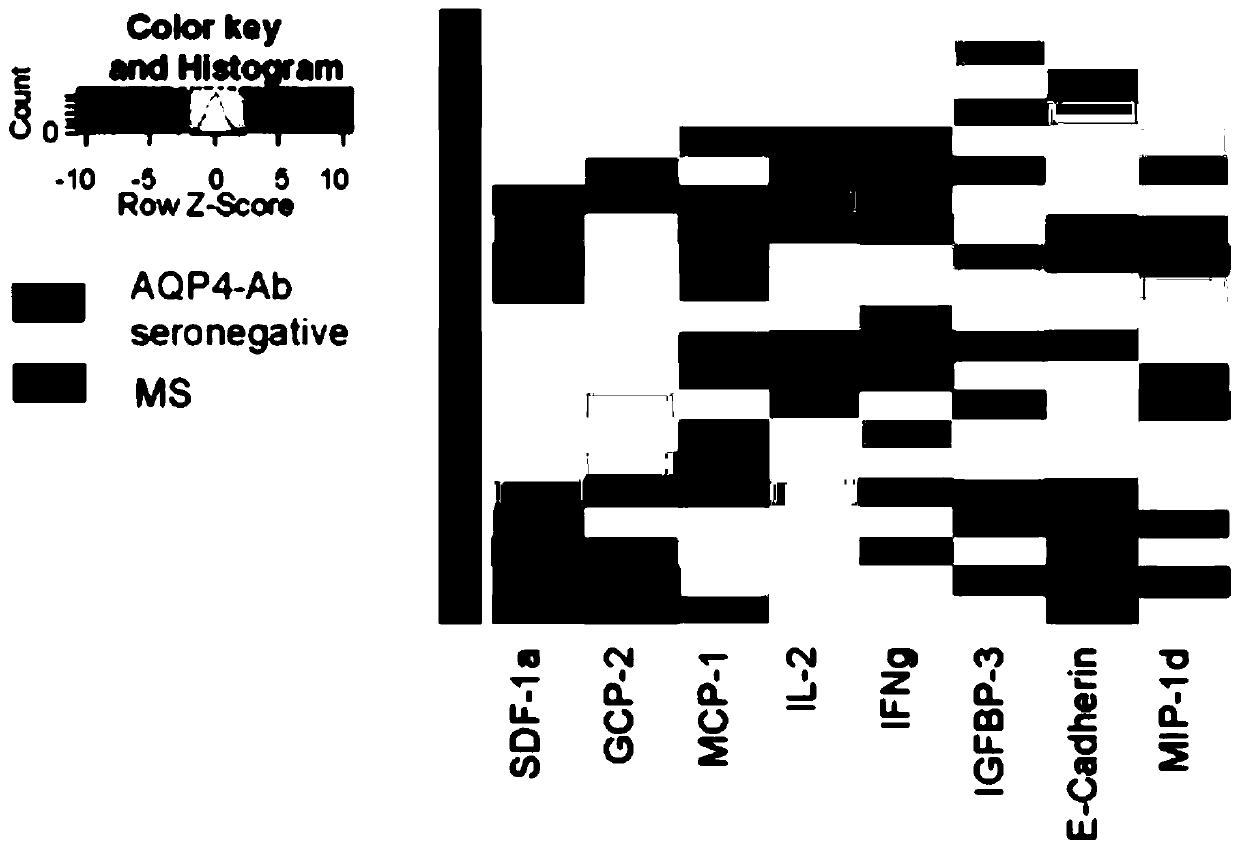
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological medicines, and particularly relates to a biomarker group, application thereof, a protein chip, a protein chip kit and an ELISA kit. The provided biomarker group is applied to preparation of a product for diagnosing demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system, and comprises a stromal cell derivative factor-1, granulocyte chemotactic protein 2, mononuclear cell chemotactic protein-1, interleukin-2, gamma-interferon, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, E-cadherin and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 delta; and the demyelinating diseases include an aquaporin 4 antibody negative neuromyelitis spectrum disease and an aquaporin 4 antibody negative multiple sclerosis. The blank there is no reliable product and method for diagnosing and identifying multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis spectrum diseases under negative aquaporin 4 antibody clinically at present is filled.
Owner:RAYBIOTECH INC GUANGZHOU
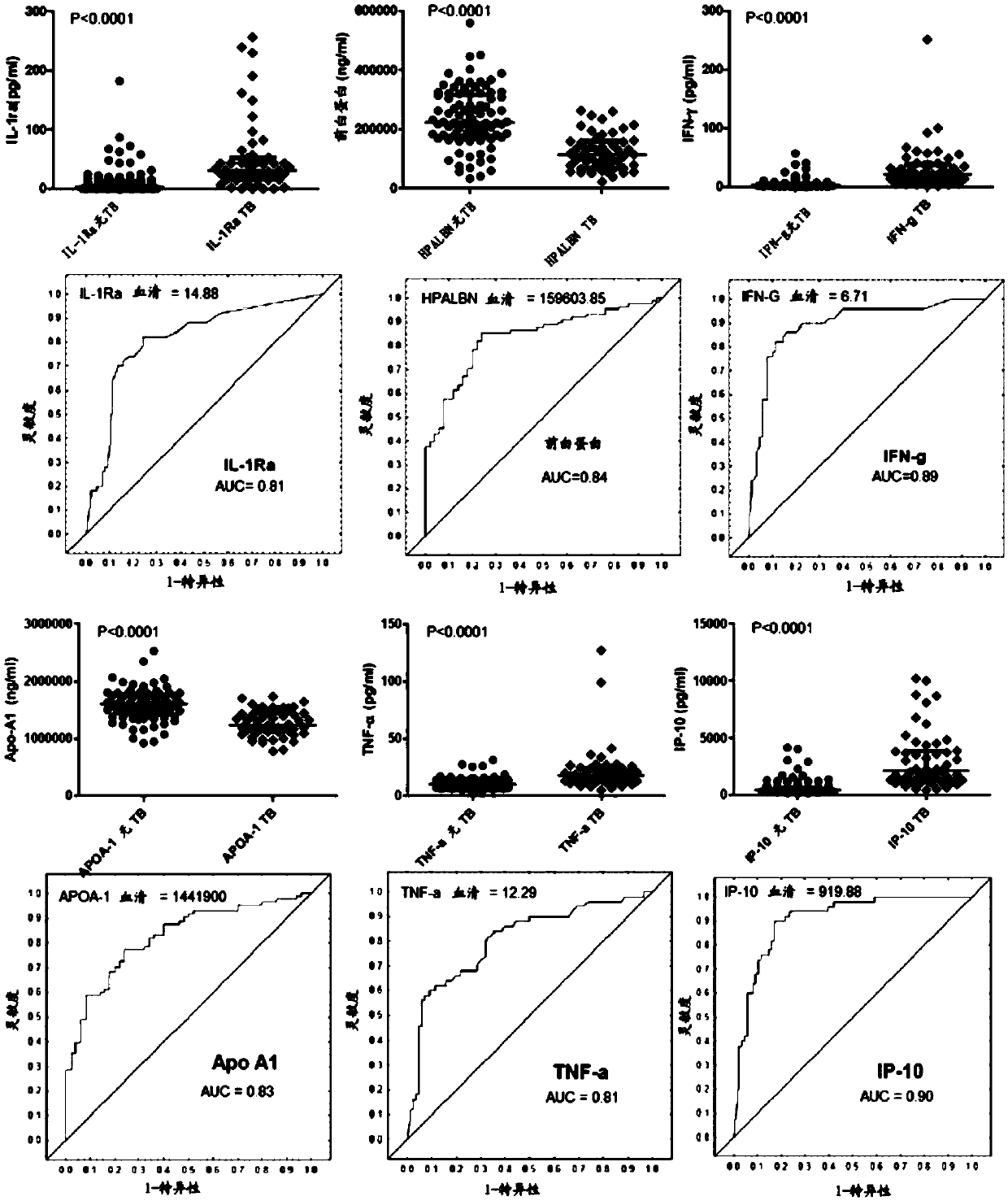
Methods used to diagnose tuberculosis
ActiveCN106461675BMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisApolipoproteins EBiomarker (petroleum)
Owner:STELLENBOSCH UNIVERSITY
Series connection expression method from virus macrophage inflammatory protein IIN end 15 peptide
The genetic engineering tandem expression process of pentadecapeptide originated from virus macropage inflammatory protein II N terminal includes: synthesizing one gene segment including several pentadecapeptides connected through protein cleavage sequence gene by using virus macropage inflammatory protein II N terminal pentadecapeptided as target and in a eukaryotic expression system; adding limiting cleavage sites to the 5' and 3' terminals of the gene segment; connecting the gene segment to plasmid vector by means of gene recombination, converting saccaromycete to screen, express and purify target protein; cleaving the purified protein with protease, and separating and purifying to obtain target polypeptide. The polypeptide can antagonize CXCR4 pentadecapeptide, and has the function of preventing and treating AIDS and wide medicine application foreground.
Owner:广州法蕊仕药业科技有限公司
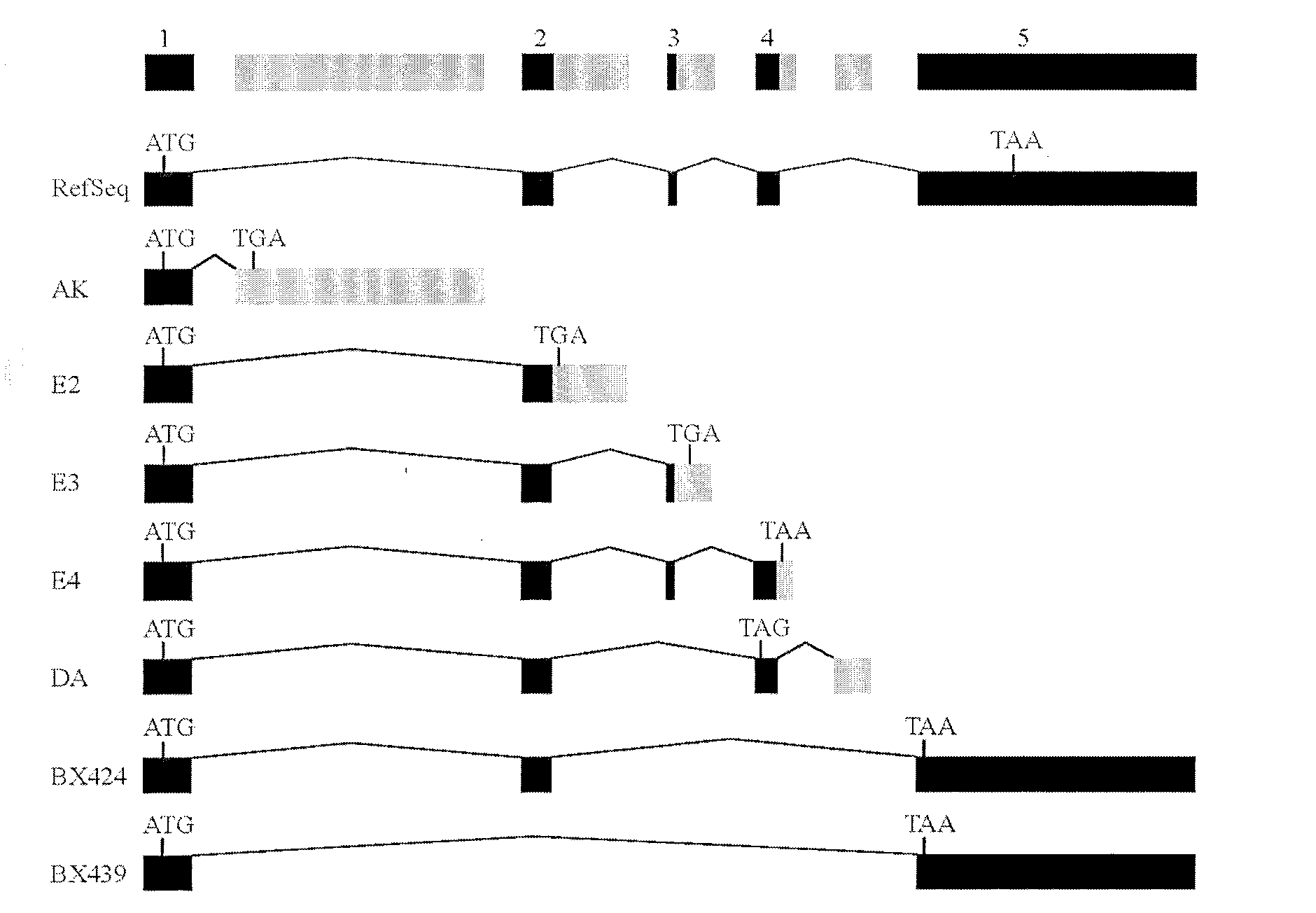
Applications of TRAIL truncated mutant in activating NF-kappaB and in inflammatory responses
InactiveCN102908612AAffect the inflammatory responsePeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticApoptosisADAMTS Proteins
The invention belongs to the field of tumor necrosis factor-(TNF-)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). Especially, the invention relates to 7 truncated mutants (AK, E2, E3, E4, DA, BX424 and BX439) of TRAIL. A protein sequence coded by DA is completely same with that of TRAILbeta, and a protein sequence coded by BX424 is completely same with that of TRAILdelta. As a result of experiments, among the truncated mutants, except BX439, the mutants have different degrees of capabilities for activating NF-kappaB. As a result of further studies, over-expressions of DA, BX424 and E4 assist in substantially activating macrophage inflammatory protein-1beta(MIP-1beta / CCL4), macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha(MIP-3alpha / CCL20), and interleukin8(IL8 / CXCL8) promoter reporter gene. The TRAIL mutant provided by the invention has wide application prospect in treating inflammatory responses.
Owner:SINOGENOMAX
Nucleic acid molecule macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP) 3 alpha antibody to nuclear antigen (ANA) 6 and application thereof to preparation of immunosuppressive medicaments
The invention belongs to the field of antisense nucleic acid medicaments, and relates to a macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP) 3 alpha antibody to nuclear antigen (ANA) 6 and preparation thereof to the preparation of immunosuppressive medicaments. The immune response of an organism plays a key role in autoimmune diseases and the exclusive reaction of the transplantation of organs and tissues. The invention provides the antisense nucleic acid molecule MIP3 alpha ANA6 used for preparing the immunosuppressive medicaments. The MIP3 alpha ANA6 is a double-stranded nucleic acid molecule. The sense strand of a DNA sequence of the MIP3 alpha ANA6 is 5'-ATATATTGTGCGTCTCCTC-3', and an antisense strand is 5'-GAGGAGACGCACAATATAT-3'. Under the condition of culture with the addition of inflammatory cytokines, the MIP3 alpha ANA6 can remarkably reduce many kinds of cell expressing MIP3 alpha mRNA and generating MIP3 alpha proteins, and functions in immunosuppression by suppressing antigen presenting cells and T cells. The invention provides the novel antisense nucleic acid medicament for treating MIP3 alpha-related immune diseases.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Solid-phase synthesis method of vMIP-II (viral macrophage inflammatory protein-II) protein
InactiveCN102241749BHigh purityHigh synthesis efficiencyVirus peptidesPeptide preparation methodsMacrophage inflammatory proteinSolid-phase synthesis
The invention discloses a solid-phase synthesis method of vMIP-II protein. The steps are as follows: add dimethyldichlorosilane to the reaction bottle and ventilate overnight to silanize the reaction bottle, roughly wash with ethanol, place it at -80°C for cooling, and wash again Dry it, weigh the resin and place it in a reaction bottle, add DCM (dichloromethane) solution 3 times the volume of the resin, drain the liquid after swelling for 30 minutes, and then detect it on the polypeptide synthesizer according to the reaction of coupling amino acid and ninhydrin The cycle of deprotection with the α-amino group proceeds from the C-terminus to the N-terminus until all amino acid residues are coupled. After the coupling is completed, remove the reaction bottle and wash it with DCM, drain the resin and cut it with pre-cooled cutting solution, and purify the cut polypeptide by HPLC. The polypeptide was purified on a Waters600E high-pressure liquid chromatograph, and a Kromasil100-5C18 column was used for high-pressure reversed-phase chromatography, and the target peak polypeptide collected was the vMIP-II protein.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
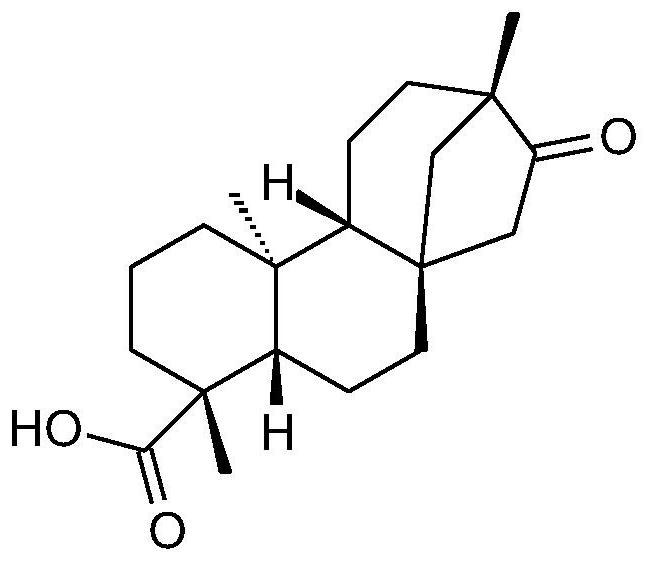
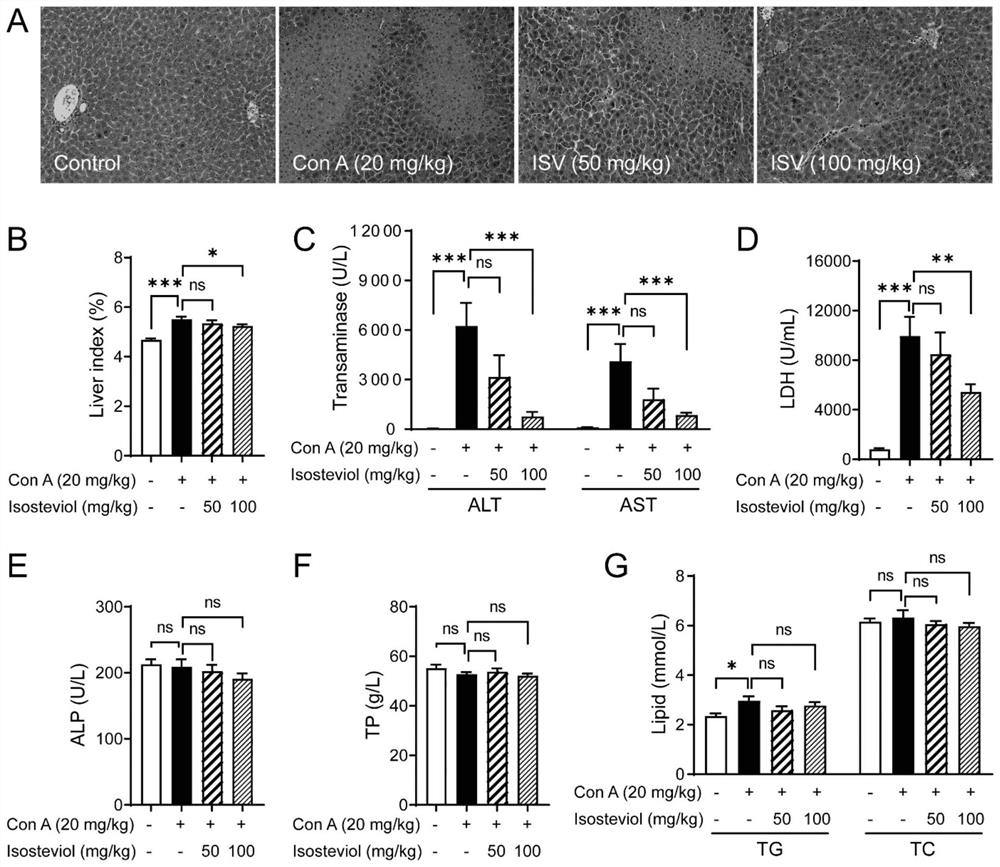
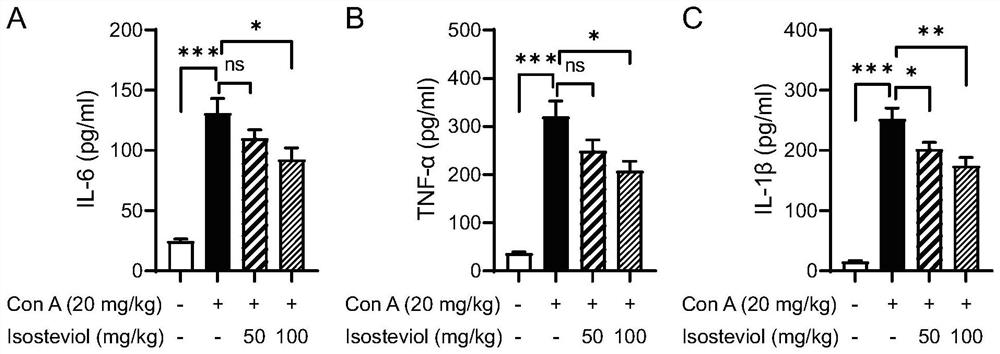
Application of isosteviol in preparation of medicine for treating autoimmune hepatitis
ActiveCN114557989AAvoid damagePrevent infiltrationDigestive systemImmunological disordersInterleukin 6Inflammatory factors
The invention discloses an application of isosteviol in preparation of a medicine for treating autoimmune hepatitis. Compared with the prior art, the invention discovers that the isosteviol can be used for improving the immune liver injury of mice induced by concanavalin A (concanavalin A). The isosteviol can relieve mouse liver cell swelling and necrosis induced by concanavalin A. The isosteviol is used for inhibiting the rise of serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase, glutamic oxalacetic transaminase and lactic dehydrogenase levels; the levels of serum inflammatory factor interleukin 6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin 1 beta (IL-1beta) are reduced. The expression of IL-6, TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, macrophage inflammatory protein 1alpha, intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and C-X-C motif chemotactic factor 10 in the liver tissue of the mouse is reduced. The effects show that the isosteviol can be used for treating the autoimmune hepatitis and has the prospect of developing medicines.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A biomarker combination and application for detecting gastric cancer autoantibodies in patients with gastritis
The present application belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and particularly relates to a biomarker combination and application for detecting gastric cancer autoantibodies in gastritis patients. The present application can detect autoantibodies in gastric cancer patient serum in gastritis patients. The present application provides a biomarker combination for detecting gastric cancer autoantibodies in patients with gastritis, including disintegrin-metalloproteinase-17, macrophage inflammatory protein-1β and matrix metalloproteinase-7. The present application provides a biomarker combination for detecting gastric cancer autoantibodies in gastritis patients, which can effectively solve the technical defects of low specificity, sensitivity and accuracy of existing markers for detecting gastric cancer autoantibodies.
Owner:RAYBIOTECH INC GUANGZHOU
Preparation method of alginate microparticles capable of inducing tumor immune response
InactiveCN102120029AEfficient inductionInduce strongPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEscherichia coliMicroparticle
The invention provides a preparation method of alginate microparticles capable of inducing a tumor immune response, which comprises the steps of: establishing an MIP-3alpha (Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-3alpha) eukaryon expression plasmid and transforming tumor cells by using a gene engineering technology, and sieving to obtain the tumor cells stably expressing the MIP-3alpha; meanwhile, culturing escherichia coli and dissolving the escherichia coli in an alginate solution, disinfecting by means of high temperature and high pressure, uniformly mixing the MIP-3alpha tumor cells in the escherichia coli-alginate solution, atomizing the MIP-3alpha tumor cell-escherichia coli-alginate solution by using an atomizer, spraying atomized particles into a calcium chloride solution, and filtering by using a gauze element to obtain injectable MIP-3alpha tumor cell-escherichia coli-alginate microparticles, which can express secretion MIP-3alpha protein in an in-vitro culture environment. After being injected into a mouse mantle cavity, the microparticles are demonstrated to be effective in inhibiting tumor growth and transfer in a tumor model and have obvious effects on treating tumors.
Owner:HAINAN MEDICAL COLLEGE
Enzyme-linked immunoassay panels and kits for predicting ali/ards and estimating their prognosis
The invention provides an ELISA (Enzyme-linked Immunoassay Assay) plate and kit for predicting ALI (Acute Lung Injury) / ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) and assessing prognosis of the ALI / ARDS. The ELISA plate comprises a solid phase carrier which is provided with a monoclonal antibody of bone morphogenetic protein 15, a monoclonal antibody of CXC chemokine ligand 16, a monoclonal antibody of CXC chemokine receptor 3, a monoclonal antibody of interleukin-6, a monoclonal antibody of nephroblastoma overexpression genes, a monoclonal antibody of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 4, a monoclonal antibody of interleukin-5, a monoclonal antibody of interleukin 5 receptor, a monoclonal antibody of interleukin 22 receptor binding protein, a monoclonal antibody of leptin, a monoclonal antibody of macrophage inflammatory protein-1D, a monoclonal antibody of orexin B, a monoclonal antibody of CC type chemokine receptor 2, a monoclonal antibody of transforming growth factor-beta5 and blank control holes. The ELISA plate and kit can achieve accurate results and are simple to operate.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Antiviral fusion protein and application thereof
ActiveCN102311500BAvoid infectionNot immunogenicPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemHepatitis B virusAnti viral immunity
The invention provides an antiviral fusion protein and application thereof. The fusion protein mainly comprises a cell penetrating peptide (CPP) structural domain and viral macrophage inflammatory protein (vMIP), wherein the cell penetrating peptide structural domain and the viral macrophage inflammatory protein form a serial structure. The fusion protein can enter cells in a non-receptor and non-energy-dependence mode, so that the antiviral immune gene expression level in the cells is effectively improved, finally, infection of viruses such as HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus), HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) and the like is suppressed, and a brand-new idea and a method are provided for prevention and treatment of acquired immune deficiency syndrome.
Owner:南通九思医疗器械有限公司
A biomarker combination for detecting gastric cancer autoantibodies and its application
Owner:RAYBIOTECH INC GUANGZHOU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com