Biopolymer structures and components including column and rail system
a biopolymer and column technology, applied in the field of biopolymer structures and components, can solve the problems of low cost fillers, degrading some of the qualities of plastics, and difficult processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
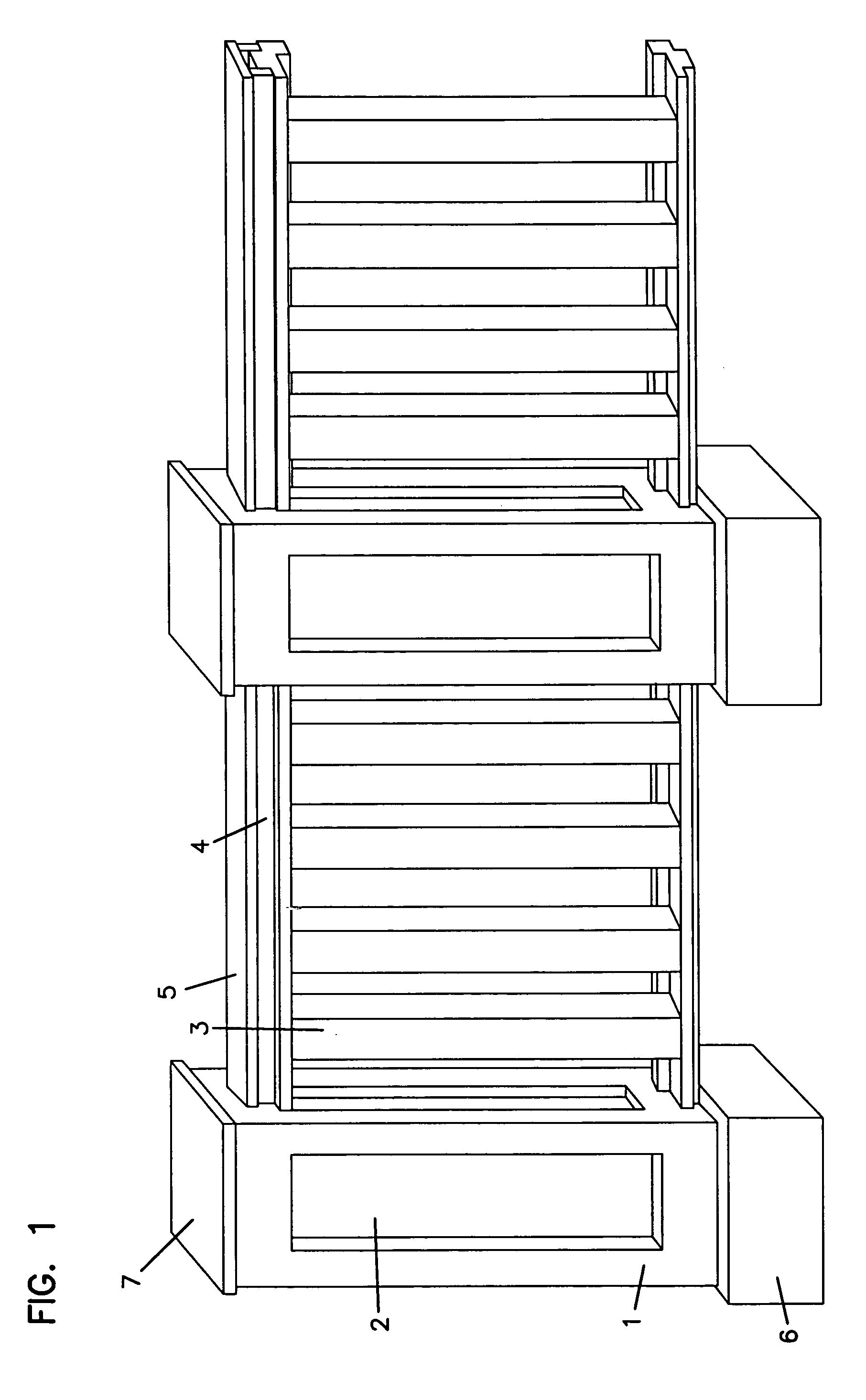
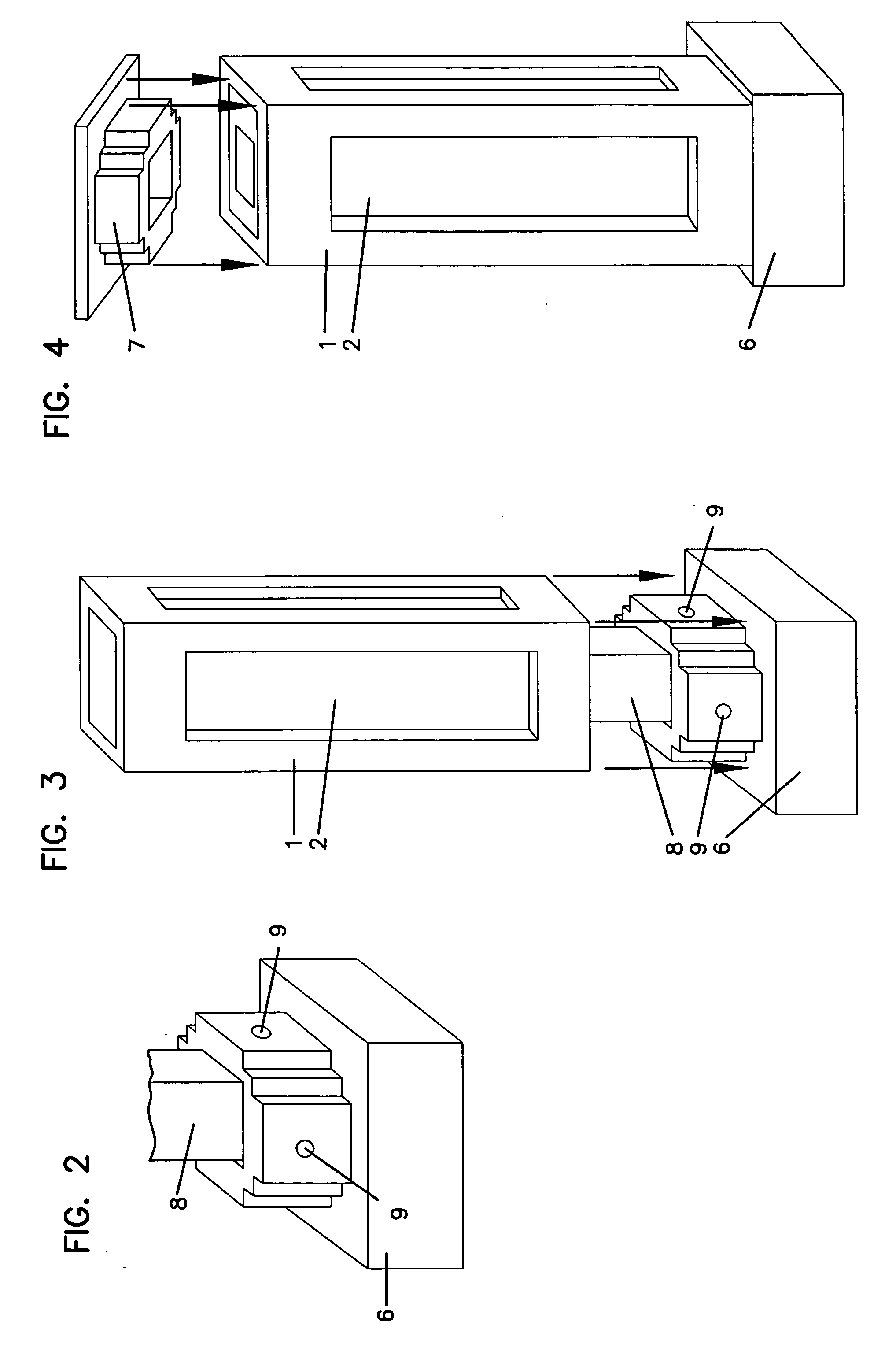
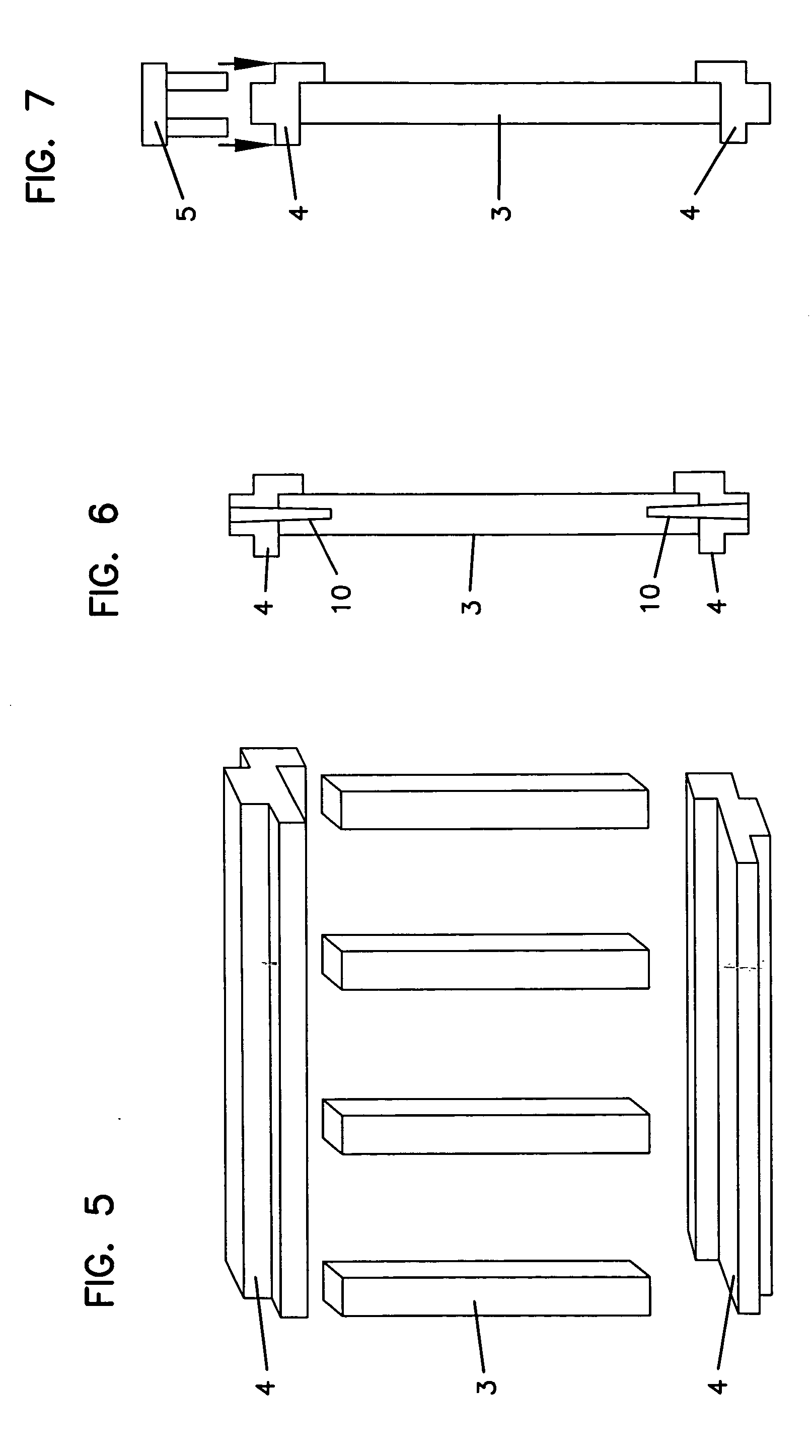
[0024] Overview
[0025] The present invention relates to articles fabricated from or including biopolymers including fermentation solid and thermoactive material. The present biopolymer can exhibit properties typical of plastic materials, properties advantageous compared to conventional plastic materials, and / or properties advantageous compared to aggregates including plastic and, for example, wood or cellulosic materials. The present biopolymer can be formed into useful articles using any of a variety of conventional methods for forming items from plastic.
[0026] The present biopolymer can take any of a variety of forms. U.S. patent application Ser. No. ______ entitled “BIOPOLYMER AND METHODS OF MAKING IT” and filed evendate herewith describes the present biopolymer and related methods. This application is incorporated herein by reference.
[0027] Definitions
[0028] As used herein, the term “biopolymer” refers to a material including a thermoactive material and a fermentation solid. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com