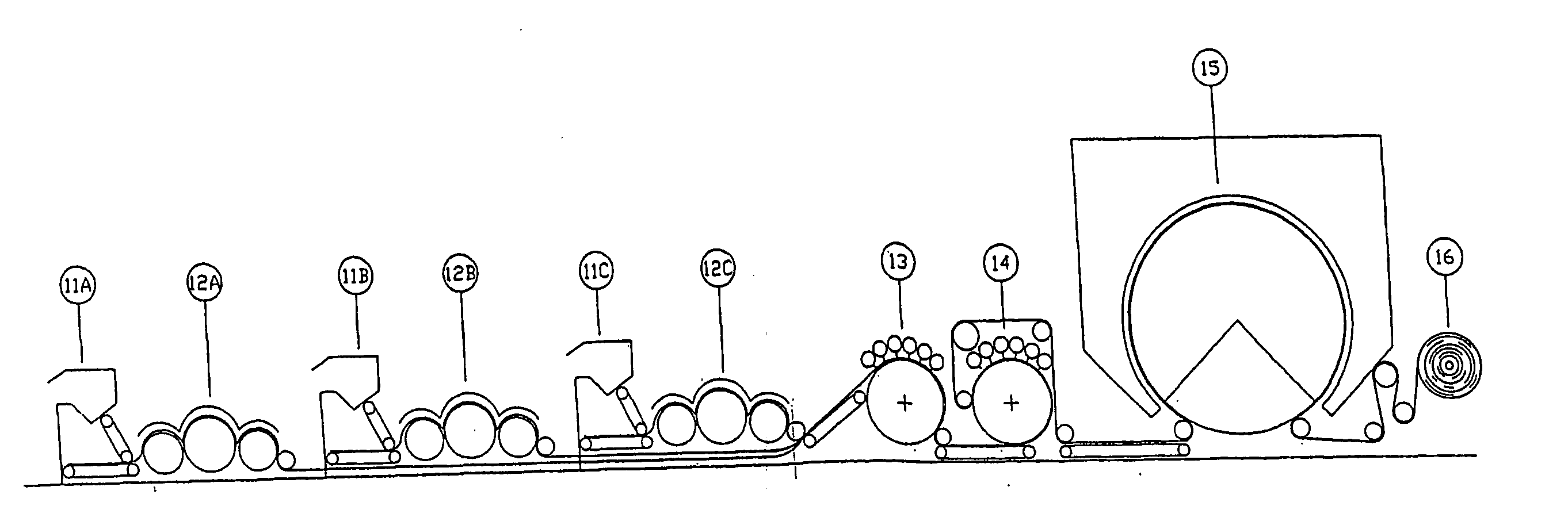
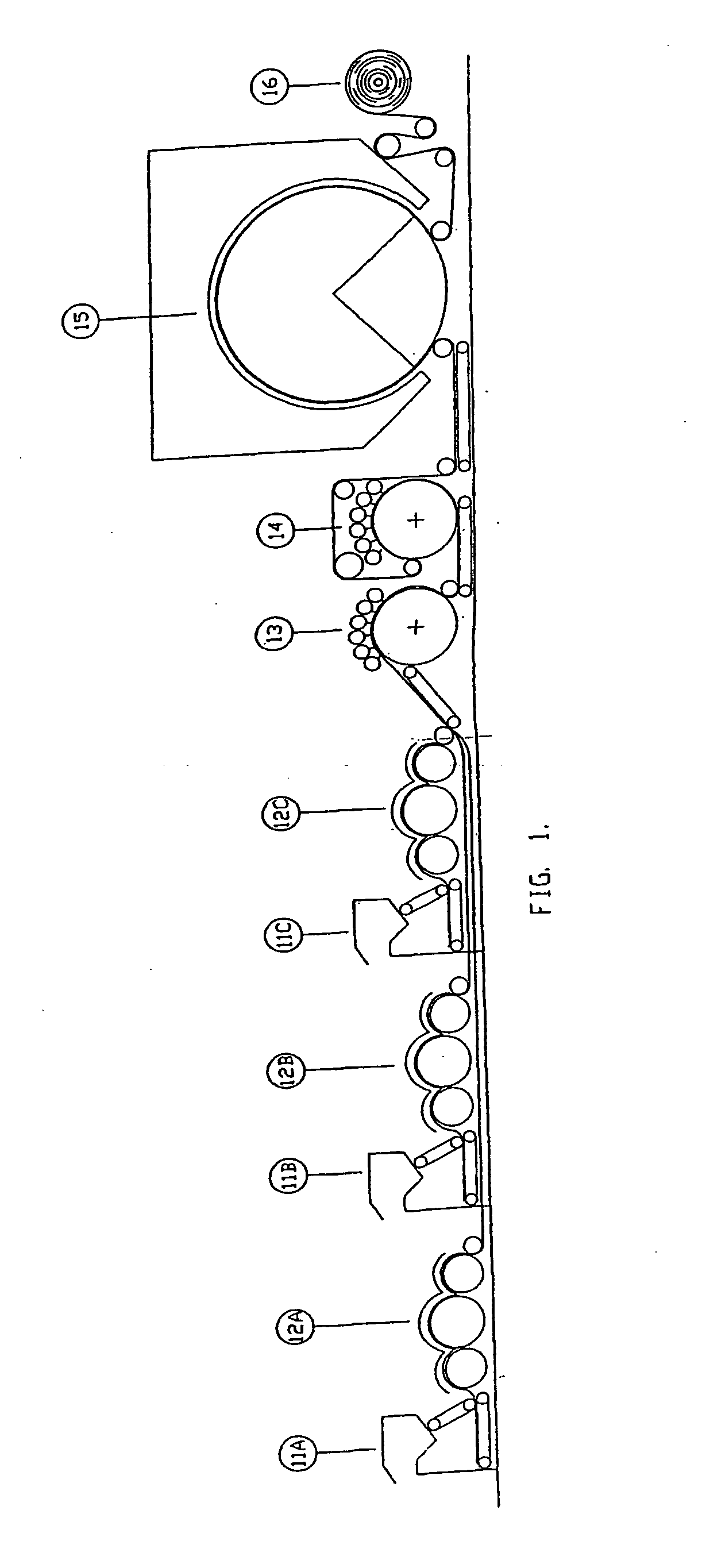
Composite nonwoven its use and method of manufacture
a technology of composite nonwovens and nonwoven fabrics, which is applied in the direction of weaving, woven fabrics, non-woven fabrics, etc., can solve the problems of reducing absorption properties, limited use of hydrophobic polypropylene fibers in nonwovens to be used as substrates for wiping articles, and reducing liquid absorption properties, so as to improve liquid absorption properties and improve liquid release properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
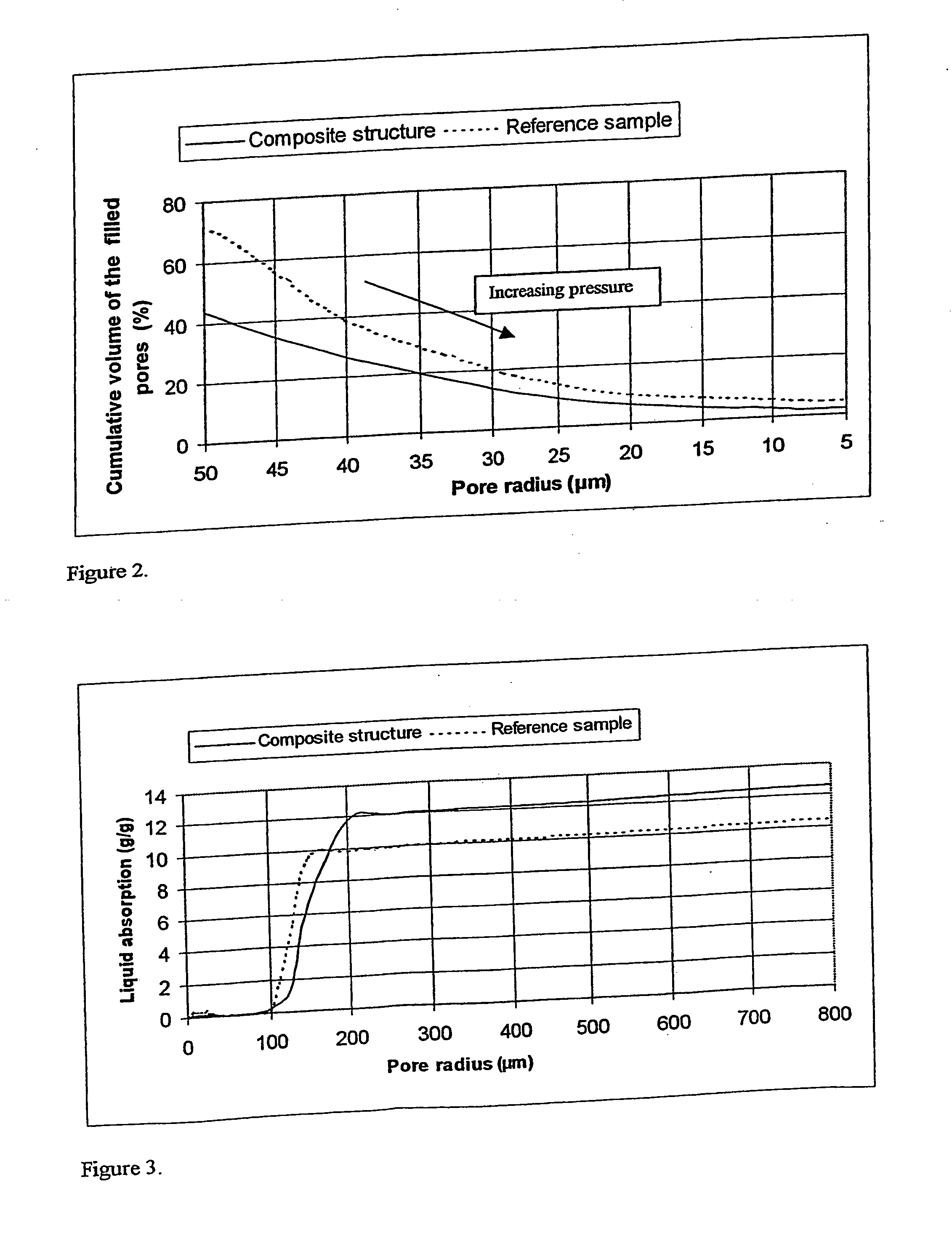
[0068] The liquid porosimeter was employed in both advancing and receding modes. During the advancing run, the sample was wetted by the test liquid and the receding part was used to determine the liquid release properties. Cumulative volumes of the filled pores are shown in FIG. 2. The pore radius range 5-50 μm corresponds to the pressure range 13200-1320 Pa. Cumulative volumes of filled pores at 10, 20, 30, 40 and 50 μm as a percentage (correspond to the pressures of 6600, 3300, 2200, 1650 and 1320 Pa) are presented in Table III. The selection of this pressure range is based on the estimate of pressures used during the wiping procedure in different wiping applications (baby wet wipe, household etc.). From FIG. 2 and Table III it is seen that the amount of filled pores in the composite structure is smaller than in the reference sample. Thus, according to the liquid porosimeter measurements, the release properties of the composite structure are better as compared to the reference sam...
example 2
[0070] Wiping Test (Wet Sample)
[0071] The wiping test with wet samples indicated the difference between the composite structure and the reference sample (FIG. 4). The liquid release is higher for the composite structure than for the reference sample. For example, after three consecutive releases the composite structure retained about 10% less liquid than the reference sample.
[0072] Wiping Test (Dry Sample)
[0073] The results from the wiping test with dry samples showed that the wiping efficiency was better for the composite structure (FIG. 5). The composite structure is capable of absorbing 12.4-16.7% more liquid during the wiping test than the reference sample.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com