Ultra high throughput microfluidic analytical systems and methods
a microfluidic and high-throughput technology, applied in the field of systems and methods for performing chemical and biological analyses, can solve the problems of not being easily adaptable to be used with other substrates, significant demands may be placed on analytical units, and significantly reduce the flexibility and cost advantages of microfluidic systems. achieve the effect of cost-effective and efficien
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Chip Design and Manufacture
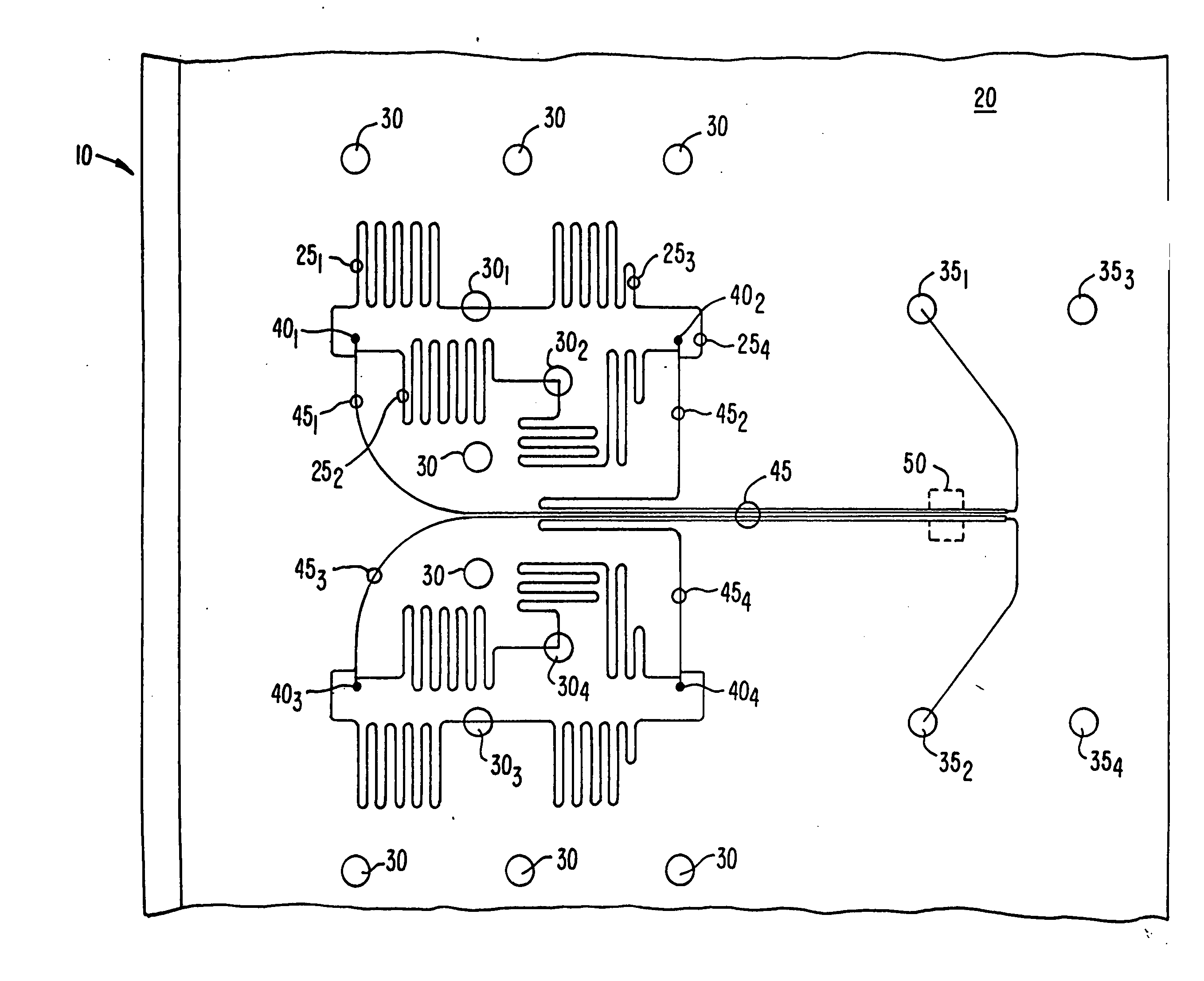
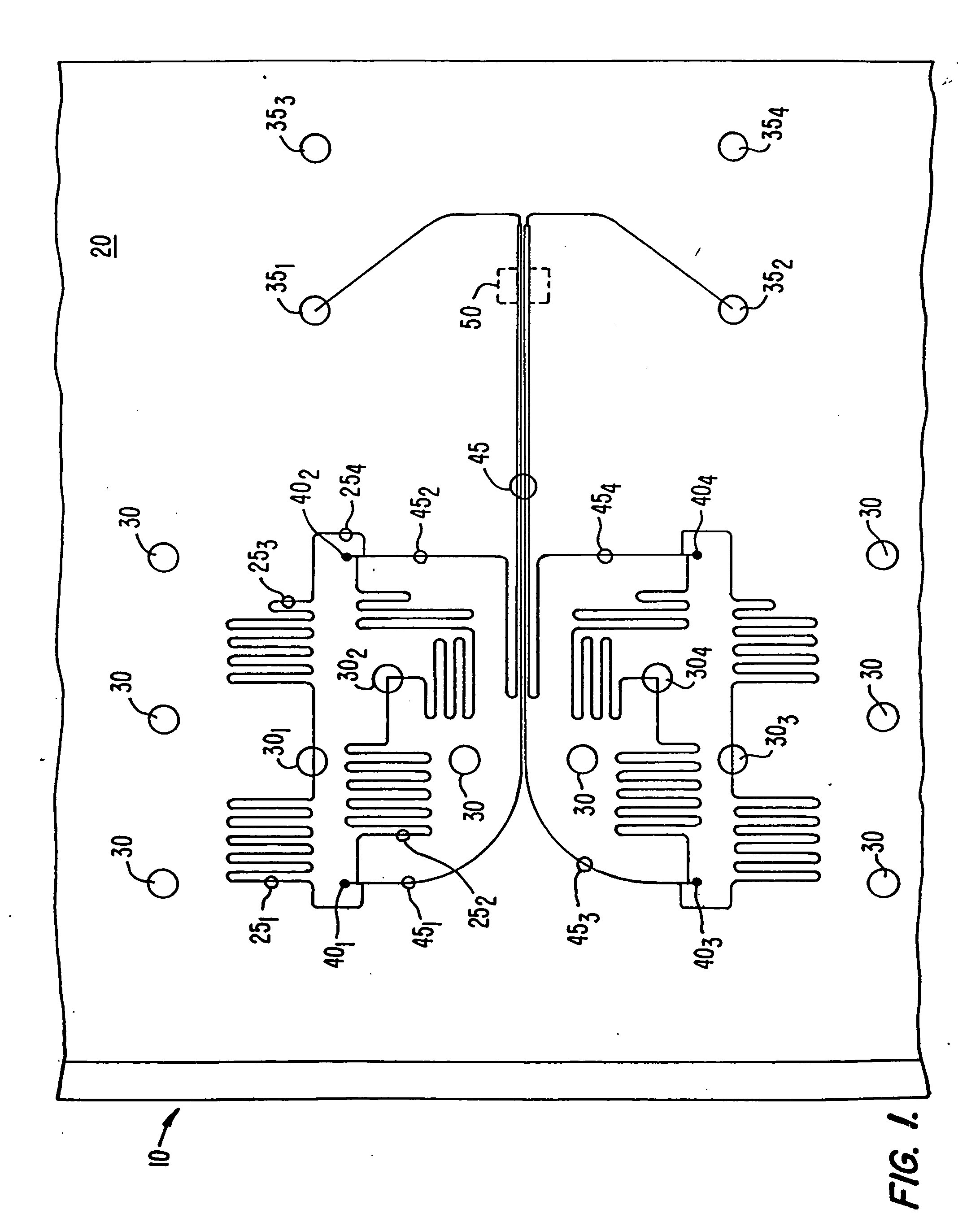
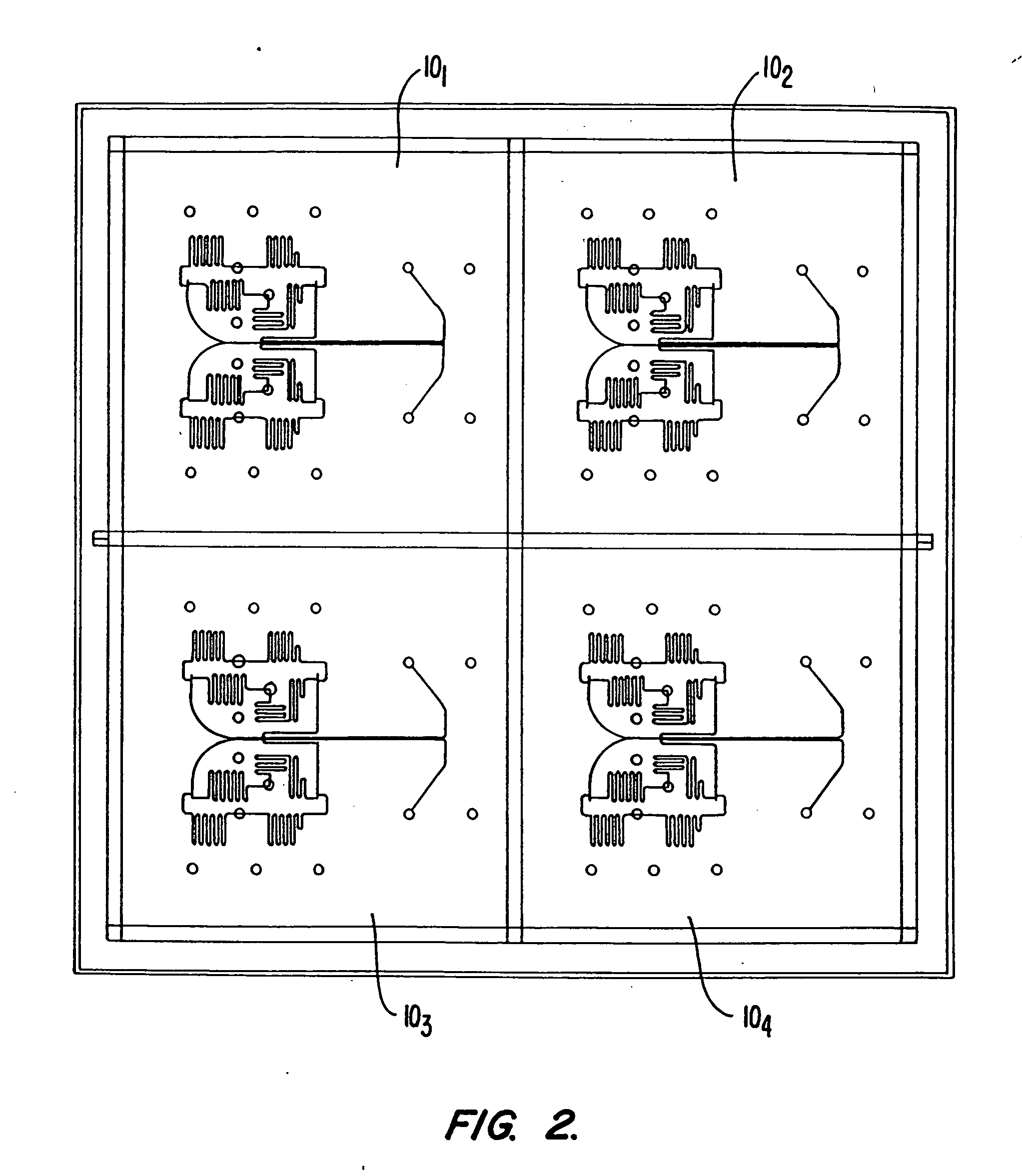
[0033]FIG. 1 illustrates an example of a microfluidic device 10 according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown, device 10 includes a body structure 20 which has an integrated network of microfluidic channels 25 disposed therein. In a preferred embodiment, device 10 includes at least two intersecting microfluidic channels to provide for various reactions, material combinations, etc. as desired. The body structure 20 also includes a plurality of reservoirs 30 disposed therein for holding reagents, sample materials and the like. The network 25 of microfluidic channels is used to connect any combination, or all, of the reservoirs 30 in any fashion as is desired by the substrate designer for the specific class of assays to be performed. Also included are waste reservoirs 35 and sampling capillary connection regions 40. Sampling capillary connection regions 40 each provide an interface with a sampling capillary that brings compounds onto device ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com