Patents
Literature
203results about "Apparatus with spatial temperature gradients" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
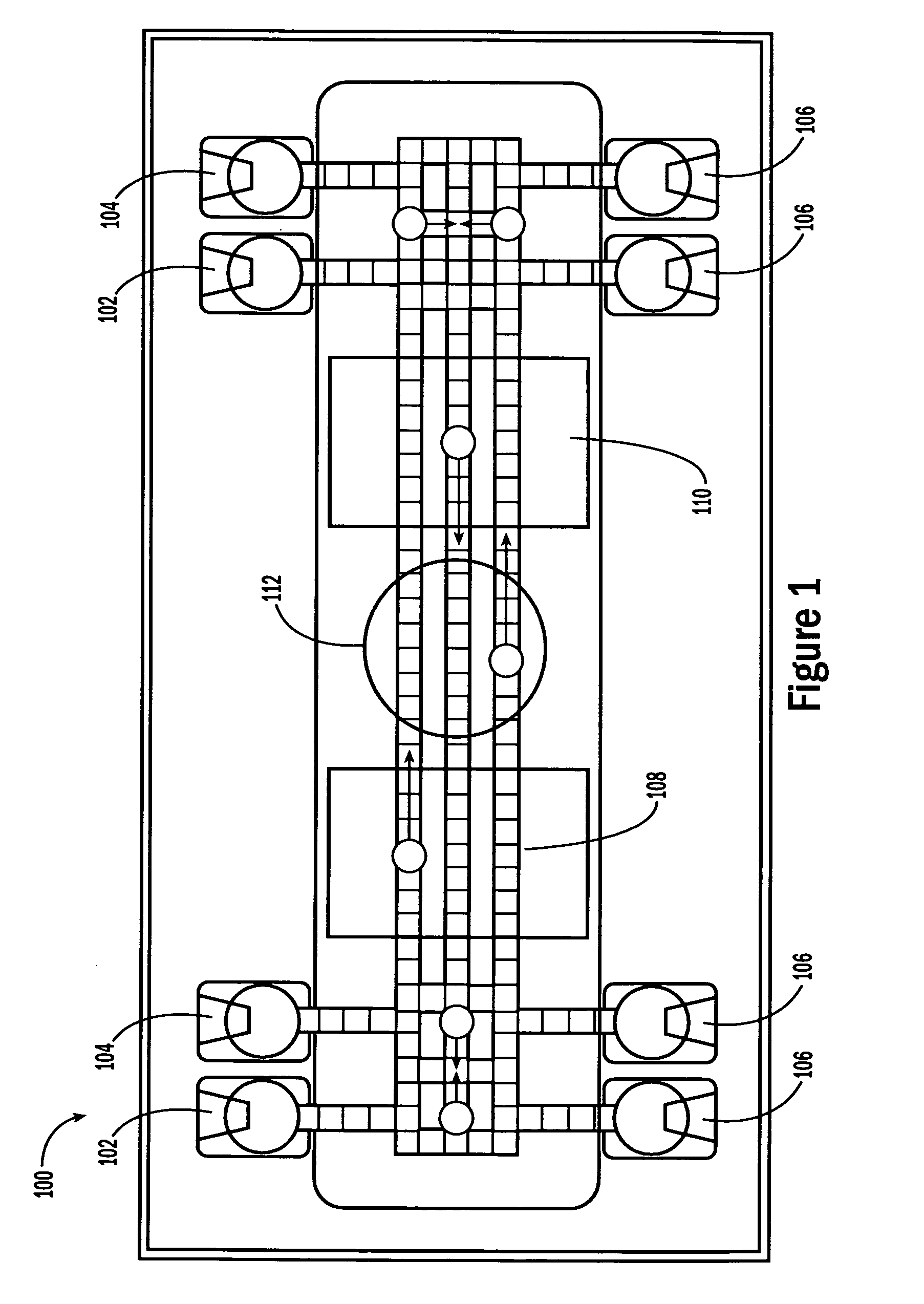
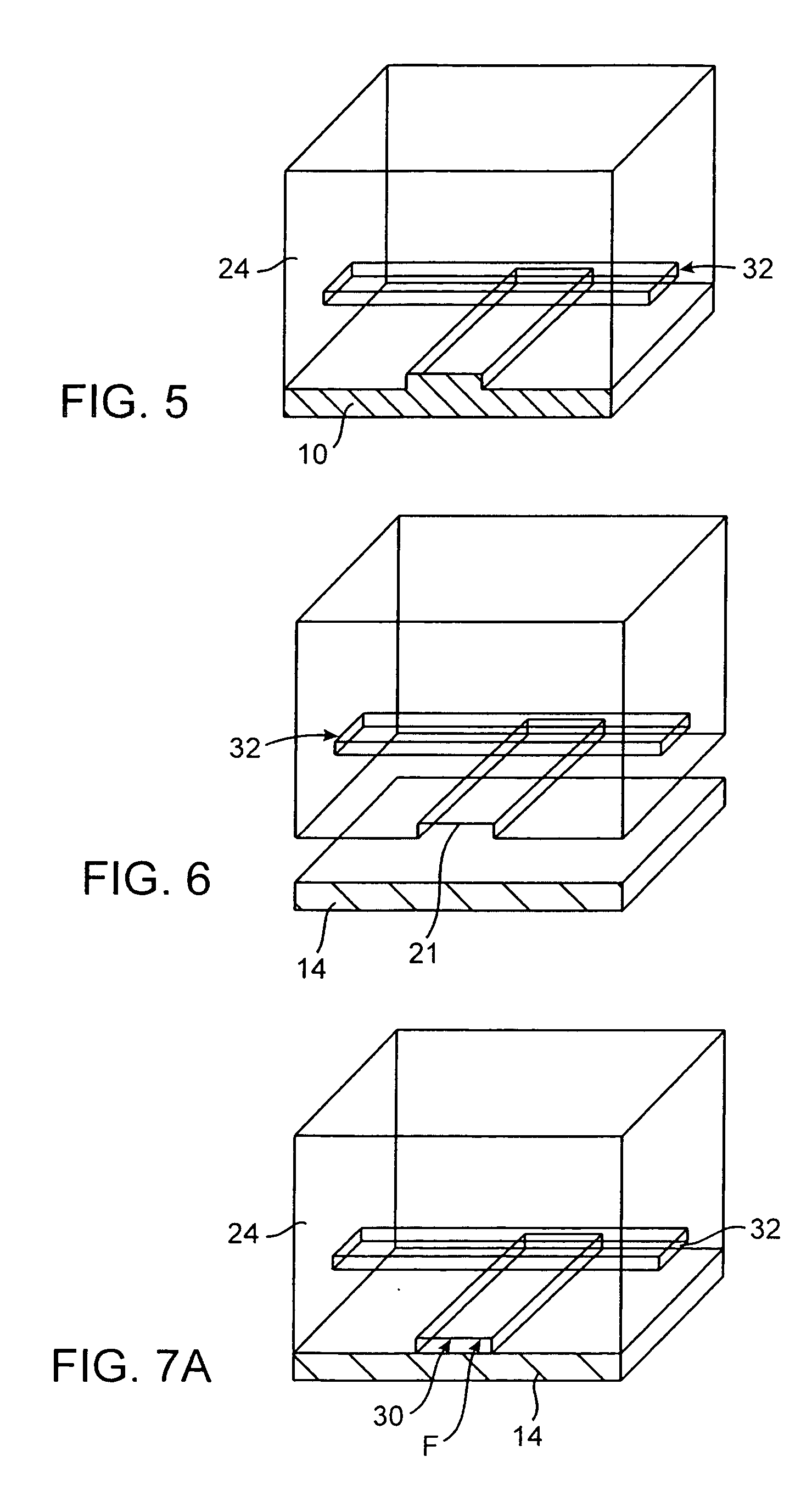
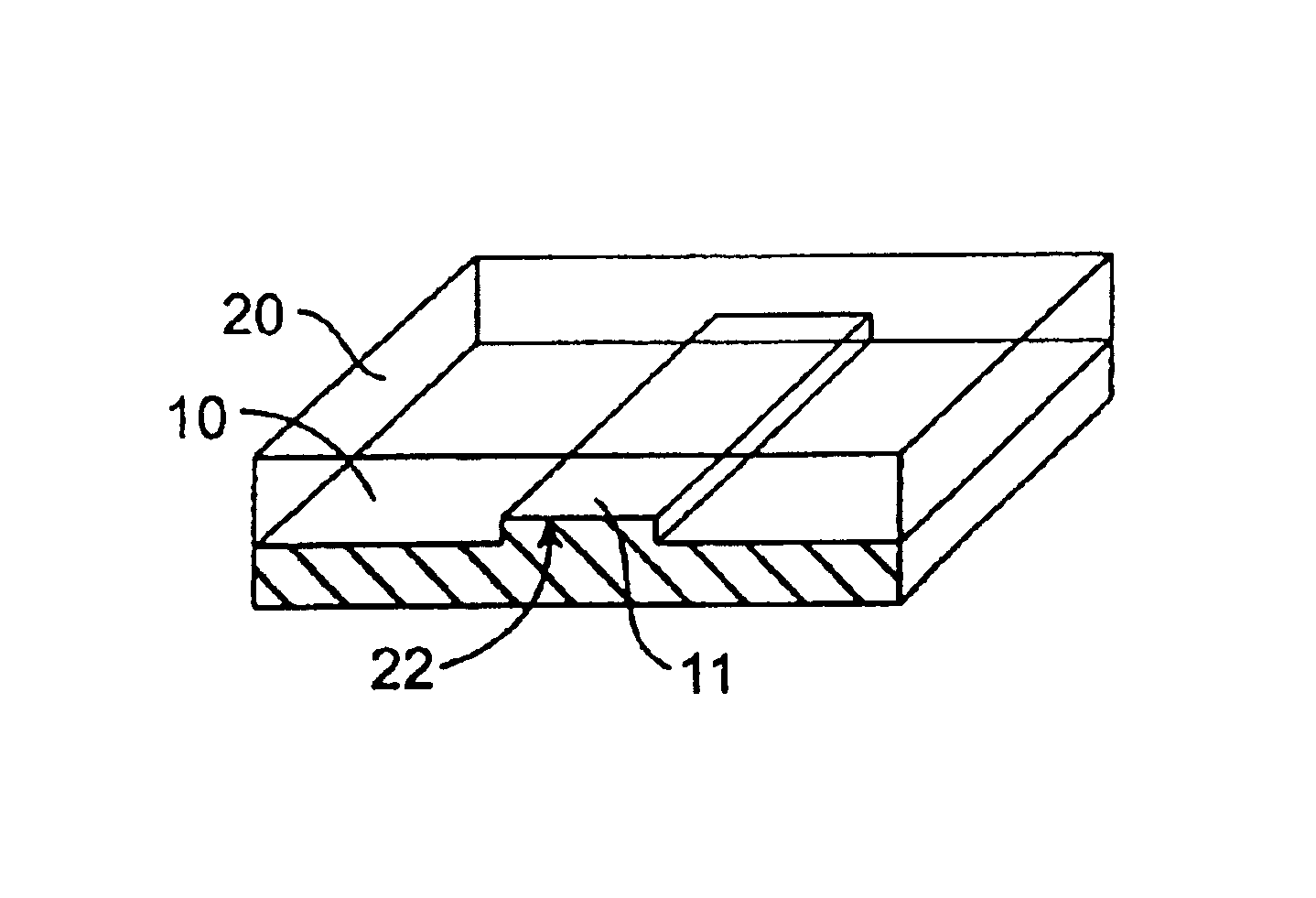
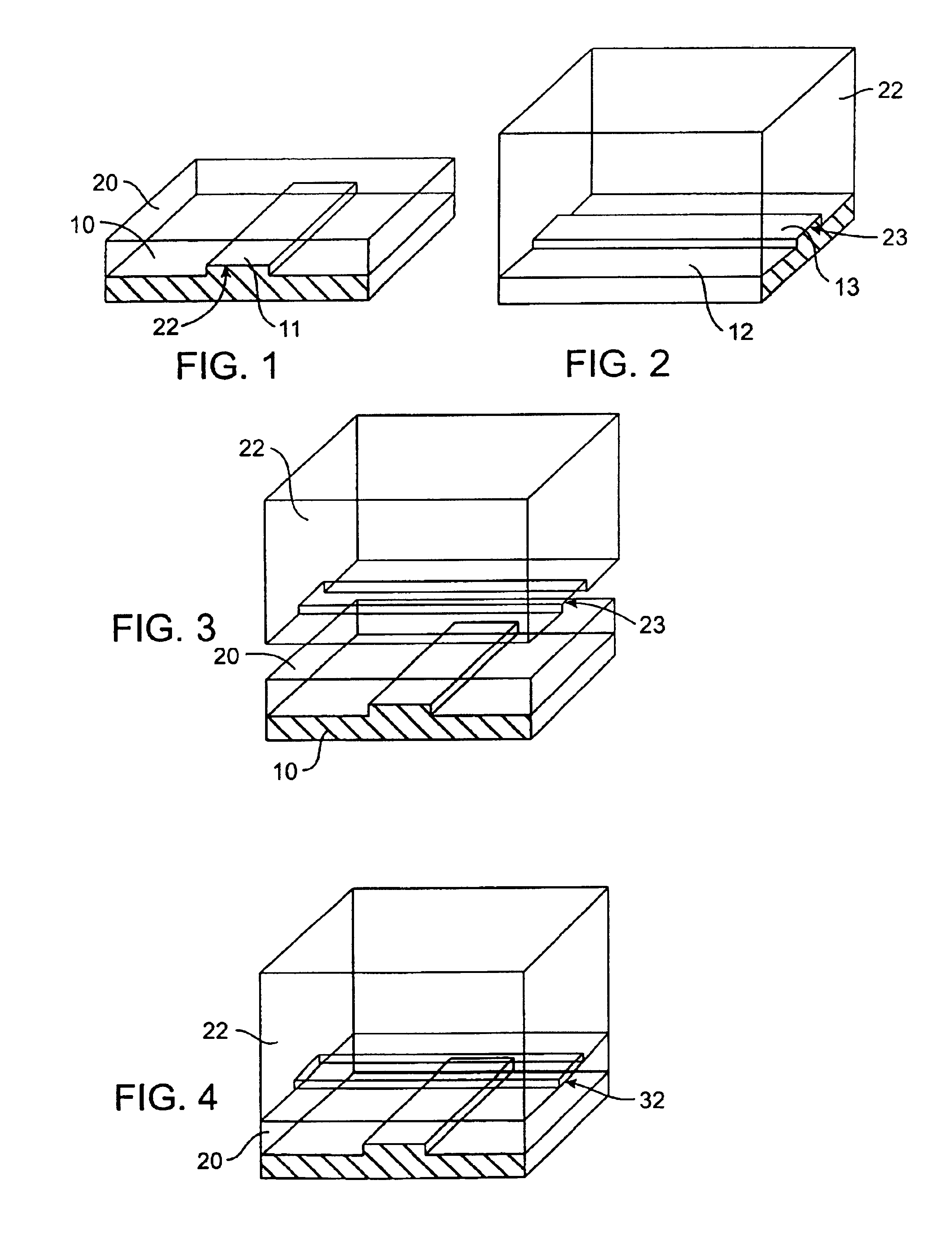
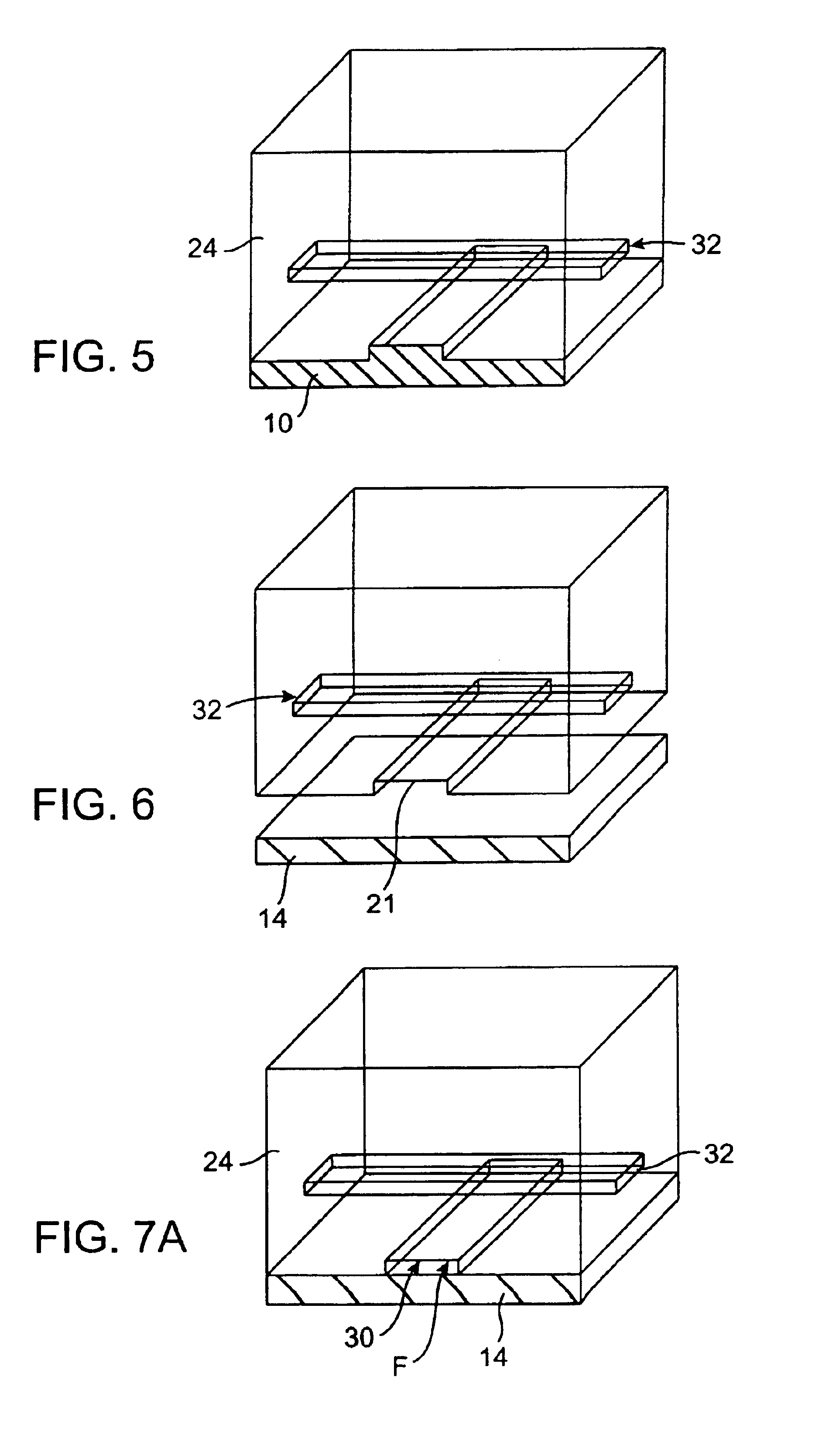
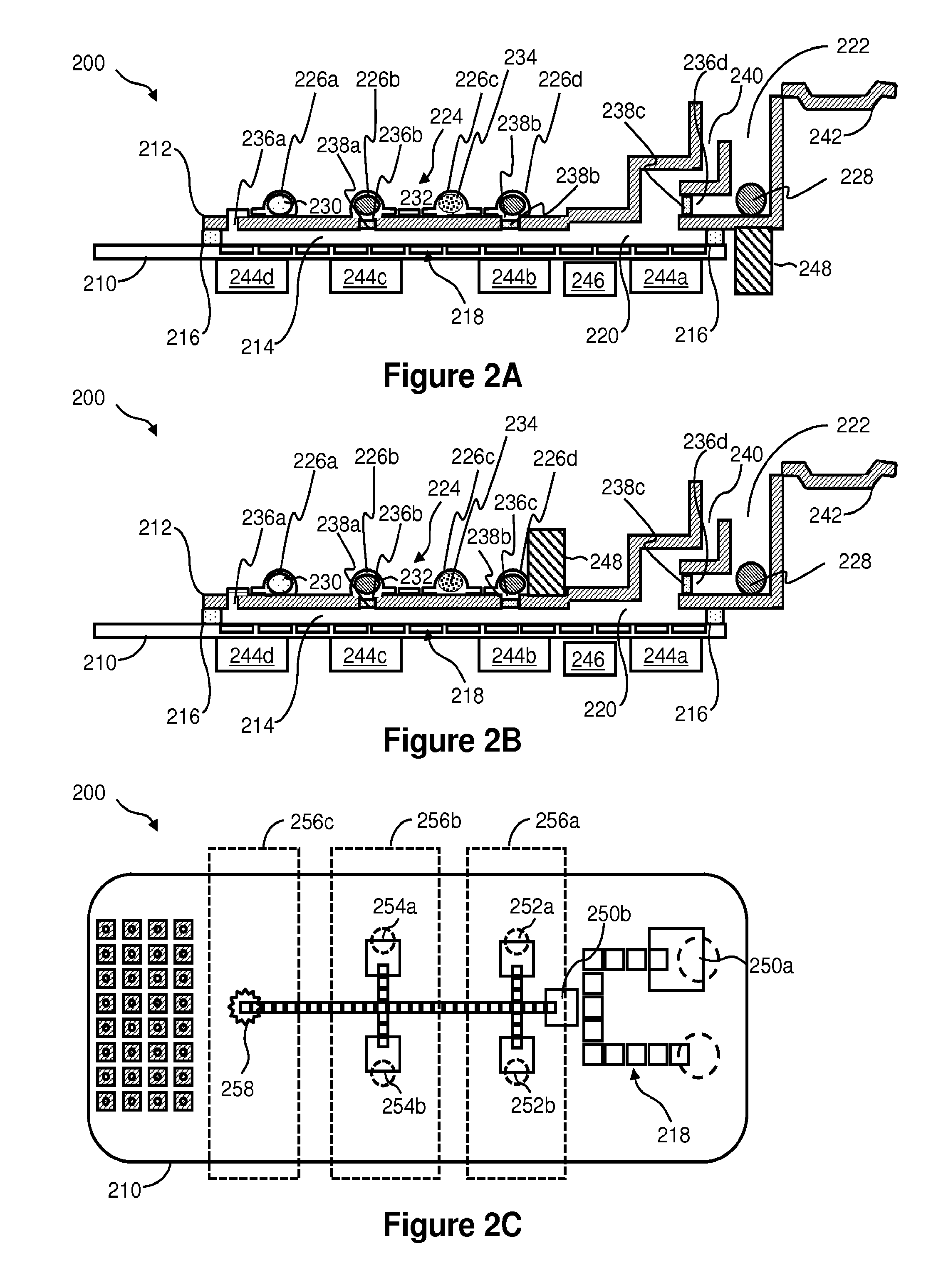
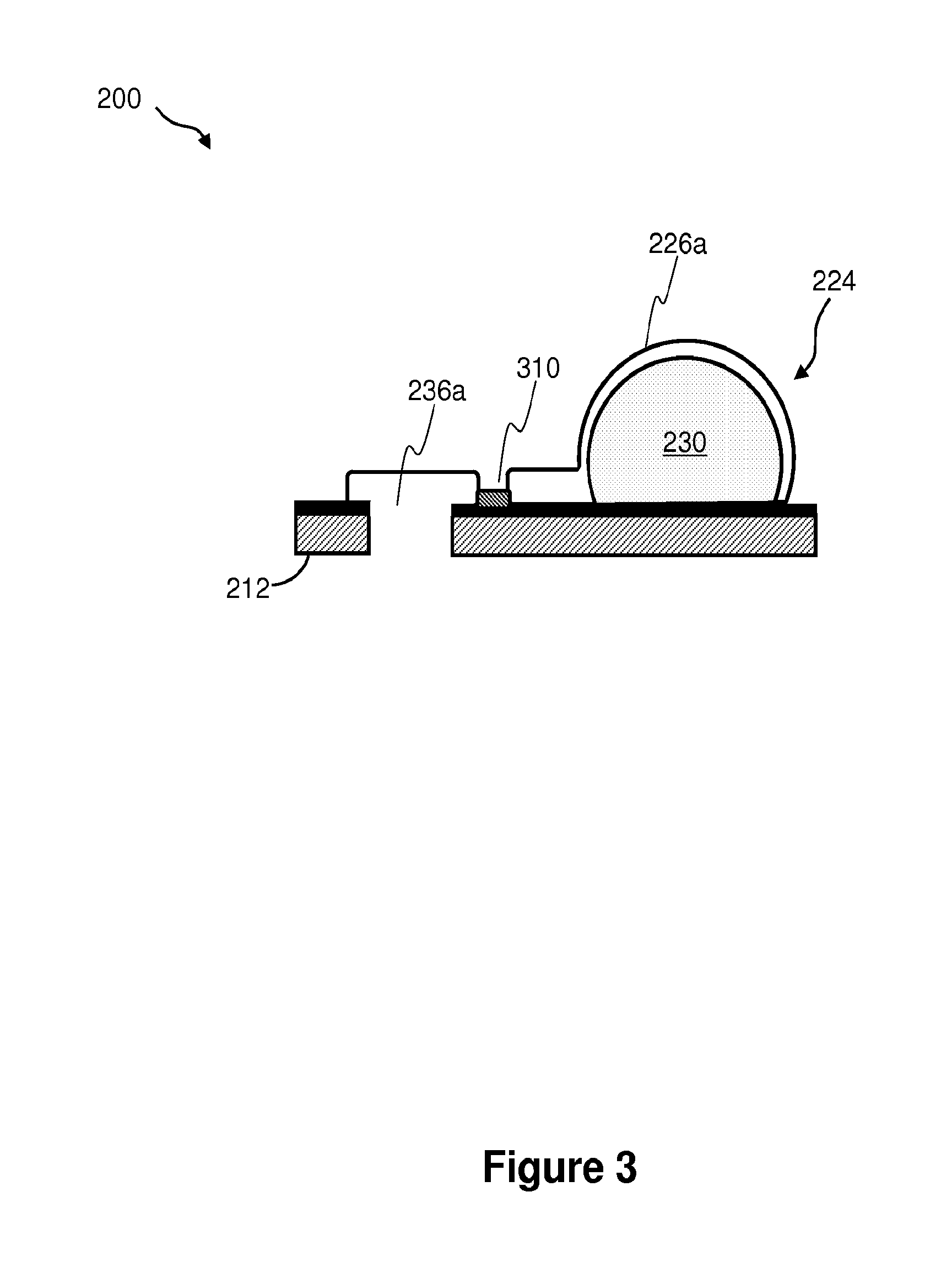
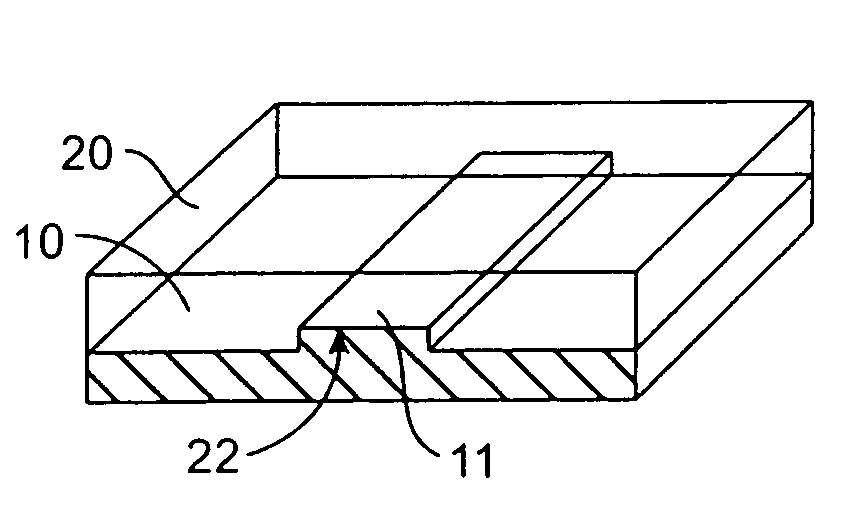
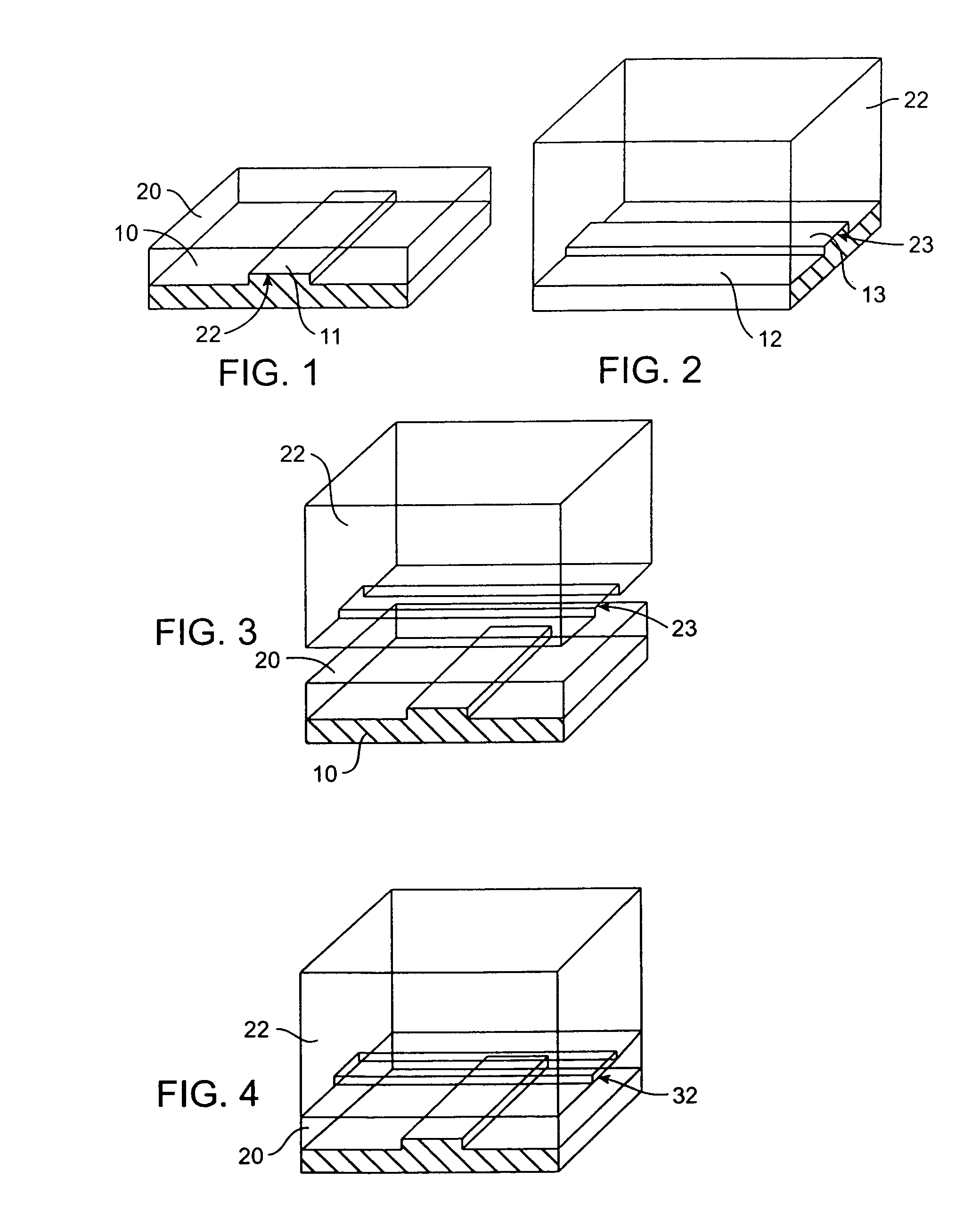
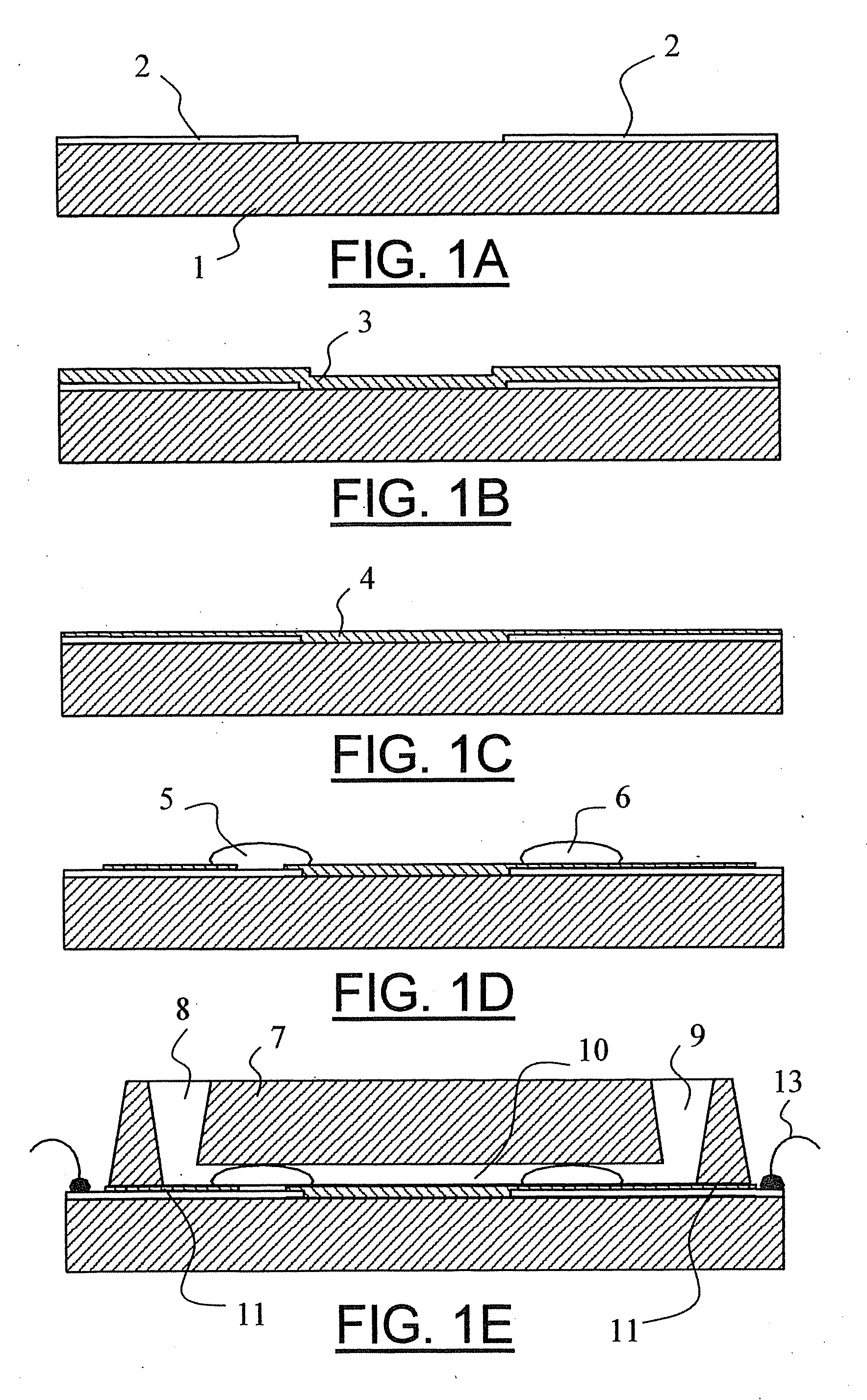
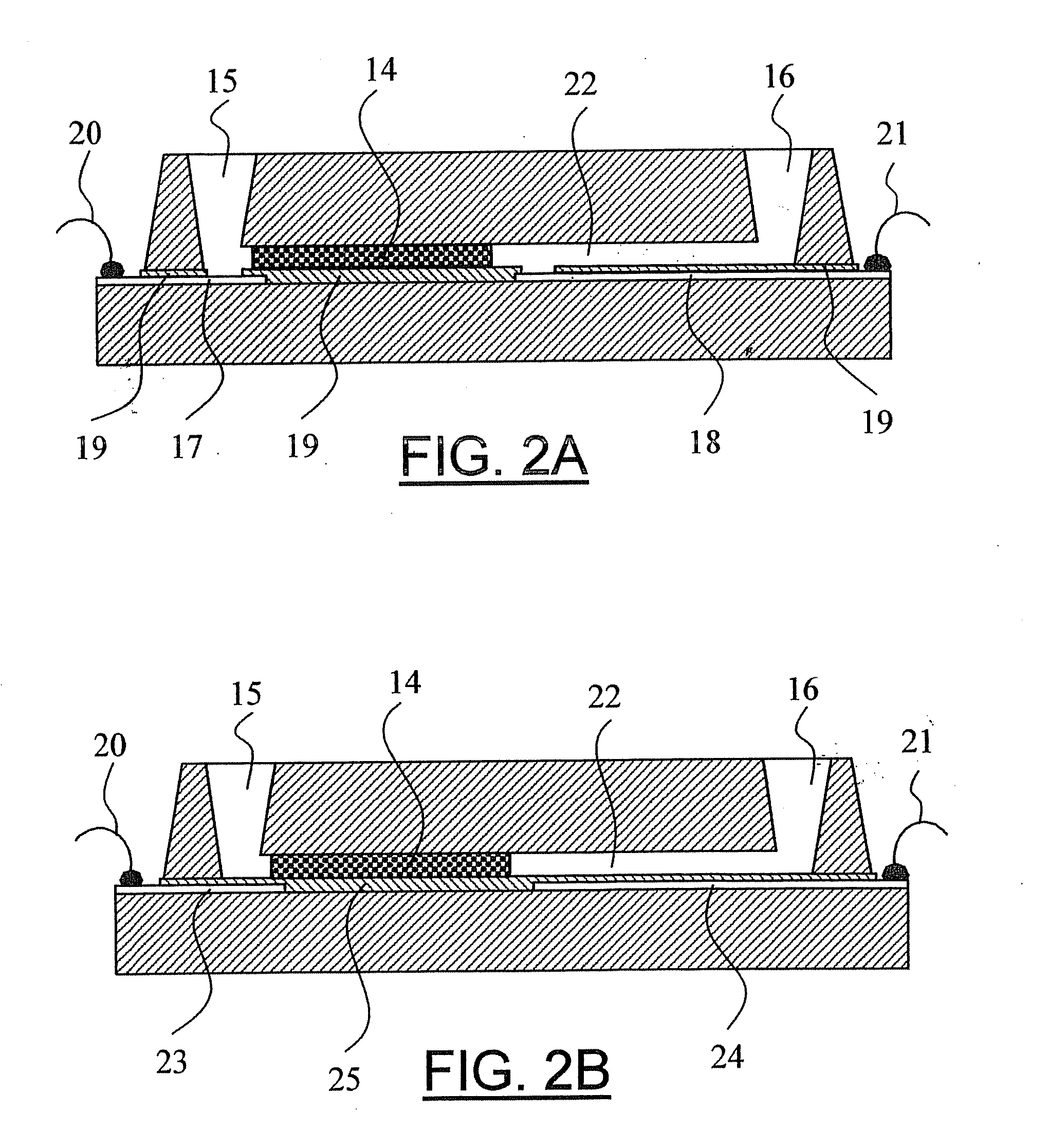
Microfabricated elastomeric valve and pump systems
InactiveUS6899137B2Increase speedSmall sizeFixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementElastomerPlanar substrate
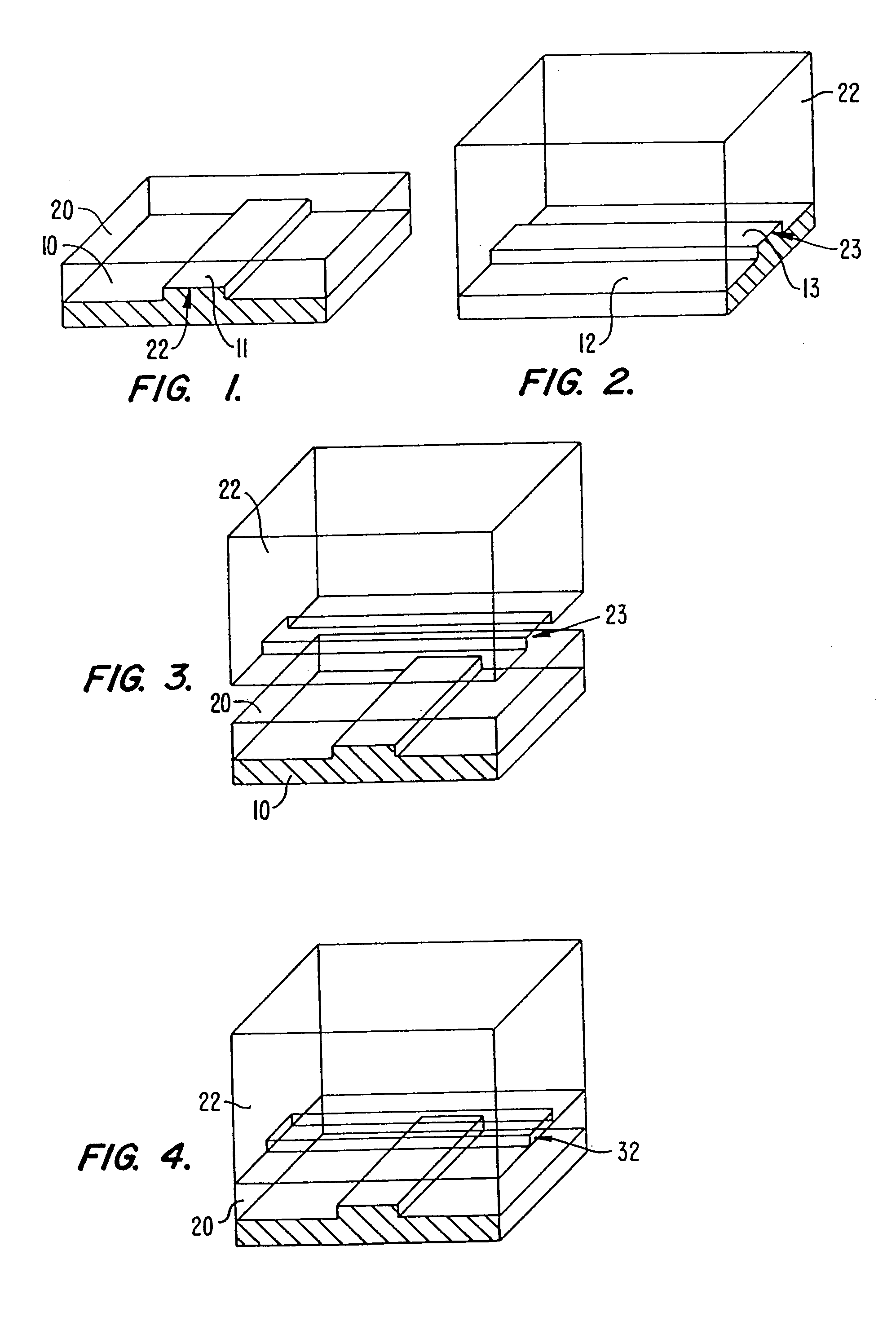
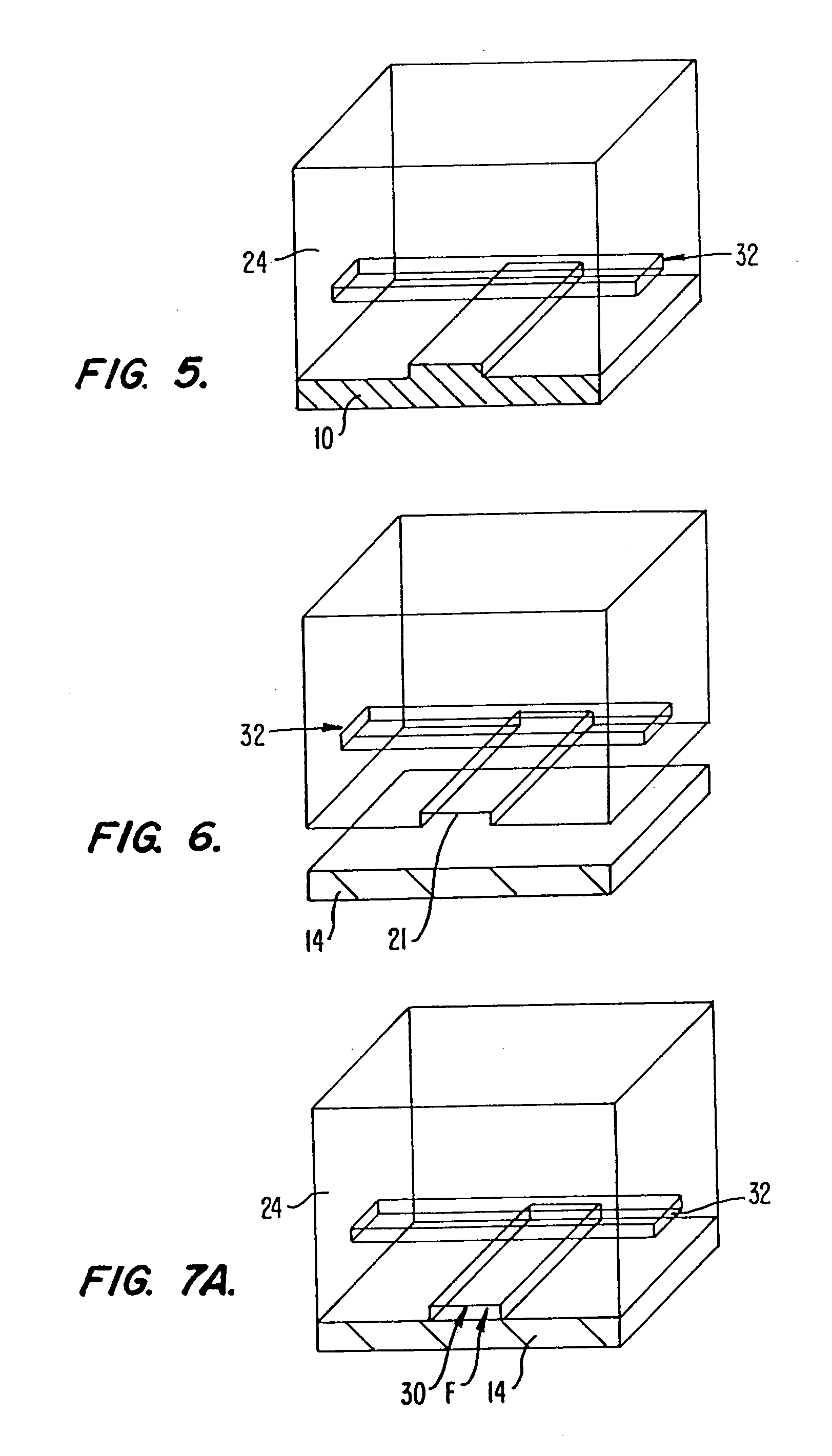
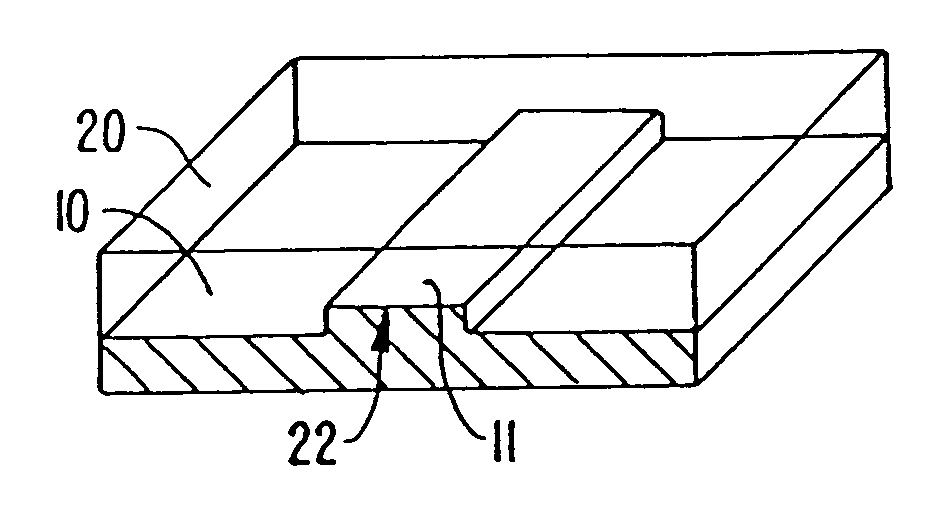
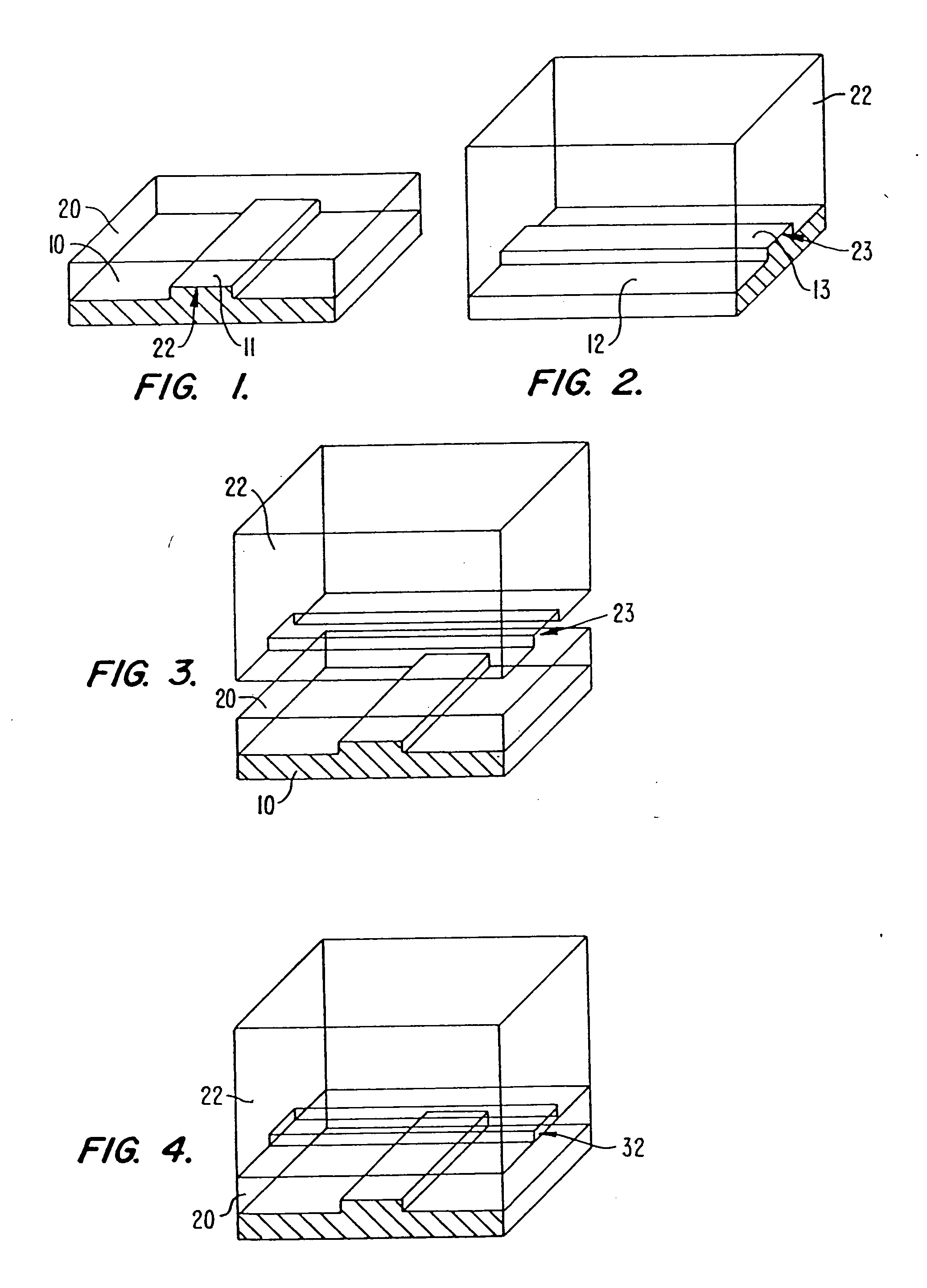
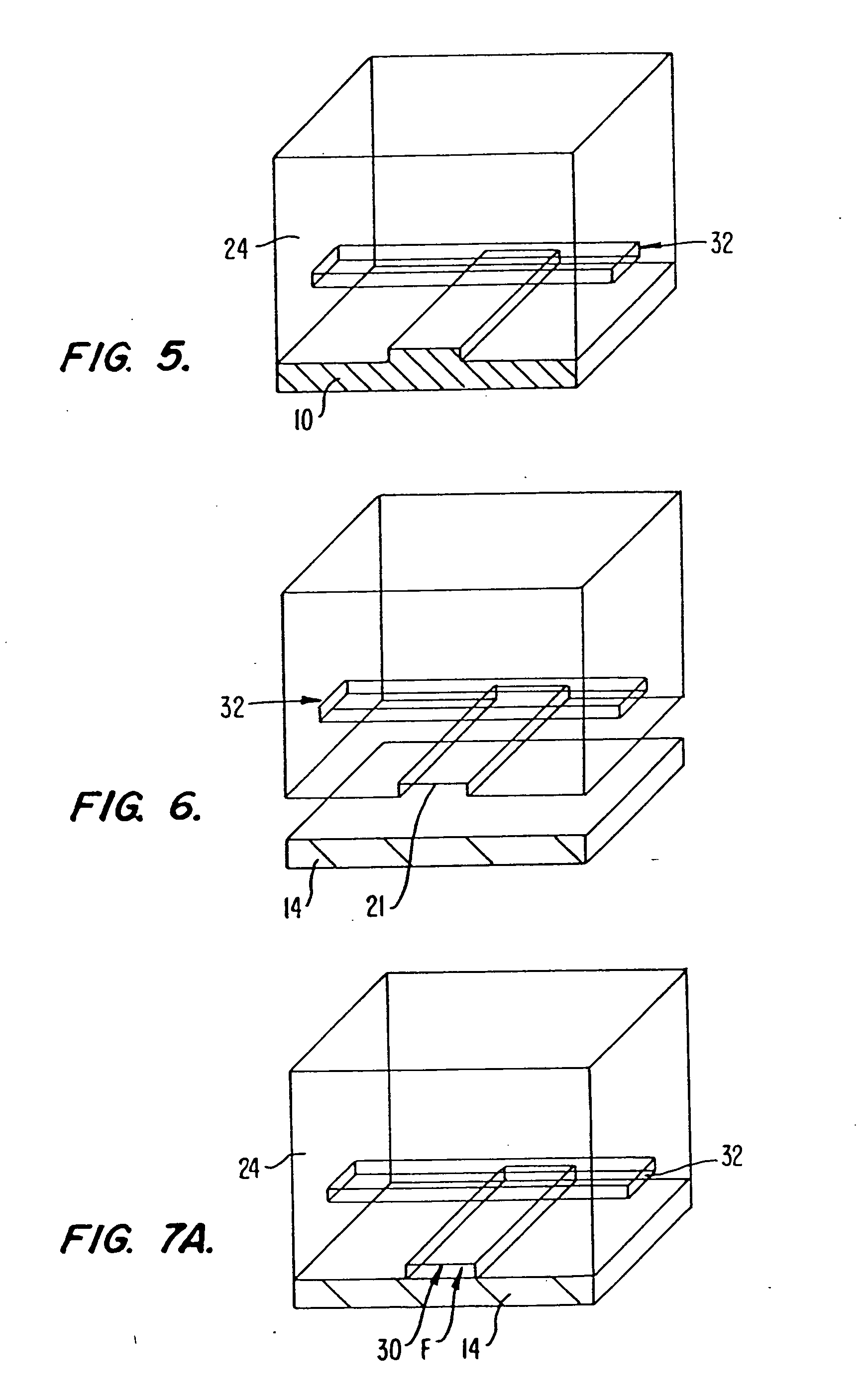
A method of fabricating an elastomeric structure, comprising: forming a first elastomeric layer on top of a first micromachined mold, the first micromachined mold having a first raised protrusion which forms a first recess extending along a bottom surface of the first elastomeric layer; forming a second elastomeric layer on top of a second micromachined mold, the second micromachined mold having a second raised protrusion which forms a second recess extending along a bottom surface of the second elastomeric layer; bonding the bottom surface of the second elastomeric layer onto a top surface of the first elastomeric layer such that a control channel forms in the second recess between the first and second elastomeric layers; and positioning the first elastomeric layer on top of a planar substrate such that a flow channel forms in the first recess between the first elastomeric layer and the planar substrate.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
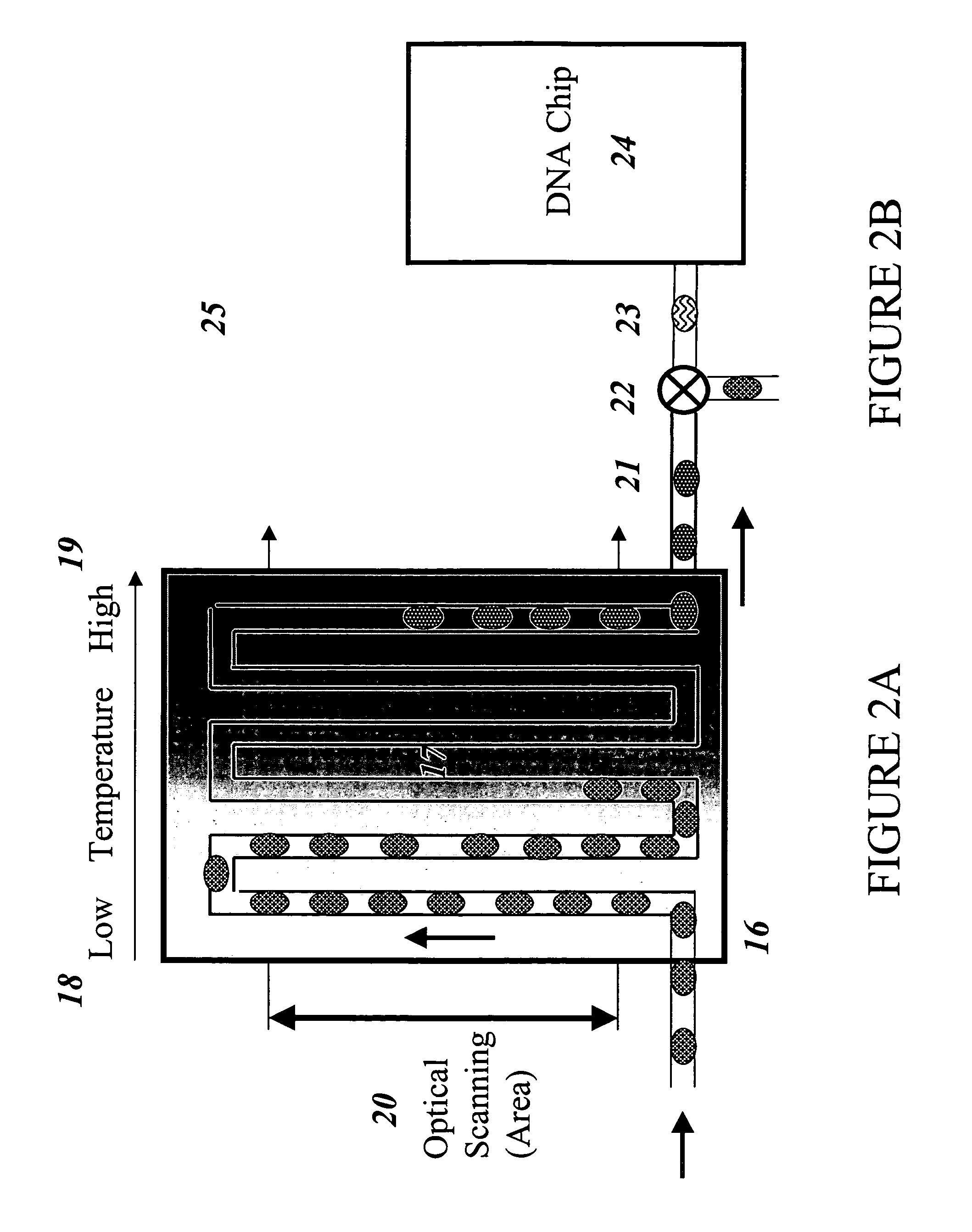
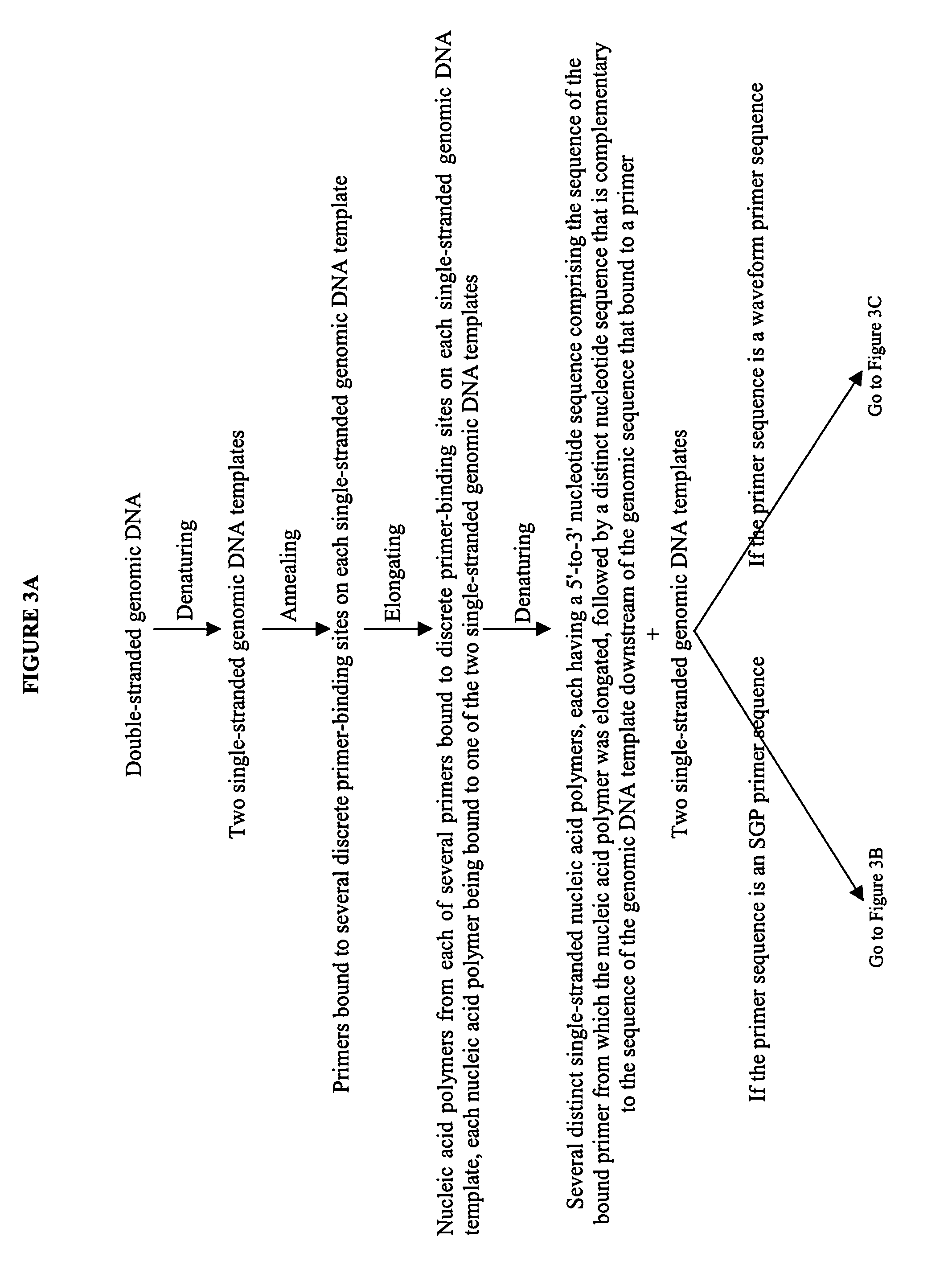
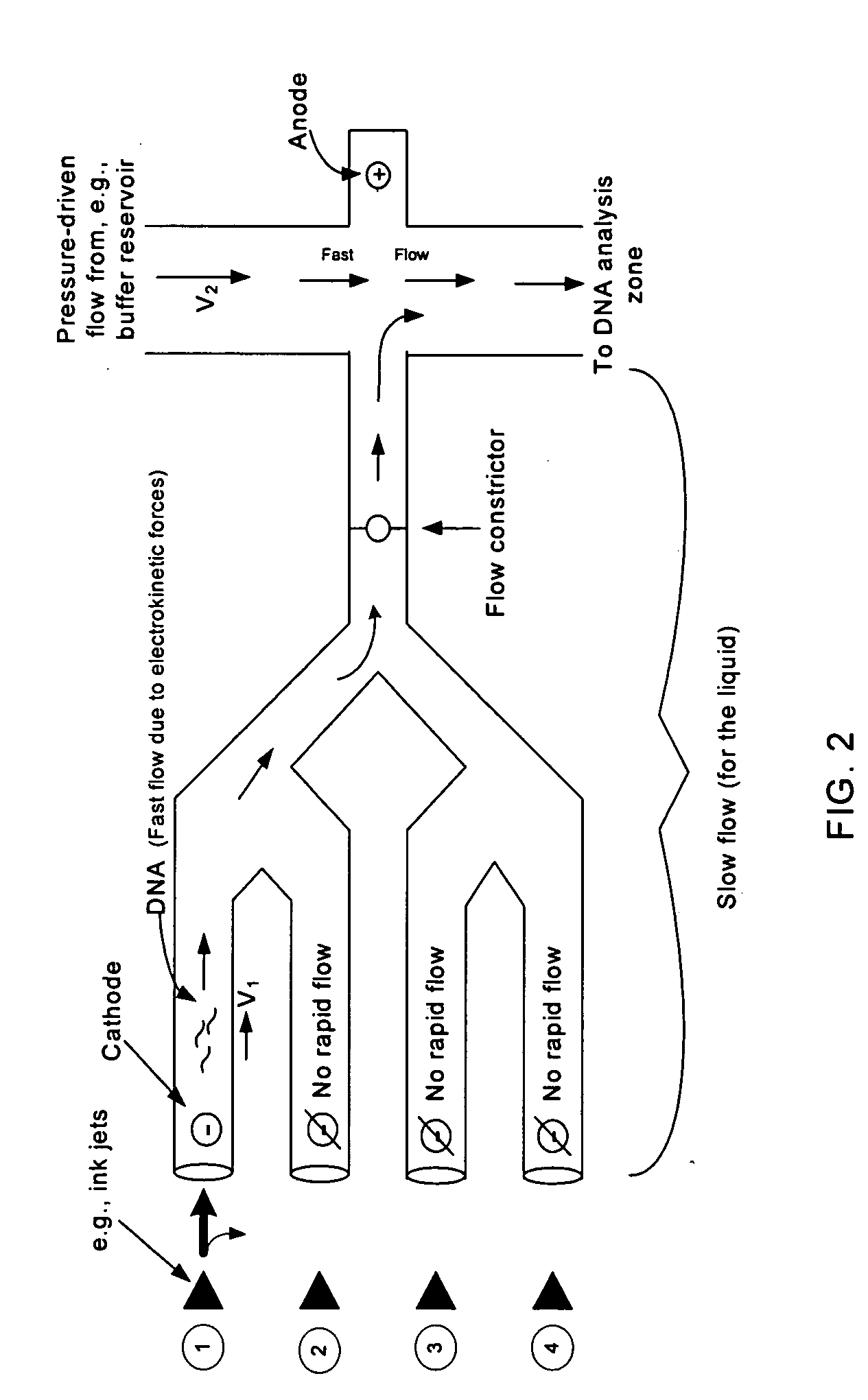
Devices and methods for monitoring genomic DNA of organisms
InactiveUS7604938B2Low costAvoid pollutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic DNADna amplification
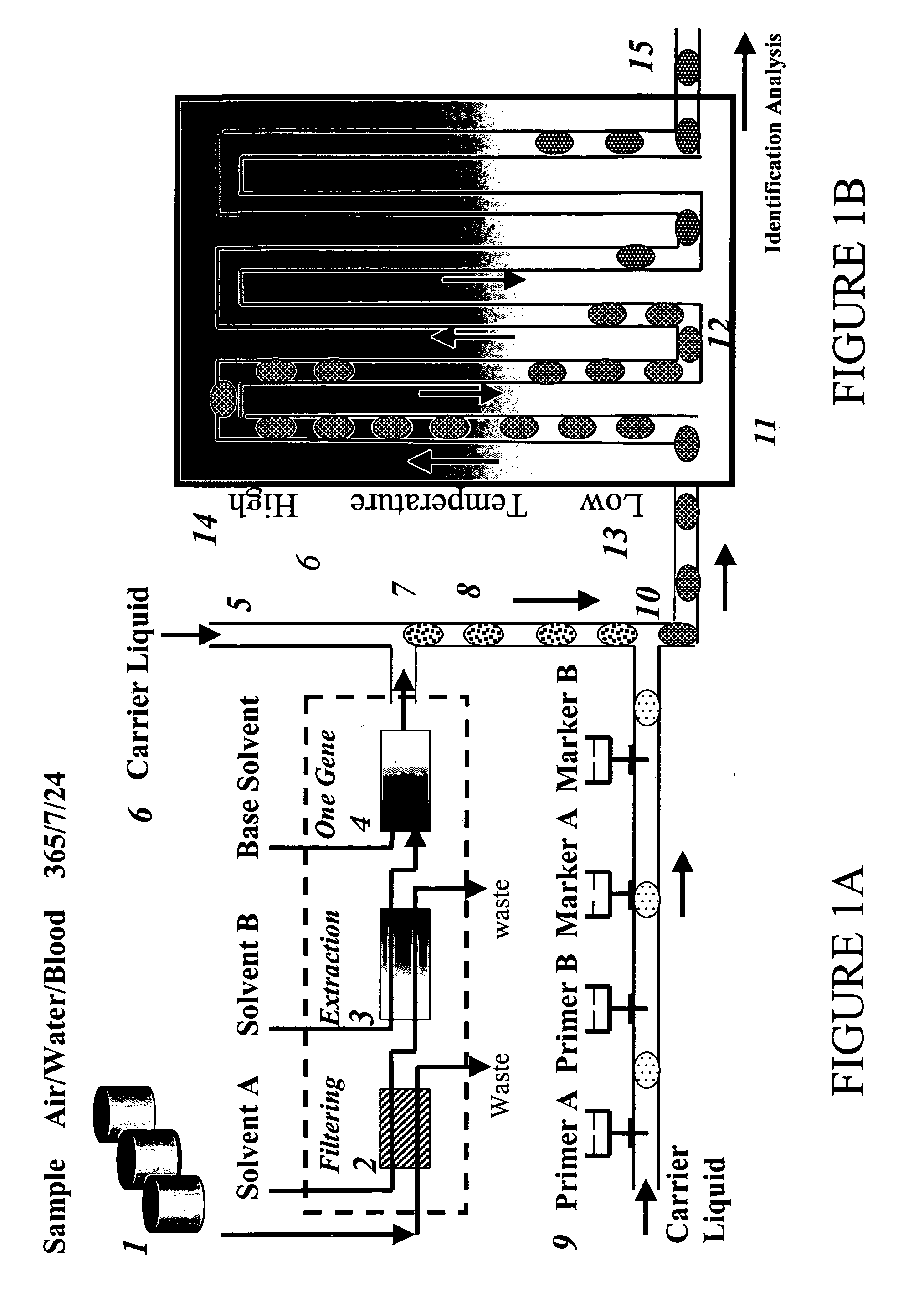
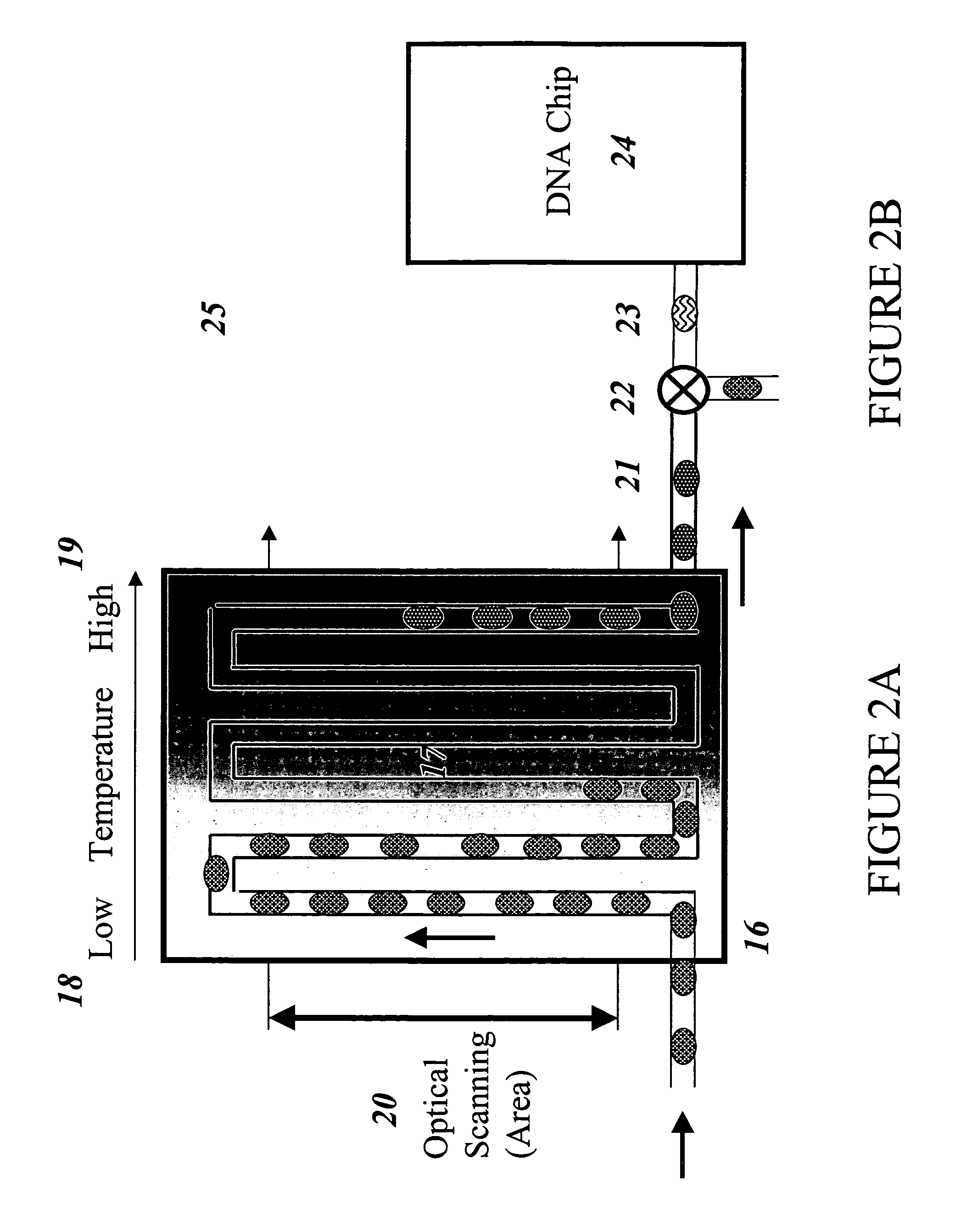
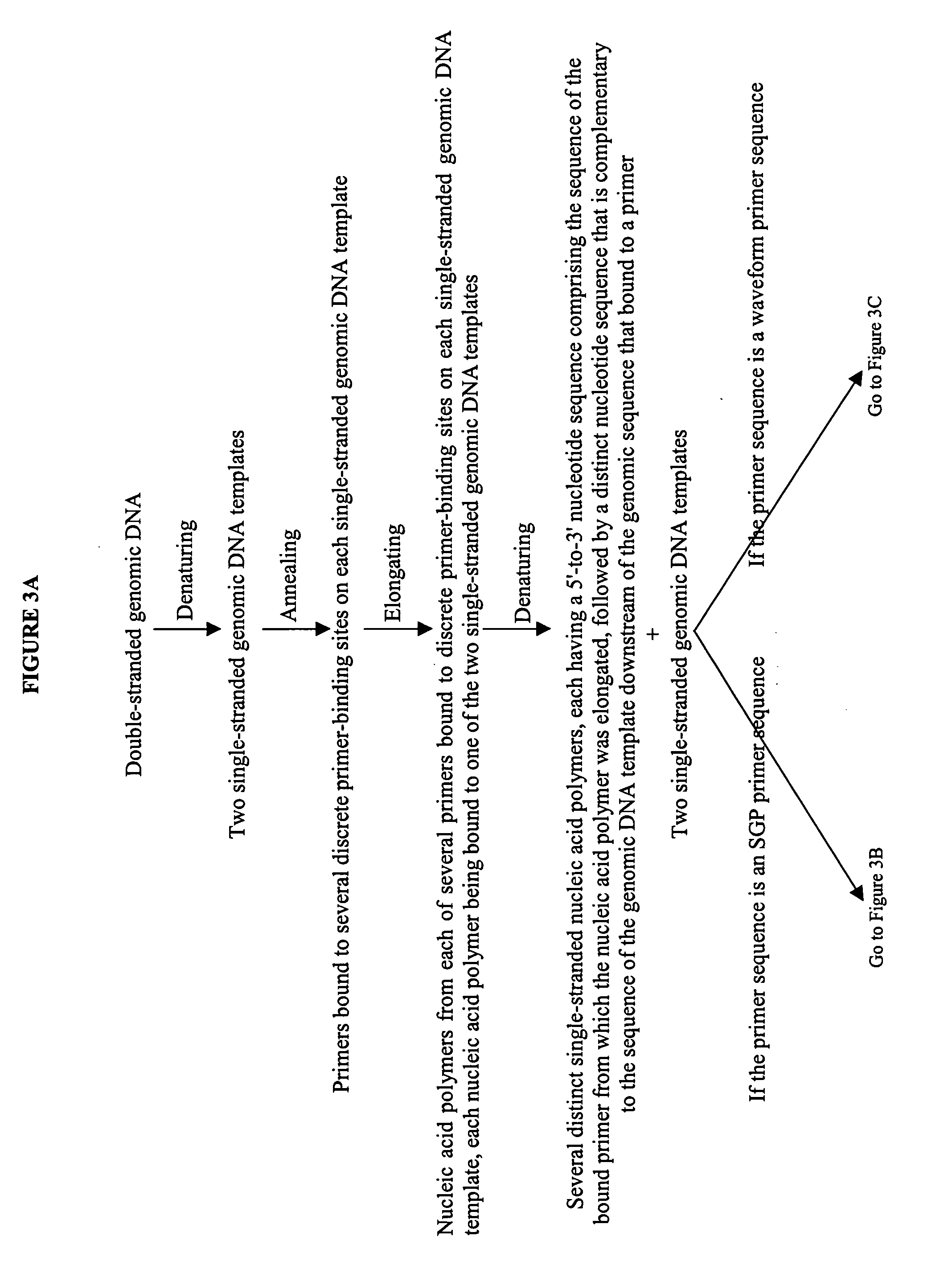
The invention provides an apparatus that can be used in methods of preparing, amplifying, detecting, and / or optionally selecting for further analysis the genomic material from an organism for the rapid detection and / or classification of an organism in a sample (e.g., screening for, identifying, quantifying, and / or optionally further analyzing, e.g., sequencing, the genomic material of the organism). The invention further provides methods of using the apparatus, e.g., in combination with novel SGP primers for improved use in waveform-profiling methods of DNA amplification. It is an object of the invention to provide an apparatus for fully automated analysis of genomic material, and multiple methods of using the apparatus that are beneficial to society, e.g., the apparatus may be used in methods of screening for, identifying, quantifying, and / or selecting genomic material for further analysis (e.g., sequencing) in relation to monitoring a source for the presence of contaminating organisms.
Owner:CANON US LIFE SCIENCES INC
Filler fluids for droplet operations
ActiveUS20070242105A1Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyElectrostatic separatorsFixed microstructural devicesEngineeringLiquid drop
The present invention relates to filler fluids for droplet operations. According to one embodiment of this aspect, a droplet microactuator is provided and includes: (a) a first substrate comprising electrodes configured for conducting droplet operations on a surface of the substrate; (b) a second substrate spaced from the surface of the substrate by a distance sufficient to define an interior volume between the first substrate and second substrate, wherein the distance is sufficient to contain a droplet disposed in the space on the first substrate; and (c) a droplet arranged in the interior volume and arranged with respect to the electrodes in a manner which permits droplet operations to be effected on the droplet using the electrodes.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Parallel flow process optimization reactors
InactiveUS20020048536A1Extreme flexibilityAdvantageously and flexibly employedProcess control/regulationSequential/parallel process reactionsProcess optimizationDistribution system
Owner:FREESLATE
Devices and methods for monitoring genomic DNA of organisms
InactiveUS20060257893A1Low costAvoid pollutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic DNADna amplification
The invention provides an apparatus that can be used in methods of preparing, amplifying, detecting, and / or optionally selecting for further analysis the genomic material from an organism for the rapid detection and / or classification of an organism in a sample (e.g., screening for, identifying, quantifying, and / or optionally further analyzing, e.g., sequencing, the genomic material of the organism). The invention further provides methods of using the apparatus, e.g., in combination with novel SGP primers for improved use in waveform-profiling methods of DNA amplification. It is an object of the invention to provide an apparatus for fully automated analysis of genomic material, and multiple methods of using the apparatus that are beneficial to society, e.g., the apparatus may be used in methods of screening for, identifying, quantifying, and / or selecting genomic material for further analysis (e.g., sequencing) in relation to monitoring a source for the presence of contaminating organisms.
Owner:CANON US LIFE SCIENCES INC
Parallel flow reactor having variable composition
InactiveUS20020045265A1Extreme flexibilityAdvantageously and flexibly employedProcess control/regulationSequential/parallel process reactionsDistribution systemEngineering
Owner:FREESLATE
Ultra high throughput microfluidic analytical systems and methods
InactiveUS20050135655A1Efficient and cost-effectiveMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresExcitation beamControl system
Analytical systems and methods that use a modular interface structure for providing an interface between a sample substrate and an analytical unit, where the analytical unit typically has a particular interface arrangement for implementing various analytical and control functions. Using a number of variants for each module of the modular interface structure advantageously provides cost effective and efficient ways to perform numerous tests using a particular substrate or class of substrates with a particular analytical and control systems interface arrangement. Improved optical illumination and detection system for simultaneously analyzing reactions or conditions in multiple parallel microchannels are also provided. Increased throughput and improved emissions detection is provided by the present invention by simultaneously illuminating multiple parallel microchannels at a non-normal incidence using an excitation beam including multiple excitation frequencies, and simultaneously detecting emissions from the substances in the microchannels in a direction normal to the substrate using a detection module with multiple detectors.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
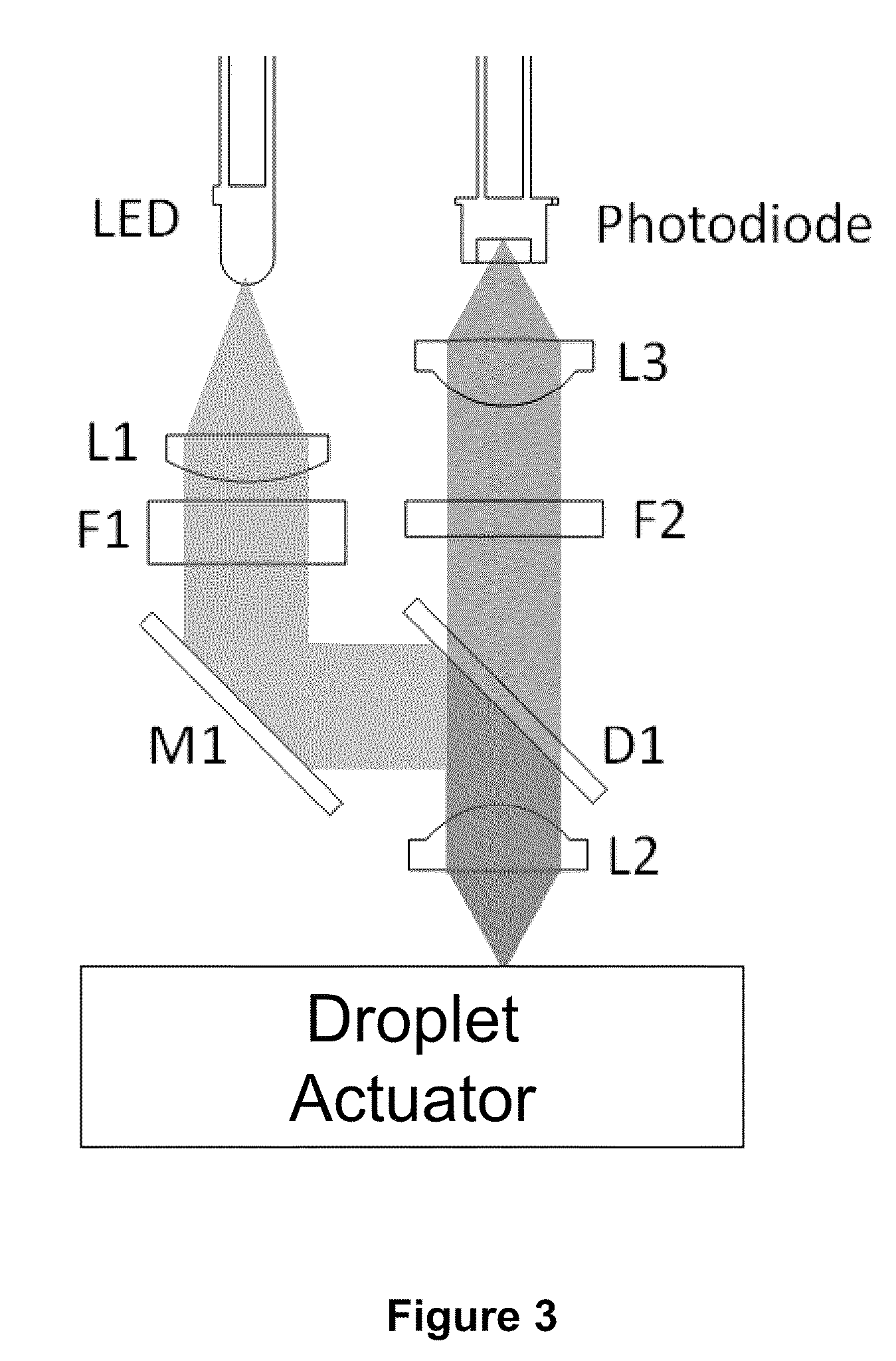
Enzyme Assays for a Droplet Actuator
ActiveUS20100041086A1Easy to useFacilitates of propertyTransportation and packagingMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme assayActuator
The invention relates to a microfluidic platform and methods of using the platform for conducting enzyme assays using a droplet actuator. The enzyme assays of the invention are useful for, among other things, identifying and / or characterizing disorders resulting from conditions in which enzymes are defective or are produced in inappropriate amounts. Enzyme assays of the invention may, for example, be used to detect altered activity of a particular enzyme in a sample, which may serve as an indicator of a particular disease. Altered activity may, for example, be caused by conditions which result in the increased or reduced production of a certain enzyme or its substrate and / or conditions which result in defective enzymes and / or substrates exhibiting increased or decreased effectiveness relative to corresponding normal enzymes and / or substrates.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
Enzyme assays for a droplet actuator
ActiveUS8202686B2Easy to useFacilitates of propertyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransportation and packagingEnzyme assayActuator
The invention relates to a microfluidic platform and methods of using the platform for conducting enzyme assays using a droplet actuator. The enzyme assays of the invention are useful for, among other things, identifying and / or characterizing disorders resulting from conditions in which enzymes are defective or are produced in inappropriate amounts. Enzyme assays of the invention may, for example, be used to detect altered activity of a particular enzyme in a sample, which may serve as an indicator of a particular disease. Altered activity may, for example, be caused by conditions which result in the increased or reduced production of a certain enzyme or its substrate and / or conditions which result in defective enzymes and / or substrates exhibiting increased or decreased effectiveness relative to corresponding normal enzymes and / or substrates.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
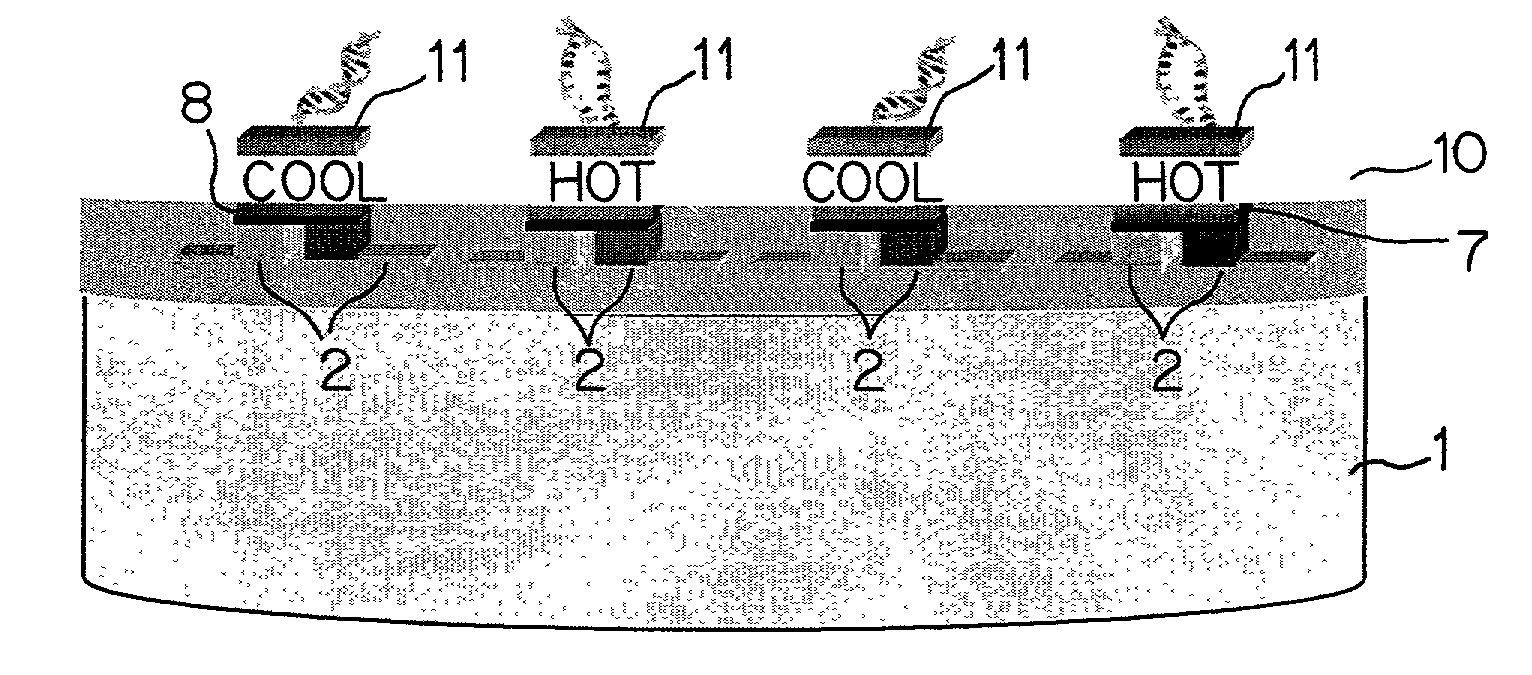
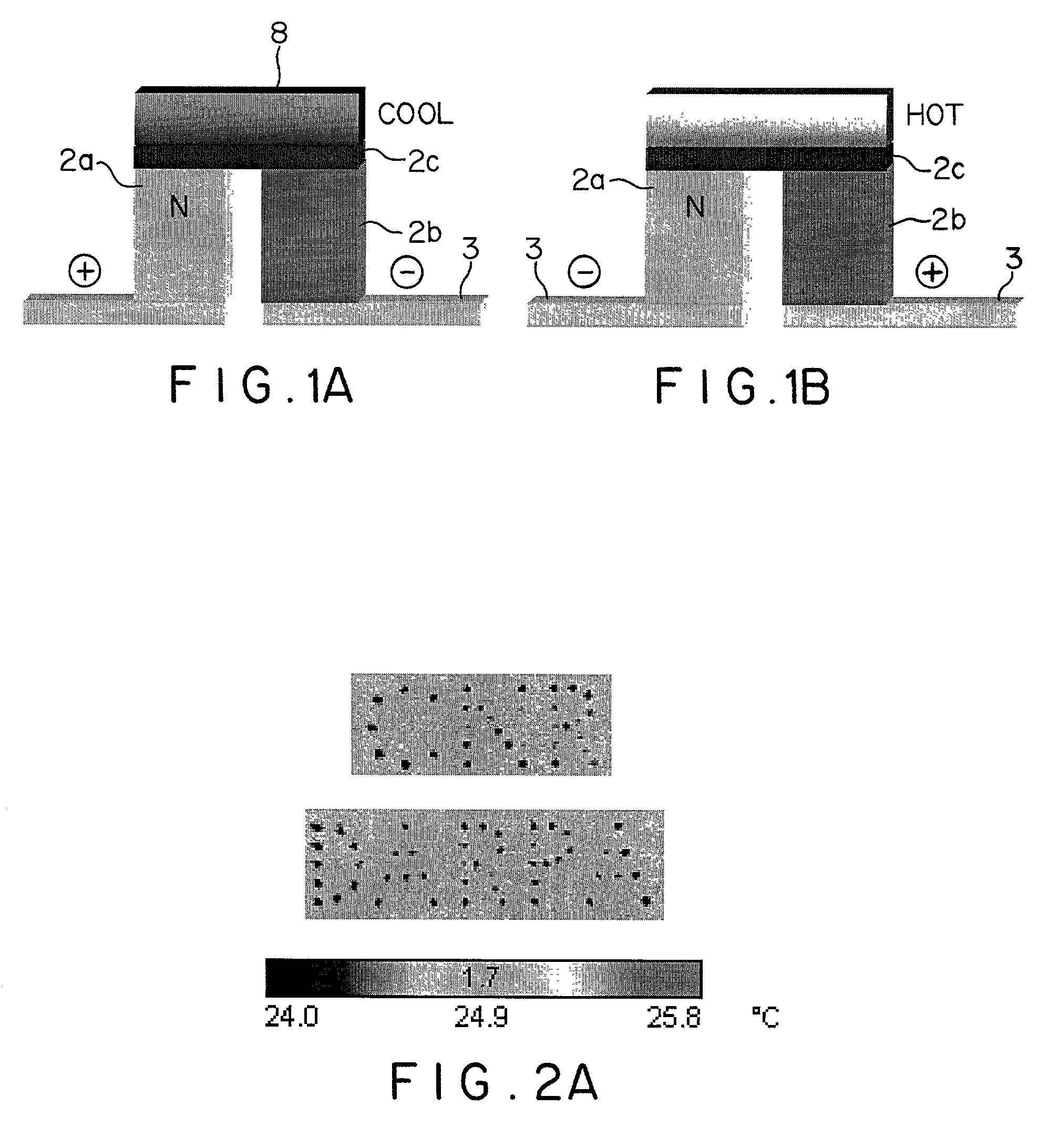
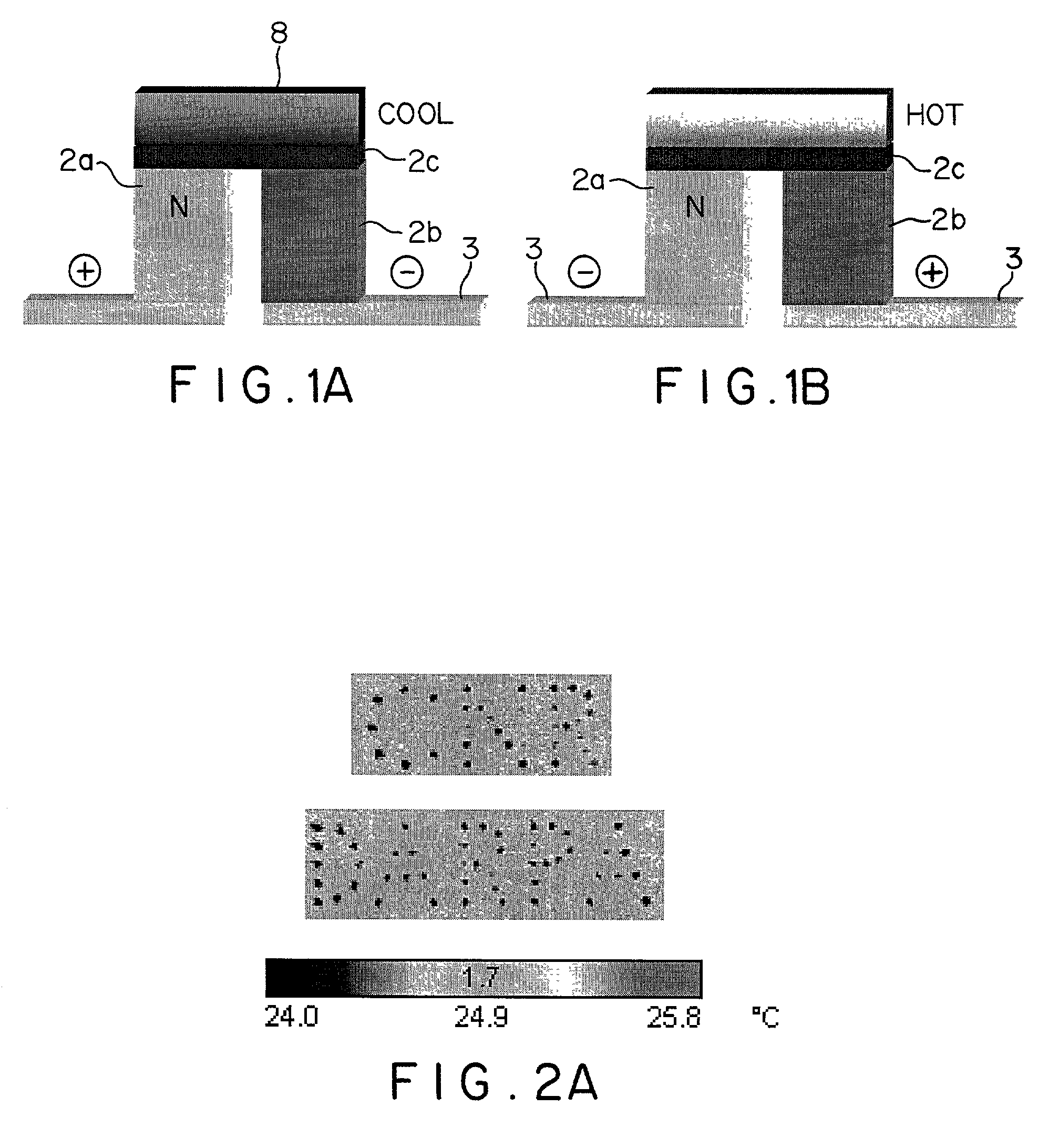
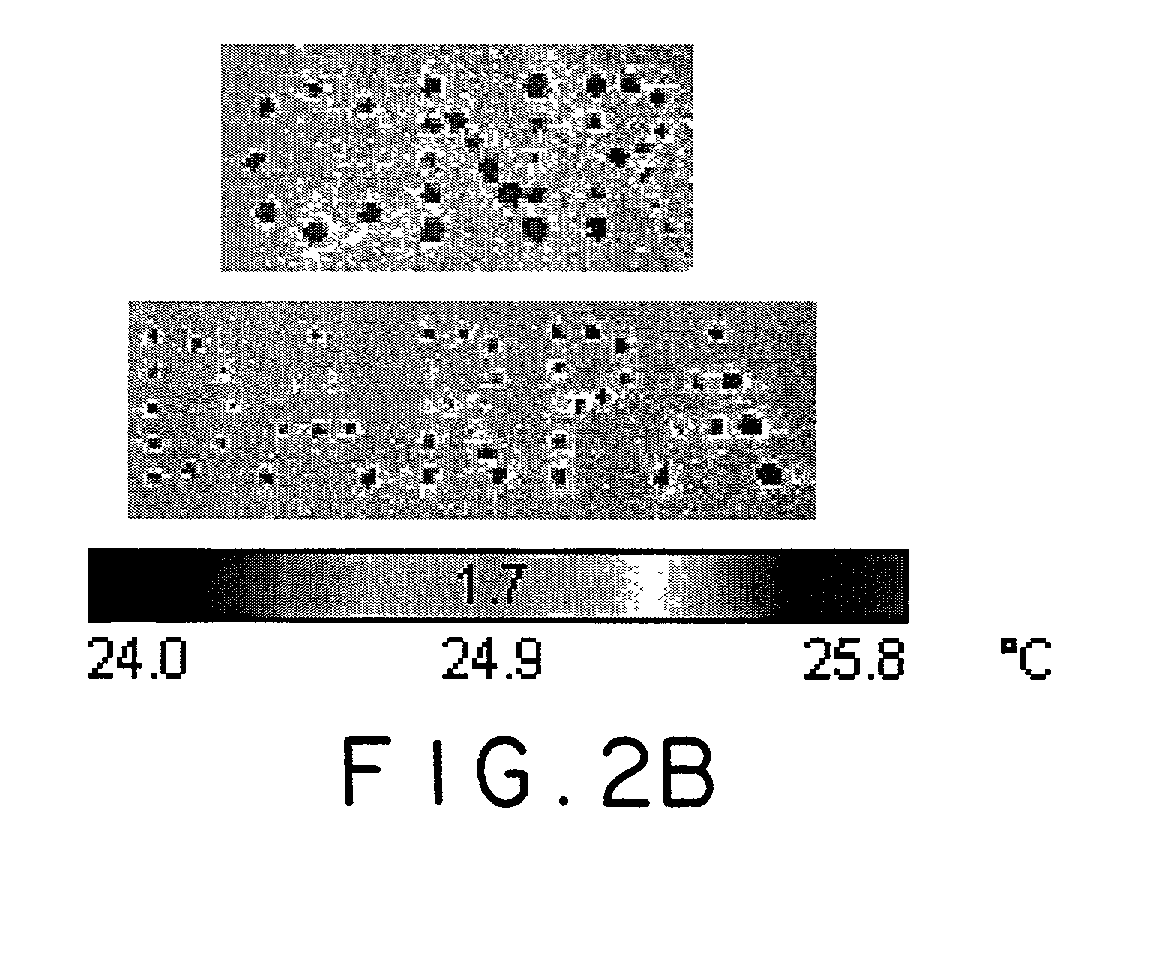
Thin-film thermoelectric cooling and heating devices for DNA genomic and proteomic chips, thermo-optical switching circuits, and IR tags
ActiveUS7164077B2Rapid heating and coolingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanostructure manufactureThermoelectric coolingThermoelectric materials
A thermoelectric cooling and heating device including a substrate, a plurality of thermoelectric elements arranged on one side of the substrate and configured to perform at least one of selective heating and cooling such that each thermoelectric element includes a thermoelectric material, a Peltier contact contacting the thermoelectric material and forming under electrical current flow at least one of a heated junction and a cooled junction, and electrodes configured to provide current through the thermoelectric material and the Peltier contact. As such, the thermoelectric cooling and heating device selectively biases the thermoelectric elements to provide on one side of the thermolectric device a grid of localized heated or cooled junctions.
Owner:LAIRD THERMAL SYST INC
Modular systems and methods for using sample processing devices
InactiveUS6889468B2Rapid and easy removalRapid and easy and replacementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiomedical engineeringModular system
Sample processing systems and methods of using those systems for processing sample materials located in devices that are separate from the system are disclosed. The sample processing systems include a rotating base plate on which the sample processing devices are located during operation of the systems. The systems also include connection apparatus that allow for rapid and easy removal and / or replacement of base plates.
Owner:DIASORIN ITALIA SPA
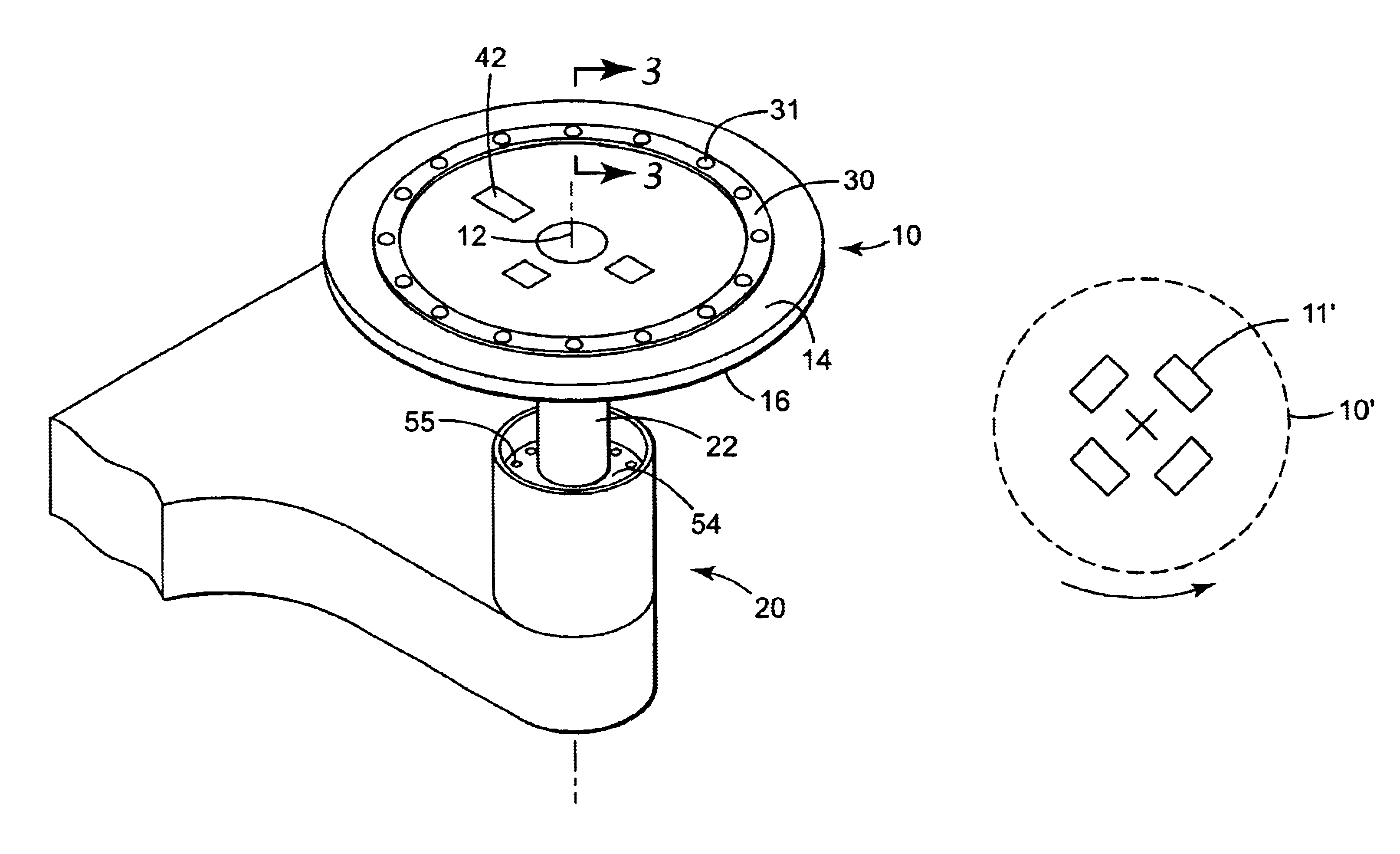
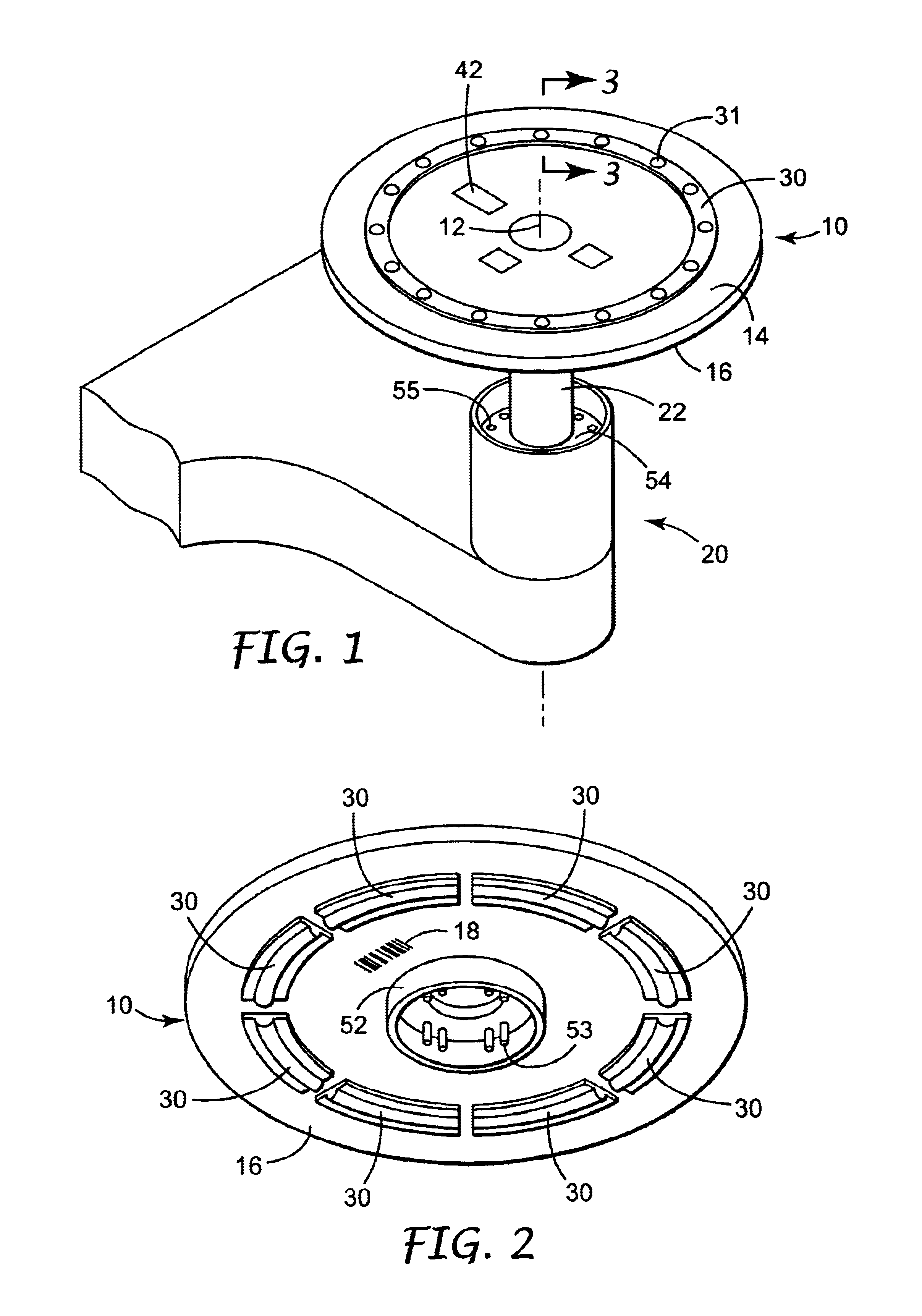
Localized temperature control for spatial arrays of reaction media
ActiveUS20050009070A1Improve uniformityImprove reliabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlEngineering
Individual temperature control in multiple reactions performed simultaneously in a spatial array such as a multi-well plate is achieved by thermoelectric modules with individual control, with each module supplying heat to or drawing heat from a single region within the array, the region containing either a single reaction vessel or a group of reaction vessels.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
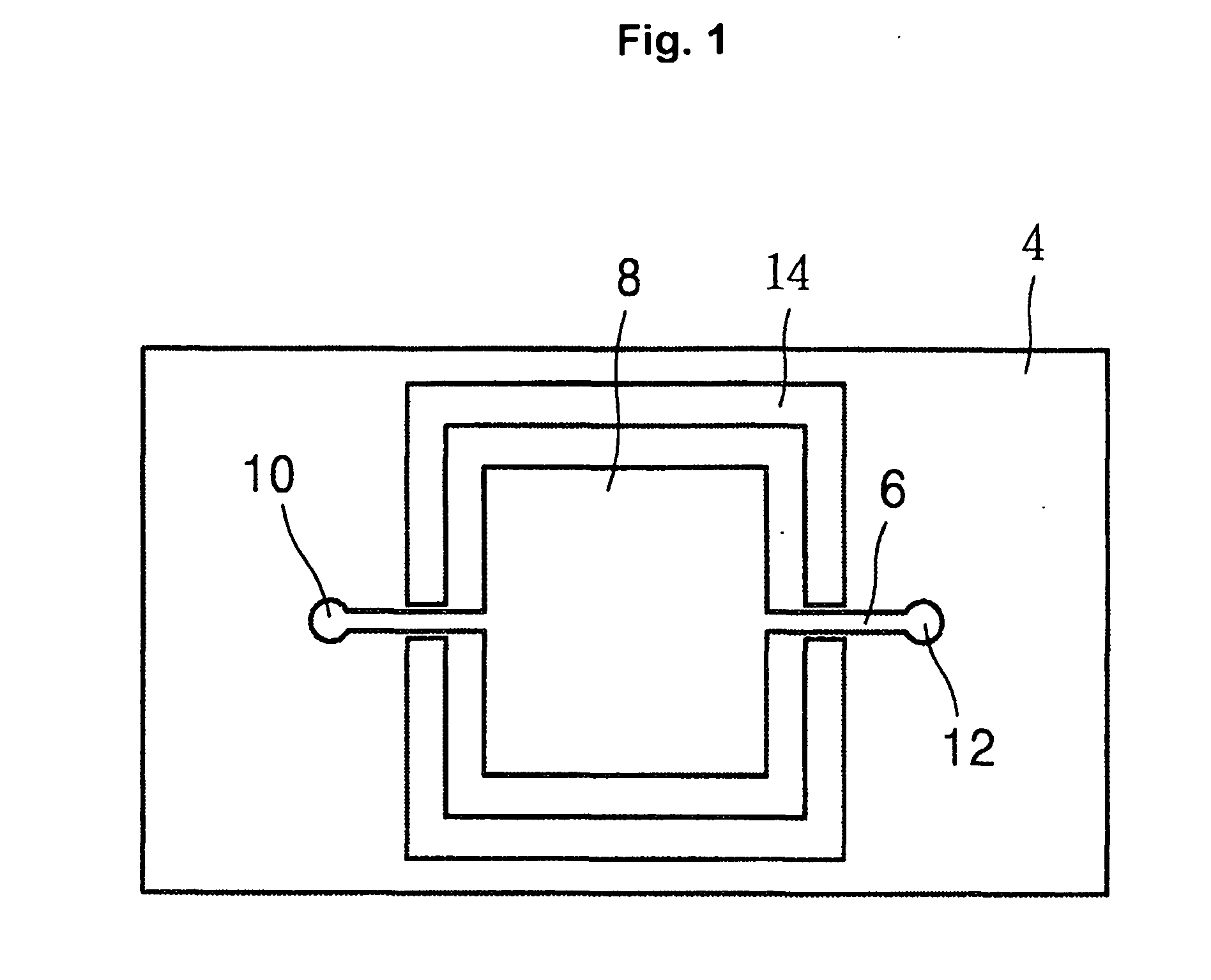
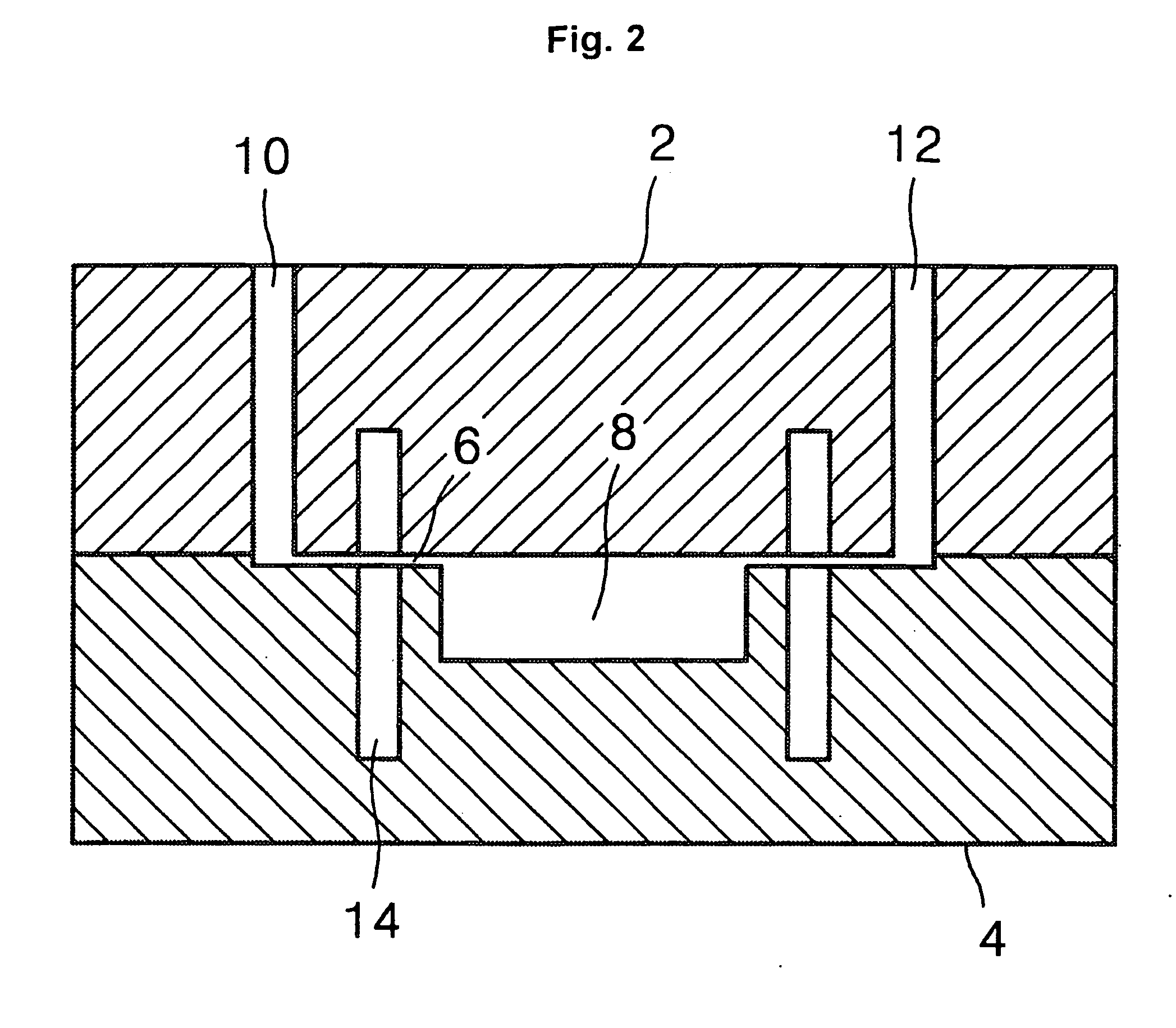
Apparatus for performing biochemical processing using container having wells
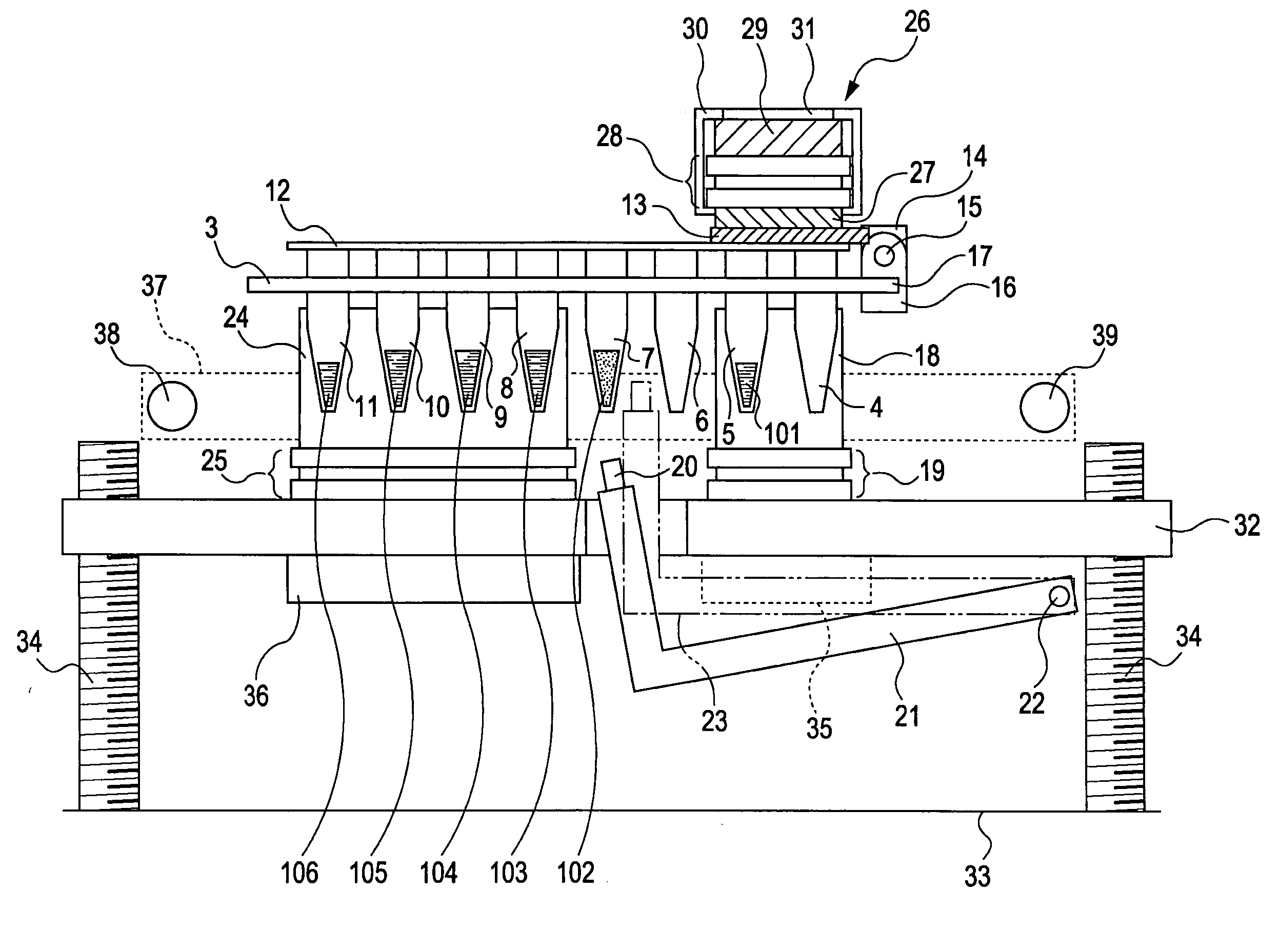
InactiveUS20070077648A1Equipment miniaturizationReduce processing timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiochemical engineeringThermal cycle
A biochemical processing apparatus includes a thermal cycle section, a processing section for performing a processing not requiring heating or cooling, and a cooling section. These sections are arranged in that order and opposed to a container with a plurality of wells.
Owner:CANON KK
Device for carrying out chemical or biological reactions
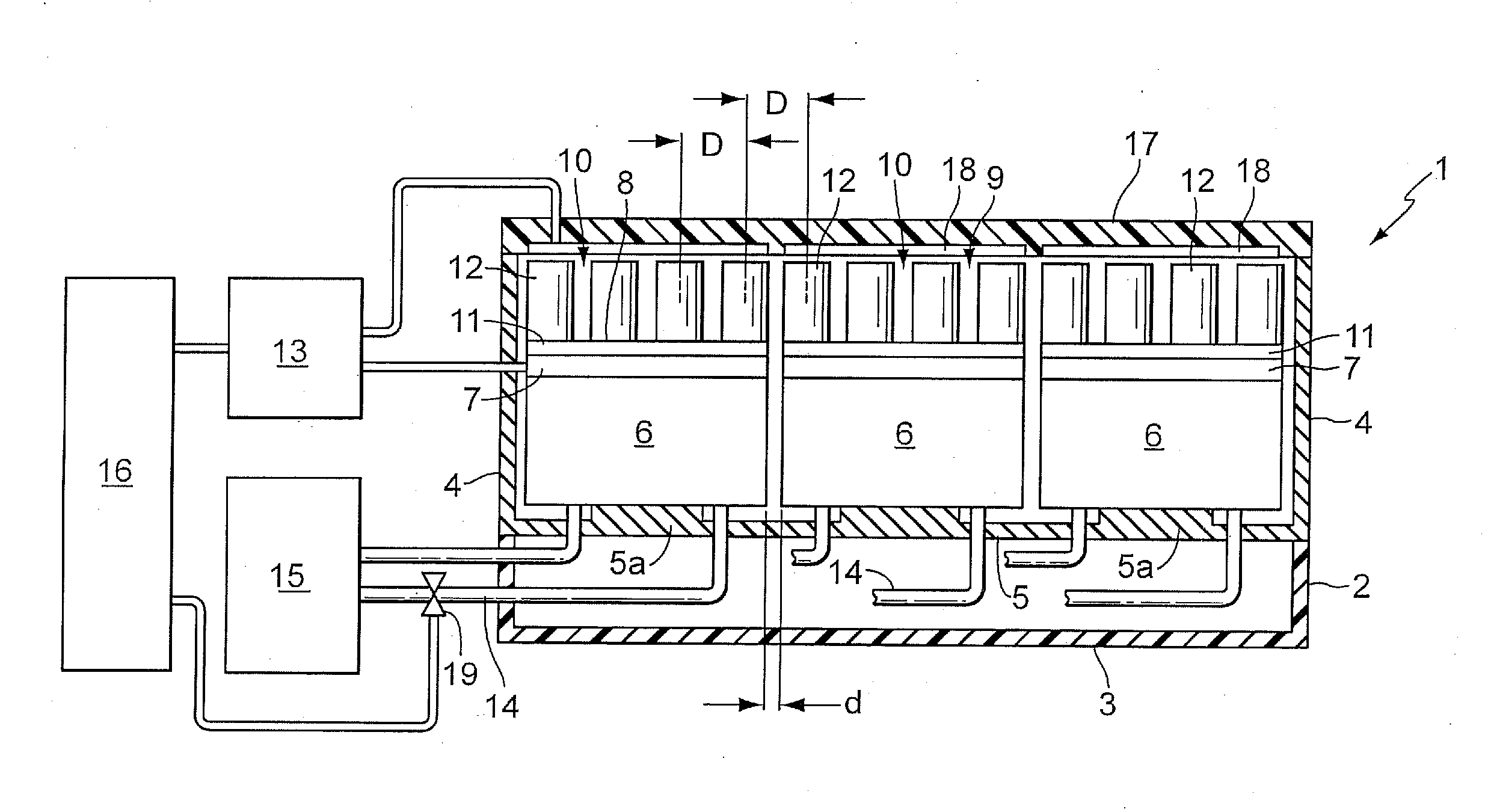
ActiveUS20080274511A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRegular patternMicrotiter plate
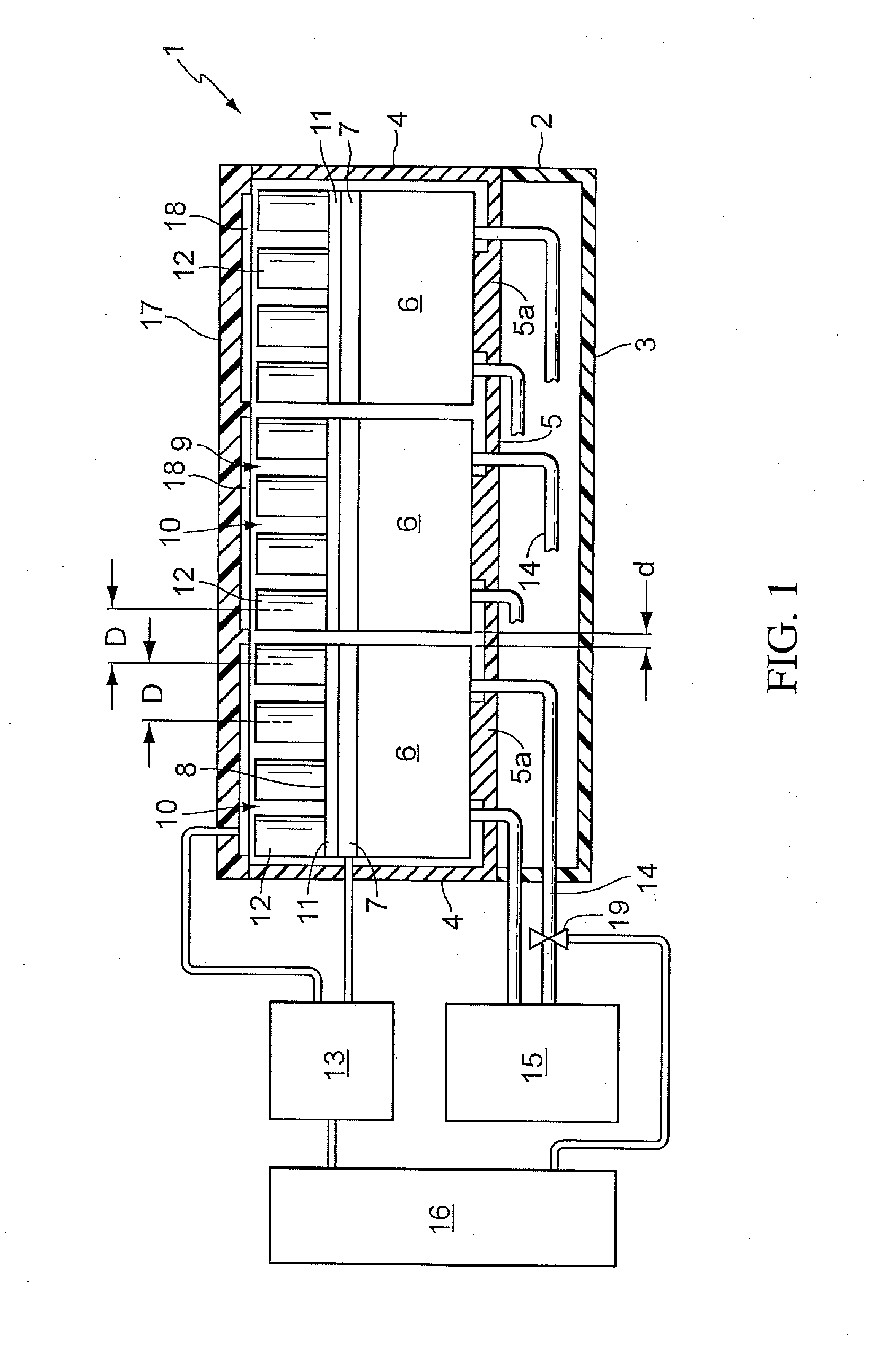
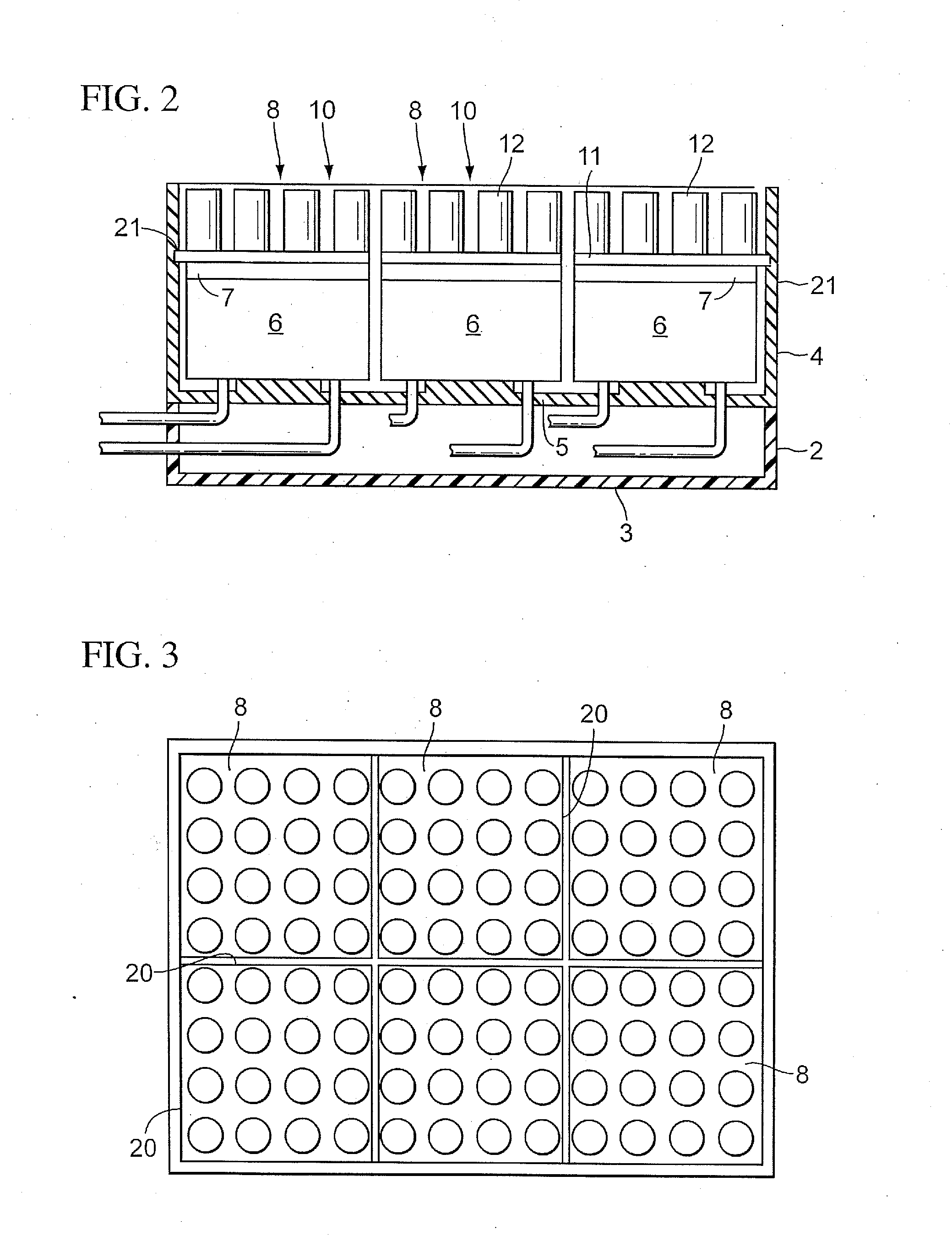
The invention relates to a device for carrying out of chemical or biological reactions with a reaction vessel receiving element for receiving a microtiter plate with several reaction vessels, wherein the reaction vessel receiving element has several recesses arranged in a regular pattern to receive the respective reaction vessels, a heating device for heating the reaction vessel receiving element, and a cooling device for cooling the reaction vessel. The invention is characterized by the fact that the reaction vessel receiving element is divided into several segments. The individual segments are thermally decoupled from one another, and each segment is assigned a heating device which may be actuated independently of the others. By means of the segmentation of the reaction vessel receiving element, it is possible for zones to be set and held at different temperatures. Because the reaction vessel receiving element is suitable for receiving standard microtiter plates, the device according to the invention may be integrated in existing process sequences.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Microfluidic protein crystallography
InactiveUS20050205005A1High throughput screeningImprove throughputValve arrangementsPeptide librariesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsAgent Combination
The use of microfluidic structures enables high throughput screening of protein crystallization. In one embodiment, an integrated combinatoric mixing chip allows for precise metering of reagents to rapidly create a large number of potential crystallization conditions, with possible crystal formations observed on chip. In an alternative embodiment, the microfluidic structures may be utilized to explore phase space conditions of a particular protein crystallizing agent combination, thereby identifying promising conditions and allowing for subsequent focused attempts to obtain crystal growth.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
High throughput screening of crystallization of materials
InactiveUS7052545B2Sequential/parallel process reactionsFrom normal temperature solutionsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsSize determination
High throughput screening of crystallization of a target material is accomplished by simultaneously introducing a solution of the target material into a plurality of chambers of a microfabricated fluidic device. The microfabricated fluidic device is then manipulated to vary the solution condition in the chambers, thereby simultaneously providing a large number of crystallization environments. Control over changed solution conditions may result from a variety of techniques, including but not limited to metering volumes of crystallizing agent into the chamber by volume exclusion, by entrapment of volumes of crystallizing agent determined by the dimensions of the microfabricated structure, or by cross-channel injection of sample and crystallizing agent into an array of junctions defined by intersecting orthogonal flow channels.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Apparatus for high throughput chemical reactions
ActiveUS20080176290A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical reactionReaction temperature
Apparatus, systems, chips, and methods of performing a large number of simultaneous chemical reactions are provided herein. The chips of the invention comprise addressable units that can be addressed according to the temperature of the reaction to be run. The subject apparatus, systems, and chips are particularly suited for performing polymerase chain reactions on thousands of nucleic acid sequences, up to and including sequences of an entire genome of an organism of interest.
Owner:TAKARA BIO USA INC
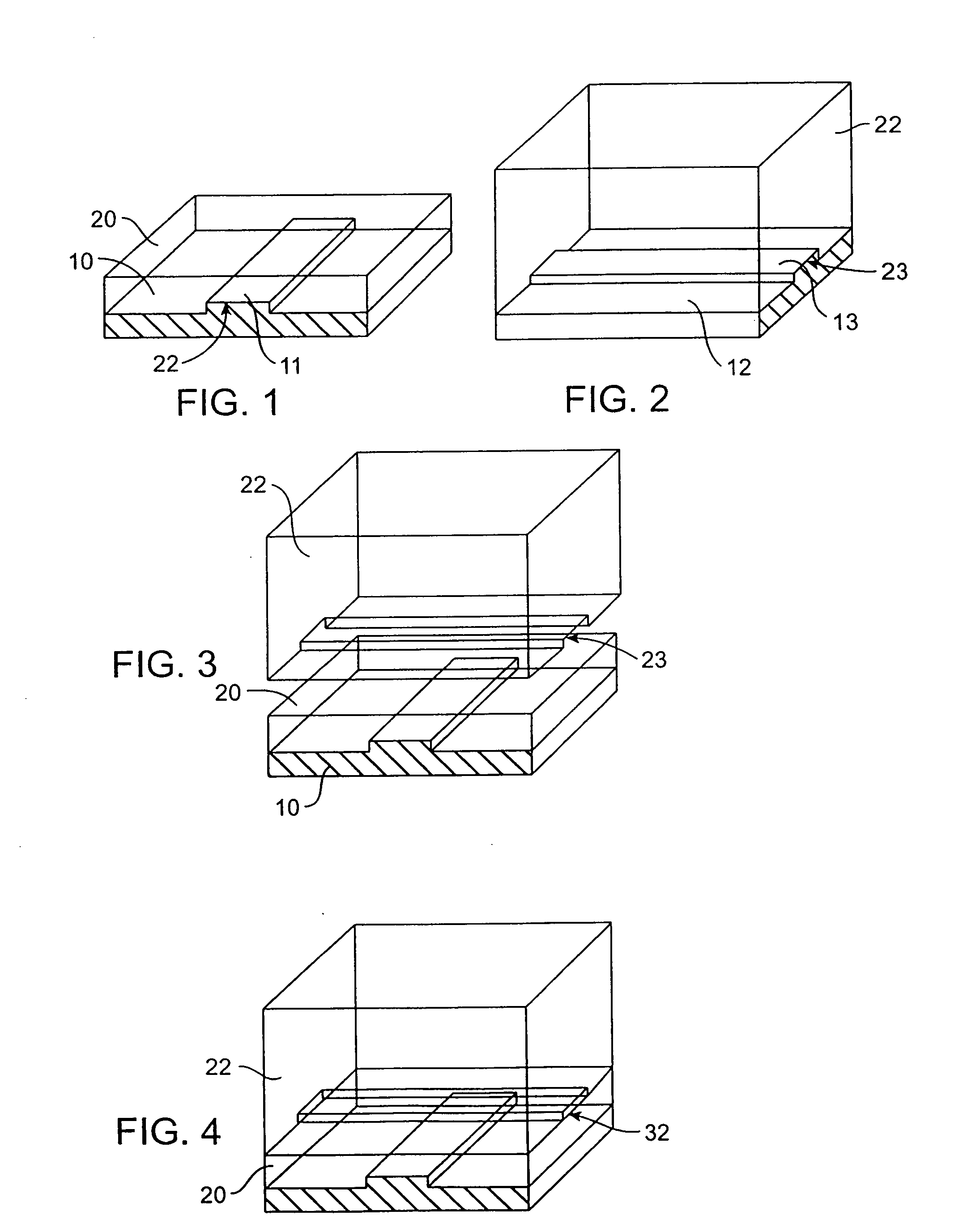
Microfabricated elastomeric valve and pump systems
InactiveUS20080289710A1Increase speedSmall sizeButtonsServomotor componentsElastomerPlanar substrate
A method of fabricating an elastomeric structure, comprising: forming a first elastomeric layer on top of a first micromachined mold, the first micromachined mold having a first raised protrusion which forms a first recess extending along a bottom surface of the first elastomeric layer; forming a second elastomeric layer on top of a second micromachined mold, the second micromachined mold having a second raised protrusion which forms a second recess extending along a bottom surface of the second elastomeric layer; bonding the bottom surface of the second elastomeric layer onto a top surface of the first elastomeric layer such that a control channel forms in the second recess between the first and second elastomeric layers; and positioning the first elastomeric layer on top of a planar substrate such that a flow channel forms in the first recess between the first elastomeric layer and the planar substrate.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method and molecular diagnostic device for detection, analysis and identification of genomic DNA
ActiveUS20070111303A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic DNAMatrix analysis
At least one exemplary embodiment of the invention is directed to a molecular diagnostic device that comprises a cartridge configured to eject samples comprising genomic material into a microfluidic chip that comprises an amplification area, a detection area, and a matrix analysis area.
Owner:CANON USA
Thin-film thermoelectric cooling and heating devices for DNA genomic and proteomic chips, thermo-optical switching circuits, and IR tags
ActiveUS20020174660A1Fast heatingFast coolingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanostructure manufactureThermoelectric coolingThermoelectric materials
A thermoelectric cooling and heating device including a substrate, a plurality of thermoelectric elements arranged on one side of the substrate and configured to perform at least one of selective heating and cooling such that each thermoelectric element includes a thermoelectric material, a Peltier contact contacting the thermoelectric material and forming under electrical current flow at least one of a heated junction and a cooled junction, and electrodes configured to provide current through the thermoelectric material and the Peltier contact. As such, the thermoelectric cooling and heating device selectively biases the thermoelectric elements to provide on one side of the thermolectric device a grid of localized heated or cooled junctions.
Owner:LAIRD THERMAL SYST INC
Microfabricated elastomeric valve and pump systems
InactiveUS20050166980A1Fast formingEasy to manufactureFixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementElastomerPlanar substrate
A method of fabricating an elastomeric structure, comprising: forming a first elastomeric layer on top of a first micromachined mold, the first micromachined mold having a first raised protrusion which forms a first recess extending along a bottom surface of the first elastomeric layer; forming a second elastomeric layer on top of a second micromachined mold, the second micromachined mold having a second raised protrusion which forms a second recess extending along a bottom surface of the second elastomeric layer; bonding the bottom surface of the second elastomeric layer onto a top surface of the first elastomeric layer such that a control channel forms in the second recess between the first and second elastomeric layers; and positioning the first elastomeric layer on top of a planar substrate such that a flow channel forms in the first recess between the first elastomeric layer and the planar substrate.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
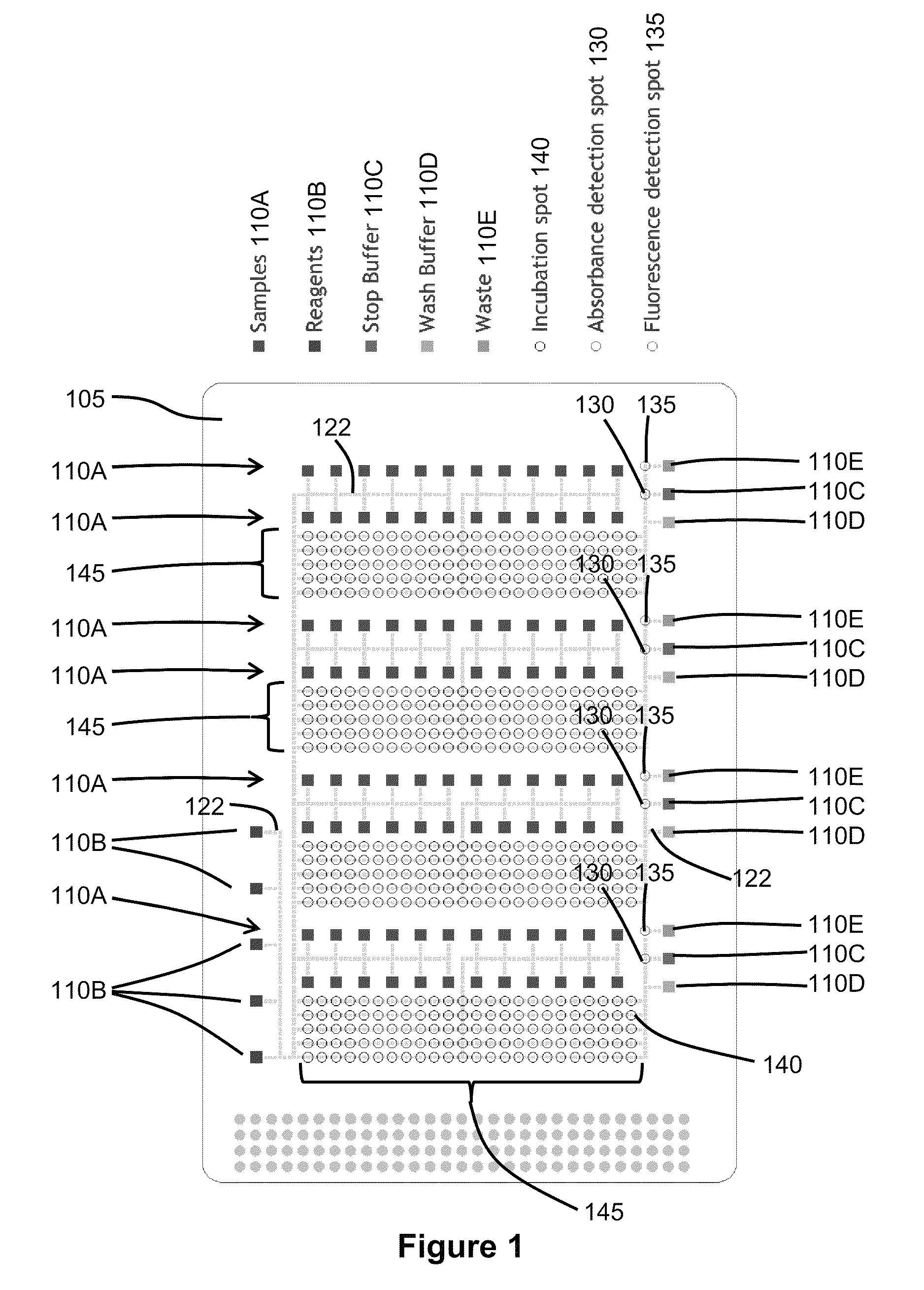
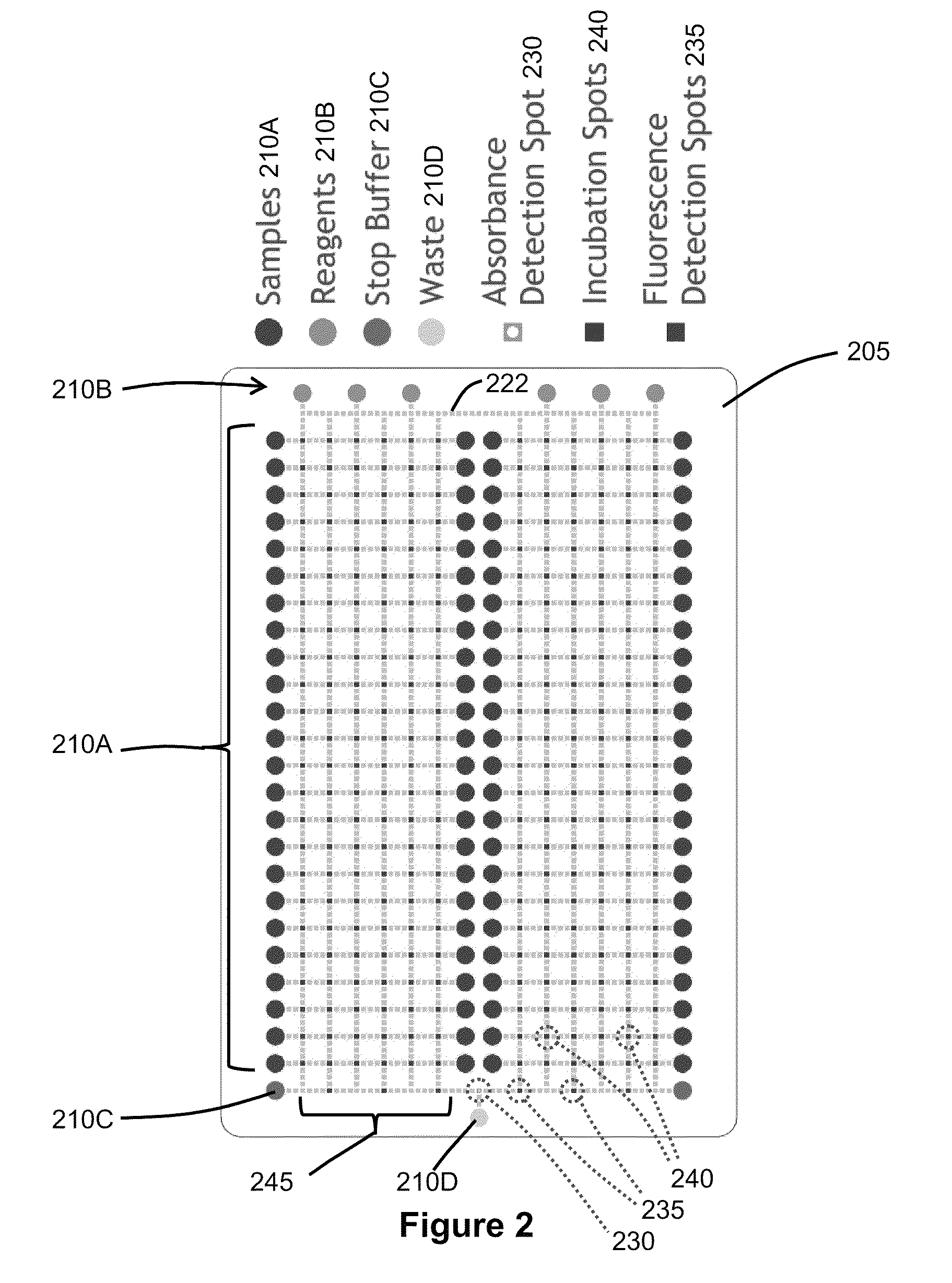
Droplet Operations Platform
ActiveUS20130217103A1Quick captureFast concentrationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringActuator
The invention relates to a droplet actuator device and methods for integrated sample preparation and analysis of a biological sample. A droplet actuator device is provided for conducting droplet operations. The droplet actuator device may include a bottom substrate and a top substrate separated from each other to form a gap therebetween; an arrangement of droplet operations electrodes arranged on one or both of the bottom and / or top substrates for conducting droplet operations thereon; a reagent storage layer comprising one or more compartments bound to the top substrate; and one or more openings arranged to provide a fluidic path from the one or more compartments into the gap, upon breach of a breachable seal separating the one or more compartments and openings.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
Microfluidic free interface diffusion techniques
InactiveUS20080182273A1Reduce concentrationFrom normal temperature solutionsFlow mixersFree interfaceCompetitive binding
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Device for thermal cycling
InactiveUS6990290B2Delayed reaction timeVolume of sample can be handledBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsThermodynamicsEngineering
An apparatus for performing temperature cycling, comprising a micro channel reactor structure (46, 48, 50), and having a heating structure (b1, b2, B1, B2) defining a desired temperature profile. A preferred embodiment of a heating element structure comprises a pattern of areas of a material capable of providing heat when energized, disposed over said micro channel reactor structure.
Owner:GYROS
Method and apparatus for effecting rapid thermal cycling of samples in microtiter plate size
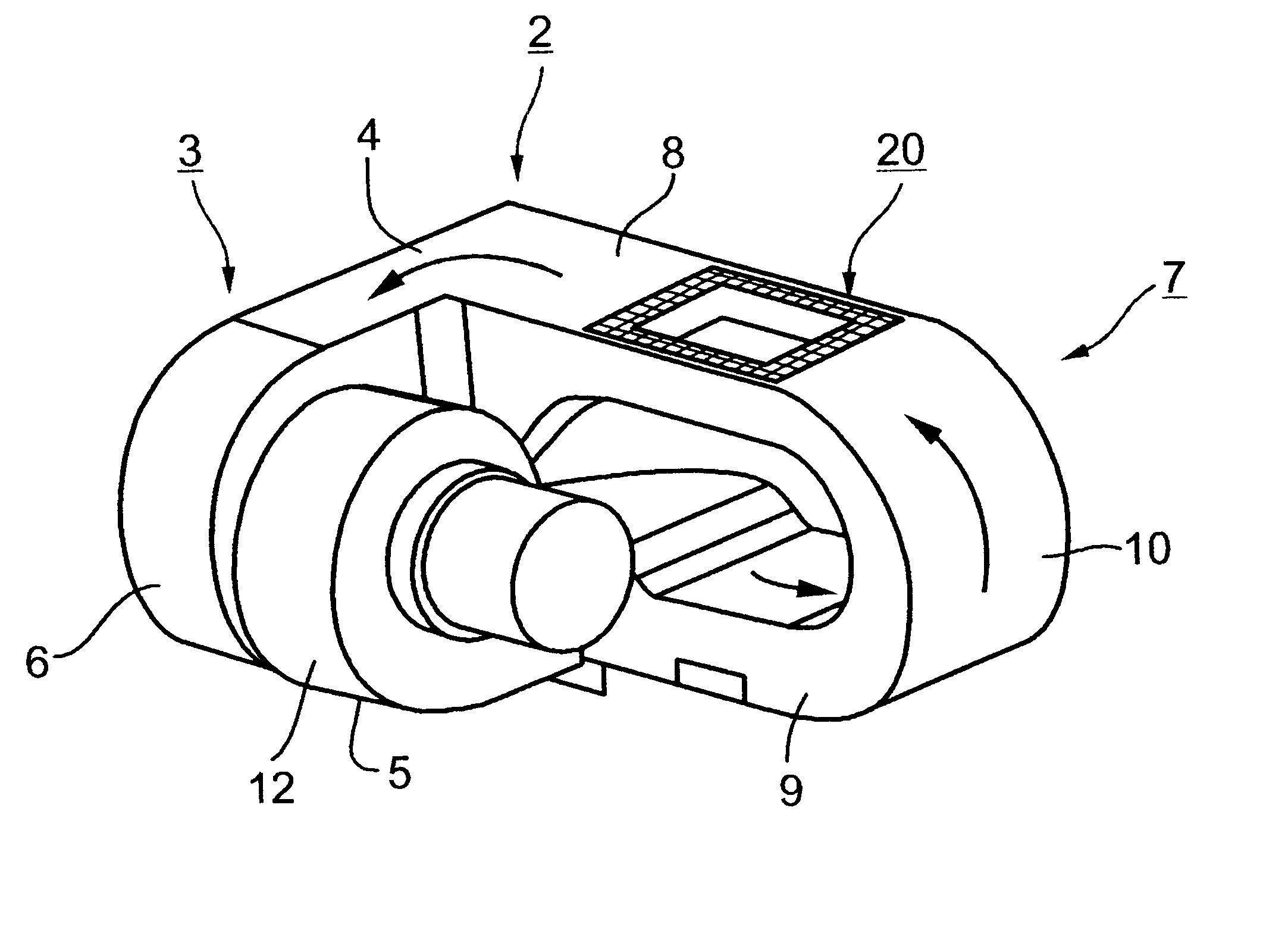
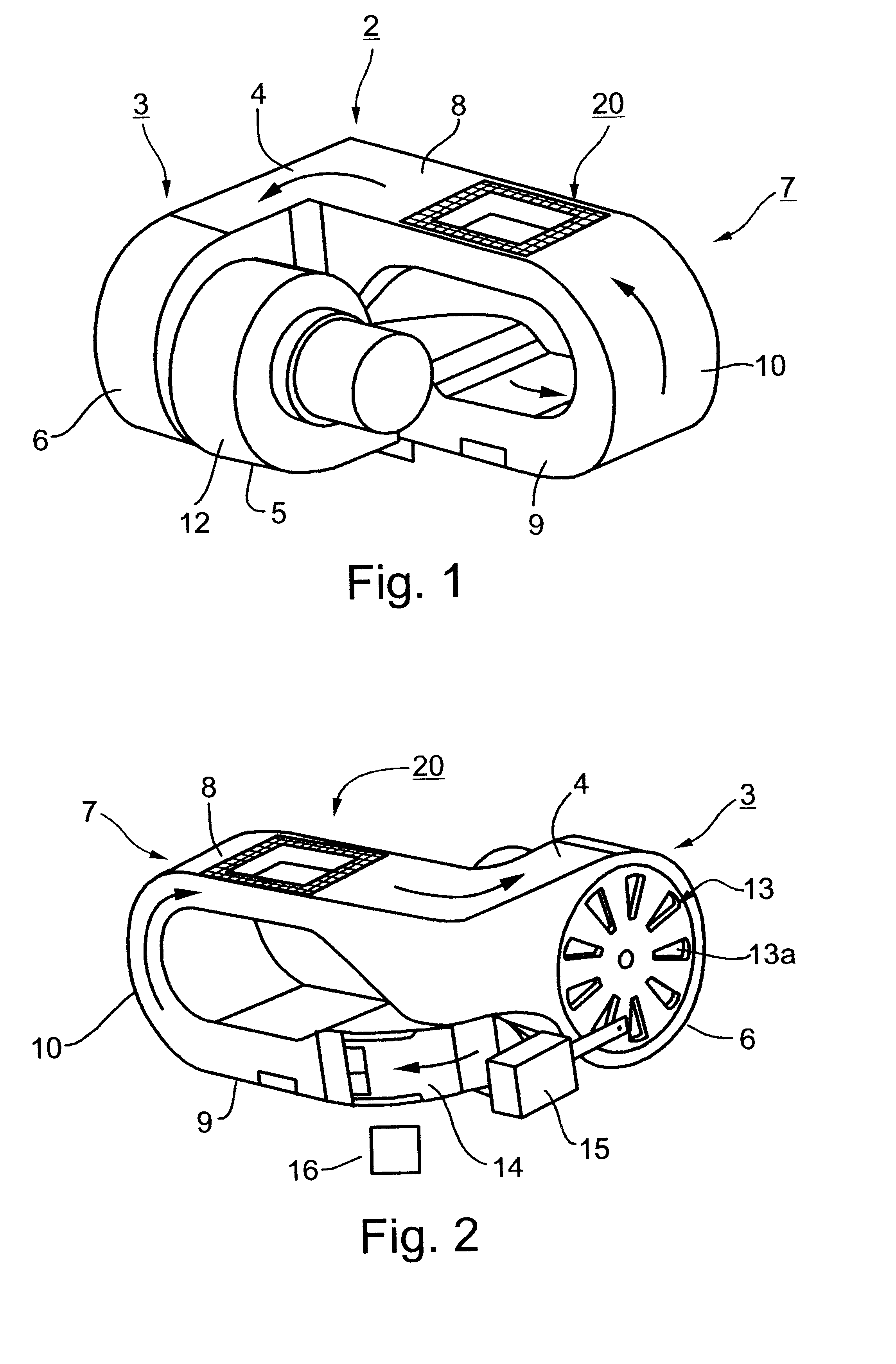
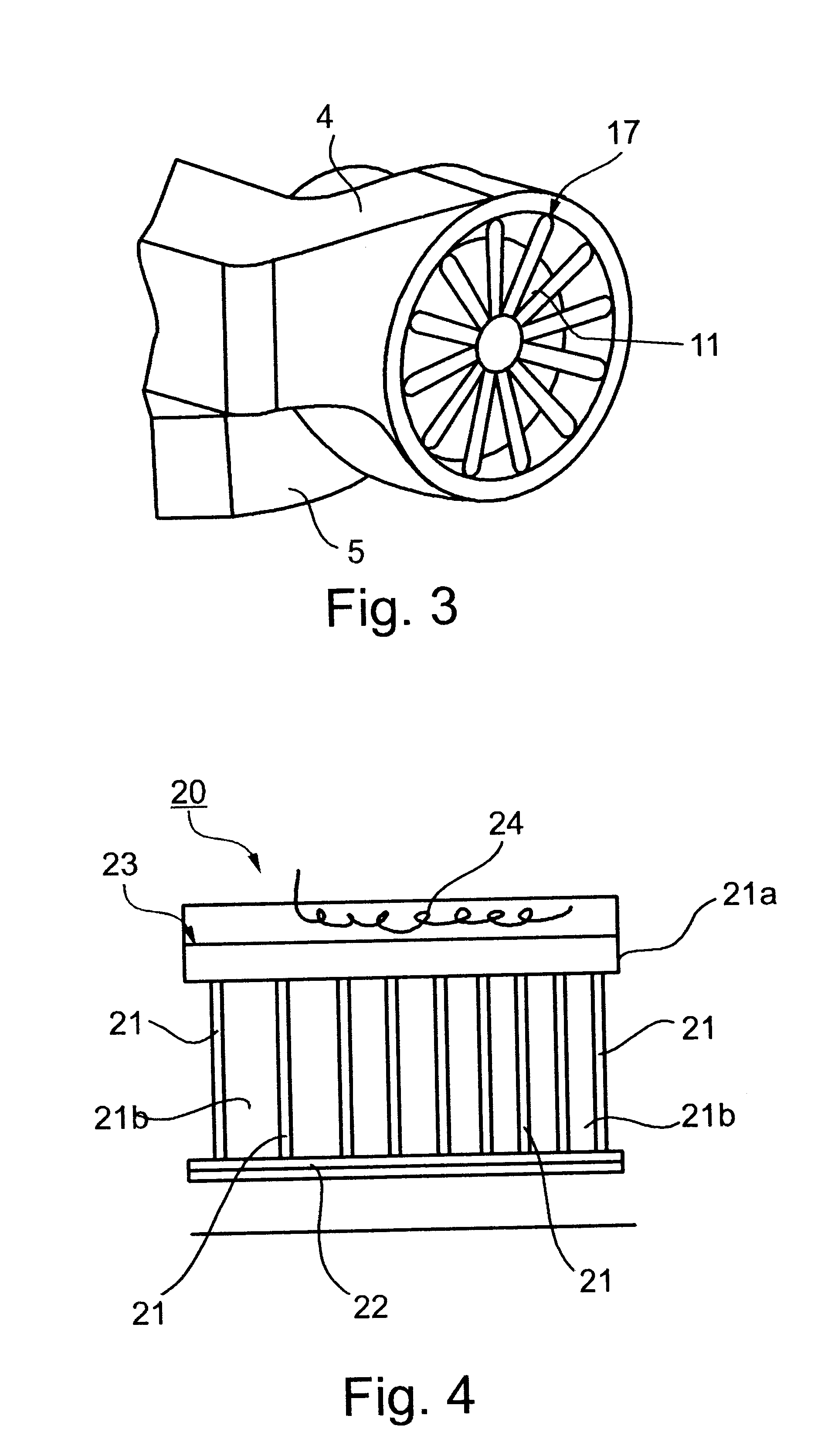
InactiveUS6482615B2Heating fastUniform heating and/or cooling of the samplesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrotiter plateClosed loop
A method and apparatus for effecting rapid thermal cycling of samples, by producing a high-velocity air flow through a closed loop flow path, and energizing an electrical heater within the closed loop flow path to heat the air flowing therethrough to a desired temperature. A sample holder is introduced into the closed loop flow path for exposing the sample holder to the high-velocity heated air flowing therethrough for rapidly heating the sample. The sample is rapidly cooled to a desired temperature by de-energizing the electrical heater, and opening an air outlet from the closed loop flow path, while continuing to produce the high-velocity air flow therethrough.
Owner:INTEGRATED GENETIC DEVICES
Apparatus and method for amplifying a polynucleotide
InactiveUS20050112754A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringPolynucleotide
The present invention provides an apparatus for amplifying a polynucleotide, comprising a substrate, a microflow channel system disposed in the substrate and comprising a sample inlet port, a sample flow channel extending from the sample inlet port, and a polynucleotide polymerization reaction chamber in fluid communication with the sample flow channel, a first insulation groove formed around the reaction chamber, and a means for regulating a temperature of the reaction chamber. Accordingly, a multiple chamber device for amplifying a polynucleotide, comprising multiple polymerization reaction chambers formed in a substrate can be manufactured.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High throughput screening of crystallization of materials
InactiveUS7195670B2From normal temperature solutionsFixed microstructural devicesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsSize determination
High throughput screening of crystallization of a target material is accomplished by simultaneously introducing a solution of the target material into a plurality of chambers of a microfabricated fluidic device. The microfabricated fluidic device is then manipulated to vary the solution condition in the chambers, thereby simultaneously providing a large number of crystallization environments. Control over changed solution conditions may result from a variety of techniques, including but not limited to metering volumes of crystallizing agent into the chamber by volume exclusion, by entrapment of volumes of crystallizing agent determined by the dimensions of the microfabricated structure, or by cross-channel injection of sample and crystallizing agent into an array of junctions defined by intersecting orthogonal flow channels.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Chemical processing microsystems comprising high-temperature parallel flow microreactors
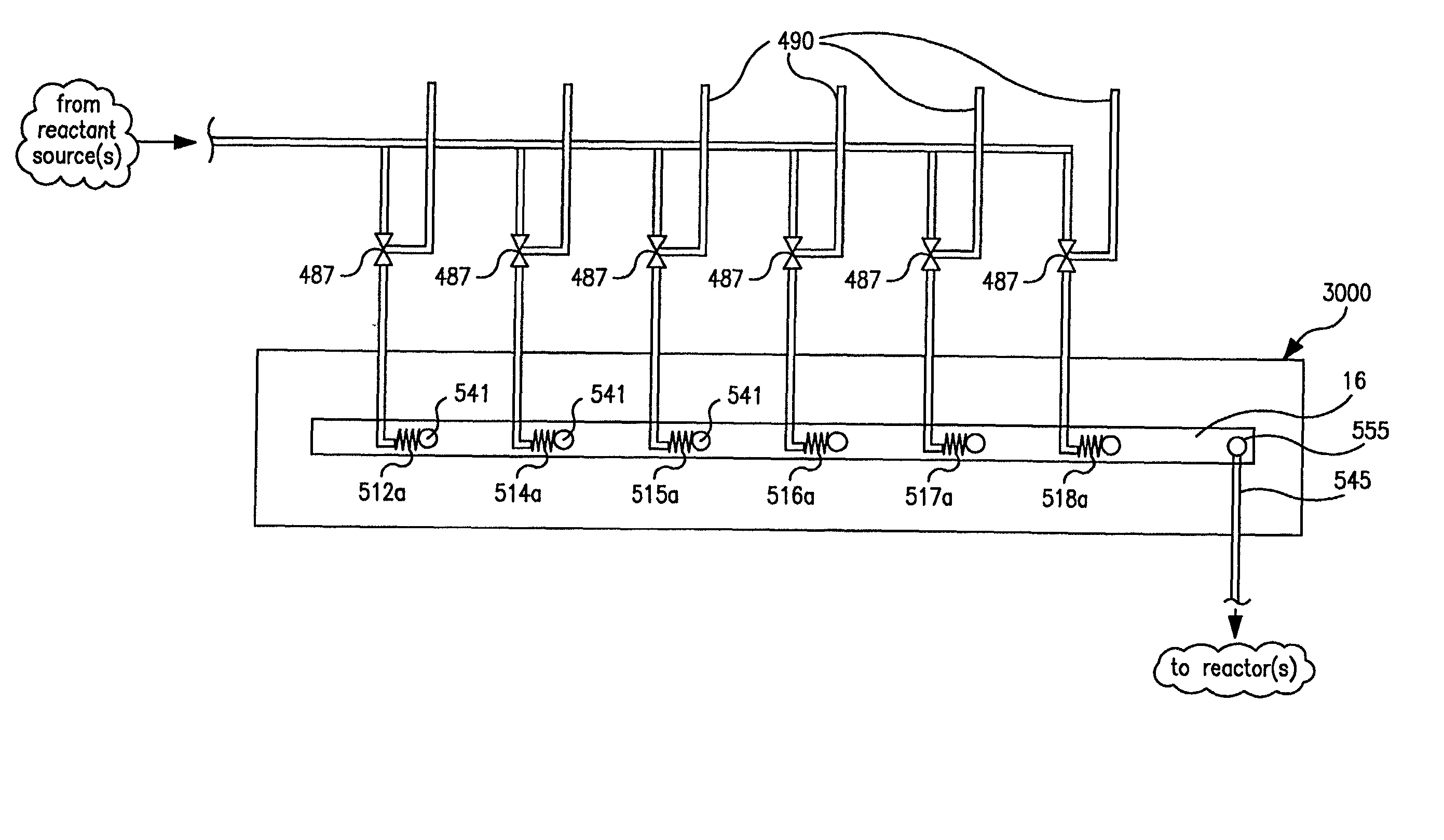
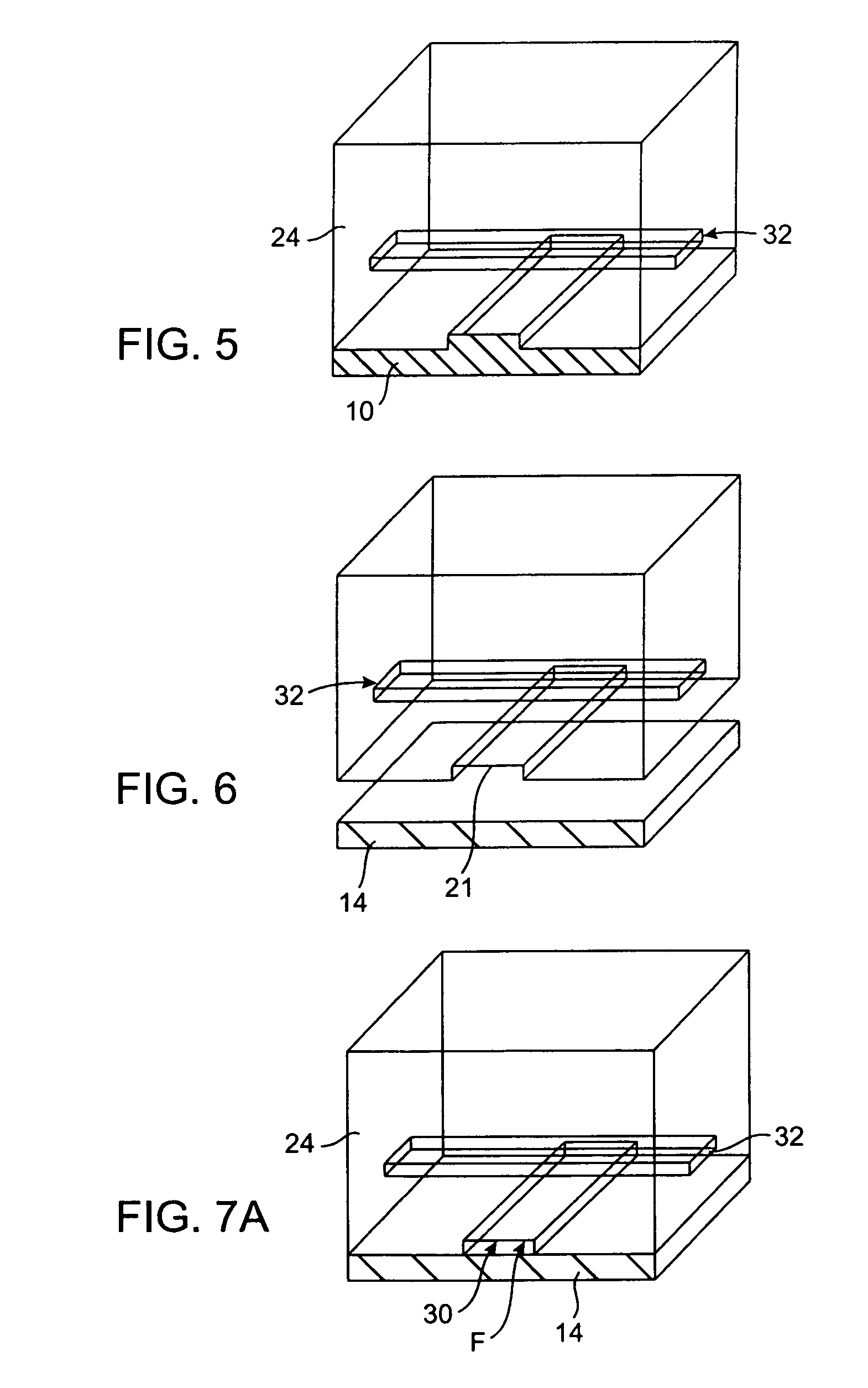
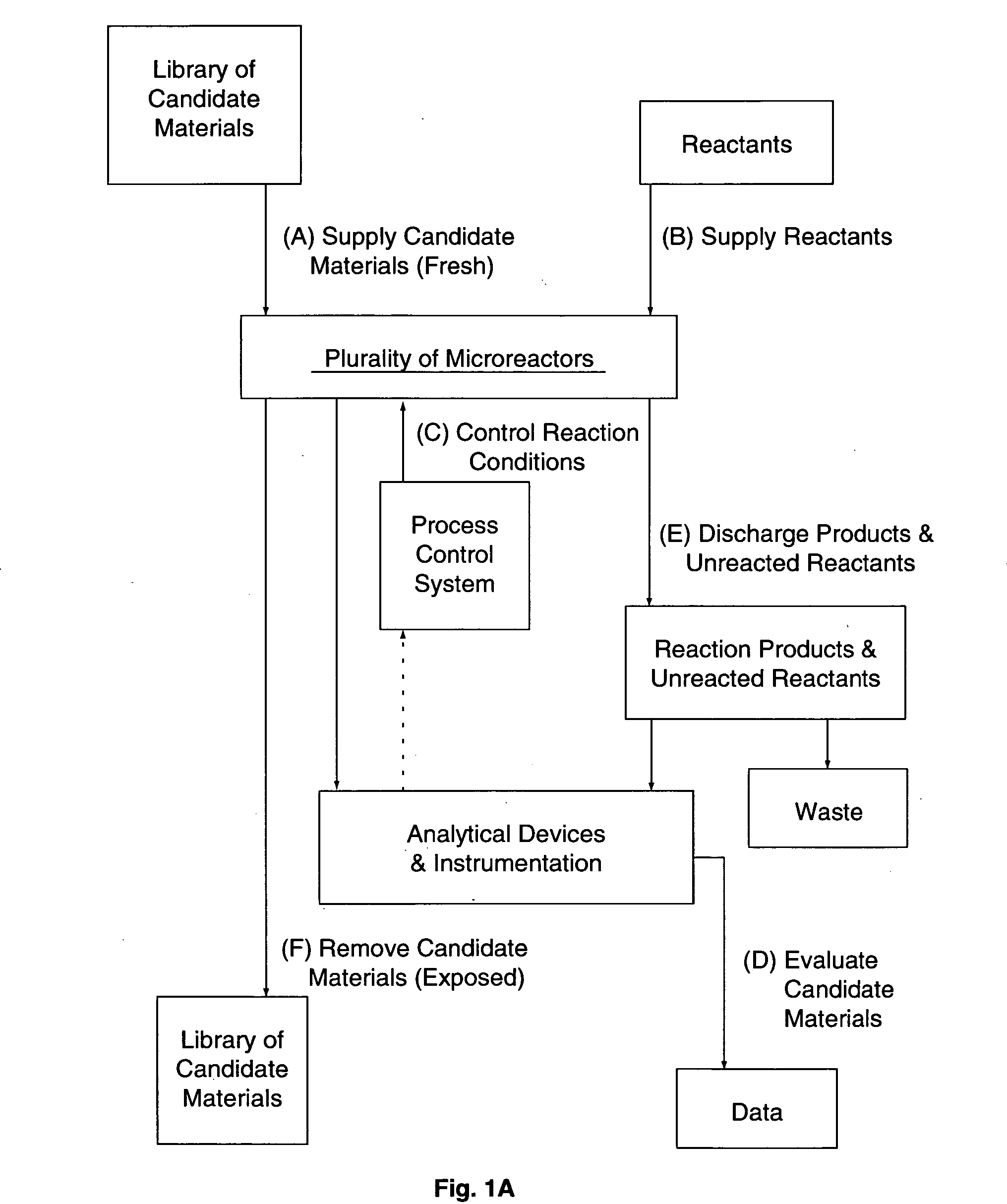
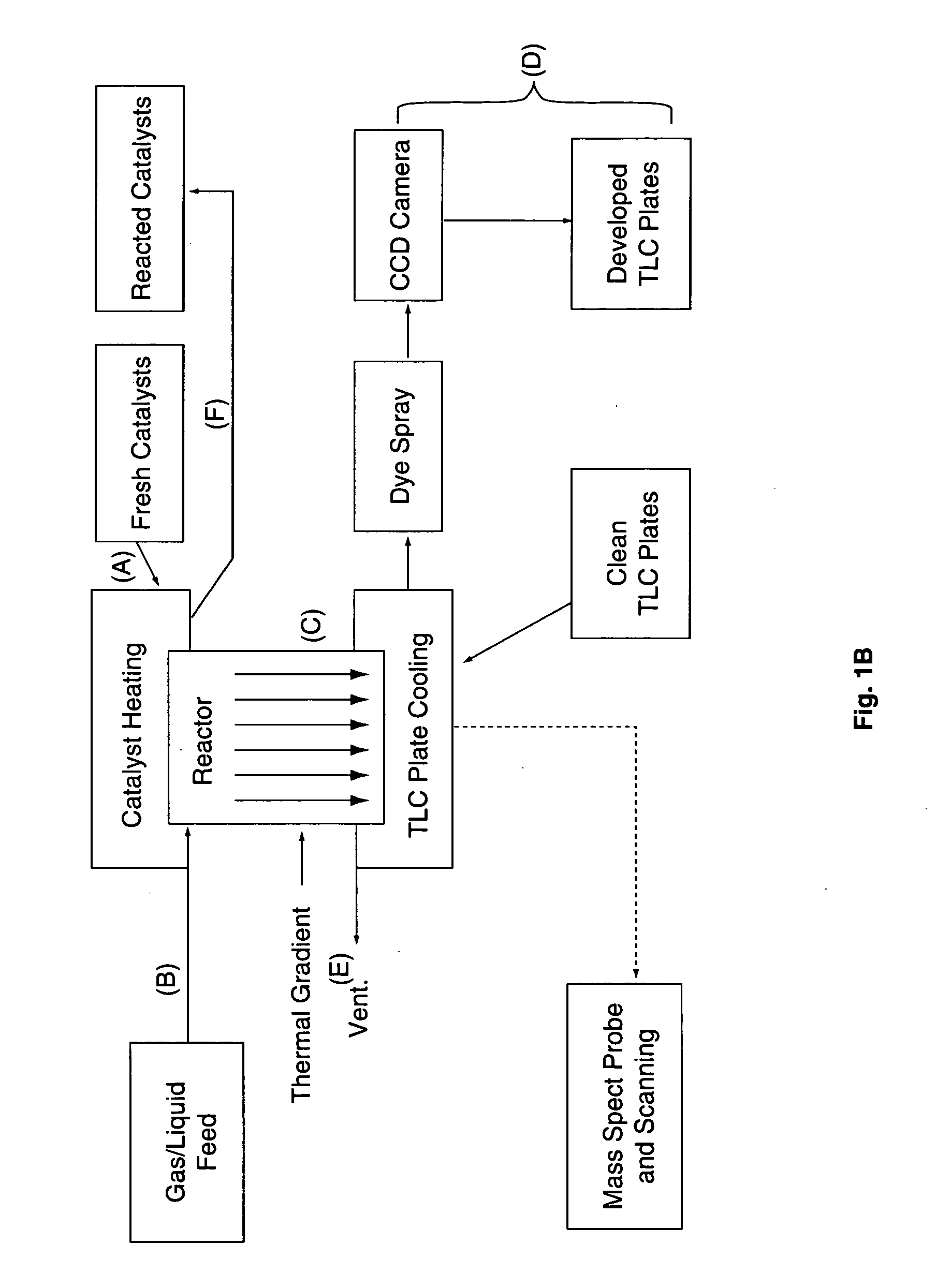
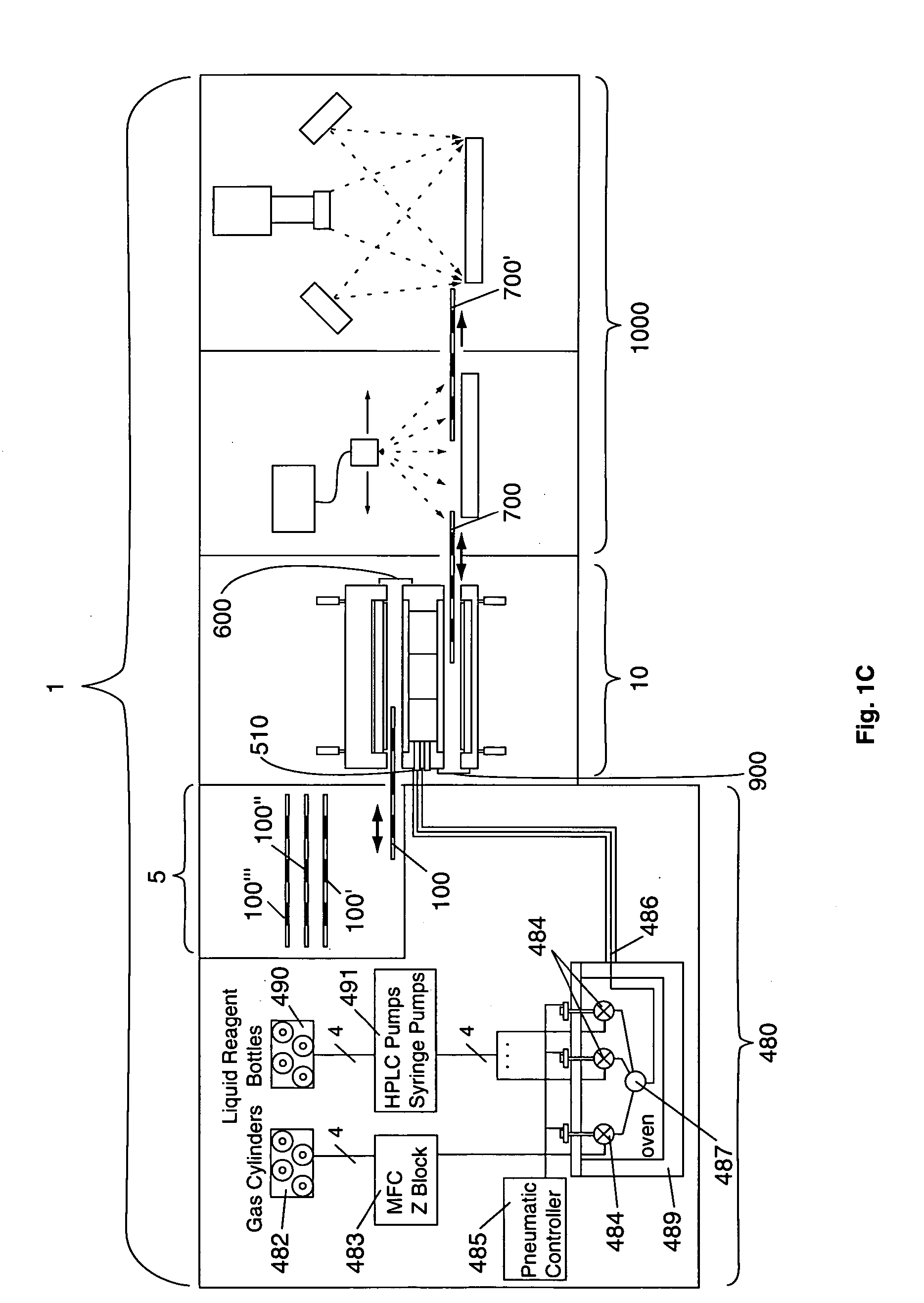
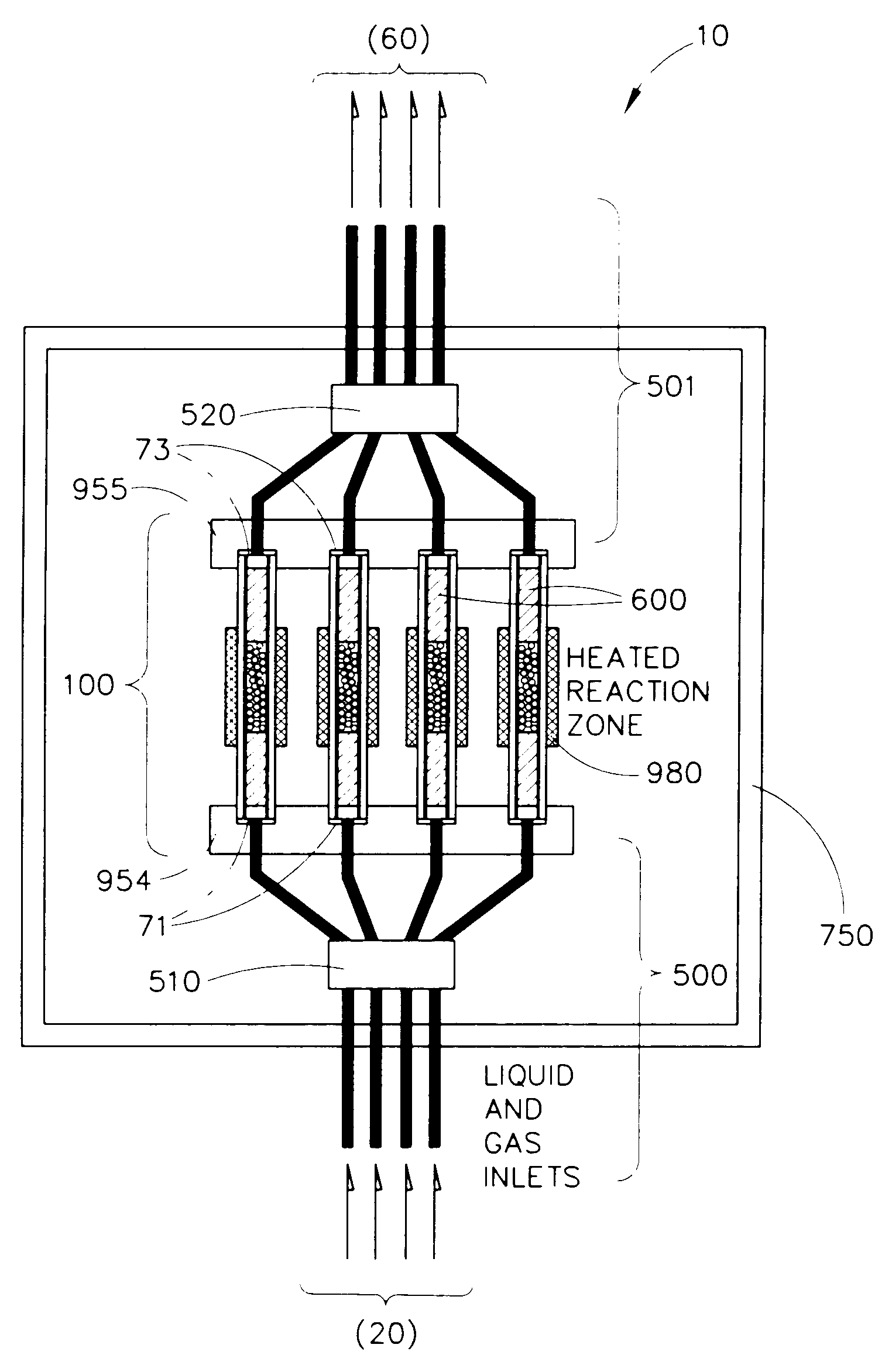
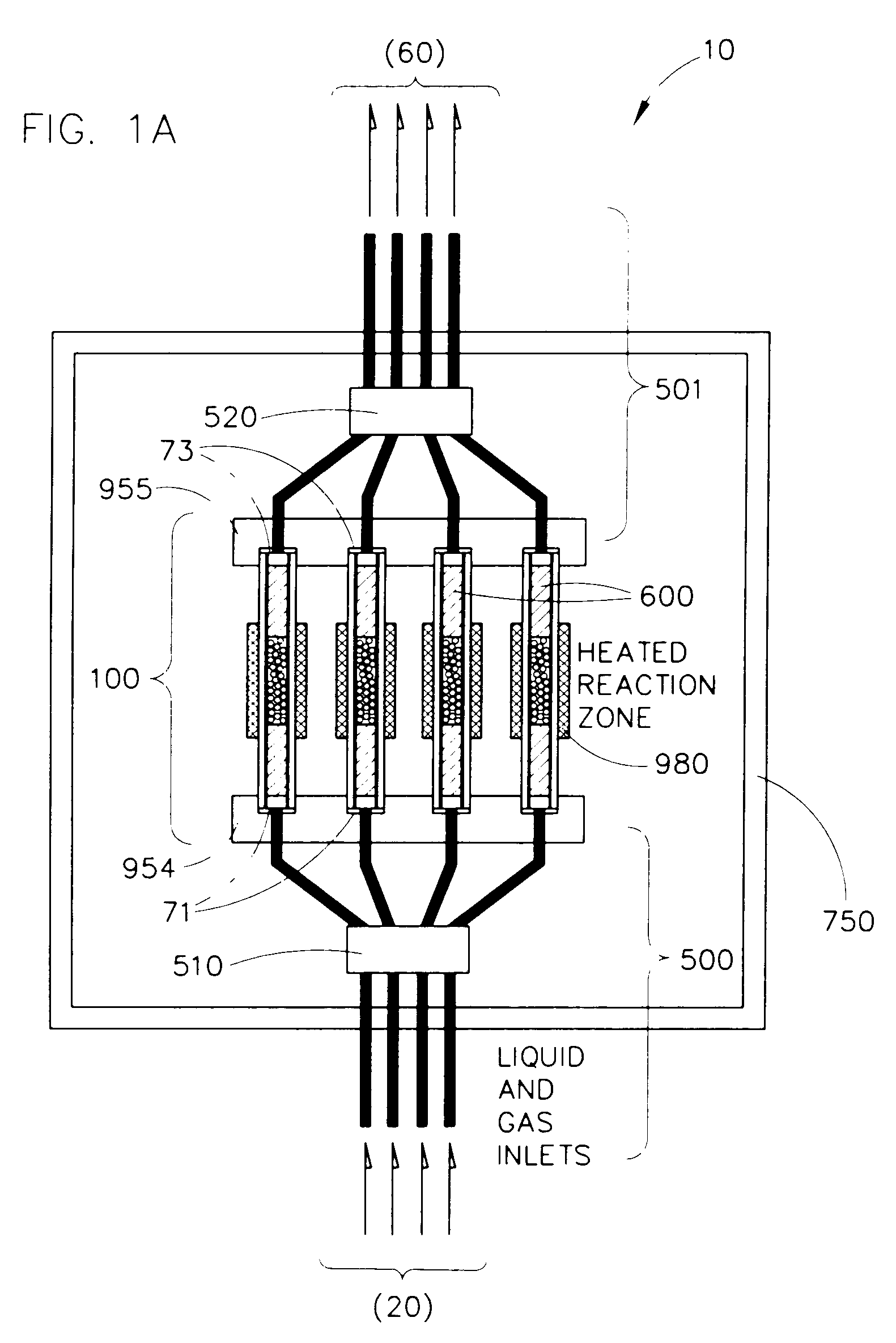
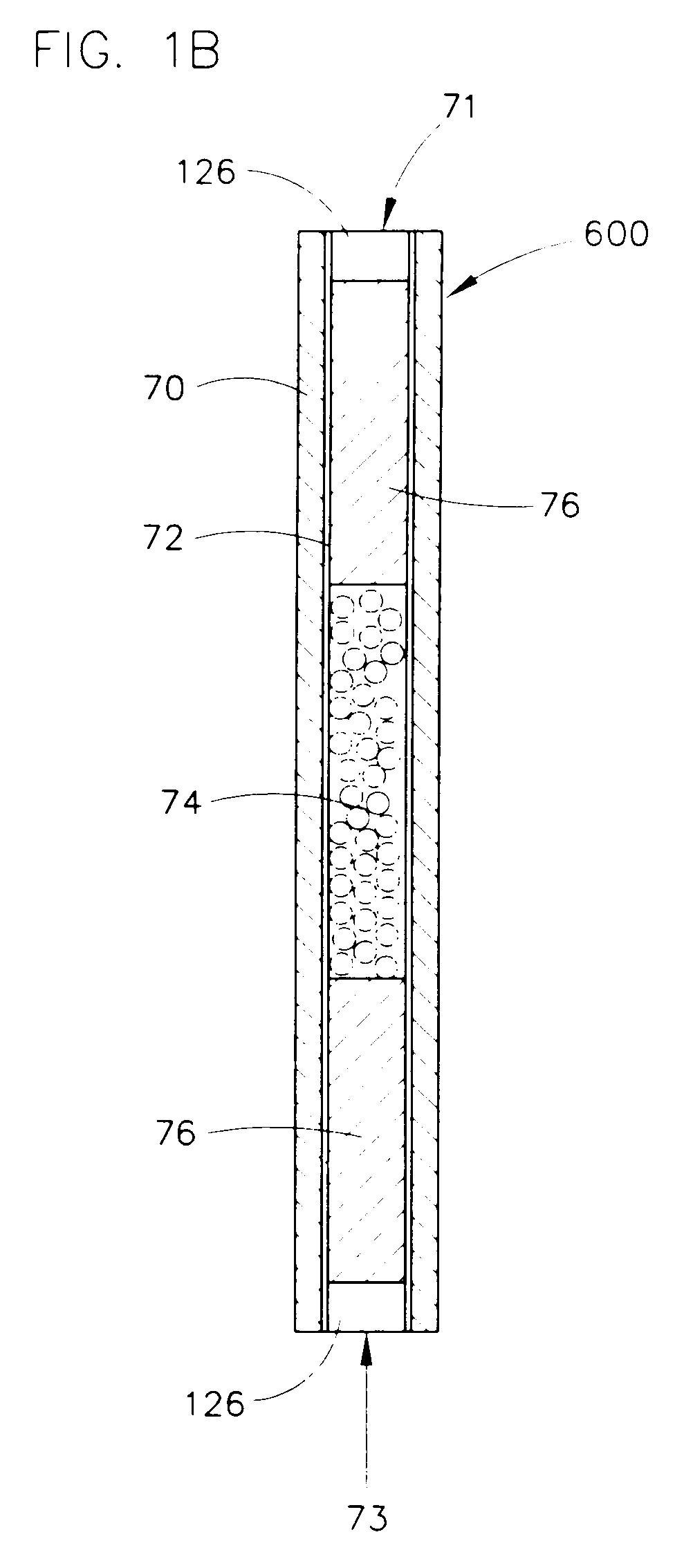
InactiveUS20050009175A1Large degree of analytical flexibilityReduce manufacturing costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsChemical treatmentMicroreactor
A chemical processing microsystem useful for identifying and optimizing materials (e.g., catalysts) that enhance chemical processes or for characterizing and / or optimizing chemical processes is disclosed. The chemical processing microsystem comprises a plurality of microreactors 600 and, in a preferred embodiment, a plurality of microseparators 900 integral with the chemical processing microsystem 10. The microreactors 600 are preferably diffusion-mixed microreactors formed in a plurality of laminae that include a modular, interchangeable candidate-material array 100. The material array 100 comprises a plurality of different candidate materials (e.g., catalysts), preferably arranged at separate, individually addressable portions of a substrate (e.g., wafer). The microseparators 900 are similarly formed in a plurality of laminae that include a modular, interchangeable adsorbent array 700. The adsorbent array 700 comprises one or more adsorbents, preferably arranged at separate, individually addressable portions of a substrate to spatially correspond to the plurality of different candidate materials. Modular microfluidic distribution systems are also disclosed. The chemical processing microsystem can be integrated into a material evaluation system that enables a comprehensive combinatorial material science research program.
Owner:FREESLATE
Parallel flow reactor having improved thermal control
InactiveUS7118917B2Efficient identificationEfficiency optimizationSequential/parallel process reactionsLighting and heating apparatusChemical treatmentThermal isolation
Parallel flow chemical processing systems, such as parallel flow chemical reaction systems are disclosed. These systems are adapted to simultaneously and independently vary temperature between separate flow channels, preferably by employing separate, individual heating elements in thermal communication with each of four or more parallel flow reactors. The flow reactors are preferably isolated from each other using a thermal isolation system comprising fluid-based heat exchange. In preferred embodiments, the axial heat flux can be fixedly or controllably varied.
Owner:FREESLATE
Microfluidic Device
InactiveUS20070286773A1Prevent liquid leakageHigh sealing degreeMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEngineeringSubstrate surface
The present invention relates to a method of fabricating a microfluidic device including at least two substrates provided with a fluid channel, comprising the steps of: a) etching at least a channel and one or more fluid ports in a first and / or a second substrate; b) depositing a first layer on a surface of the second substrate; c) partially removing the first layer in accordance with a predefined geometry; d) depositing a second layer on top of the first layer and the substrate surface; e) planarizing the second layer so as to smooth the upper surface thereof; f) aligning the first and second substrate; and g) bonding the first substrate on the planarized second layer of the second substrate.
Owner:MICRONIT MICROTECHNOLOGIES BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com