Aminotetralin-derived urea modulators of vanilloid VR1 receptor
a vanilloid receptor and urea modulator technology, applied in the field of aminotetralin-derived ureas, can solve the problems that applications do not disclose or describe -substituted -aminotetralins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0599] Human or Rat VR1 Binding Assay
[0600] Compounds of the present invention were tested for their ability to inhibit the binding of [3H] RTX to hVR1 receptors in a [3H] RTX binding assay as previously described (Zhang, Sui-Po. Improved ligand binding assays for vantiloid receptors. PCT Int. Appl. (2002), 29 pp. CODEN: PIXXD2 WO 0233411 A1 20020425 AN 2002:315209; Grant, Elfrida R.; Dubin, Adrienne E.; Zhang, Sui-Po; Zivin, Robert A.; Zhong, Zhong Simultaneous intracellular calcium and sodium flux imaging in human vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1)— transfected human embryonic kidney cells: a method to resolve ionic dependence of VR1-mediated cell death. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics (2002), 300(1), 9-17.)
[0601] HEK293 cells were transfected with human VR1 vanilloid receptors and washed with Hank's Balanced Salt Solution, dissociated with cell dissociation buffer (Sigma), and then centrifuged at 1000×g for 5 min. Cell pellets were homogenized in cold 20 mM HEPES ...
example 2
Human VR1 Functional Assay
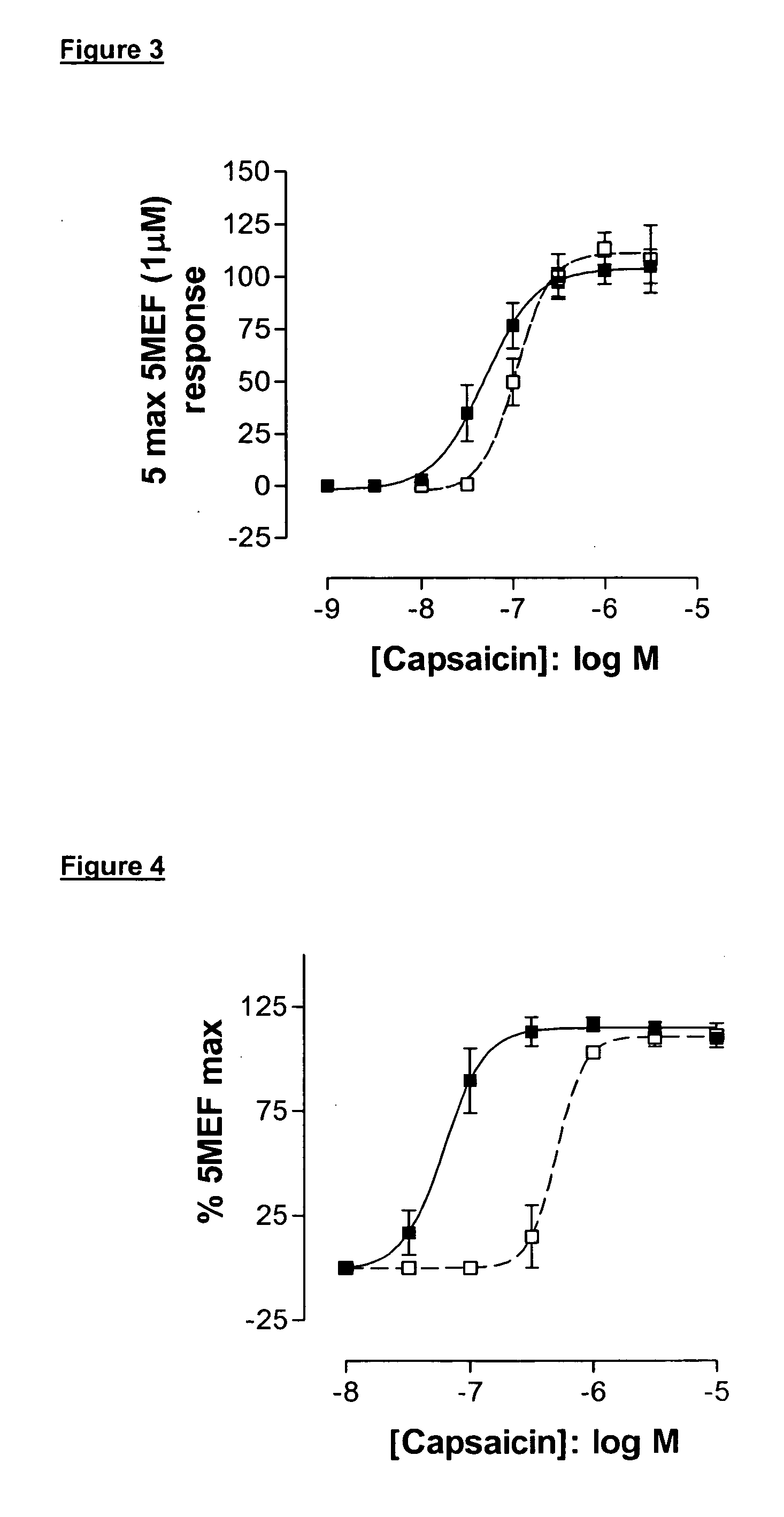
[0604] The functional activity of the test compounds was determined by measuring changes in intracellular calcium concentration using a Ca++-sensitive fluorescent dye and FLIPR™ technology. Increases in Ca++ concentration were readily detected upon challenge with capsaicin.
[0605] HEK293 Cells expressing human VR1 were grown on poly-D-lysine coated 96 well black-walled plates (BD 354640) and 2 days later loaded with Fluo-3 / AM for 1 hour and subsequently tested for agonist-induced increases in intracellular Ca2+ levels using FLIPR technology. Cells were challenged with test compounds (at varying concentrations) and intracellular Ca++ was measured for 3 min prior to the addition of capsaicin to all wells to achieve a final concentration of 0.015 μM eliciting 80% maximal response. EC50 or IC50 values were determined from dose-response studies.
TABLE 2Vanilloid In vitro assay dataCompound No.hVR1 Ki (nM)Rat VR1 Ki (nm)IC50 or EC50 (nM) 12530NT780 231600NTNT 3...
example 3
Broadly Stimulated Recombinant Human VR1 and rat VR1 Functional Assays
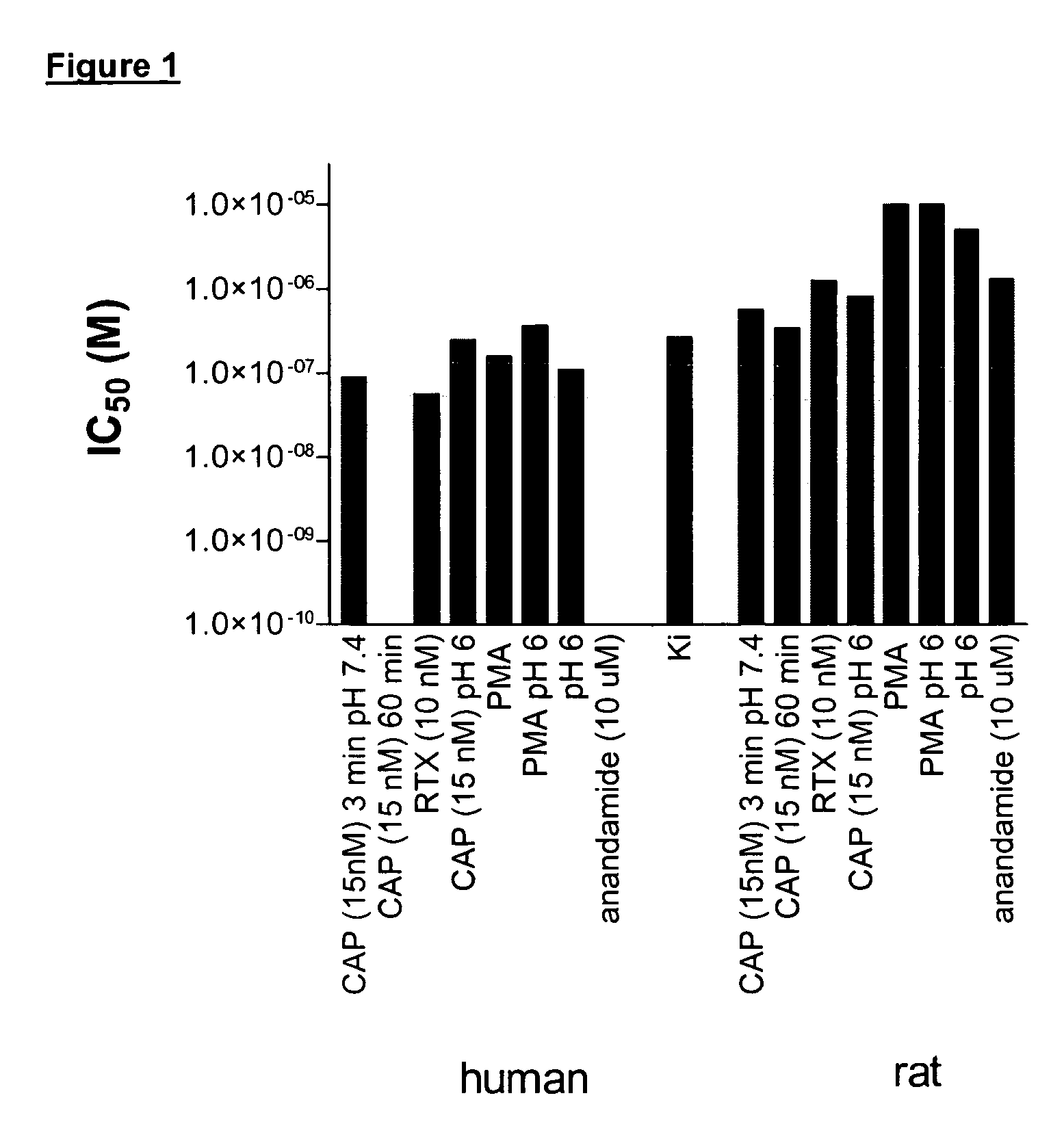
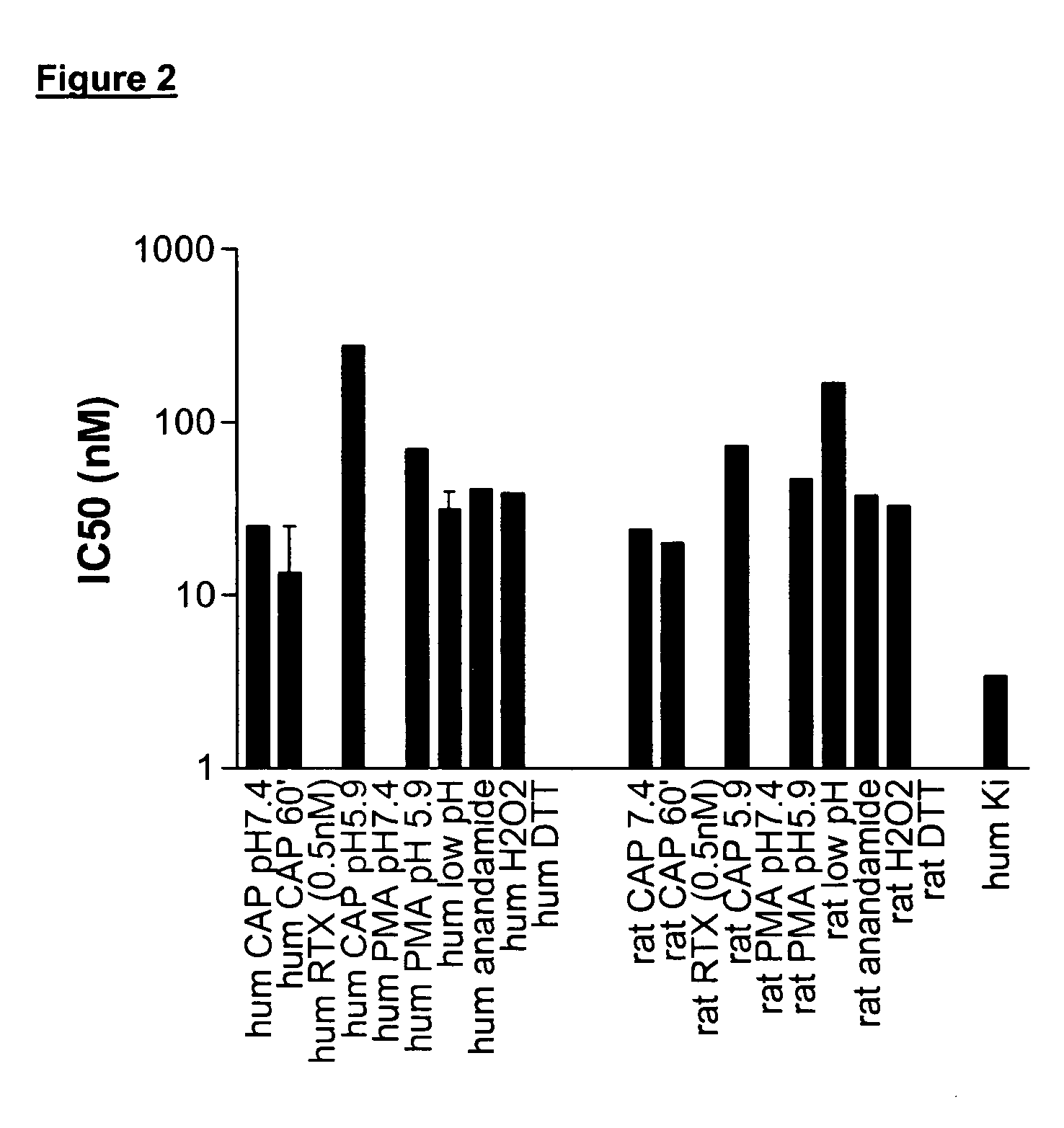
[0606] When nociceptors are exposed to tissue damaging stimuli, VR1 receptors are activated by a plethora of stimuli. In an effort to identify potent and efficacious antagonists at human and rat VR1 that were active under conditions simulating aspects of in vivo inflammation functional assays were developed using FLIPR to determine antagonist activity against endogenous activators and stimuli likely to be present in inflammation. Cell lines were constructed that stably expressed recombinant rat VR1 (rVR1 / HEK293). Cells were exposed to various stimuli at their EC80, with the exception of the low pH and DTT stimuli.
[0607] Low pH (pH 5.9 (rat) or pH 6.5 (human). Cells were challenged for 5 min with low pH solution which produced an increase in intracellular Ca2+ which was subsequently reduced by exposure to antagonists. After 3 min, other stimuli (a phorbol ester to induce phosphorylation, capsaicin, anandamide, re...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| total volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| total volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com