Burst switching in a high capacity network
a high-capacity network and burst switching technology, applied in transmission systems, transmission, time-division multiplexing selection, etc., can solve the problems of low network utilization, burst may be lost, and the source node is unknown to the core node, and achieves efficient utilization of network resources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
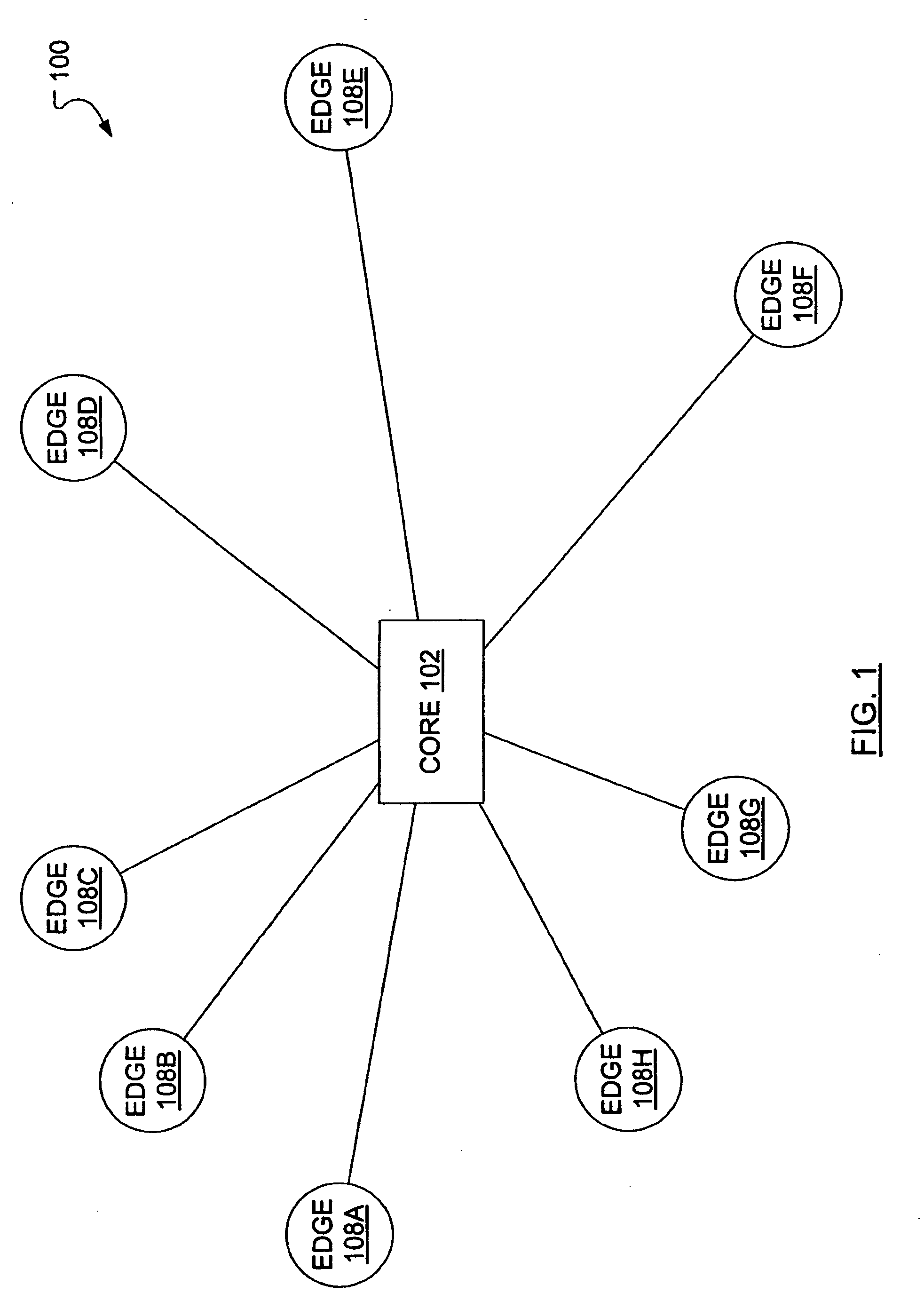
[0039]FIG. 1 illustrates a rudimentary “hub and spoke” data network 100 wherein a number of edge nodes 108A, 108B, 108C, 108D, 108E, 108F, 108G, 108H (referred to individually or collectively as 108) connect to each other via a core node 102. An edge node 108 includes a source node that supports traffic sources and a sink node that supports traffic sinks. Traffic sources and traffic sinks (not shown) are usually paired and each source node is usually integrated with a sink node with which it shares memory and control.
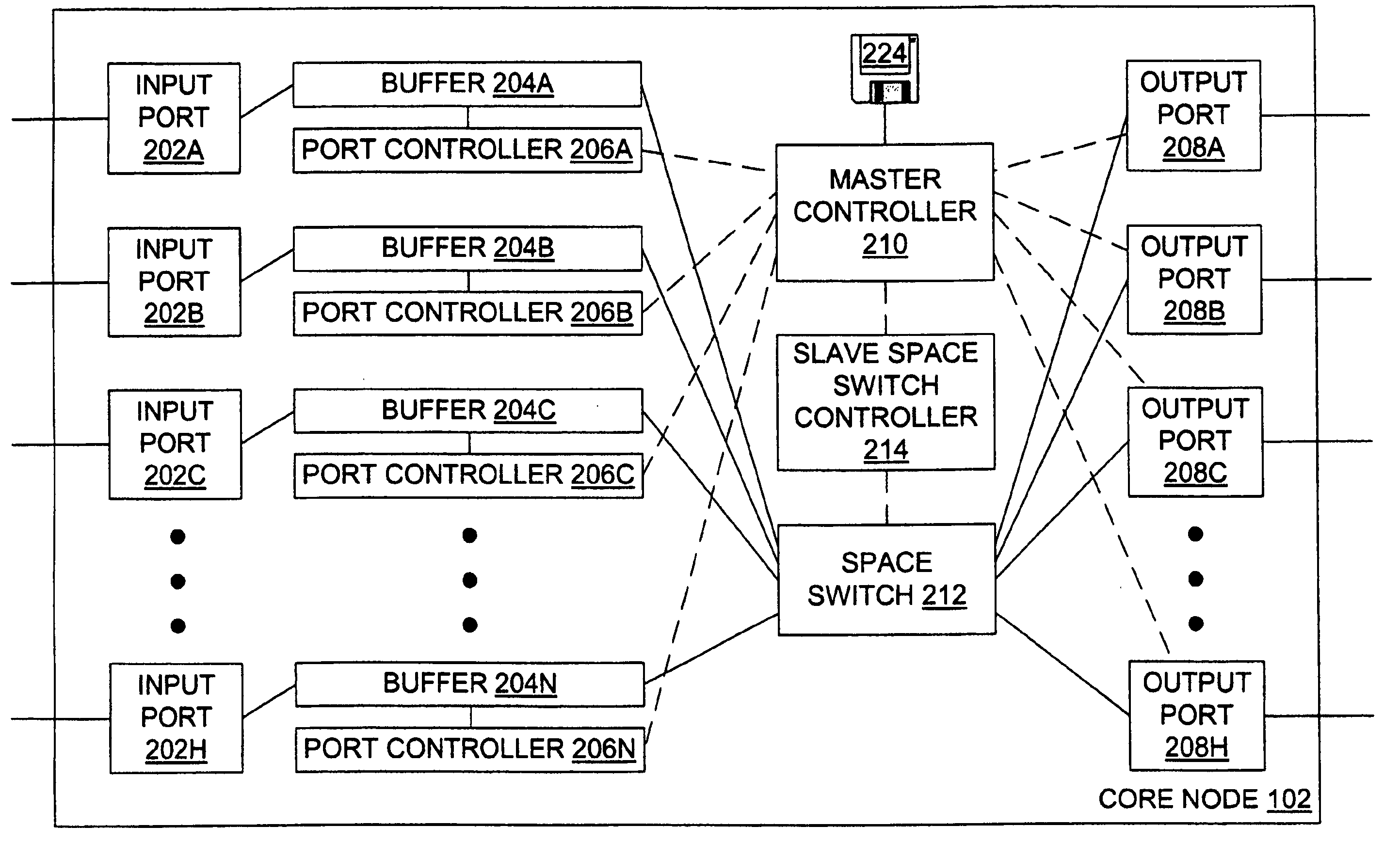
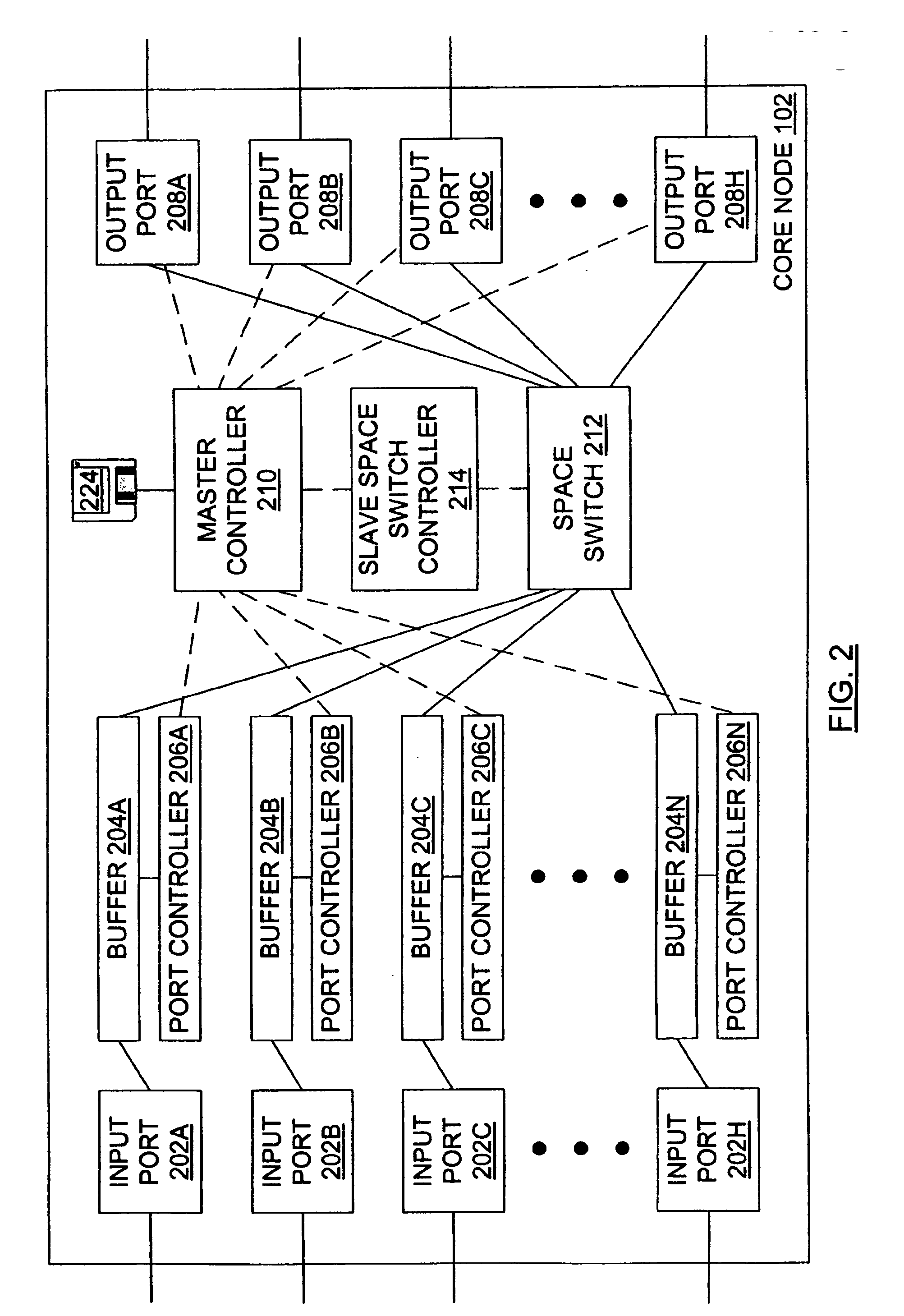
[0040] The core node 102 may be considered in greater detail in view of FIG. 2, which illustrates an electronic core node. The core node 102 includes N input ports 202A, 202B, 202C, . . . , 202N (referred to individually or collectively as 202) for receiving data from the edge nodes 108 of FIG. 1. Each of the N input ports 202 is connected to a corresponding buffer 204A, 204B, 204C, . . . , 204N (referred to individually or collectively as 204) that is connected to a c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com