Universal T-cell epitopes for anti-malarial vaccines
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Anti-Malarial Vaccines Comprising MAPs
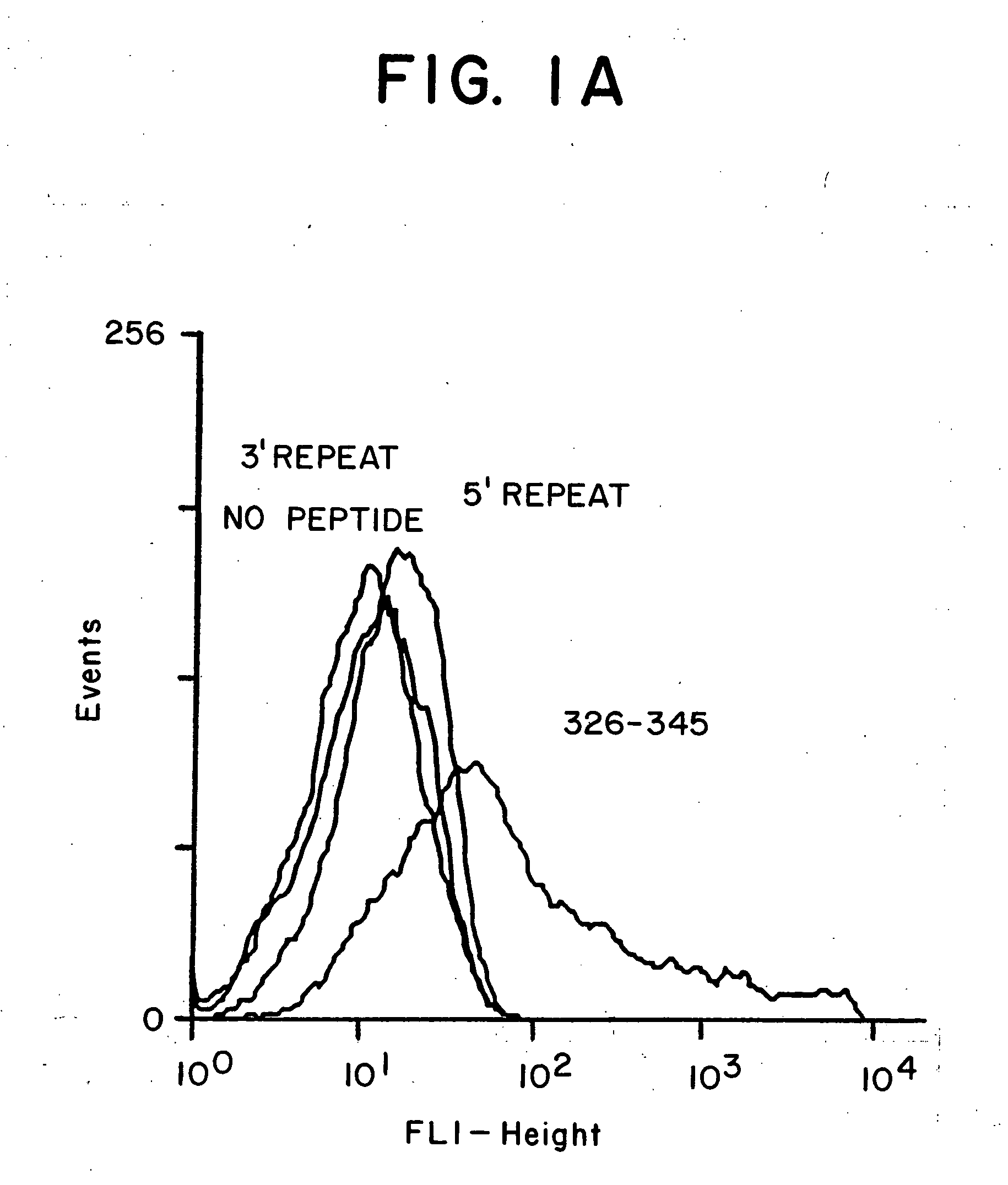
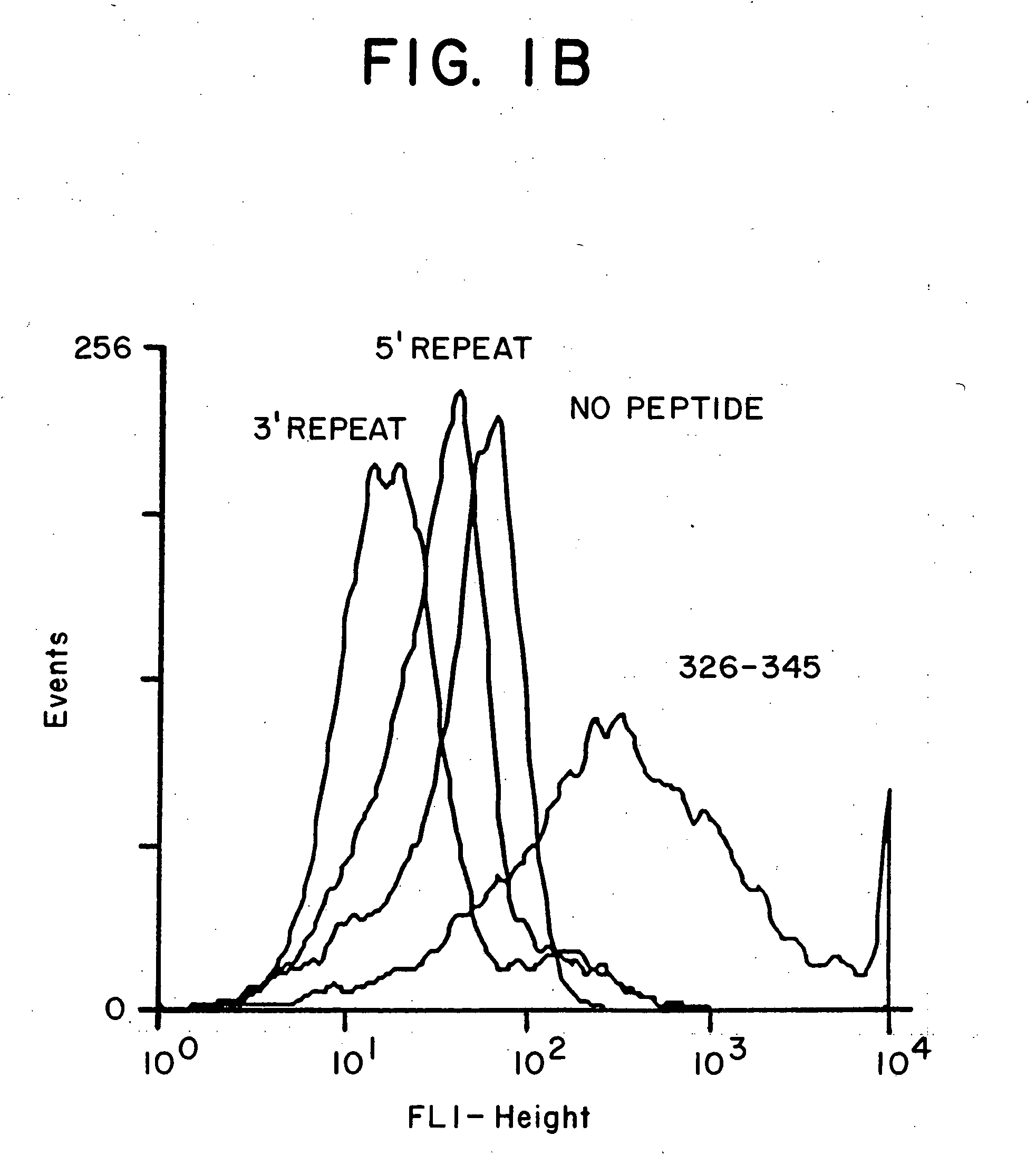
[0095] Studies in mice of different genetic backgrounds have shown that peptide-based vaccines containing the T* epitope (see above) are immunogenic in the absence of adjuvant, i.e., when administered in phosphate buffer alone.
[0096] Enhanced antibody responses were obtained by the addition of adjuvants, such as alum (Rehydragel, Reheis N.J.) or QS21 (Cambridge Biotech, Cambridge Mass.).
[0097] A typical anti-malarial vaccine comprising MAPs contains 1 mg (T*T1B)4 MAP mixed with 100 μg QS21. This vaccine is administered by subcutaneous injection.
example 2
Elicitation of CS-Specific Antibodies in Humans
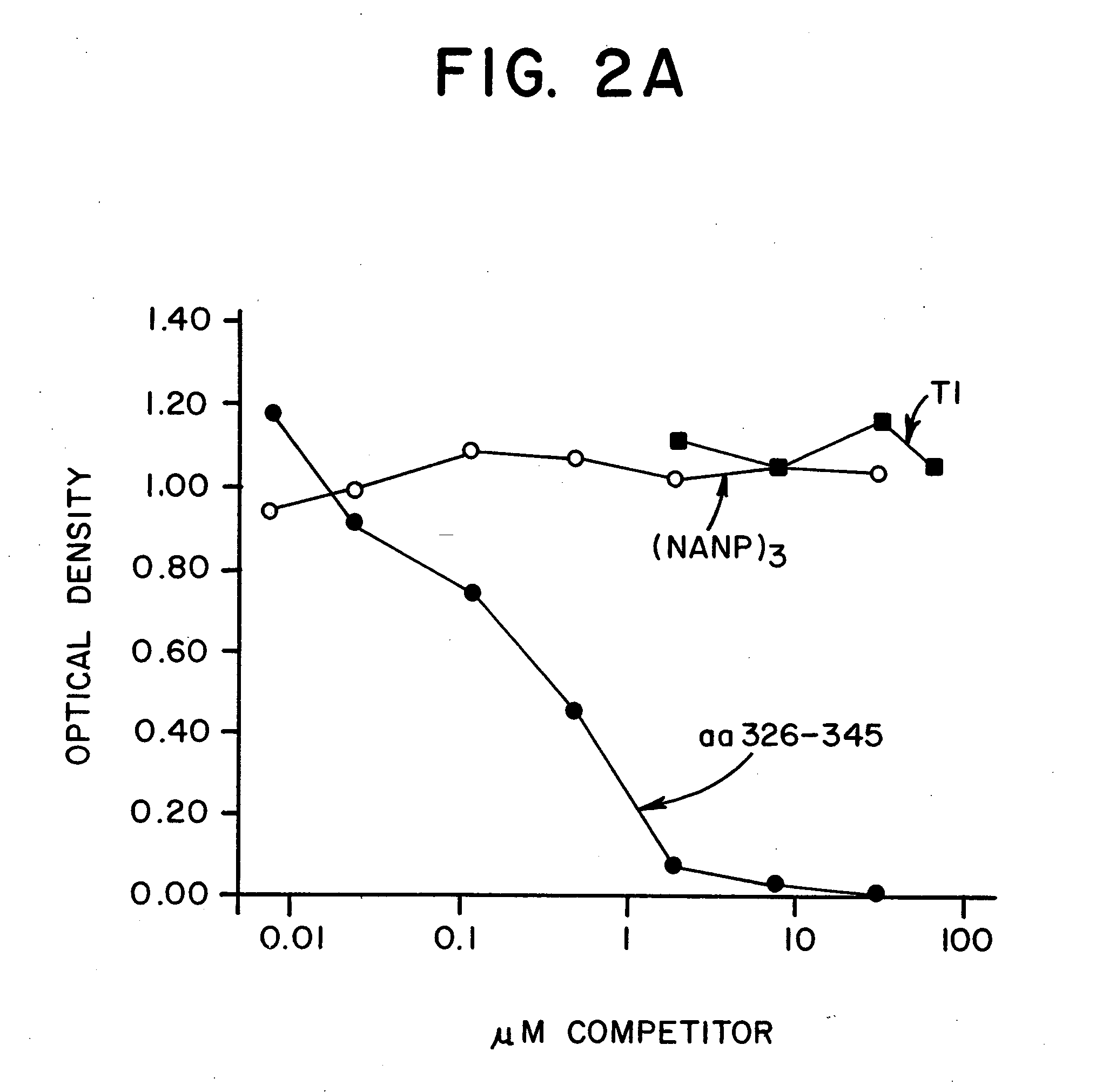
[0098] The following study was performed to examine the effect of immunization with a universal T-cell epitope-containing vaccine on humans of diverse genetic backgrounds.
[0099] Methods: A polyoxime synthetic malaria vaccine, termed (T1BT*)4-P3C, was synthesized. The vaccine contains the universal T-cell epitope (T*) described above in combination with a 28-residue repeated sequence derived from the P. falciparum CS repeats, (DPNANPNV)2(NANP)3 termed T1B (SEQ ID NO: 10). The vaccine also contained a covalently linked synthetic adjuvant, tri-palmitoyl cysteine (Pam3Cys), linked to the lysine core. Methods for synthesis of immunogenic polyoxime compositions in general are disclosed in International Patent Application WO 94 / 25071. Methods for synthesis of T*-containing polyoximes are disclosed in co-pending application Ser. No. 08 / 998,335, filed Dec. 24, 1997, based on provisional application Ser. No. 60 / 034,506, filed Dec. 24, 1996.
[01...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com