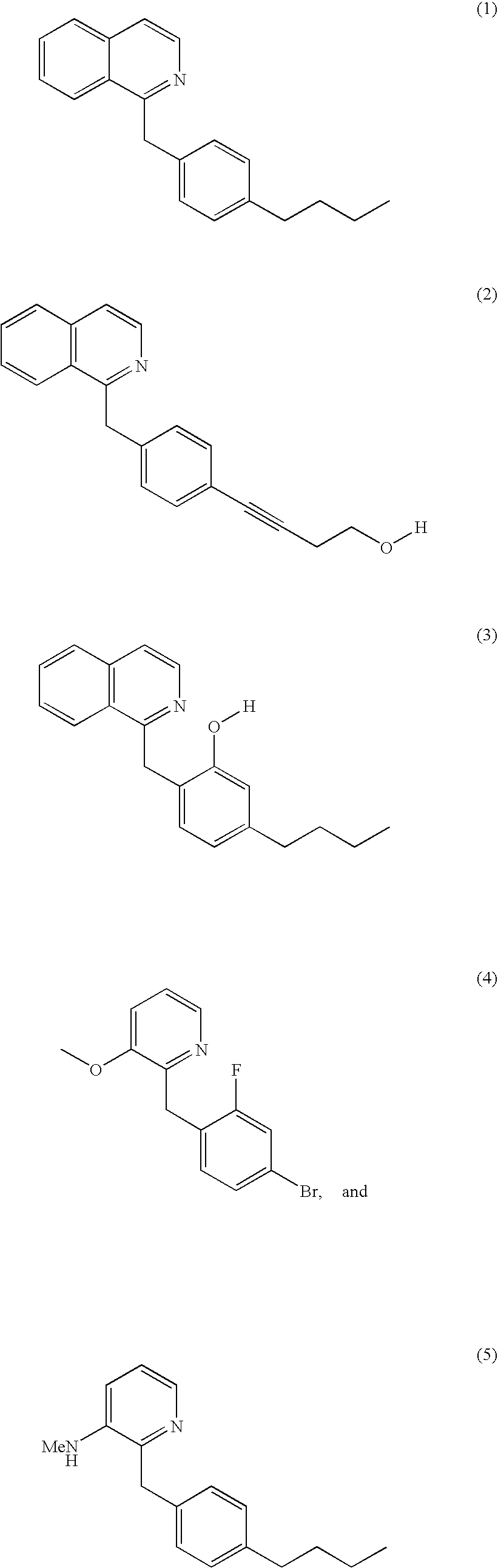
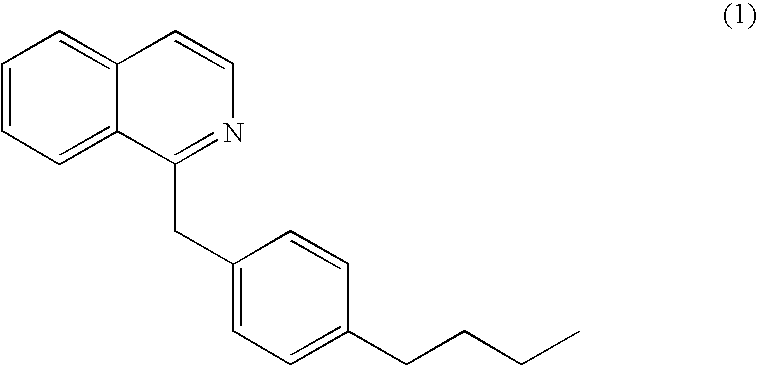
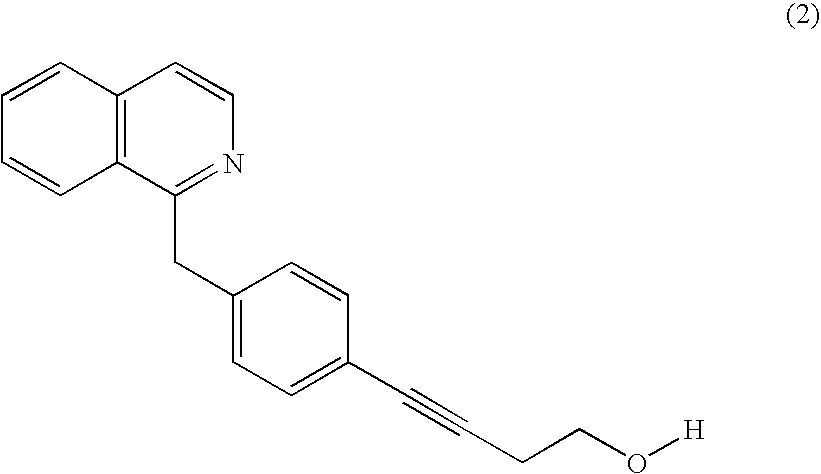
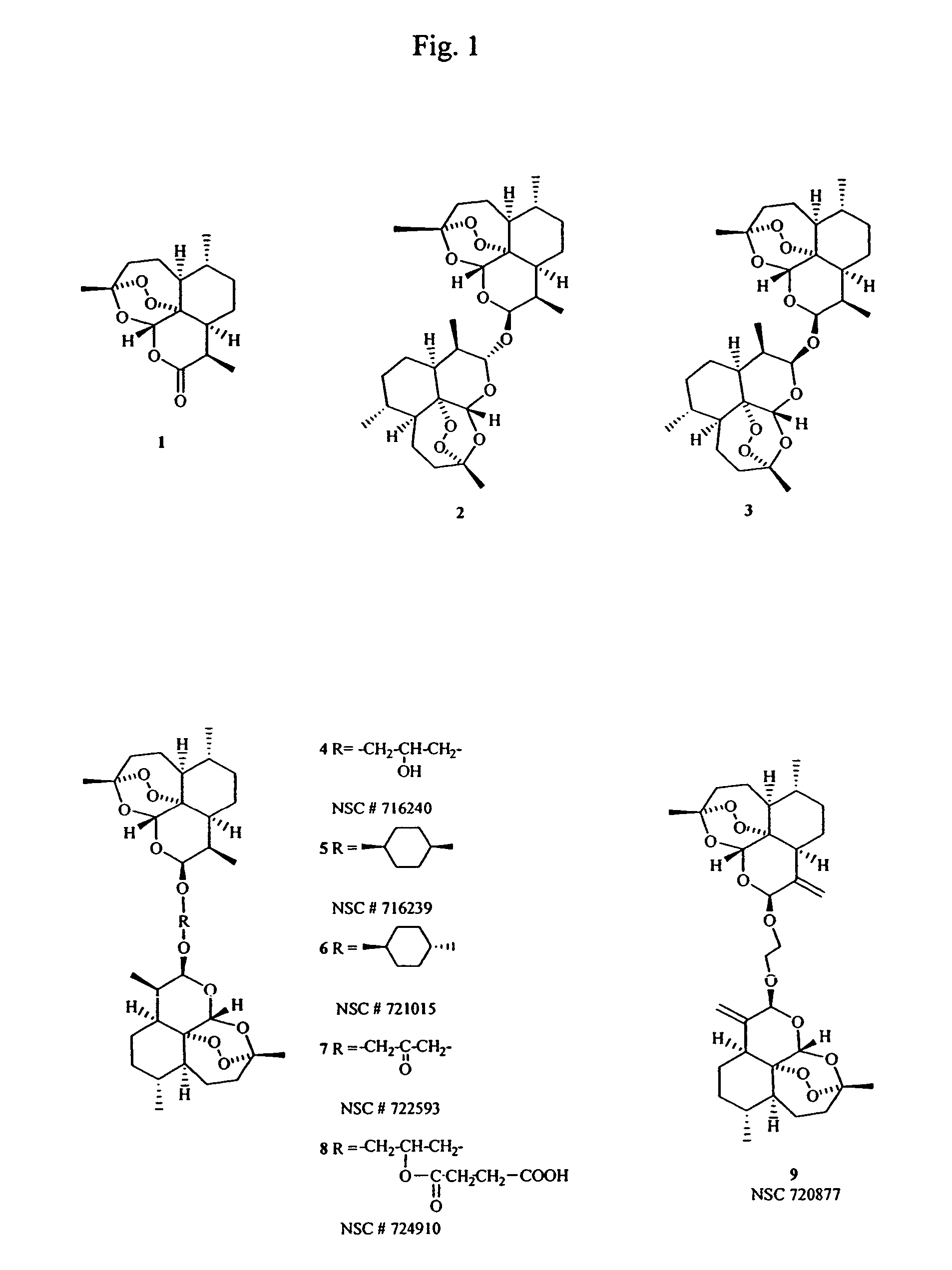
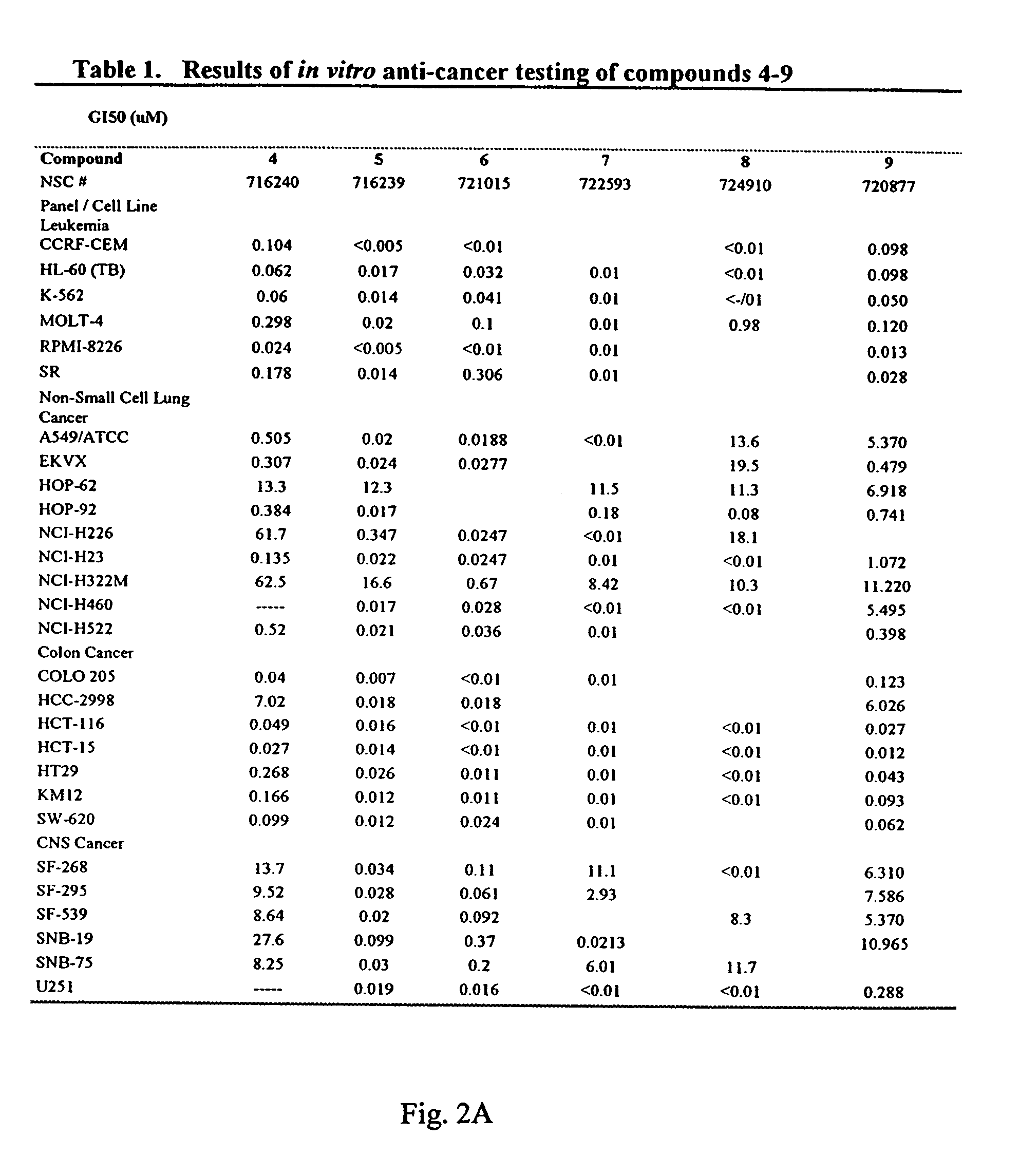
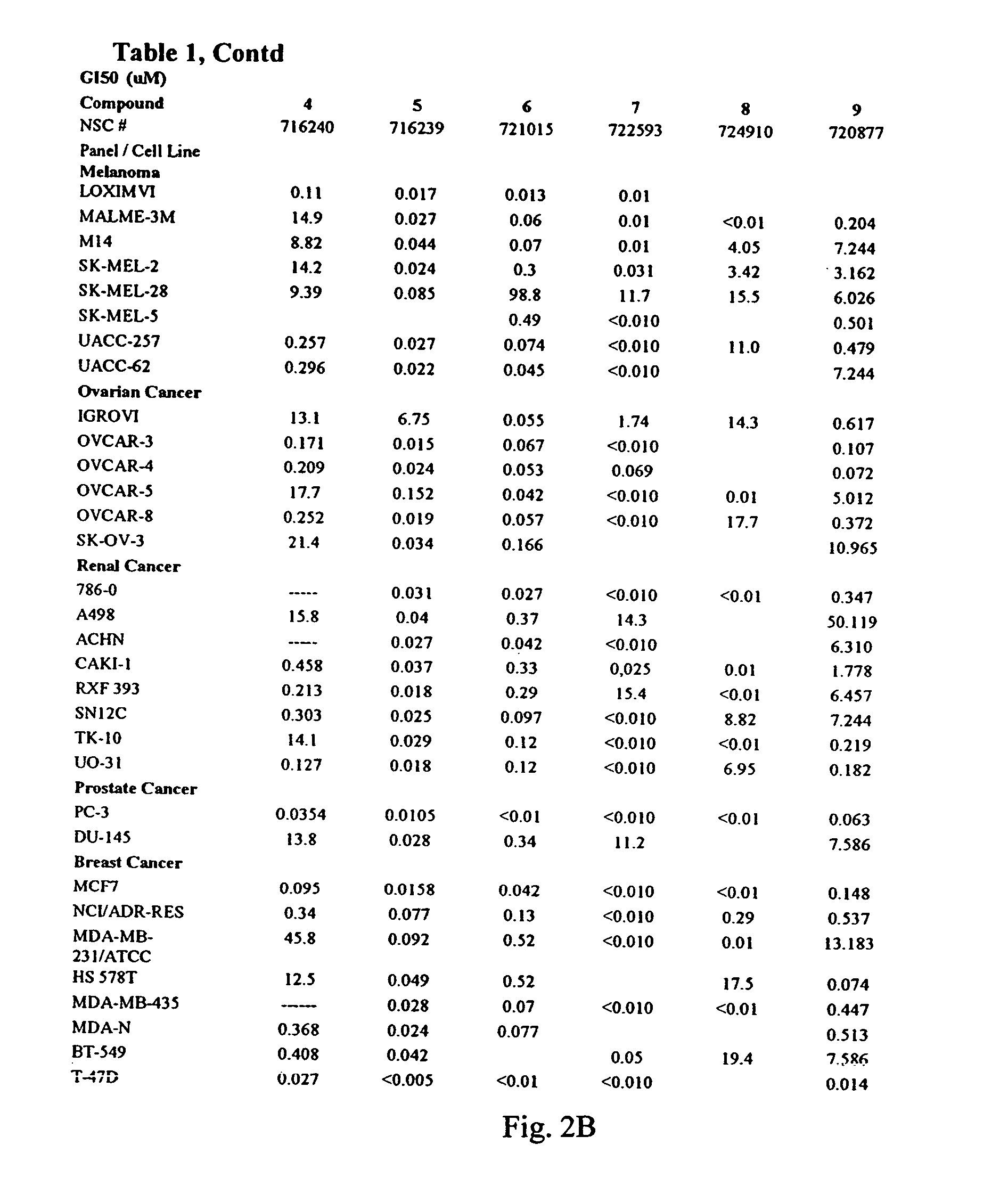
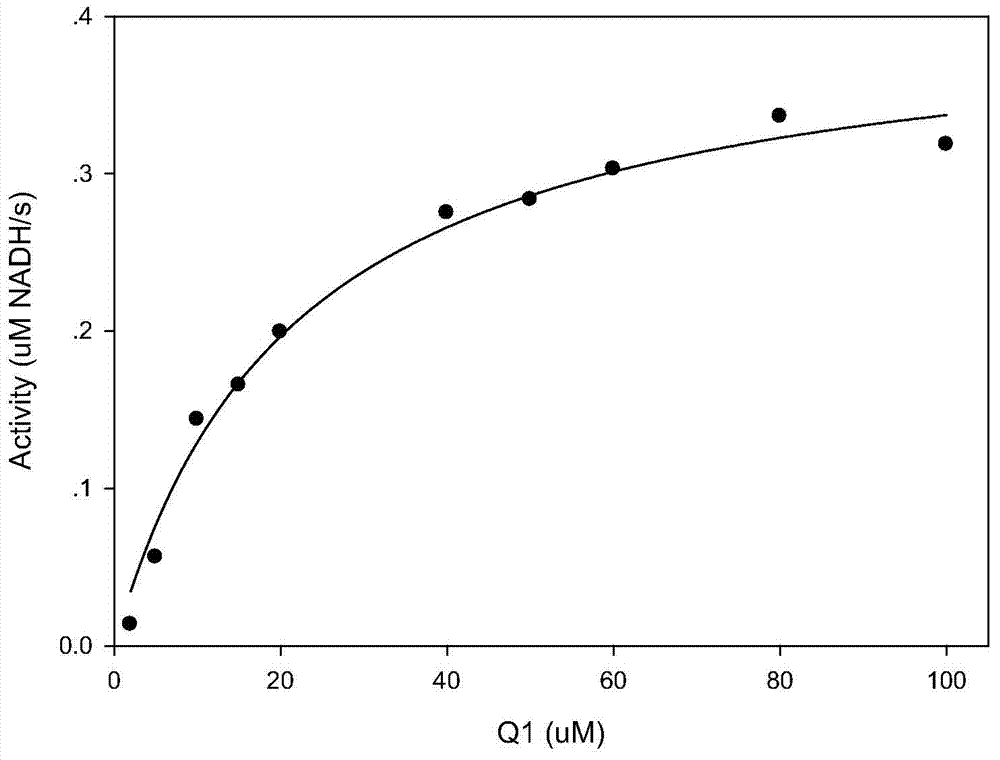
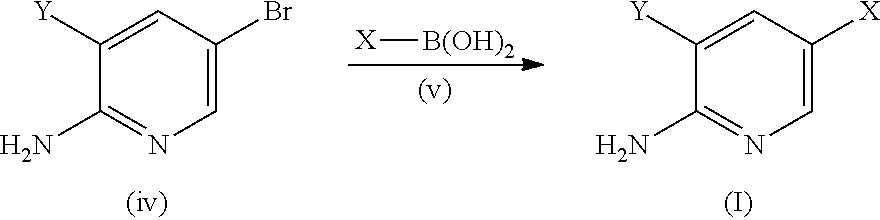Patents
Literature
83 results about "Anti malarial" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods of screening for compounds that inhibit the biosynthesis of gpi in malaria parasites
InactiveUS20060172404A1Reduce in quantityInhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDna encodingMalaria
The present inventors succeeded in isolating GWT1 (PfGWT1), which is one of the enzymes involved in GPI biosynthesis in the malaria parasite P. falciparum. In addition, the inventors revealed that degenerate mutant DNAs, with a lower AT content than the DNA encoding the PfGWT1 protein, can complement the phenotype of GWT1-deficient yeast. Based on the findings, the present invention provides the GWT1 protein of malaria parasites and the use of the protein in methods of screening for antimalarial drugs. The present invention also provides degenerate mutant DNAs encoding proteins involved in GPI biosynthesis, and which have a lower AT content than the original DNAs. The present invention also provides methods of screening for antimalarial drugs which use the degenerate mutant DNAs.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
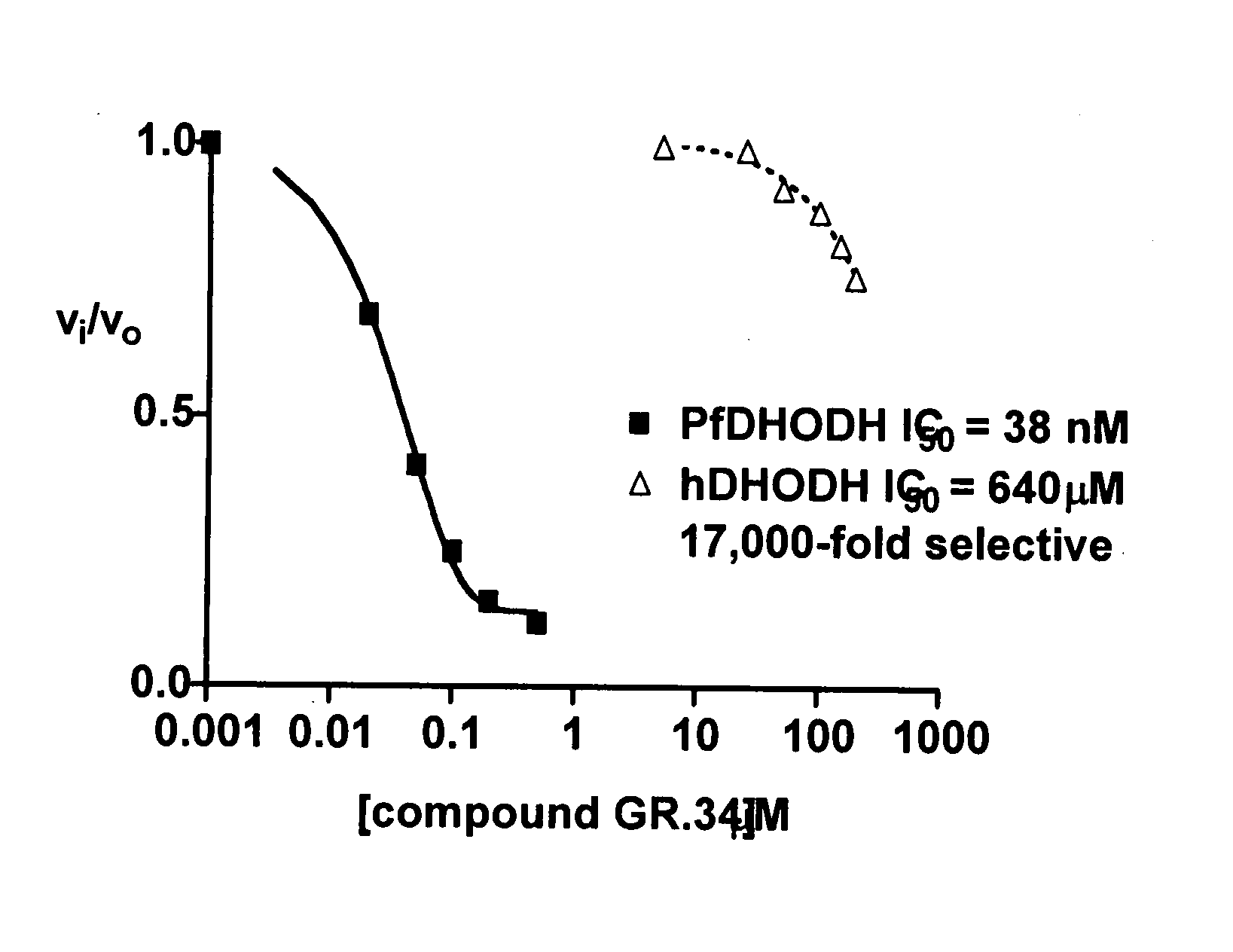
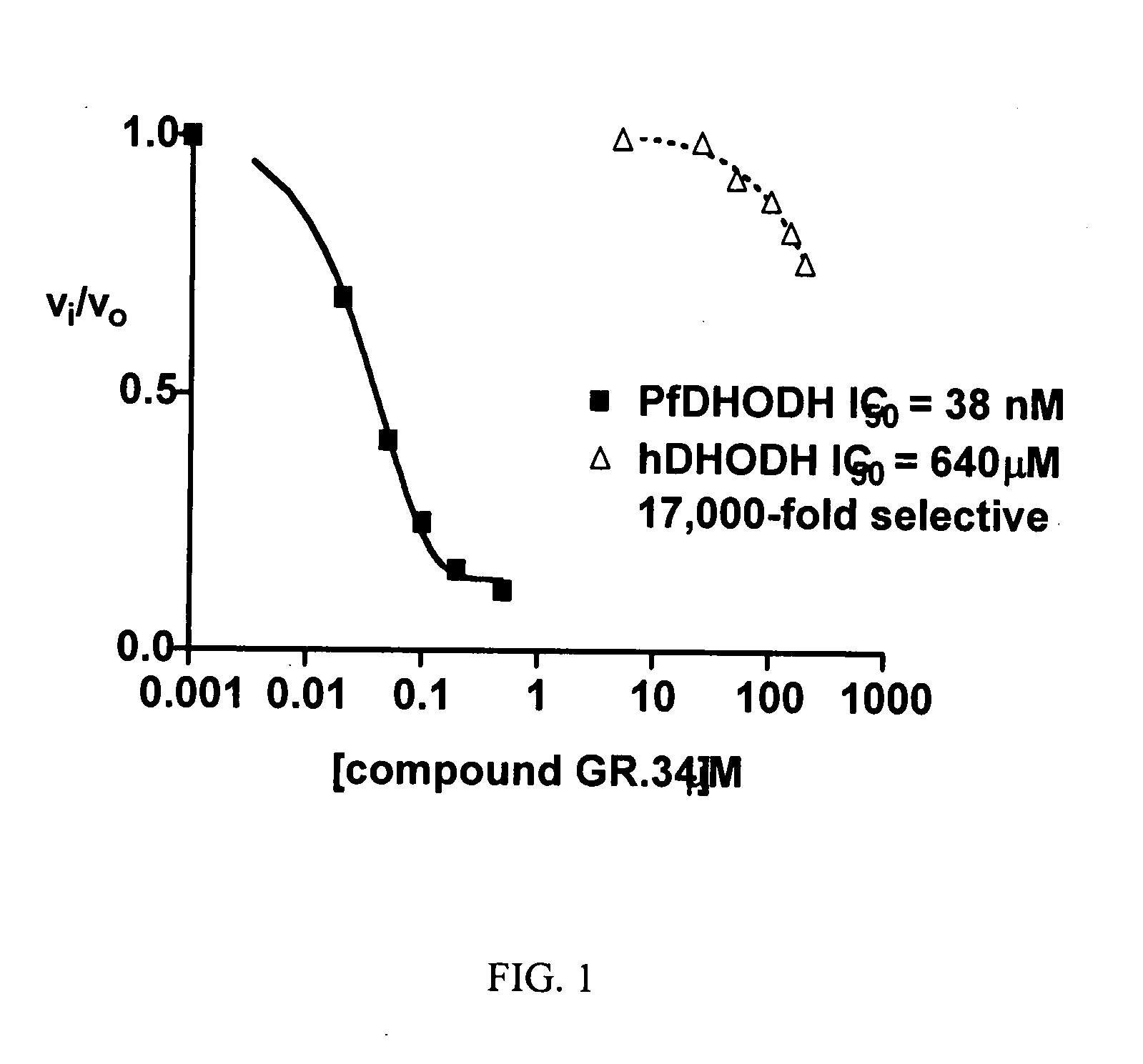
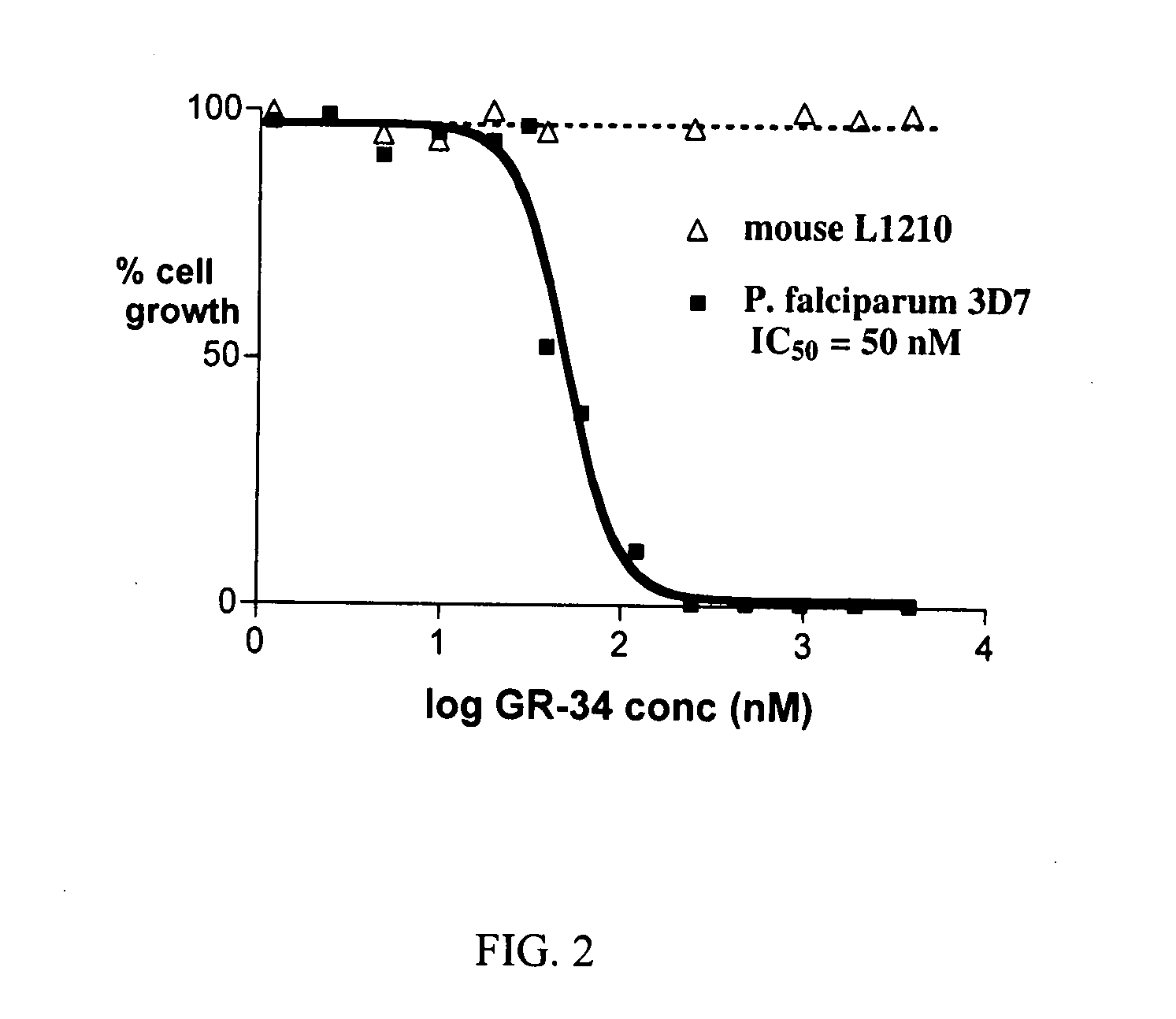
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors with selective Anti-malarial activity
InactiveUS20080027079A1Not be inhibitBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMedicineDihydroorotate Dehydrogenase Inhibitor
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising compounds of the formula where R1, R2, and R3 are described here, have therapeutic utility in selectively inhibiting P. falciparum dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. Accordingly, such compositions have use in the treatment and prevention of malaria.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Malarial animal model having a chimeric human liver
InactiveUS7273963B2Full recoveryUseful for developmentVectorsGenetic engineeringHuman animalHepatica
The present invention features a non-human animal model of malaria, e.g., Plasmodium, particularly Plasmodium falciparum. The model is based on a non-human, immunocompromised transgenic animal having a human-mouse chimeric liver, where the transgene provides for expression of a urokinase-type plasminogen activator in the liver. The invention also features methods for identifying candidate therapeutic agents, e.g., agents having anti-pathogenic activity against malaria.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE +1
Compositions and methods for the treatment of malaria
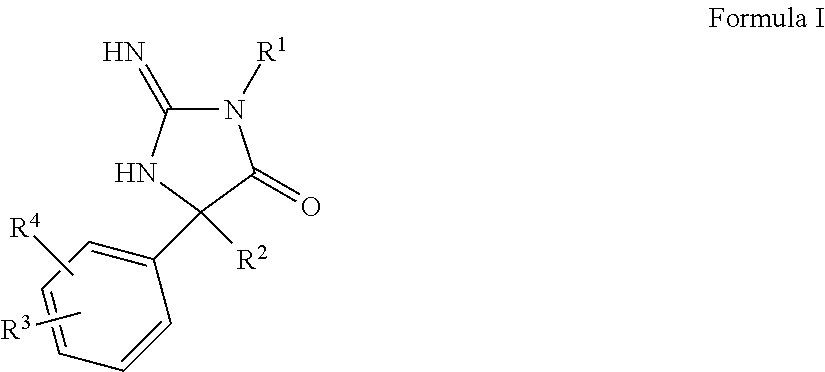
The present invention provides aminohydantoin anti-malarial agents. In some embodiments, these agents have the property of functions of targeting malarial aspartic proteases while at the same time having low activity against human BACE. Methods of employing such agents are also provided.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY +1
Dihydroartemisinin and dihydroartemisitene dimers as anti-cancer and anti-infective agents
This invention comprises compositions containing dihydroartemisinin and dihydroartemisitene dimers with activity as anticancer agents and anti-protozal, including anti-malarial and anti-leishmanial properties. This invention also describes methods of preparation of these compositions and methods of use of such compositions for the treatment of cancer, and protozoal infections, including malaria, or leishmaniasis.The compounds of this invention represent a potential new class of anti-tumor agents, one that has shown promising activity against solid tumors, and with a pattern of selectivity that suggests a possible new mechanism of action.
Owner:ELSOHLY LAB
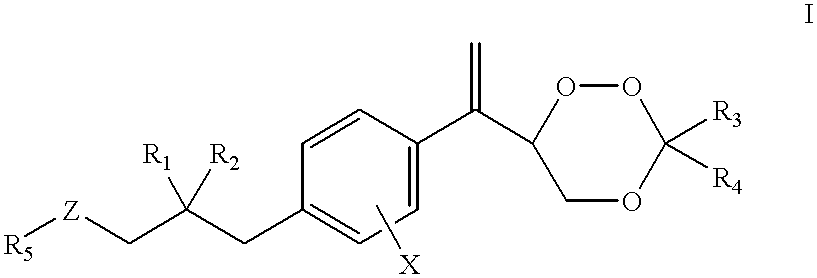
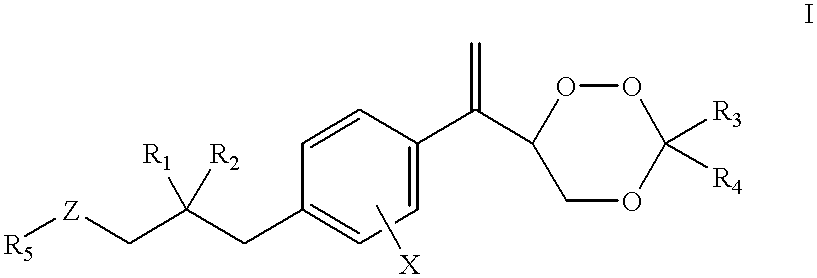
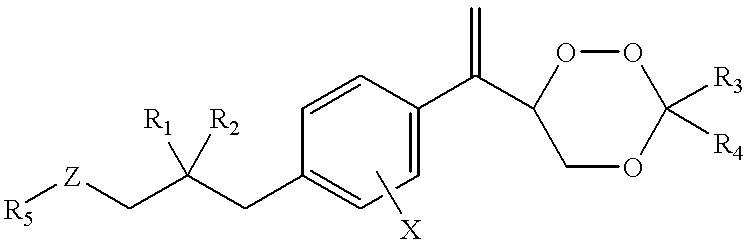
Compounds and application thereof in preparation of anti-parasitosis drugs
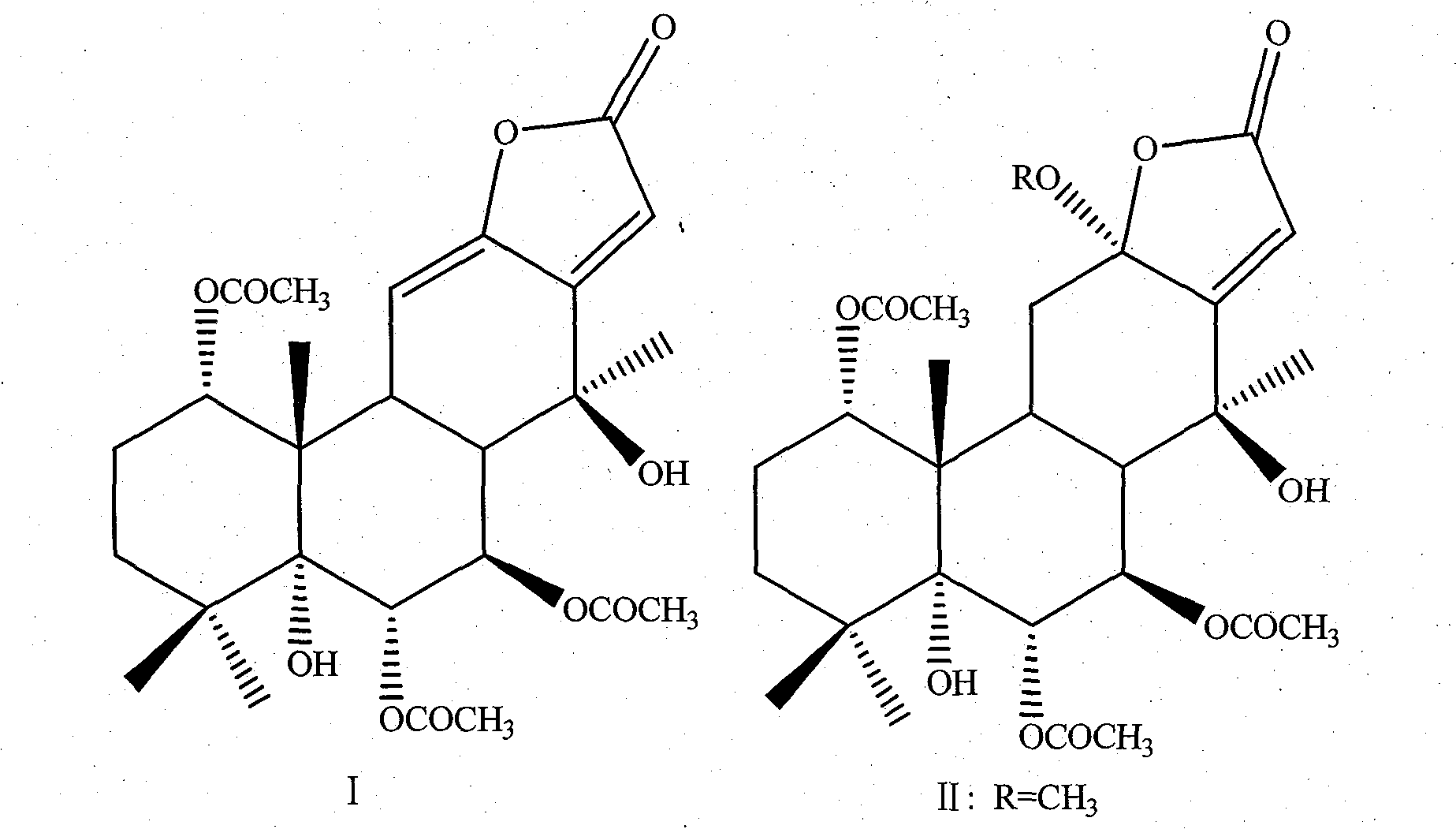
InactiveCN104761524AEnhanced inhibitory effectEasy to separate and purifyOrganic chemistryAntiparasitic agentsSide effectParasitic disease
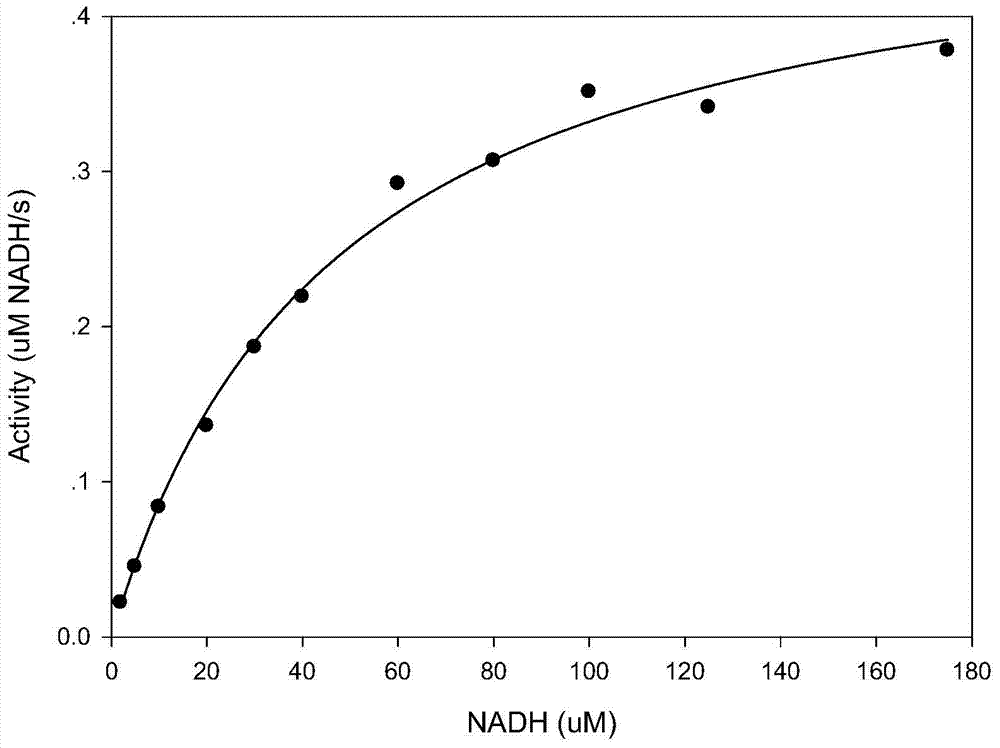
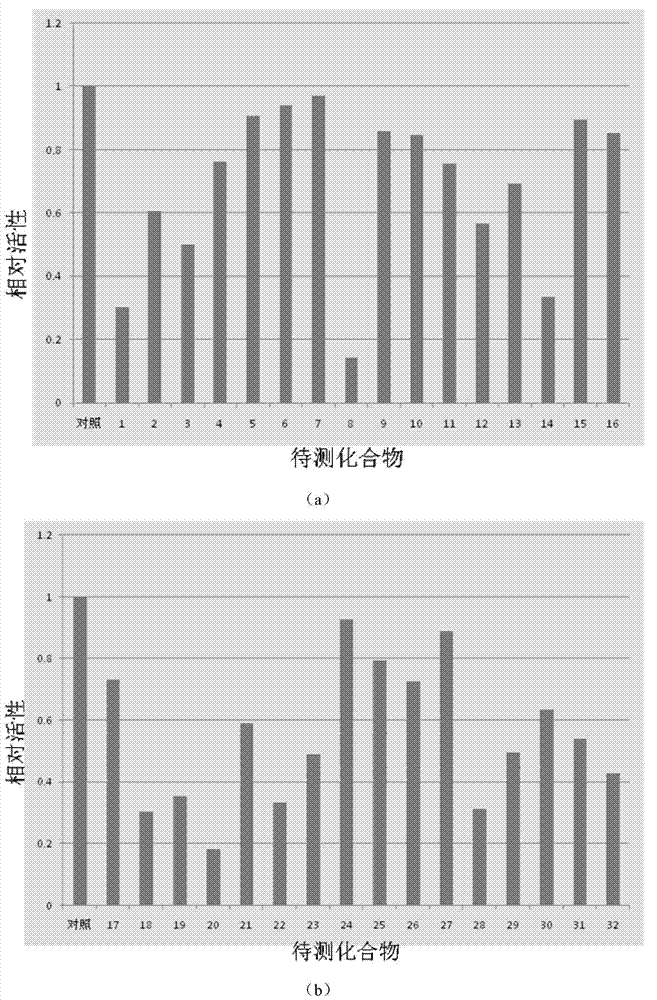
The invention discloses compounds and an application thereof in preparation of anti-parasitosis drugs. The compounds have a structural formula represented by the formula I or the formula II. The compounds provided by the invention have rich functional group diversity and modificability, and the products are relatively easy to separate and purify. The compounds provided by the invention have quite good inhibitory effect on pernicious malaria NDH protein activity and are new anti-malarial action targets and mechanisms, and thus the compounds also have quite good inhibitory effect on many plasmodium species and strains generating resistance to traditional drugs, thereby providing a new breakthrough for current increasingly-serious plasmodium drug resistance aspect. At the same time, the plasmodium NDH and human NADH oxidordeuctase belong to different species, so that the compounds can be expected to produce fewer side effects on human. In summary, the compounds have broad development and application prospects.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
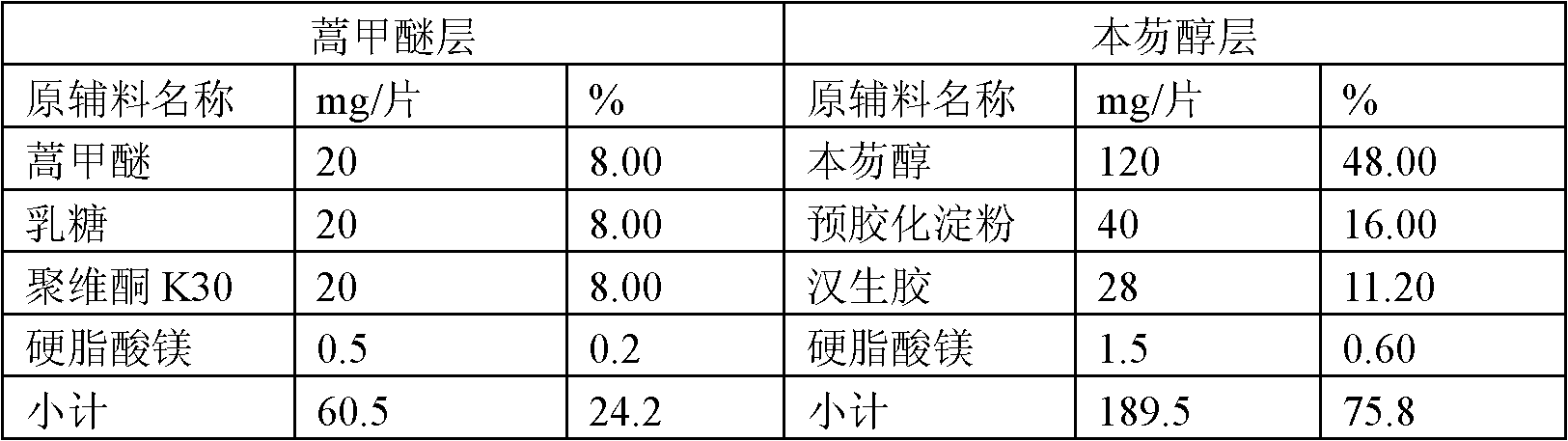
Anti-malarial medicinal composition and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102283829BPromote absorptionGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsPill deliveryLumefantrineCurative effect
Owner:恩威医药股份有限公司
Substituted 1,2,4-trioxanes as antimalarial agents and a process of producing the substituted 1,2,4-trioxanes
InactiveUS6316493B1Promising anti-malarial activityPromising activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsArylHydrogen
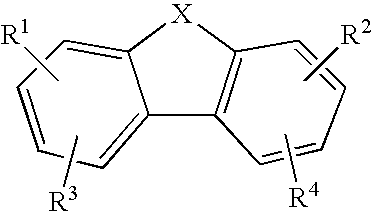
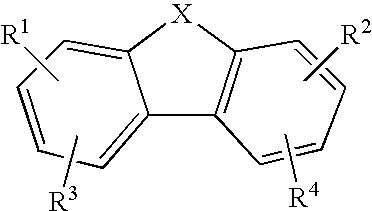
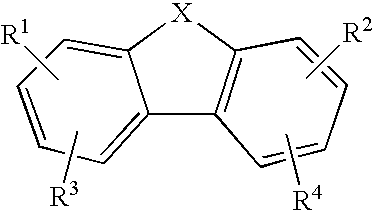
The present invention relates to novel substituted 1,2,4-trioxanes that are useful as anti-malarial agents, and have a general formula 1,wherein R1 and R2 are selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen, a C1-11 alkyl group; R3 and R4 are selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen, a C1-11 alkyl group, a C3-10 aryl group, a C1-2CO2H carboxyalkyl group; and X represents hydrogen or a lower alkoxy group having 1 to 6 carbons.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
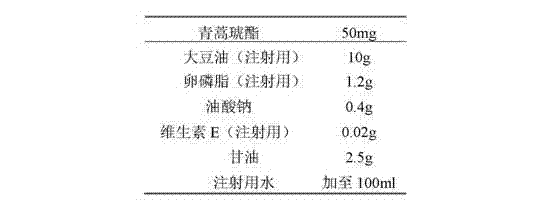
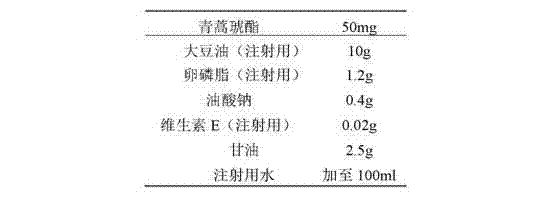
Preparation of artesunate fat emulsion for injection and application of artesunate fat emulsion in treatment of malaria
InactiveCN102895186AImprove lymphocyte activityContributes to resistanceOrganic active ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsSide effectBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses an artesunate fat emulsion injection preparation which contains 0.01 to 30 wt% of artesunate, 10.0 to 30.0 wt% of oil for injection, 0.6 to 30.0 wt% of an emulsifier, 0 to 10 wt% of a solubilizer, 0 to 5 wt% of a co-emulsifier, 2.25 to 7 wt% of an isotonic agent and 0.002 to 0.075 wt% of an anti-oxidant, with the balance being injection water. The invention also discloses a preparation method and pharmacodynamic and safety evaluation for the artesunate fat emulsion injection preparation. The artesunate fat emulsion provided by the invention has the characteristics of good biocompatibility, high physical stability, convenient preparation, good security, high drug loading capacity and the like, has a particle size of less than 200 mu m and is suitable for injection, e.g, intravenous injection and intramuscular injection. According to the invention, the characteristic that a soybean oil fat emulsion inhibits growth of plasmodium falciparum is utilized to enhance anti-malarial effects of drugs, to improve bioavailability of the drugs and to reduce toxic and side effects of the drugs; nutrients needed by the body of a patient with malaria can be provided, the activity of lymphocytes of the patient is improved, which assists the patient in resisting malaria and recovering.
Owner:福州欣瑞普医药科技有限公司
Universal T-cell epitopes for anti-malarial vaccines
InactiveUS20050249750A1Hinders its propagationProtozoa antigen ingredientsDepsipeptidesProtective immunityMalaria
The present invention provides methods and compositions for eliciting protective immunity against malaria. In particular, the invention relates to universal T-cell epitopes that elicit T-cell responses; in individuals of differing genetic backgrounds. Immunogenic compositions and vaccines comprising malaria-specific universal T-cell epitopes are disclosed.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Uses for anti-malarial therapeutic agents
A diversity of inflammatory diseases can be treated via local delivery to the patient of a composition containing a therapeutically effective amount of an anti-malarial agent. In a preferred embodiment of the method of the invention, a pulmonary inflammatory condition, such as asthma, is treated by inhalation of an aerosolized anti-malarial agent, such as hydroxychloroquine.
Owner:CHAROUS LAUREN
New Anti-malarial agents
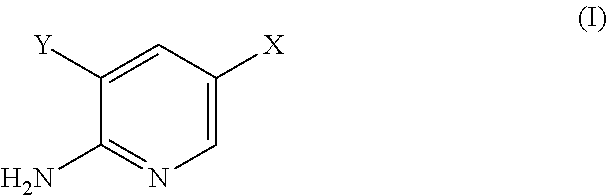
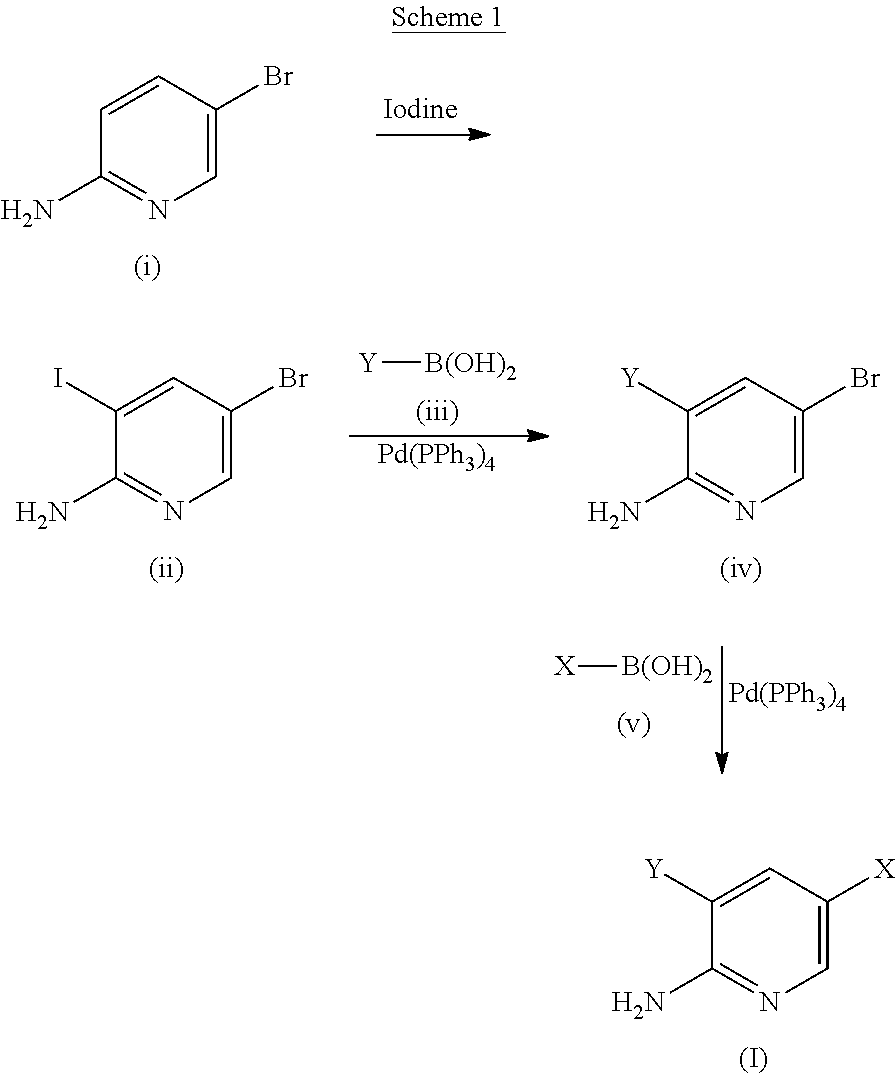
The present invention is related to a use of aminopyridine derivatives in the manufacture of a medicament for preventing or treating malaria. Specifically, the present invention is related to aminopyridine derivatives useful for the preparation of a pharmaceutical formulation for the inhibition of malaria parasite proliferation.
Owner:MMV MEDICINES FOR MALARIA VENTURE
Method for preparing anti-malarial medicament with reversal of medicament resistance and multi-target effect
InactiveCN101632778AHigh recurrence rateRapid symptomsInorganic non-active ingredientsUnknown materialsDiseaseMicrosphere
The invention discloses a method for preparing an anti-malarial medicament with reversal of medicament resistance and multi-target effect, which comprises the process flow of performing stock preparation, preparing water-soluble Chinese medicament inclusion microspheres, preparing alcohol-soluble Chinese medicament inclusion microspheres, and preparing water-soluble chemical medicament inclusion microspheres. The method takes beta-cyclodextrin as a framework material, and includes a nano-magnetic biomaterial (carrier material) and a pharmaceutical composition; and the medicament-loaded nano-magnetic microspheres can be quickly combined with target cells, penetrate target cell membranes to enter the cells, realize the transmembrane transport of medicament molecules, inhibit the gene expression and amplification of the target cells to ensure that the target cells degenerate, necrotize or apoptosize, and achieve the effect of the reversal of medicament resistance at the same time. An anti-malarial oral preparation interferes the processes of DNA replication and RNA transcription of schizonts of plasmodiums, kills schizonts of erythrocytic phases of the plasmodiums, and effectively kills exoerythrocyte stages of the plasmodiums and gametophytes of the plasmodiums at the same time; and at the same time, the anti-malarial oral preparation achieves the aims of preventing disease causes, and controlling the prevalence and propagation of malaria.
Owner:黄云清
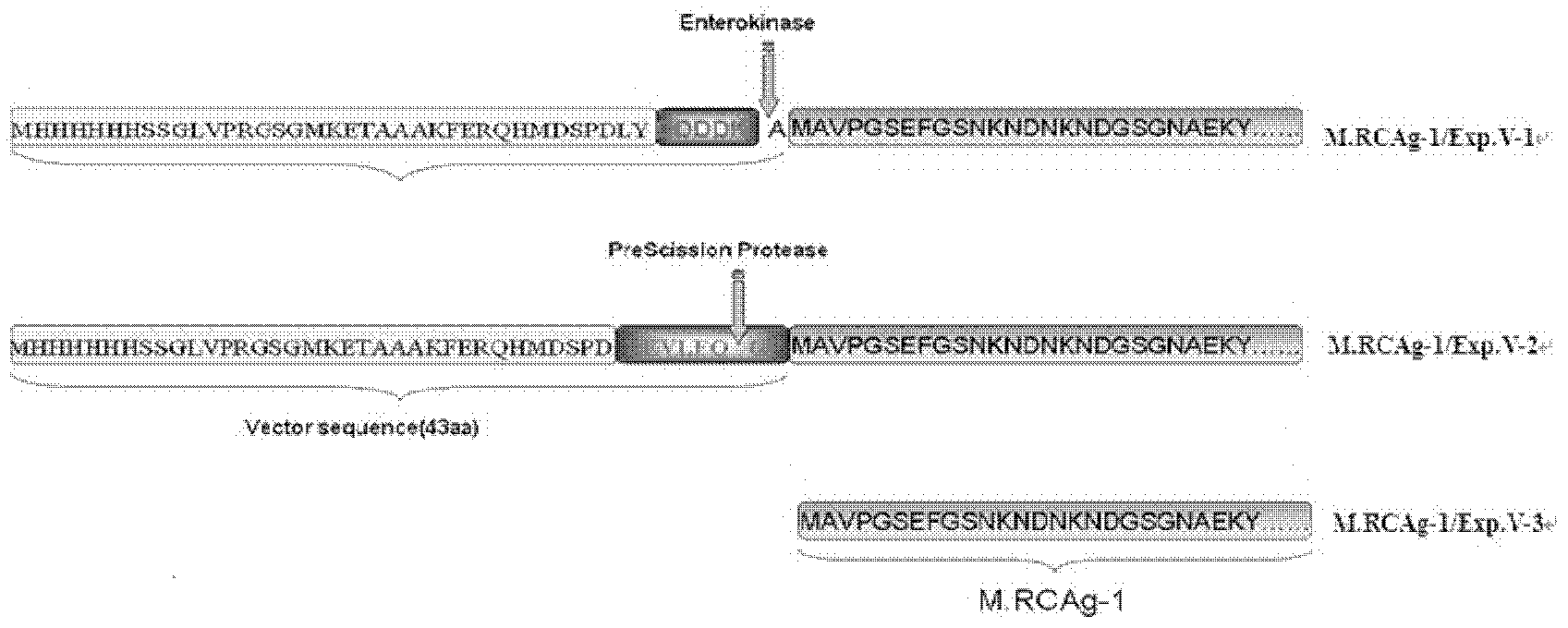
Fusion protein, use thereof, and anti-malarial vaccine and antibody thereof
ActiveCN103159855AImproving immunogenicityStable physical and chemical propertiesSerum immunoglobulinsAntibody ingredientsIn vitro growthC-terminus
The invention provides use of a fusion protein, and an anti-malarial vaccine and an antibody thereof. The amino acid sequence of the fusion protein of the present invention from N to C terminal in sequence comprises an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.: 7 and an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.: 5. The fusion protein of the invention and the vaccine have advantages and positive effects that: the recombinant protein has strong immunogenicity, physicochemical properties are stable, sustainable and high-titer specific antibodies can be stimulated, plasmodium falciparum natural antigens can be identified in mouse immune sera, significant T-cell response can be induced, and in vitro growth of plasmodium falciparum can be suppressed, and the vaccine is a high promising candidate and has good development prospects.
Owner:NAT VACCINE & SERUM INST
Pyronaridine compounds and applications thereof
InactiveCN103570711AHigh antimalarial activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryIn vivoHigh activity
The invention provides pyronaridine compounds and applications thereof. The general formula of the pyronaridine compounds is shown as the formula I, wherein R1, R2, R3, and R4 are acting sites, and therefore the compounds have activity of inhibiting plasmodium in-vivo PDE. The pyronaridine compounds have a binding free energy lower than pyronaridine, and therefore the pyronaridine compounds have higher activity of inhibiting the plasmodium in-vivo PDE than the pyronaridine, and therefore the pyronaridine compounds have stronger anti-malarial activity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Combination kit used in the treatment of malaria
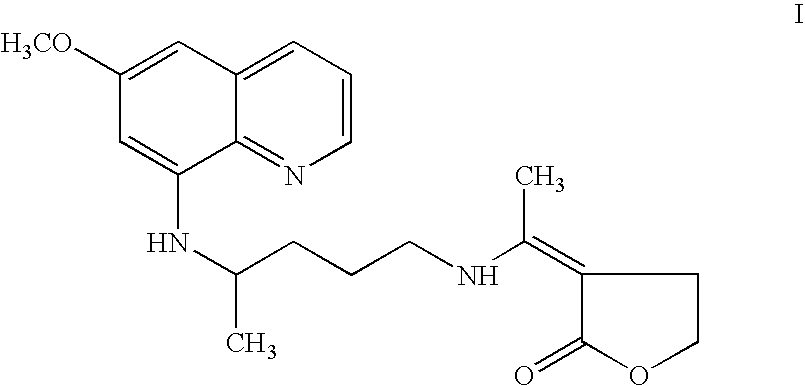
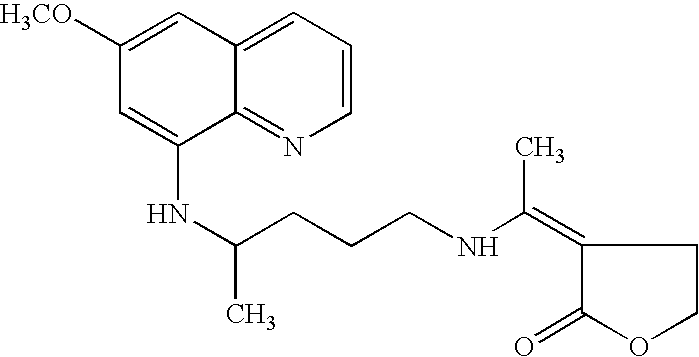
A combination kit for the treatment of malaria caused by Plasmodium vivax (P. vivax) having individual doses of an anti-malarial agent, 3-[1-[[4-[(6-methoxy-8-quinolinyl)amino]pentyl]amino]ethylidene]-dihydro-2(3H)-furanone (I) in the form of capsules; individual doses of the anti-malarial agent, chloroquine in the form of tablets; and instruction material for the administration of the two anti-malarial drugs. The combination kit is particularly suited for a 6 days treatment regimen where the treatment is rendered by five tablets containing 500 mg of chloroquine phosphate (equivalent to 300 mg base), three to be taken on day one and one each on days two and three; and five capsules containing 25 mg of 3-[1-[[4-[(6-methoxy-8-quinolinyl)amino]pentyl]amino]ethylidene]-dihydro-2(3H)-furanone (I), one each to be taken on days two to six.
Owner:NICHOLAS PIRAMAL INDIA LTD +1
Anti-malarial pharmaceutical composition
InactiveUS20110015260A1Promote absorptionMinimize the possibilityPowder deliveryBiocideMedicineMalaria
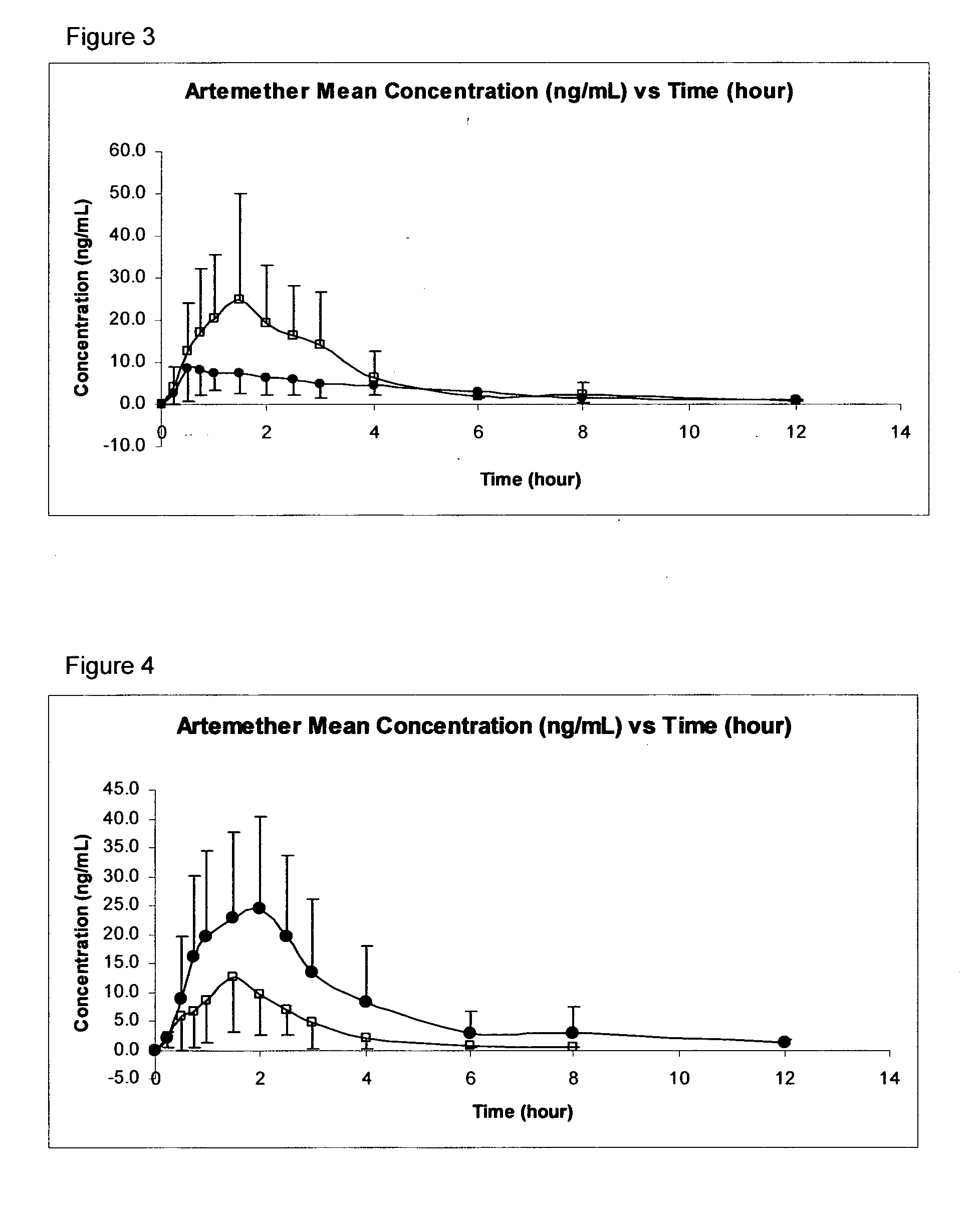
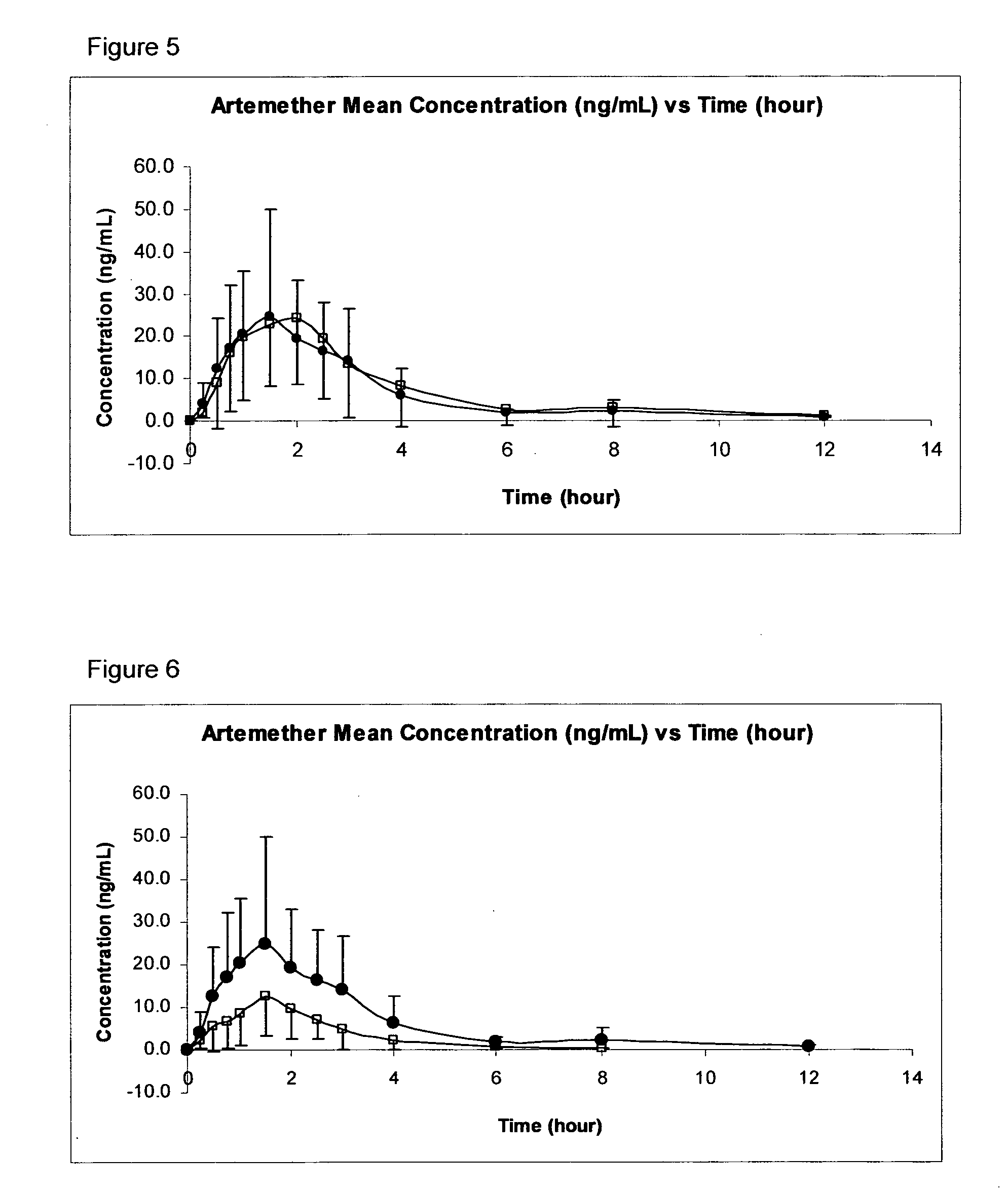
The invention provides pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment and prophylaxis of malaria, comprising artemether and a medium chain triglyceride formulated for transmucosal sublingual, buccal or nasal delivery, especially by a spray. Also provided are delivery devices containing the compositions.
Owner:PROTOPHARMA
Anti-malaria prime/boost vaccines
InactiveCN101068568AStrong immune responseAntiparasitic agentsImmunological disordersMalarial parasiteAdjuvant
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV +2
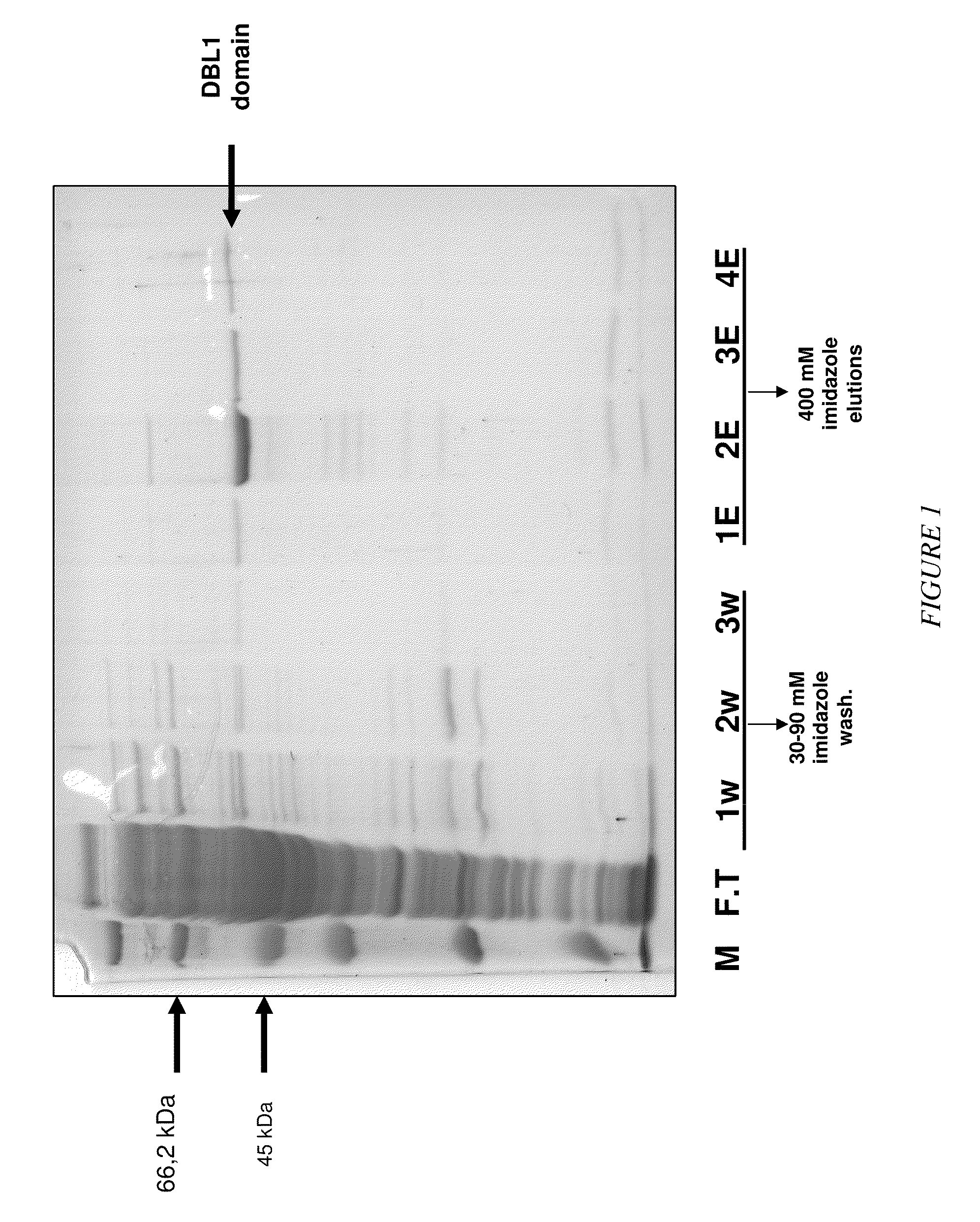
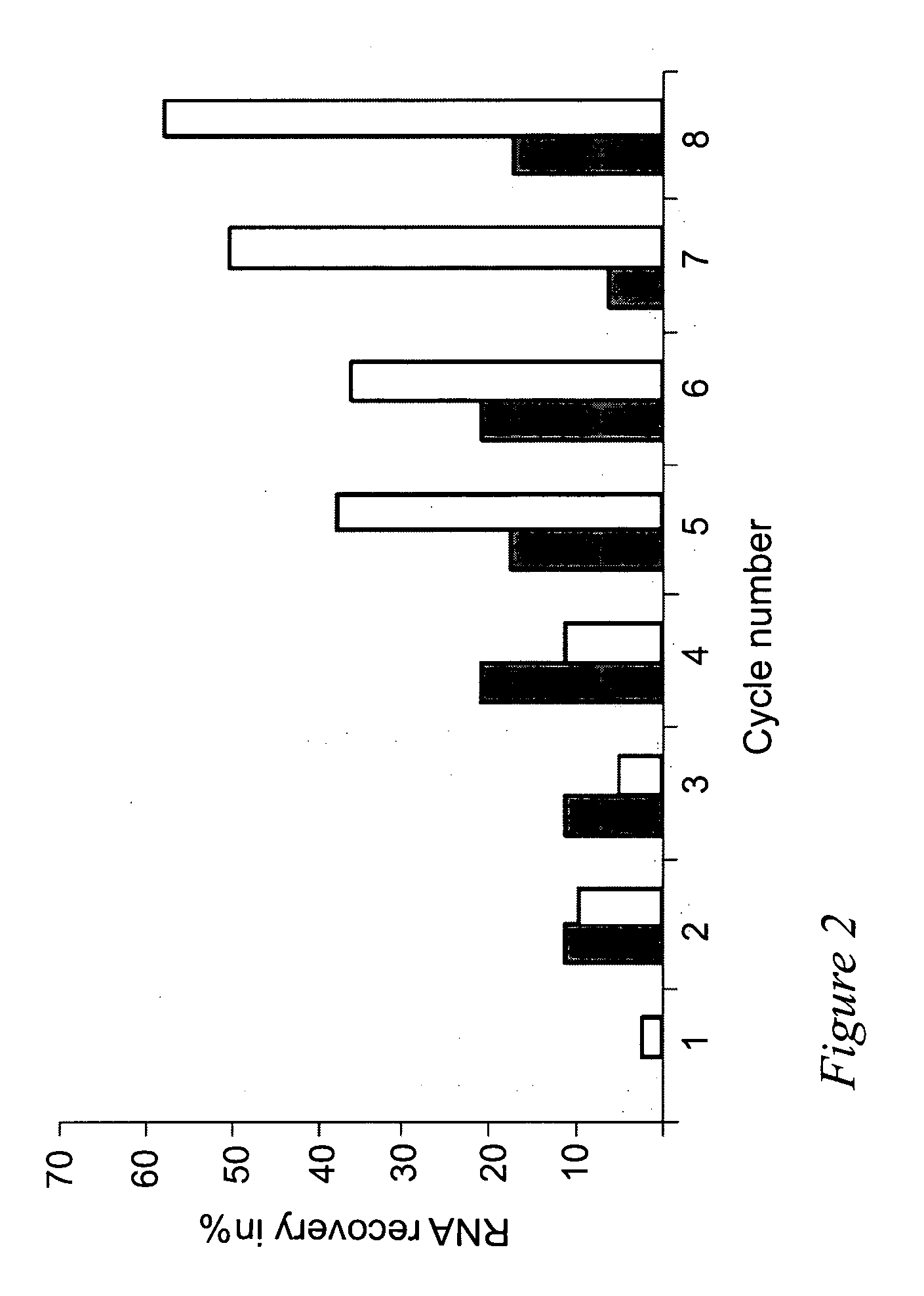
Selection of RNA aptamers as Anti-malaria agents
The present invention relates to an aptamer or an active fragment thereof raised against the semi-conserved duffy binding ligand domain 1α, DBL1α, region of the Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1, PfEMPI, which aptamer has an effect against malaria, in particular severe cerebral malaria.
Owner:APTAHEM
Malaria assistance bi-hydrogen arteannuin suppository
InactiveCN101361706AGood treatment effectFast absorptionOrganic active ingredientsSuppositories deliveryDiseaseRegimen
The invention aims at providing an anti-malarial dihydroartemisinin suppository, which is a rectum or anus dosage regimen, and has the advantages of low recurrence rate, low toxicity, safety, short treatment period, quick results, low cost and speeding up healing process after being used by malaria-patients, thus removing the diseases. The anti-malarial dihydroartemisinin suppository is prepared by adding dihydroartemisinin with suppository base, and the content of the dihydroartemisinin in each grain of the suppository is 10-100mg.
Owner:HUBEI CHENGTIAN PHARMA
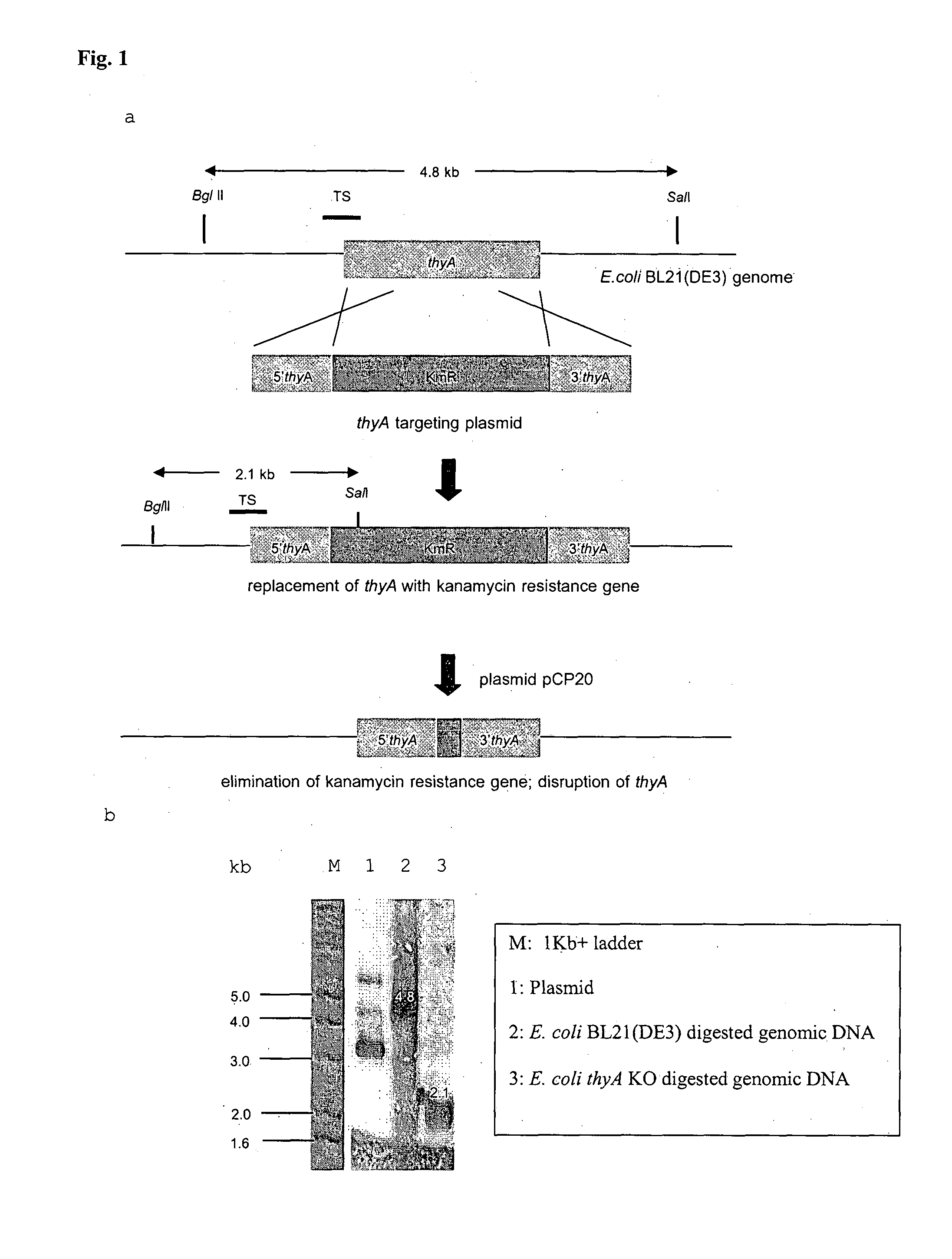
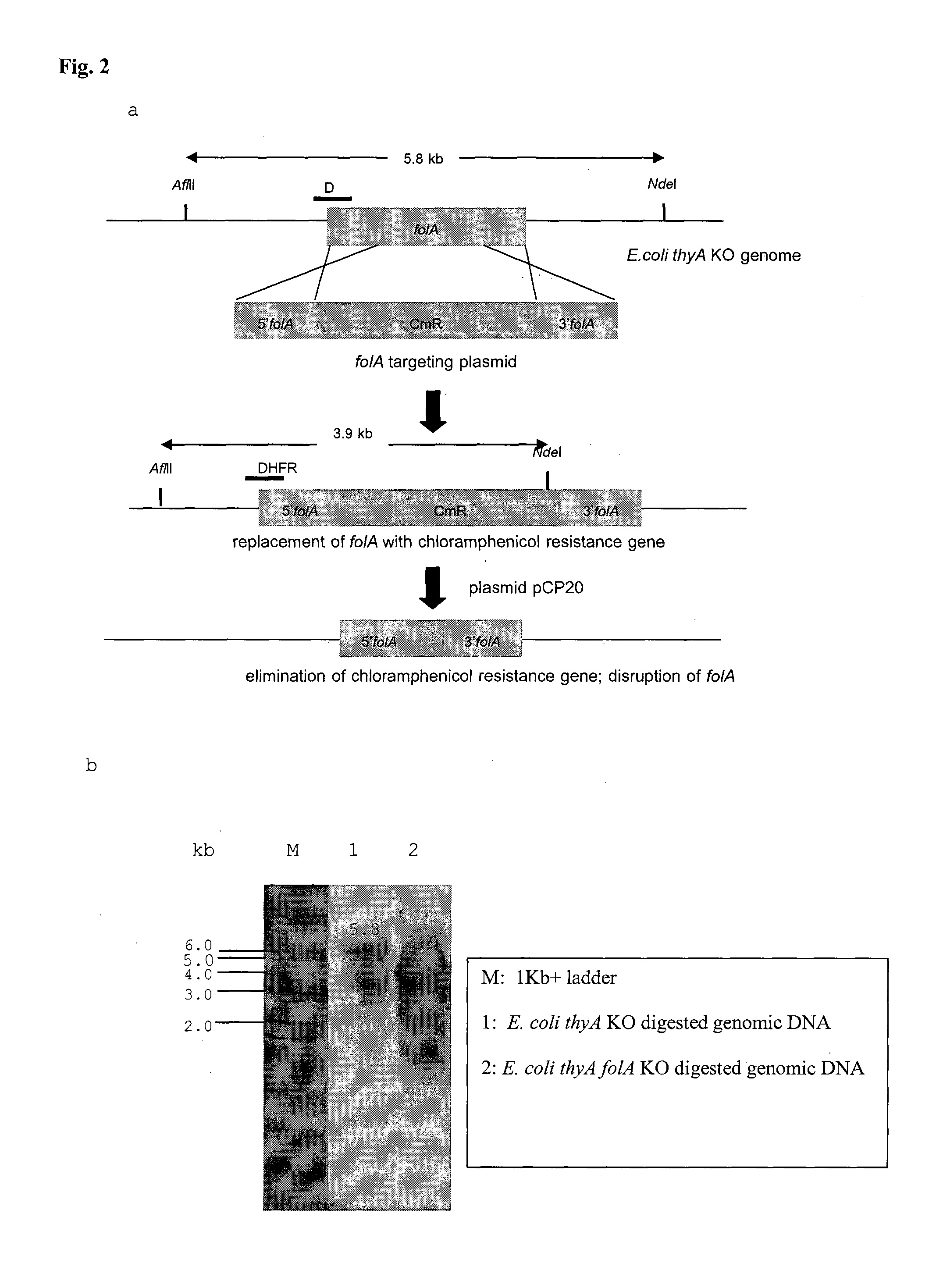
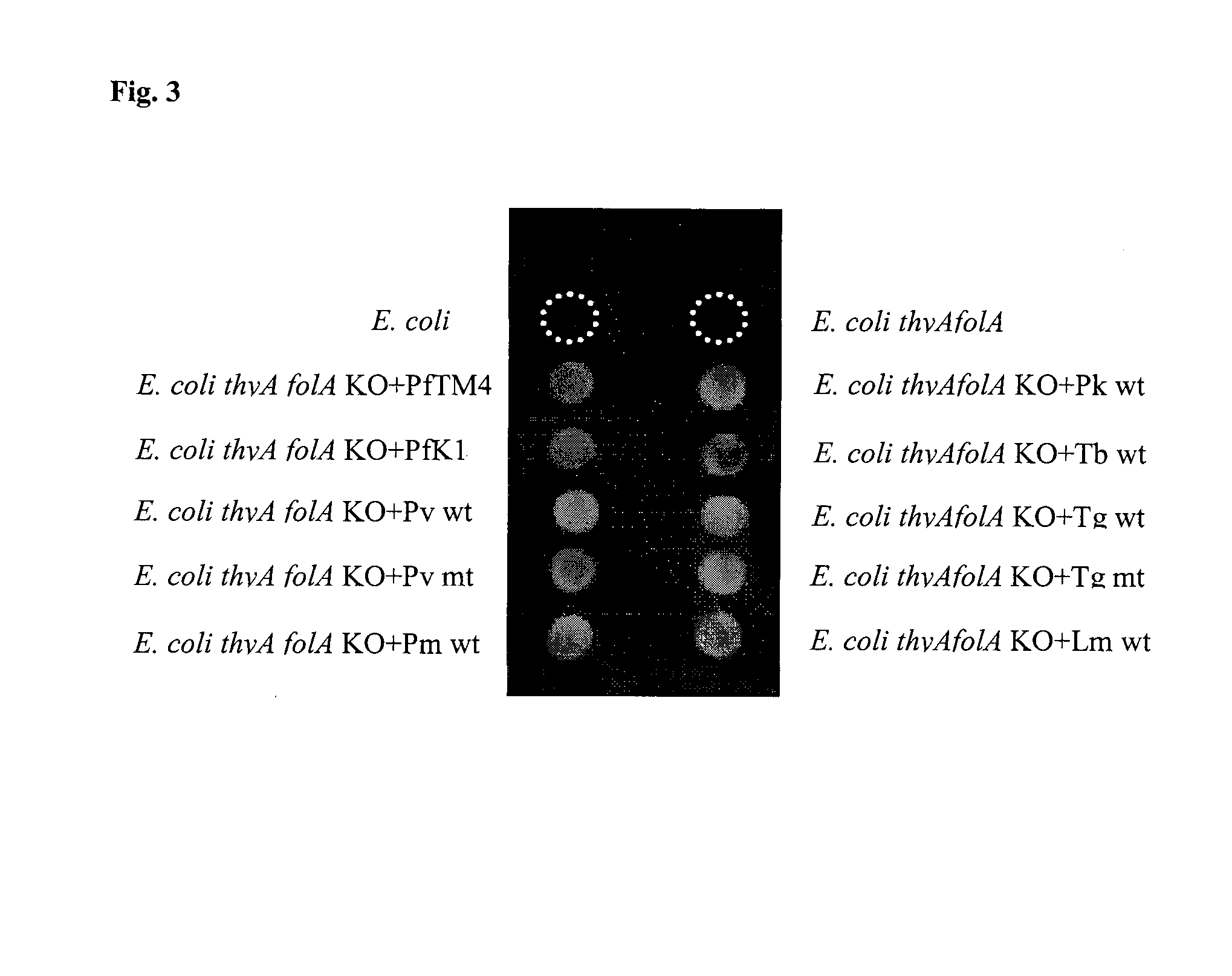
BACTERIAL SURROGATE FOR TESTING OF ANTIMALARIALS: thyA KNOCKOUT AND folA KNOCKOUT BACTERIA FOR TESTING OF INHIBITION OF MALARIAL DIHYDROFOLATE REDUCTASE-THYMIDYLATE SYNTHASE
The objective of this invention is to create a double thyA folA knockout Escherichia coli (E. coli) strain for antifolate screening against DHFR of malaria and other parasites. This strain is used together with a plasmid expressing DHFR-TS from the desired pathogenic organism, which constitutes an anti-DHFR assay against the pathogenic organism of interest. The benefit of this invention is that there is no interference from either host DHFR or trimethoprim, a bacterial DHFR inhibitor. This tool is easy to use and maintain. It provides quick and reliable results as compared with conventional anti-malarial and anti-parasitic assays. This invention should facilitate discovery of new anti-DHFR compounds against malaria and other parasitic diseases.
Owner:NAT SCI & TECH DEV AGENCY
4-quinolinemethanols as Anti-malarial agents
The present invention relates to substituted 4-qinolinemethanols and pharmaceutical compositions thereof and methods of using the same for treating of malaria, tuberculosis, and other infectious diseases.
Owner:JENRIN DISCOVERY
Inhibitors of plasmepsins
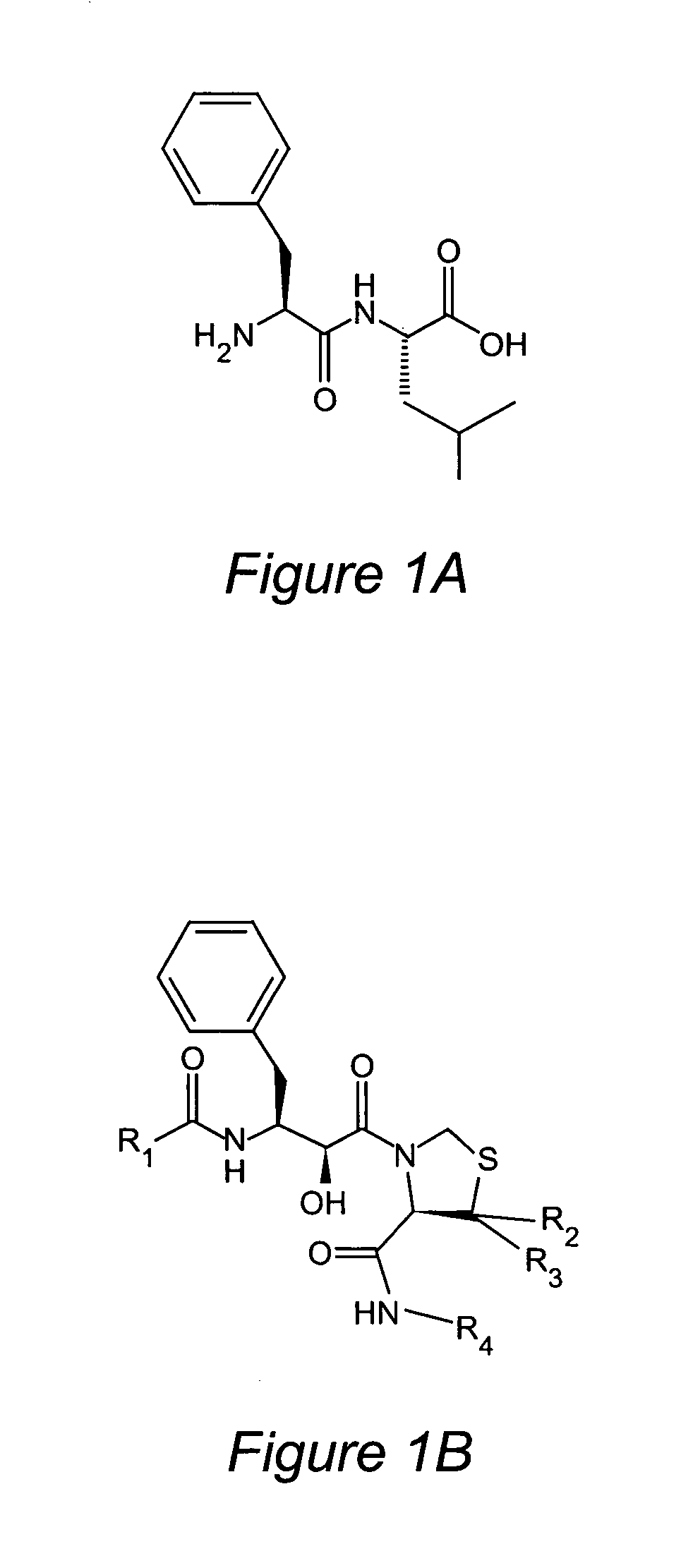
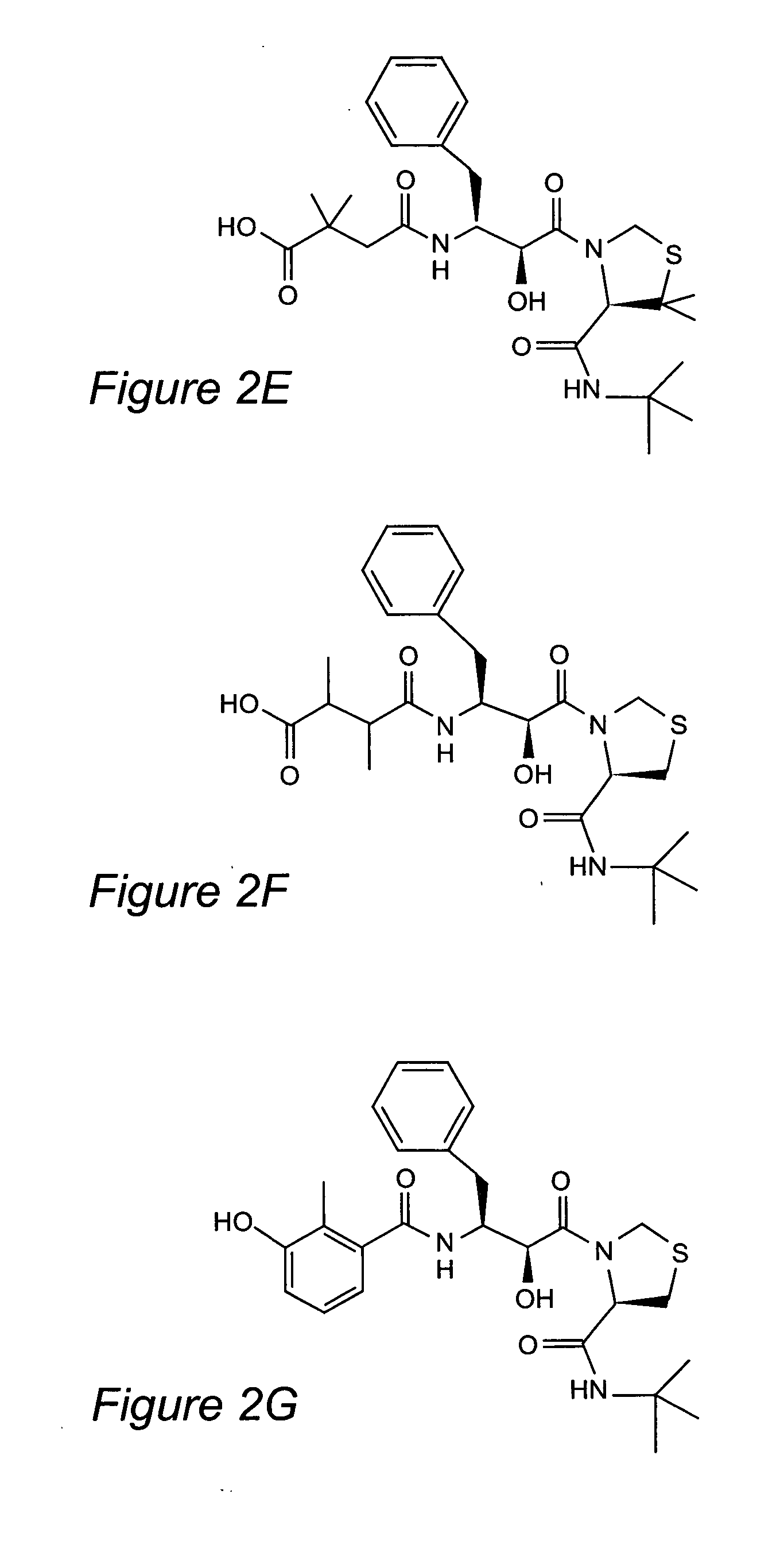
Compounds and methods for the inhibition of anti-malarial target aspartyl protease plasmepsins (e.g. Plasmepsin I, Plasmepsin II, Plasmepsin IV and HAP) are provided. The compounds are based on allophenylnorstatine substituted at positions R1-R4, such that R1 is isoquinoline, carboxyl, naphtalene, phenyl, phenol, benzene, an amino acid, and derivatives thereof; R2 and R3 are aliphatic groups; and R4 is indan, naphthalene, benzylamine, phenyl, phenol, cyclopentane, tert-butylamine, or derivatives thereof. The compounds may be used to inhibit Plasmepsin II, to kill malarial parasites, and to treat malaria in a patient. Certain of the substituted allophenylnorstatine-based compounds also exhibit inhibitory activity against Cathepsin D.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Anticancer and antiprotozoal dihydroartemisinene and dihydroartemisitene dimers with desirable chemical functionalities
This invention comprises compositions containing dihydroartemisinin- and dihydroartemisitene-dimers with activity as anticancer or anticancer metastasis agents and anti-protozal, including anti-malarial and anti-leishmanial properties. This invention also describes methods of preparation of these compositions and methods of use of such compositions for the treatment of cancer or prevention of cancer metastasis, and protozoal infections, including malaria, or leishmaniasis. The compounds of this invention represent a potential new class of anti-tumor or anti-metastasis agents, one that has shown promising activity against solid tumors.
Owner:ELSOHLY LAB
Universal T-cell epitopes for anti-malarial vaccines
The present invention provides methods and compositions for eliciting protective immunity against malaria. In particular, the invention relates to universal T-cell epitopes that elicit T-cell responses in individuals of differing genetic backgrounds. Immunogenic compositions and vaccines including malaria-specific universal T-cell epitopes are disclosed.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Malaria vaccine
InactiveUS20020160017A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsPlasmodium merozoiteMalaria
A non-naturally occurring variant of a C-terminal fragment of a Plasmodium merozoite surface protein-1 (MSP-1) wherein said variant has (i) a reduced affinity, compared with a naturally occurring Plasmodium MSP-119, for at least one first antibody capable of blocking the binding of a second antibody, which second antibody inhibits the proteolytic cleavage of Plasmodium MSP-142 and (ii) substantially the same affinity for at least one third antibody compared with said naturally occurring Plasmodium MSP-119. which third antibody inhibits the proteolytic cleavage of Plasmodium MSP-142 is provided for use in an anti-malarial vaccine.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Malaria vaccine
InactiveUS7078043B2Improve efficiencyMinimize disruptionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsMalariaMerozoite Surface Protein 1
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
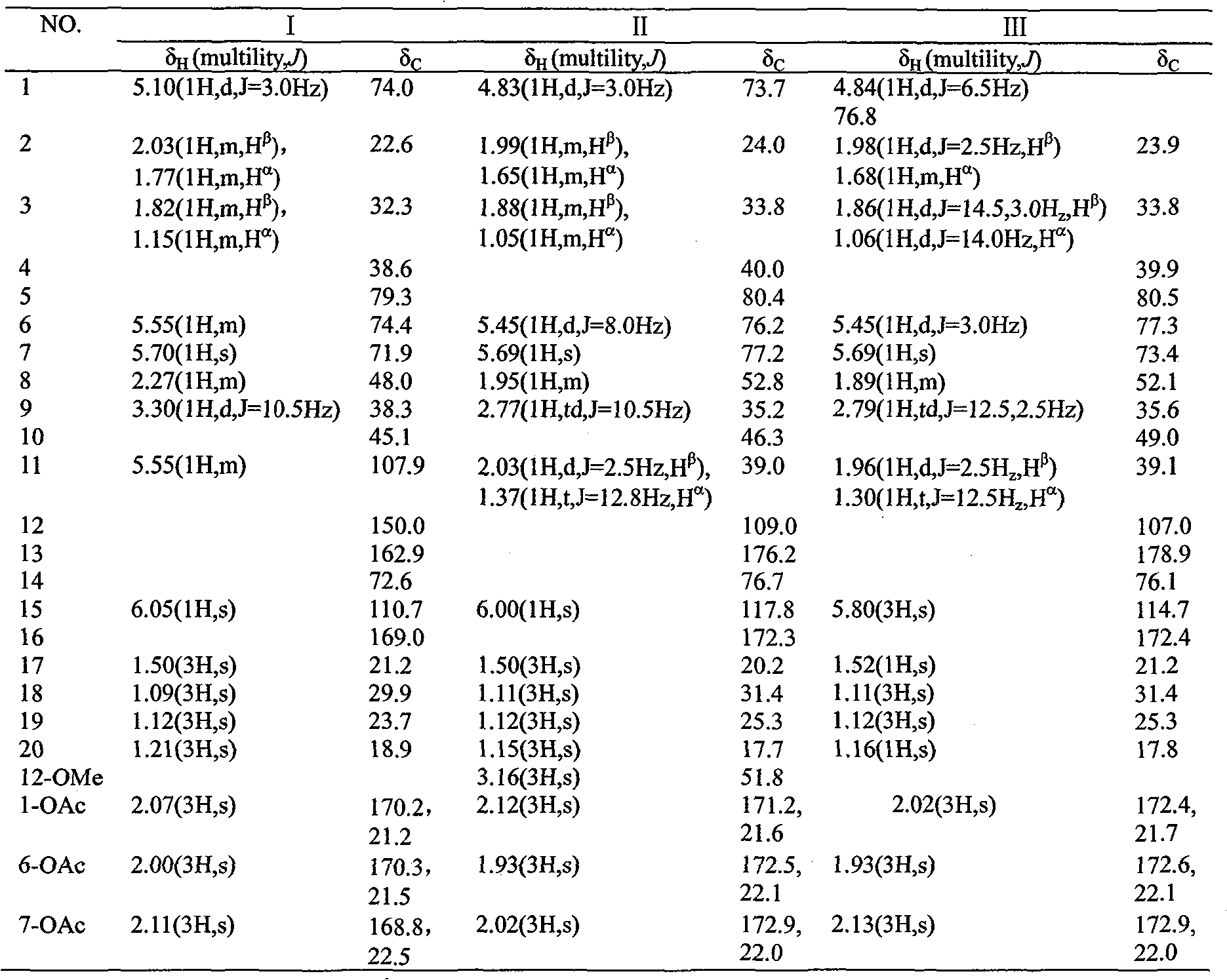
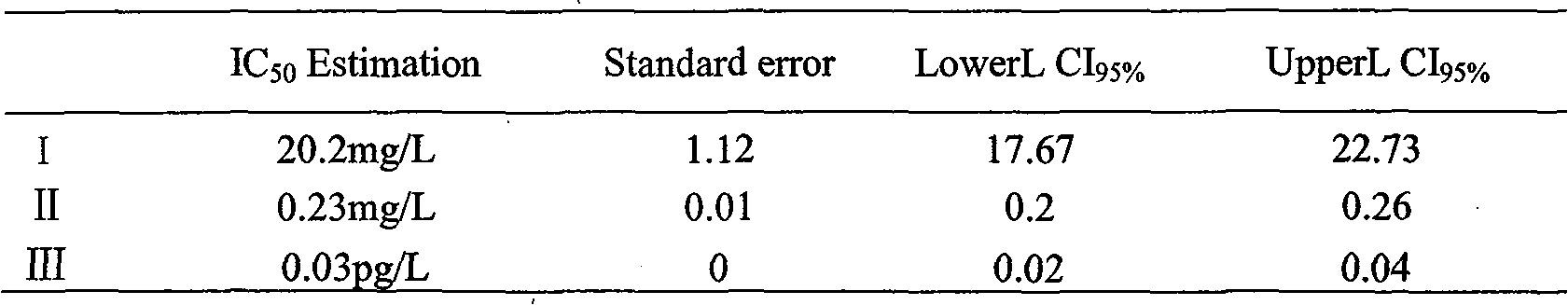
Three cassane type diterpenoid lactone compounds with activity against plasmodium falciparum
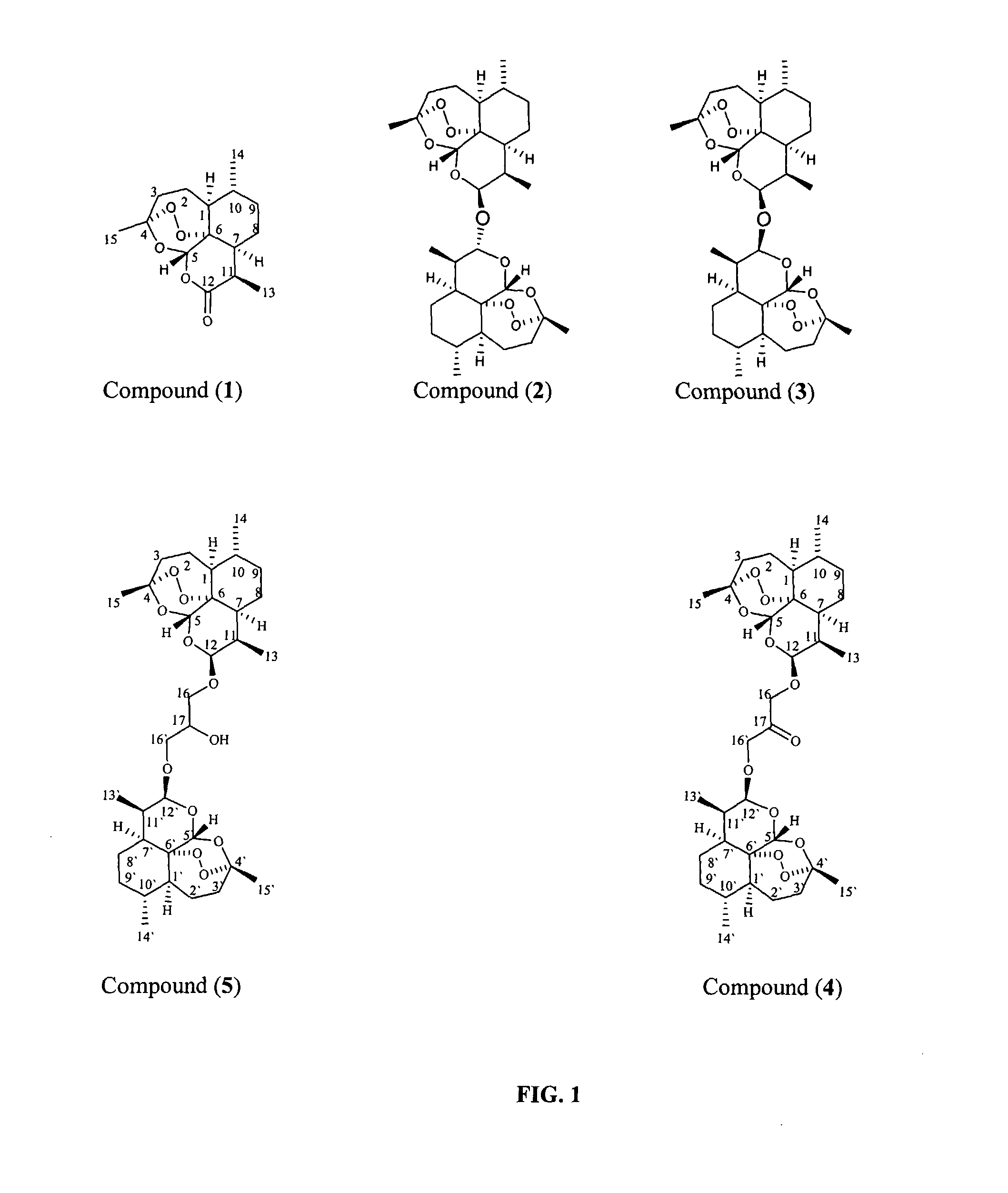
The invention relates to a type of cassane type diterpenoid lactone compounds with activity against plasmodium falciparum, which are prepared by taking seeds of a leguminous medicinal plant of caesalpinia minax hance as raw materials, using a specific solvent for extraction, carrying out a variety of chromatography and finally obtaining three cassane type diterpenoid lactone monomeric compounds, which are 5 alpha, 14 beta-dihydroxy-1 alpha, 6 alpha, 7 beta-triacetyl-13(15), 11(12)-diene-16, 12-lactone (I), 12 alpha-methoxy, 5 alpha, 14 beta-dihydroxy-1 alpha, 6 alpha, 7 beta-triacetyl-13(15)-ene-16, 12-lactone (II) and neocaesalpin L (III) respectively, wherein the compound I and the compound II are new compounds. The first research test of in vitro anti-malarial pharmacodynamics of the three compounds shows that the three compounds have obvious effect of suppressing the plasmodium falciparum and can be used for preparing drugs for treating and / or preventing malaria.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Novel assay to screen for anti-malarials
InactiveUS20060183167A1Improve throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningResistant strainDrug target
Malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum is responsible for the most severe form of malaria in humans, causing about 2 million deaths every year. Lack of effective vaccines and emergence of drug-resistant strains necessitate the need of novel drug targets to treat the disease. The present invention describes a novel assay method of identifying candidate compounds as anti-malarials based on the property of binding to plasmodial parasite 90 kDa heat shock protein.
Owner:THE REGISTRAR INDIAN INST OF SCI
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com