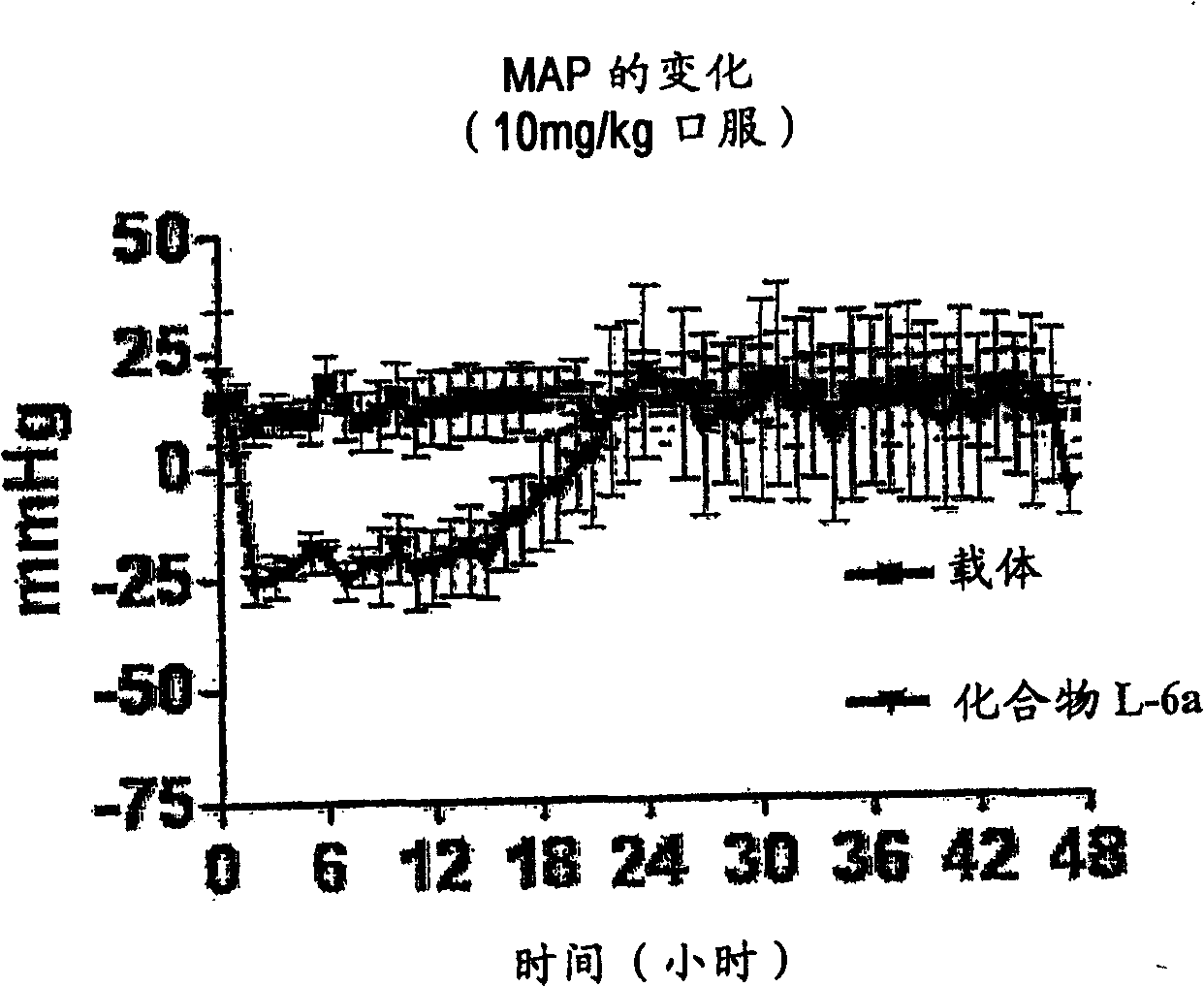
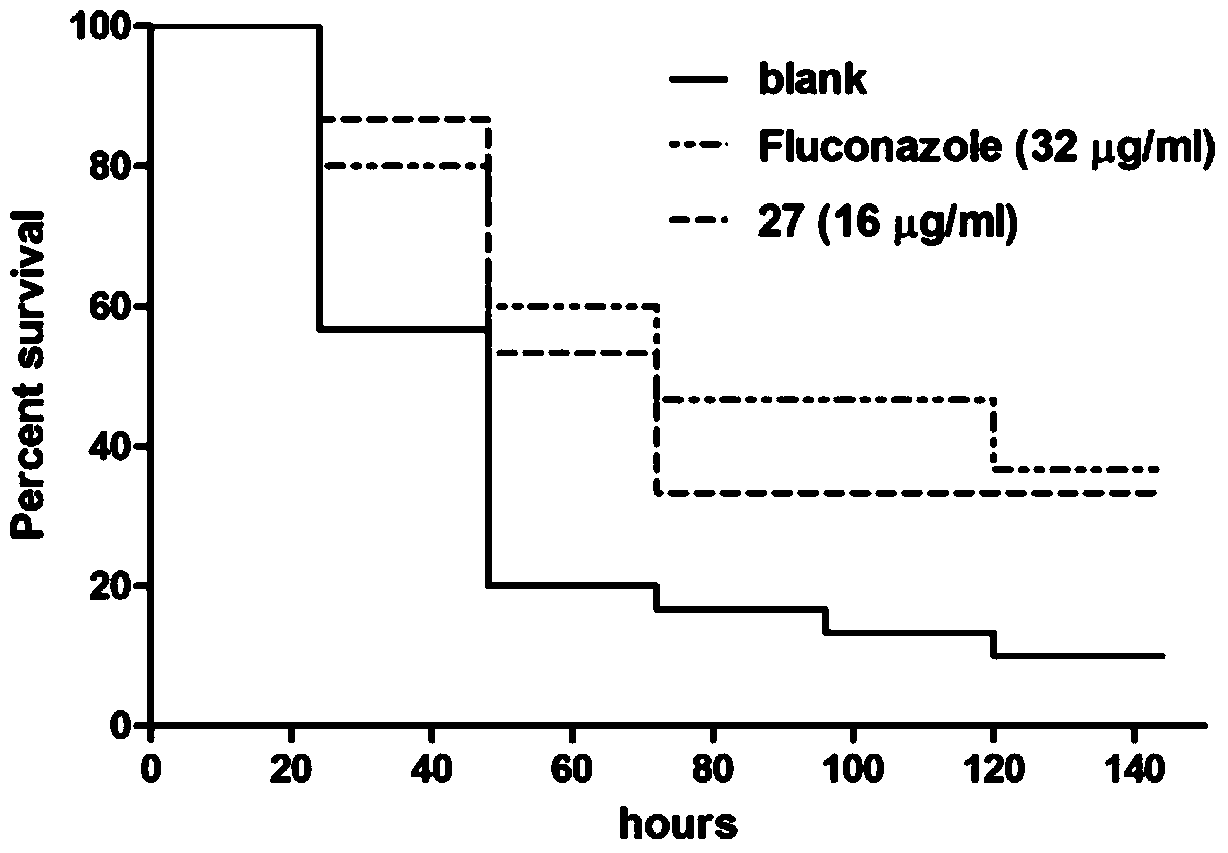
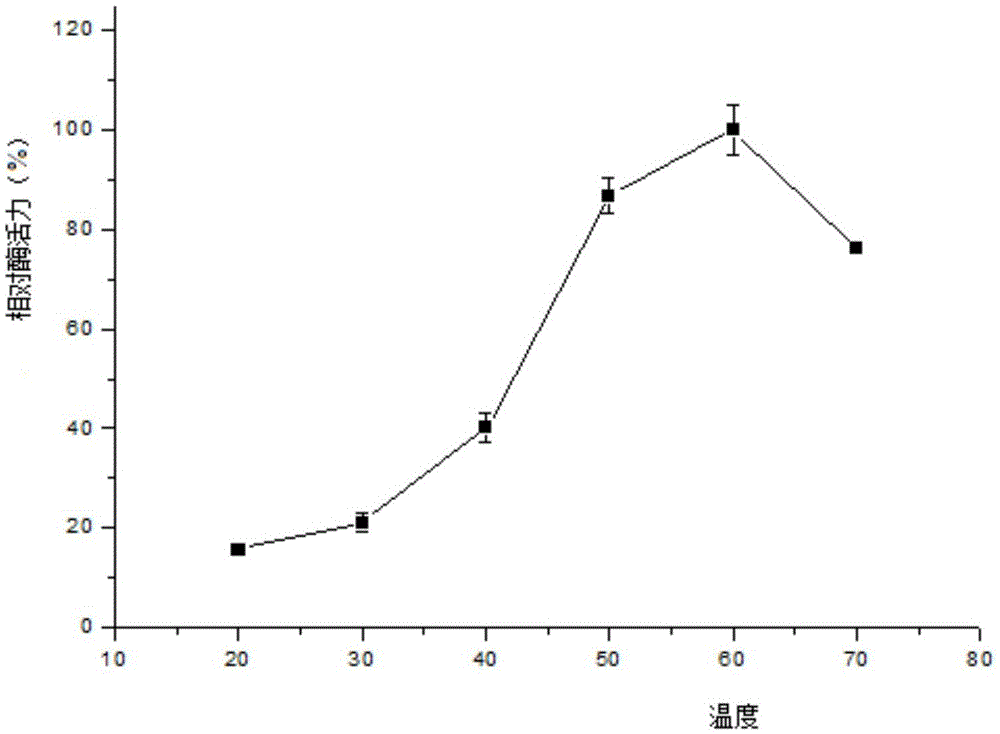
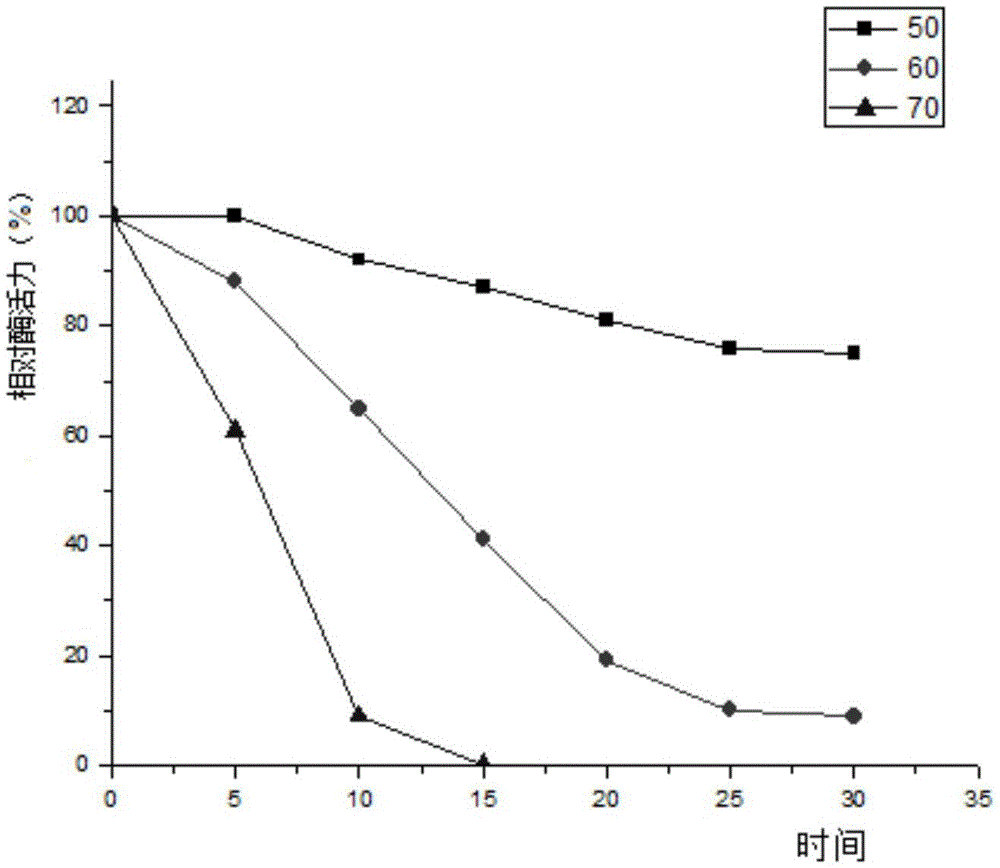
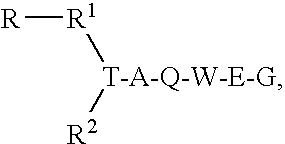
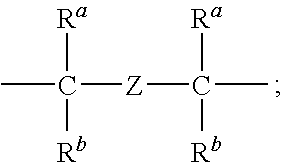
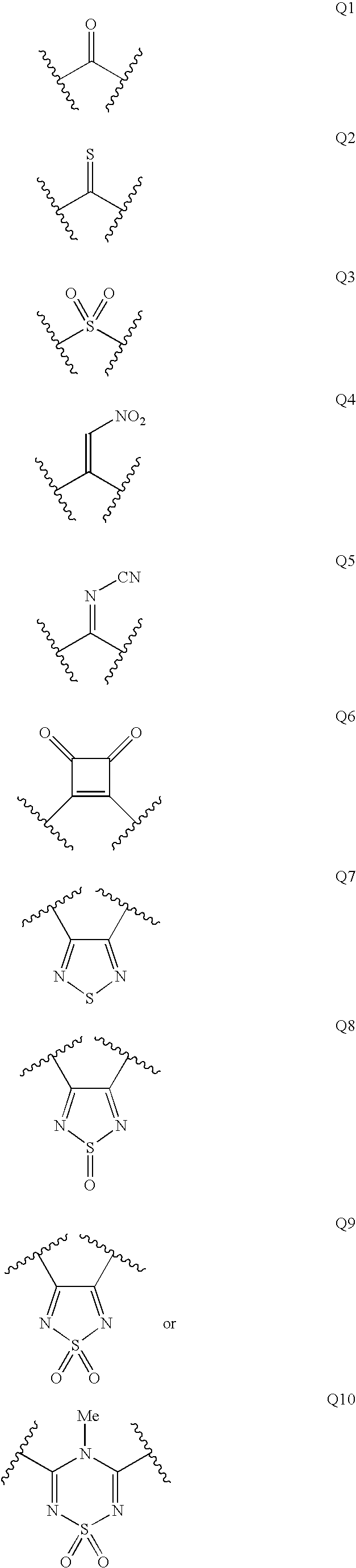
Patents
Literature
68 results about "Aspartate protease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
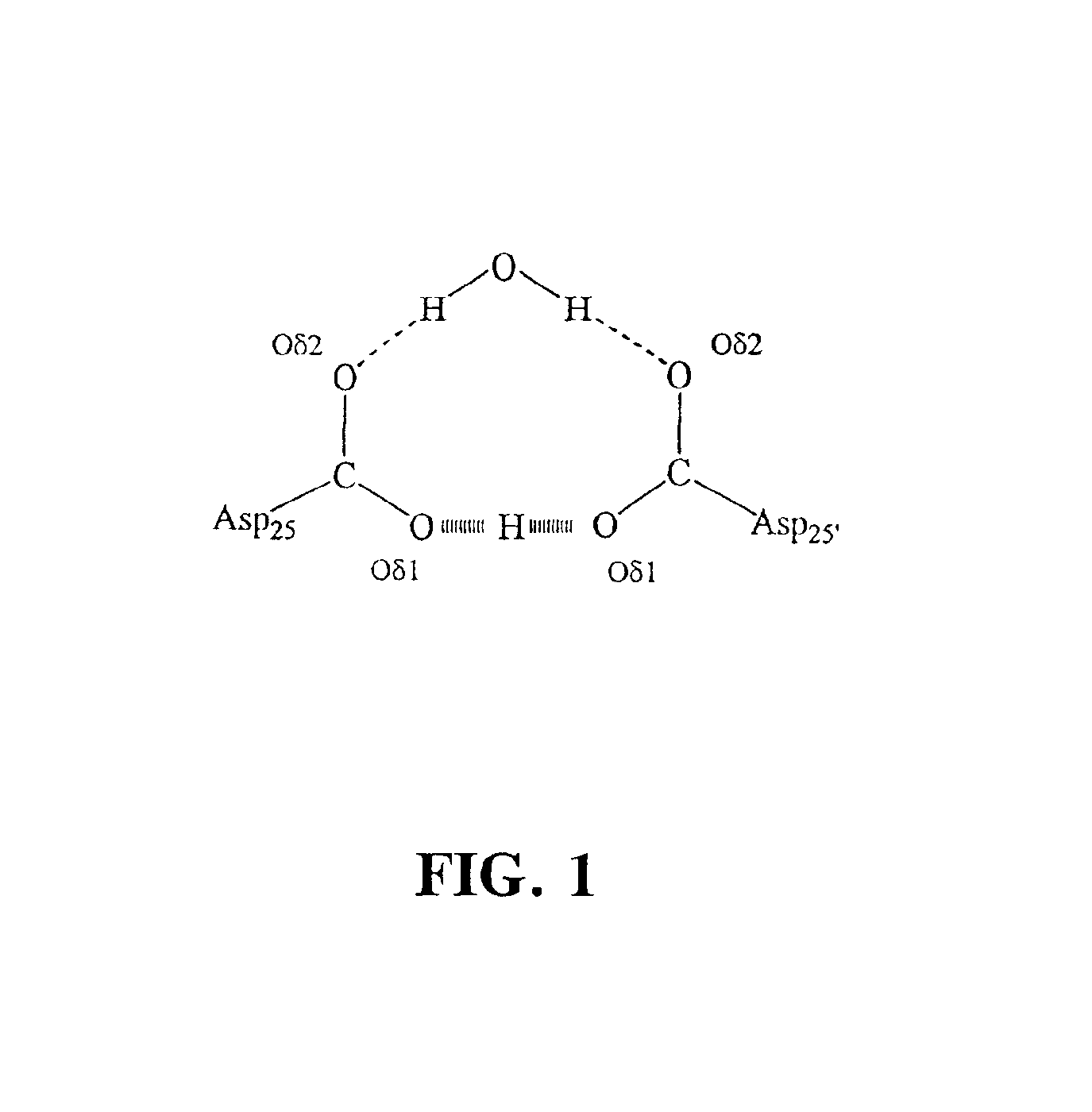
Aspartic proteases are a catalytic type of protease enzymes that use an activated water molecule bound to one or more aspartate residues for catalysis of their peptide substrates. In general, they have two highly conserved aspartates in the active site and are optimally active at acidic pH. Nearly all known aspartyl proteases are inhibited by pepstatin.
Method for increasing protein content in plant cells
InactiveUS20050055746A1High in proteinImprove agronomic valueOther foreign material introduction processesPlant peptidesProteinase activityPlant cell
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
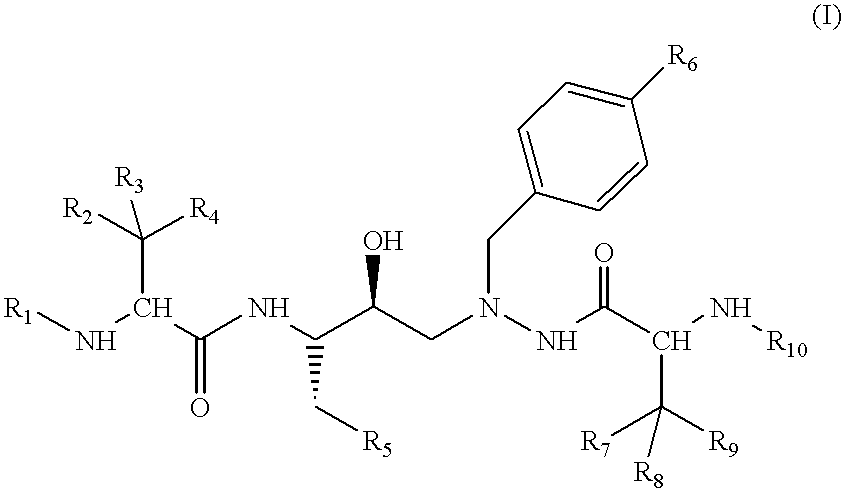
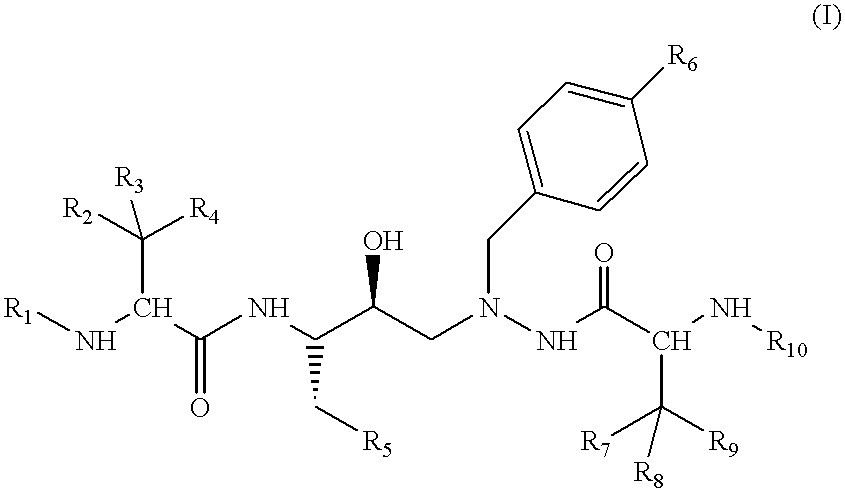
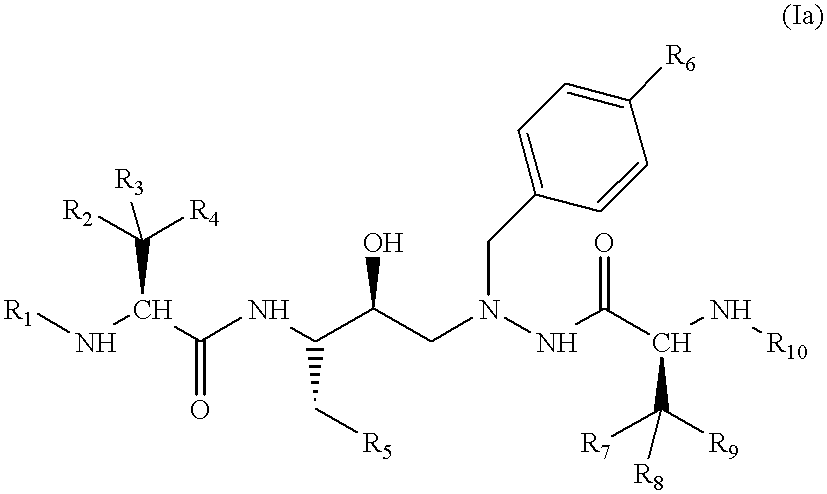
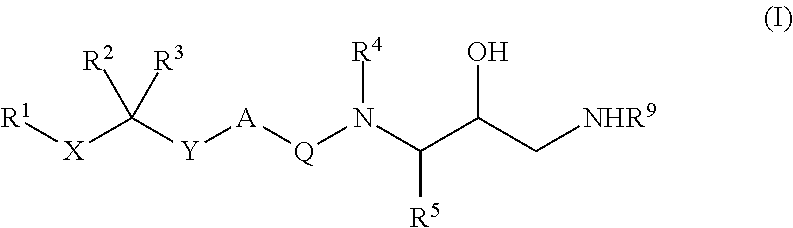
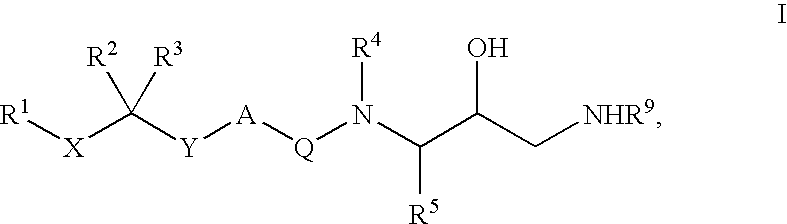
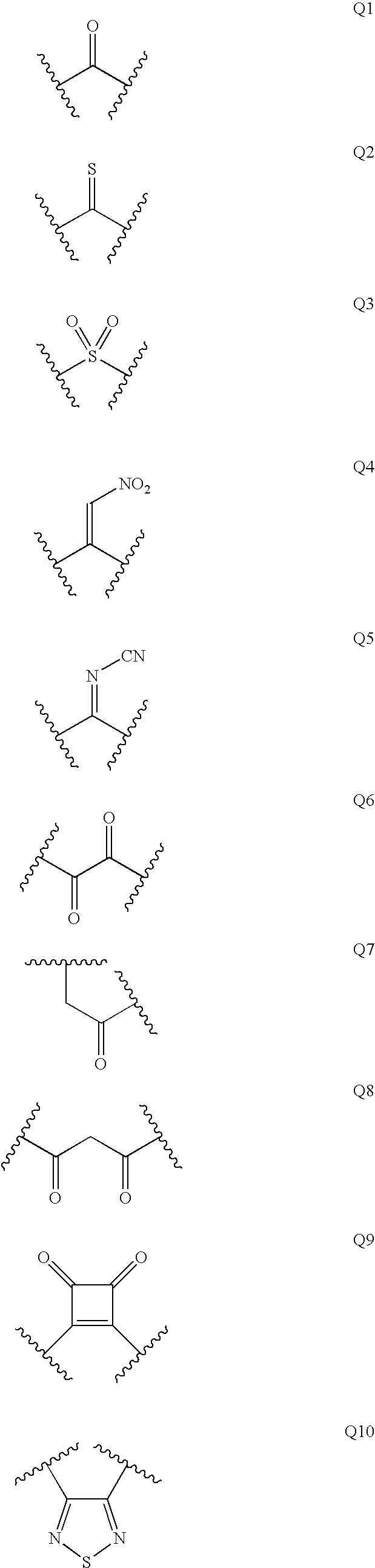
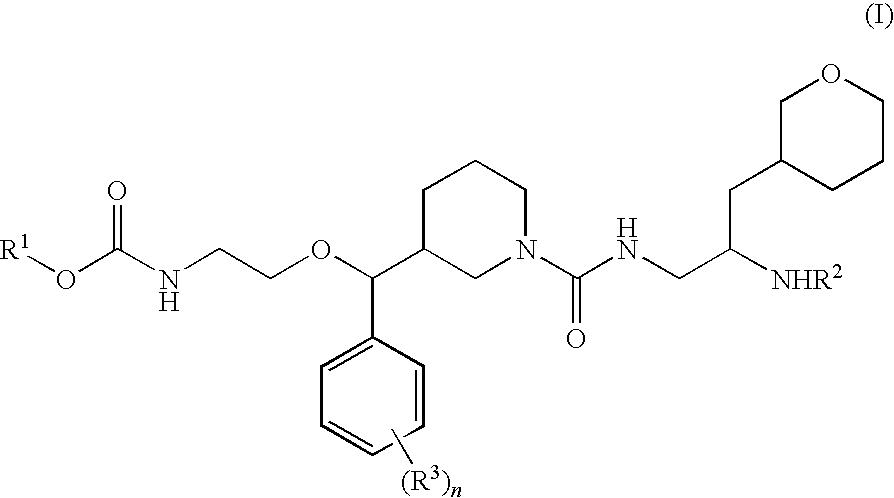
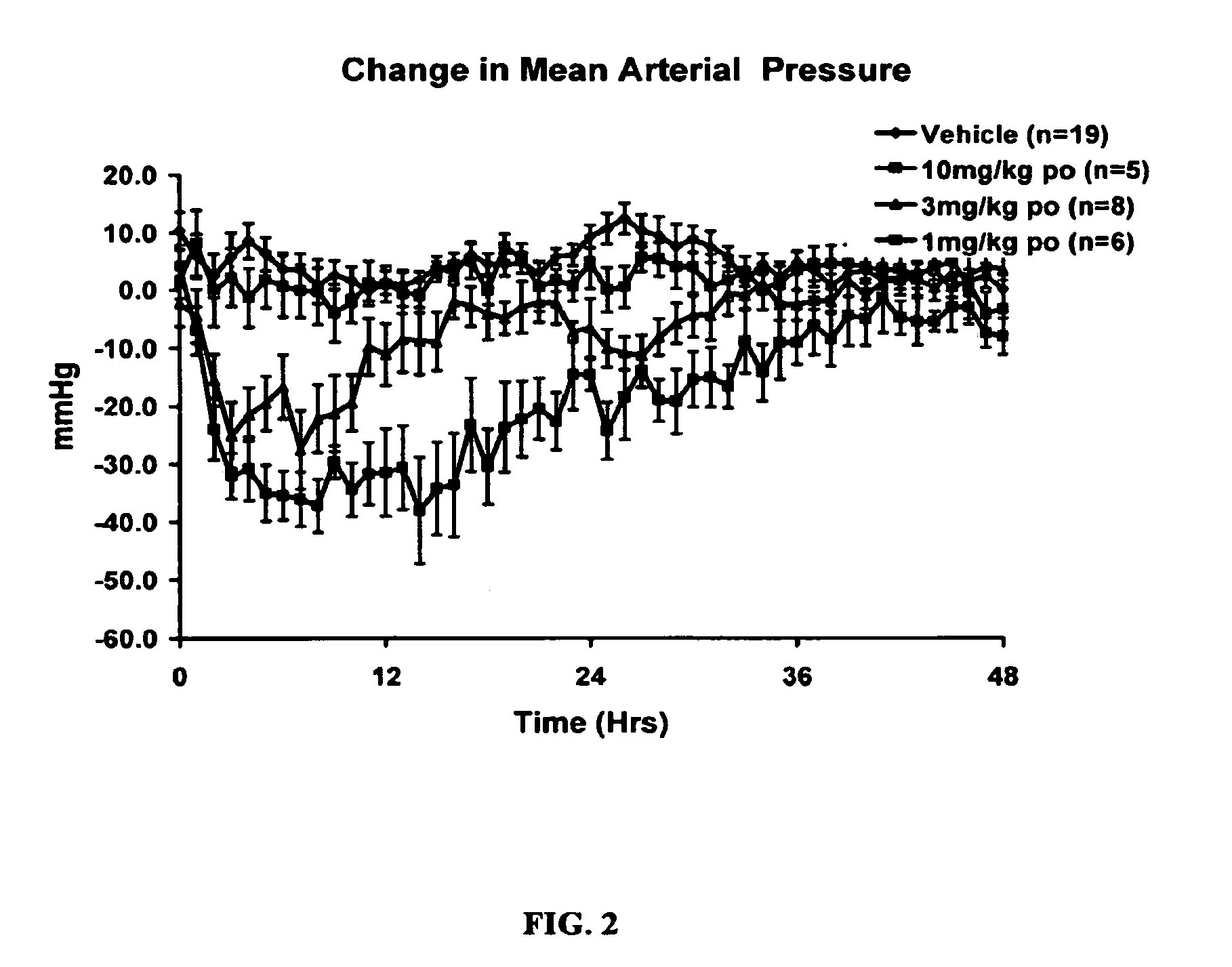
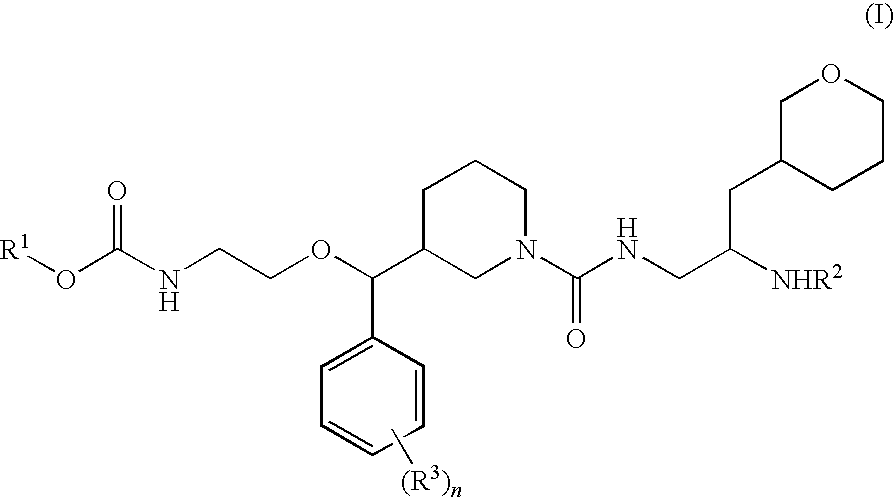
Piperidine derivatives as renin inhibitors
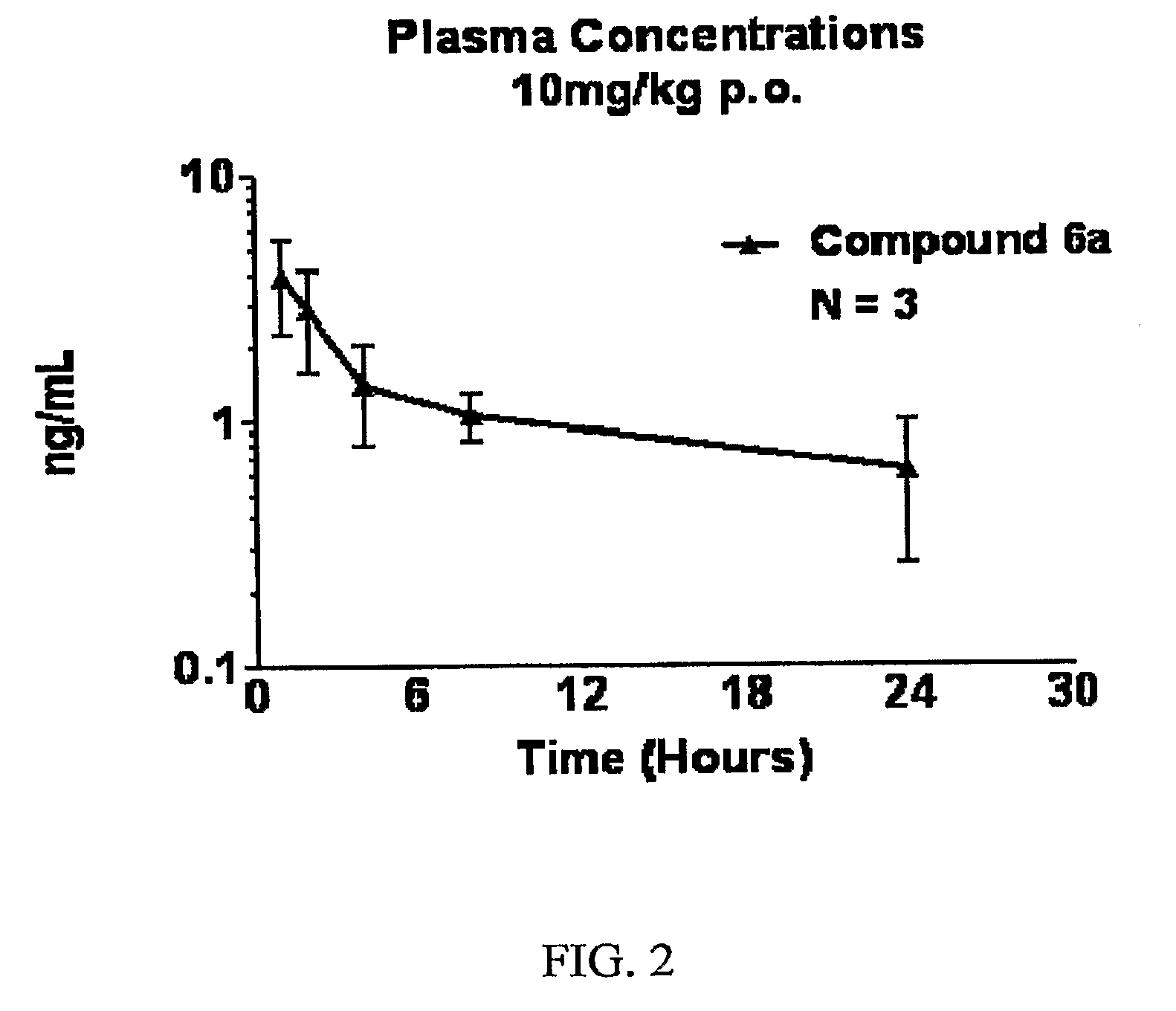
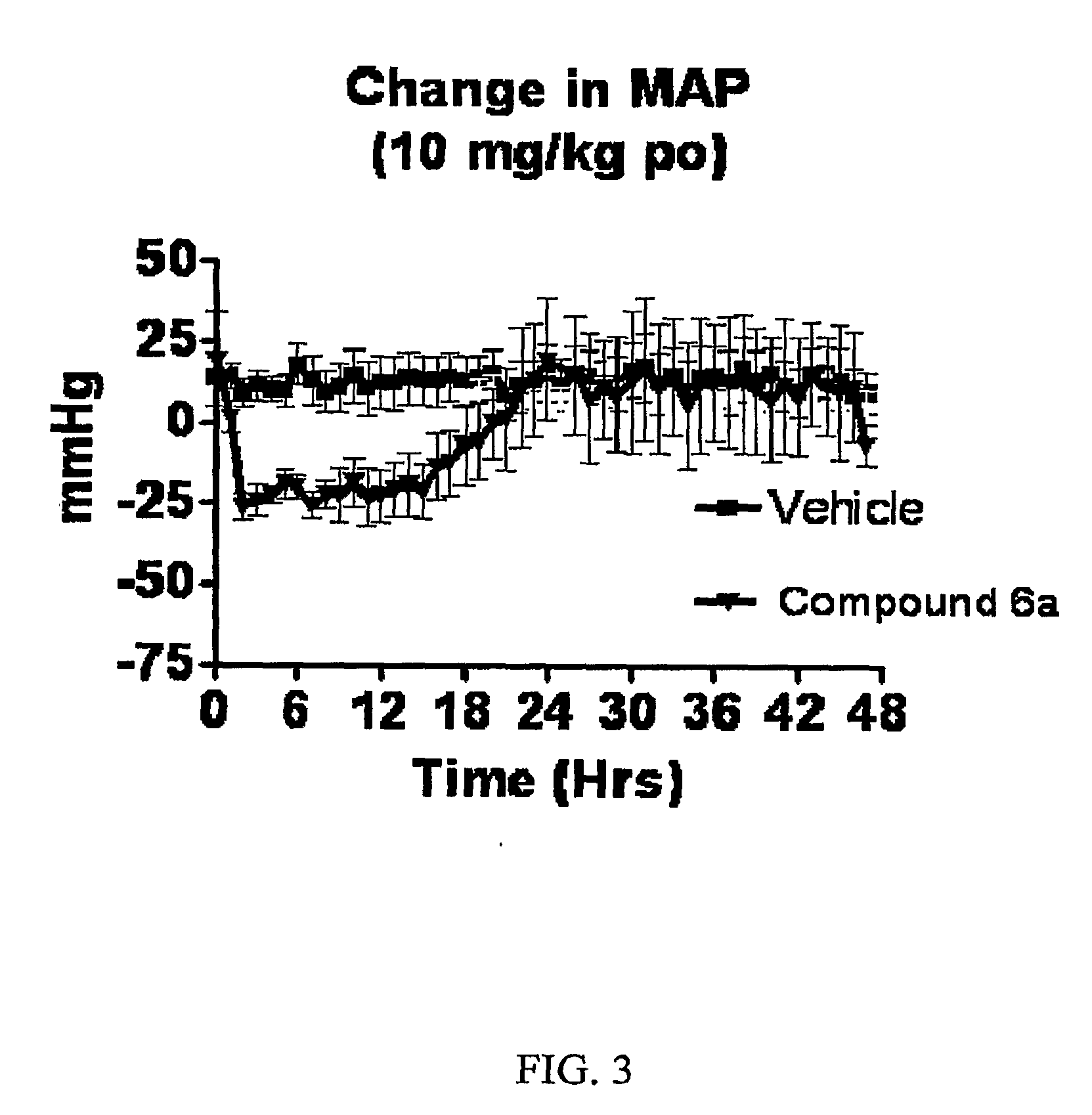
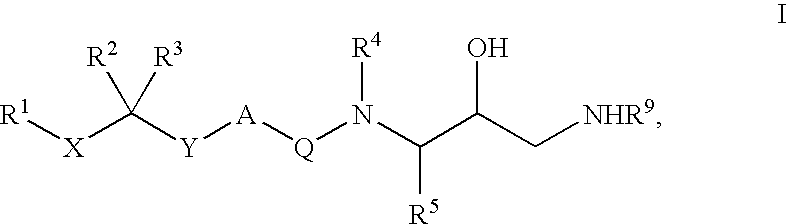
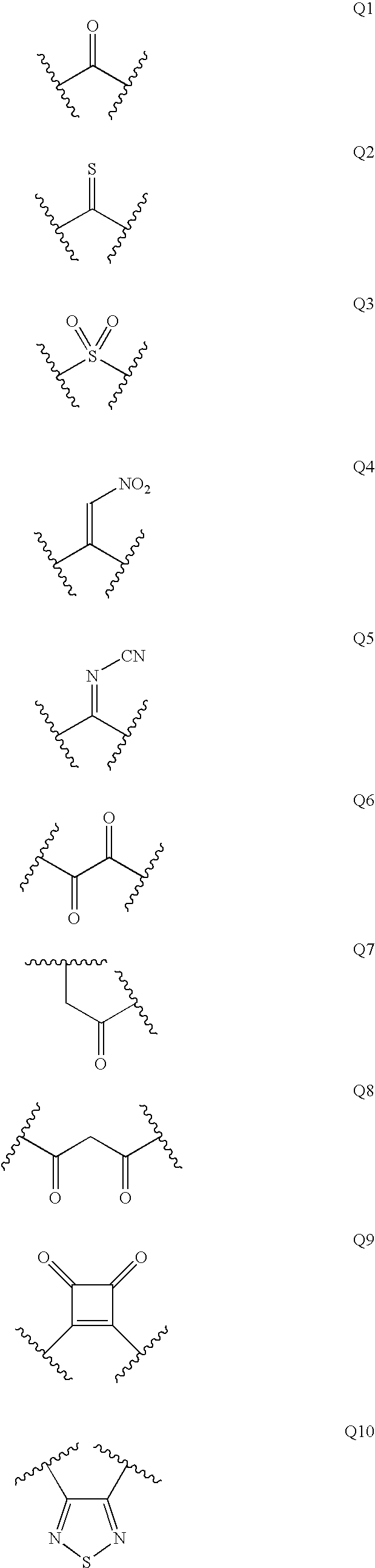
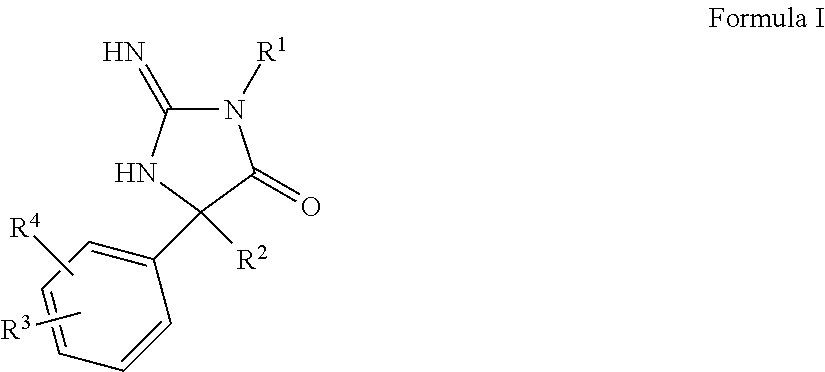
The present invention is directed to aspartic protease inhibitors represented by the following structural formula; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The present invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the aspartic protease inhibitors of Structural Formula (I). Methods of antagonizing one or more aspartic proteases in a subject in need thereof, and methods for treating an aspartic protease mediated disorder in a subject using these aspartic protease inhibitors are also disclosed.
Owner:VITAE PHARMA INC
Diaminopropanol Renin Inhibitors
Described are diaminopropanols of which are orally active and bind to renin to inhibit its activity. They are useful in the treatment or amelioration of diseases associated with elevated levels of renin activity or in the treatment of aspartic protease mediated disorders. Also described is a method for the use of the diaminopropanols in ameliorating or treating renin related disorders in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:VITAE PHARMA INC
Microbially derived enzymes having enhanced milk clotting activity and method of producing same
InactiveUS6127142AIncrease production costAdvantageously producedMilk preparationHydrolasesAspergillus oryzaeAspartic acid
PCT No. PCT / DK95 / 00511 Sec. 371 Date Aug. 14, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Aug. 14, 1997 PCT Filed Dec. 20, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 19582 PCT Pub. Date Jun. 27, 1996A method of producing a milk clotting enzyme including the steps of (a) fermenting a strain of Rhizomucor miehei or Aspergillus oryzae to form a fermentation product having a glycoslated Rhizomucor miehei aspartic protease and other proteins, and (b) subjecting a quantity of the fermentation product to a deglycosylating treatment to form a coagulant preparation having an at least partly deglycoslated aspartic protease and the other proteins. The at least partly deglycosylated protease has a milk clotting activity that is at least 10% higher than a milk clotting activity of the glycosylated aspartic protease.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Azahexane derivatives as substrate isosters of retroviral asparate proteases
InactiveUS6225345B1BiocideCarbamic acid derivatives preparationProteinase activityAspartate protease
The invention relates to compounds of formula (I):wherein R1 and R10 are each independently of the other lower alkoxycarbonyl; either R2, R3 and R4 are each independently of the other C1-C4alkyl and R7, R8 and R9 are each selected from hydrogen and C1-C4alkyl, with not more than 2 of the radicals being hydrogen; or R7, R8 and R9 are each independently of the other C1-C4alkyl and R2, R3 and R4 are each selected from hydrogen and C1-C4alkyl, with 1 or 2 of the radicals being hydrogen; R5 is phenyl or cyclohexyl; and R6 is phenyl or cyanophenyl; or salts thereof; those compounds are inhibitors of retroviral aspartate proteases and are effective, for example, against HIV.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Diaminopropanol renin inhibitors
Described are diaminopropanols of which are orally active and bind to renin to inhibit its activity. They are useful in the treatment or amelioration of diseases associated with elevated. levels of renin activity or in the treatment of aspartic protease mediated disorders. Also described is a method for the use of the diaminopropanols in ameliorating or treating renin related disorders in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:VITAE PHARMA INC
Methods for producing polypeptidies in protease-deficient mutants of trichoderma
The present invention relates to mutants of a parent Trichoderma strain, comprising a polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide and one or more (several) genes selected from the group consisting of a first subtilisin-like serine protease gene, a first aspartic protease gene, a trypsin-like serine protease gene, a second subtilisin-like serine protease gene, and a second aspartic protease gene, wherein the one or more (several) genes are modified rendering the mutant strain deficient in the production of one or more (several) enzymes selected from the group consisting of a first subtilisin-like serine protease, a first aspartic protease, a trypsin-like serine protease, a second subtilisin-like serine protease, and a second aspartic protease, respectively, compared to the parent Trichoderma strain when cultivated under identical conditions. The present invention also relates to methods of producing a polypeptide in such mutants and methods for producing such mutants.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Renin Inhibitors
The present invention is directed to aspartic protease inhibitors represented by the following structural formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The present invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the aspartic protease inhibitors of Structural Formula (I). Methods of antagonizing one or more aspartic proteases in a subject in need thereof, and methods for treating an aspartic protease mediated disorder in a subject using these aspartic protease inhibitors are also disclosed.
Owner:VITAE PHARMA INC
An antiviral feed additive for promoting the growth of soft-shelled turtles
Owner:BENGBU HUAIJING LYUWAN ECOLOGICAL AGRI
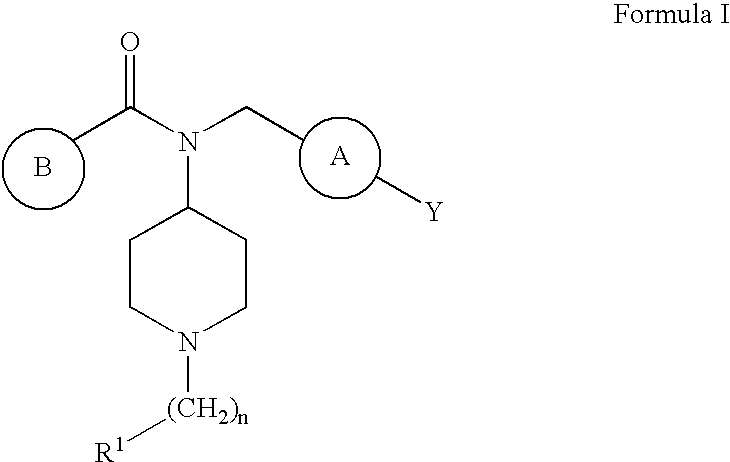
Novel 4-Aminopiperidine Derivatives
Novel substituted 4-aminopiperidine derivatives of the formula I: wherein n, R1, Y, and are as defined in claim 1, and optically pure enantiomers, mixtures of enantiomers, racemates, diastereomers, mixtures of diastereomers, diastereomeric racemates, mixtures of diastereomeric racemates and meso-forms, as well as salts and solvent complexes of such compounds, and morphological forms, that exhibit useful parasite aspartic proteases inhibiting properties and can thus be used in the form of pharmaceutical compositions as antimalarial medicines.
Owner:ACTELION PHARM LTD
Compositions and methods for the treatment of malaria
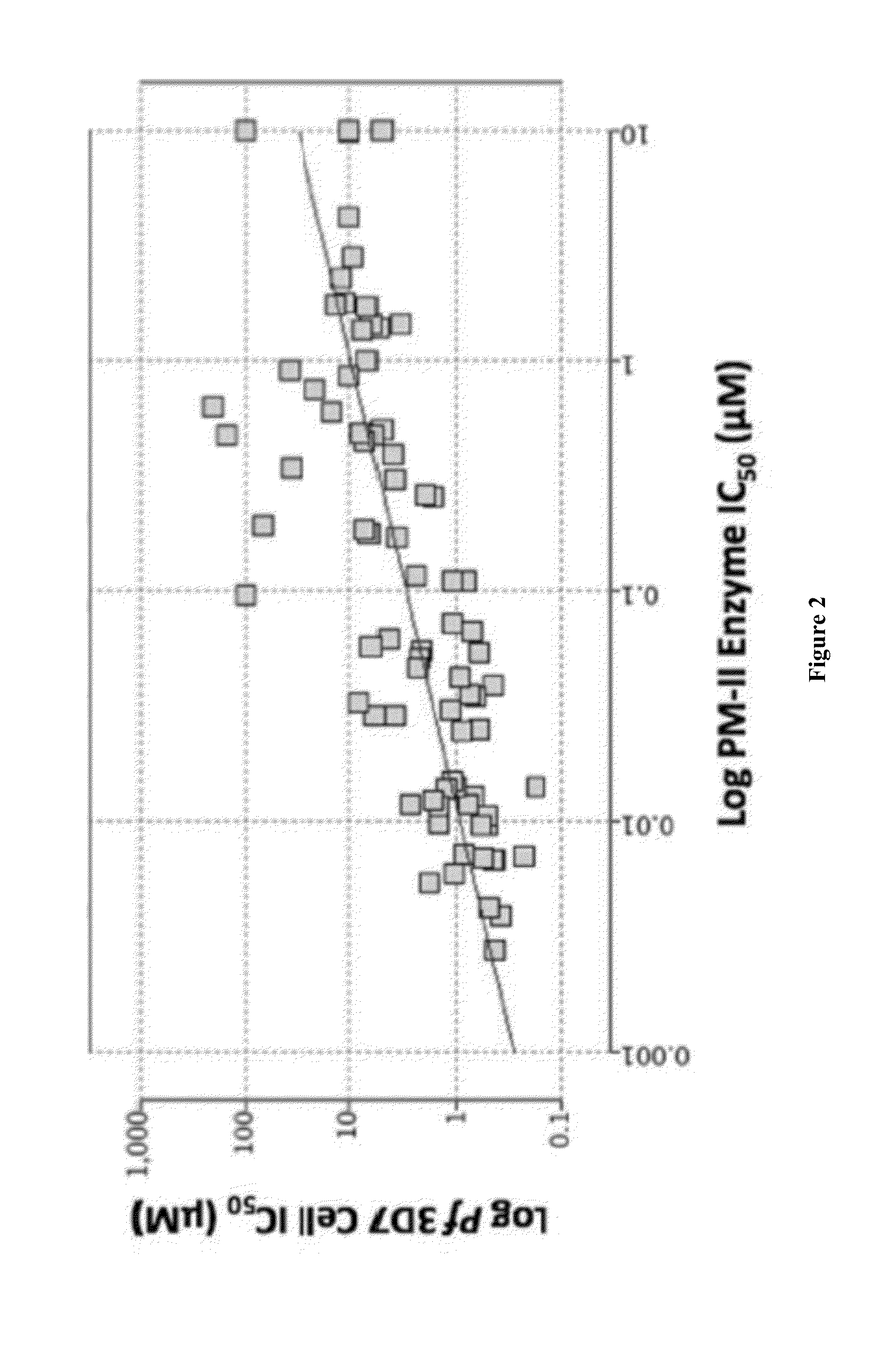
The present invention provides aminohydantoin anti-malarial agents. In some embodiments, these agents have the property of functions of targeting malarial aspartic proteases while at the same time having low activity against human BACE. Methods of employing such agents are also provided.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY +1
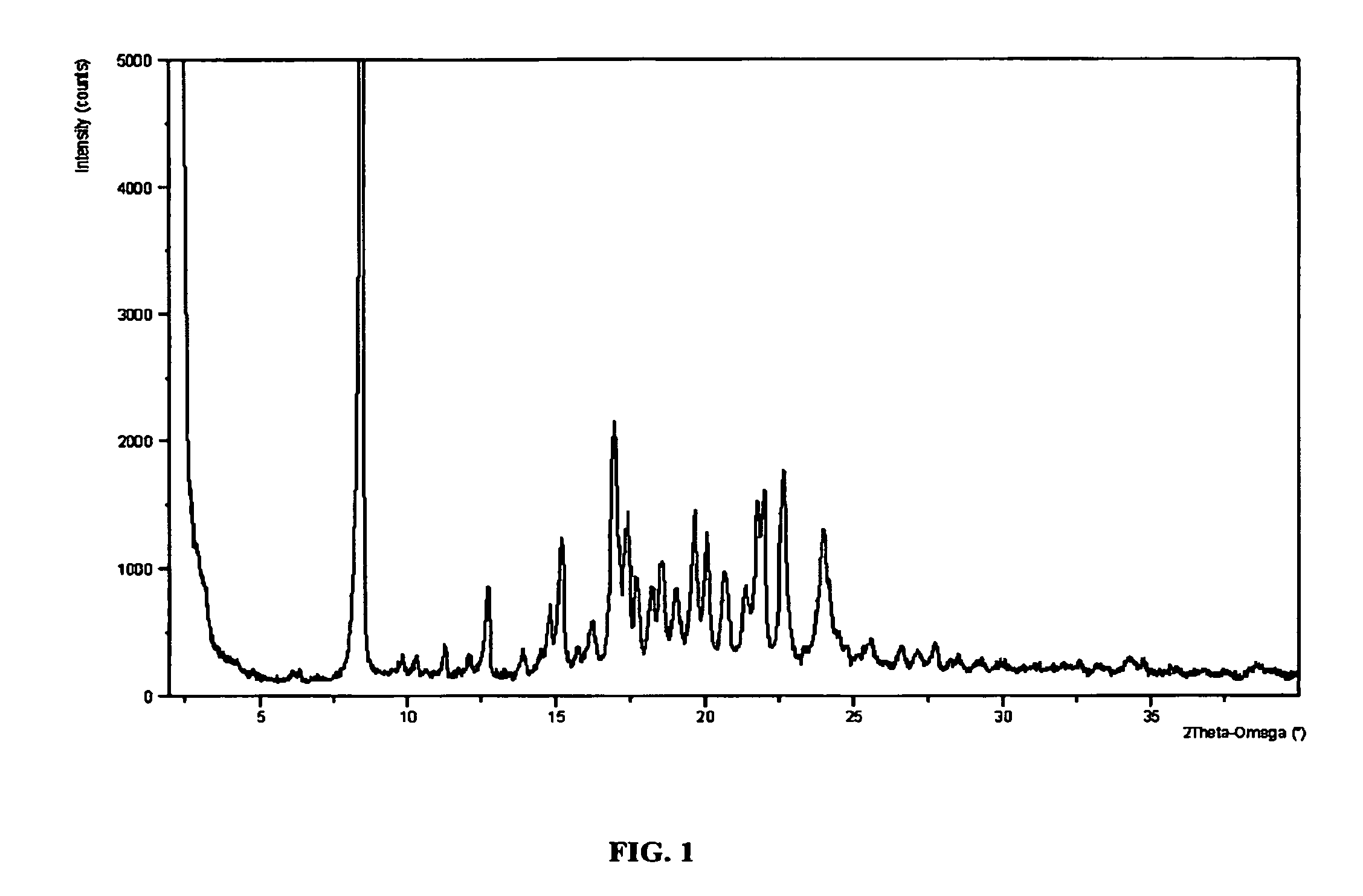
Preparation method of potato aspartic proteinase inhibitor
InactiveCN101597332AEliminate pollutionAvoid wastingPeptide preparation methodsProtease inhibitorsFreeze-dryingHigh pressure
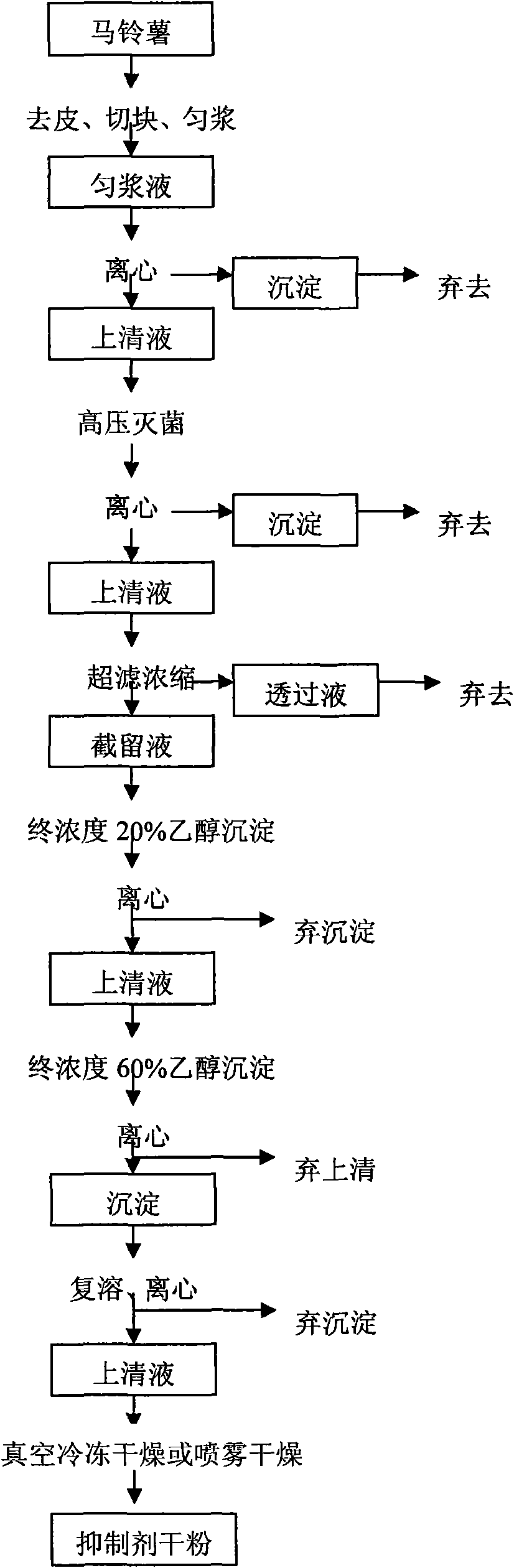
The invention relates to a preparation method of potato aspartic proteinase inhibitor and belongs to the technical field of bioactive products extracted from plant. The preparation method comprises the following steps: directly peeling, cutting and mixing potatoes evenly; carrying out high-speed centrifugation; completing high-pressure sterilization of the supernatant fluid and then carrying out high-speed centrifugation again; completing hyperfiltration and concentration; carrying out fractionated precipitation of ethanol; eliminating undissolved substance through centrifugation after deposition and redissolution; and finally, obtaining the dry powder of the aspartic proteinase inhibitor through vacuum freeze drying. The aspartic proteinase inhibitor prepared by the preparation method has higher inhibitory activity on pepsin and can be directly extracted from potatoes, thereby having low cost and application safety without causing pigment influence; therefore, the inhibitor has broad application prospects in the fields of foodstuff, medicament, agriculture, and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Specific promoter of soybean seeds and use thereof
InactiveCN101818151ADistinct promoter propertiesDNA preparationDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to a specific promoter of soybean seeds, which belongs to the sequence and use of a soybean aspartic protease gene promoter. The nucleotide sequence of the promoter is represented by the sequence No.1. The preparation method of the promoter comprises the following steps of: cloning the upstream distal sequence of gene soyAP1, analyzing the upstream sequence of the ATG of the gene soyAP1 and determining the deleted fragments SAP1, SAP2, soyAP1-p and SAP4; and amplifying the soyAP1-p fragment, linking the amplified fragment of the soyAP1-p with a cloning vector pMD 18-T, performing identification, measuring the sequence, and verifying the sequence. In the invention, the soyAP1-p promoter of soybean is cloned and expressed in the soybean seeds specifically, and the promoter obtained can be used as a favorable tool in researches on soybean transgenosis and particularly creates conditions for researching and developing soybean seed bioreactors.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
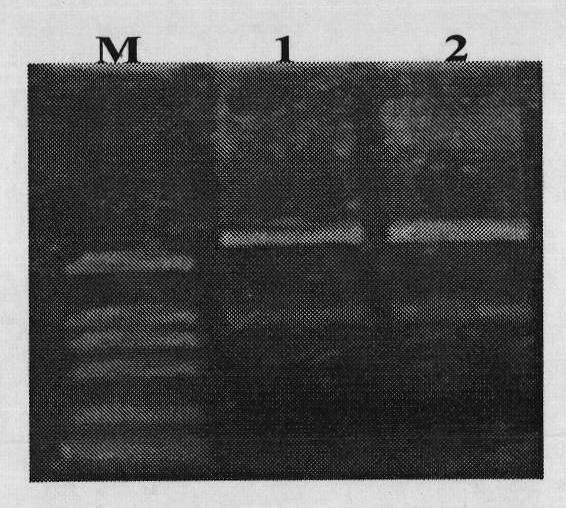
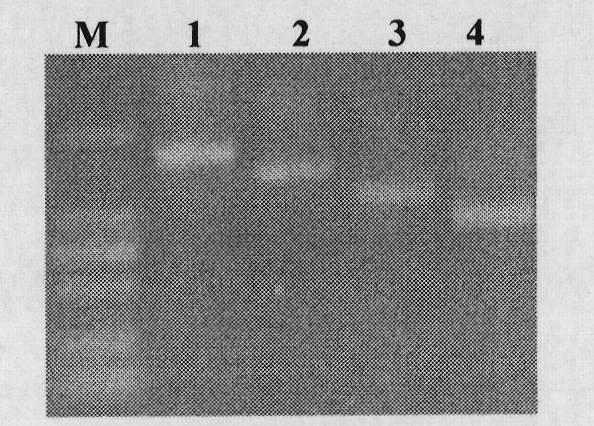
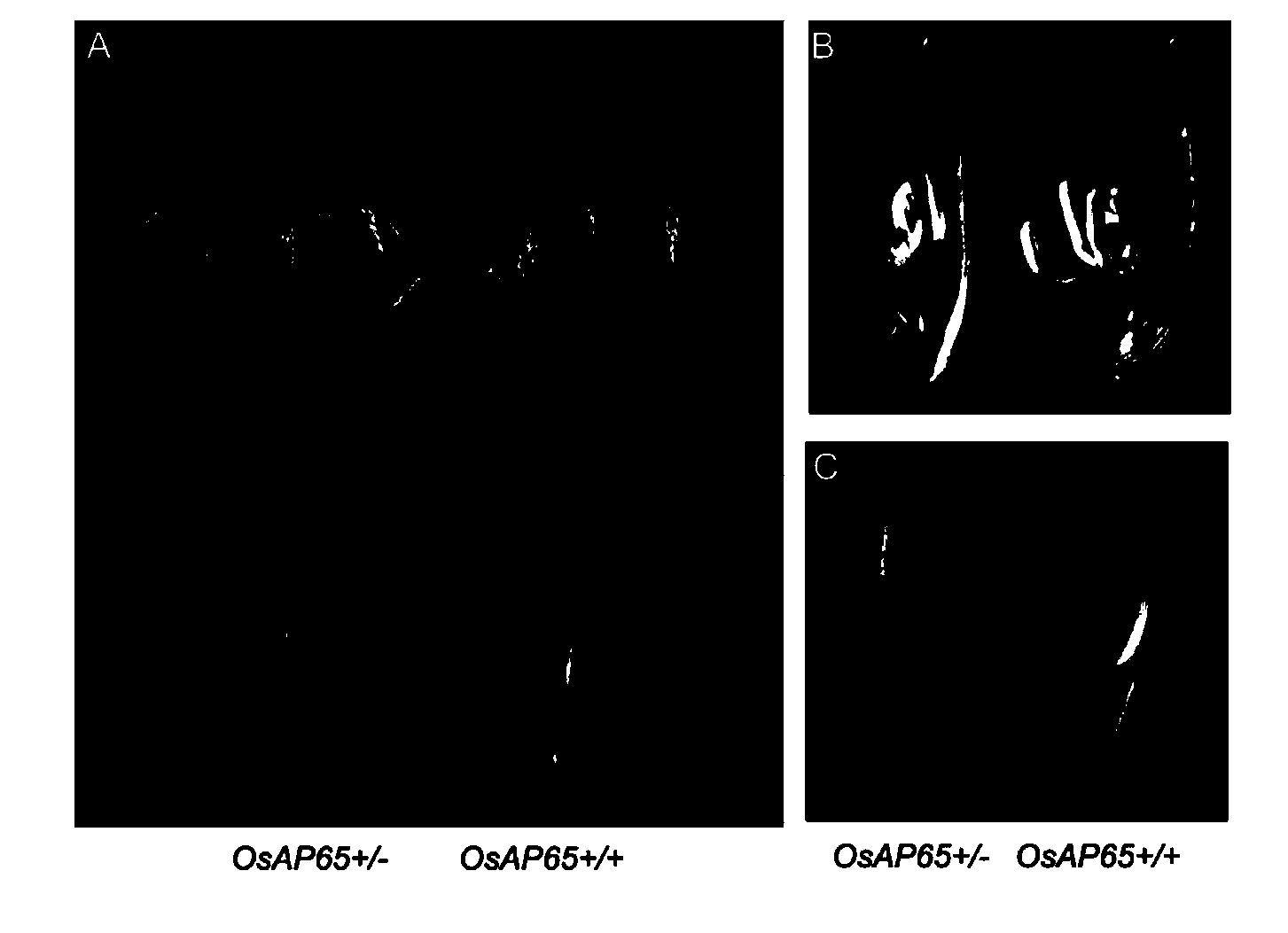
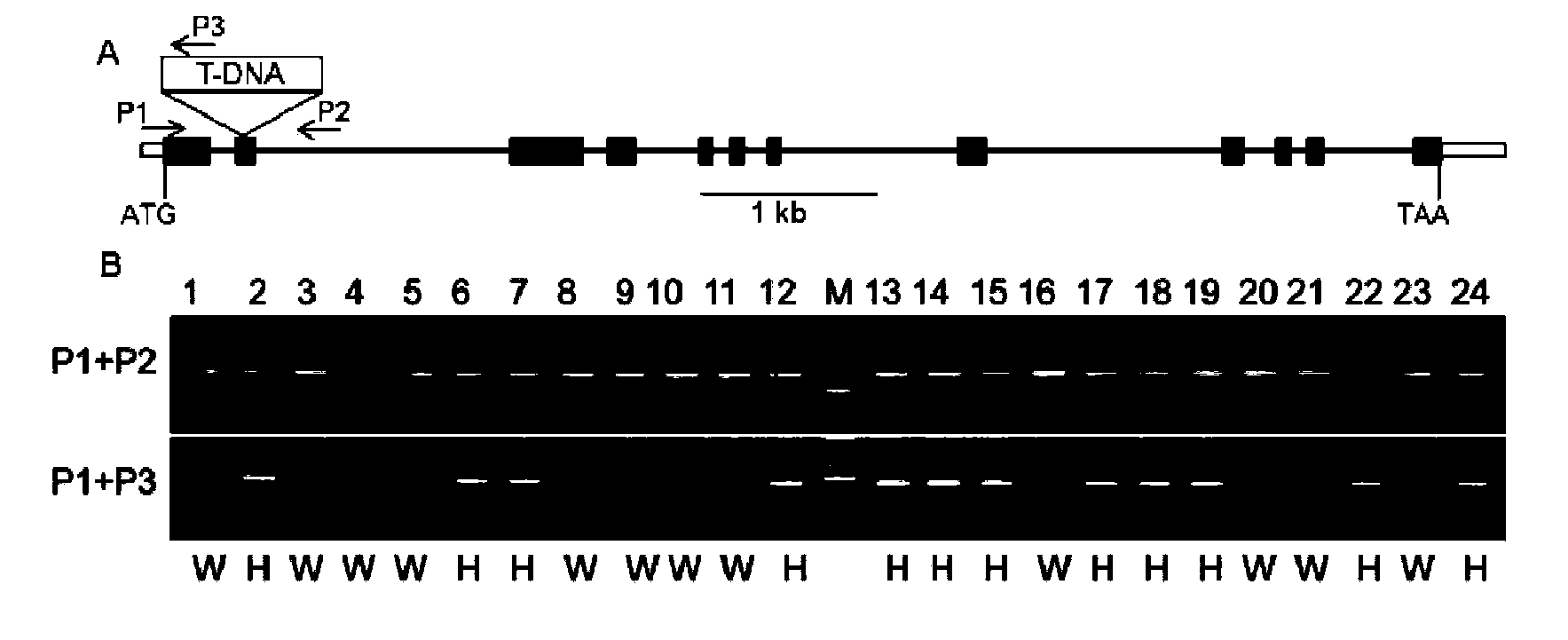
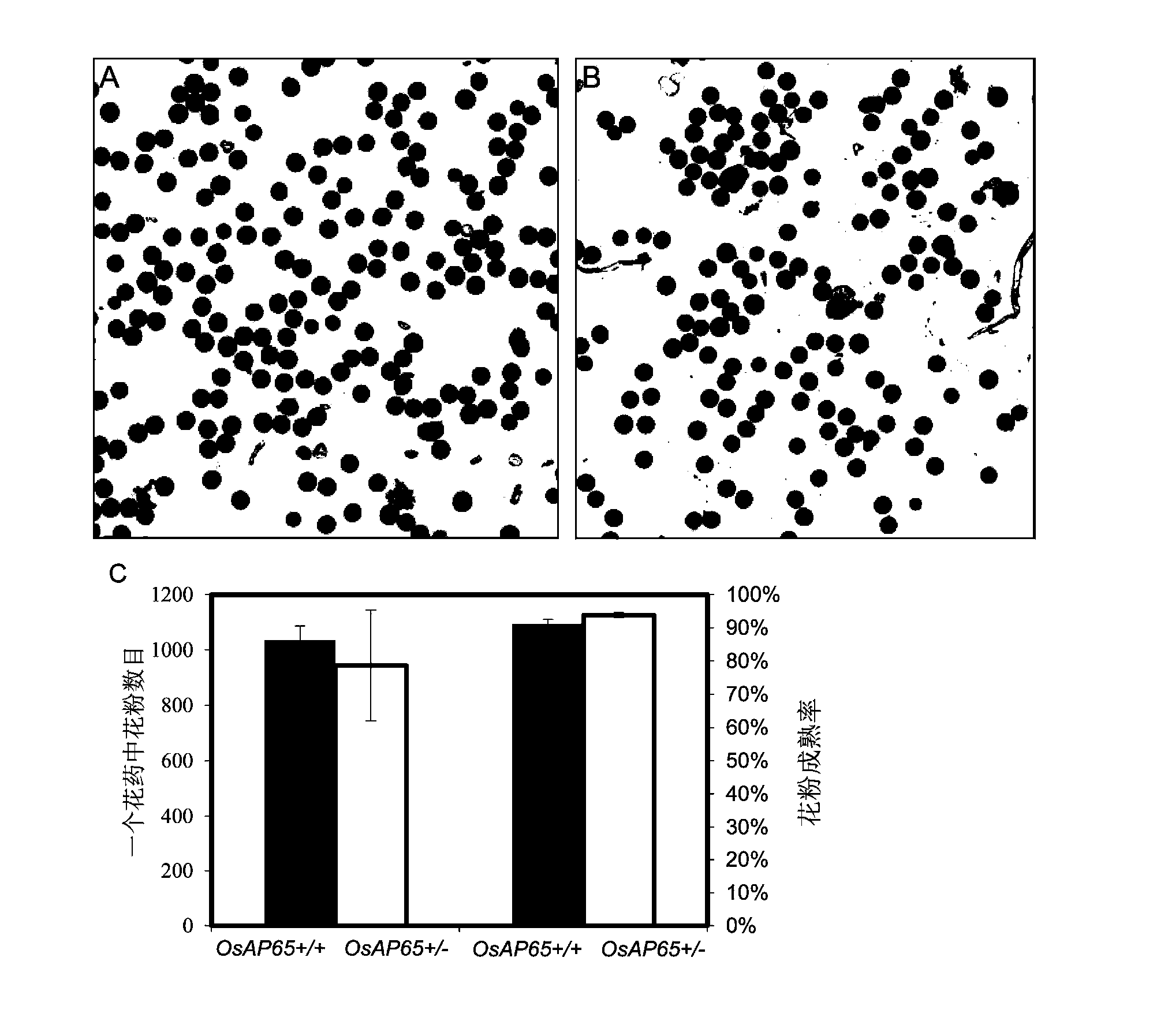
Cloning and application of gene OsAP65 controlling development of paddy rice pollen tube
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and particularly relates to the cloning, functional verification and application of an aspartic protease gene OsAP65 controlling the development of a paddy rice pollen tube. The nucleotide sequence of the aspartic protease gene OsAP65 is shown as the sequence table SEQ ID NO: 1; the coding region of the aspartic protease gene OsAP65 is positioned from the 129th base to 2024th base of the gene segment; the sequence of the protein of the aspartic protease gene OsAP65 is shown as the sequence table SEQ ID NO: 2. A research result shows that the cloned aspartic protease gene OsAP65 participates in the development process of the paddy rice pollen tube and has a significant value for theoretical research such as the molecular mechanism in the development of the paddy rice pollen tube.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
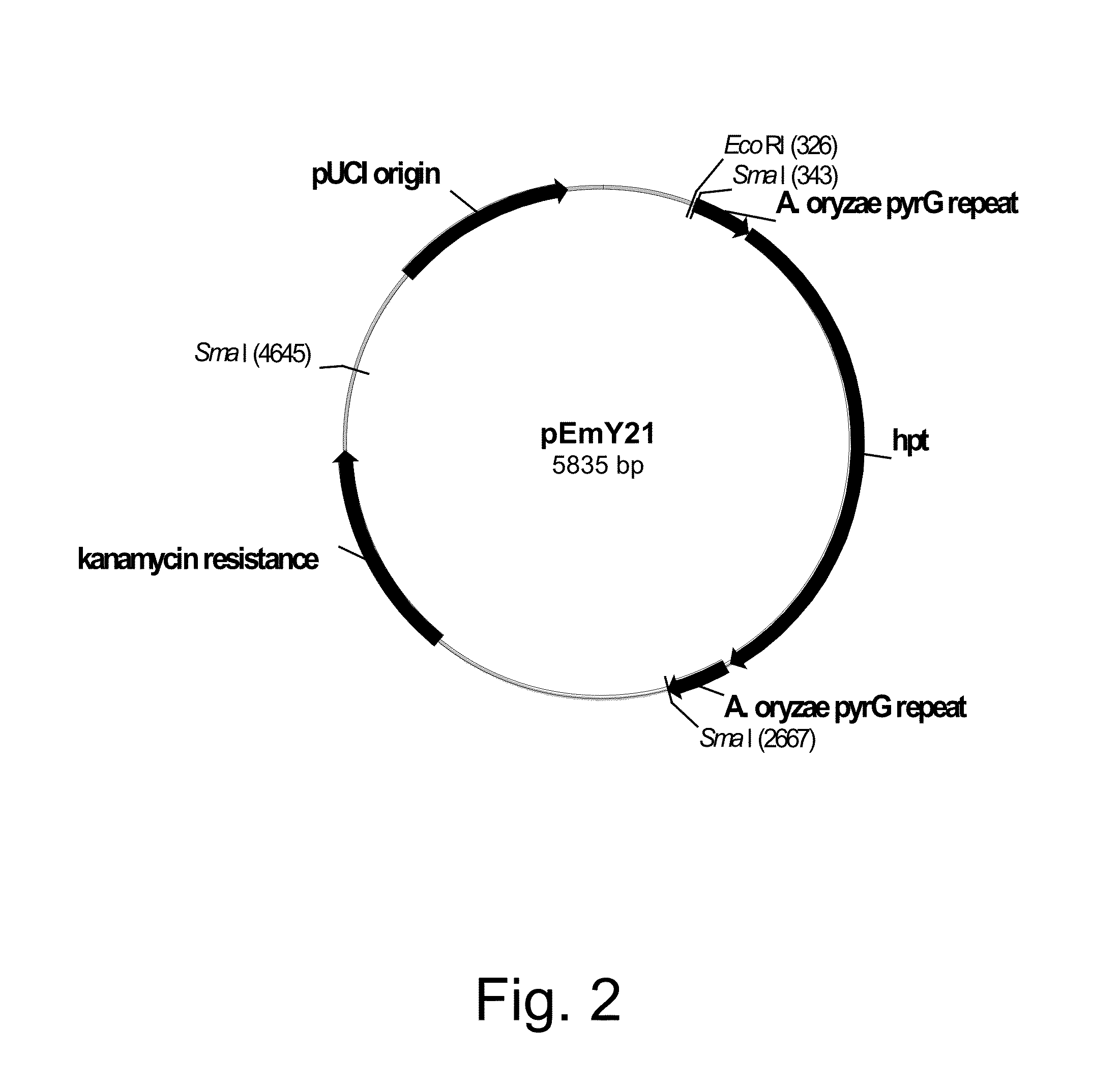
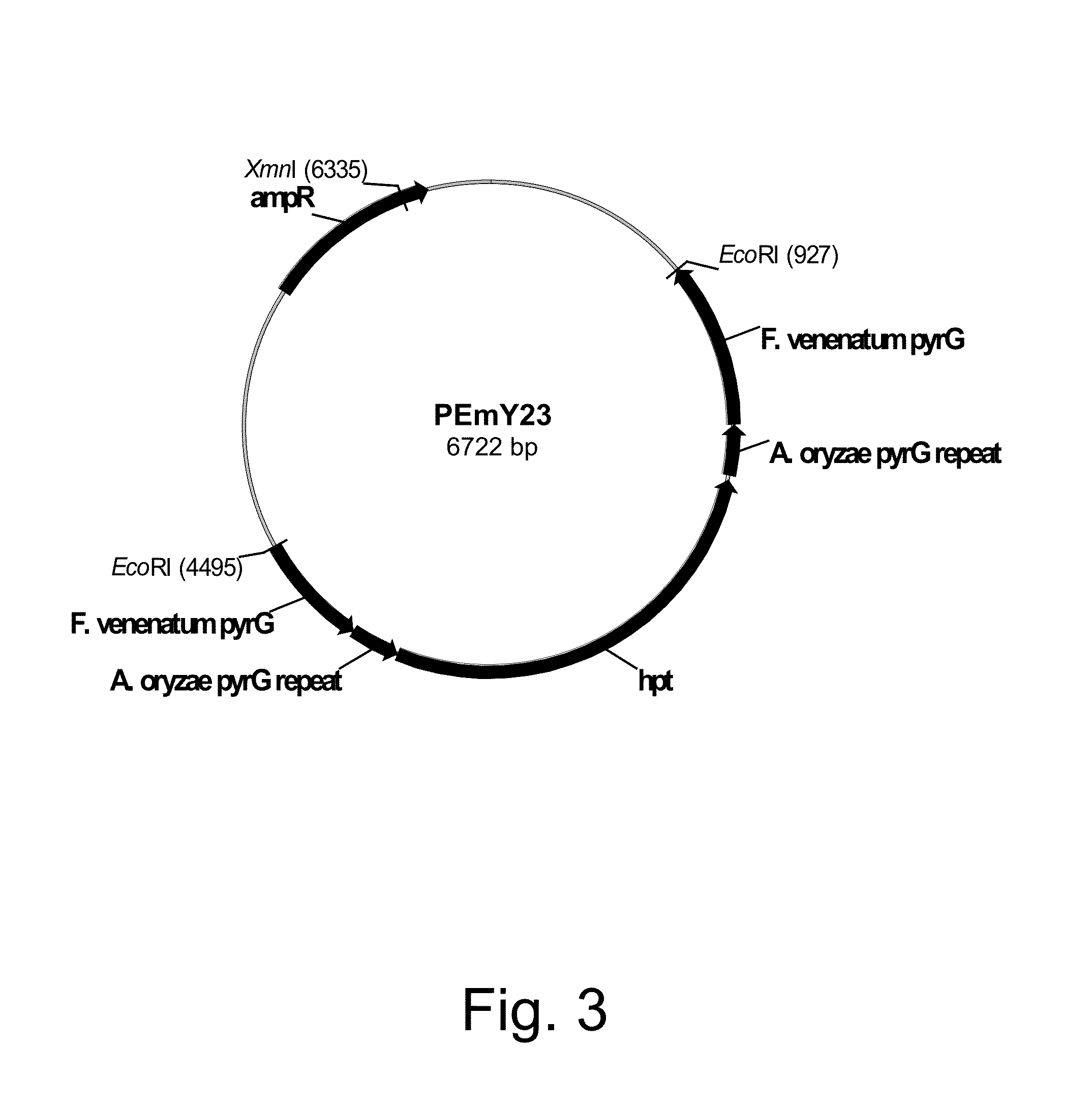
Increased production of aspartic proteases in filamentous fungal cells
Described are compositions and methods relating to filamentous fungal cells genetically engineered to provide increased production of aspartic proteases, such as PEPAa, PEPAb, PEPAc, and PEPAd. Also described are nucleic acids and methods for making the engineered filamentous fungal cells.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Bi-enzymatic hydrolysis method for preparing high-F-value oligopeptide crude liquid
InactiveCN107177651AIncrease exposureRaise the F valueFermentationCrystallographyEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention provides a bi-enzymatic hydrolysis method for preparing high-F-value oligopeptide crude liquid. The method includes steps: 1) pretreatment; 2) deodorization; 3) degreasing; 4) enzymolysis. The method has advantages that a pepsase enzyme activator and a flavourzyme enzyme activator are capable of activating pepsase and flavourzyme respectively to improve enzymolysis efficiency and shorten oligopeptide crude liquid preparation time; the pepsase which belongs to aspartic protease is inclined to shear an amino terminal or carboxyl terminal into aromatic amino acid, and aromatic amino acid residue exposure rate is high, so that exonuclease specific excision at the second step is facilitated; the flavourzyme is natural and safe and is exactly capable of serving as exonuclease to degrade bitter peptides obtained at first-step enzymolysis into amino acids. In addition, by terminal peptide hydrolysis, hydrolysis degree is raised.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
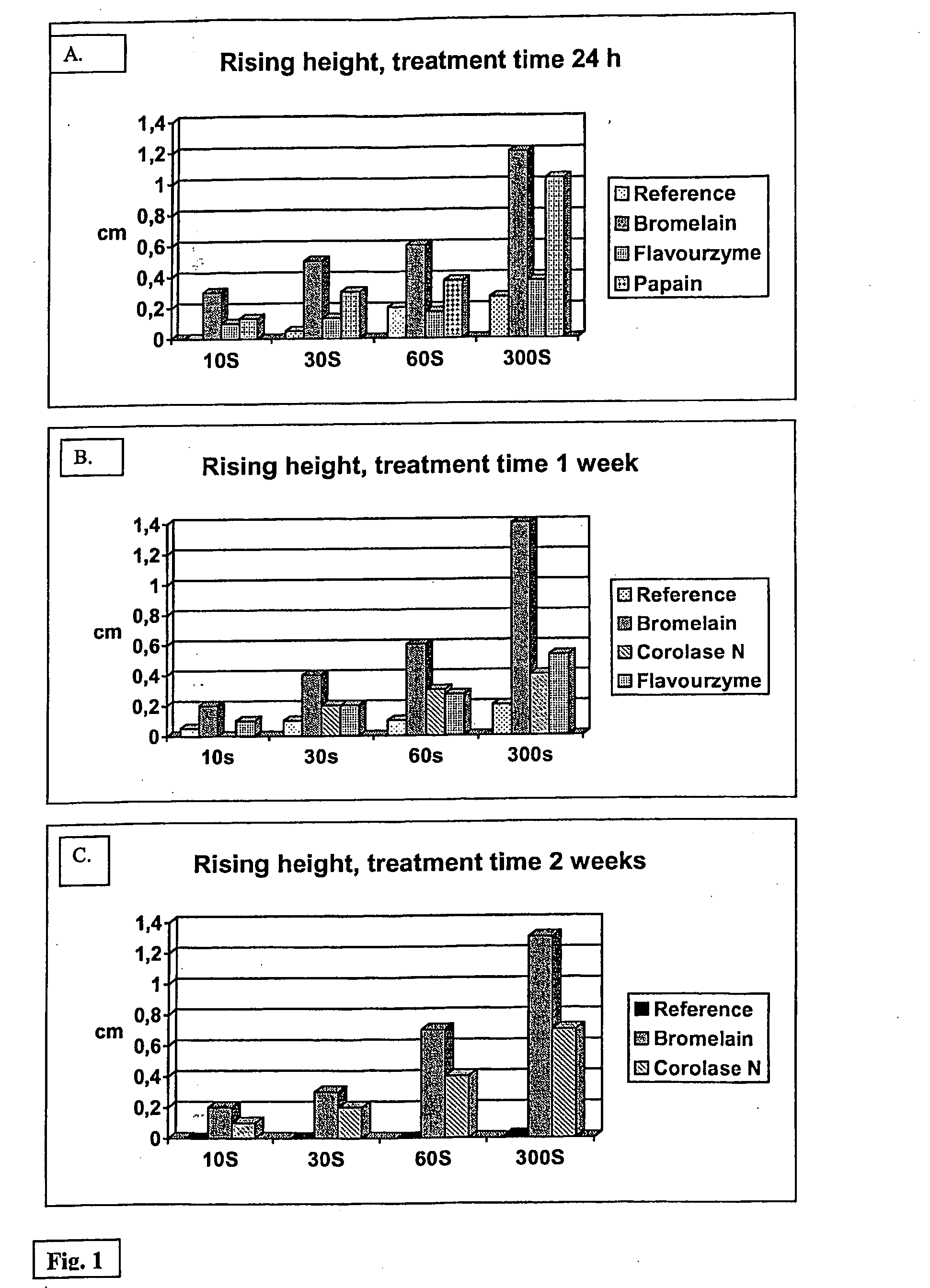
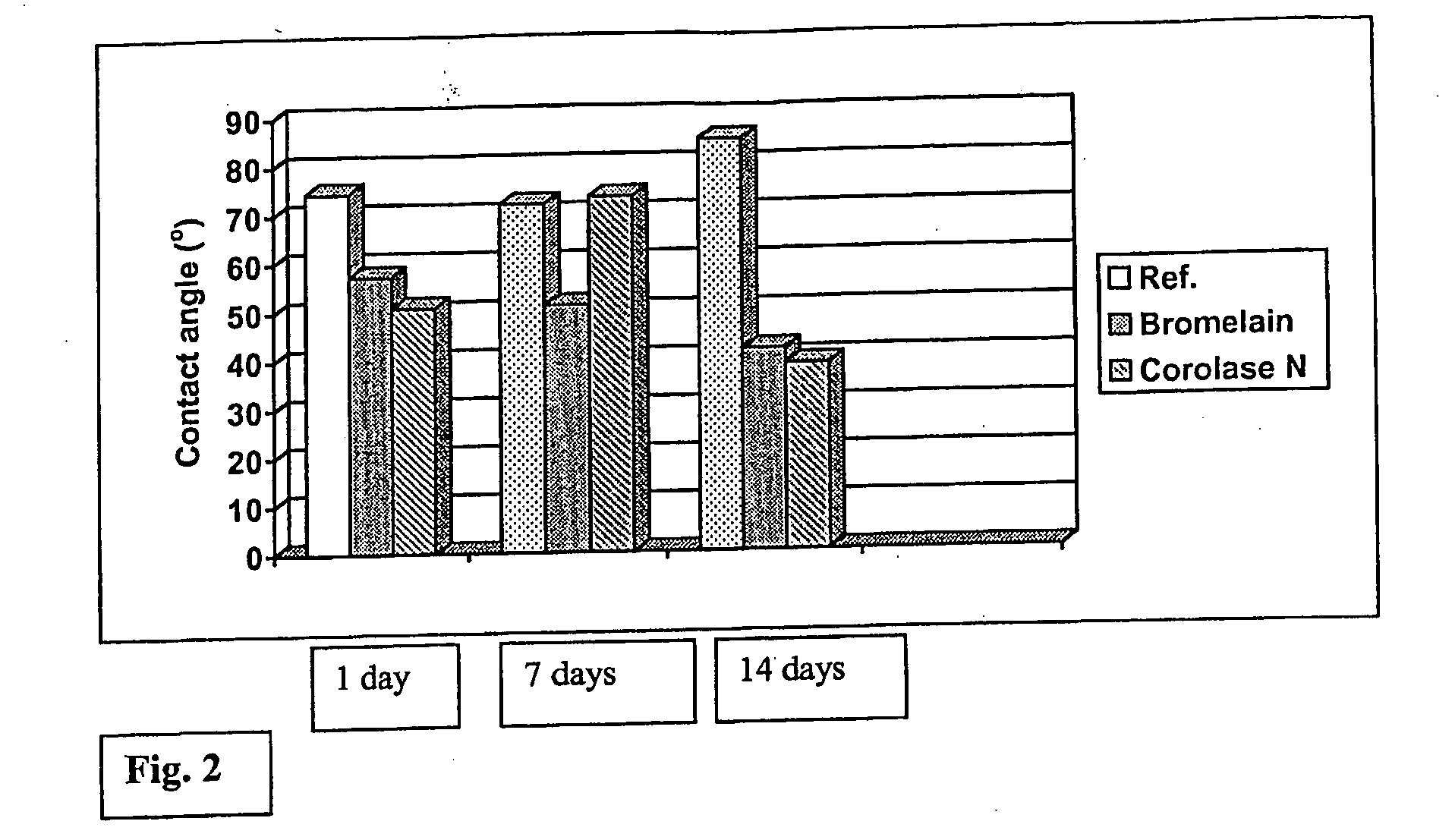
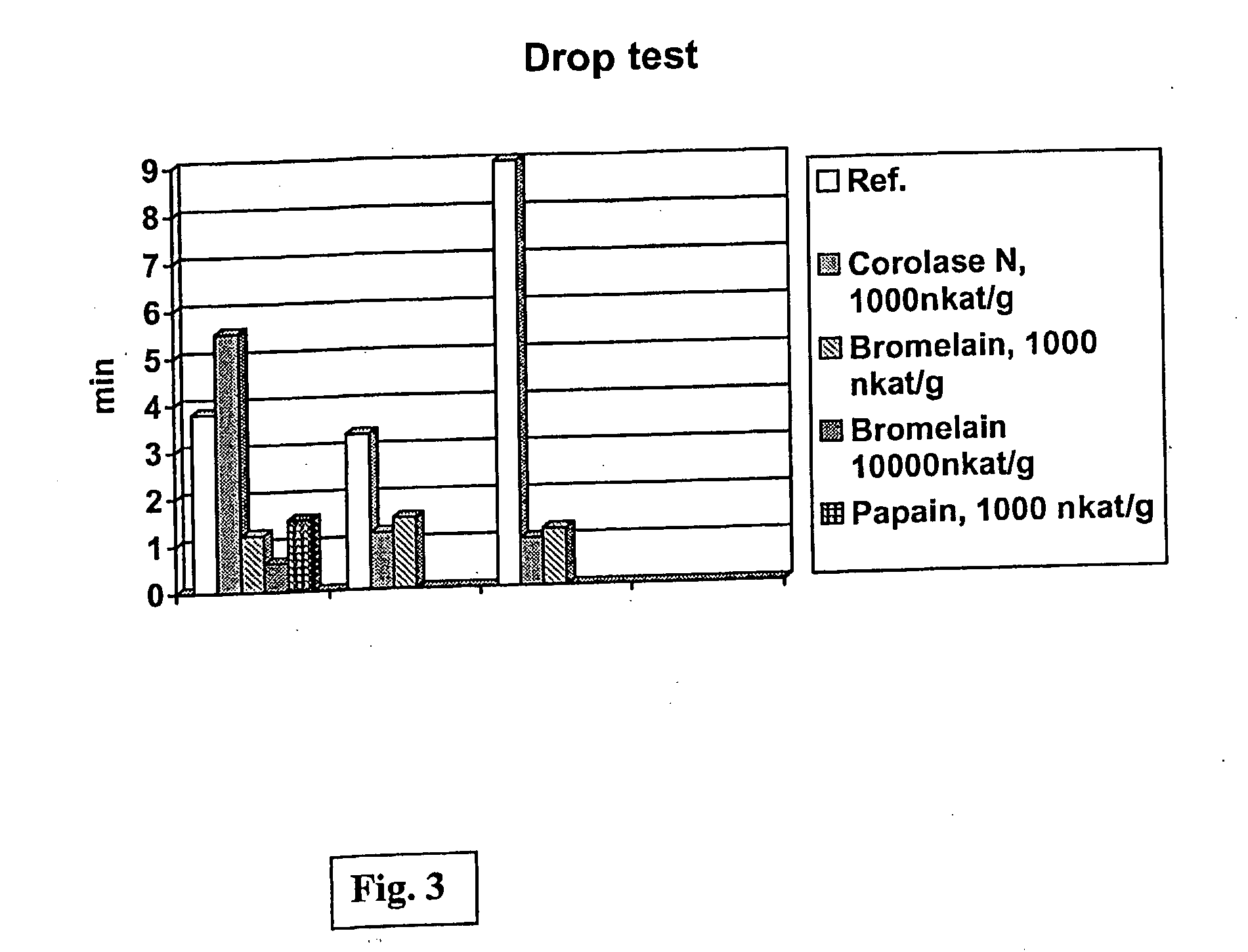
Method for Modifying Polyamide
InactiveUS20080289120A1Less harmful to the environmentImproves end-product propertyFibre typesReactive dyesProteinase activityPolyamide
The present invention relates to a method for modifying polyamide. The method comprises that polyamide is contacted with an enzyme preparation comprising an effective amount of protease enzyme in aqueous environment under conditions suitable for the function of the enzyme. The enzyme is preferably selected from the group of aspartic proteases, cysteine proteases and metallo-proteases.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
Aspartic protease inhibitors
The present invention provides an aspartic proteinase-inhibiting compound of the formula: wherein a, b, c, d, and e, can be the same or different and each are R7, OR7, SR7, NR7R7, NHCOR7, CO2R7, CN, NO2, NH2, N3, or a halogen, wherein R7 and R8 are independently H or an alkyl. Substituents R1 or R2 are each H or an alkyl. Substituent R3 is a straight chain or branched alkyl, alkenyl, or alkynyl substituent, or is a cycloalkyl. Substituent A is OH, NH2, or SH. Further provided are pharmaceutical compositions, which include a therapeutically effective amount of at least one of the foregoing compounds, and therapeutic methods of using the foregoing compounds.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
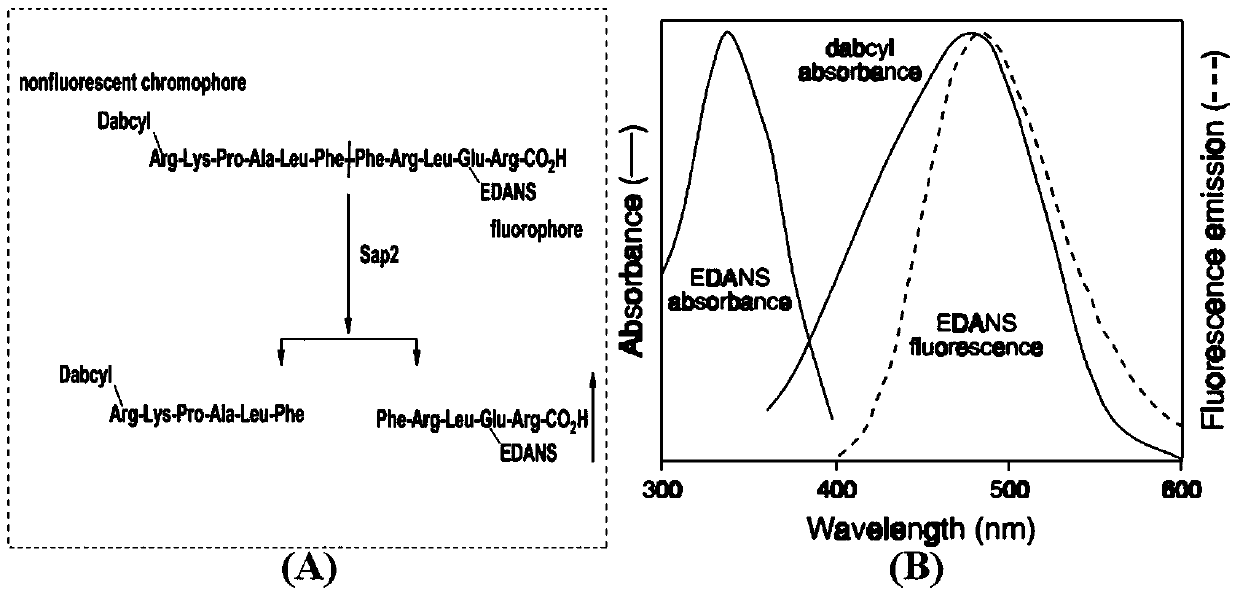
Method for evaluating inhibition of aspartic proteases
InactiveUS6951731B2High-throughput screeningCompound screeningApoptosis detectionReactive siteElectronic properties
Disclosed is a method for evaluating enzyme inhibitory activity of a known or putative inhibitor or modulator of an enzyme. The enzymes under investigation are those having a low-barrier hydrogen bond present in an active site of the enzyme. The compound whose activity is to be evaluated is contacted to an enzyme having a low-barrier hydrogen bond present in an active site of the enzyme. The presence, absence, or electronic character of the low-barrier hydrogen bond is then measured. The method is useful for designing mechanistic-based inhibitors or modulators of aspartic proteases and other enzymes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
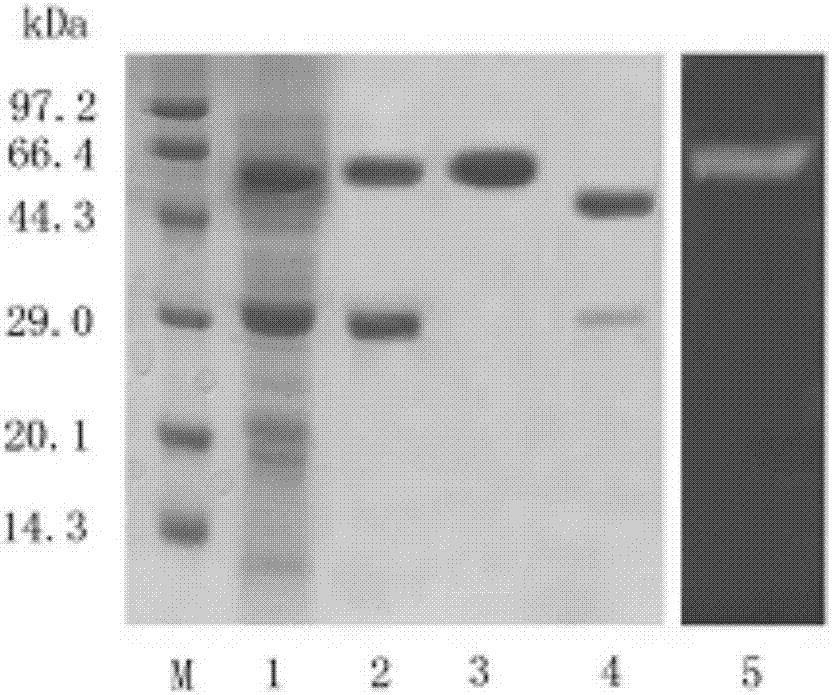
A production method and applications of a novel rhizomucor miehei aspartic protease
ActiveCN107338234AEffective tenderizationEffective hydrolysisFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
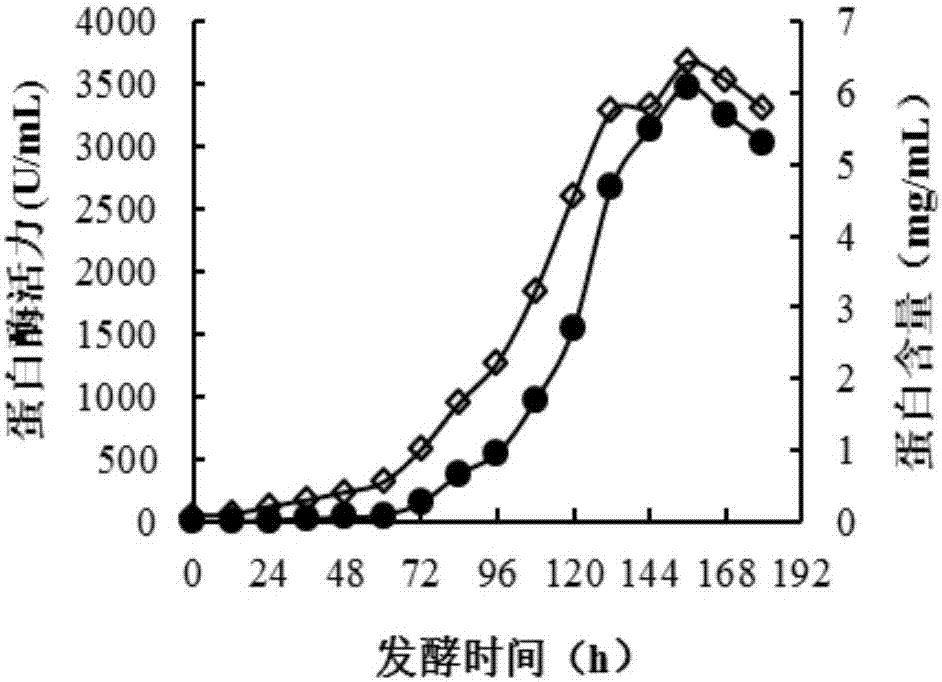
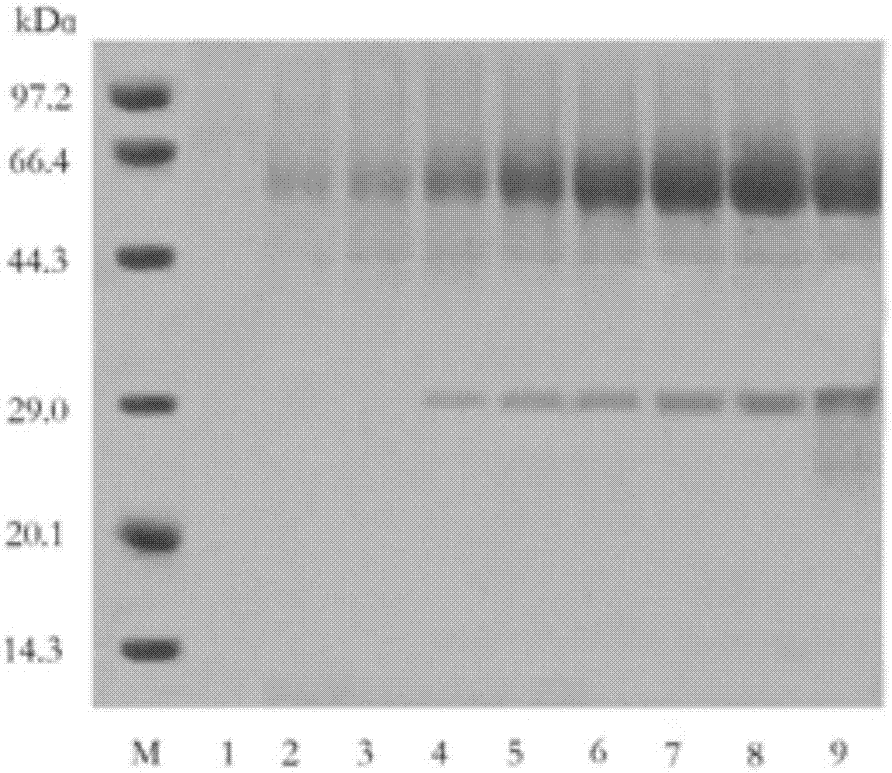
The invention discloses a production method and applications of a novel rhizomucor miehei aspartic protease, and particularly relates to a recombinant aspartic protease, a coding gene, and a production method and applications of the recombinant aspartic protease. The recombinant aspartic protease is protein having an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The coding gene of the recombinant aspartic protease is a DNA molecule shown as SEQ ID NO:2. An aspartic protease gene that is RmproA of rhizomucor miehei is connected to a pichia pastoris GS115 expression vector pPIC9K, and is converted into pichia pastoris and induced expression is performed to obtain the recombinant aspartic protease. Through high-density fermentation in a fermentation tank having a volume of 5 L, the maximum protease production activity at 156 h of a recombinant strain is 3400 U / mL, and the protein content is 6.42 mg / mL. The recombinant aspartic protease is capable of effectively tendering pork, reducing shearing force, making meat palatable, and effectively hydrolyzing animal and plant protein to prepare low-molecular-weight polypeptides.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Piperidine renin inhibitors
The present invention is directed to aspartic protease inhibitors represented by the following structural formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The present invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the aspartic protease inhibitors of Structural Formula (I). Methods of antagonizing one or more aspartic proteases in a subject in need thereof, and methods for treating an aspartic protease mediated disorder in a subject using these aspartic protease inhibitors are also disclosed.
Owner:VITAE PHARMA INC
Method of providing polypeptide preparations with reduced enzymatic side activities
InactiveUS20020160445A1Level is reduced and eliminatedHydrolasesChemical treatment enzyme inactivationMicroorganismPepsin inhibitor
A method of providing polypeptide preparations having a reduced content of undesired enzymatic side activities, the method comprising subjecting a medium containing a desired polypeptide such as an enzyme, a pharmaceutically active or immunologically active polypeptide to a pH of less than 2 for a period of time that is required to inactivate the side activities whilst retaining the activity of the desired polypeptide. The method is useful for providing milk clotting enzyme products including rennets or coagulants based on chymosin or pepsin or microbial aspartic proteases e.g. derived from bacterial species and species of filamentous fungi.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Novel imaging agents comprising caspase-3 inhibitors
The present invention relates to diagnostic imaging agents for in vivo imaging. Such imaging agents comprise synthetic caspase 3 inhibitors labeled with an imaging moiety suitable for in vivo diagnostic imaging. The invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition and a radiopharmaceutical composition comprising the imaging agent, and a kit for preparing the radiopharmaceutical composition. The present invention also provides chelator conjugates of caspase 3 inhibitors which are suitable for use in the preparation of imaging agents comprising radioactive or paramagnetic metal ions. Imaging agents of the invention are useful in vivo for diagnostic imaging and / or therapeutic monitoring in various disease states involving caspase 3.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
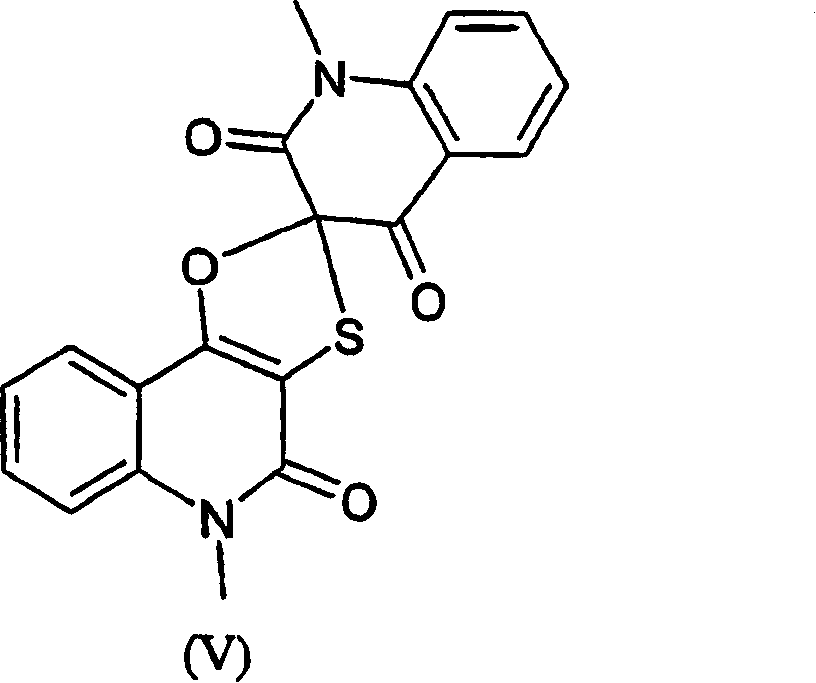
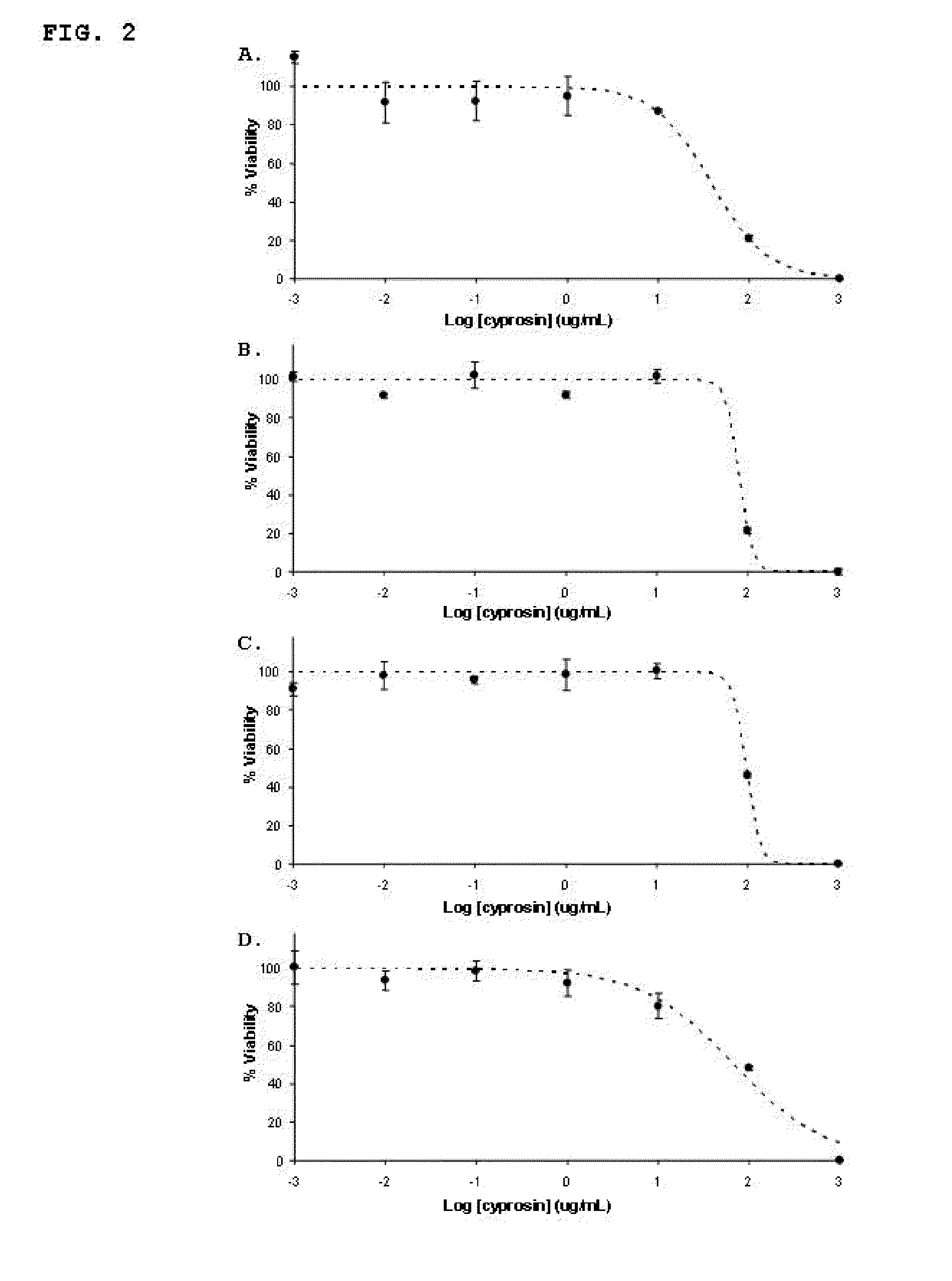
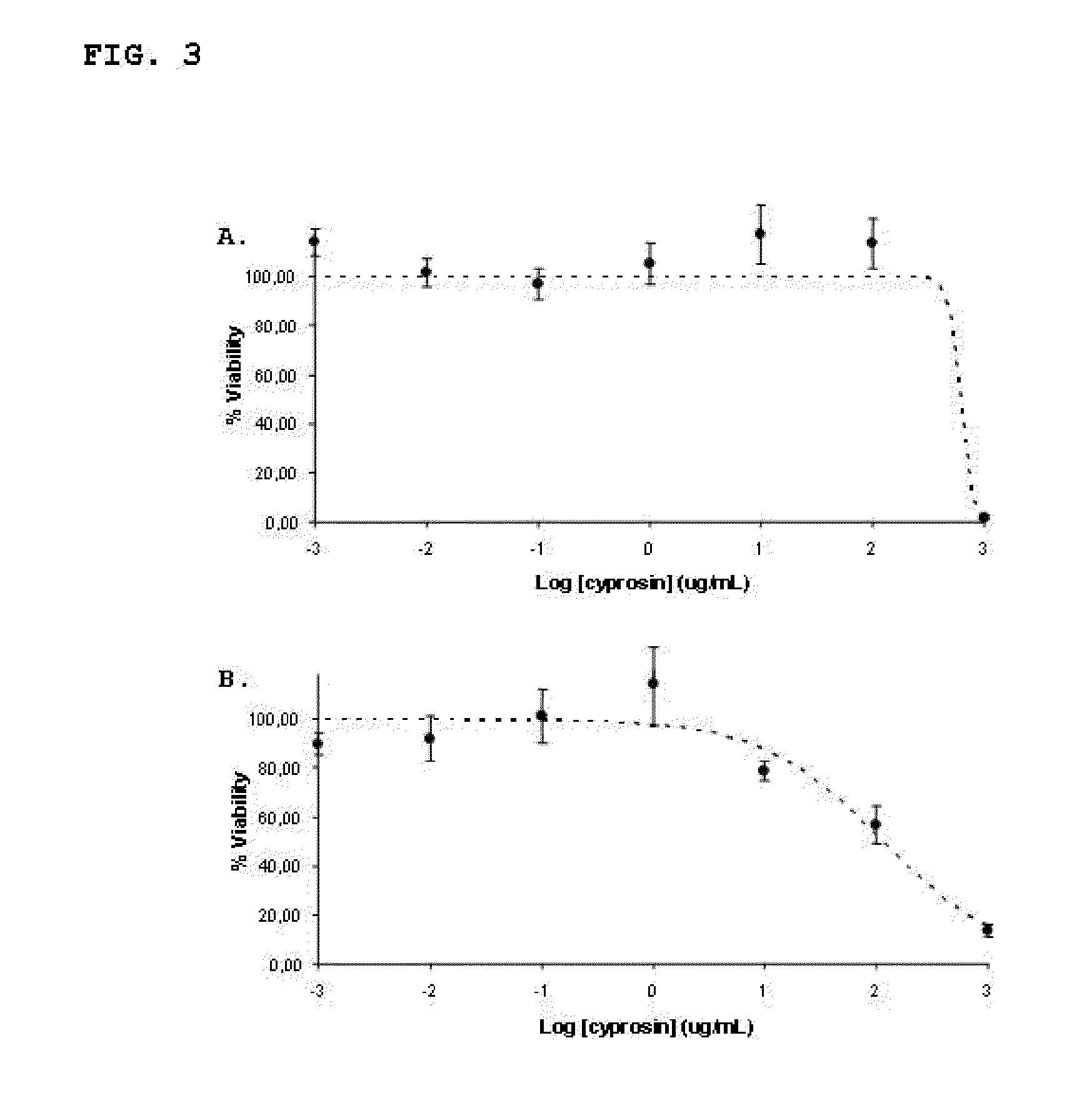
Pharmaceutical compositions containing the enzyme cyprosin, an aspartic peptidase from cynara cardunculus and its inclusion in antitumour formulations
InactiveUS20110104286A1Inhibit cell proliferationPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousMyokine
An aspect of the present invention is the use of a preparation containing a phytepsin, more specifically a cyprosin, containing the heterodimer, its N-terminal pro-peptide, the mature N-terminal peptide, and mature C-terminal peptide, as well as other precursor species, processing products, and aggregate species, either isolated or in any combinations of the former, native, extracted and partially purified from flowers of Cynara cardunculus, or recombinant, extracted from the supernatant from a culture of Saccharomyces cereviseae genetically modified for the heterologous production of cyprosin, for therapeutic applications more precisely for its use as an antitumor agent.
Owner:ECBIO INVESTIGACAO E DESENVOLVIMENTO EM BIOTECHA
Micro-molecular chip, its preparation method and application
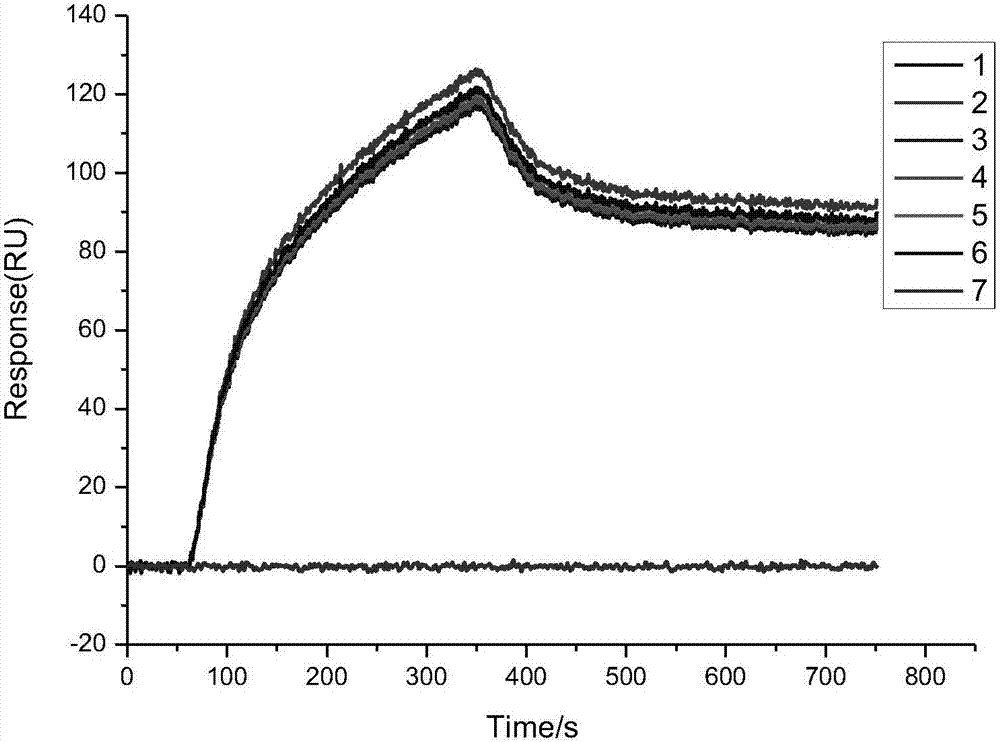
ActiveCN107202892AEasy to operateThe test result is accurateMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological testingHemagglutinin proteinAspartate protease
The invention belongs to the technical field of a biological chip, and discloses a micro-molecular chip, its preparation method and an application. The micro-molecular chip comprises a chip and a micro-molecular compound; the chip comprises light crosslinking agent, and the micro-molecular compound is connected with the chip through the light crosslinking agent. The micro-molecular compound in the micro-molecular chip can be combined with plasmodium aspartic protease II protein or hemagglutinin protein, and used for detecting the plasmodium aspartic protease II protein and / or hemagglutinin protein in a to-be-detected sample; the micro-molecular chip has advantages of being simple in operation during detection process, exact in detection result, good in reproducibility, short in time, time-saving and labor-saving.
Owner:苏州普芯生命科学技术有限公司
Aspartic protease inhibitors
InactiveCN101356156AOrganic chemistryHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsCrystallographyHIV Protease Inhibitor
The present invention is directed to aspartic protease inhibitors. Certain aspartic protease inhibitors of the invention can be represented by the following structural formula or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The present invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the disclosed aspartic protease inhibitors. The present invention is further directed to methods of antagonizing one or more aspartic proteases in a subject in need thereof, and methods for treating an aspartic protease mediated disorder in a subject using the disclosed aspartic protease inhibitors.
Owner:VITAE PHARMA INC
Methods and Compositions for Inhibiting Fungal Infection and Disease
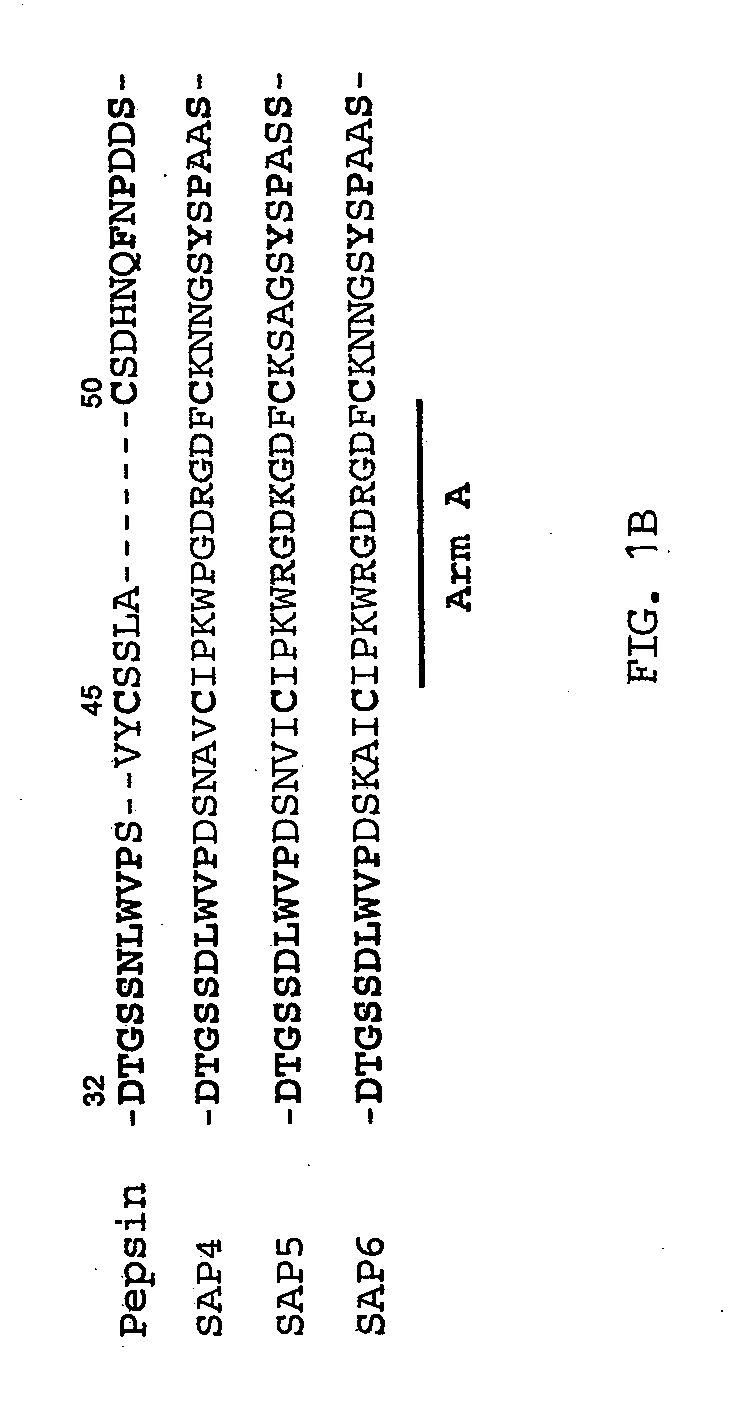
The present invention describes a previously unknown interaction between secreted aspartic proteases (SAPs), including SAPs 4-6 of Candida albicans, and integrins on host cells. The SAPs secure entry into the host cell through RGD-like binding motifs and subsequently induce apoptosis, thereby clearing the way for systemic infection. The invention thus provide a new target for therapeutic intervention and describes peptides and antibodies that inhibit the action of SAPs in this context, including their interaction with integrins.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND
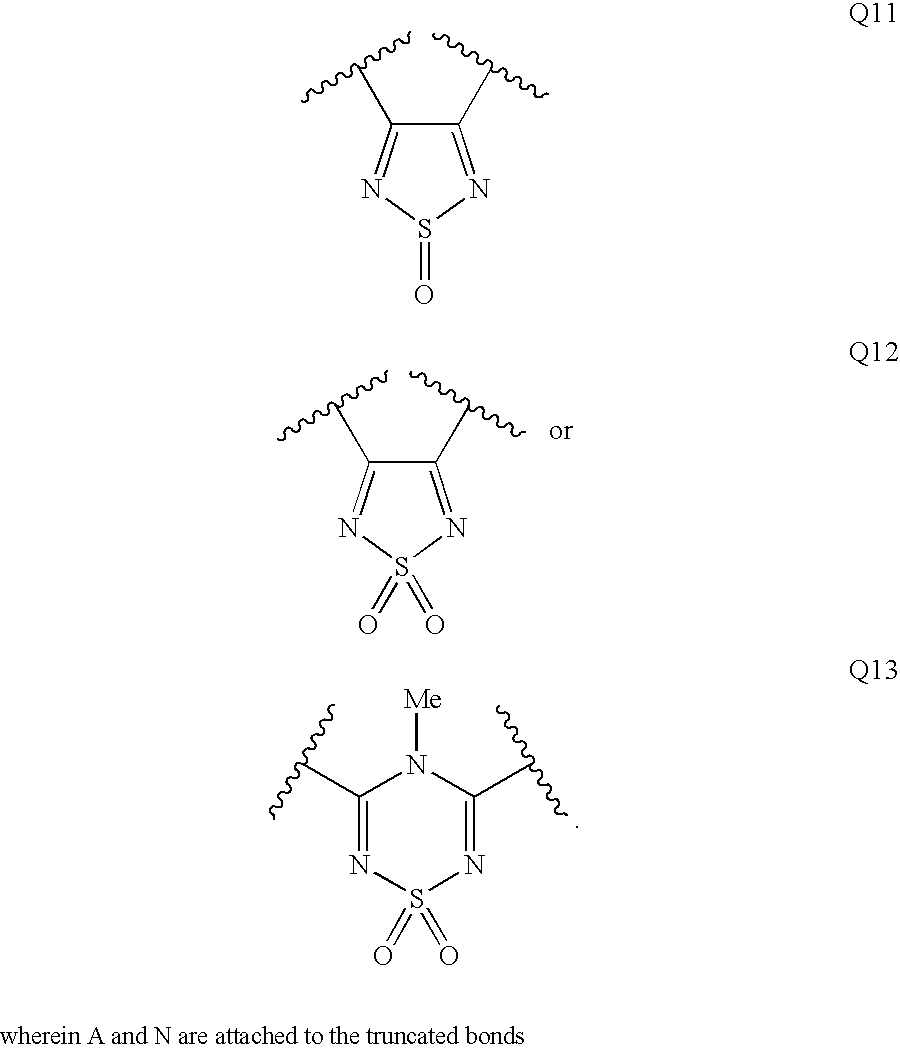
Substituted triaminotriazine secreting-type aspartic protease inhibitor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104974142AGood enzyme inhibitory activityGood antifungal activity in nematodesAntimycoticsOrganic chemistryAntifungal drugAntimicrobial drug
The invention relates to a substituted triaminotriazine compound and its preparation method and use in pharmacy. The substituted triaminotriazine compound has a general structural formula shown in the following description, and in the formula, R1 represents substituted phenyl ring and R2 represents substituted aromatic ring, naphthalene ring or heterocyclic aromatic. Through structure-based virtual screening and further structure reconstruction, the novel substituted triaminotriazine compound is synthesized. The novel substituted triaminotriazine compound is a fungus Sap2 inhibitor with a novel structure, has good enzyme inhibition activity and nematode in-vivo antifungal activity, provides a novel approach for deep research and development of novel-structure antifungal drugs and can be used for preparation of antifungal drugs and drugs for combination with the existing antibacterial drugs.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Aspartic protease and encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN105420220AHigh optimum reaction temperatureImprove thermal stabilityFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousReaction temperature
The invention provides aspartic protease and an encoding gene and an application thereof. The aspartic protease is a protein shown as (a) or (b), wherein (a) is constituted by an amino acid residue sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:3, or (b) is obtained by performing substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues on the amino acid residue sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:3, has the functions of the aspartic protease and is derived from (a). Through a gene engineering technology, an aspartic protease gene is amplified from Geomycespannorum, and is transferred into Aspergillus oryzae, thereby realizing successful heterologous expression. The aspartic protease provided by the invention has a relatively high optimal reaction temperature, high thermal stability and a good industrial application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Renin Inhibitors
InactiveUS20100168243A1Low costHigh activityBiocideOrganic chemistryAspartic proteinase inhibitorAspartate protease
The present invention is directed to aspartic protease inhibitors. The present invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the disclosed aspartic protease inhibitors. The present invention is further directed to methods of antagonizing one or more aspartic proteases in a subject in need thereof, and methods for treating an aspartic protease mediated disorder in a subject using the disclosed aspartic protease inhibitors.
Owner:VITAE PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com