A production method and applications of a novel rhizomucor miehei aspartic protease
A technology of aspartic acid and protease, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, applications, protein food processing, etc., can solve the problem of few reports on the application of protease genes and proteases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1: Construction and identification of recombinant strains
[0047] The RNA of Rhizomucor miehei was extracted, reverse transcribed into cDNA, cDNA was used as a template, primers were designed, and the RmproA gene was obtained by PCR and cloned into the expression vector pPIC9K to obtain the recombinant plasmid pPIC9K-RmproA, which was transformed into Pichiapastoris GS115. Identify and obtain recombinant strains. The transformation of Pichia pastoris adopts electrotransformation method, spreads on MD plates, cultures for 3-4 days, picks out single clones for next step screening.
[0048] The primers are as follows:
[0049] Upstream: CCGGAATTCCTCCCTGTCACTAATGTTTCCCAG
[0050] Downstream: GCGGCCGCTTACATGTTAAGAGCTGCCGCGGAC
[0051] Experimental results: After comparing with the protein sequence, the protease and the reported Mucor chymosin derived from Rhizopus miehei (Mucorpepsin, P00799.1) (Yang J., Teplyakov A., &Quail JWCrystal structure of the aspartic proteinase) ...
Embodiment 2
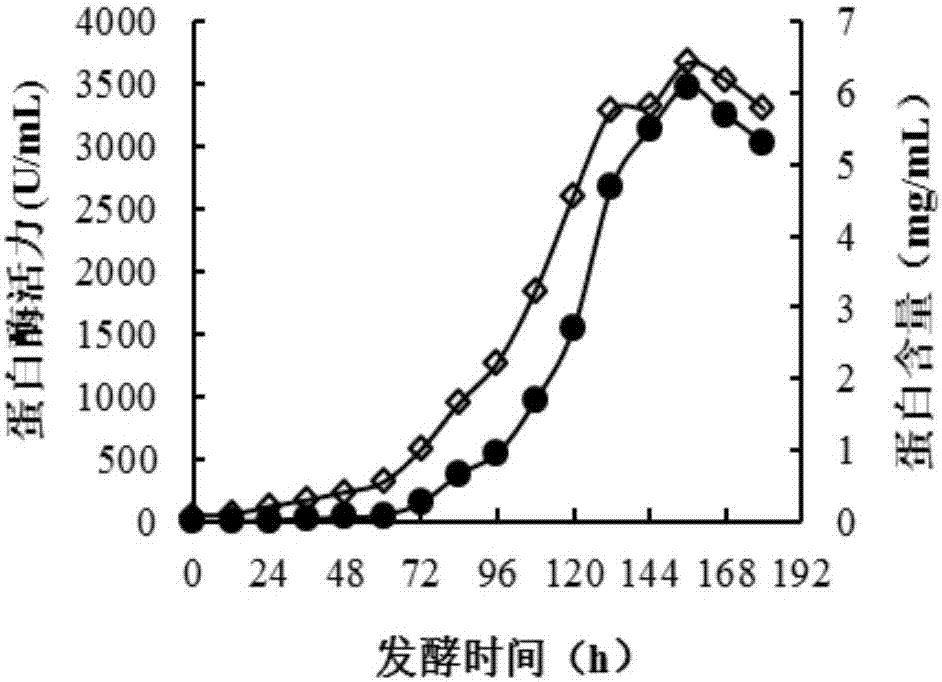
[0052] Example 2: Fermentation and cultivation of recombinant aspartic protease in a 5L fermentor
[0053] Pick a single colony from the solid medium plate and inoculate it in YPD medium (50 mL in a 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask), cultivate it at 30°C and 220 rpm for 24 hours as the seed solution, and then inoculate the 1.5L batch fermentation with 10% inoculum Medium (CaSO 4 0.93g, K 2 SO 4 18.2g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 14.9g, KOH 4.13g, glycerol 40g, 85% phosphoric acid 26.7mL, PTM 1 4.35mL / L) 5L fermentor, the initial stirring speed is 600 rpm, the aeration is 1.0vvm, 25% ammonia water adjusts pH 5.0, the culture temperature is 30℃, when the glycerin is exhausted and the dissolved oxygen rebounds, it will be fed by flow 50% glycerol (w / v, containing 12mL / LPTM 1 ), when the glycerol is depleted again and the dissolved oxygen rebounds, hungry for 1 h, and then fed with induction medium (100% methanol containing 12mL / LPTM 1 ), the stirring speed is increased to 800rpm to induce protease expr...
Embodiment 3
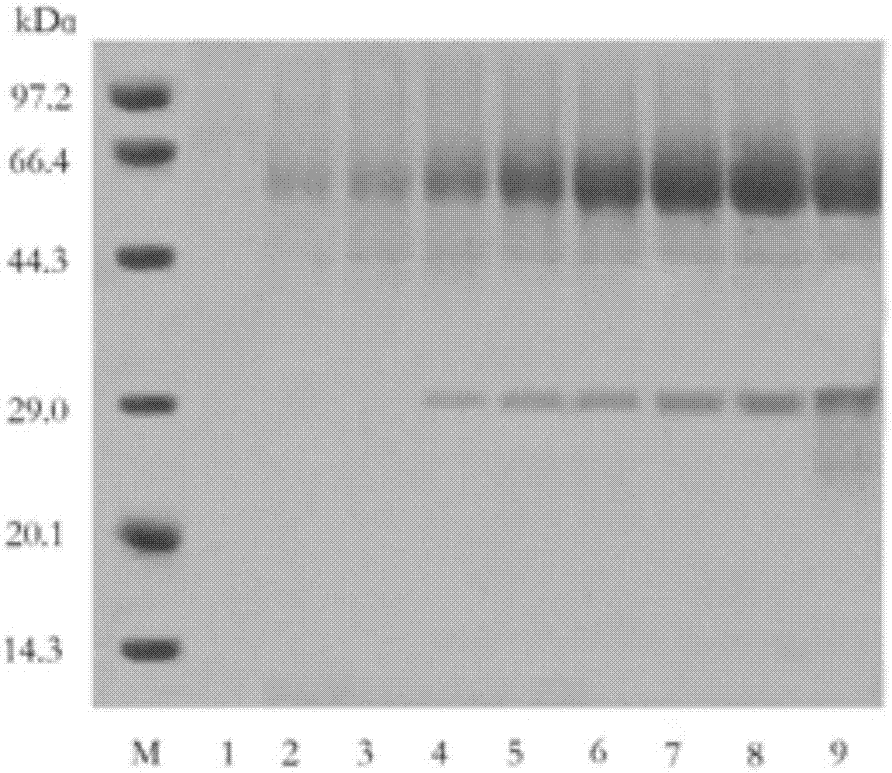
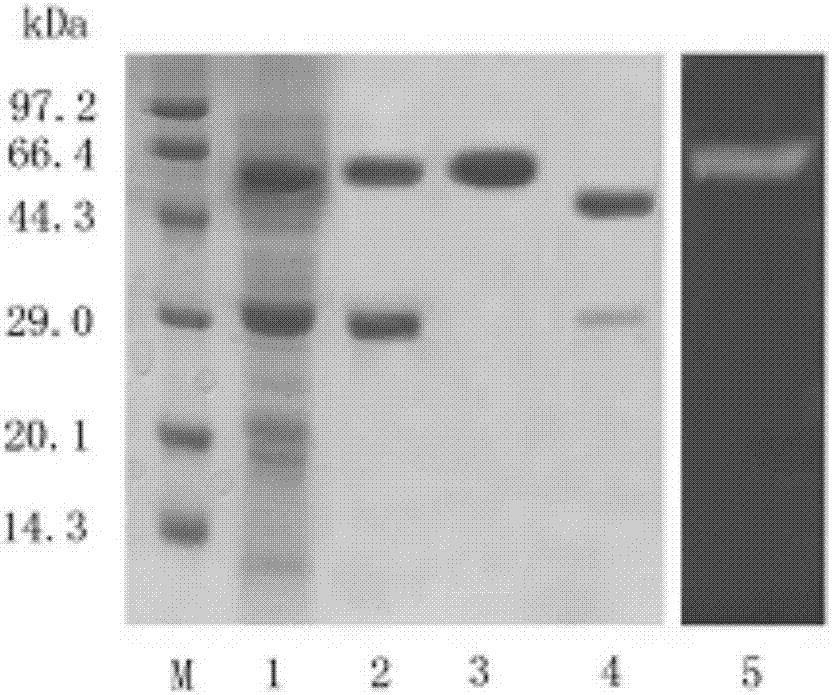
[0059] Example 3: Purification and enzymatic properties of recombinant aspartic protease
[0060] 1. Purification of recombinant aspartic protease
[0061] 1. Cultivation of recombinant aspartic protease in fermenter
[0062] The same as in Example 2. The fermentation broth was frozen and centrifuged at 10,000×g for 10 min, and the supernatant (crude enzyme solution) was taken.
[0063] 2. Ion exchange chromatography
[0064] (1) The supernatant obtained in step 1 was subjected to QSFF strong anion exchange chromatography at a flow rate of 0.1 mL / min, and 10 column volumes were eluted with a linear gradient of 0-500 mM NaCl aqueous solution to collect the active components with protease enzymes. The enzyme activity determination conditions are the same as in Example 2.
[0065] (2) The solution collected in step (1) through the column is subjected to ultrafiltration treatment (filter membrane selection can cut off proteins with molecular weight above 10kDa), collect protein macromolecu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com