Aspartic protease and encoding gene and application thereof
A technology of aspartic acid and protease, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems such as not meeting industrial application requirements, achieve good industrial application prospects, high optimum reaction temperature, and good thermal stability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1 Amplification of Aspartic Protease Gene
[0033] 1.1 Strains and their cultivation
[0034] The Antarctic low-temperature bacterium Geomycespannorum (bacteria identification NCBI accession number: JF20026, which has been deposited in CCTCC, number AF2014016) was donated from the cooperation project of the Faculty of Biological Sciences, University of Malaysia.
[0035] Wash G. pannorum spores from the 10-day-cultivated PDA slant with sterile water, inoculate liquid medium, and culture at 20°C for 7 days to collect mycelia for genome extraction: inoculate milk powder solid medium with a toothpick, and culture at 20°C After 5 days, the hyphae were collected for total RNA extraction.
[0036] 1.2 Genome Extraction
[0037] Follow the instructions of the Omega Fungal Genome Extraction Kit.
[0038] 1.3 Total RNA extraction
[0039] Follow the instructions of the Takara RNA extraction kit.
[0040] 1.4 cDNA first-strand synthesis
[0041] Using the extract...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Embodiment 2 Contains the construction of the Aspergillus oryzae recombinant expression vector of aspartic acid protease gene and its transformation
[0070] 2.1 Primer design
[0071] SKP10f: 5'CTAGCTAGCTAGATGCCTTCTTCGGCGGCCGT3'
[0072] SKP10r: 5'TCCCCCGGGGGATCAAACAACAATCAACAATC3'
[0073] 2.2 Construction of recombinant expression vector
[0074] Use the pSKNHG with the open reading frame of the aspartate protease gene as a template, and use the primers shown in 2.1 to carry out PCR amplification; the PCR product is double-digested with NheI and SmaI, and then mixed with rice Aspergillus expression vector pSKNHG was ligated and screened to obtain a recombinant plasmid (pSKNHGP10).
[0075] 2.3 Preparation of Aspergillus oryzae Competent Cells
[0076] Aspergillus oryzae slant spores were washed with sterile water, inserted into liquid medium, and cultured overnight.
[0077] When a large number of tiny mycelia appear in the medium, stop the culture, filter the m...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Induced expression and purification of embodiment 3 Aspergillus oryzae recombinant bacteria
[0087] 3.1 Pick a single clone of the recombinant bacteria on the MM plate described in 2.5, inoculate the dextrin-induced liquid medium, and culture at 20°C and 200 rpm for 3 to 5 days.
[0088] 3.2 Collect the supernatant by suction filtration through the membrane, measure the enzyme activity, determine the protein concentration, and conduct protein electrophoresis.
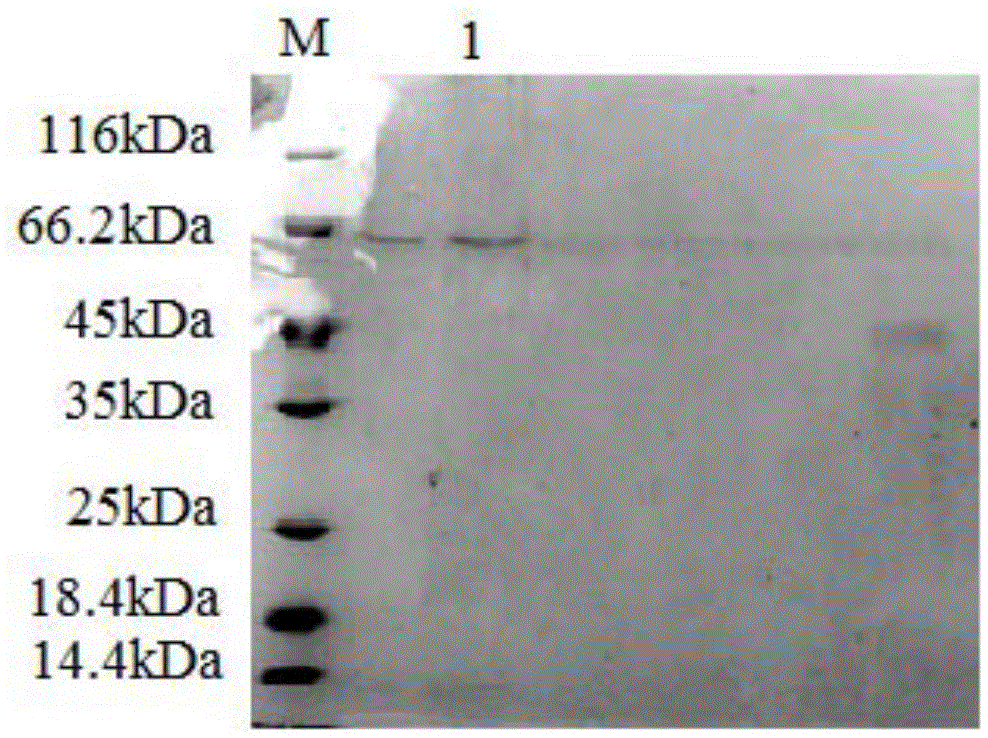
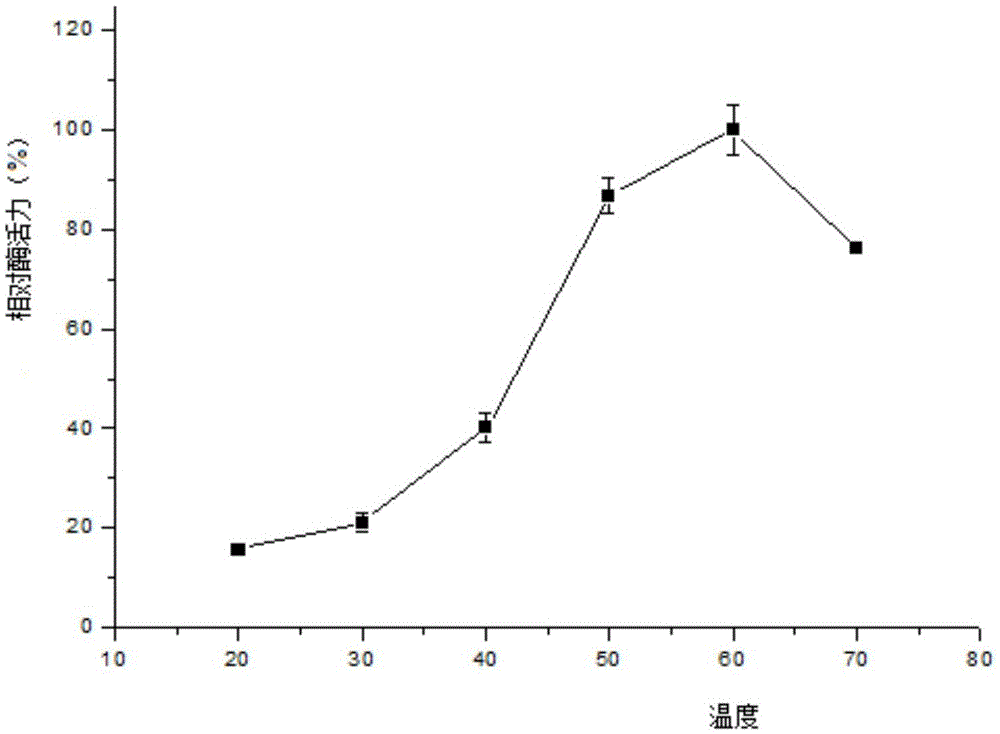
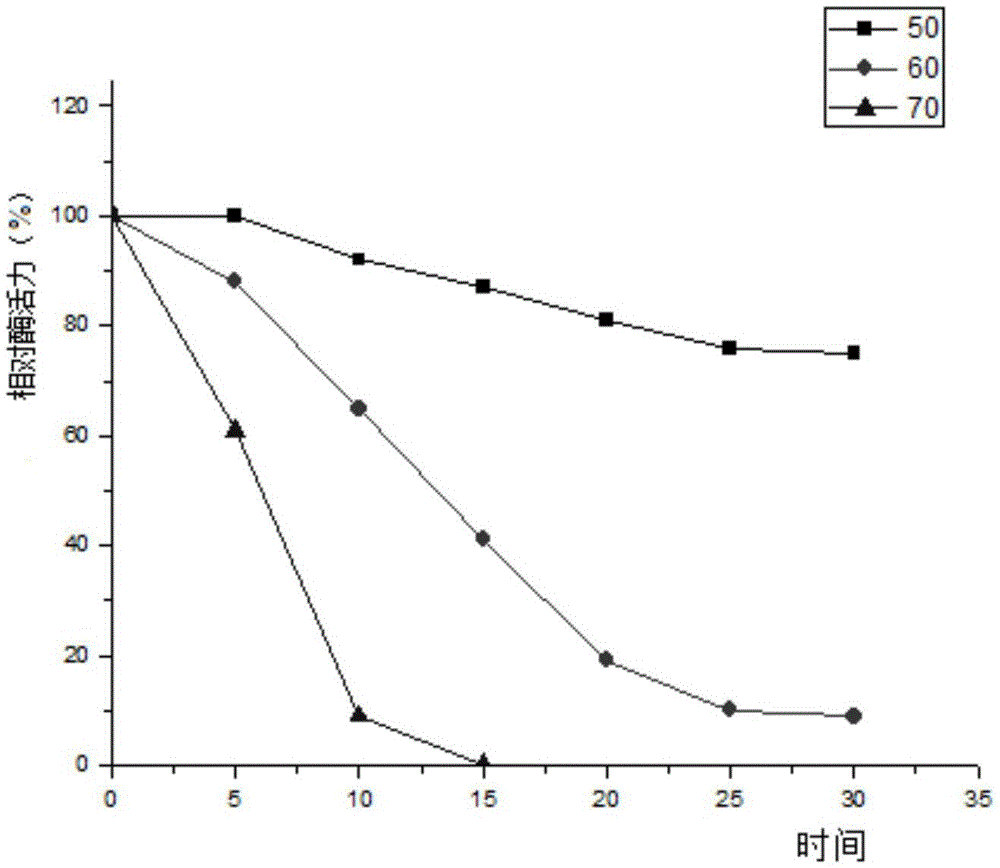
[0089] 3.3 The collected supernatant was first loaded onto a Ni-NTA affinity column with a column volume of 1 mL with 10 mL of NPI solution containing 10 mM imidazole at a rate of 1.0 mL / min. Then use NPI-enzyme solution, NPI solutions containing 20mM, 50mM, and 200mM to elute the affinity column in turn, measure the enzyme activity of the eluate and perform SDS-PAGE electrophoresis to determine the optimal purification conditions and obtain pure GpP10 protein ,Such as figure 1 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com