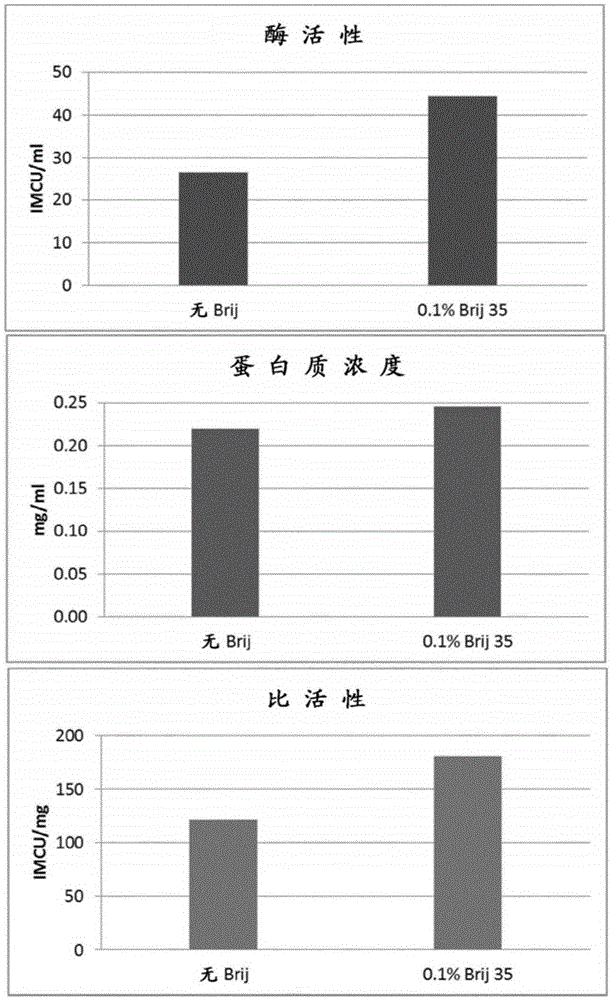
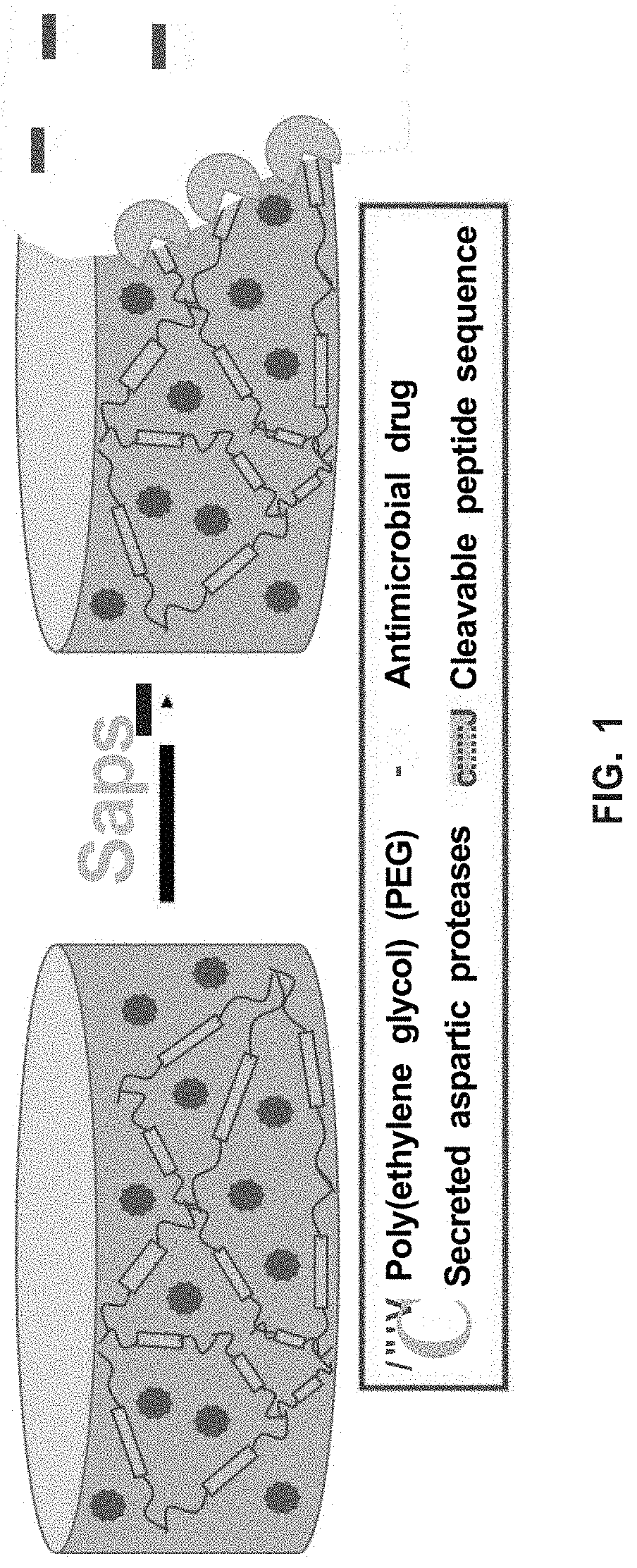
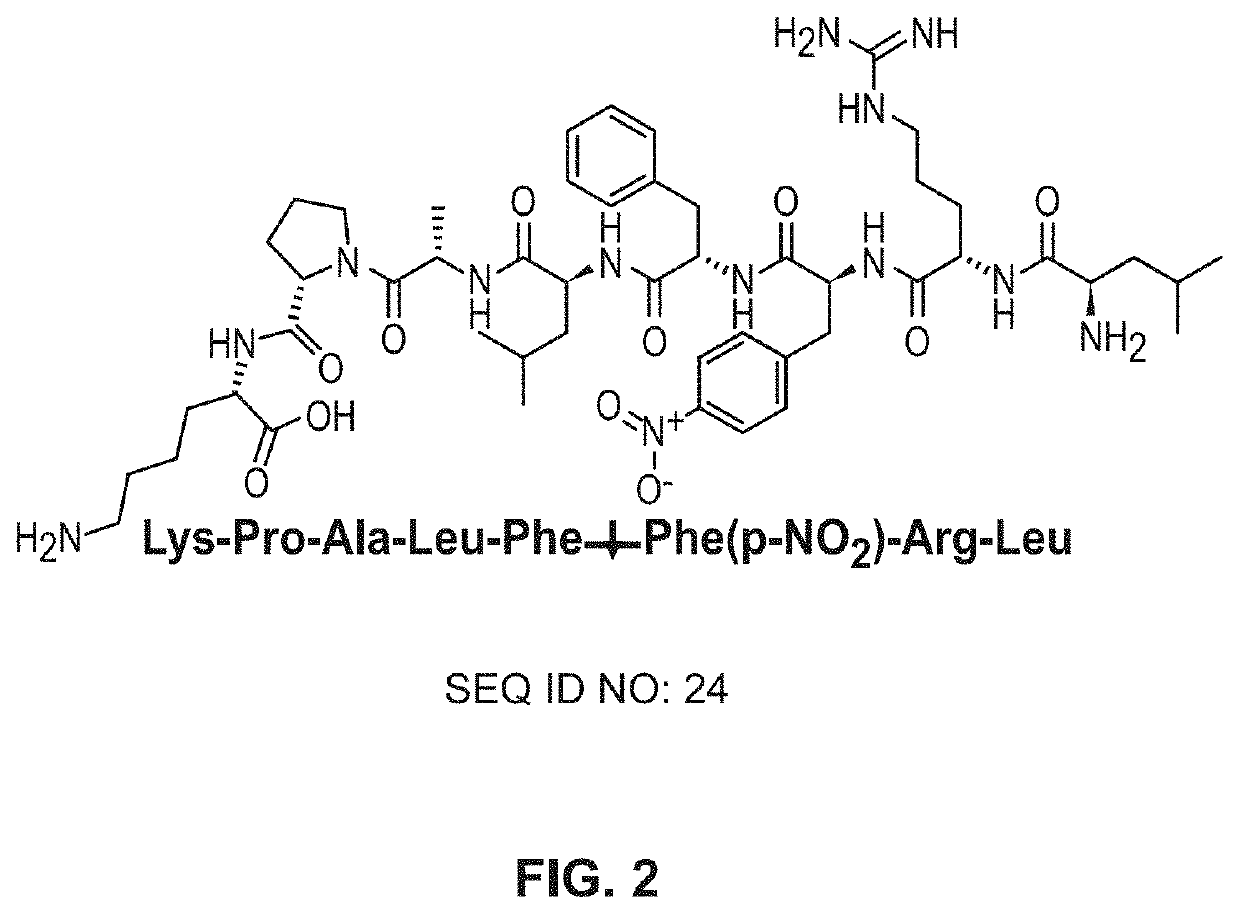
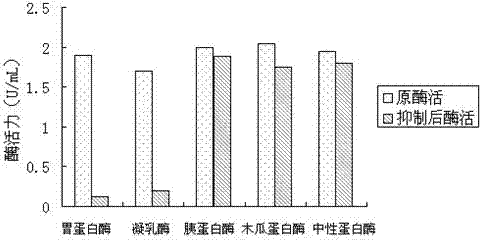
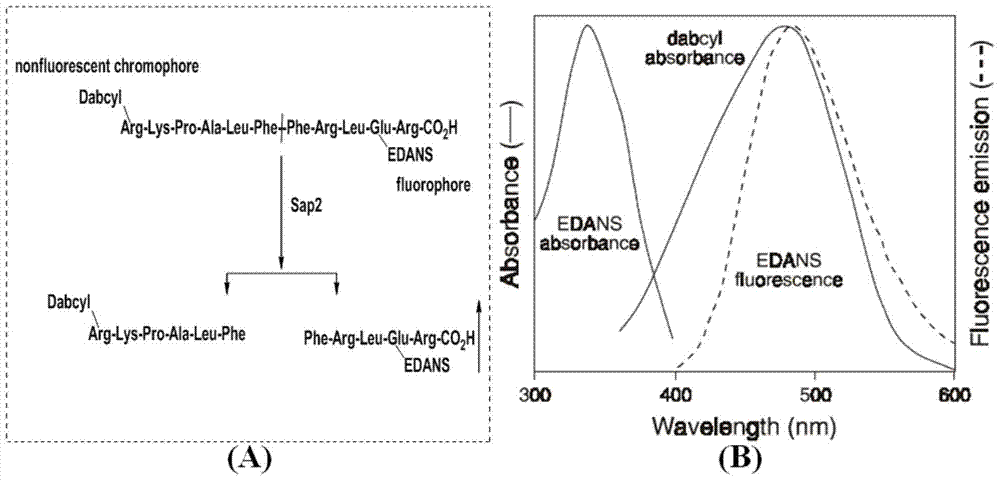
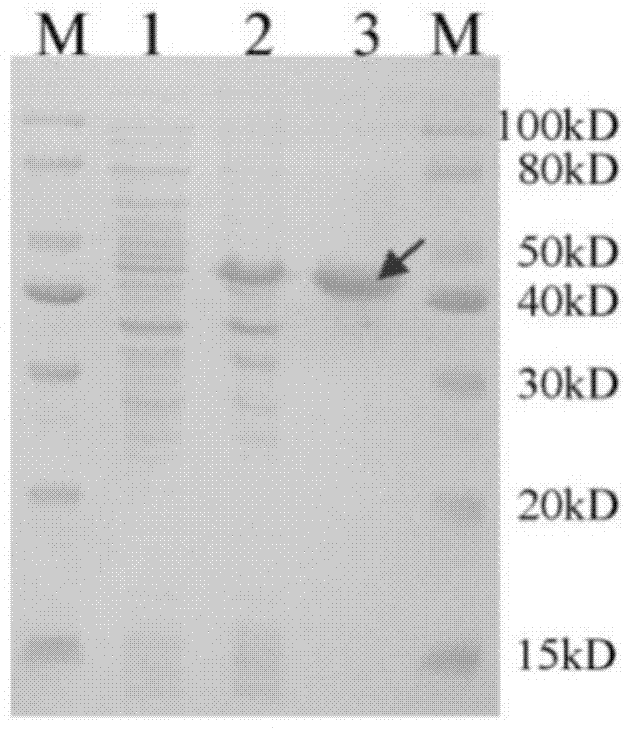
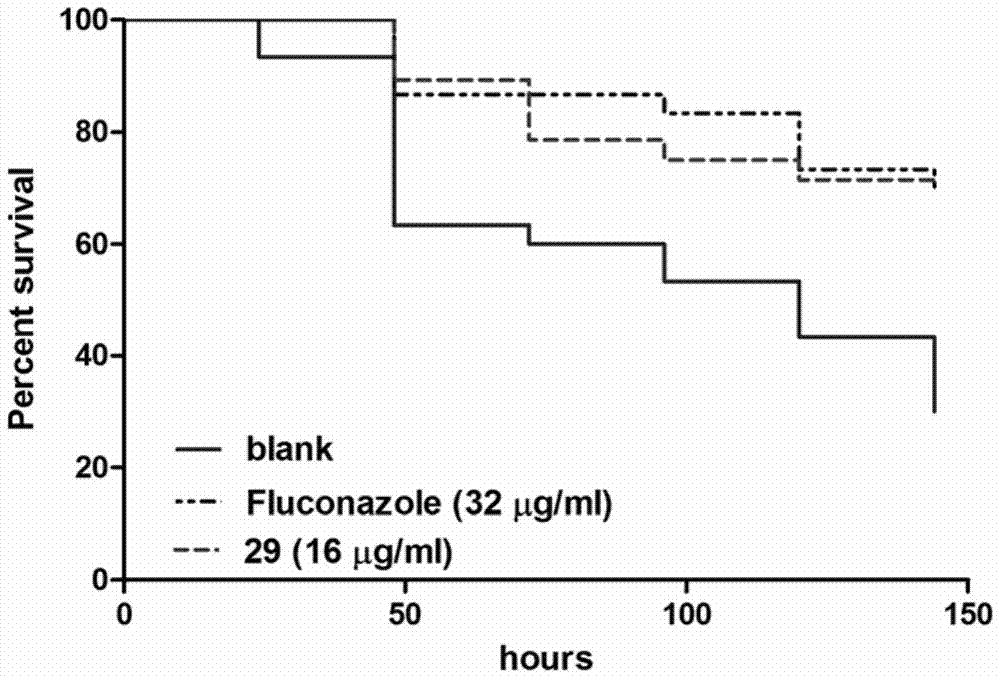
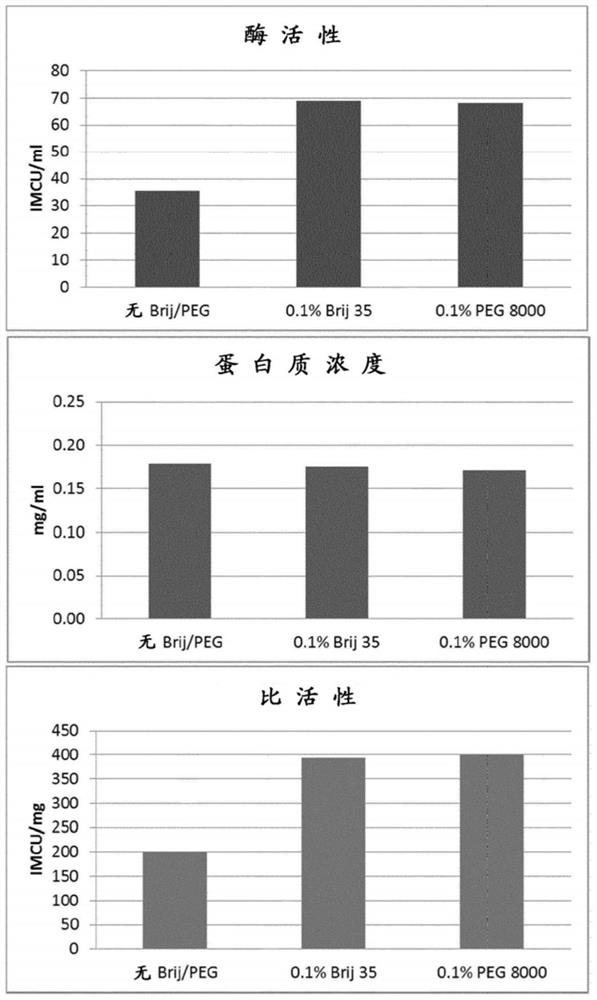
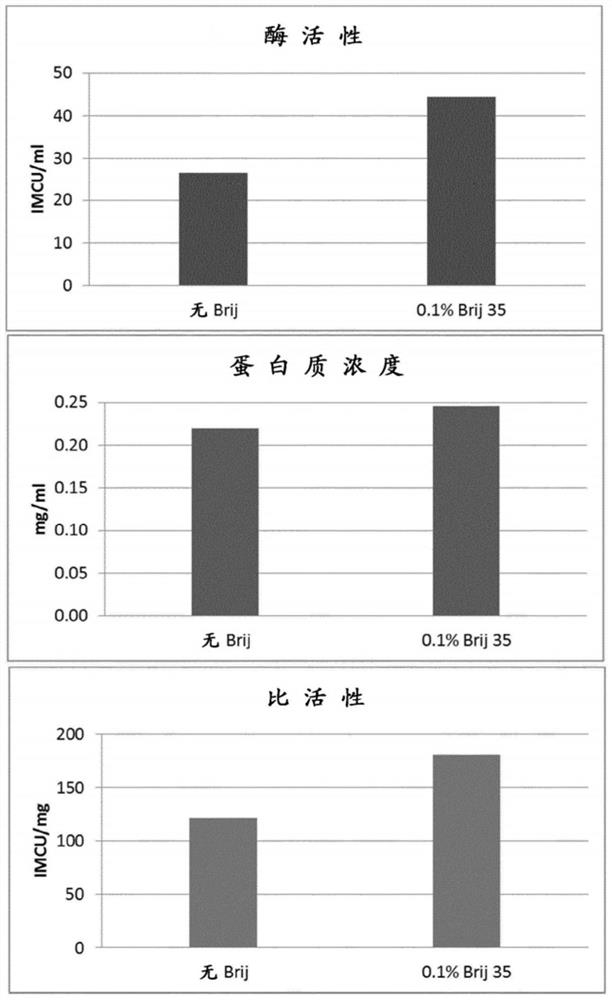
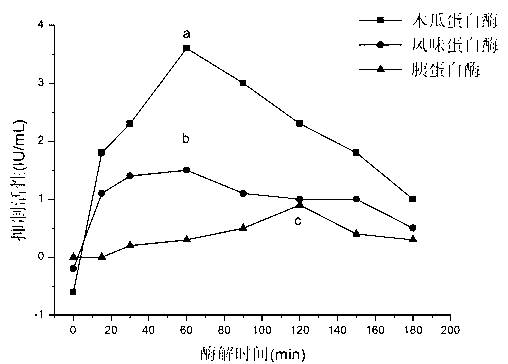
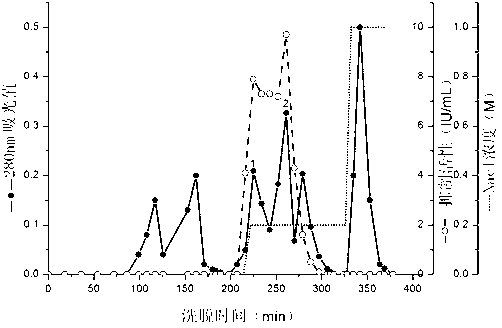
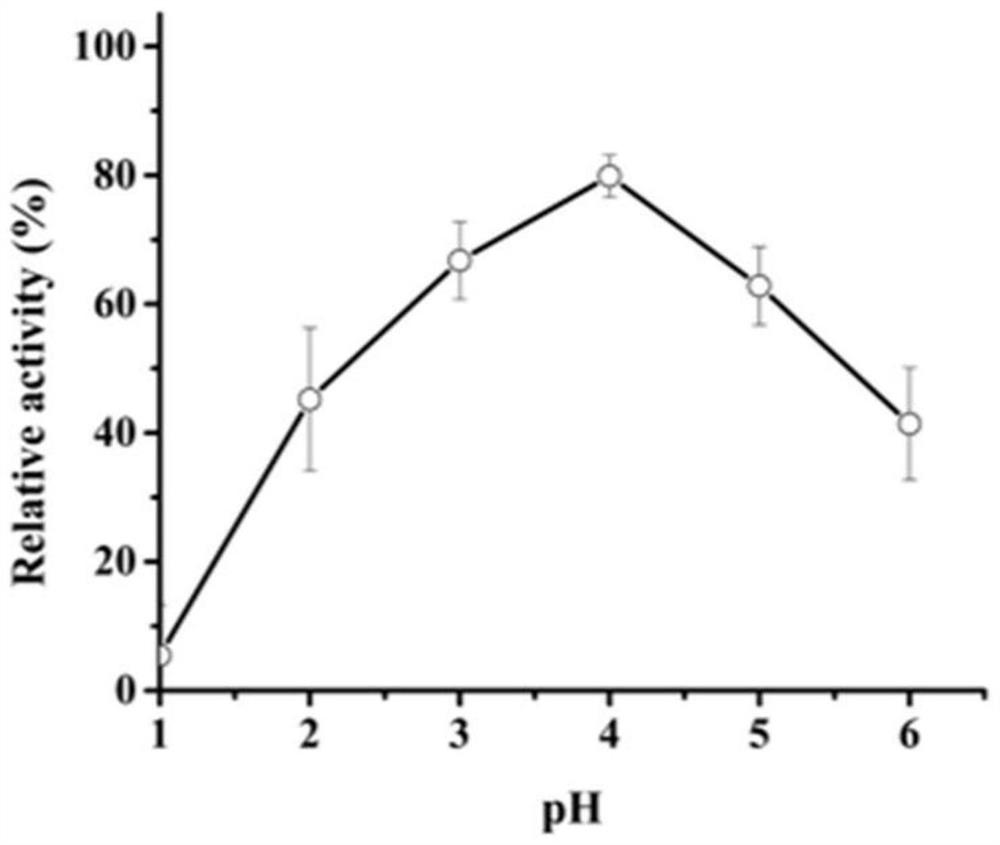
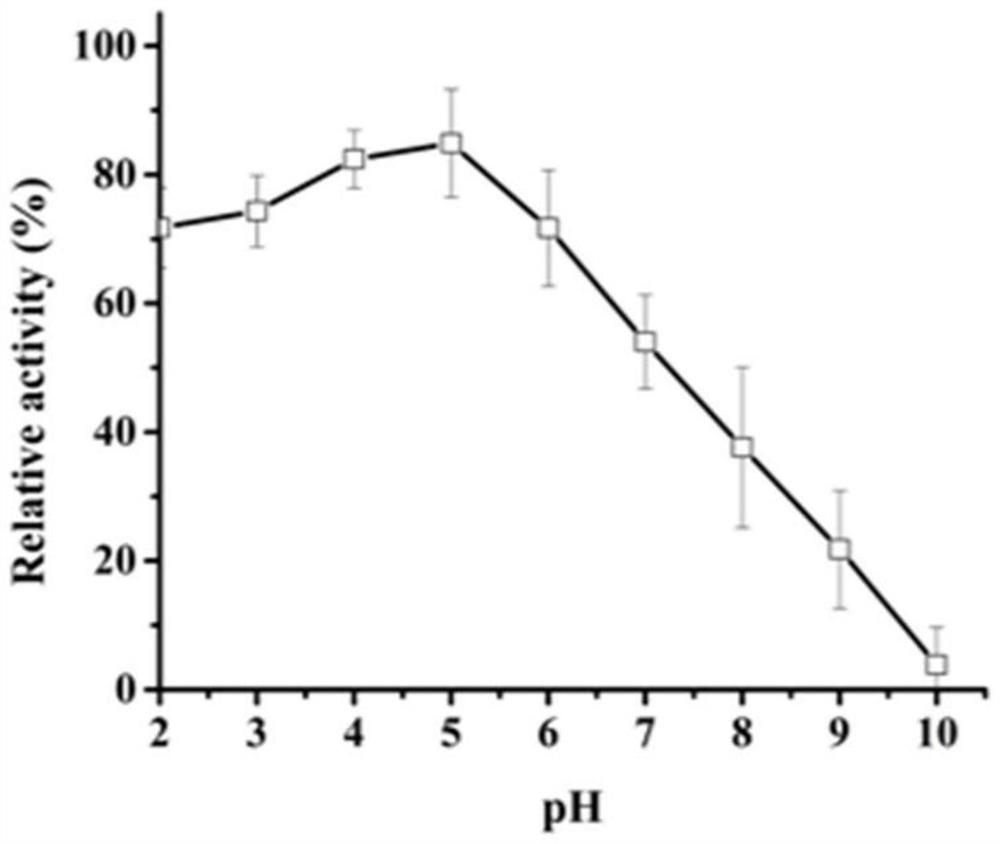
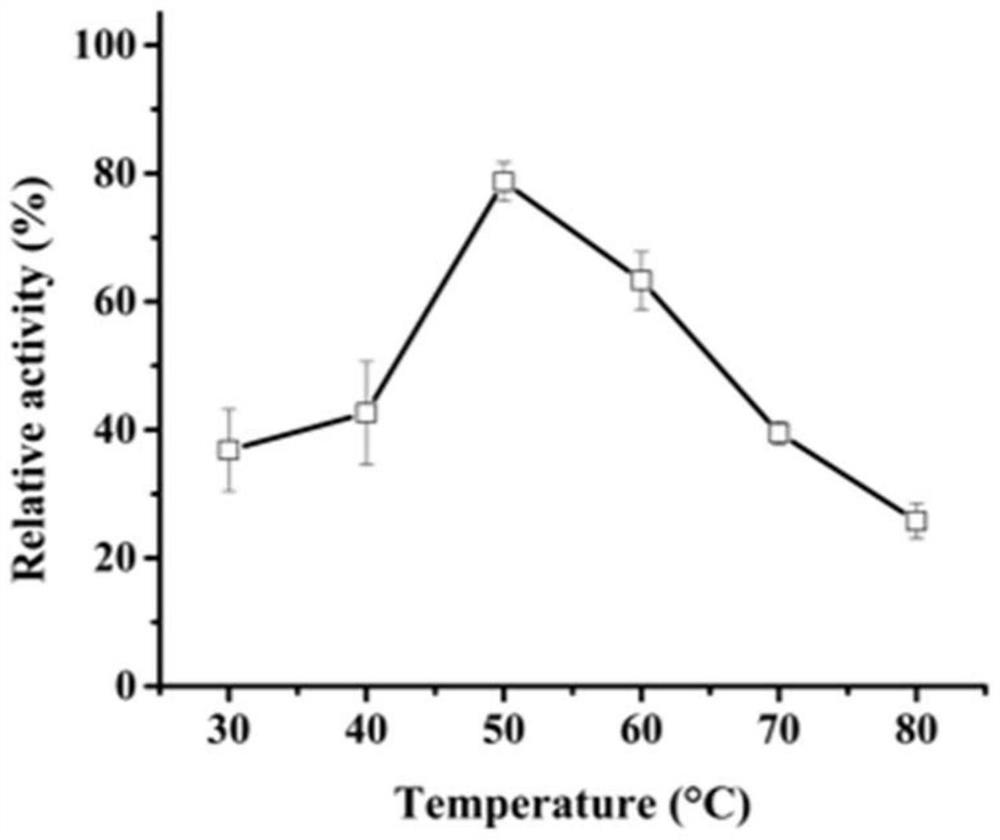
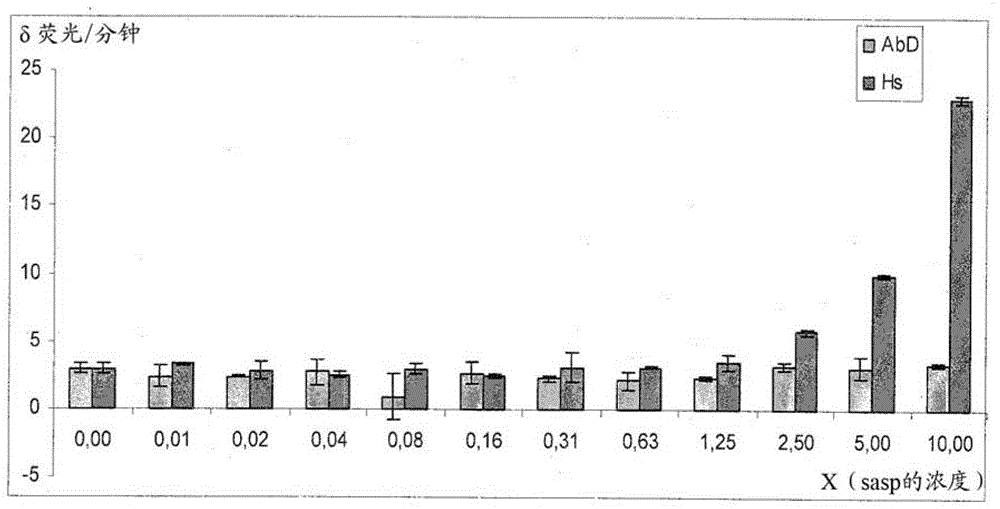
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Aspartic Acid Proteases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A subclass of peptide hydrolases that depend on an ASPARTIC ACID residue for their activity.
Diaminoalkane aspartic protease inhibitors
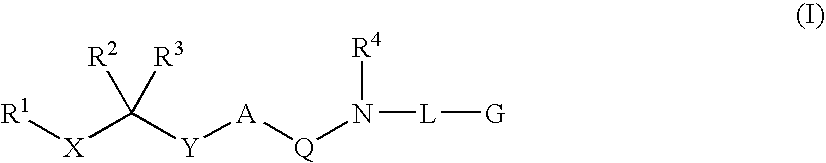
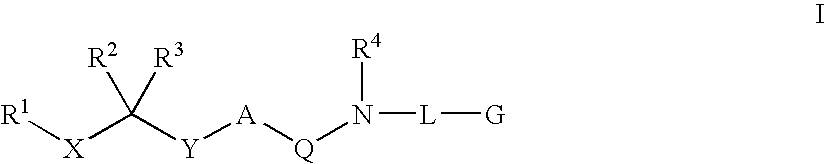
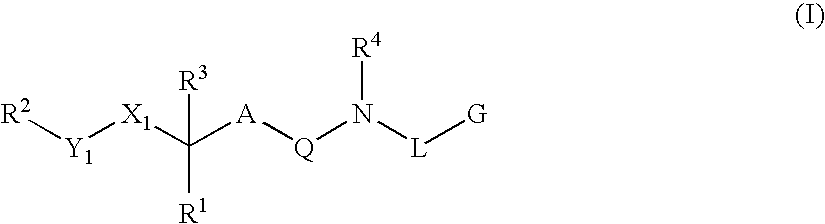
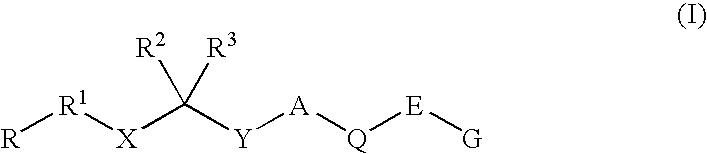
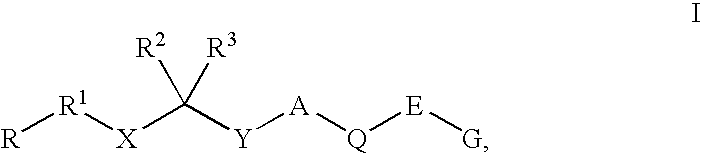
Diaminoalkanes of Formula I have now been found which are orally active and bind to aspartic proteases to inhibit their activity. They are useful in the treatment or amelioration of diseases associated with elevated levels of aspartic protease activity. The invention also relates to a method for the use of the compounds of Formula I in ameliorating or treating aspartic protease related disorders in a subject in need thereof comprising administering to said subject an effective amount of a compound of Formula I.
Owner:VITAE PHARMA INC
Renin inhibitors
InactiveUS20100160424A1Low costHigh activityBiocideCarbamic acid derivatives preparationDiseaseAspartic protease activity
Described are compounds that bind to aspartic proteases to inhibit their activity. They are useful in the treatment or amelioration of diseases associated with aspartic protease activity. Also described are methods of use of the compounds described herein in ameliorating or treating aspartic protease related disorders in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:VITAE PHARMA INC
Kit for determining mitochondria aspartate aminotransferase
InactiveCN102010890AUndisturbedThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementLactate dehydrogenaseActivity ratios
The invention discloses a kit for determining mitochondria aspartate aminotransferase, containing a reagent 1 and a reagent 2, wherein the reagent 1 contains aspartic acid protease, alpha- ketoglutaric acid, L-aspartic acid, malate dehydrogenase, lactate dehydrogenase, a preservative and PEG6000. The enzyme activity ratio of the aspartic acid protease to the malate dehydrogenase to the lactate dehydrogenase in the reagent 1 is (0.1-50):(0.1-50):(0.1-10); the ratio of the alpha- ketoglutaric acid to the malate dehydrogenase is (0.1-60)g:(0.1-50)KU; the mass ratio of the alpha- ketoglutaric acid to the L-aspartic acid to the preservative to the PEG6000 is (0.1-60):(5-200):(0.2-10):(1-100); and the mass ratio of NADH (Reduced Form of Nicotinamide-Adenine Dinucleotid) to a preservative to EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid).2Na is (0.5-10):(0.2-10):(1-50). The kit for determining the mitochondria aspartate aminotransferase is used for determining the activity of the determining mitochondria aspartate aminotransferase, is free from the interference of high cell plasma aspartate aminotransferase and obtains accurate result.
Owner:北京迪迈医学诊断技术有限公司
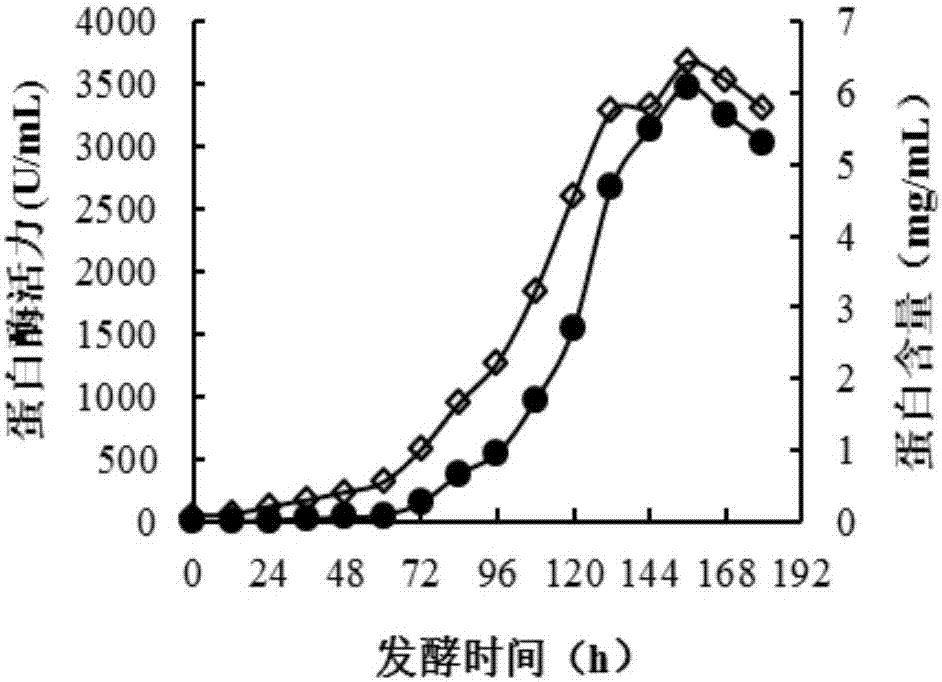
A production method and applications of a novel rhizomucor miehei aspartic protease
ActiveCN107338234AEffective tenderizationEffective hydrolysisFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
The invention discloses a production method and applications of a novel rhizomucor miehei aspartic protease, and particularly relates to a recombinant aspartic protease, a coding gene, and a production method and applications of the recombinant aspartic protease. The recombinant aspartic protease is protein having an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The coding gene of the recombinant aspartic protease is a DNA molecule shown as SEQ ID NO:2. An aspartic protease gene that is RmproA of rhizomucor miehei is connected to a pichia pastoris GS115 expression vector pPIC9K, and is converted into pichia pastoris and induced expression is performed to obtain the recombinant aspartic protease. Through high-density fermentation in a fermentation tank having a volume of 5 L, the maximum protease production activity at 156 h of a recombinant strain is 3400 U / mL, and the protein content is 6.42 mg / mL. The recombinant aspartic protease is capable of effectively tendering pork, reducing shearing force, making meat palatable, and effectively hydrolyzing animal and plant protein to prepare low-molecular-weight polypeptides.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Renin Inhibitors
Described are compounds of the formula (I) which are orally active and bind to aspartic proteases to inhibit their activity. They are useful in the treatment or amelioration of diseases associated with aspartic protease activity. Also described are methods of use of the compounds described herein in ameliorating or treating aspartic protease related disorders in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:VITAE PHARMA INC
Cleaning fluid for water treatment ultrafiltration membranes
The invention provides a cleaning fluid for water treatment ultrafiltration membranes. The cleaning fluid for the water treatment ultrafiltration membranes is composed of deionized water, inulase, gentiobiase, citrulline, beta-amylase, zytase and aspartic protease. The deionized water in each cubic meter comprises the components of 20-60g inulase, 40-90g gentiobiase, 5-20g citrulline, 80-200g beta-amylase, 60-200g zytase and 5-10g aspartic protease. The invention further provides a method for cleaning the ultrafiltration membranes. The cleaning fluid for the water treatment ultrafiltration membranes is simple in formula and simple and easy to produce. The cleaning fluid is basically composed of active enzymes, and can effectively removing the organic pollutants in the ultrafiltration membranes.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Method for modifying polyamide
InactiveCN1965124AImprove propertiesHarmful littleFibre typesBiochemical treatment with enzymes/microorganismsPolymer scienceEnzyme action
The present invention relates to a method for modifying polyamide. The method comprises that polyamide is contacted with an enzyme preparation comprising an effective amount of protease enzyme in aqueous environment under conditions suitable for the function of the enzyme. The enzyme is preferably selected from the group of aspartic proteases, cysteine proteases and metallo-proteases.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
Application of aspartic protease gene in improvement of beauveria bassiana variety
ActiveCN113403209AImprove high temperature resistanceIncrease productionBiocideFungiNucleotideWild type
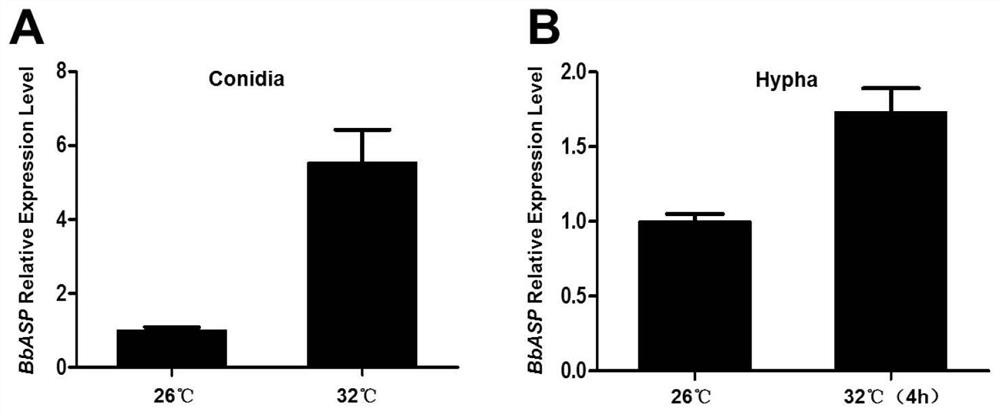
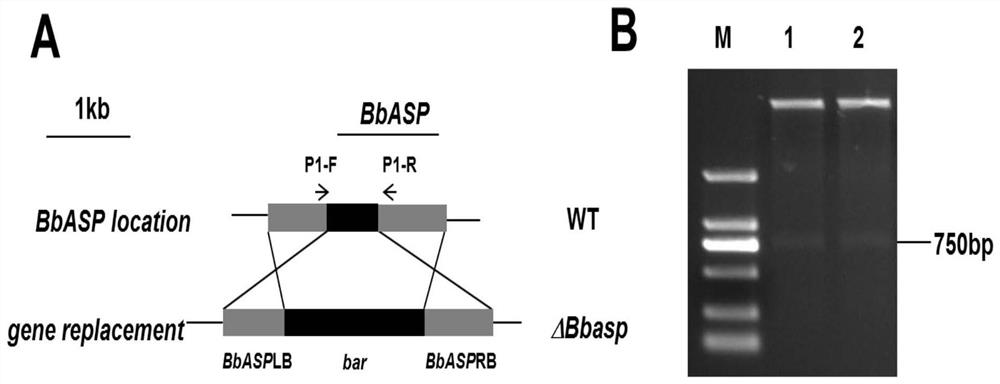
The invention discloses application of an aspartic protease gene in improvement of beauveria bassiana variety. The yield and toxicity of conidia of the beauveria bassiana are improved by knocking out the aspartic protease gene BbASP, or the high-temperature tolerance of the beauveria bassiana is improved by over-expressing the aspartic protease gene BbASP, and the nucleotide sequence of the aspartic protease gene BbASP is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 20; if the BbASP knockout strain is cultured for 10 d at 26 DEG C, the conidium yield is 72.57% higher than that of a wild type, if the BbASP knockout strain is cultured for 20 d at 26 DEG C, the conidium yield is 59.43% higher than that of a wild type, the survival rate of a host is reduced, the half lethal time is shortened, the time that entomogenous thalli penetrate out of the dead host is shortened, and the growth rate of the BbASP over-expression strain is increased under the high-temperature stress of 32 DEG C; and after the conidia are stressed at the high temperature of 43 DEG C for 2 h and 4 h, the germination rates are respectively increased by 7% and 11.34%.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Renin Inhibitors
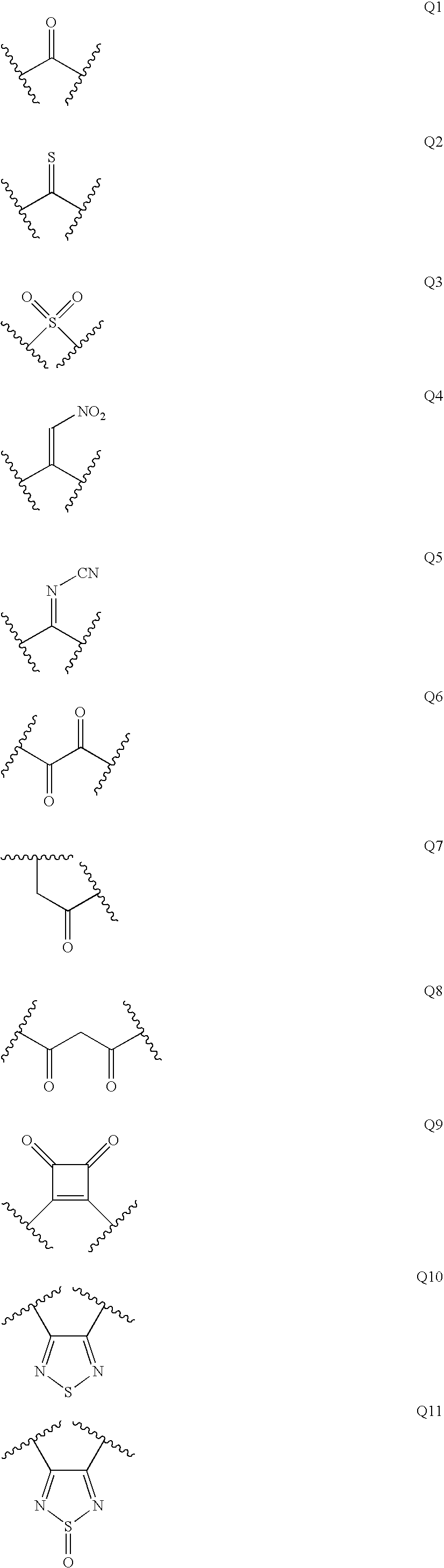
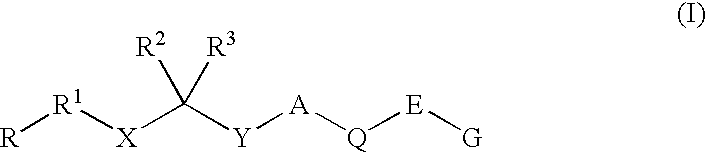
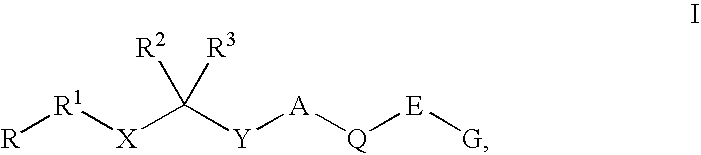
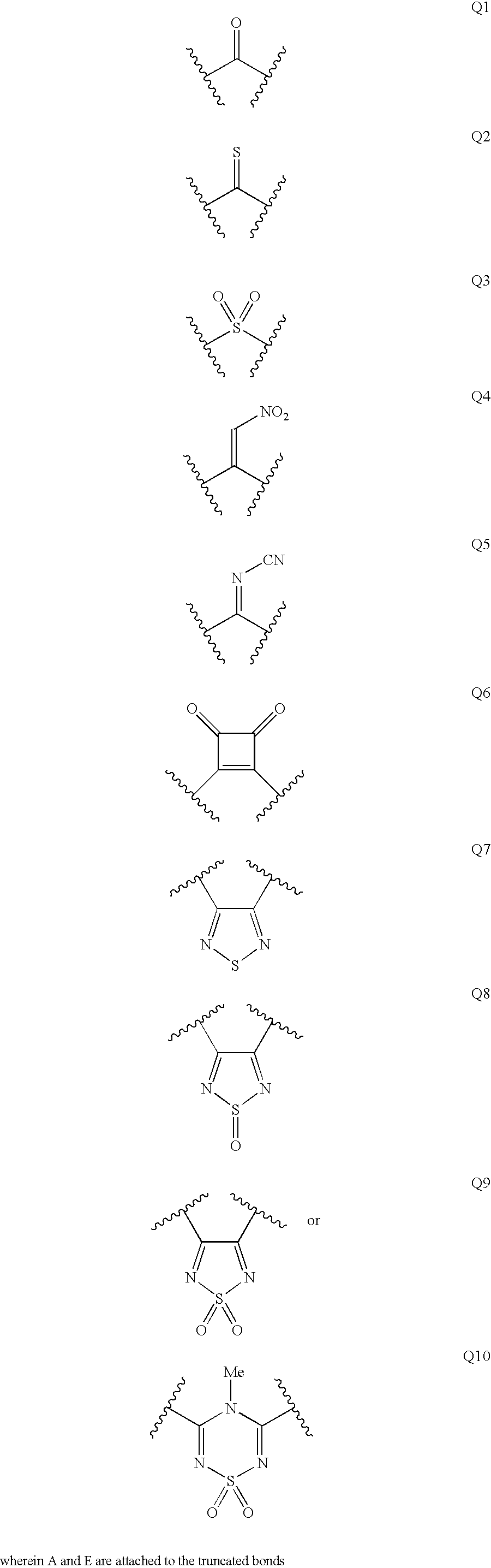
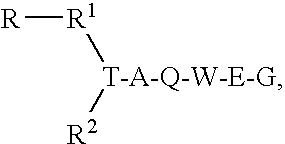
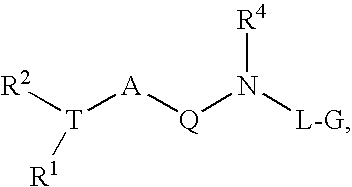
Disclosed are compounds of Formula I, wherein the R, R1, R2, R3, X, Y, A, Q, E, and G are defined herein. These compounds bind to aspartic proteases to inhibit their activity and are useful in the treatment or amelioration of diseases associated with aspartic protease activity. Also disclosed are methods of use of the compounds of Formula I for ameliorating or treating aspartic protease related disorders in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:VITAE PHARMA INC
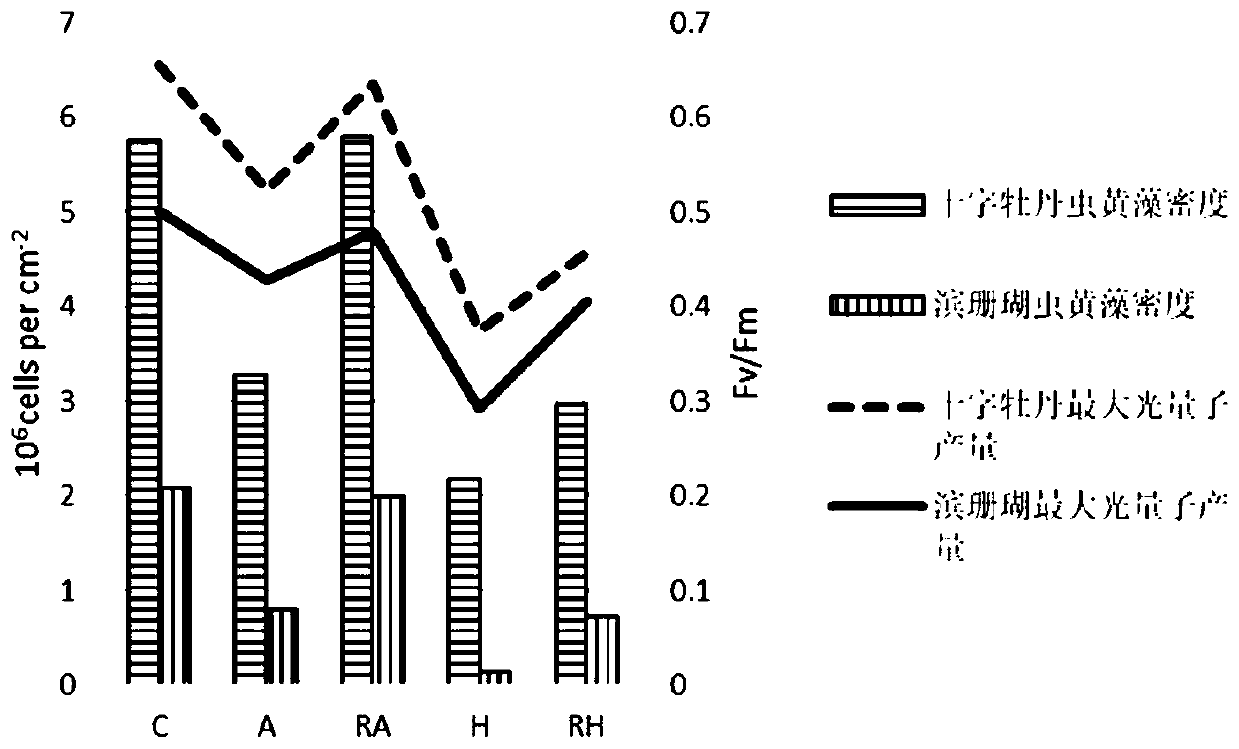
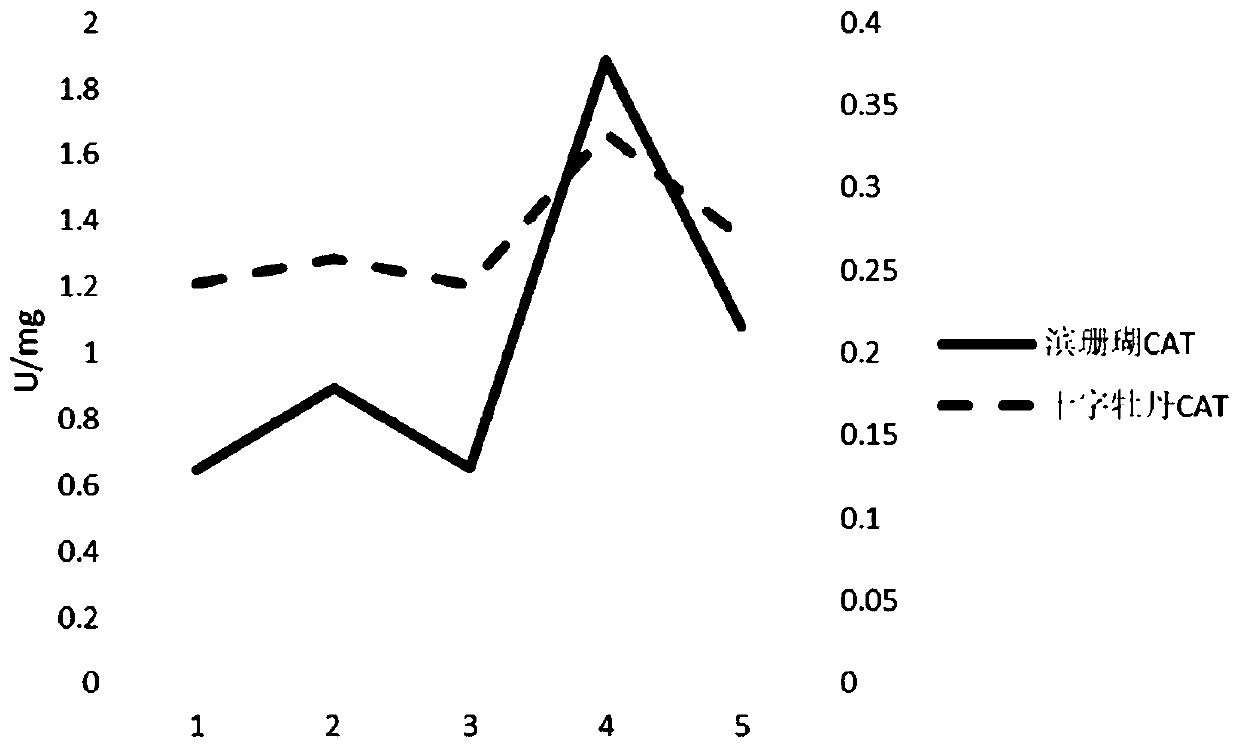
Method for assessing heat resistance of coral
InactiveCN110506674AEvaluate heat resistanceEasy to operateClimate change adaptationMaterial analysis by optical meansZooxanthellaeHeat resistance
The invention discloses a method for assessing the heat resistance of a coral, and belongs to the field of ecological restoration of a marine environment. The method comprises the step that with phenotypic characteristics of the hermatypic coral, the symbiotic zooxanthellae density, the photosynthetic rate, superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), the aspartic acid protease (Caspase3) and the like as indexes, the heat resistance of the coral is assessed. The method has the advantages of multiple parameters, high precision, quantifiable comparison and the like, the method can be used for guiding coral transplanting and restoration, and a basis is provided for protection of a coral reef ecosystem. The method is easy and convenient to operate and easy to use, and the heat resistance of thecoral can be quickly assessed; by analyzing the phenotypic characteristics of the hermatypic coral, and the heat resistances of different kinds of corals can be compared so as to be used for seed selection in the coral breeding and coral transplanting and restoration processes; the heat resistances of the same kind of corals obtained before domestication and after domestication can be compared soas to used for assessing the domestication effect; moreover, the domestication effects of different kinds of corals can be compared so as to be used for seed selection during scientific research or coral transplanting and restoration.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
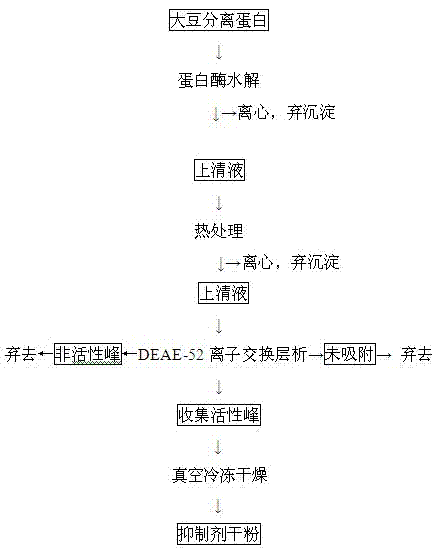
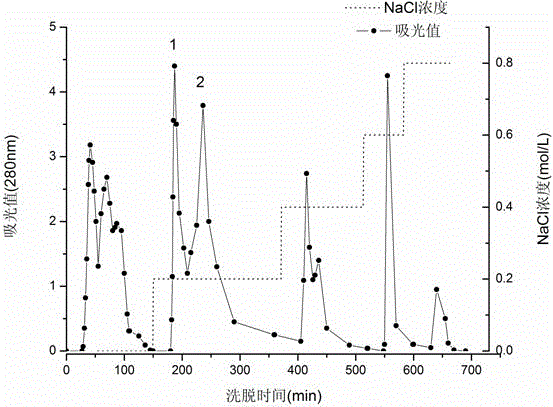
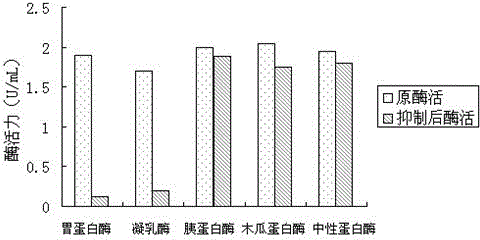
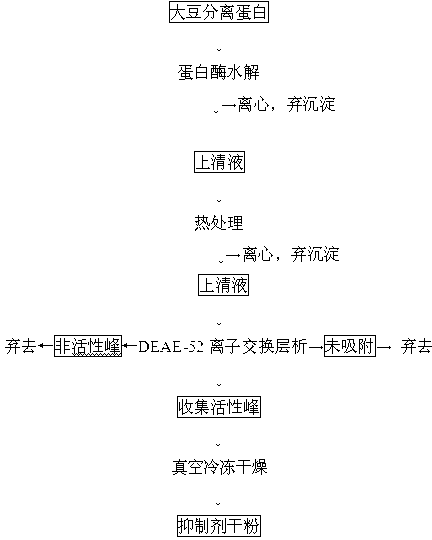
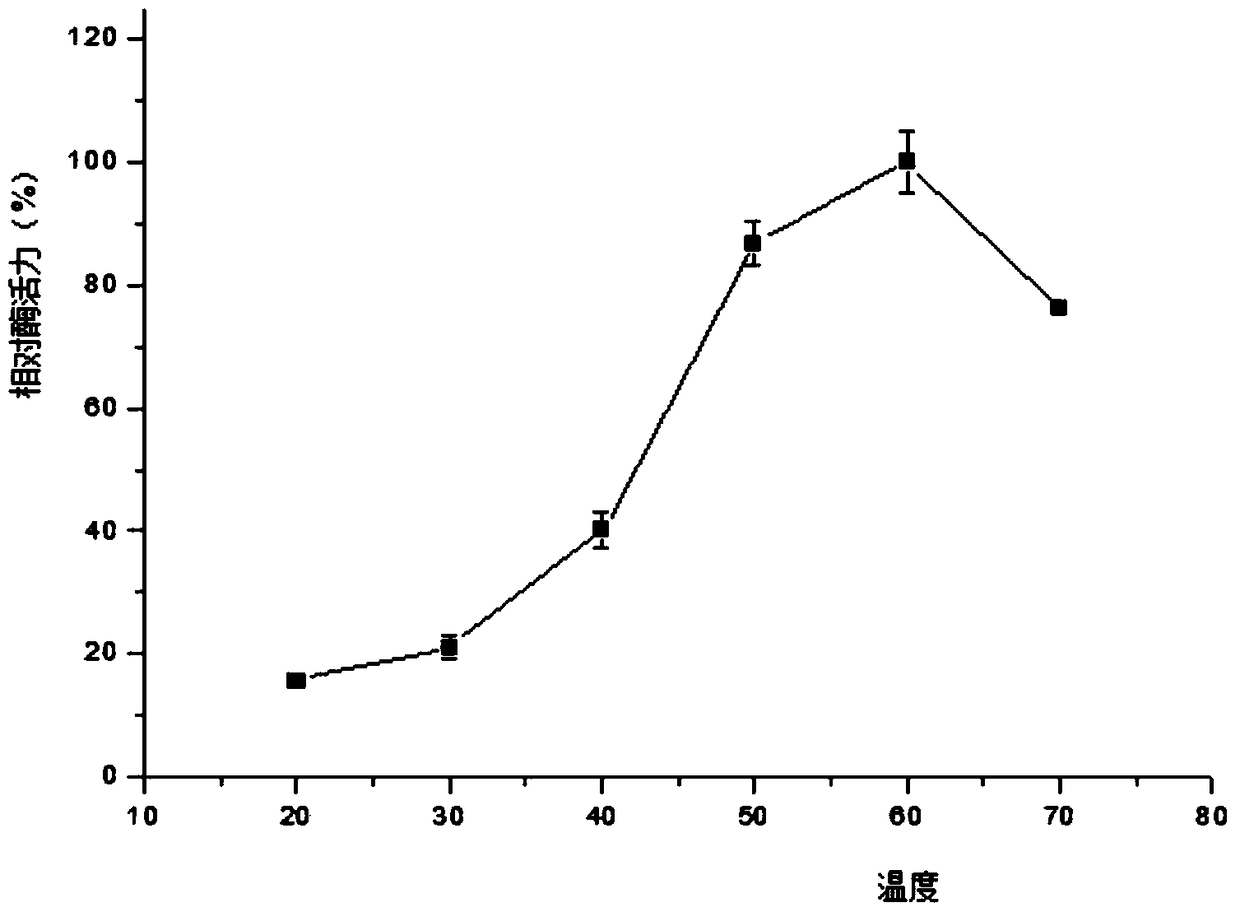
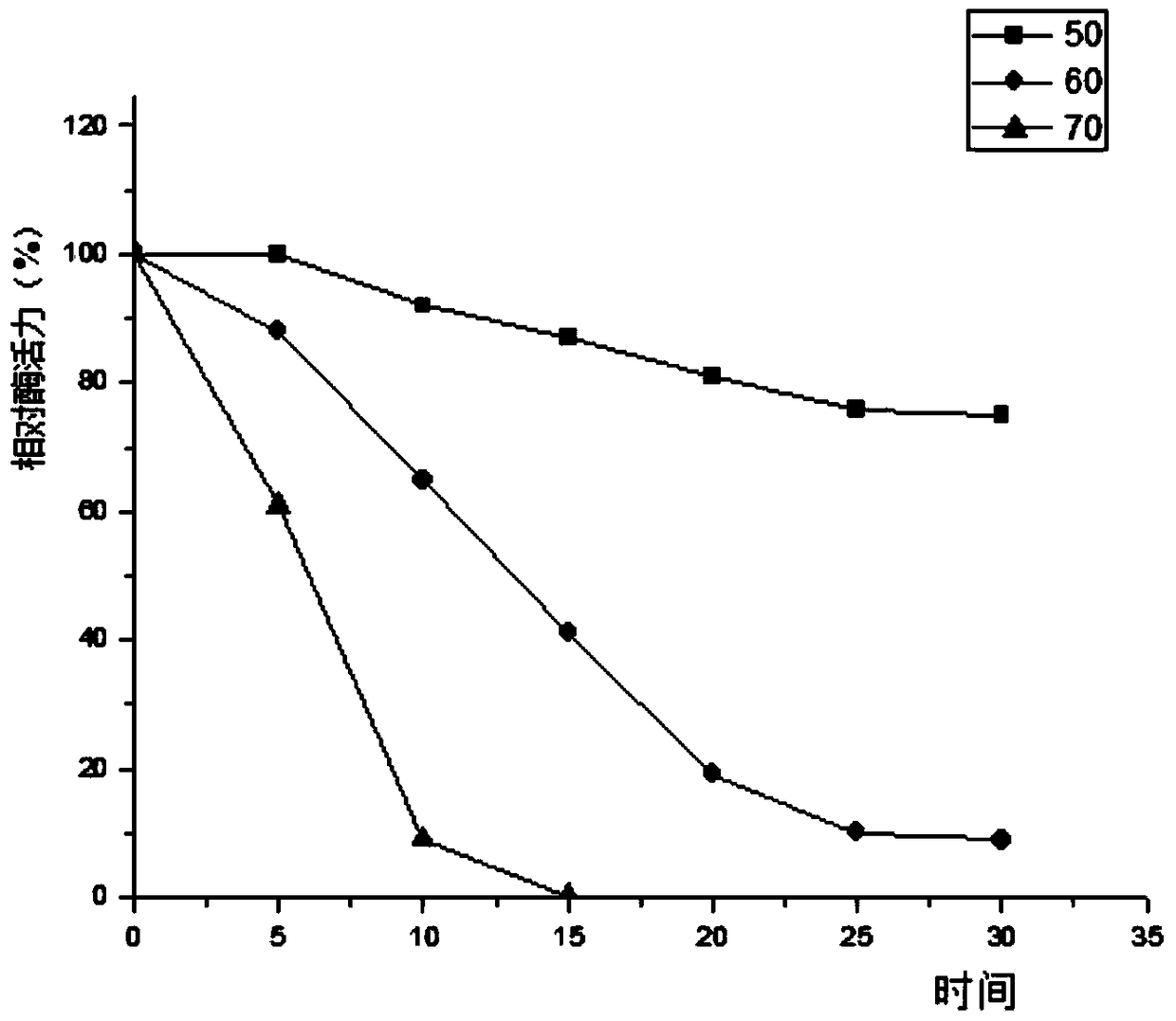
Preparation method for aspartic protease inhibitor in enzymatic hydrolysis products of soybean protein isolate
The invention provides a preparation method for an aspartic protease inhibitor in enzymatic hydrolysis products of soybean protein isolate, which belongs to the field of separation and purification of biological products. The invention relates to enzymatic hydrolysis of soybean protein isolate with papain for obtainment of a crude product of the aspartic protease inhibitor. The aspartic protease inhibitor is prepared from the crude product by carrying out heat treatment and high speed centrifugation on an enzymatic hydrolysate and carrying out DEAE-52 ion exchange chromatography and separation on an obtained supernatant, and dry powder of the aspartic protease inhibitor is obtained by carrying out vacuum freeze drying on the obtained aspartic protease inhibitor. The aspartic protease inhibitor prepared in the invention has high inhibitory activity on pepsin and chymosin in the family of aspartic protease; the aspartic protease inhibitor extracted from the natural processing material soybean protein isolate which has undergone enzymatic hydrolysis has good specificity, good stability, safety in application and an application prospect in a wide variety of fields, e.g., medicines andhealth care, food additives, control of insect diseases, etc.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Rennets
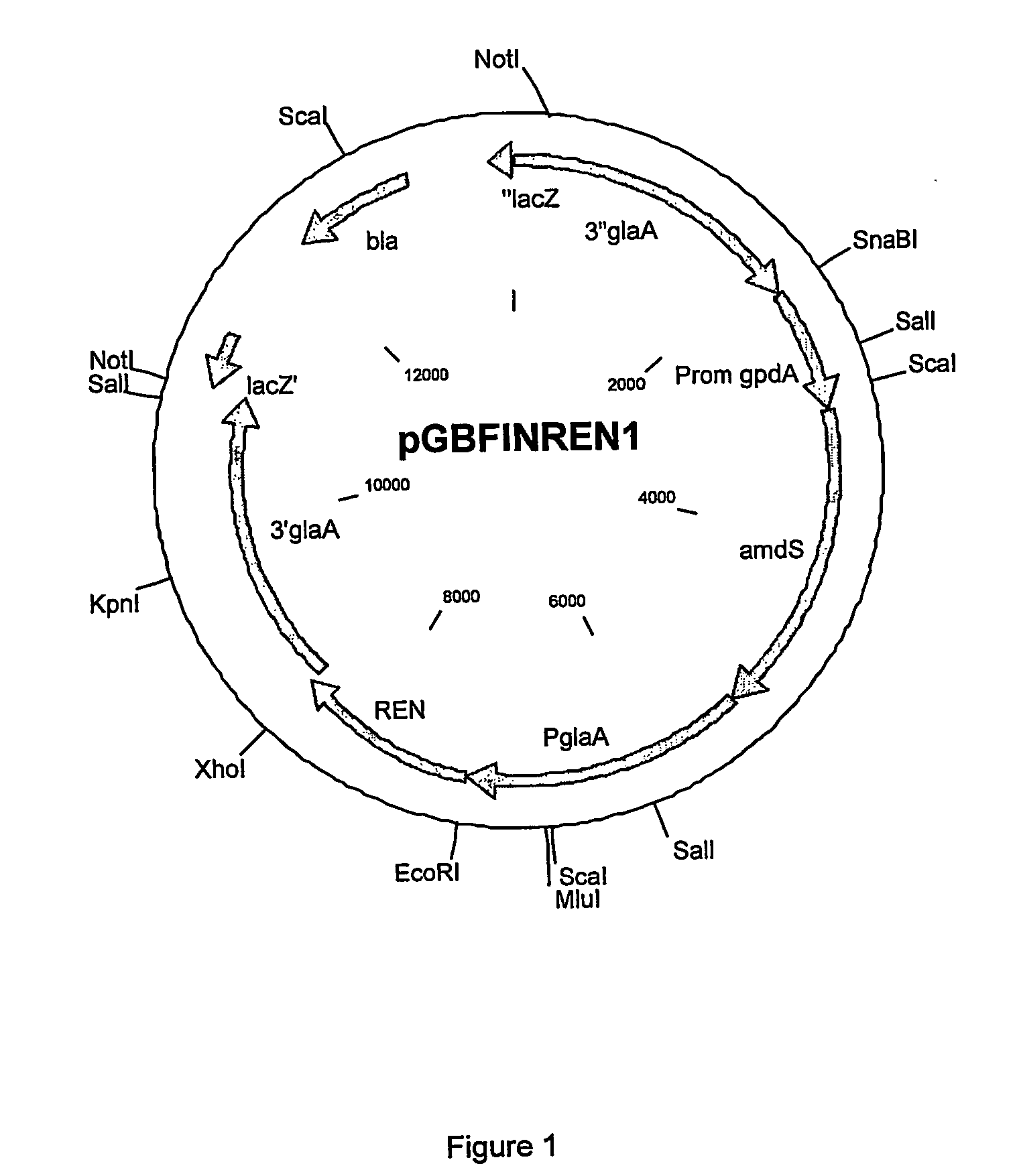
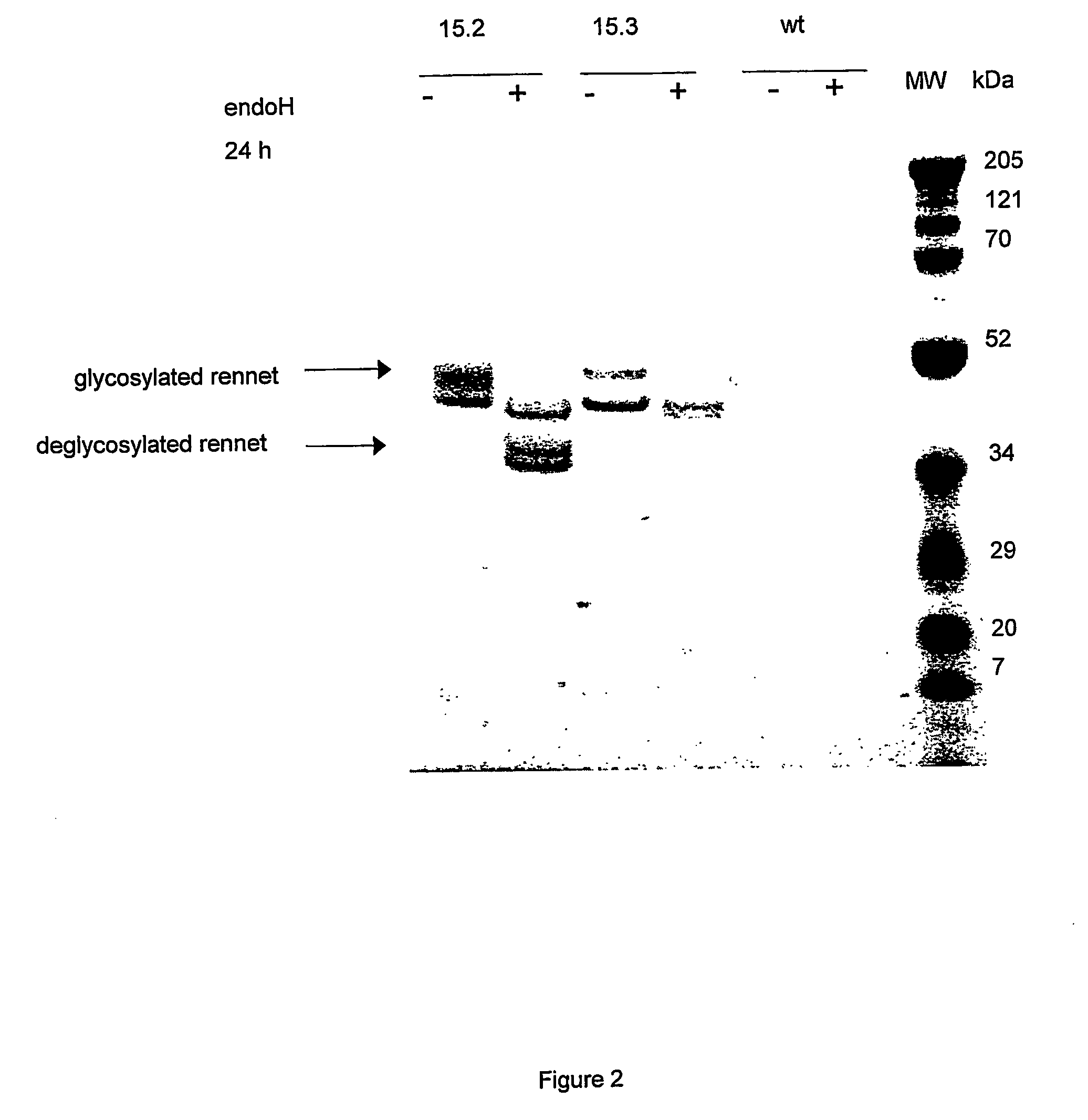
The present invention describes an aspartic protease produced by a fungus from the class Eurotiomycetes, comprising the amino acid sequence of FDTGSSD or FDTGSSE. The present invention further provides a process for identifying new milk clotting enzymes comprising screening an amino acid sequence for the presence of FDTGSSD or FDTGSSE. The enzymes of the invention may he useful in cheese production.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
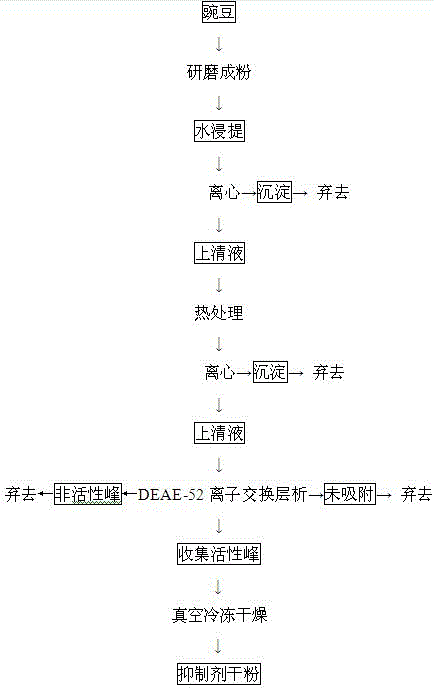
Preparation method for pea aspartic acid protease inhibitor
InactiveCN102408481BEliminate pollutionAvoid wastingPeptide preparation methodsProtease inhibitorsBiotechnologyFood additive
The invention discloses a preparation method for a pea aspartic acid protease inhibitor, and belongs to the technical field of a plant extraction biological activity product. The method comprises the following steps of: directly grinding pea into powder; leaching with water; performing high-speed centrifugation; thermally treating supernatant; performing high-speed centrifugation again; separating the purified aspartic acid protease inhibitor from the supernatant by a DEAE (Diethylaminoethyl)-52 ion exchange column chromatography; and then freeze-drying under vacuum to obtain the aspartic acid protease inhibitor dry powder. The aspartic acid protease inhibitor prepared by the invention has higher inhibition activity on pepsin and rennin in aspartic acid protease family, is directly extracted from pea, is low in cost and safe in application, and has broad application prospect in the fields of food additives, medicines, agriculture and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Renin Inhibitors
InactiveUS20100168243A1Low costHigh activityBiocideOrganic chemistryAspartic proteinase inhibitorAspartate protease
The present invention is directed to aspartic protease inhibitors. The present invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the disclosed aspartic protease inhibitors. The present invention is further directed to methods of antagonizing one or more aspartic proteases in a subject in need thereof, and methods for treating an aspartic protease mediated disorder in a subject using the disclosed aspartic protease inhibitors.
Owner:VITAE PHARMA INC
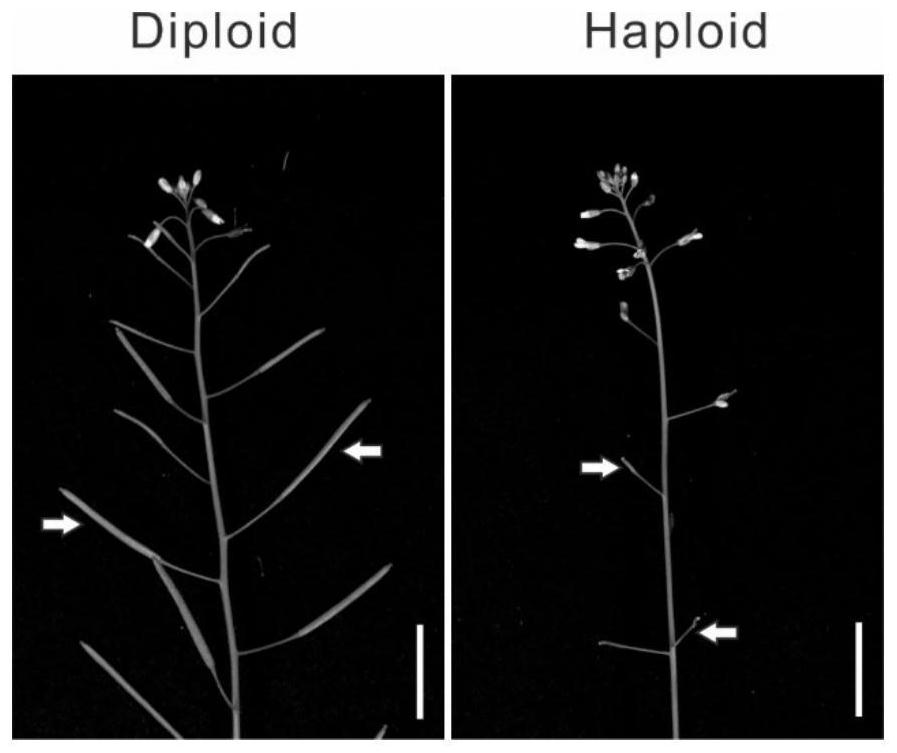
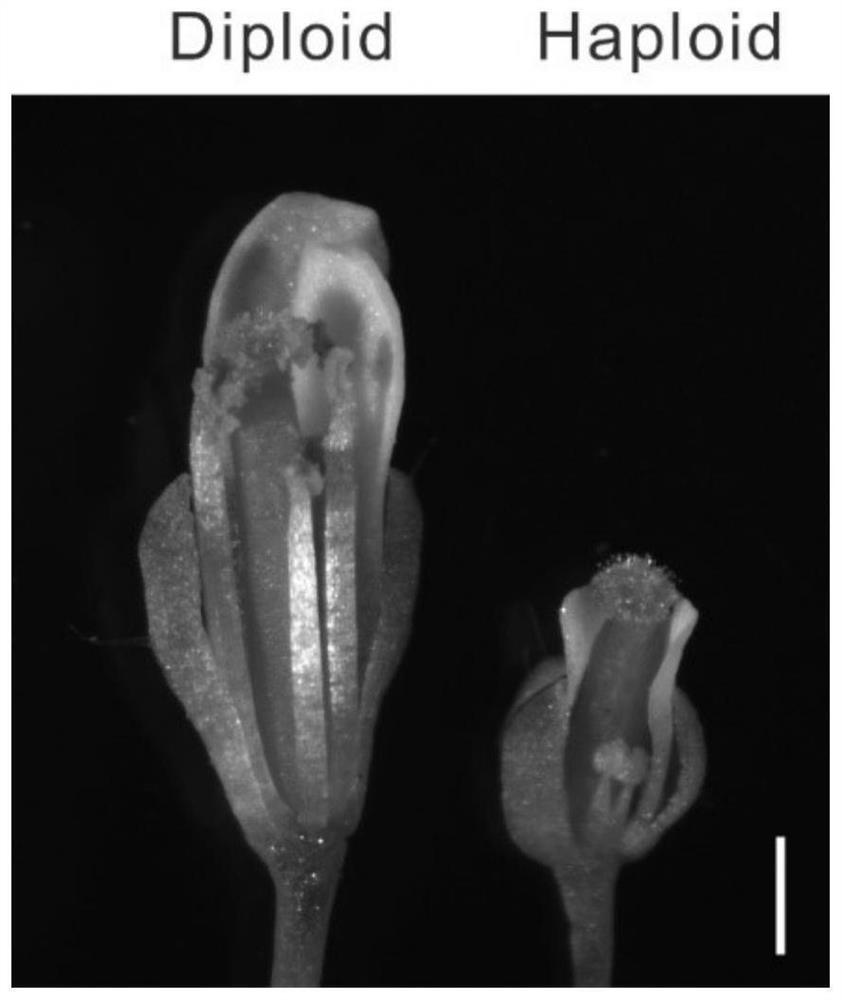
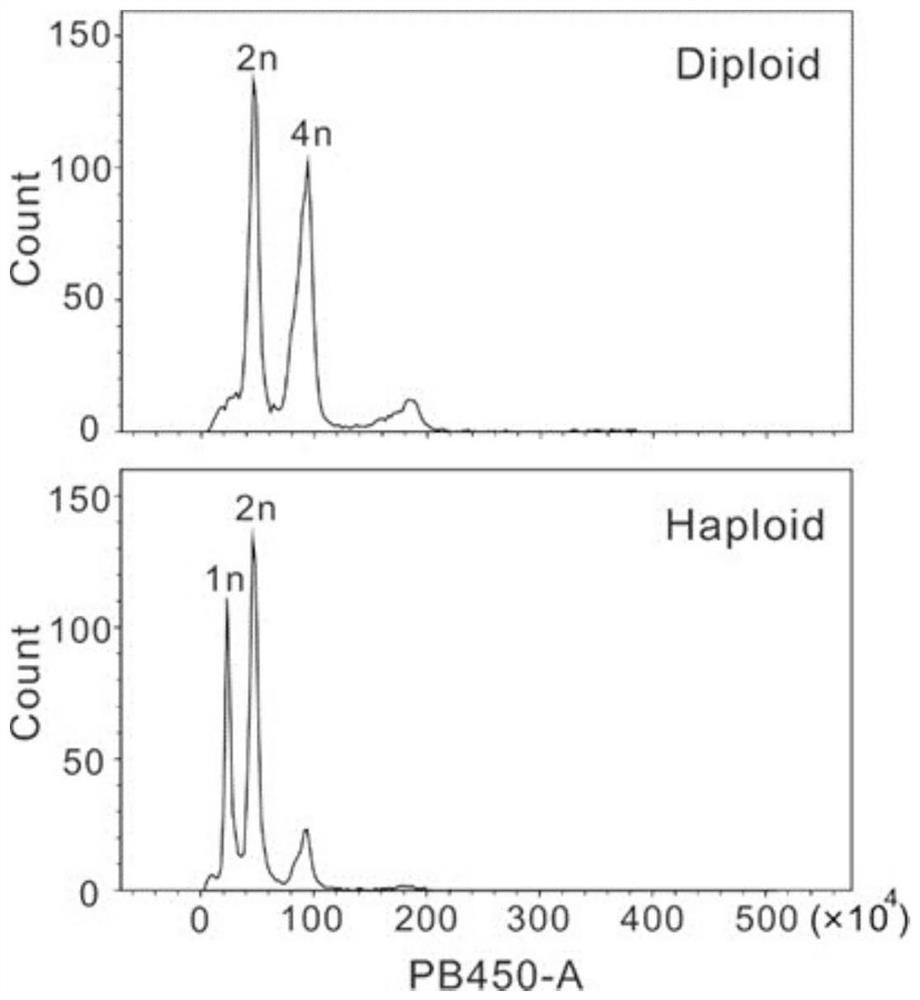
Method for preparing angiosperm haploid from egg cell specific expression gene ECS and application of angiosperm haploid
PendingCN114350701ADoes not affect developmentDoes not affect germinationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyAspartic Acid Proteases
The invention discloses a method for preparing a plant haploid by regulating an egg cell specific expression gene and application of the method in preparation of angiosperm haploid. The aspartic protease ecs1 ecs2 double mutant specifically expressed by the egg cells can be used for producing haplobionts for breeding. The method overcomes the influence of deletion of haploid induced genes expressed by a traditional male parent on pollen and fertility, provides a new thought for the biological action of aspartic protease in the haploid production process, and can improve the breeding efficiency of crop haploids.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Renin Inhibitors
InactiveUS20100144825A1Low costHigh activityUrea derivatives preparationBiocidePharmaceutical drugBiochemistry
The present invention is directed to aspartic protease inhibitors. The present invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the disclosed aspartic protease inhibitors. The present invention is further directed to methods of antagonizing one or more aspartic proteases in a subject in need thereof, and methods for treating an aspartic protease mediated disorder in a subject using the disclosed aspartic protease inhibitors.
Owner:VITAE PHARMA INC
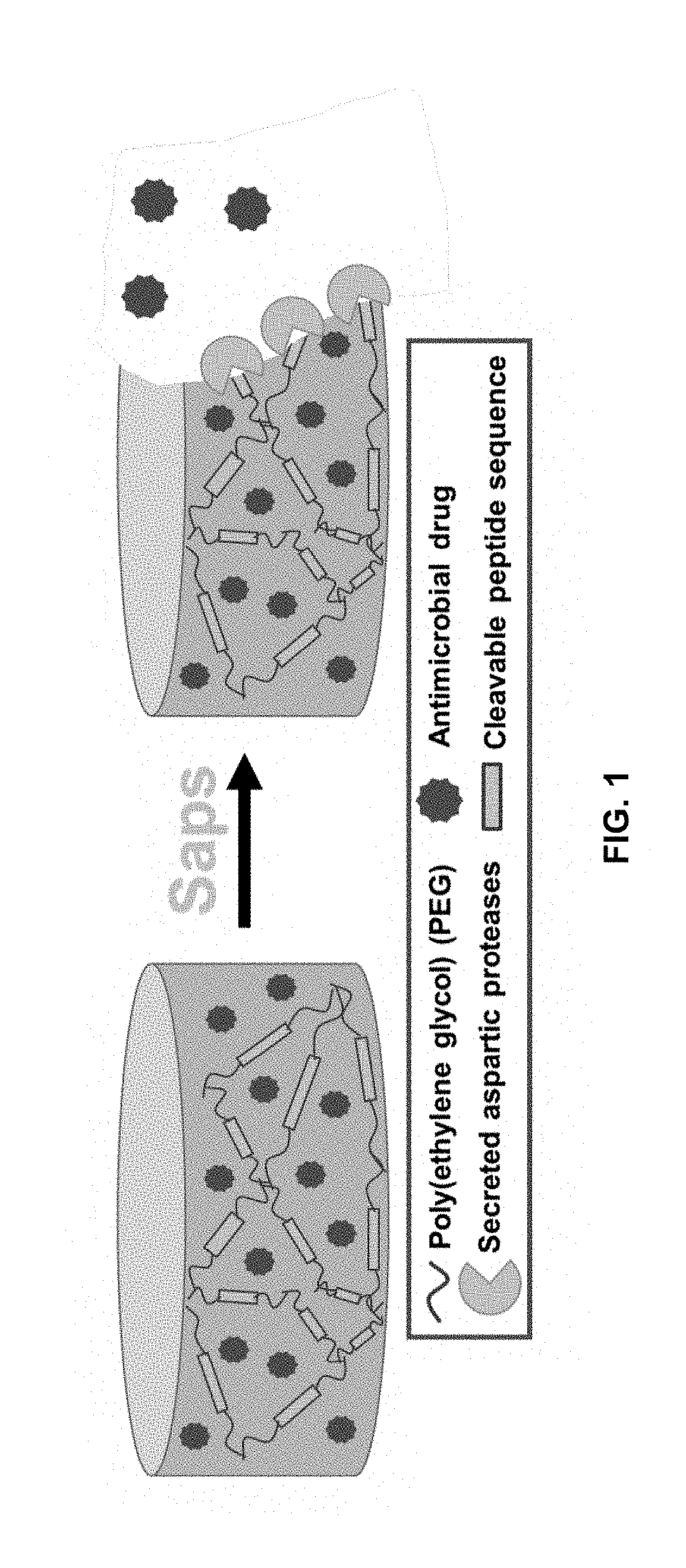
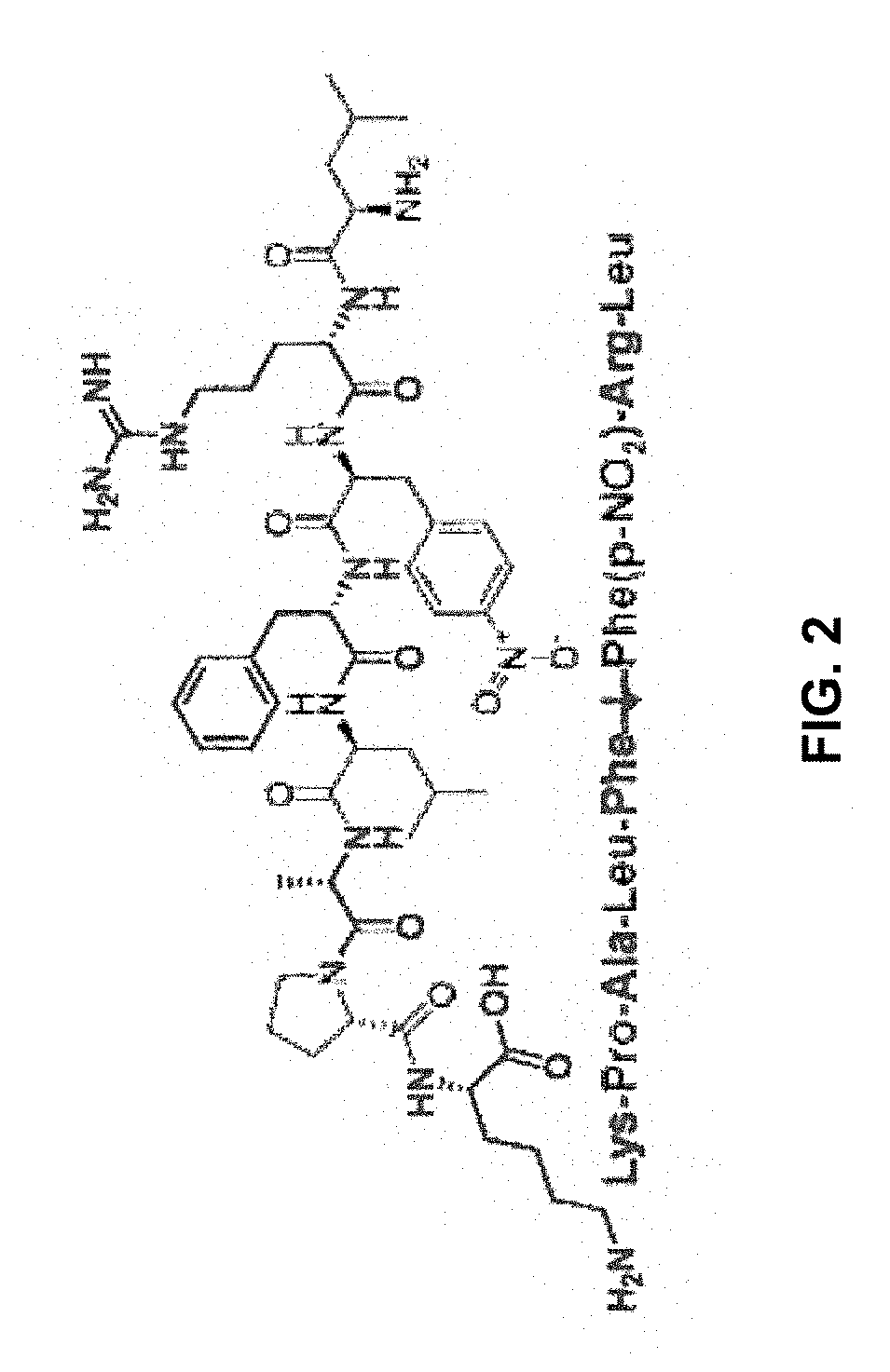
Aspartic protease-triggered antifungal hydrogels
InactiveUS20190151455A1Guaranteed functionEasy to modifyOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAntifungal drugMicrobiology
The present invention relates generally to antifungal hydrogels to locally deliver antifungal drugs. Specifically, the present invention provides aspartic protease-triggered antifungal hydrogels to locally deliver antifungal drugs that specifically respond to aspartic proteases secreted by virulent, pathogenic Candida.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
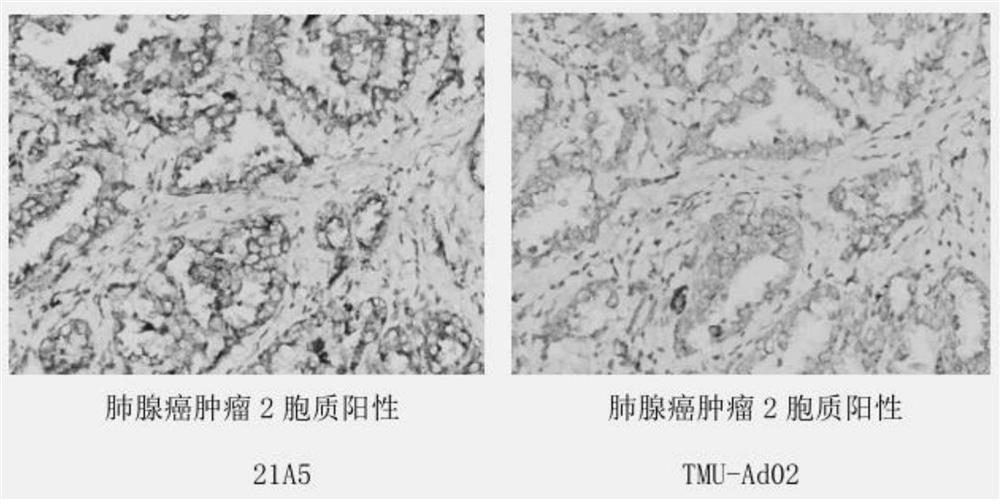
Anti-napsin A protein monoclonal antibody and its cell line, preparation method and application
ActiveCN108467433BStrong characteristicIncreased sensitivityMicroorganism based processesTissue cultureChemical synthesisAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to a new pepsin-like aspartic acid protease (Napsin A) monoclonal antibody, a preparation method of the hybridoma cell line 21A5, and the application of the monoclonal antibody in tumor occurrence and prognosis evaluation. The antigen for preparing the antibody is a preferred antigenic peptide, which is chemically synthesized and coupled with KLH carrier protein as an immunogen to immunize mice. The finally obtained antibody belongs to IgG2b subtype, and the sequence encoding its variable region is cloned by gene way to get. The immunohistochemical detection of the finally obtained antibody on a variety of tumor tissues found that the antibody can well identify the occurrence of tumors and can be used for the immunological diagnosis of these tumors.
Owner:FUZHOU MAIXIN BIOTECH CO LTD
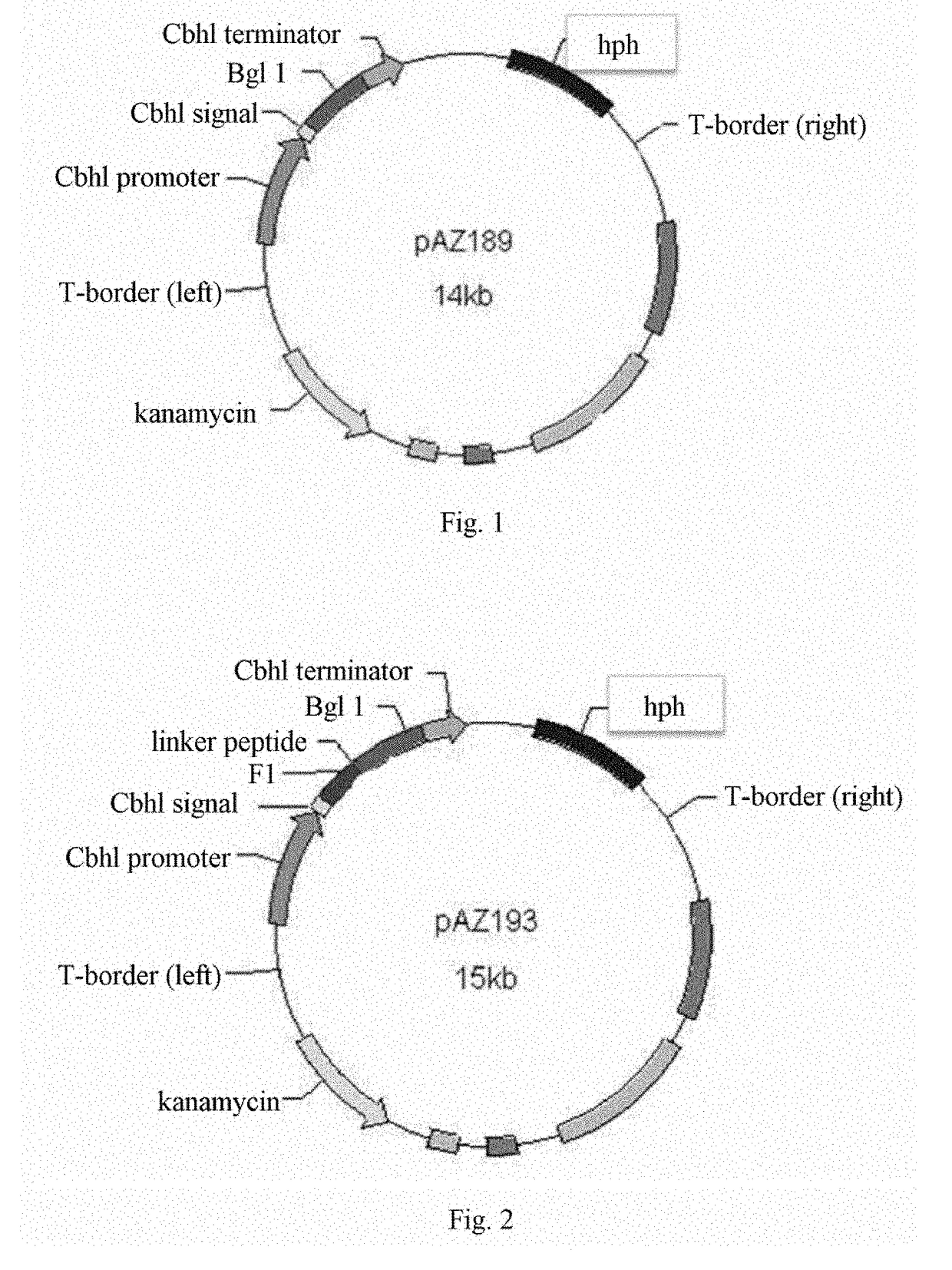
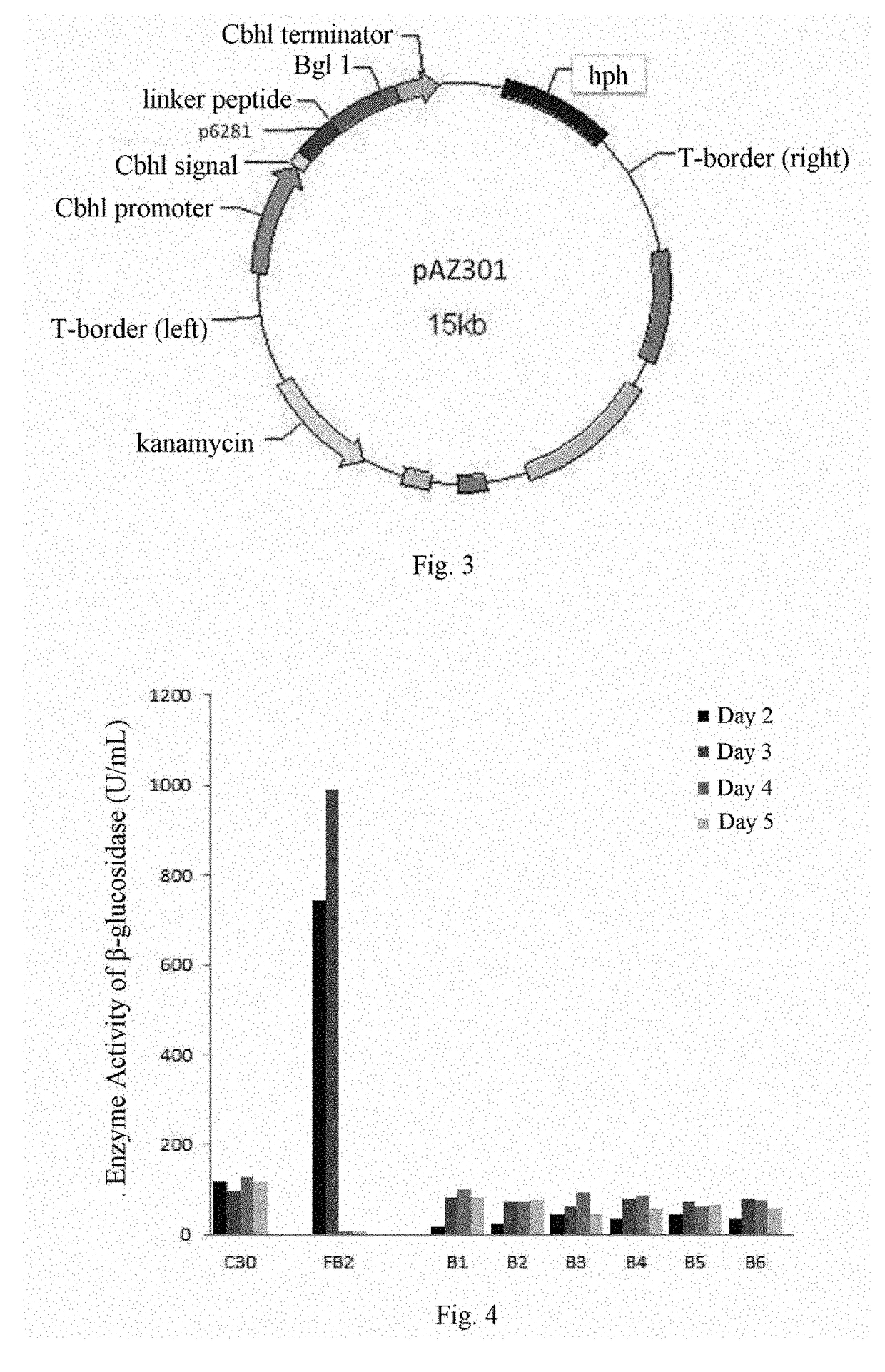
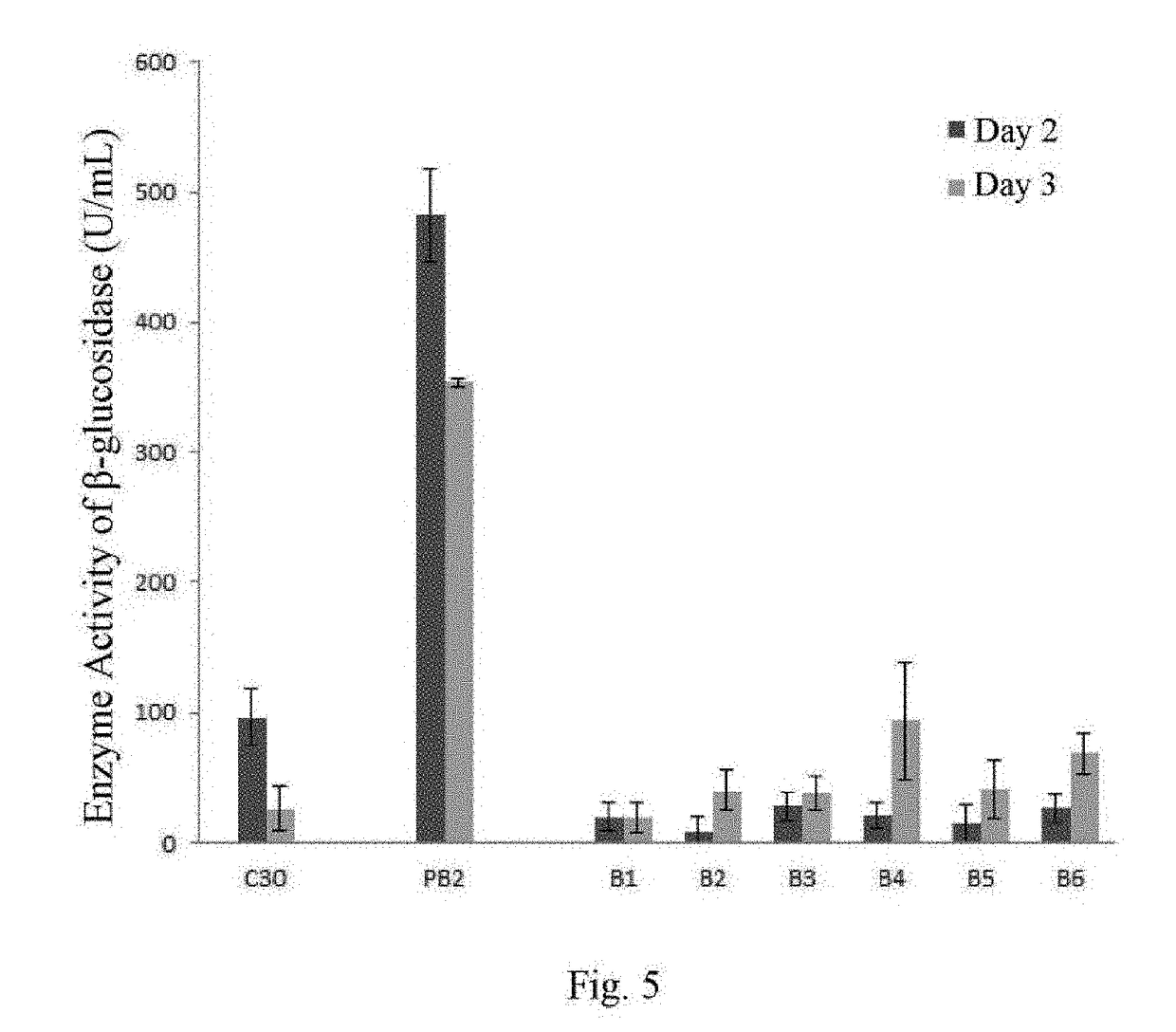
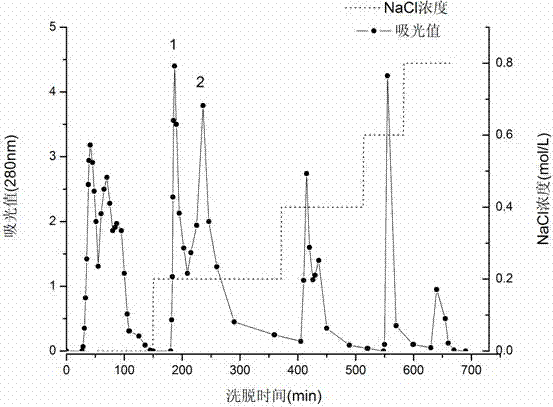
Methods for recombinant expression of beta-glucosidase gene
ActiveUS9969995B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAlgluceraseMicroorganism
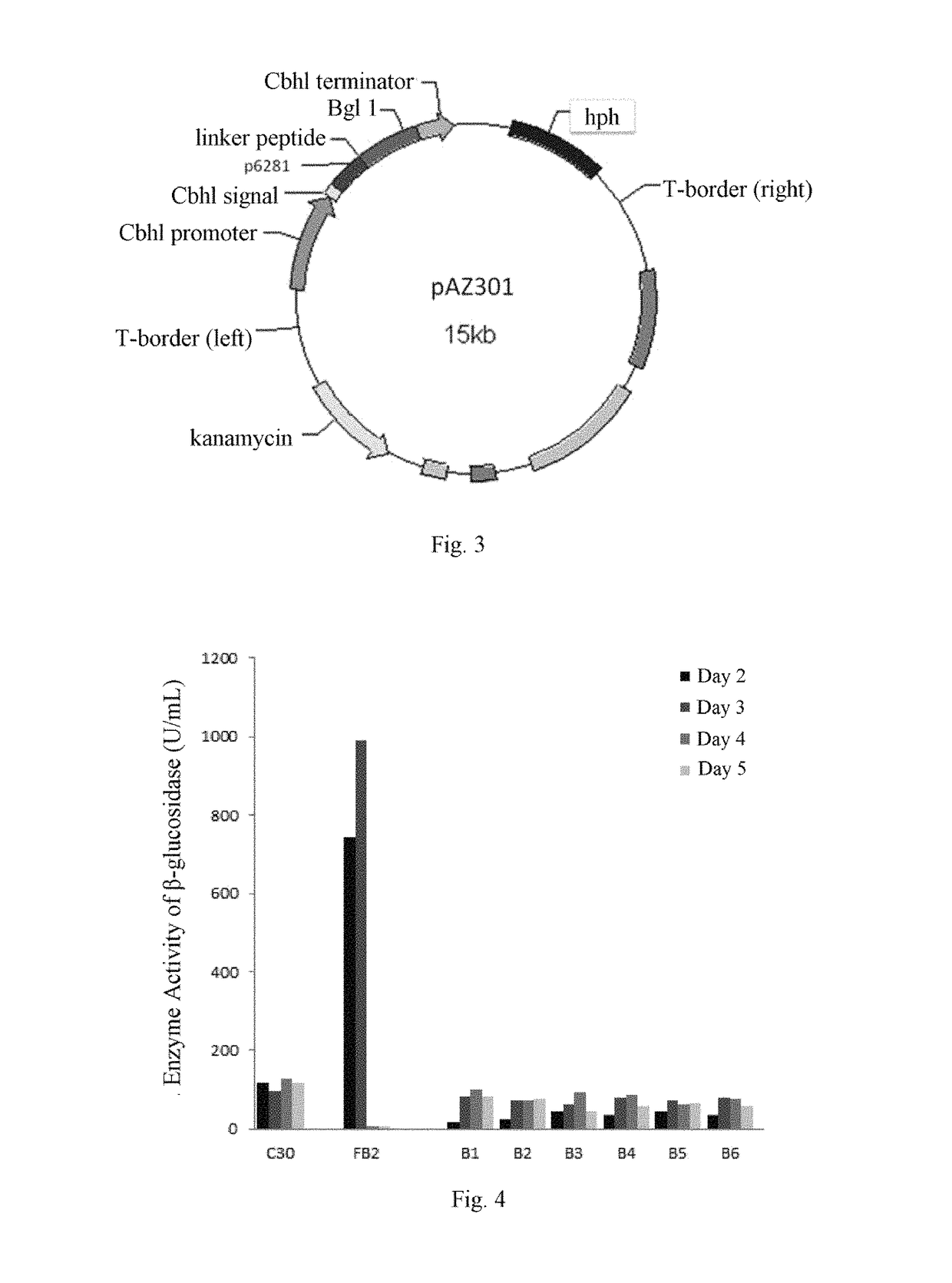
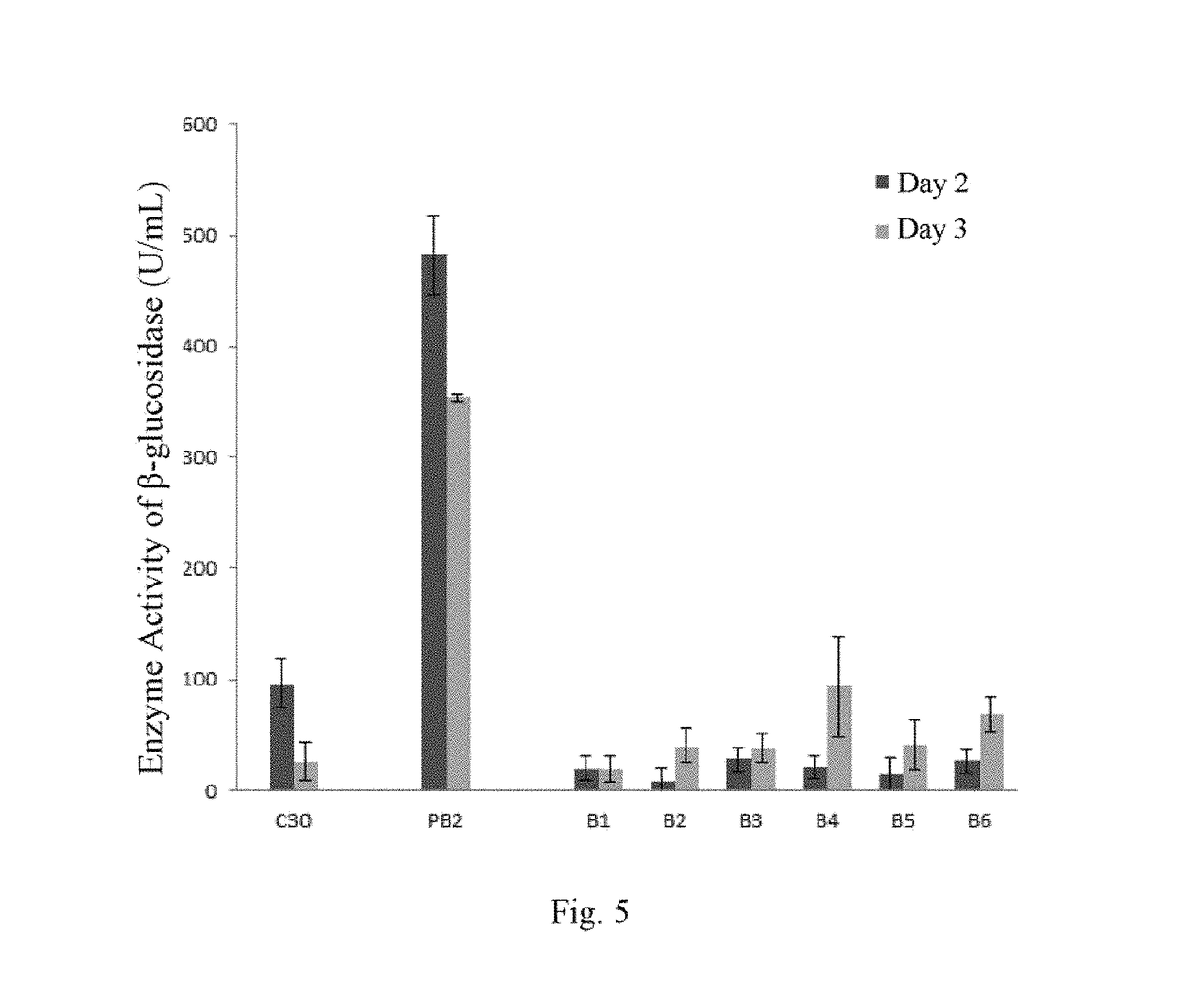
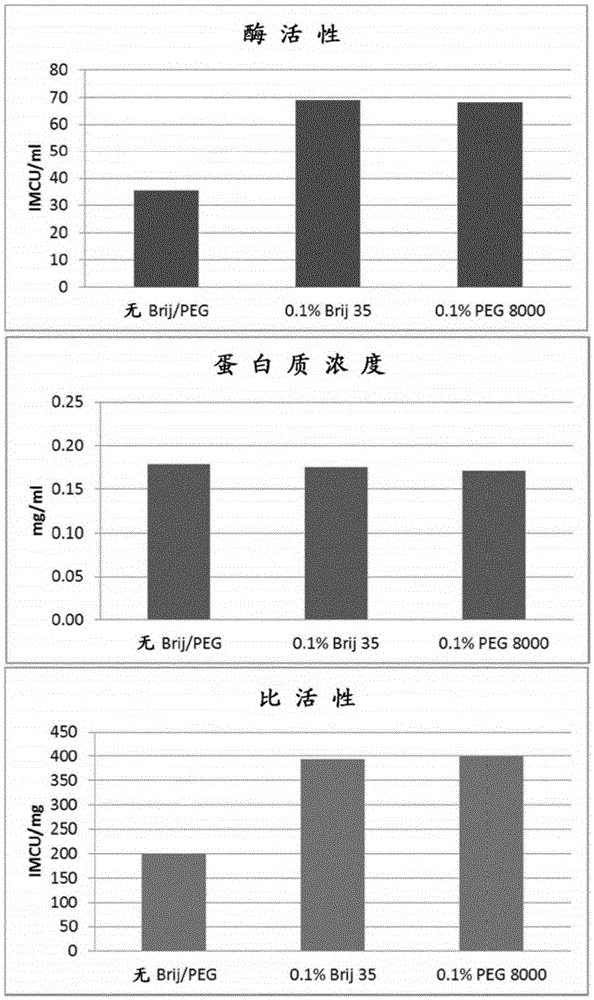
Provided is a method for recombinant expression of β-glucosidase gene. Also provided is a recombinant expression vector comprising: (a) a coding sequence of an aspartic protease or active fragment thereof, (b) a coding sequence of β-glucosidase or active fragment thereof, and optionally (c) a linker sequence between (a) and (b). Further provided are the recombinant host cell and the recombinant cellulose-degrading microorganism comprising the recombinant expression vector, the preparation method and uses thereof.
Owner:WILMAR SHANGHAI BIOTECH RES & DEV CENT
Aspartic protease-triggered antifungal hydrogels
PendingUS20220265833A1Guaranteed functionEasy to modifyOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAntifungal drugMicrobiology
The present invention relates generally to antifungal hydrogels to locally deliver antifungal drugs. Specifically, the present invention provides aspartic protease-triggered antifungal hydrogels to locally deliver antifungal drugs that specifically respond to aspartic proteases secreted by virulent, pathogenic Candida.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Methods for recombinant expression of beta-glucosidase gene
ActiveUS20170327807A1Increase productionShorten the overall cyclePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAlgluceraseMicroorganism
Provided is a method for recombinant expression of β-glucosidase gene. Also provided is a recombinant expression vector comprising: (a) a coding sequence of an aspartic protease or active fragment thereof, (b) a coding sequence of β-glucosidase or active fragment thereof, and optionally (c) a linker sequence between (a) and (b). Further provided are the recombinant host cell and the recombinant cellulose-degrading microorganism comprising the recombinant expression vector, the preparation method and uses thereof.
Owner:WILMAR SHANGHAI BIOTECH RES & DEV CENT
Preparation method for pea aspartic acid protease inhibitor
InactiveCN102408481AEliminate pollutionAvoid wastingPeptide preparation methodsProtease inhibitorsBiotechnologyFood additive
The invention discloses a preparation method for a pea aspartic acid protease inhibitor, and belongs to the technical field of a plant extraction biological activity product. The method comprises the following steps of: directly grinding pea into powder; leaching with water; performing high-speed centrifugation; thermally treating supernatant; performing high-speed centrifugation again; separating the purified aspartic acid protease inhibitor from the supernatant by a DEAE (Diethylaminoethyl)-52 ion exchange column chromatography; and then freeze-drying under vacuum to obtain the aspartic acid protease inhibitor dry powder. The aspartic acid protease inhibitor prepared by the invention has higher inhibition activity on pepsin and rennin in aspartic acid protease family, is directly extracted from pea, is low in cost and safe in application, and has broad application prospect in the fields of food additives, medicines, agriculture and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
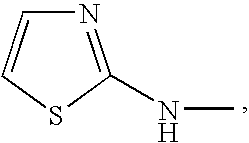
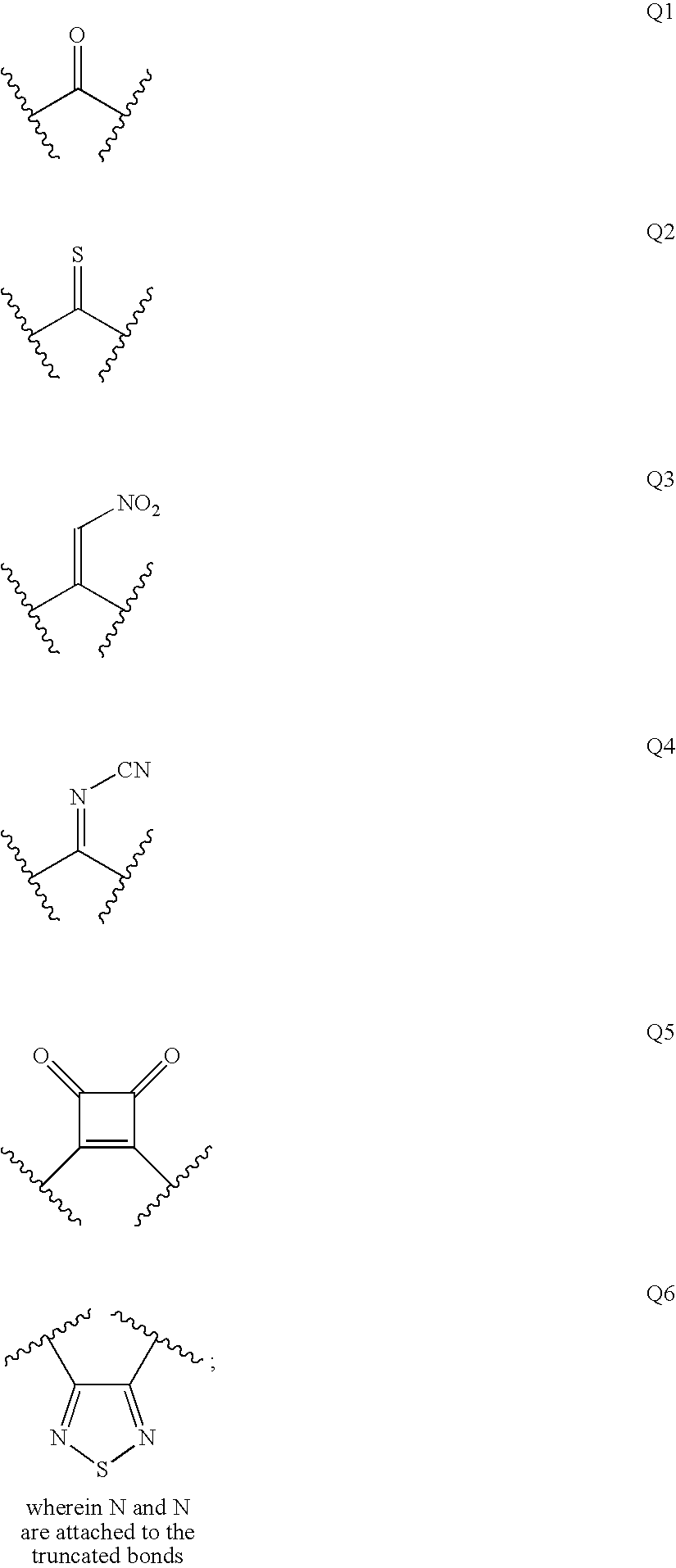
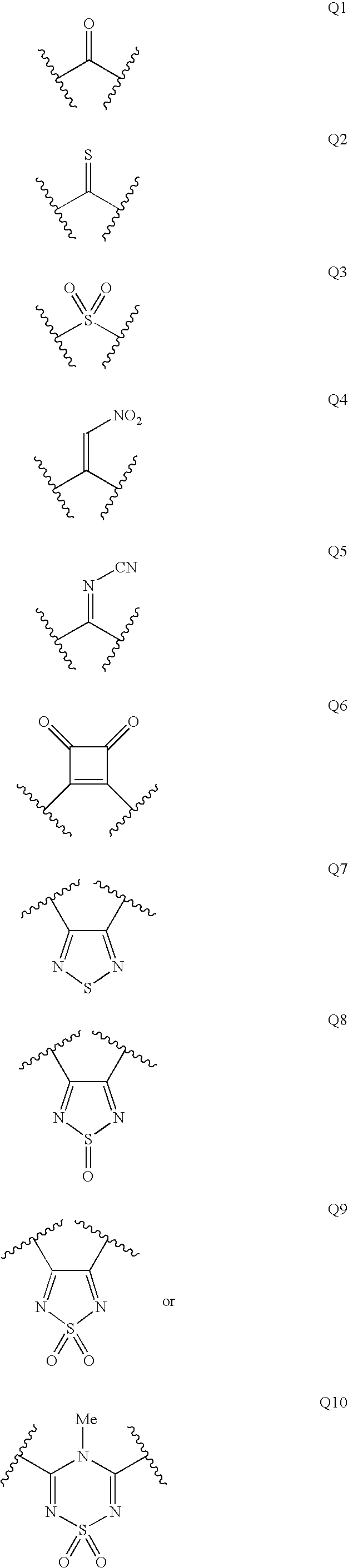
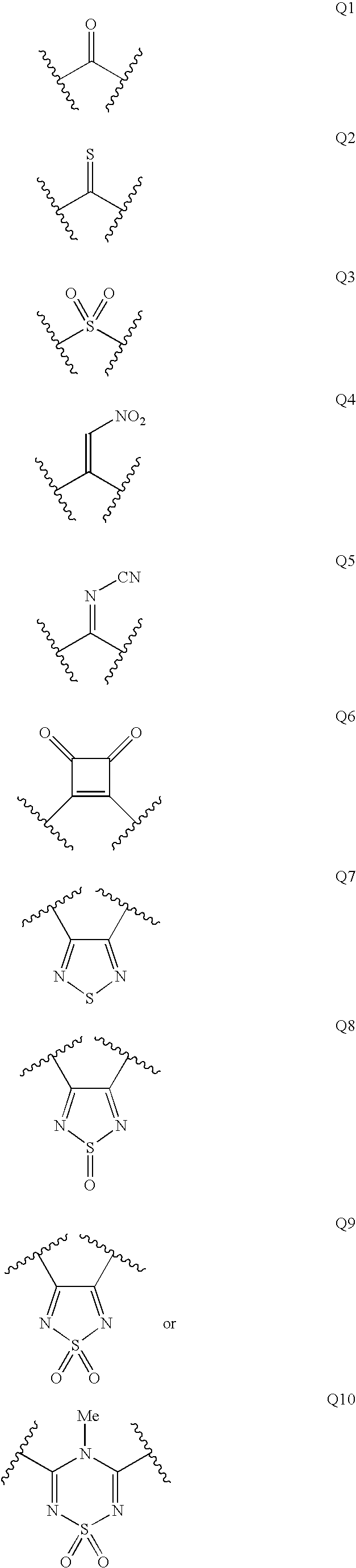
Substituted thiazolone secreted aspartic acid protease inhibitor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104961707BCombination of antifungal drugs works wellOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAntifungalThiazole
The invention relates to a substituted thiazole ketones secretory aspartic protease inhibitor and a preparation method thereof, and particularly provides a novel thiazole ketones compound. The general structural formula of the novel thiazole ketones compound is shown as follows. The thiazole ketones compound is high in Sap2 enzyme inhibiting activity and nematode and mouse in-vivo antifungal activity, and has good antifungal medicine combination effect on fluconazole resistant bacteria, thereby being capable of being used for preparing medicine for preventing fungal infection or being combined with existing antifungal medicine. A new approach is created for deeply studying and developing novel antifungal medicine.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
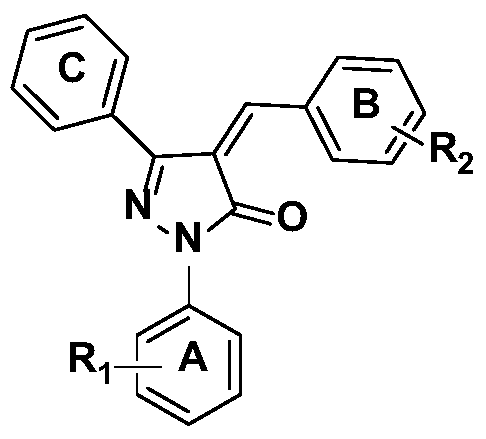
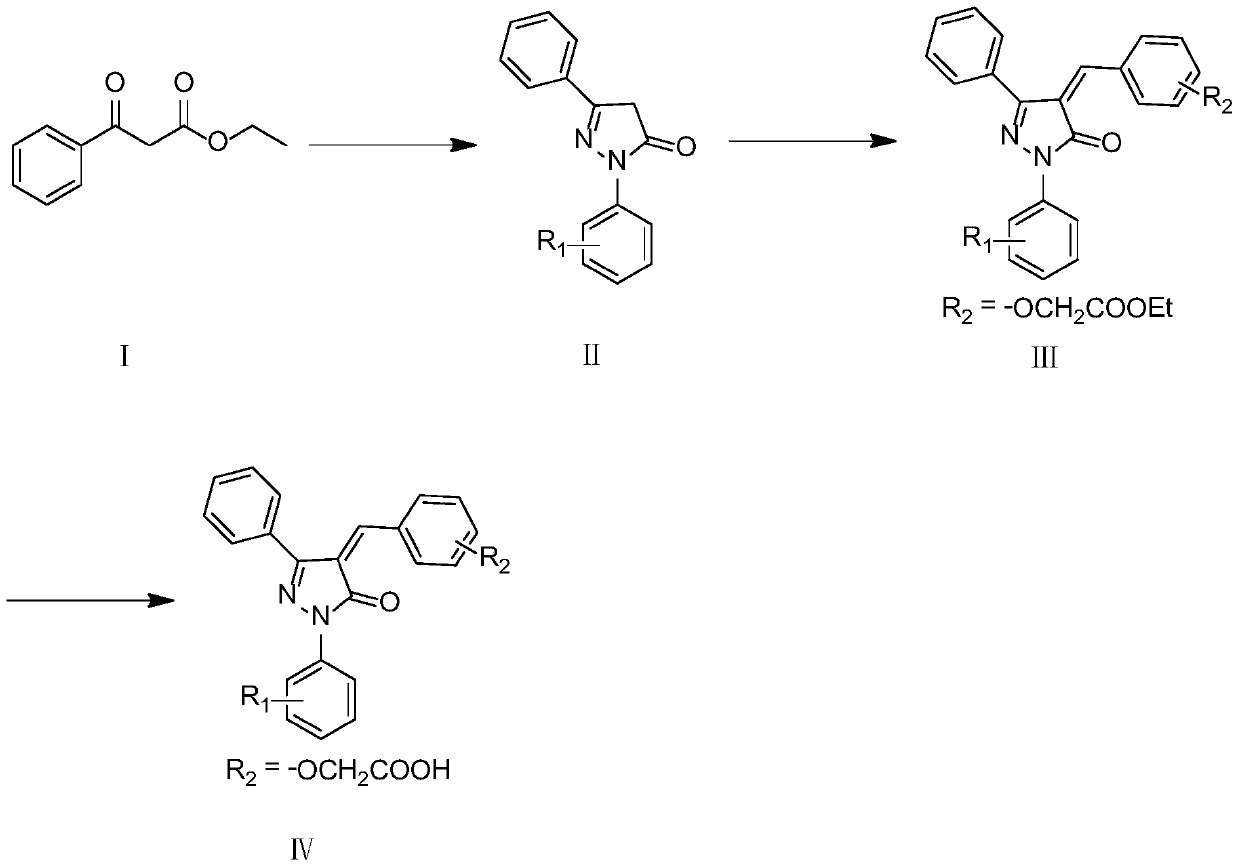
Substituted pyrazolone secreted aspartic acid protease inhibitor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105037269BGood enzyme inhibitory activityAntimycoticsOrganic chemistryAntifungal drugsChemical compound
The present invention relates to a substituted pyrazolone compound, a method for preparing the same, and application thereof in drug production, and belongs to the field of pharmaceutical technologies. The substituted pyrazolone compound is a newly discovered inihbitor of fungi Sap 2, and has certain antifungal activity. The prevent invention provides a substituted pyrazolone compound. The structure of the compound is as shown by the structural formula in the specification. The substituted pyrazolone compound provided by the prevent invention has better anti-cholinesterase activity of Sap 2. Compounds of the class can be used to prepare medicines used to treat fungal infections, which provides a new path to further research and development of new antifungal medicines.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Milk-clotting aspartic protease composition
The present invention relates to a liquid or dry granular milk-clotting aspartic acid protease composition and a method for isolating the target milk-clotting aspartic acid protease.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Preparation method for aspartic protease inhibitor in enzymatic hydrolysis products of soybean protein isolate
The invention provides a preparation method for an aspartic protease inhibitor in enzymatic hydrolysis products of soybean protein isolate, which belongs to the field of separation and purification of biological products. The invention relates to enzymatic hydrolysis of soybean protein isolate with papain for obtainment of a crude product of the aspartic protease inhibitor. The aspartic protease inhibitor is prepared from the crude product by carrying out heat treatment and high speed centrifugation on an enzymatic hydrolysate and carrying out DEAE-52 ion exchange chromatography and separation on an obtained supernatant, and dry powder of the aspartic protease inhibitor is obtained by carrying out vacuum freeze drying on the obtained aspartic protease inhibitor. The aspartic protease inhibitor prepared in the invention has high inhibitory activity on pepsin and chymosin in the family of aspartic protease; the aspartic protease inhibitor extracted from the natural processing material soybean protein isolate which has undergone enzymatic hydrolysis has good specificity, good stability, safety in application and an application prospect in a wide variety of fields, e.g., medicines andhealth care, food additives, control of insect diseases, etc.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A kind of aspartic acid protease and its coding gene and application
ActiveCN105420220BHigh optimum reaction temperatureImprove thermal stabilityFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousAspergillus oryzae
The invention provides aspartic protease and an encoding gene and an application thereof. The aspartic protease is a protein shown as (a) or (b), wherein (a) is constituted by an amino acid residue sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:3, or (b) is obtained by performing substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues on the amino acid residue sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:3, has the functions of the aspartic protease and is derived from (a). Through a gene engineering technology, an aspartic protease gene is amplified from Geomycespannorum, and is transferred into Aspergillus oryzae, thereby realizing successful heterologous expression. The aspartic protease provided by the invention has a relatively high optimal reaction temperature, high thermal stability and a good industrial application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Engineering bacterium for producing recombinant aspartic protease and application of engineering bacterium
ActiveCN113322195AExcellent hydrolysis potentialIncrease the degree of hydrolysisFungiMicroorganism based processesAspergillusEngineered genetic
The invention relates to an engineering bacterium for producing recombinant aspartic protease and application of the engineering bacterium. The engineering bacterium is characterized in that an aspartic protease gene Af293 from fungus Aspergillus fumigatusAf293 is obtained through PCR, the Af293 is constructed on a pPIC9 gamma plasmid to obtain a recombinant plasmid Pic9 gamma-Af293, and the recombinant plasmid Pic9 gamma-Af293 is transformed into pichia pastoris GS115 to obtain the recombinant gene engineering bacterium. The recombinant aspartic protease expressed by the genetically engineered bacterium is stable when the pH value is 4.0-5.0 and the temperature is 45-55 DEG C, and the specific activity is 8408.9 + / -305.6 U / mg. In the application of hydrolyzing silkworm chrysalis protein, the recombinant aspartic protease shows excellent hydrolysis potential, the hydrolysis degree is improved by 50 + / -6.1% and the solubility is improved by 80% after hydrolysis is performed for 6 hours, and the potential capability of the recombinant aspartic protease in industrial application, especially in food and feed industries, is enhanced by the stability characteristic and hydrolysis performance of the recombinant aspartic protease.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
saspase-flg2 complex, modulators and uses thereof
The present invention relates to compounds suitable for modulating the interaction between a first partner protein and a second partner protein, respectively natural Aspartic acid protease SASPase and filaggrin-2 or FLG2 as compounds for the treatment and / or prevention of aesthetic defects of the skin and / or its covering associated with an imbalance in the differentiation and / or proliferation of epidermal cells active agent.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com