Engineering bacterium for producing recombinant aspartic protease and application of engineering bacterium
A technology of aspartic acid and protease, which is applied in application, genetic engineering, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of limited production of aspartic acid protease, low expression, low efficiency, etc., and achieve excellent hydrolysis potential and improved solubility , the effect of increasing the degree of hydrolysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Cloning of Example 1 Aspartic Protease Encoding Gene
[0031] Using Af293 derived from Aspergillus fumigatus Af293 as the female parent, the PCR method was used to amplify the aspartic protease coding gene SEQ ID NO.1, and the cloning method reference (You, et al., 2018).
Embodiment 2
[0032] The preparation of embodiment 2 aspartic acid proteases
[0033] The expression vector pPIC9γ was double-enzymatically digested (EcoR I+Not I), and the gene encoding aspartic acid protease was double-enzymatically digested (EcoR I+Not I), and then the enzyme-digested mature high specific activity xylan The gene fragment of the enzyme mutant is connected with the expression vector pPIC9γ to obtain a recombinant plasmid containing the gene of the high specific activity xylanase mutant and transform it into Pichia pastoris GS115 to obtain a recombinant yeast strain.
[0034] Take the GS115 strain containing the recombinant plasmid, inoculate it into a 1L Erlenmeyer flask with 300mL of BMGY medium, place it at 30°C, and culture it on a shaker at 220rpm for 48h; then centrifuge the culture solution at 3000×g for 5min, discard the supernatant, and use 100mL of sediment containing 0.5 The BMMY medium with % methanol was resuspended, and placed again at 30° C., 220 rpm to induc...
Embodiment 3
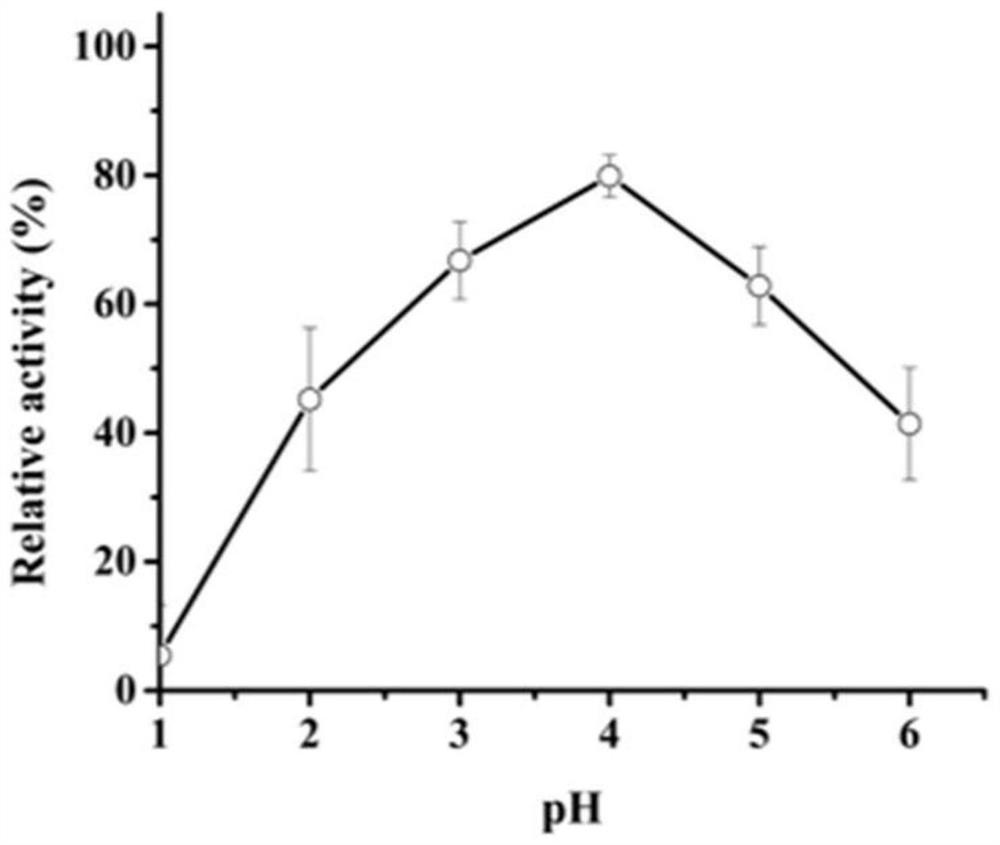
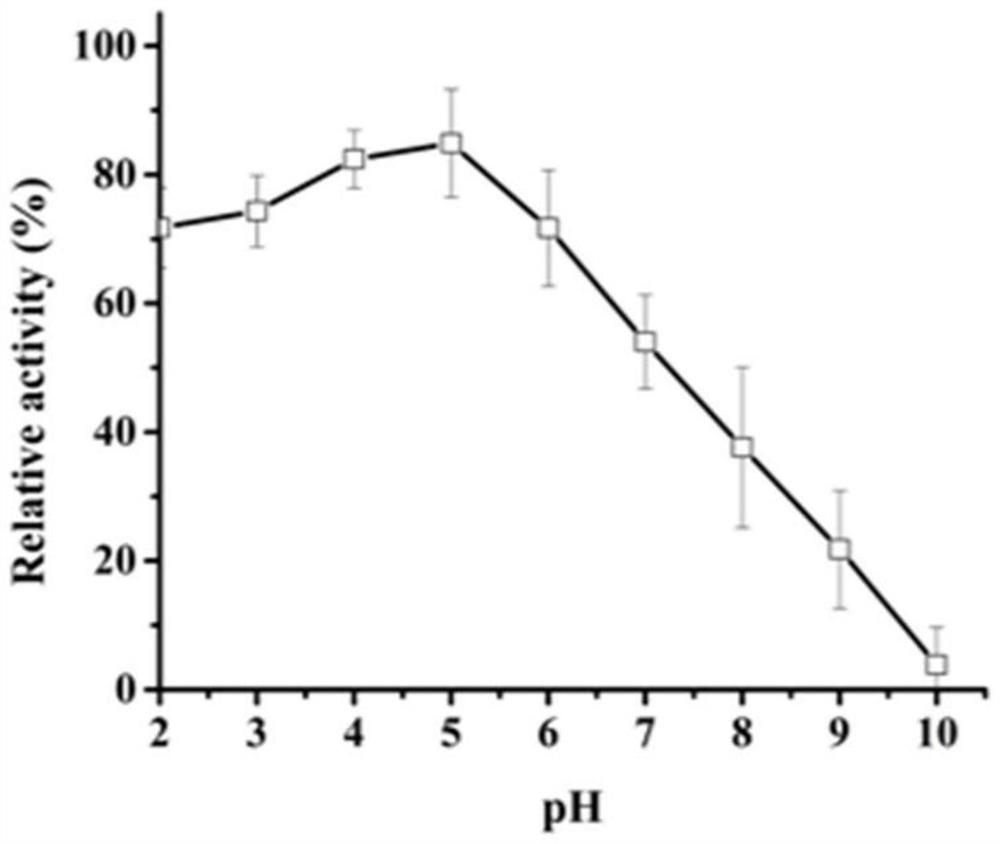
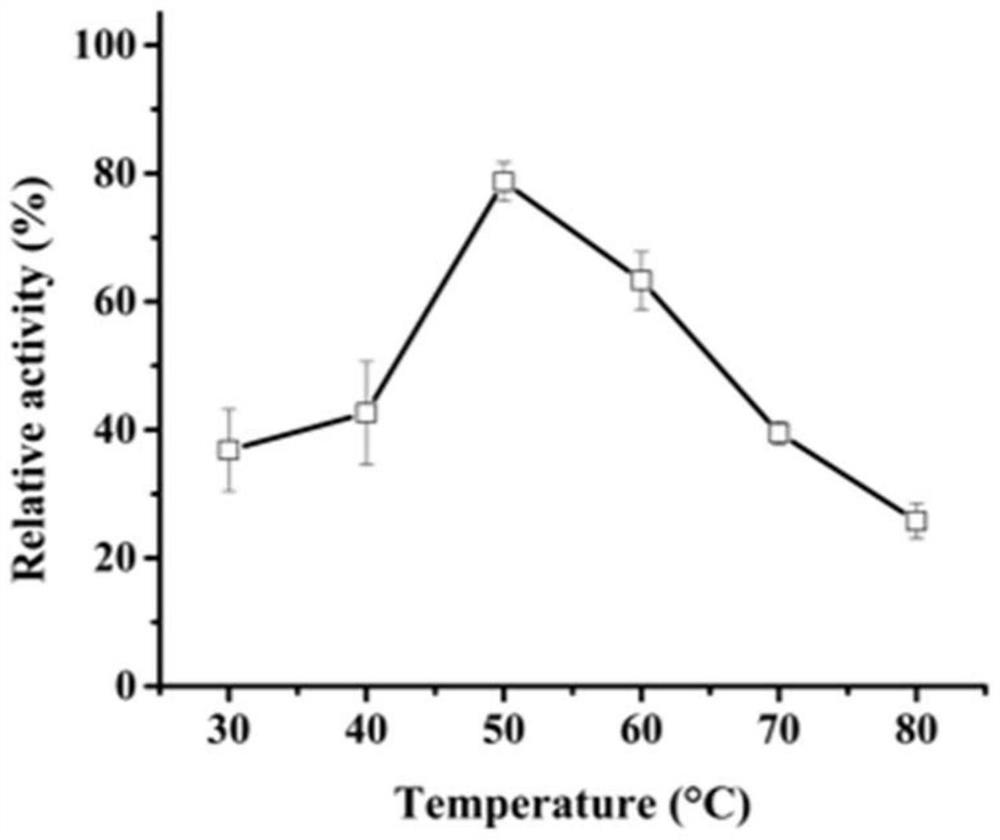
[0035] The activity analysis of embodiment 3 recombinant aspartic acid proteases
[0036] Casein method: the specific method is as follows: use casein as a substrate to measure the protease activity of AF293. Under given pH and temperature conditions, 1 mL of reaction system consisted of 500 μL of 1% casein and 500 μL of enzyme solution, and incubated for 10 minutes. Add 1 mL of 10% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) to stop the reaction, centrifuge at 12,000 × g for 5 min, and then add the supernatant (500 μL) to a solution made of 2.5 mL of 0.4 M Na 2 CO 3 In the composed test tube, Folin and Ciocalteu reagent (500 μL) were added last. The mixture was further incubated at 40 °C for 20 min, and the absorbance was measured at 680 nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| catalytic efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com