Method and apparatus for splicing
a technology of splicing and splicing, applied in the field of digital image data processing, can solve the problems of affecting video quality, affecting the shape of operation complexity, and comparatively expensive, and achieve the effect of less computing capacity and avoiding the introduction of discontinuities in clocks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
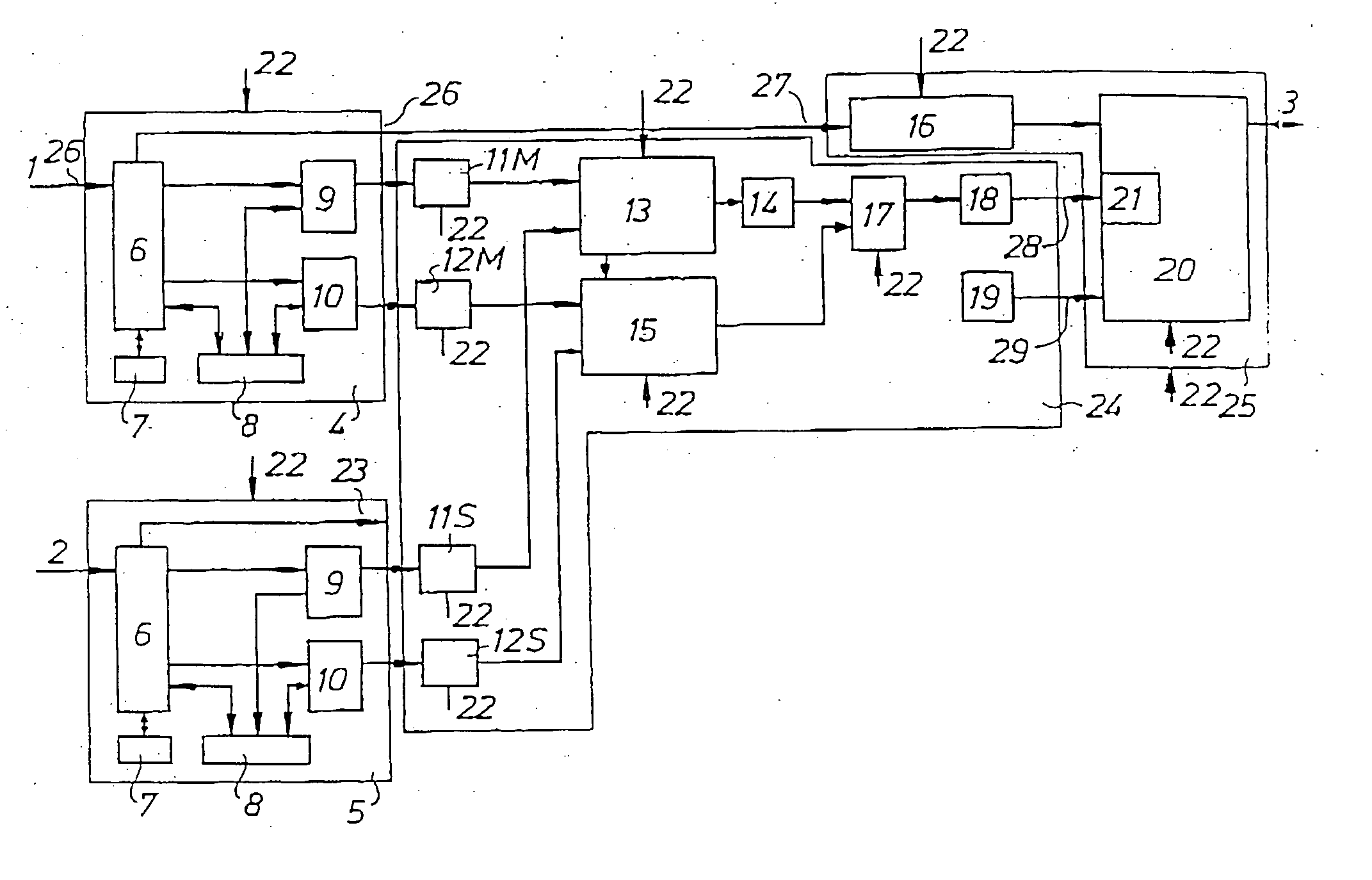
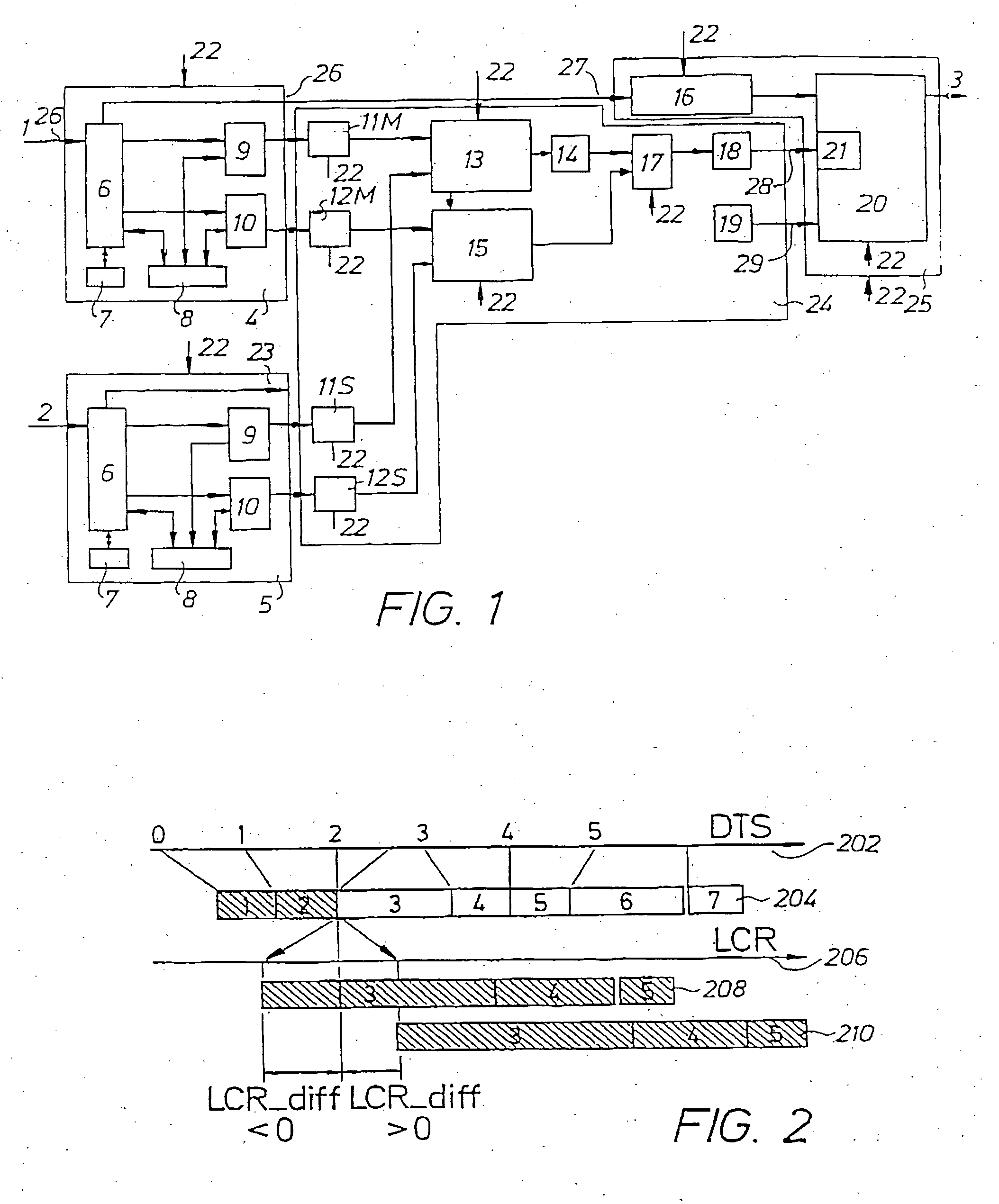
[0042] The splicing method and system according to the invention, hereinafter also called the splicer referring to the method as well as to the apparatus, is intended to be used for seamless splicing of image data streams in the MPEG domain. The splicer receives as an input one or more source MPEG transport streams (TS), and delivers as an output one or more resulting MPEG transport streams.
[0043] In one embodiment of the invention the splicer is applied in a local network station. This local network would typically receive TS:s from different national broadcasters as well as local TS:s. There may also be a selectable input of TS:s from hardware in the network station.
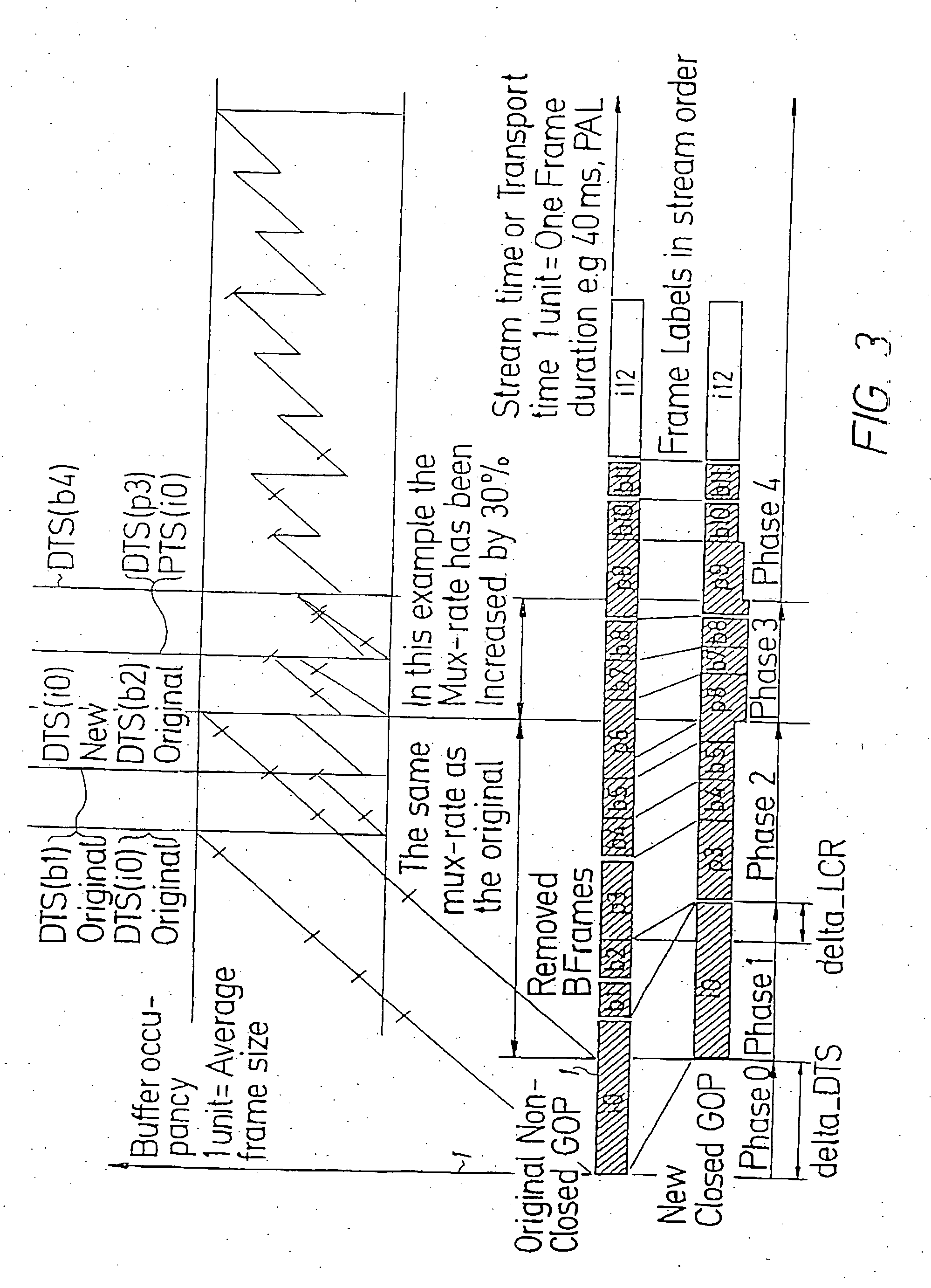
[0044] The problem of splicing concerns the problem of interleaving one stream of data, i.e. video, audio, etc, in an MPEG transport stream (TS) with another stream of the same kind of data in the same TS or in another TS. Isolated bits of data strongly associated to each other constitute a frame. In the video case, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com