Systems and methods for dynamically adjusting a taxonomy used to categorize digital assets
a technology of dynamic adjustment and taxonomies, applied in the field of managing digital assets, can solve the problems of difficult installation and configuration, high cost of tools, and require end-users to change the manner, and achieve the effect of improving productivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
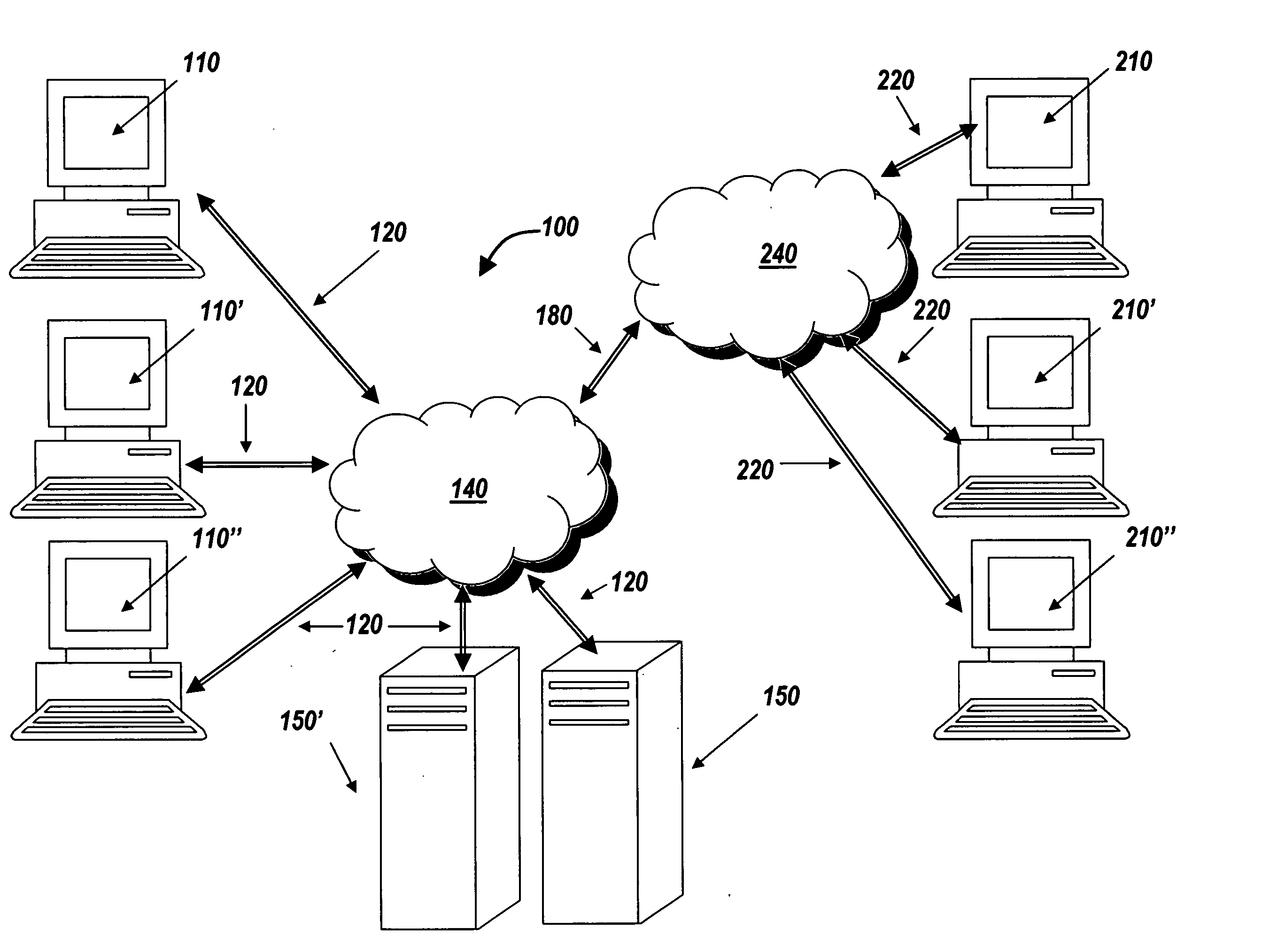
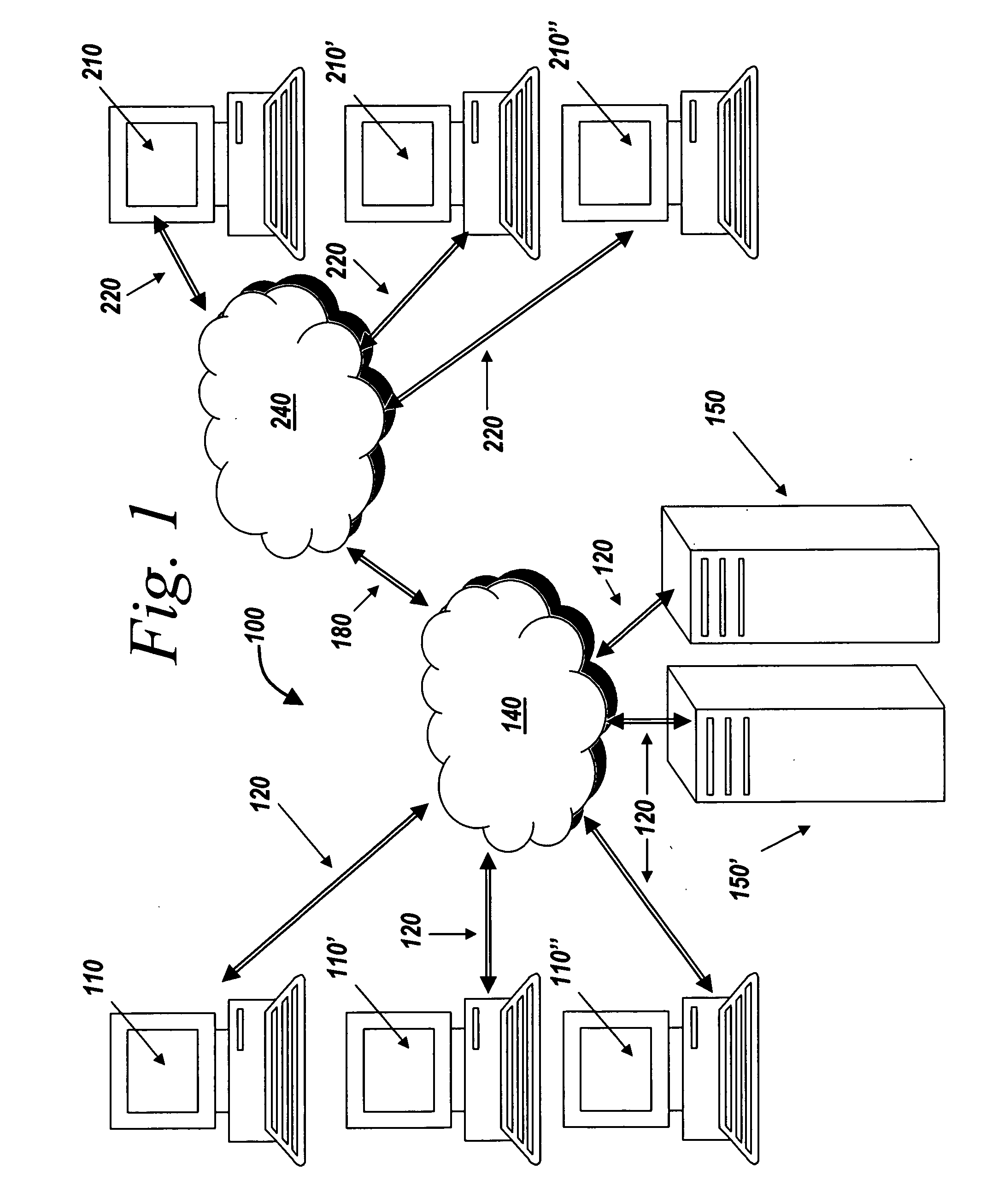
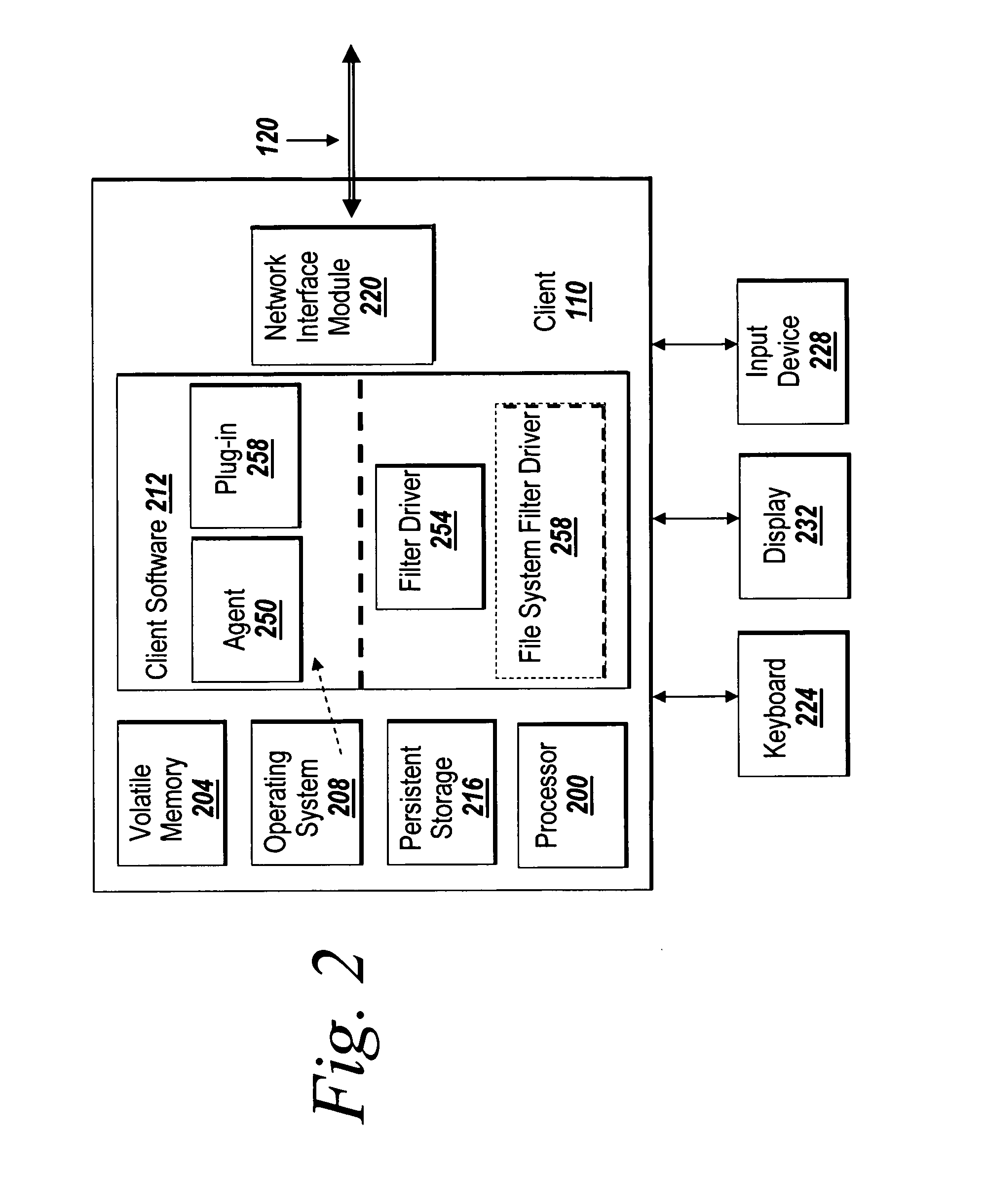
[0035] The present invention provides systems and methods for managing digital assets in a distributed computing environment (DCE). The invention relates generally to the collection, recording and maintenance of meta-data that identifies and categorizes stored digital assets for later location, retrieval and application of business controls. The term meta-data and asset identification tag are used synonymously throughout the specification to refer to the information that is created and used by the present invention to identify and categorize digital assets. Although some of the meta-data created by the present invention corresponds to known meta-data of a file system (e.g., the i-node associated with a file by the Unix operating system or a Master File Table Record used by the WINDOWS operating system, manufactured by Microsoft Corporation of Redmond, Wash.) the meta-data of the present invention supplements and extends the known file system meta-data.
[0036] With reference to FIG. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com