Lymphatic endothelial cells materials and methods
a technology of lymphatic endothelial cells and materials, applied in the field of lymphatic endothelial cell materials and methods, can solve the problems of insufficient methods for obtaining isolated lymphatic endothelial cells, the therapeutic and diagnostic implications of the dysfunction of these interactions remain elusive, and the inability to ascertain the mechanism of action of these important regulators of lymphatic endothelial cell function, etc., to achieve the effect of improving the ability to manipula
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
[0219] The present example provides details of materials and methods employed throughout the application and in the Examples presented herein below.
[0220] Antibodies and growth factors. The primary antibodies used in immunofluorescence were mouse mAbs against human CD31 (Dako), vWF (Dako) or VEGFR-3 (clones 9D9F9, 2E11D11 and 7B3F9; Jussila et at., Cancer Res. 58:1599-1604, 1998), rabbit antiserum against human LYVE-1 (Banerji et al., J. Biol. Chem., 144(4)789-801, 1999), affinity purified rabbit anti-human podoplanin (Breiteneder-Geleff et al., et al., Am. J. Path., 154(2) 385-394, 1999) or rabbit anti-human VEGF-C (882; Joukov et al., EMBO J., 15:290-298, 1996). Monoclonal antibody against proliferating cell nuclear antigen (clone PC10) was from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. FITC- or TRITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG, goat anti-mouse IgG and donkey anti-mouse IgG were obtained from Jackson Immunoresearch. The rabbit antiserum against human VEGFR-2 was a kind...
example 2
Human Dermal Microvascular Endothelial Cells Consist of Distinct Populations of Blood Vascular and Lymphatic Endothelial Cells
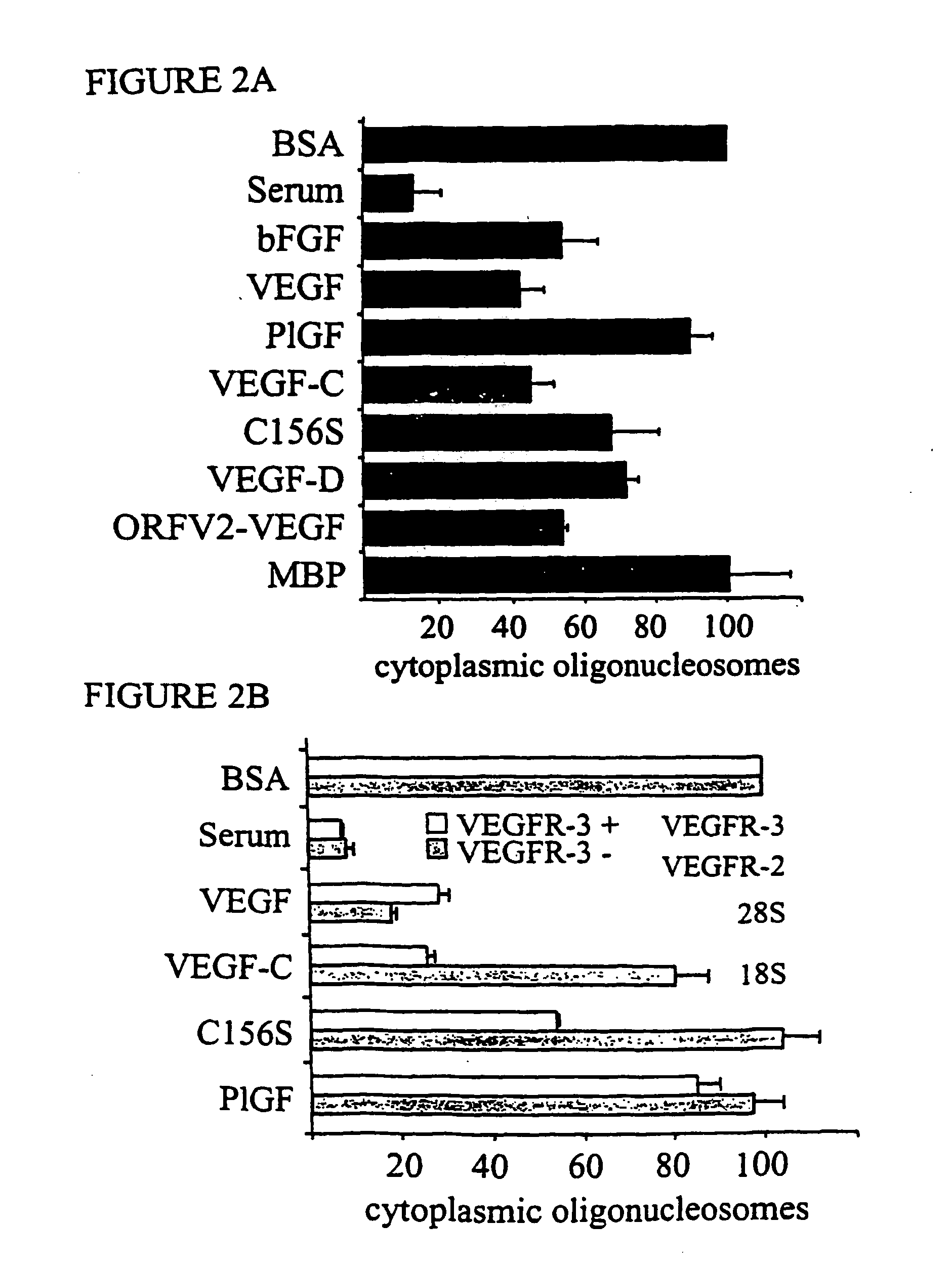
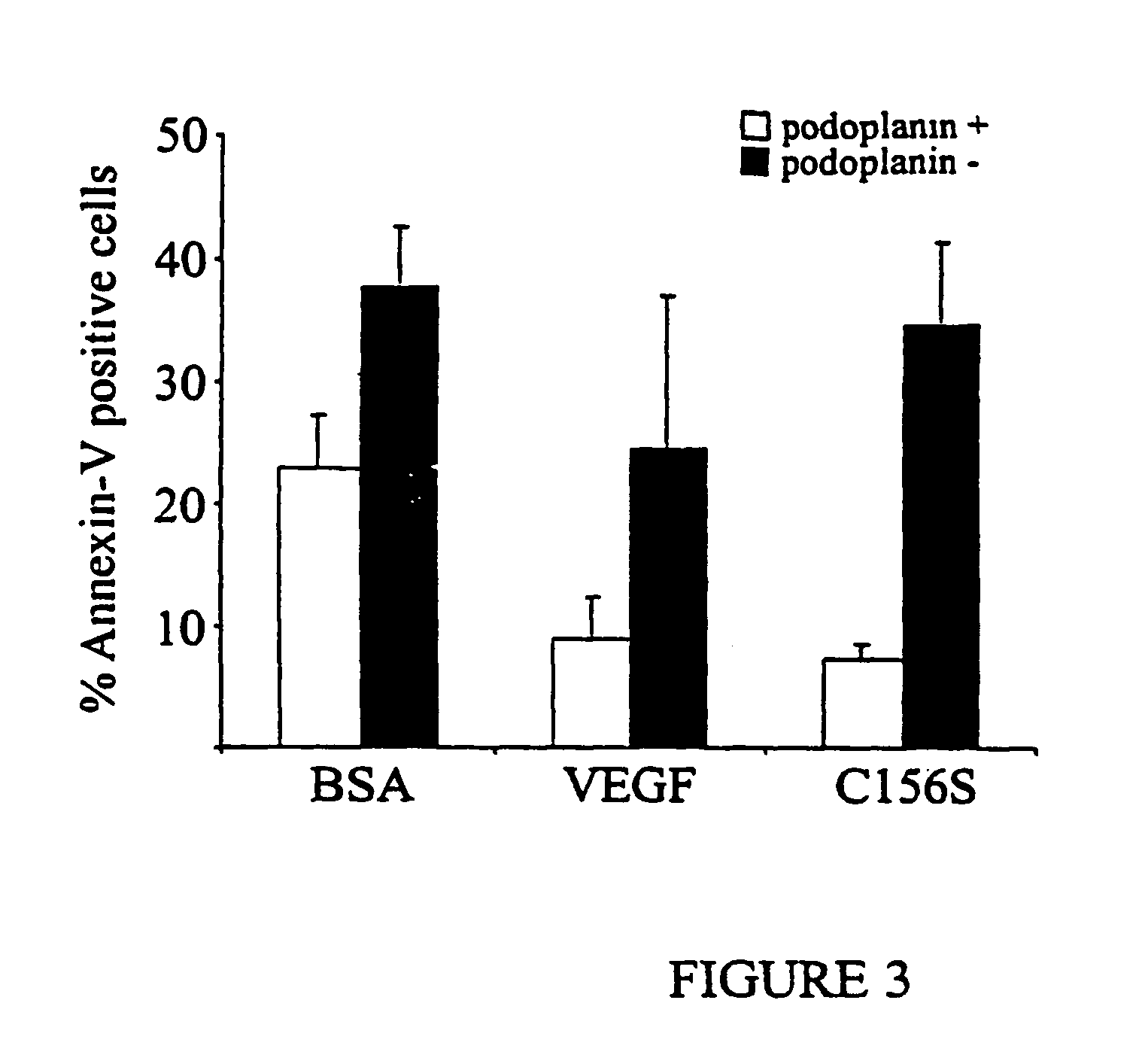
[0229] The functions of different VEGF receptors have been extensively studied in transfected cell lines, but the lack of an appropriate cellular background can compromise results obtained from such studies. Therefore, the inventors set out to separate microvascular endothelial cells into specific constituent populations of endothelial cells of one type which were substantially free of other types of endothelial cells. More particularly, the inventors generated populations of lymphatic endothelial cells that were substantially free of blood vascular endothelial cells and vice versa. In order to pursue this endeavor and to elucidate VEGFR-3 signaling pathways promoting endothelial cell survival, the inventors used primary endothelial cells, human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HMVEC) and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). It was determin...
example 3
Analysis of VEGFR Specific Ligands Used for the Cell Survival Experiments
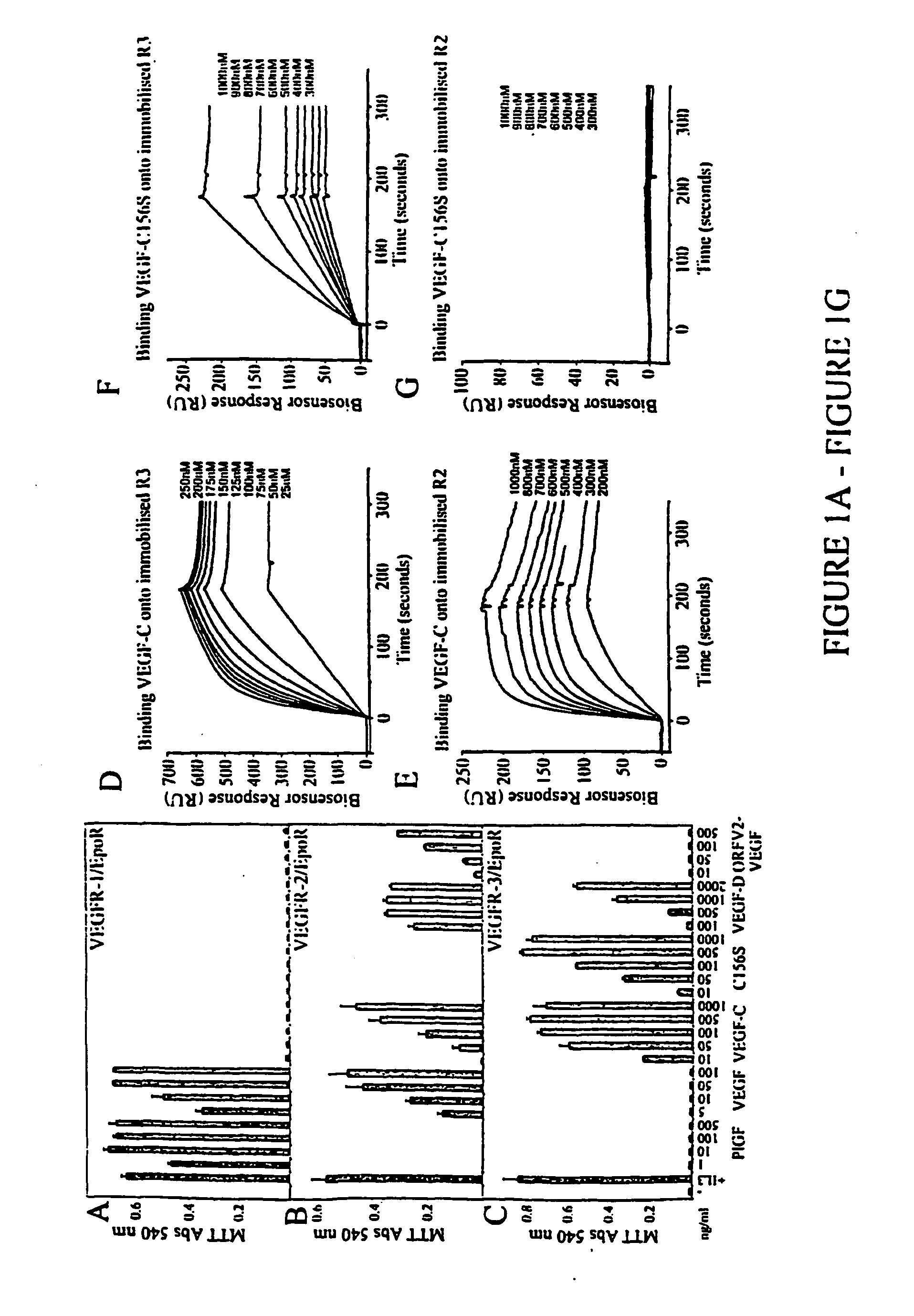
[0233] VEGF is an endothelial cell mitogen which has been also shown to protect endothelial cells from starvation and TNF-a induced apoptosis via activation of VEGFR-2 (Gerber et al., J. Biol Chem., 273:30336-30343, 1998; Spyridopoulos et al., J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol., 29:1321-1330, 1997). The abilities of the different VEGFRs to promote endothelial cell survival were compared by using VEGFR specific VEGFs. The specificities of the growth factors used were determined using a cell survival bioassay. For the bioassay, Ba / F3 pre-B cells were stably transfected with a chimeric receptor containing the extracellular domain of human VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2 or VEGFR-3 fused with the transmebrane and cytoplasmic domains of the mouse erythropoietin receptor.
[0234] As expected, only VEGF and PIGF were able to induce the survival of VEGFR-1 / EpoR cells (FIG. 1A). VEGF, VEGF-C, VEGF-D and orf viral NZ2 (ORFV2-VEGF) were able to sup...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com