Multicomponent fiber comprising a phase change material
a phase change material and multi-component technology, applied in the direction of yarn, fibre chemical features, lap-winding devices, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to secure the phase change material throughout the garment, the bulky pouch is large, and the phase change material is incorporated
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Temperature-Regulating
Fiber Component
[0106] A precursor material highly loaded with a phase change material was prepared according to the following steps. First, a phase change material was prepared in a molten state. Polypropylene was added, and the combination was mixed until the polypropylene was molten. The same was then done with EVA and fumed silica. While the components are described above in a sequential addition, the method is not limited to such a sequence. For example, all components could be added at once and heated to a molten state. Further, the above components could be combined according to a different order than described above.
[0107] Once all components of the precursor material were in a molten state, the mixture was cooled and then ground into a powder. The powdered precursor material comprised 67.3% by weight of the phase change material.
[0108] The powdered precursor material was then combined with an additional amount of fumed silica, followe...
example 2
Preparation of Bicomponent Fiber
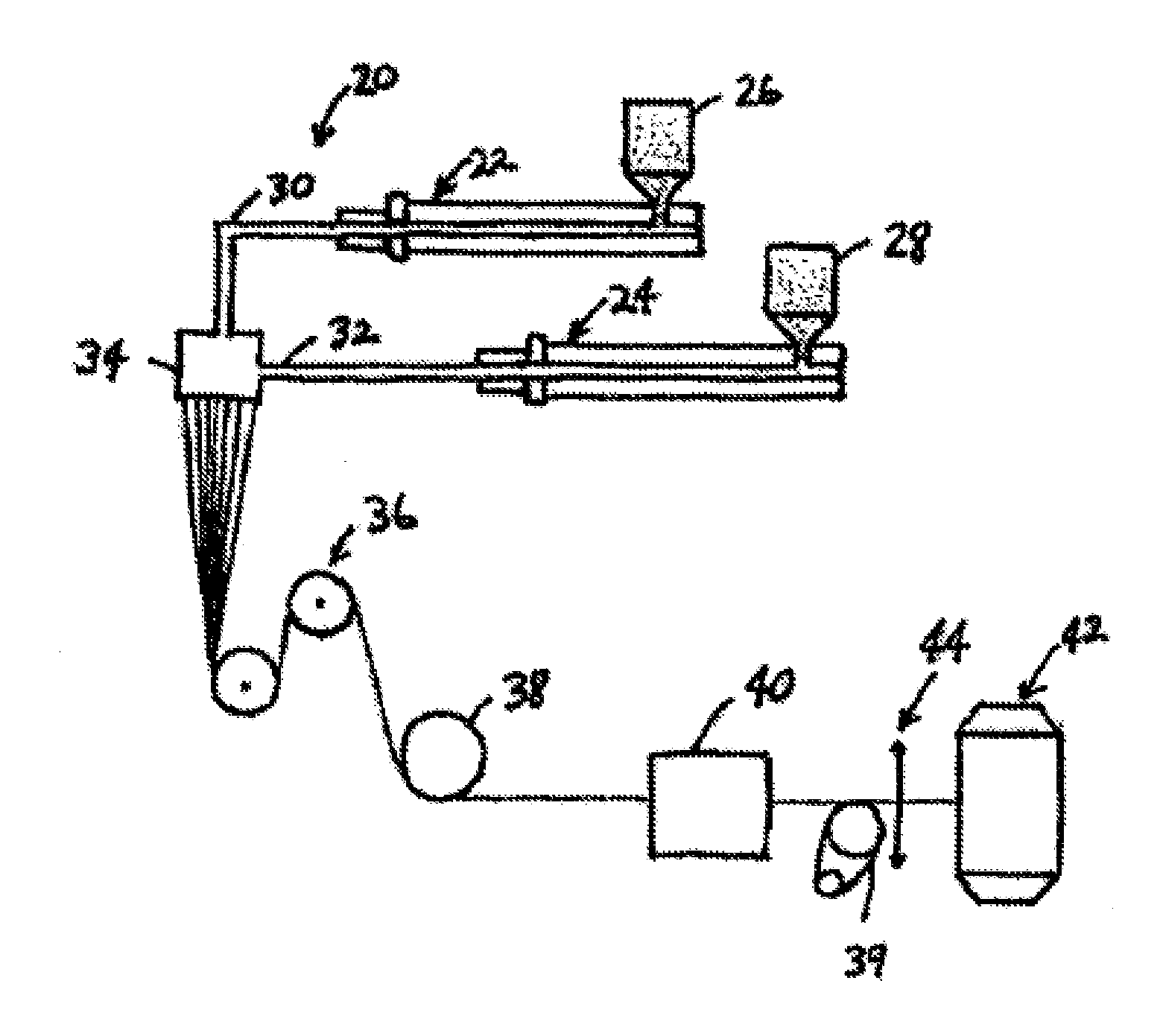
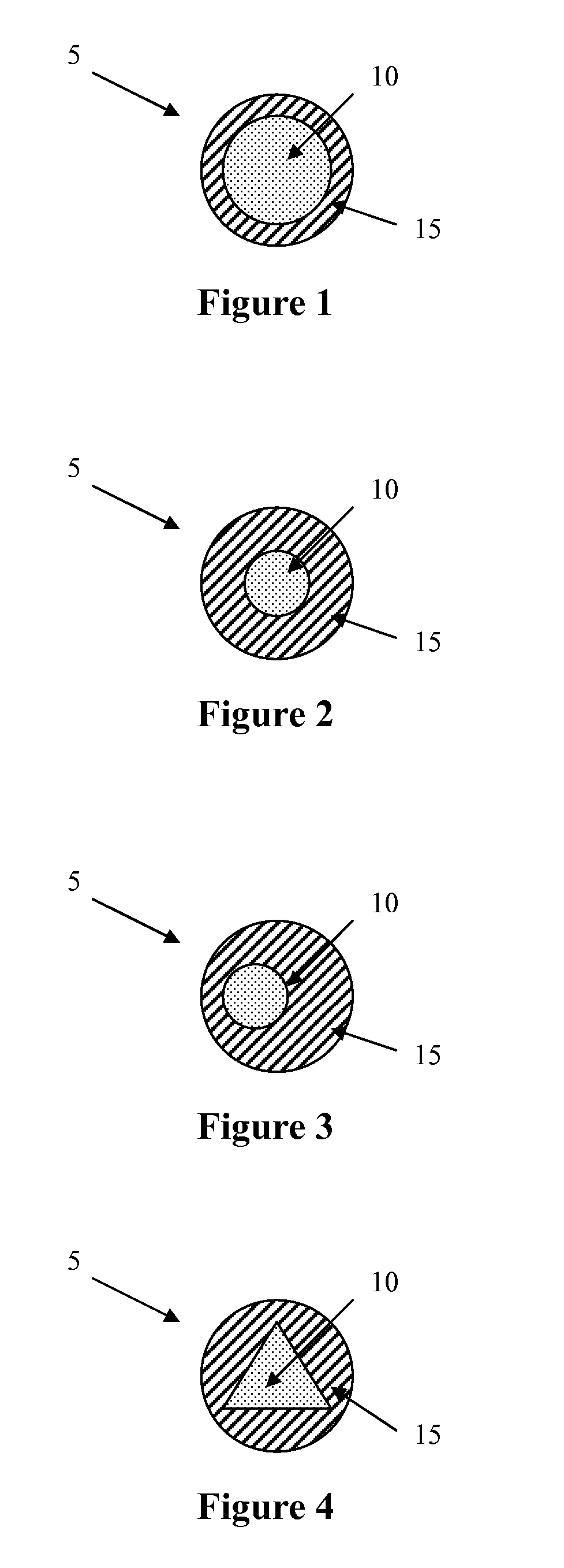
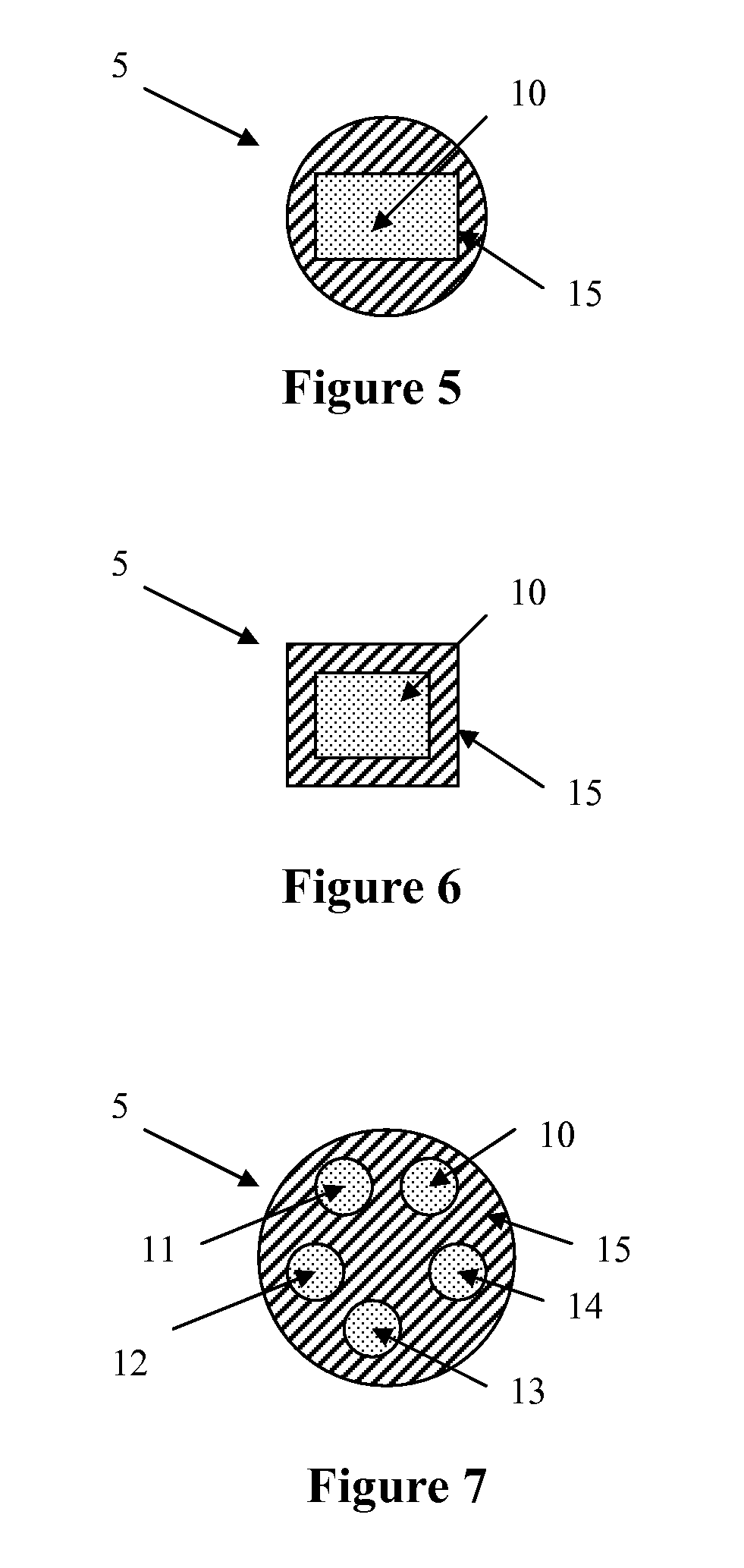
[0109] A bicomponent fiber, in a sheath / core embodiment, was prepared using a temperature-regulating fiber component as described in Example 1 as the inner fiber component (i.e., the core). The outer fiber component comprised polylactic acid (PLA).
[0110] The bicomponent fiber was prepared using a standard extruding apparatus, such as illustrated in FIG. 8, with a granular PLA loaded into one hopper and the granular temperature-regulating component loaded into a second hopper. The bicomponent fiber was extruded at a temperature of 220° C., with the temperature-regulating inner fiber component comprising 75% of the bicomponent fiber's cross-section and the PLA outer fiber component comprising 25% of the bicomponent fiber's cross-section. The bicomponent fibers were spun at a rate of 1,500 meters / minute and subsequently drawn to a linear density of 6 denier per filament.
[0111] The bicomponent fibers can be used in the form of the plain filament descri...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com