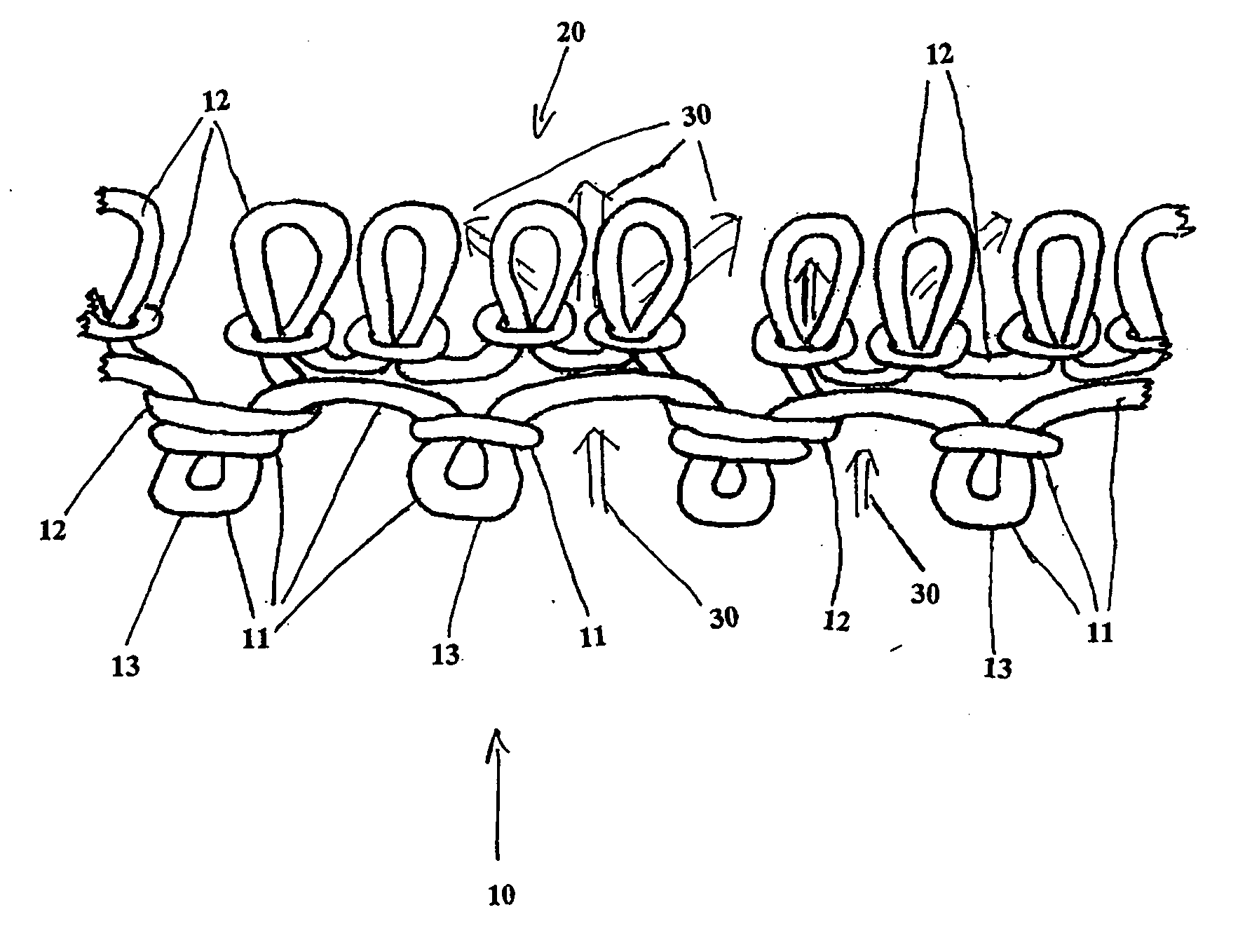
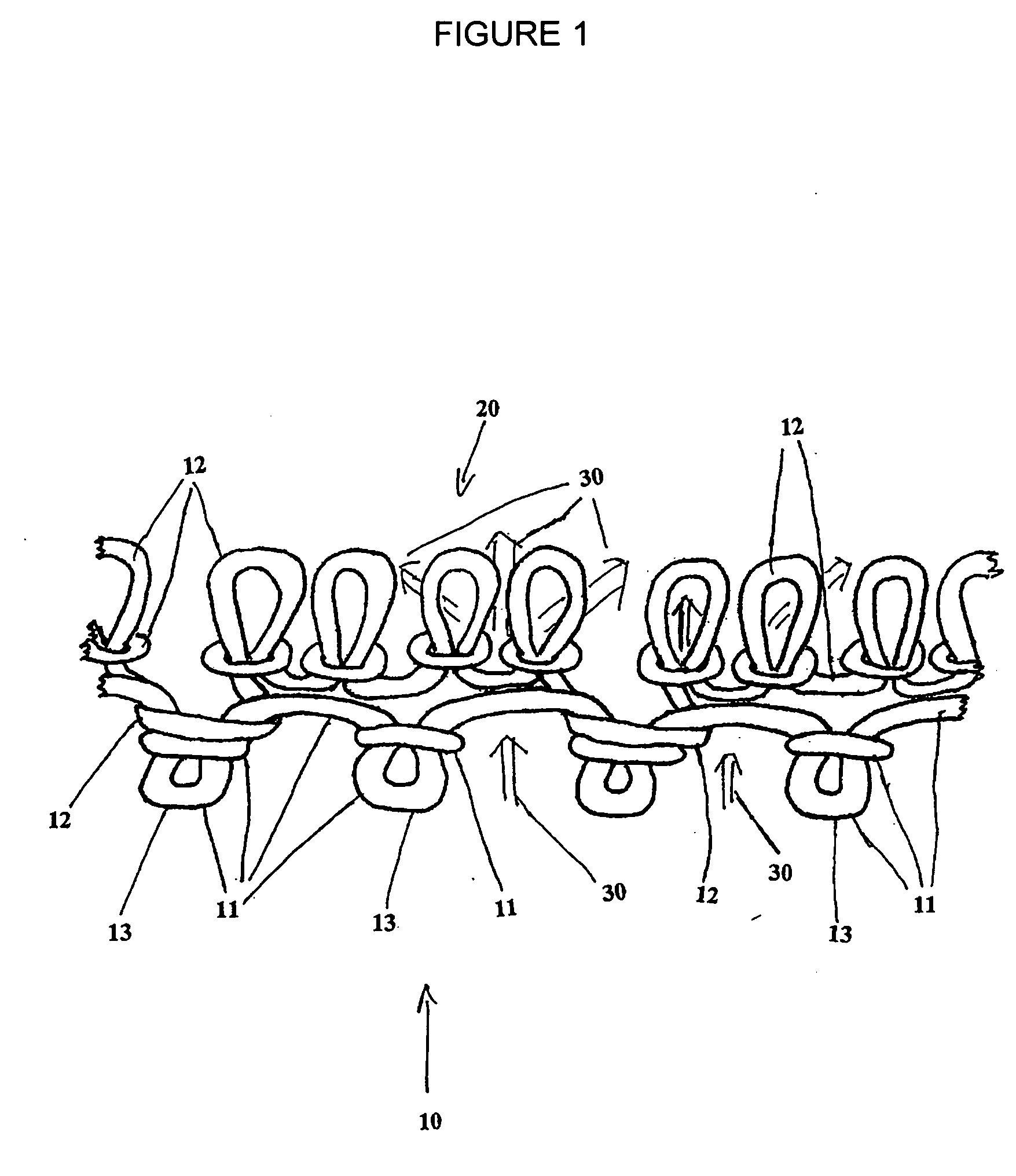
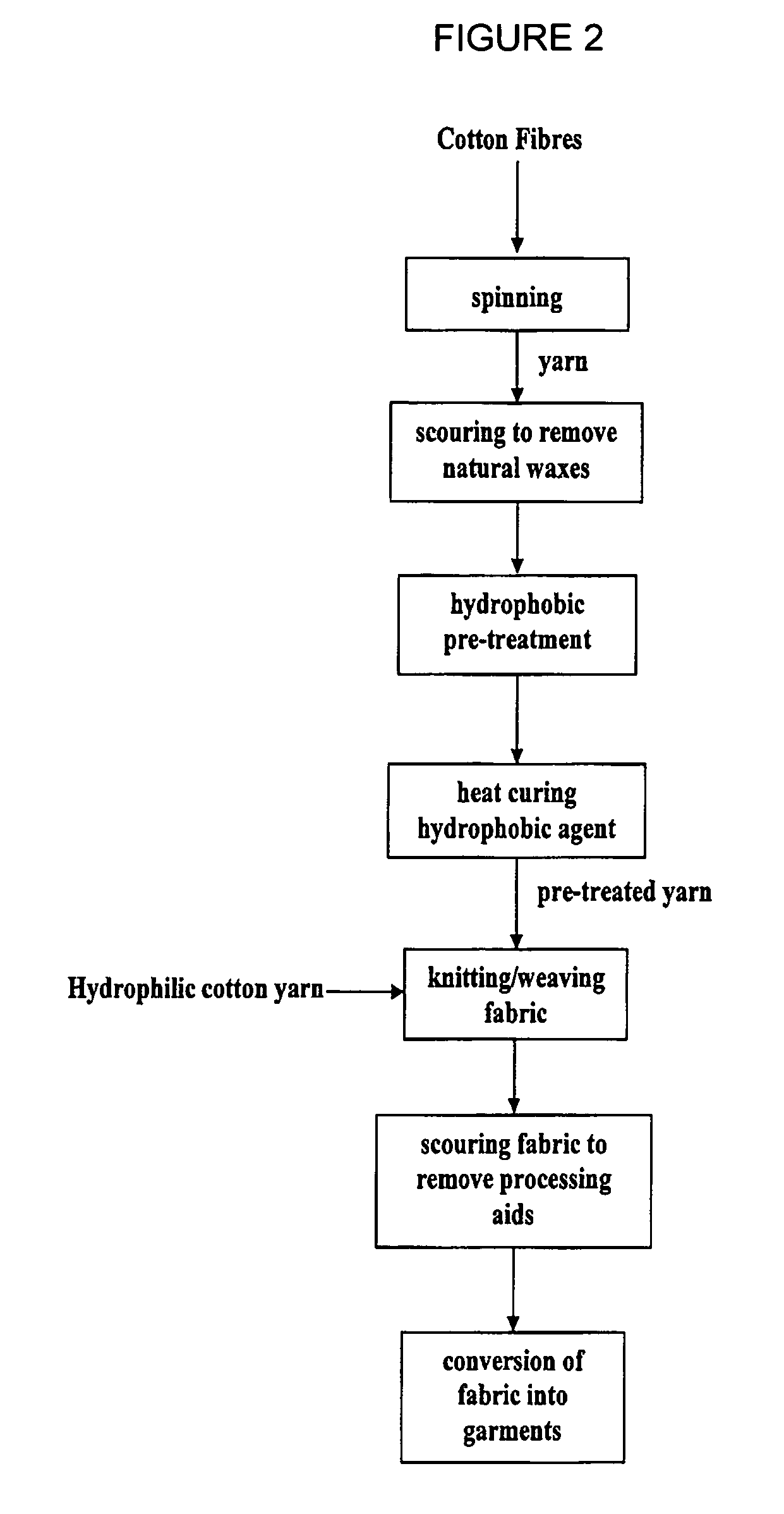
Fabric and a method of making the fabric
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0137] This example demonstrates fabrication of a double knit fabric manufactured from hydrophilic cotton yarn for the outer face and hydrophobic cotton yarn for the inner face. Both yarns are first scoured and bleached using a conventional cotton procedure. This renders the surface of the cotton hydrophilic. The yarn to be used for the inner face of the fabric is then treated with Nuva TTC (Clariant) by an exhaust process using the apparatus and method described above to render it hydrophobic. The yarn package size used is 900 g wound to a density of 0.3 g / cc and the yarn is treated under the follows conditions:
Liquor ratio12:1Nuva TTC5%on mass of yarnSodium Sulphate8g / lStart temperature20°C.Finish temperature70°C.Temperature increase0.5°C. / minHold time at 70° C.15minLiquor flow cycle4minutes out-to-in,3minutes in-to-out
[0138] The liquor clears progressively during the treatment cycle and at the end of the treatment time, the liquor is completely clear, indicating that exhaustion...
example 2
[0142] This example is the same as Example 1, save for the step of curing the fabric being carried out after knitting and before the final scour to remove lubricant.
[0143] The fabric exhibits differential wicking behaviour that is retained for a minimum of 30 home laundry wash and tumble dry cycles. Washing is carried out at 60° C. using a 2A Cotton Cycle in accordance with ISO 6330 with ECE detergent, while tumble drying is carried out cool for 60 minutes.
example 3
[0144] This example is the same as Example 1, except for the softener / lubricant Sandolube SVN being co-applied with the hydrophobic agent atthe rate of 1% on mass of fiber during the yarn treatment step. The Sandolube replaces the paraffin knitting lubricant added during re-winding in Example 1.
[0145] The fabric exhibits differential wicking behaviour that is retained for a minimum of 30 home laundry wash and tumble dry cycles. Washing is carried out at 60° C. using a 2A Cotton Cycle in accordance with ISO 6330 with ECE detergent, while tumble drying is carried out cool for 60 minutes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com