Bandage for wound or incision closure
a technology for wounds and incisions, applied in the field of bandages, can solve the problems of inability to achieve popular acceptance, invasive procedures, and often unsightly scars, and achieve the effects of promoting wound healing, preventing wound inversion, and promoting wound or incision healing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
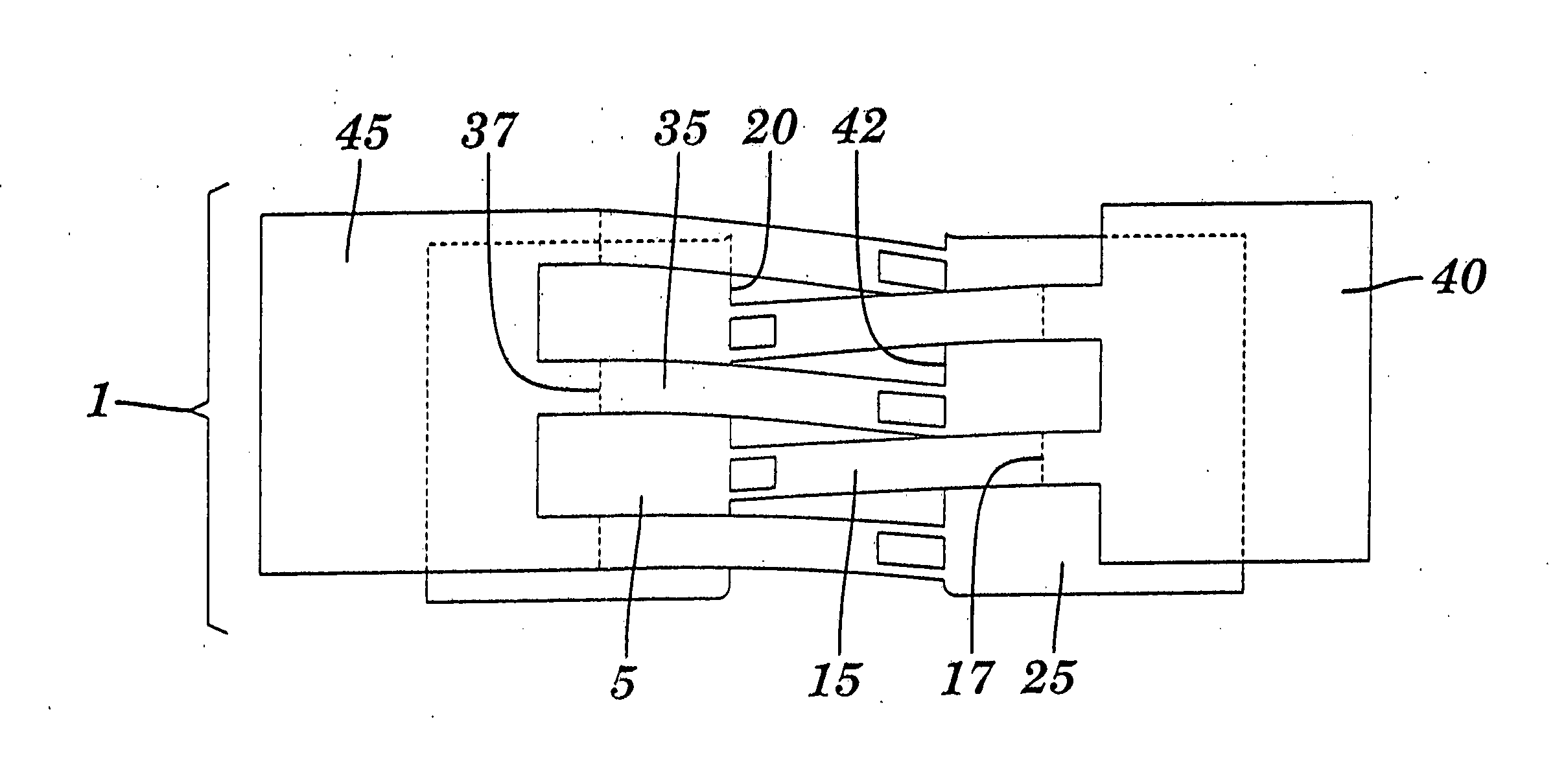
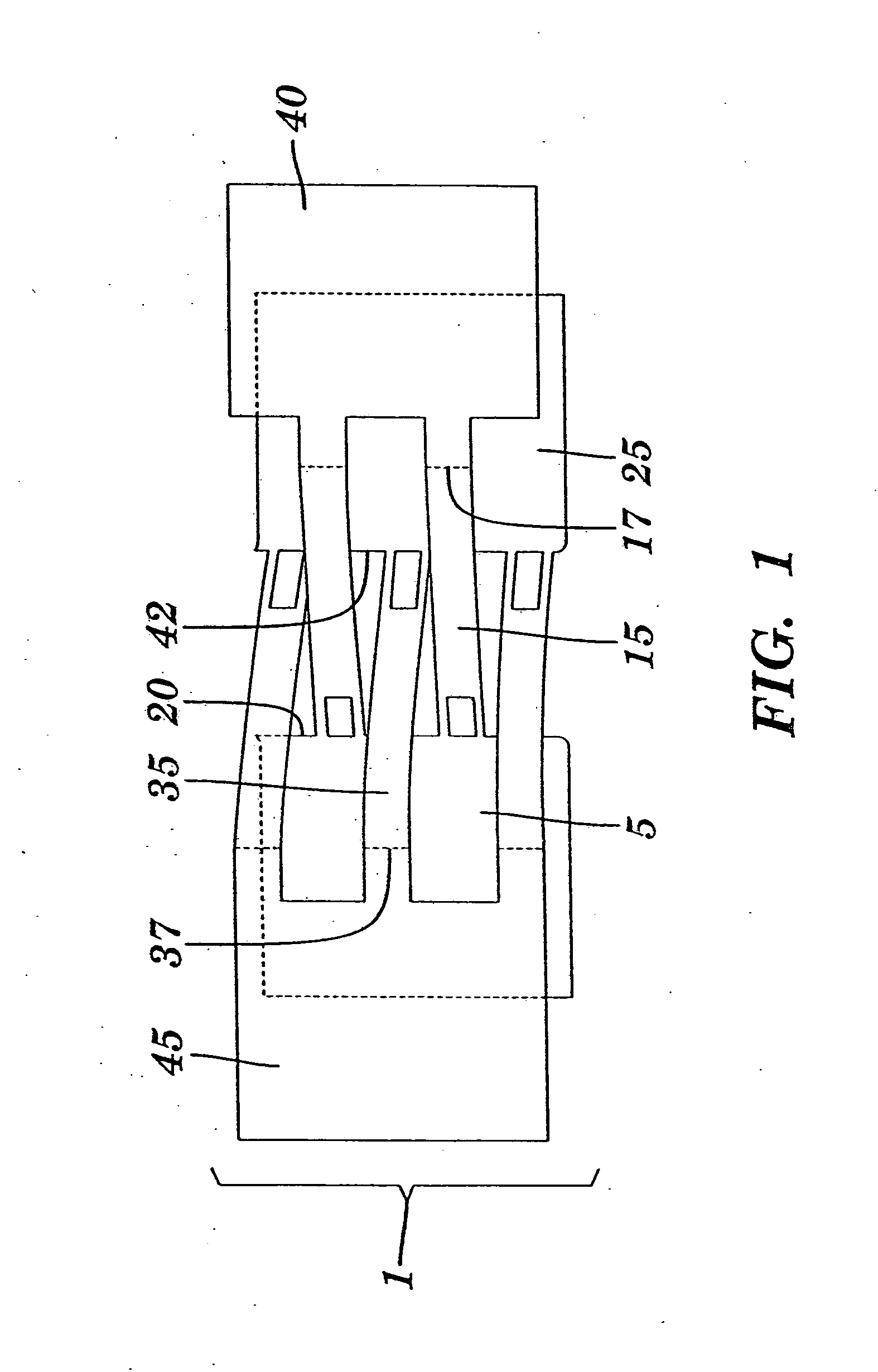
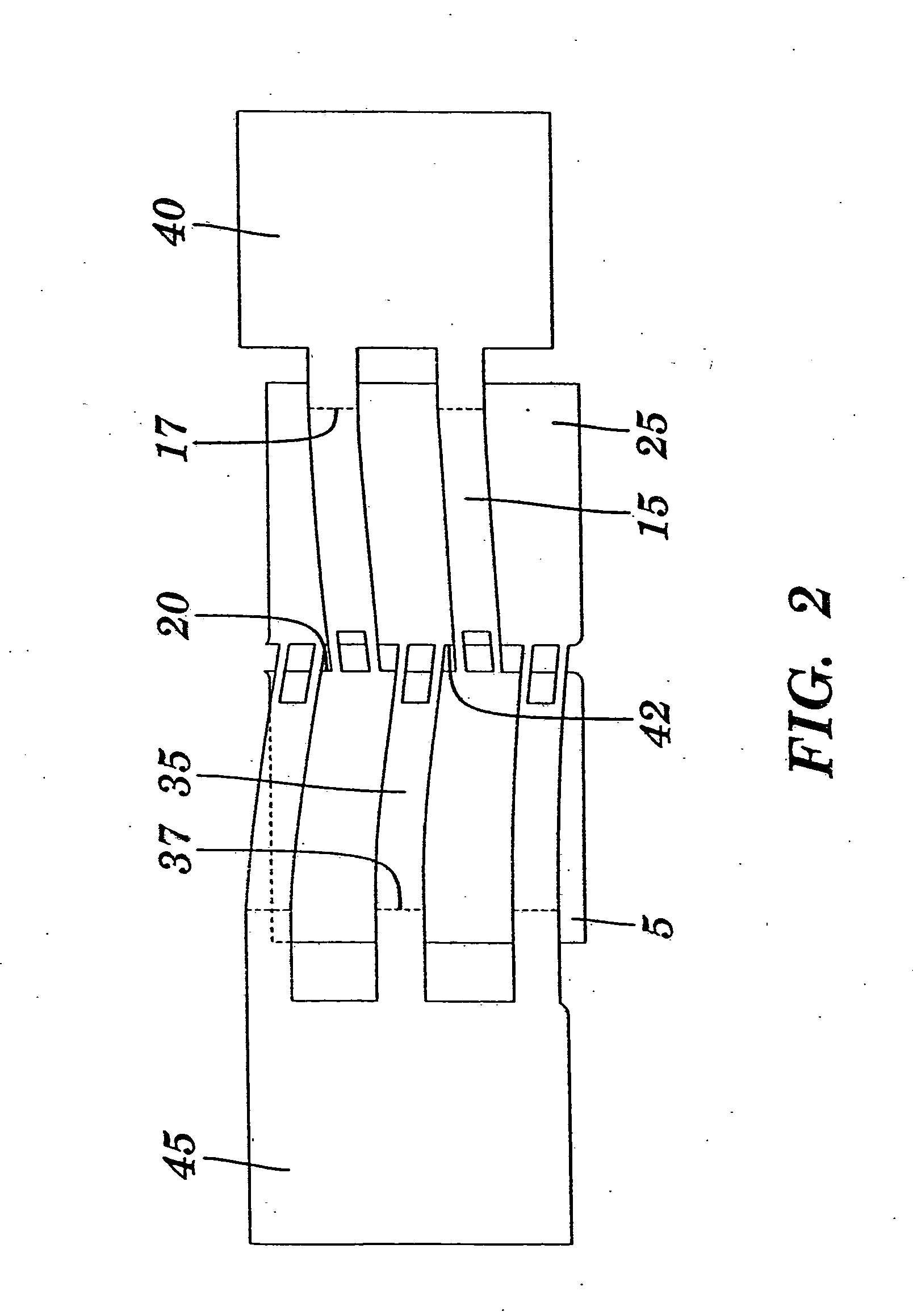
[0036] A bandage of the present invention in a non-tensioned state is depicted in FIG. 1. Bandage (1) includes a first flat flexible component (5) and a second flat flexible component (25). Each of these components has an upper surface to which lead lines 5 and 25 are directed, and lower surfaces which are not visible in the drawing. The lower surfaces are coated with adhesive to facilitate attachment to the skin. A plurality of first elongated connectors (15) extend from the wound edge (20) of the first flat flexible component (5) in a first direction, and a plurality of second elongated connectors (35) extend from the wound edge (42) of the second flat flexible component in a second direction which is generally opposite to the first direction. A first pulling element (40) is joined to the first elongated connectors (15) and adapted for lateral translation of the first flat flexible component (5) toward a wound or incision. Similarly, a second pulling element (45) is joined to the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com